Современная астрометрия -лекция для 2 курса .ppt
- Количество слайдов: 105
 СОВРЕМЕННАЯ АСТРОМЕТРИЯ В. В. Витязев
СОВРЕМЕННАЯ АСТРОМЕТРИЯ В. В. Витязев
 Cодержание • Классическая астрометрия • Миллисекундная революция • На пути к микросекундной революции
Cодержание • Классическая астрометрия • Миллисекундная революция • На пути к микросекундной революции
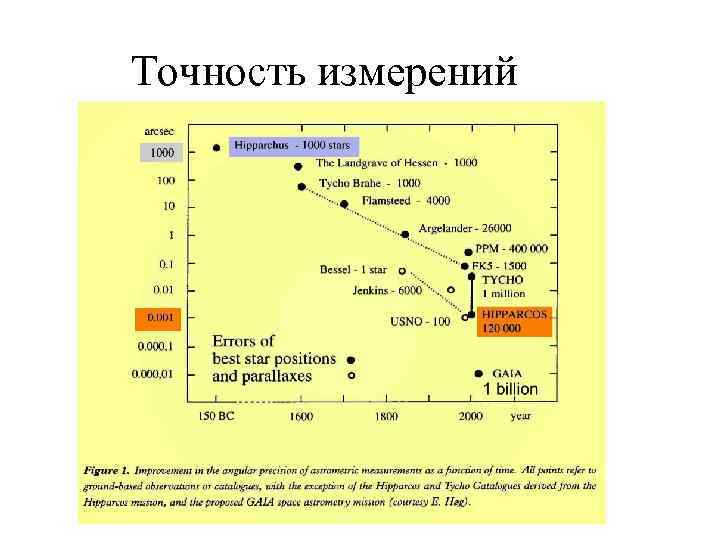 Точность измерений
Точность измерений
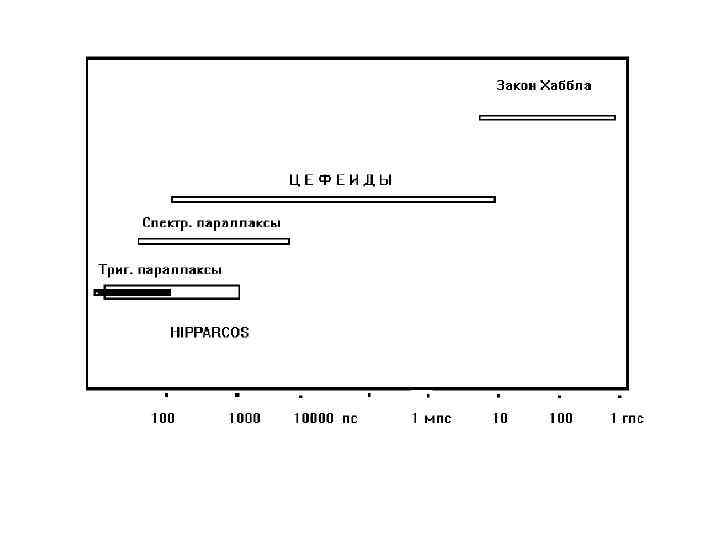
 Наглядное представление
Наглядное представление
 Классическая астрометрия – спокойная наука • Точность одного измерения 0. 2 - 0. 5" • В быту: «Астрономическая точность» • Астрометрия – это то, чем занимаются астрометристы
Классическая астрометрия – спокойная наука • Точность одного измерения 0. 2 - 0. 5" • В быту: «Астрономическая точность» • Астрометрия – это то, чем занимаются астрометристы
 Задачи классической астрометрии • • Система отсчета на небе Система отсчета на Земле Измерение времени Астрономические постоянные Движение планет и их спутников Кинематика звезд Вращение Земли
Задачи классической астрометрии • • Система отсчета на небе Система отсчета на Земле Измерение времени Астрономические постоянные Движение планет и их спутников Кинематика звезд Вращение Земли
 Пространство и время в классической астрометрии FK 5 (1535 звезд) PPM (370 тыс. звезд)
Пространство и время в классической астрометрии FK 5 (1535 звезд) PPM (370 тыс. звезд)
 АБСОЛЮТНАЯ МОНОПОЛИЯ вплоть до 60 -годов ХХ века СОЗДАНИЕ СИСТЕМ ОТСЧЕТА ПРОСТРАНСТВА ВРЕМЕНИ
АБСОЛЮТНАЯ МОНОПОЛИЯ вплоть до 60 -годов ХХ века СОЗДАНИЕ СИСТЕМ ОТСЧЕТА ПРОСТРАНСТВА ВРЕМЕНИ
 Прорывы в астрометрии • Шкала атомного времени неравномерность вращения Земли • Радиолокация планет Солнечной системы независимое определение меры АЕ • · Лазерная локация ИСЗ и Луны движение полюсов в теле Земли
Прорывы в астрометрии • Шкала атомного времени неравномерность вращения Земли • Радиолокация планет Солнечной системы независимое определение меры АЕ • · Лазерная локация ИСЗ и Луны движение полюсов в теле Земли
 Astronomical unit gets redefined IAU 2012 A VOTE AT A MEETING OF THE INTERNATIONAL ASTRONOMICAL UNION HAS REDEFINED THE ASTRONOMICAL UNIT, THE AU, AS EXACTLY 149 597 870 700 METERS. FROM GIOVANNI CASSINI’S MEASUREMENT IN 1672 UNTIL LATE IN THE 20 TH CENTURY, THE AU WAS DEFINED AS THE LENGTH OF THE SEMIMAJOR AXIS OF EARTH’S ELLIPTICAL ORBIT AROUND THE SUN; ITS VALUE WAS DETERMINED BY PARALLAX CALCULATIONS. THE MOST RECENT, MORE PRECISE DEFINITION WAS “THE RADIUS OF AN UNPERTURBED CIRCULAR NEWTONIAN ORBIT ABOUT THE SUN OF A PARTICLE HAVING INFINITESIMAL MASS, MOVING WITH A MEAN MOTION OF 0. 01720209895 RADIANS PER DAY (KNOWN AS THE GAUSSIAN CONSTANT). ” THAT CALCULATION HAS SEVERAL FLAWS BUT HAD REMAINED UNCHANGED FOR MANY YEARS BECAUSE OF CONCERNS OVER HOW THE CHANGE WOULD AFFECT SOFTWARE AND OTHER APPLICATIONS. THE NEW, NONCALCULATED VALUE MAKES THE UNIT MUCH EASIER TO EXPLAIN TO STUDENTS, AND NO LONGER VARIES BECAUSE OF GENERAL RELATIVITY OR THE DECREASING MASS OF THE SUN.
Astronomical unit gets redefined IAU 2012 A VOTE AT A MEETING OF THE INTERNATIONAL ASTRONOMICAL UNION HAS REDEFINED THE ASTRONOMICAL UNIT, THE AU, AS EXACTLY 149 597 870 700 METERS. FROM GIOVANNI CASSINI’S MEASUREMENT IN 1672 UNTIL LATE IN THE 20 TH CENTURY, THE AU WAS DEFINED AS THE LENGTH OF THE SEMIMAJOR AXIS OF EARTH’S ELLIPTICAL ORBIT AROUND THE SUN; ITS VALUE WAS DETERMINED BY PARALLAX CALCULATIONS. THE MOST RECENT, MORE PRECISE DEFINITION WAS “THE RADIUS OF AN UNPERTURBED CIRCULAR NEWTONIAN ORBIT ABOUT THE SUN OF A PARTICLE HAVING INFINITESIMAL MASS, MOVING WITH A MEAN MOTION OF 0. 01720209895 RADIANS PER DAY (KNOWN AS THE GAUSSIAN CONSTANT). ” THAT CALCULATION HAS SEVERAL FLAWS BUT HAD REMAINED UNCHANGED FOR MANY YEARS BECAUSE OF CONCERNS OVER HOW THE CHANGE WOULD AFFECT SOFTWARE AND OTHER APPLICATIONS. THE NEW, NONCALCULATED VALUE MAKES THE UNIT MUCH EASIER TO EXPLAIN TO STUDENTS, AND NO LONGER VARIES BECAUSE OF GENERAL RELATIVITY OR THE DECREASING MASS OF THE SUN.
 Мера Астрономической единицы · НАЗЕМНАЯ ОПТИЧЕСКАЯ АСТРОМЕТРИЯ (отн. погрешность 1. 1%) (149 504 312 000 170 400 000) м · РАДИОЛОКАЦИЯ ПЛАНЕТ · 1960 г. (149 540 000 13 600 000) м · 1961 г. (149 599 500 000 800 000) м 1991 г. (149 597 870 660 30) м · · 1998 г. (149 597 870 691 2) м · 1999 г. (149 597 870 691. 0 1. 0) м · 1999 г. (149 597 870 691. 1 0. 2) IAU 2012 adopted value 149 597 870 700
Мера Астрономической единицы · НАЗЕМНАЯ ОПТИЧЕСКАЯ АСТРОМЕТРИЯ (отн. погрешность 1. 1%) (149 504 312 000 170 400 000) м · РАДИОЛОКАЦИЯ ПЛАНЕТ · 1960 г. (149 540 000 13 600 000) м · 1961 г. (149 599 500 000 800 000) м 1991 г. (149 597 870 660 30) м · · 1998 г. (149 597 870 691 2) м · 1999 г. (149 597 870 691. 0 1. 0) м · 1999 г. (149 597 870 691. 1 0. 2) IAU 2012 adopted value 149 597 870 700
 МИЛЛИСЕКУНДНАЯ РЕВОЛЮЦИЯ mas (мсд) 0. 001 секунды дуги
МИЛЛИСЕКУНДНАЯ РЕВОЛЮЦИЯ mas (мсд) 0. 001 секунды дуги
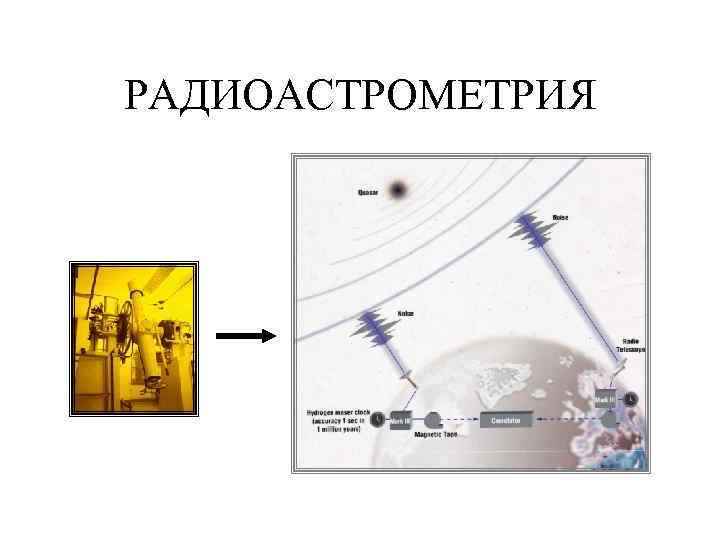 РАДИОАСТРОМЕТРИЯ
РАДИОАСТРОМЕТРИЯ
 ПЕРЕСТРОЙКА В АСТРОМЕТРИИ • Переход от НТТ к ОТО • Релятивистские шкалы времени • Новая система отсчета ICRS (ICRF)
ПЕРЕСТРОЙКА В АСТРОМЕТРИИ • Переход от НТТ к ОТО • Релятивистские шкалы времени • Новая система отсчета ICRS (ICRF)
 CONVENTIONS 2003 CHAPTER 1 General Definitions and Numerical Standards CHAPTER 2 Conventional Celestial Reference Frame CHAPTER 3 Conventional Dynamical Reference Frame CHAPTER 4 Conventional Terrestrial Reference System CHAPTER 5 Transformation Between the Celestial and Terrestrial Systems CHAPTER 6 Geopotential CHAPTER 7 Displacement of Reference Points CHAPTER 8 Tidal Variations in UT 1 CHAPTER 9 Tropospheric Model CHAPTER 10 General Relativistic Models for Time, Coordinates and Equations of Motion CHAPTER 11 General Relativistic Models for Propagation
CONVENTIONS 2003 CHAPTER 1 General Definitions and Numerical Standards CHAPTER 2 Conventional Celestial Reference Frame CHAPTER 3 Conventional Dynamical Reference Frame CHAPTER 4 Conventional Terrestrial Reference System CHAPTER 5 Transformation Between the Celestial and Terrestrial Systems CHAPTER 6 Geopotential CHAPTER 7 Displacement of Reference Points CHAPTER 8 Tidal Variations in UT 1 CHAPTER 9 Tropospheric Model CHAPTER 10 General Relativistic Models for Time, Coordinates and Equations of Motion CHAPTER 11 General Relativistic Models for Propagation
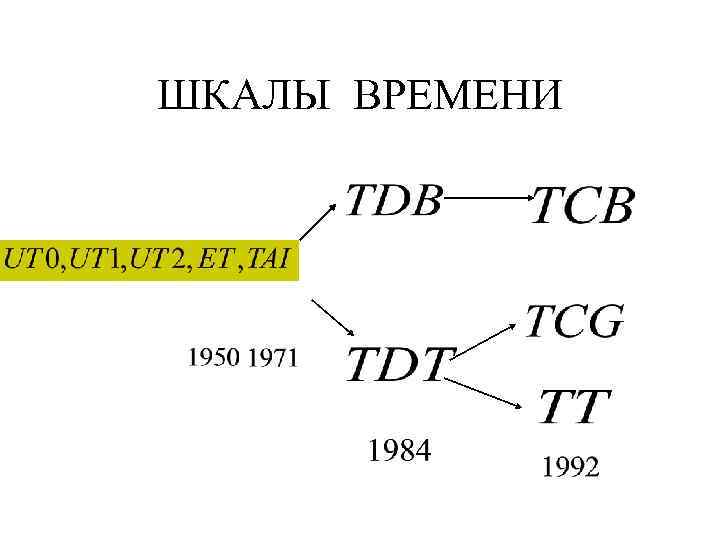 ШКАЛЫ ВРЕМЕНИ
ШКАЛЫ ВРЕМЕНИ
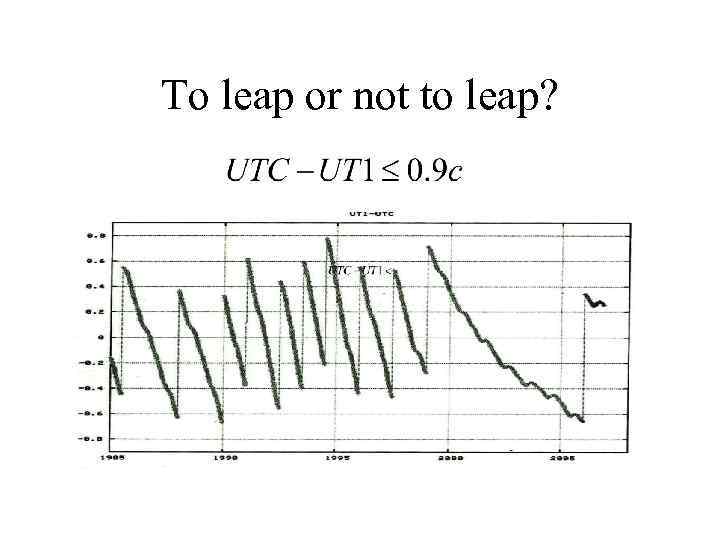 To leap or not to leap?
To leap or not to leap?
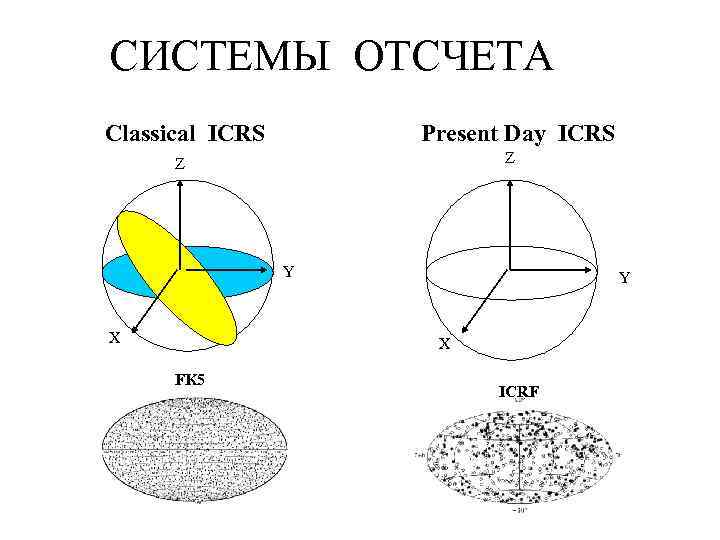 СИСТЕМЫ ОТСЧЕТА Classical ICRS Present Day ICRS Z Z Y X FK 5 ICRF
СИСТЕМЫ ОТСЧЕТА Classical ICRS Present Day ICRS Z Z Y X FK 5 ICRF
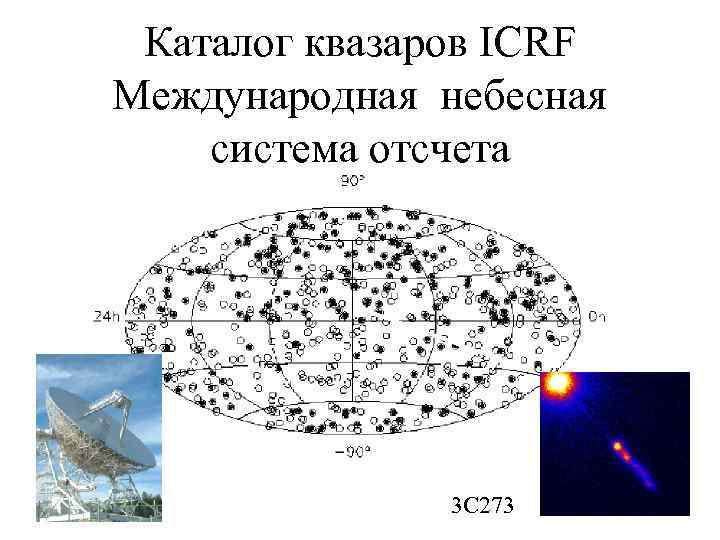 Каталог квазаров ICRF Международная небесная система отсчета 3 С 273
Каталог квазаров ICRF Международная небесная система отсчета 3 С 273
 Международная Земная Система Отсчета ITRF
Международная Земная Система Отсчета ITRF
 Возможности РСДБ
Возможности РСДБ
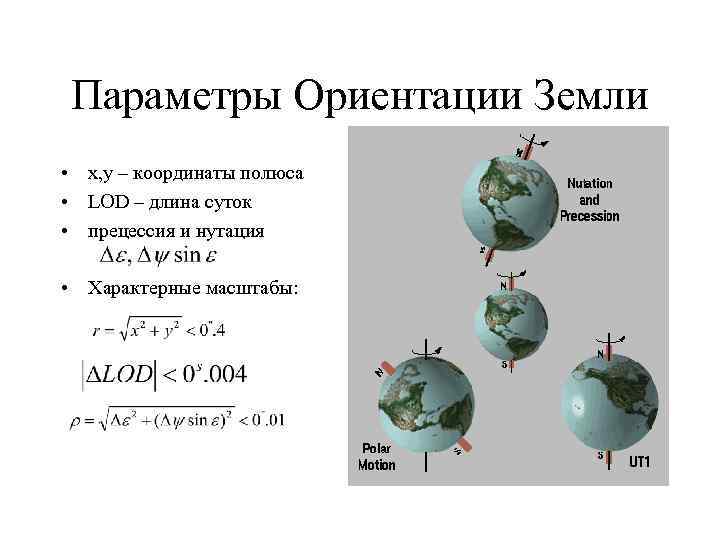 Параметры Ориентации Земли • x, y – координаты полюса • LOD – длина суток • прецессия и нутация • Характерные масштабы:
Параметры Ориентации Земли • x, y – координаты полюса • LOD – длина суток • прецессия и нутация • Характерные масштабы:
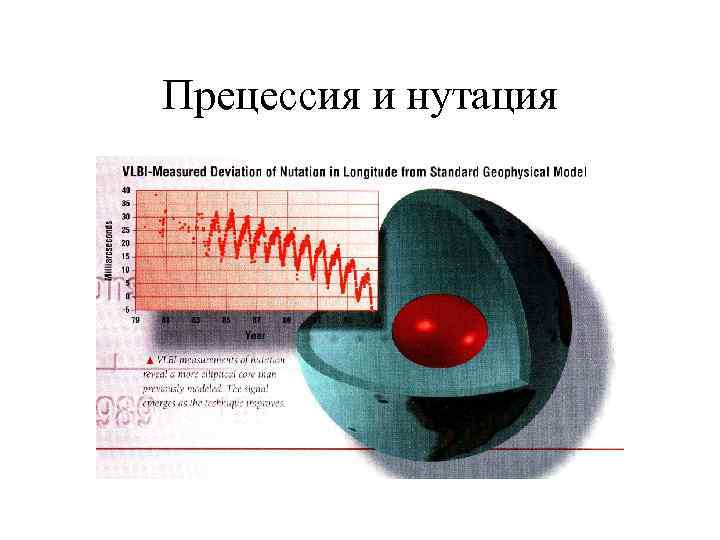 Прецессия и нутация
Прецессия и нутация
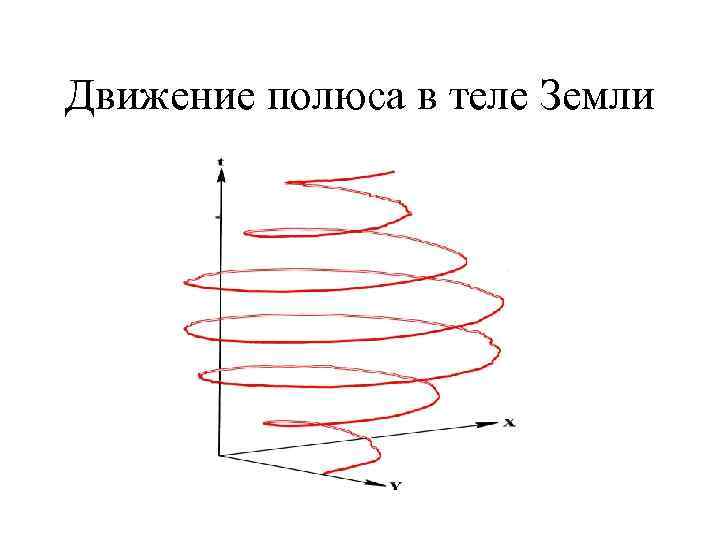 Движение полюса в теле Земли
Движение полюса в теле Земли
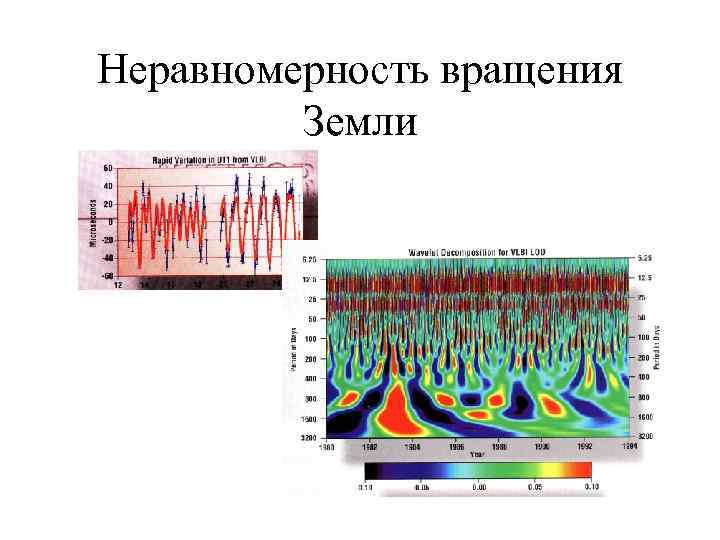 Неравномерность вращения Земли
Неравномерность вращения Земли
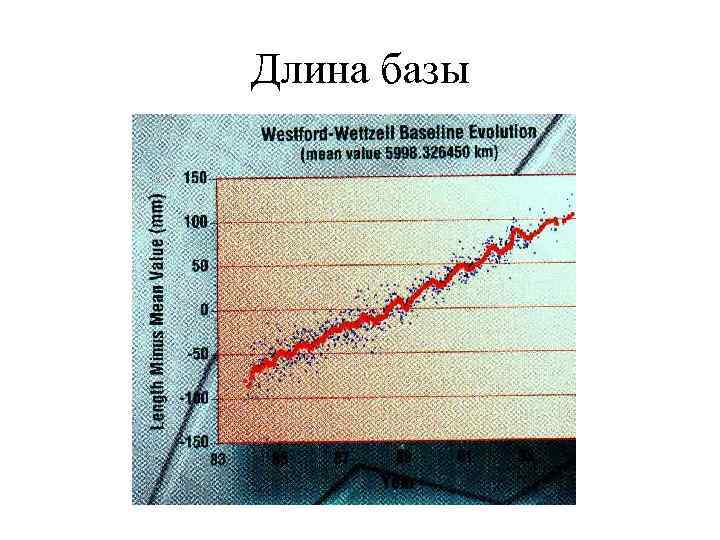 Длина базы
Длина базы
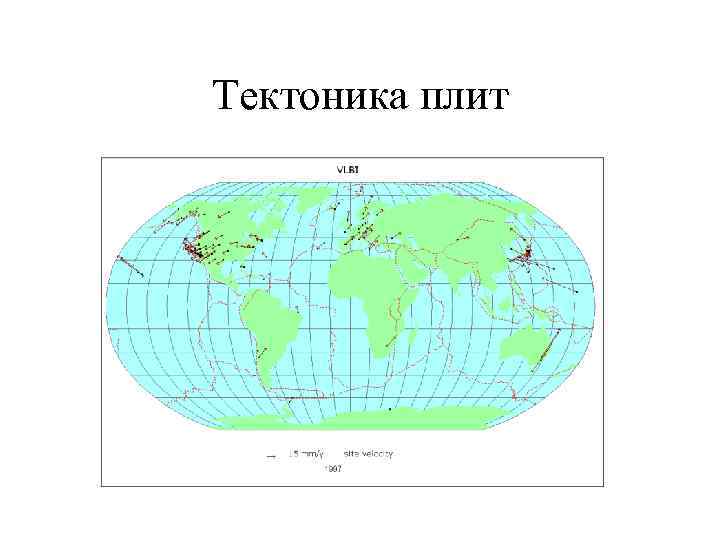 Тектоника плит
Тектоника плит
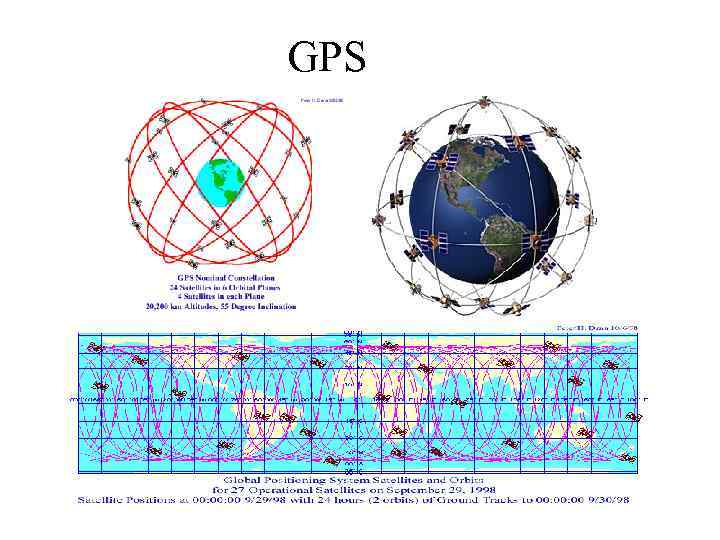 GPS
GPS
 GPS: Движение плит
GPS: Движение плит
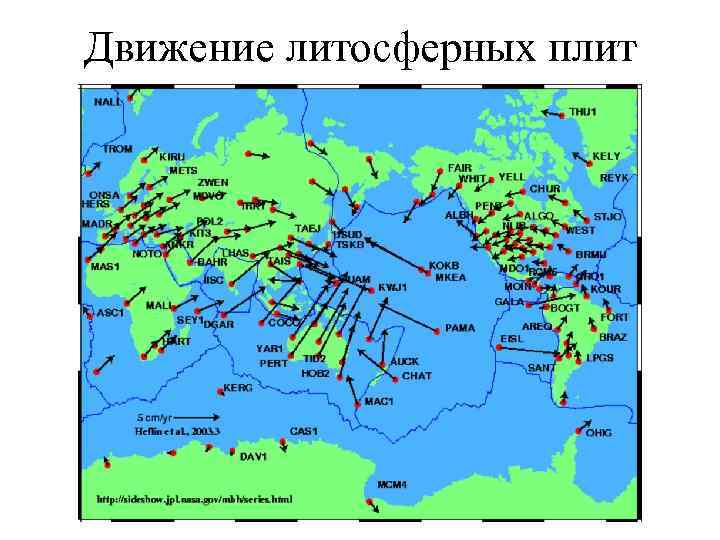 Движение литосферных плит
Движение литосферных плит
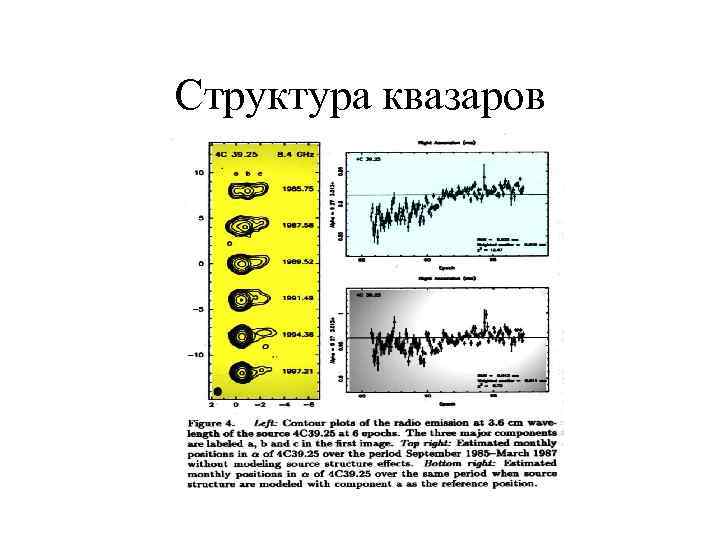 Структура квазаров
Структура квазаров
 Р С Д Б : ИЗУЧЕНИЕ ЗЕМЛИ и КВАЗАРОВ
Р С Д Б : ИЗУЧЕНИЕ ЗЕМЛИ и КВАЗАРОВ
 Космическая астрометрия
Космическая астрометрия
 Спутник HIPPARCOS HIgh Precision Parallax COllecting Satellite 1989 -1993, 1997
Спутник HIPPARCOS HIgh Precision Parallax COllecting Satellite 1989 -1993, 1997
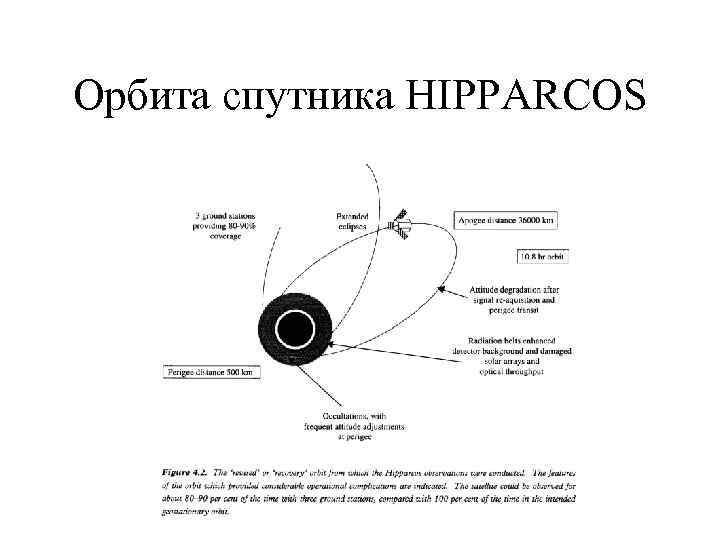 Орбита спутника HIPPARCOS
Орбита спутника HIPPARCOS
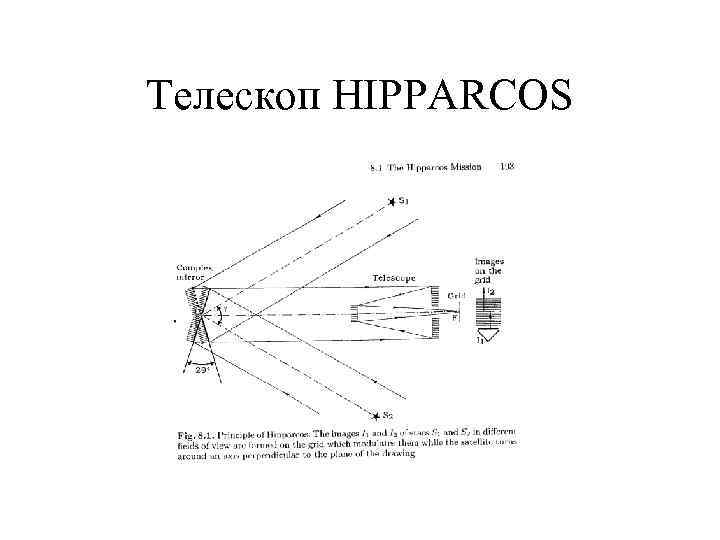 Телескоп HIPPARCOS
Телескоп HIPPARCOS
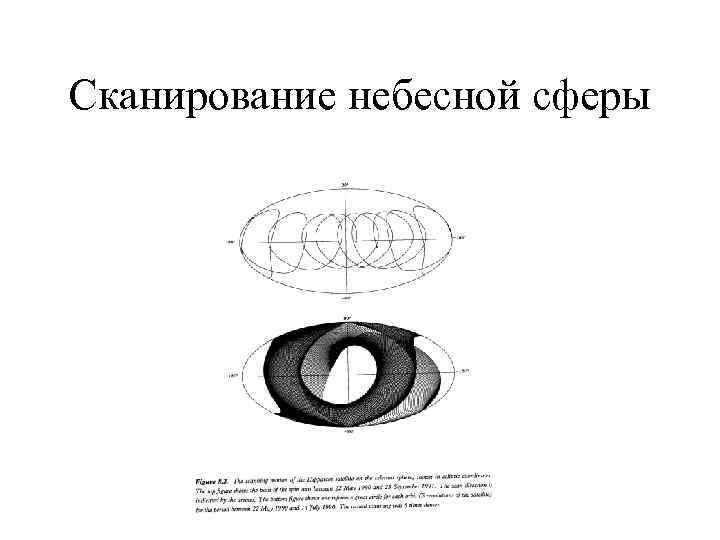 Сканирование небесной сферы
Сканирование небесной сферы
 Этапы проекта HIPPARCOS
Этапы проекта HIPPARCOS
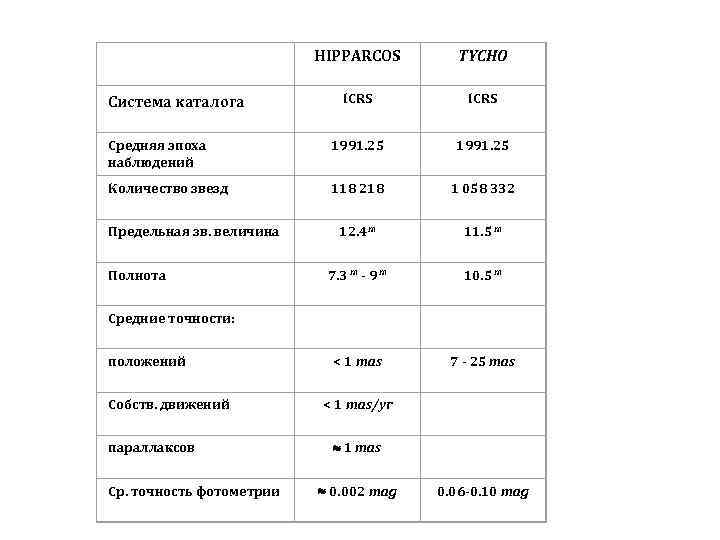 HIPPARCOS TYCHO ICRS Средняя эпоха наблюдений 1991. 25 Количество звезд 118 218 1 058 332 12. 4 m 11. 5 m 7. 3 m - 9 m 10. 5 m < 1 mas 7 - 25 mas < 1 mas/yr 1 mas 0. 002 mag 0. 06 -0. 10 mag Система каталога Предельная зв. величина Полнота Средние точности: положений Собств. движений параллаксов Ср. точность фотометрии
HIPPARCOS TYCHO ICRS Средняя эпоха наблюдений 1991. 25 Количество звезд 118 218 1 058 332 12. 4 m 11. 5 m 7. 3 m - 9 m 10. 5 m < 1 mas 7 - 25 mas < 1 mas/yr 1 mas 0. 002 mag 0. 06 -0. 10 mag Система каталога Предельная зв. величина Полнота Средние точности: положений Собств. движений параллаксов Ср. точность фотометрии
 Каталог HIPPARCOS
Каталог HIPPARCOS
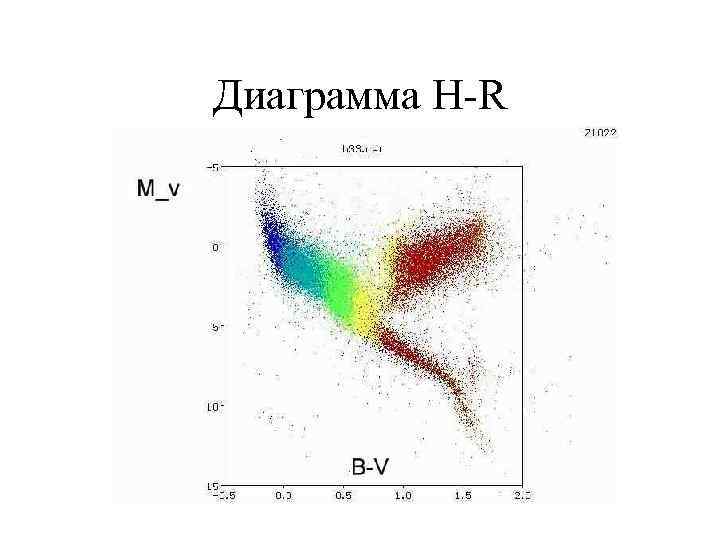 Диаграмма H-R
Диаграмма H-R
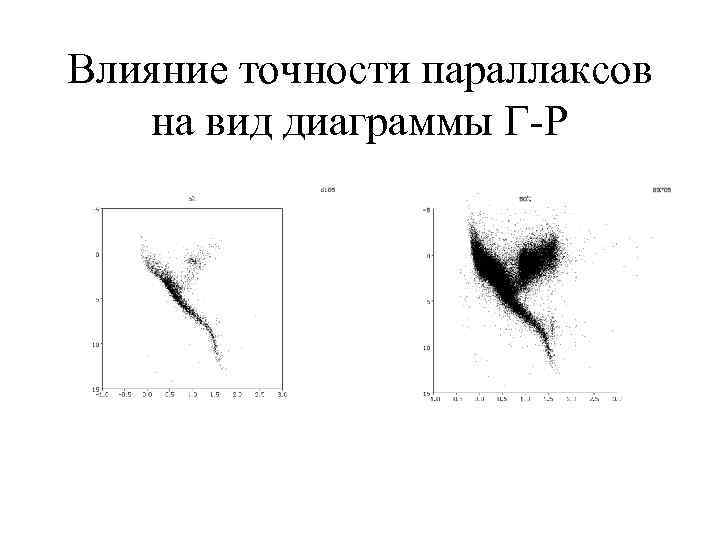 Влияние точности параллаксов на вид диаграммы Г-Р
Влияние точности параллаксов на вид диаграммы Г-Р
 Что дал HIPPARCOS • Для астрометрии • Для Галактической астрономии • Для астрофизики
Что дал HIPPARCOS • Для астрометрии • Для Галактической астрономии • Для астрофизики
 Научные задачи, решаемые по данным спутника HIPPARCOS Произведен анализ 1485 статей, авторы которых использовали каталоги HIPPARCOS и TYCHO. Статьи вышли в 1996 -2000 гг.
Научные задачи, решаемые по данным спутника HIPPARCOS Произведен анализ 1485 статей, авторы которых использовали каталоги HIPPARCOS и TYCHO. Статьи вышли в 1996 -2000 гг.
 Классическая астрономия Астрометрия 327 22% Кинематика звезд 127 Двойные и кратные звезды 113 Звездные скопления 124 Шкала расстояний 53 Итого 744 50%
Классическая астрономия Астрометрия 327 22% Кинематика звезд 127 Двойные и кратные звезды 113 Звездные скопления 124 Шкала расстояний 53 Итого 744 50%
 Астрофизика • • • Переменные звезды 143 Характеристики звезд 139 Звездная эволюция 43 Химический состав звезд 45 Прочие темы 371 • Итого 741 50%
Астрофизика • • • Переменные звезды 143 Характеристики звезд 139 Звездная эволюция 43 Химический состав звезд 45 Прочие темы 371 • Итого 741 50%
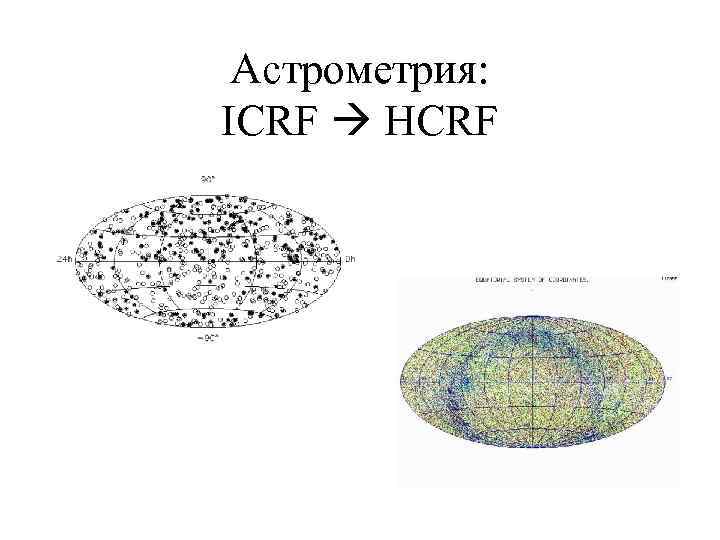 Астрометрия: ICRF HCRF
Астрометрия: ICRF HCRF
 Точность привязки к ICRF
Точность привязки к ICRF
 3 D Astrometry
3 D Astrometry
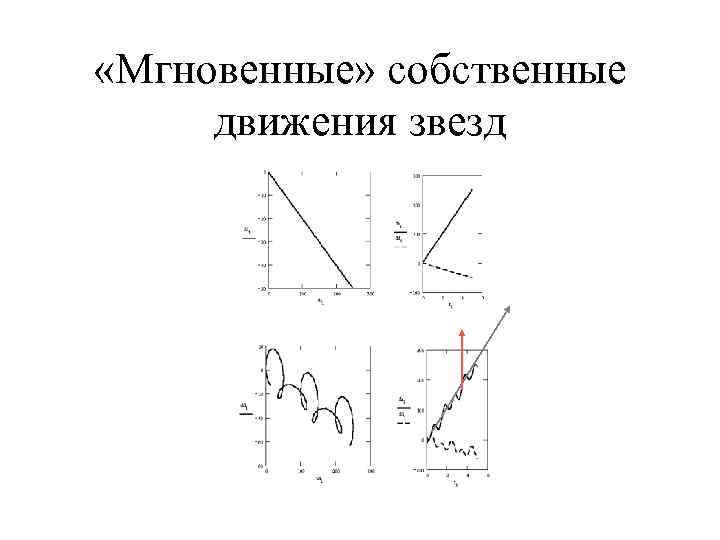 «Мгновенные» собственные движения звезд
«Мгновенные» собственные движения звезд
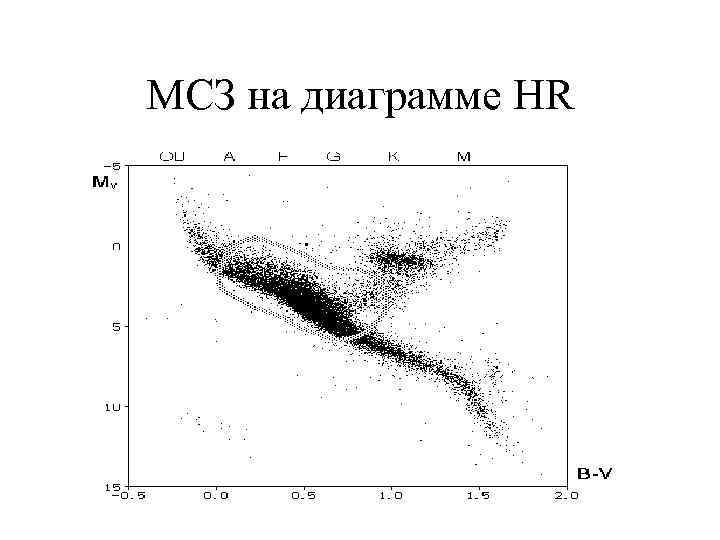 МСЗ на диаграмме HR
МСЗ на диаграмме HR
 Галактическая астрономия The Milky Way: it's floppy and it changes shape From Hipparcos results on many distant stars, astronomers from Turin Observatory, Italy, and Oxford University, UK, deduce that the disk is slightly warped, like the brim of a hat. What's more, the distant stars are travelling in unexpected directions which, if continued, will change the shape of the Milky Way.
Галактическая астрономия The Milky Way: it's floppy and it changes shape From Hipparcos results on many distant stars, astronomers from Turin Observatory, Italy, and Oxford University, UK, deduce that the disk is slightly warped, like the brim of a hat. What's more, the distant stars are travelling in unexpected directions which, if continued, will change the shape of the Milky Way.
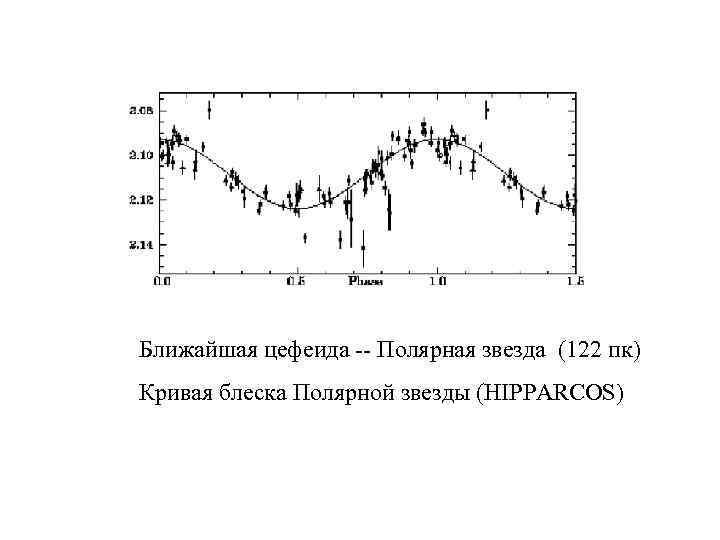 Ближайшая цефеида -- Полярная звезда (122 пк) Кривая блеска Полярной звезды (HIPPARCOS)
Ближайшая цефеида -- Полярная звезда (122 пк) Кривая блеска Полярной звезды (HIPPARCOS)
 ЗАВИСИМОСТЬ "СВЕТИМОСТЬ - ПЕРИОД" M = -1. 25 - 3. 00 lg. P Lg r = 0. 2(m - M) + 1 HIPPARCOS: -- M = (-1. 43+-0. 1) - 2. 81 lg. P (Feast et al. MNRAS v. 286, Issue 1, pp. L 1 -L 5, 1997) -- distance moduli: Large Magellanic Cloud 18. 70+-0. 1, M 31 -- 24. 77+-0. 11 --- Hubble constant now need to be decreased by ~10 per cent --- The age of the oldest Galactic globular cluster is ~11 Gyr
ЗАВИСИМОСТЬ "СВЕТИМОСТЬ - ПЕРИОД" M = -1. 25 - 3. 00 lg. P Lg r = 0. 2(m - M) + 1 HIPPARCOS: -- M = (-1. 43+-0. 1) - 2. 81 lg. P (Feast et al. MNRAS v. 286, Issue 1, pp. L 1 -L 5, 1997) -- distance moduli: Large Magellanic Cloud 18. 70+-0. 1, M 31 -- 24. 77+-0. 11 --- Hubble constant now need to be decreased by ~10 per cent --- The age of the oldest Galactic globular cluster is ~11 Gyr
 Звезды стали моложе, а Вселенная - старше "Hipparcos cured a headache for cosmologists, " said Michael Feast of Cape Town University, South Africa. "We now judge the Universe to be bigger and therefore older, by about a billion years. The oldest stars are much younger than supposed, by about 4 billion years. If the Universe is about 12 billion years old, everything fits nicely. "
Звезды стали моложе, а Вселенная - старше "Hipparcos cured a headache for cosmologists, " said Michael Feast of Cape Town University, South Africa. "We now judge the Universe to be bigger and therefore older, by about a billion years. The oldest stars are much younger than supposed, by about 4 billion years. If the Universe is about 12 billion years old, everything fits nicely. "
 Примеры Interstellar extinction Stellar seismology Variable Star Distance Scales Post-Hipparcos cosmic candles Confirming a Nobel Prize winning theory with the HIPPARCOS space-craft: Accurately determining distances and diameters of white dwarf stars
Примеры Interstellar extinction Stellar seismology Variable Star Distance Scales Post-Hipparcos cosmic candles Confirming a Nobel Prize winning theory with the HIPPARCOS space-craft: Accurately determining distances and diameters of white dwarf stars
 Примеры Consequences of HIPPARCOS parallaxes for stellar evolutionary models. White Dwarf Magnetic Fields and the Mass. Radius Relation A new constraint on theory of stellar шnteriors and model atmospheres Interstellar reddening from the HIPPARCOS and TYCHO catalogues.
Примеры Consequences of HIPPARCOS parallaxes for stellar evolutionary models. White Dwarf Magnetic Fields and the Mass. Radius Relation A new constraint on theory of stellar шnteriors and model atmospheres Interstellar reddening from the HIPPARCOS and TYCHO catalogues.
 Примеры интересных тем Fate of the Universe Age of the Universe Dark Matter
Примеры интересных тем Fate of the Universe Age of the Universe Dark Matter
 Союз Земли и Неба
Союз Земли и Неба
 Каталог FK 6 (1999) FK 6 = FK 5 + HIPPARCOS Ошибки собственных движений 878 звезд: FK 6 0. 35 mas/y HIPPARCOS 0. 67 mas/y Достигнуто ДВУКРАТНОЕ увеличение точности
Каталог FK 6 (1999) FK 6 = FK 5 + HIPPARCOS Ошибки собственных движений 878 звезд: FK 6 0. 35 mas/y HIPPARCOS 0. 67 mas/y Достигнуто ДВУКРАТНОЕ увеличение точности
 Каталог TYCHO-2 (2000) . Наблюдательный материал: TYCHO-1 CUO, USNO, ARI, ESO 2. 5 млн. звезд Всего 2 539 913 звезд Полнота: 99% для V = 11. 0 90% для V = 11. 5 Ошибки координат звезд: 10 mas (V < 9) и 100 mas (V < 12) Ошибки с. дв. звезд : 1. 3 mas/y (V < 9) и 3. 0 mas/y (V < 12)
Каталог TYCHO-2 (2000) . Наблюдательный материал: TYCHO-1 CUO, USNO, ARI, ESO 2. 5 млн. звезд Всего 2 539 913 звезд Полнота: 99% для V = 11. 0 90% для V = 11. 5 Ошибки координат звезд: 10 mas (V < 9) и 100 mas (V < 12) Ошибки с. дв. звезд : 1. 3 mas/y (V < 9) и 3. 0 mas/y (V < 12)
 Массовые каталоги • Astrographic Catalog AC 2000. 2 4. 6 mln stars, 11 -13 mag, mean epoch 1907 • USNO –B 1. 1 mln stars, complete up V= 21 • ACR (around equator) 1. 3 mln stars, mean epoch 1996. 0, complete to V=17 • GSC 2. 2, 19 mln stars, up to V=19. 5
Массовые каталоги • Astrographic Catalog AC 2000. 2 4. 6 mln stars, 11 -13 mag, mean epoch 1907 • USNO –B 1. 1 mln stars, complete up V= 21 • ACR (around equator) 1. 3 mln stars, mean epoch 1996. 0, complete to V=17 • GSC 2. 2, 19 mln stars, up to V=19. 5
 Инфракрасная Астрометрия 2 MASS (пока на уровне 500 мсд)
Инфракрасная Астрометрия 2 MASS (пока на уровне 500 мсд)
 Распределение галактик по небу
Распределение галактик по небу
 Центр Галактики
Центр Галактики
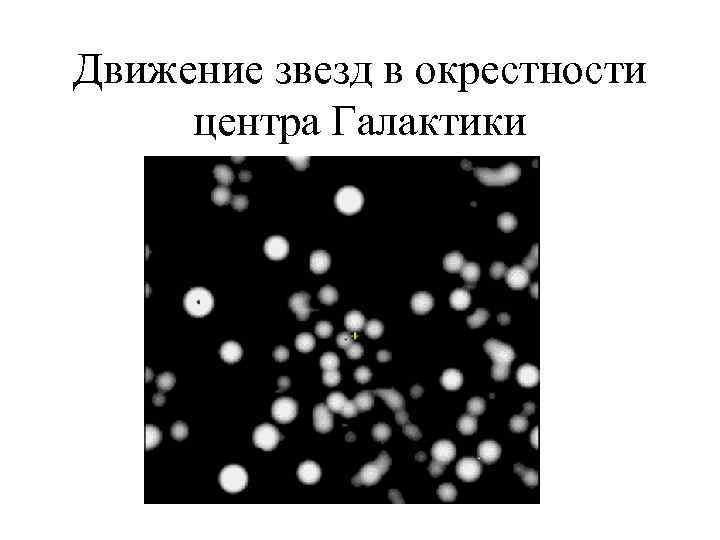 Движение звезд в окрестности центра Галактики
Движение звезд в окрестности центра Галактики


 Будущие космические астрометрические проекты
Будущие космические астрометрические проекты
 Проекты космической астрометрии • Проекты, не получившие поддержки: Roemer, FAME, SIM DIVA, Ломоносов, Струве, AMEX ЕКА США Гер Россия США • Проекты, получившие поддержку: Gaia (ЕКА), JASMINE (Япония)
Проекты космической астрометрии • Проекты, не получившие поддержки: Roemer, FAME, SIM DIVA, Ломоносов, Струве, AMEX ЕКА США Гер Россия США • Проекты, получившие поддержку: Gaia (ЕКА), JASMINE (Япония)


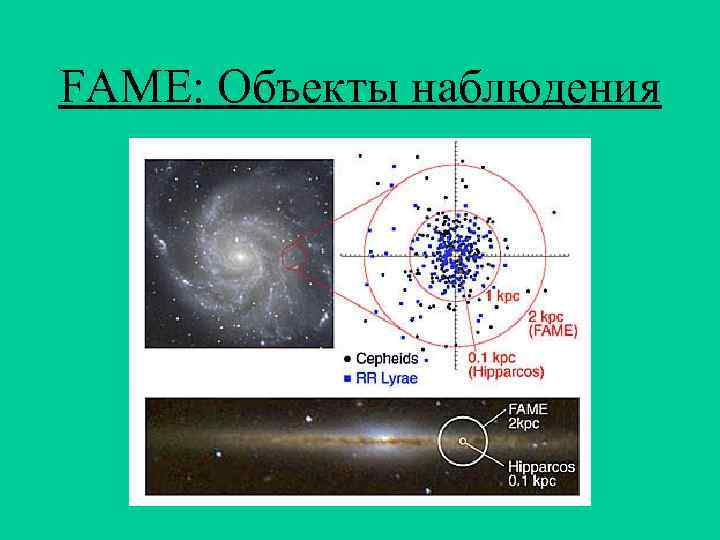 FAME: Объекты наблюдения
FAME: Объекты наблюдения

 • 109 звезд Gaia • 10 µas @ V = 15 mag • Фотометрия ( 4 + 11 каналов) • Радиальная скорость Запуск: 2013 Продолжительность наблюдений: 5+1 лет • Спектроскопия
• 109 звезд Gaia • 10 µas @ V = 15 mag • Фотометрия ( 4 + 11 каналов) • Радиальная скорость Запуск: 2013 Продолжительность наблюдений: 5+1 лет • Спектроскопия
 What‘s in the name? • Изначально: Global Astrometric Interferometer for Astrophysics • Исследования показали: интерферометер – не выгоден Gaia - английское имя греческой богини Земли греческий: или сокращенное имя английский: Gaia, Gaea, Ge русский: Гея • Фольклор: Galactic Astrophysics through Imaging and Astrometry General Astrometric Instrument for Astronomy Great Accuracy In Astrometry Great Advances In Astrophysics
What‘s in the name? • Изначально: Global Astrometric Interferometer for Astrophysics • Исследования показали: интерферометер – не выгоден Gaia - английское имя греческой богини Земли греческий: или сокращенное имя английский: Gaia, Gaea, Ge русский: Гея • Фольклор: Galactic Astrophysics through Imaging and Astrometry General Astrometric Instrument for Astronomy Great Accuracy In Astrometry Great Advances In Astrophysics
 Gaia и Hipparcos
Gaia и Hipparcos
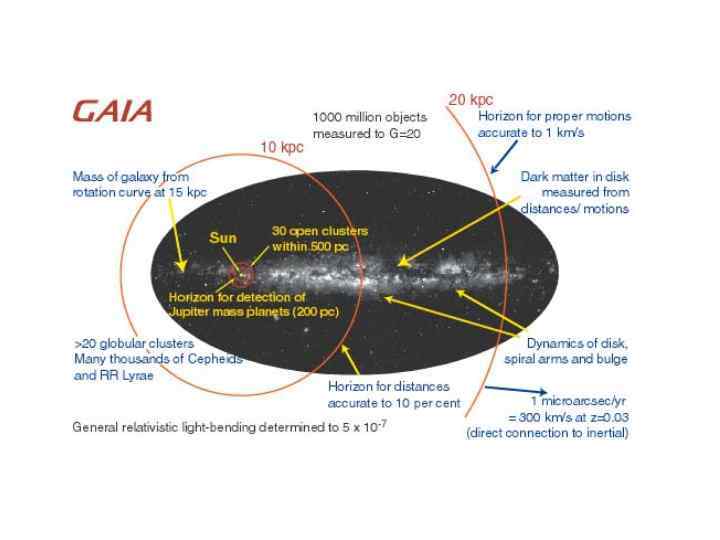
 Научные цели проекта Gaia • Картирование Галактики • Физика звезд (классификация, M, L, Ln g, Teff, [Fe/H] ) • Кинематика и динамика Галактики • Космические расстояния (тригонометрически до 10 кпк с 10%, диаграмма Г-Р, цефеиды, RR Lyr) • Возраст Вселенной (расстояния, светимости) • Темная материя (микролинзирование, коричневые карлики) • Фундаментальная система отсчета (квазары, астрометрия) • Планеты (~ MJ, астрометрически и фотометрически) • Фундаментальная физика ( ~ 10 -7 , ~ 10 -5 ) • Солнечная система (массы, орбиты, 5 x 105 тел)
Научные цели проекта Gaia • Картирование Галактики • Физика звезд (классификация, M, L, Ln g, Teff, [Fe/H] ) • Кинематика и динамика Галактики • Космические расстояния (тригонометрически до 10 кпк с 10%, диаграмма Г-Р, цефеиды, RR Lyr) • Возраст Вселенной (расстояния, светимости) • Темная материя (микролинзирование, коричневые карлики) • Фундаментальная система отсчета (квазары, астрометрия) • Планеты (~ MJ, астрометрически и фотометрически) • Фундаментальная физика ( ~ 10 -7 , ~ 10 -5 ) • Солнечная система (массы, орбиты, 5 x 105 тел)
 One Billion Stars in 3 -d will Provide… • in our Galaxy… – – – the distance and velocity distributions of all stellar populations the spatial and dynamic structure of the disk and halo its formation history a rigorous framework for stellar structure and evolution theories a large-scale survey of extra-solar planets (~10– 20, 000) a large-scale survey of Solar System bodies (~100, 000) • …and beyond – – definitive distance standards out to the LMC/SMC rapid reaction alerts for supernovae and burst sources (~20, 000) QSO detection, redshifts, microlensing structure (~500, 000) fundamental quantities to unprecedented accuracy: to 10 -7 (10 -3 present)
One Billion Stars in 3 -d will Provide… • in our Galaxy… – – – the distance and velocity distributions of all stellar populations the spatial and dynamic structure of the disk and halo its formation history a rigorous framework for stellar structure and evolution theories a large-scale survey of extra-solar planets (~10– 20, 000) a large-scale survey of Solar System bodies (~100, 000) • …and beyond – – definitive distance standards out to the LMC/SMC rapid reaction alerts for supernovae and burst sources (~20, 000) QSO detection, redshifts, microlensing structure (~500, 000) fundamental quantities to unprecedented accuracy: to 10 -7 (10 -3 present)
 Planets: Expected Discoveries • Astrometric survey: – – – monitoring of hundreds of thousands of FGK stars to ~200 pc detection limits: ~1 MJ and P < 10 years complete census of all stellar types, P = 2– 9 years masses, rather than lower limits (m sin i) multiple systems measurable, giving relative inclinations • Results expected: – – 10– 20, 000 planets (~10 per day) displacement for 47 UMa = 360 as orbits for ~5000 systems masses down to 10 MEarth to 10 pc • Photometric transits: ~5000?
Planets: Expected Discoveries • Astrometric survey: – – – monitoring of hundreds of thousands of FGK stars to ~200 pc detection limits: ~1 MJ and P < 10 years complete census of all stellar types, P = 2– 9 years masses, rather than lower limits (m sin i) multiple systems measurable, giving relative inclinations • Results expected: – – 10– 20, 000 planets (~10 per day) displacement for 47 UMa = 360 as orbits for ~5000 systems masses down to 10 MEarth to 10 pc • Photometric transits: ~5000?
 Gaia: Studies of the Solar System • Asteroids etc: – – – – deep and uniform (20 mag) detection of all moving objects 105– 106 new objects expected (65, 000 presently) taxonomy/mineralogical composition versus heliocentric distance diameters for ~1000, masses for ~100 orbits: 30 times better than present, even after 100 years Trojan companions of Mars, Earth and Venus Kuiper Belt objects: ~300 to 20 mag (binarity, Plutinos) • Near-Earth Objects: – Amors, Apollos and Atens (442, 455, 75 known today) – ~1600 Earth-crossers >1 km predicted (100 currently known) – detection limit: 260– 590 m at 1 AU, depending on albedo
Gaia: Studies of the Solar System • Asteroids etc: – – – – deep and uniform (20 mag) detection of all moving objects 105– 106 new objects expected (65, 000 presently) taxonomy/mineralogical composition versus heliocentric distance diameters for ~1000, masses for ~100 orbits: 30 times better than present, even after 100 years Trojan companions of Mars, Earth and Venus Kuiper Belt objects: ~300 to 20 mag (binarity, Plutinos) • Near-Earth Objects: – Amors, Apollos and Atens (442, 455, 75 known today) – ~1600 Earth-crossers >1 km predicted (100 currently known) – detection limit: 260– 590 m at 1 AU, depending on albedo
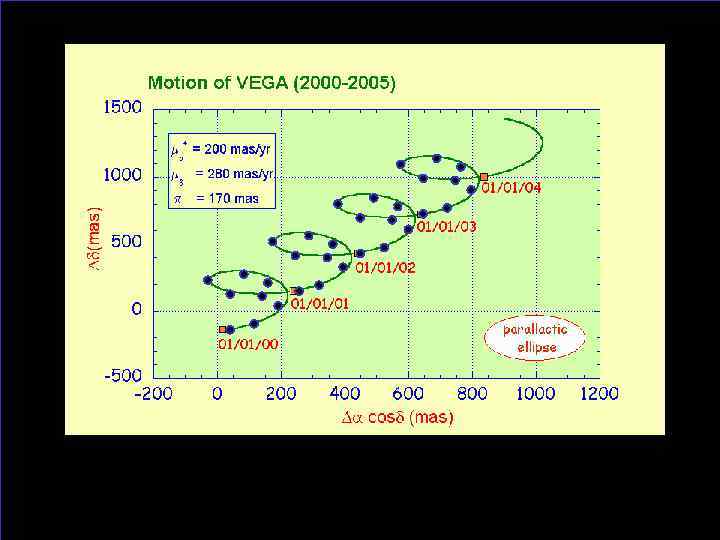
 Принципы измерений (1) • Gaia – сканирующий спутник: - невозможно навестись на конкретный объект - невозможно изменить план наблюдений - каждый источник наблюдается астрометрически ~ 80 раз фотометрически 150 раз • Gaia собирает астрометрическую, фотометрическую и спектрометрическую информацию • Gaia имеет собственную систему обнаружения источников • Объекты наблюдаются более или менее равномерно в течение всего времени работы - параллаксы, собственные движения - орбиты - кривые блеска
Принципы измерений (1) • Gaia – сканирующий спутник: - невозможно навестись на конкретный объект - невозможно изменить план наблюдений - каждый источник наблюдается астрометрически ~ 80 раз фотометрически 150 раз • Gaia собирает астрометрическую, фотометрическую и спектрометрическую информацию • Gaia имеет собственную систему обнаружения источников • Объекты наблюдаются более или менее равномерно в течение всего времени работы - параллаксы, собственные движения - орбиты - кривые блеска
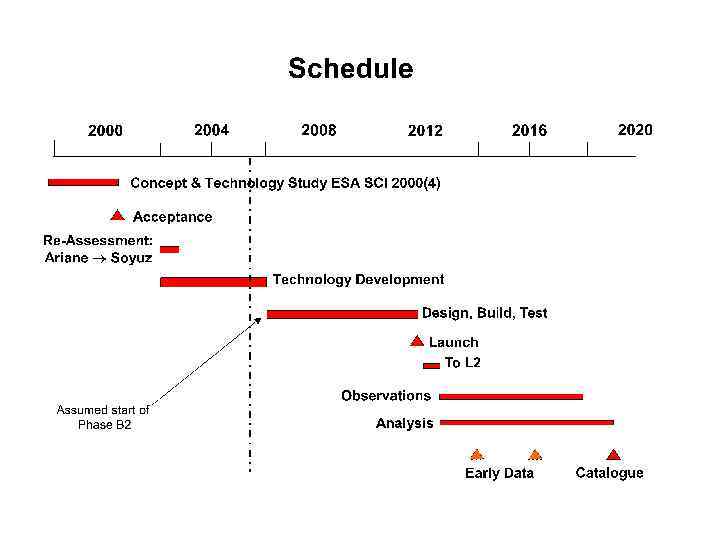
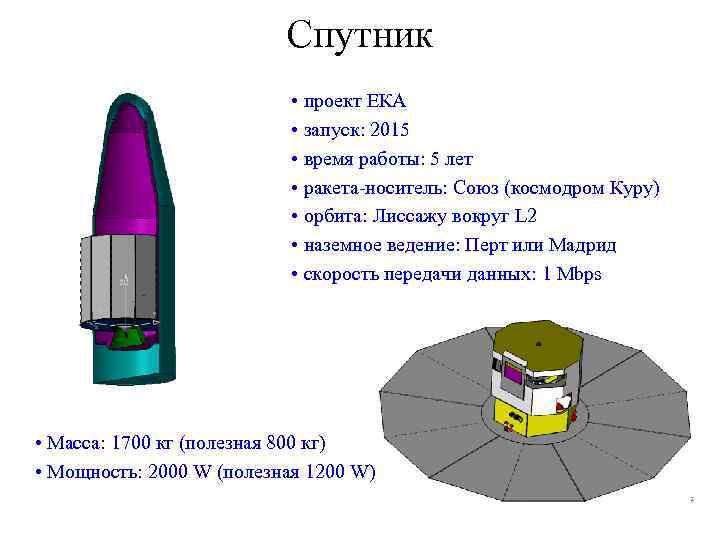 Спутник • проект ЕКА • запуск: 2015 • время работы: 5 лет • ракета-носитель: Союз (космодром Куру) • орбита: Лиссажу вокруг L 2 • наземное ведение: Перт или Мадрид • скорость передачи данных: 1 Mbps • Масса: 1700 кг (полезная 800 кг) • Мощность: 2000 W (полезная 1200 W)
Спутник • проект ЕКА • запуск: 2015 • время работы: 5 лет • ракета-носитель: Союз (космодром Куру) • орбита: Лиссажу вокруг L 2 • наземное ведение: Перт или Мадрид • скорость передачи данных: 1 Mbps • Масса: 1700 кг (полезная 800 кг) • Мощность: 2000 W (полезная 1200 W)
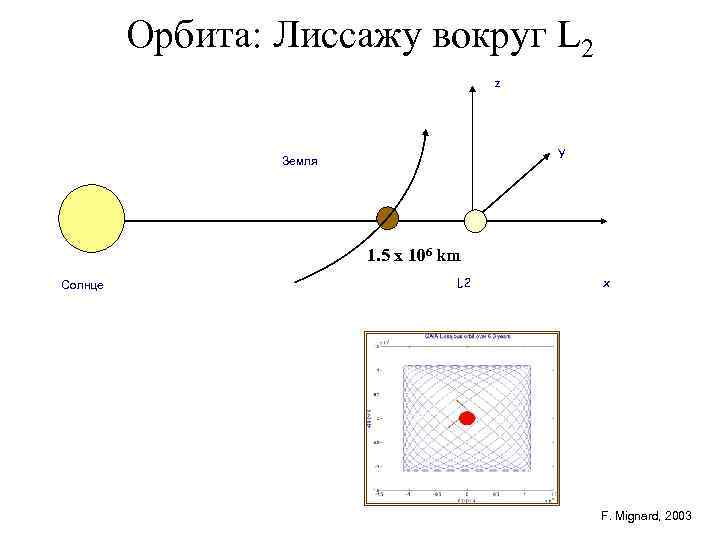 Орбита: Лиссажу вокруг L 2 z Y Земля 1. 5 x 106 km Солнце L 2 x F. Mignard, 2003
Орбита: Лиссажу вокруг L 2 z Y Земля 1. 5 x 106 km Солнце L 2 x F. Mignard, 2003
 Точки Лагранжа в системе Солнце -Земля
Точки Лагранжа в системе Солнце -Земля
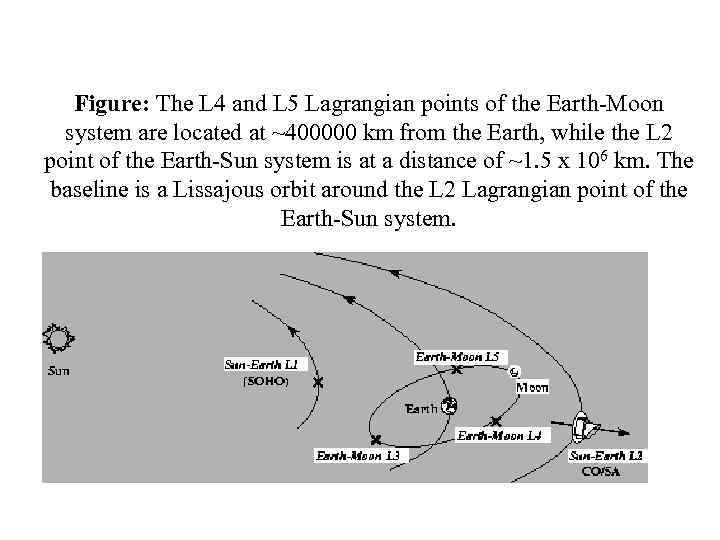 Figure: The L 4 and L 5 Lagrangian points of the Earth-Moon system are located at ~400000 km from the Earth, while the L 2 point of the Earth-Sun system is at a distance of ~1. 5 x 106 km. The baseline is a Lissajous orbit around the L 2 Lagrangian point of the Earth-Sun system.
Figure: The L 4 and L 5 Lagrangian points of the Earth-Moon system are located at ~400000 km from the Earth, while the L 2 point of the Earth-Sun system is at a distance of ~1. 5 x 106 km. The baseline is a Lissajous orbit around the L 2 Lagrangian point of the Earth-Sun system.
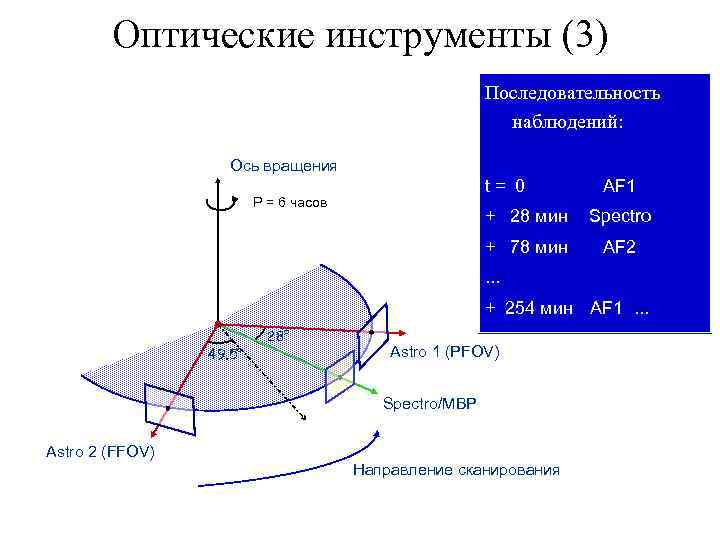 Оптические инструменты (3) Последовательность наблюдений: Ось вращения t = 0 P = 6 часов AF 1 + 28 мин Spectro + 78 мин AF 2 . . . + 254 мин AF 1 . . . 49. 5° 28° Astro 1 (PFOV) Spectro/MBP Astro 2 (FFOV) Направление сканирования
Оптические инструменты (3) Последовательность наблюдений: Ось вращения t = 0 P = 6 часов AF 1 + 28 мин Spectro + 78 мин AF 2 . . . + 254 мин AF 1 . . . 49. 5° 28° Astro 1 (PFOV) Spectro/MBP Astro 2 (FFOV) Направление сканирования
 Прецессия оси вращения (1) 50° HIP угол спин/Солнце угловая скорость "/с вращение (h) прецессия (d) опорный угол (°) Gaia 43 167 2. 2 58 58 50° 60 6. 0 70 106
Прецессия оси вращения (1) 50° HIP угол спин/Солнце угловая скорость "/с вращение (h) прецессия (d) опорный угол (°) Gaia 43 167 2. 2 58 58 50° 60 6. 0 70 106
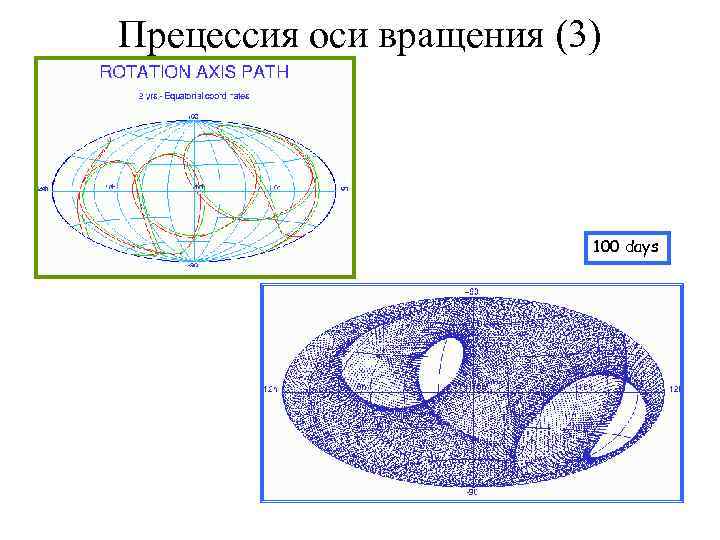 Прецессия оси вращения (3) 100 days
Прецессия оси вращения (3) 100 days
 What is JASMINE is Japan Astrometry Satellite Mission for INfrared Exploration
What is JASMINE is Japan Astrometry Satellite Mission for INfrared Exploration
 Outline of JASMINE We plan the infrared space astrometry(JASMINE) project in Japan. JASMINE is a scanning astrometric satellite and will measure parallaxes, positions, and proper motions with the precision of 10 μarcsec at z=15. 5 mag(zband: 0. 9μm). JASMINE can observe a few hundred million stars belonging to the Galactic disk and bulge components which are hidden by the interstellar dust extinction in optical bands. It will be launched in around 2014 and the orbit will be the Lissajous orbit around the Sun-Earth L 2 point with 5 years mission life. As for the payload, we adopt the 3 -mirrors optical system(modified Korsch system) with the primary mirror of 2 m diameter and 66. 7 m focal length. The beam combiner should be used for achievement of the global astrometry as used in the HIPPARCOS satellite. On the astro-focal plane, we put about 160 CCDs in which TDI mode(drift scan mode) ca be operated. The effective filed of view is 0. 23 square-degree. The main scientific objective of JASMINE is to study the fundamental structure and evolution of the Galactic disk and bulge. Furthermore its important objective is to investigate dark matters in small scales, stellar physics, exploration of other planet systems, gravitational lens objects, verification of the general relativity, etc.
Outline of JASMINE We plan the infrared space astrometry(JASMINE) project in Japan. JASMINE is a scanning astrometric satellite and will measure parallaxes, positions, and proper motions with the precision of 10 μarcsec at z=15. 5 mag(zband: 0. 9μm). JASMINE can observe a few hundred million stars belonging to the Galactic disk and bulge components which are hidden by the interstellar dust extinction in optical bands. It will be launched in around 2014 and the orbit will be the Lissajous orbit around the Sun-Earth L 2 point with 5 years mission life. As for the payload, we adopt the 3 -mirrors optical system(modified Korsch system) with the primary mirror of 2 m diameter and 66. 7 m focal length. The beam combiner should be used for achievement of the global astrometry as used in the HIPPARCOS satellite. On the astro-focal plane, we put about 160 CCDs in which TDI mode(drift scan mode) ca be operated. The effective filed of view is 0. 23 square-degree. The main scientific objective of JASMINE is to study the fundamental structure and evolution of the Galactic disk and bulge. Furthermore its important objective is to investigate dark matters in small scales, stellar physics, exploration of other planet systems, gravitational lens objects, verification of the general relativity, etc.
 Nano-JASMINE A sketch of the satellite with 5 cm primary mirror diameter observing the Milky Way. Nano-JASMINE will provide a star catalogue (200 000 stars) covering the whole sky. Nano-JASMINE is scheduled to be launched in 2013 at the Alcantara space center in Brazil by a Cyclone-4 rocket developed in Ukraine. Nano-JASMINE will operate in zw-band ( 0. 8μ m) to perform an all sky survey with an accuracy of 3 milliarcseconds for position, parallaxes and proper motions
Nano-JASMINE A sketch of the satellite with 5 cm primary mirror diameter observing the Milky Way. Nano-JASMINE will provide a star catalogue (200 000 stars) covering the whole sky. Nano-JASMINE is scheduled to be launched in 2013 at the Alcantara space center in Brazil by a Cyclone-4 rocket developed in Ukraine. Nano-JASMINE will operate in zw-band ( 0. 8μ m) to perform an all sky survey with an accuracy of 3 milliarcseconds for position, parallaxes and proper motions
 Small-JASMINE will observes towards a region around the Galactic center and other small regions, which include interesting scientific targets, with accuracies of 10 to 50 μ arcseconds in an infrared Hw-band (1. 7 μ ). The target launch date is around 2017. μ
Small-JASMINE will observes towards a region around the Galactic center and other small regions, which include interesting scientific targets, with accuracies of 10 to 50 μ arcseconds in an infrared Hw-band (1. 7 μ ). The target launch date is around 2017. μ
 (Medium-sized) JASMINE is an extended mission of Small-JASMINE, which will observe towards almost the whole region of the Galactic bulge with accuracies of 10 μ arcseconds in Kw-band (2. 0 μ m). The target launch date is the first half of the 2020 s. ∼
(Medium-sized) JASMINE is an extended mission of Small-JASMINE, which will observe towards almost the whole region of the Galactic bulge with accuracies of 10 μ arcseconds in Kw-band (2. 0 μ m). The target launch date is the first half of the 2020 s. ∼


 SIM Planet. Quest will: • search for terrestrial planets around nearby stars, and measure planetary masses • characterize the orbital ellipticity and inclination of multiple-planet systems, to determine the stability and the evolution of planetary systems • search for “Solar System analog” systems with giant planets at 5 -10 AU • investigate formation and migration scenarios that might explain the puzzling presence of ‘hot Jupiters’ in very short-period orbits
SIM Planet. Quest will: • search for terrestrial planets around nearby stars, and measure planetary masses • characterize the orbital ellipticity and inclination of multiple-planet systems, to determine the stability and the evolution of planetary systems • search for “Solar System analog” systems with giant planets at 5 -10 AU • investigate formation and migration scenarios that might explain the puzzling presence of ‘hot Jupiters’ in very short-period orbits
 ORIGIN AND DESTINY OF STARS SIM will: • Associate stars with their sites of formation to advance studies of their evolution • Assist in measuring the masses and luminosities of compact stellar remnants • Probe the formation of binary stars
ORIGIN AND DESTINY OF STARS SIM will: • Associate stars with their sites of formation to advance studies of their evolution • Assist in measuring the masses and luminosities of compact stellar remnants • Probe the formation of binary stars
 Comparison of SIM with GAIA's strength is in numbers. The mission will survey ~1 billion stars, with both astrometric and radial velocity measurements. GAIA is a global astrometric mission, with a goal of ~16 µas at 15 mag. At 18 mag the accuracy falls to ~200 µas whereas SIM will still be capable of 6 µas accuracy For astrometry of extragalactic targets, at 18 mag SIM's advantage is very large, similar to its advantage for planet search. http: //www. rssd. esa. int/index. php? project=GAIA&page=Info_sheets_accu racy
Comparison of SIM with GAIA's strength is in numbers. The mission will survey ~1 billion stars, with both astrometric and radial velocity measurements. GAIA is a global astrometric mission, with a goal of ~16 µas at 15 mag. At 18 mag the accuracy falls to ~200 µas whereas SIM will still be capable of 6 µas accuracy For astrometry of extragalactic targets, at 18 mag SIM's advantage is very large, similar to its advantage for planet search. http: //www. rssd. esa. int/index. php? project=GAIA&page=Info_sheets_accu racy
 "OSIRIS" The Institute of Astronomy of the Russian Academy of Sciences proposed the project of a space mission intended for measurements of coordinates of stars. The expected accuracy will be about 10 micro arcseconds, that a hundred times exceeds accuracy of ground observations and while achieved in space. Such measurements will allow us to determine distances up to any stars in the Galaxy and its vicinities. Besides, the reference in the Universe will be specified - the metrological basis of all researches of the environmental world. The offered instrument is based on the principle of optical interferometry. The Optical Stellar Interferometer "OSIRIS" is the only astrometric device under development that will provide the microsecond precision of a single measurement.
"OSIRIS" The Institute of Astronomy of the Russian Academy of Sciences proposed the project of a space mission intended for measurements of coordinates of stars. The expected accuracy will be about 10 micro arcseconds, that a hundred times exceeds accuracy of ground observations and while achieved in space. Such measurements will allow us to determine distances up to any stars in the Galaxy and its vicinities. Besides, the reference in the Universe will be specified - the metrological basis of all researches of the environmental world. The offered instrument is based on the principle of optical interferometry. The Optical Stellar Interferometer "OSIRIS" is the only astrometric device under development that will provide the microsecond precision of a single measurement.
 РЕЗУЛЬТАТ • Астрометрия – это то, чем раньше занимались астрометристы • Астрометрия – это то, чем теперь занимаются астрофизики • Great Accuracy In Astrometry - GAIA • Great Advances In Astrophysics - GAIA
РЕЗУЛЬТАТ • Астрометрия – это то, чем раньше занимались астрометристы • Астрометрия – это то, чем теперь занимаются астрофизики • Great Accuracy In Astrometry - GAIA • Great Advances In Astrophysics - GAIA


