ae944f072d2fb63c0672e6ec81ca07f2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 62
 Southwest Asia and North Africa
Southwest Asia and North Africa
 Introduction v Rich cultural legacy v Agricultural revolution v Urban civilization v Petroleum industry v 68% of world’s oil reserves v OPEC v Political v Islamic issues fundamentalism Aleppo, Syria
Introduction v Rich cultural legacy v Agricultural revolution v Urban civilization v Petroleum industry v 68% of world’s oil reserves v OPEC v Political v Islamic issues fundamentalism Aleppo, Syria
 Environmental Geography
Environmental Geography
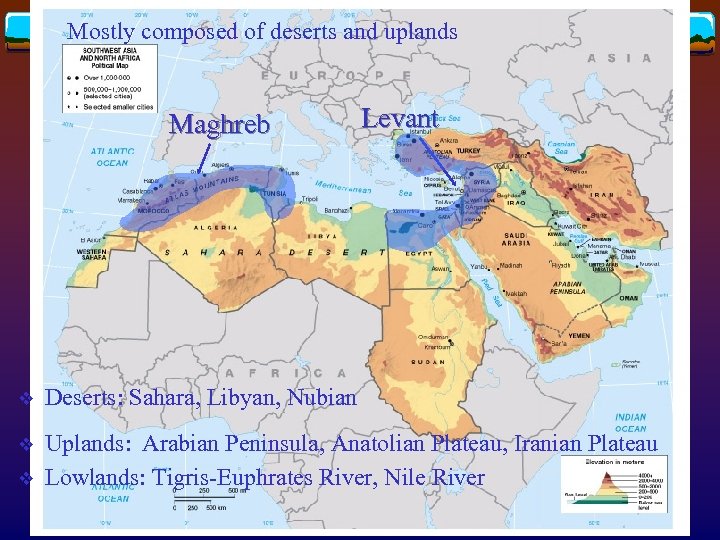 Mostly composed of deserts and uplands Maghreb Levant v Deserts: Sahara, Libyan, Nubian v Uplands: Arabian Peninsula, Anatolian Plateau, Iranian Plateau Lowlands: Tigris-Euphrates River, Nile River v
Mostly composed of deserts and uplands Maghreb Levant v Deserts: Sahara, Libyan, Nubian v Uplands: Arabian Peninsula, Anatolian Plateau, Iranian Plateau Lowlands: Tigris-Euphrates River, Nile River v
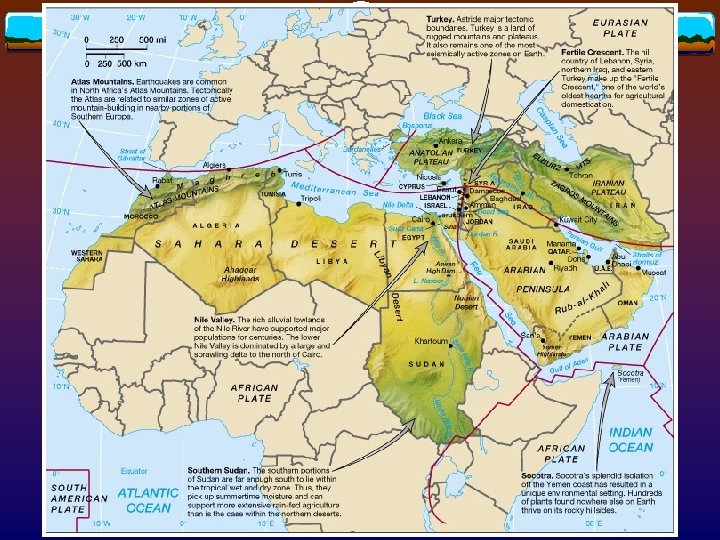
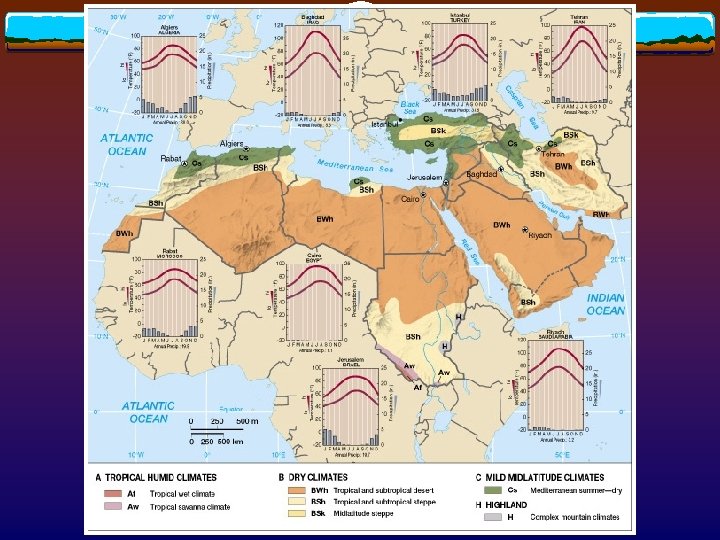
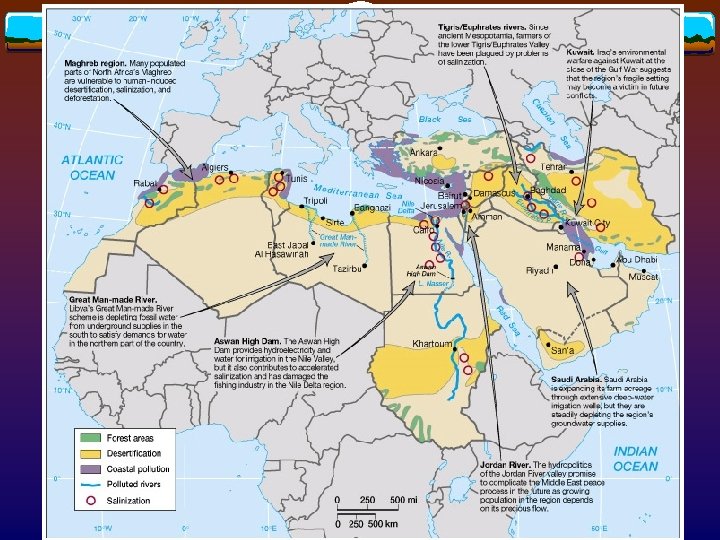
 Salinization v How? Extensive irrigation + arid climates Salt accumulation in topsoil Lower crop yields, and land abandonment v Where? Iraq, central Iran, Egypt, and irrigated Maghreb
Salinization v How? Extensive irrigation + arid climates Salt accumulation in topsoil Lower crop yields, and land abandonment v Where? Iraq, central Iran, Egypt, and irrigated Maghreb
 Water management v Qanat system Tapping into groundwater through tunnel v Iran Arabian Peninsula, and North Africa v
Water management v Qanat system Tapping into groundwater through tunnel v Iran Arabian Peninsula, and North Africa v
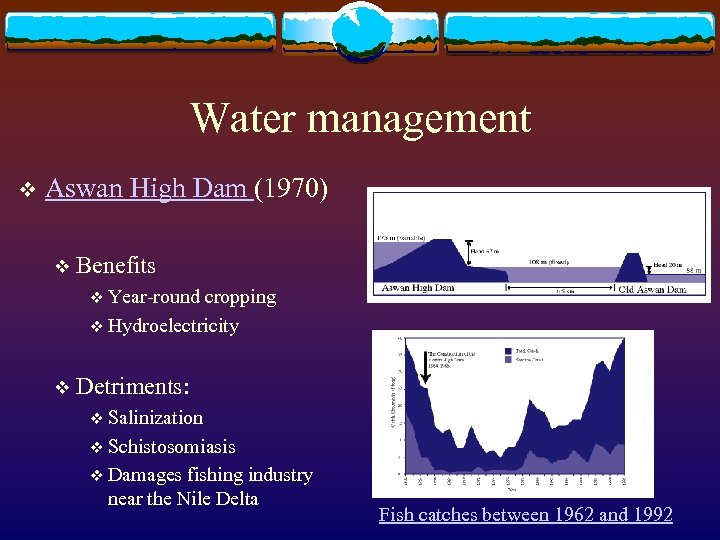 Water management v Aswan High Dam (1970) v Benefits v Year-round cropping v Hydroelectricity v Detriments: v Salinization v Schistosomiasis v Damages fishing industry near the Nile Delta Fish catches between 1962 and 1992
Water management v Aswan High Dam (1970) v Benefits v Year-round cropping v Hydroelectricity v Detriments: v Salinization v Schistosomiasis v Damages fishing industry near the Nile Delta Fish catches between 1962 and 1992
 Hydropolitics v What? Interplay of water resource issues and politics v Where? Nile River v Sudan Egypt Tigris-Euphrates River v Turkey Iraq, Syria Jordan River v Israel, Palestine, Jordan, Syria
Hydropolitics v What? Interplay of water resource issues and politics v Where? Nile River v Sudan Egypt Tigris-Euphrates River v Turkey Iraq, Syria Jordan River v Israel, Palestine, Jordan, Syria
 Population and Settlement
Population and Settlement
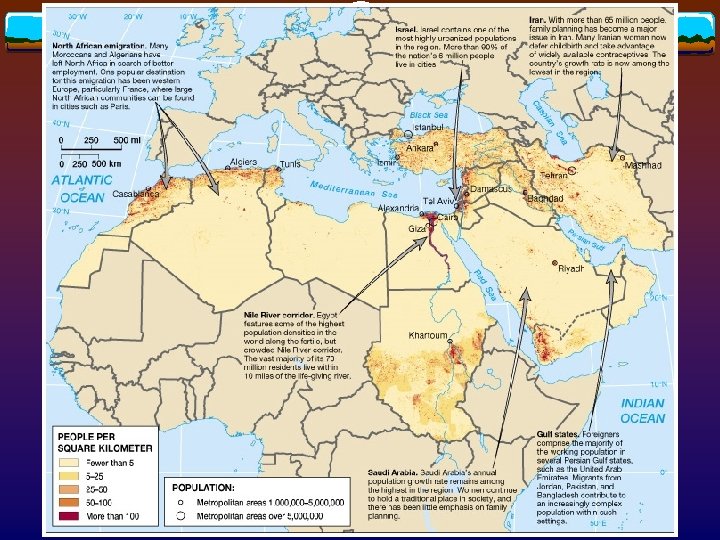
 v More than 400 million v Highest physiological densities v Tie between water and life v Population cluster v North v The Africa Nile Valley, and Maghreb region v Southwest Asia v Highlands, and better-watered shores of the Mediterranean
v More than 400 million v Highest physiological densities v Tie between water and life v Population cluster v North v The Africa Nile Valley, and Maghreb region v Southwest Asia v Highlands, and better-watered shores of the Mediterranean
 Rural settlement patterns v What is the most important indicator of rural settlement? water
Rural settlement patterns v What is the most important indicator of rural settlement? water
 Rural settlement patterns v Home to early form of agriculture v 1. Domestication v v v 10, 000 years ago Wheat, barley, cattle, sheep, goats 2. Fertile Crescent v v Early agricultural activity (5, 000 years ago) Lebanon, Syria, northern Iraq, and eastern Turkey
Rural settlement patterns v Home to early form of agriculture v 1. Domestication v v v 10, 000 years ago Wheat, barley, cattle, sheep, goats 2. Fertile Crescent v v Early agricultural activity (5, 000 years ago) Lebanon, Syria, northern Iraq, and eastern Turkey
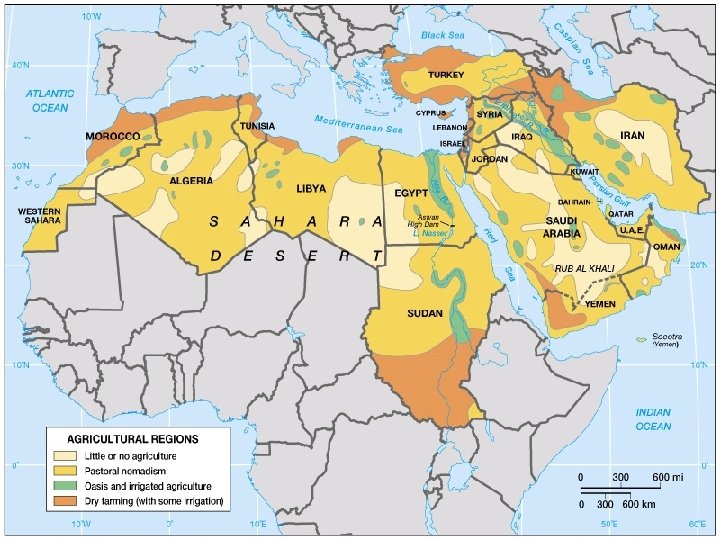
 Rural settlement patterns v Reflects interrelationship between water and life v 1. Pastoral nomadism In the drier portions of the region, inadequate moisture make permanent settlement impossible v Seasonal movement of livestock from place to place v v 2. Oasis settlement v Tightly clustered permanent settlement
Rural settlement patterns v Reflects interrelationship between water and life v 1. Pastoral nomadism In the drier portions of the region, inadequate moisture make permanent settlement impossible v Seasonal movement of livestock from place to place v v 2. Oasis settlement v Tightly clustered permanent settlement
 Rural settlement patterns v 3. Irrigated agriculture along exotic rivers v Exotic rivers v Transport water from distant, more humid lands into drier regions v eg. Nile, Tigris, Euphrates v Irrigated collective farming v eg. v Kibbutzes 4. Dryland agriculture Depends on seasonal moisture to support farming v Practiced on the Mediterranean climate regions v
Rural settlement patterns v 3. Irrigated agriculture along exotic rivers v Exotic rivers v Transport water from distant, more humid lands into drier regions v eg. Nile, Tigris, Euphrates v Irrigated collective farming v eg. v Kibbutzes 4. Dryland agriculture Depends on seasonal moisture to support farming v Practiced on the Mediterranean climate regions v
 Urban settlement patterns v What shaped the urban landscapes? v v. Trades v Political system v. Religion Colonialism v Globalization
Urban settlement patterns v What shaped the urban landscapes? v v. Trades v Political system v. Religion Colonialism v Globalization
 Cities as centers of political authority v 3500 BC Mesopotamia v 3000 BC Egypt v Temples, palaces, tombs, and public buildings
Cities as centers of political authority v 3500 BC Mesopotamia v 3000 BC Egypt v Temples, palaces, tombs, and public buildings
 Cities as trading centers v 2000 BC the shores of the eastern Mediterranean v Beirut v Port (Lebanon), Damascus (Syria) facilities, warehouse districts, and commercial thoroughfares
Cities as trading centers v 2000 BC the shores of the eastern Mediterranean v Beirut v Port (Lebanon), Damascus (Syria) facilities, warehouse districts, and commercial thoroughfares
 Cities as religious centers v Islam (622) v 8 th century Baghdad, Cairo v Walled urban core (medina), bazaar
Cities as religious centers v Islam (622) v 8 th century Baghdad, Cairo v Walled urban core (medina), bazaar
 colonialism v Added another layer of urban landscape features v Late 19 th century North Africa v Algiers (French), Cairo (British)
colonialism v Added another layer of urban landscape features v Late 19 th century North Africa v Algiers (French), Cairo (British)
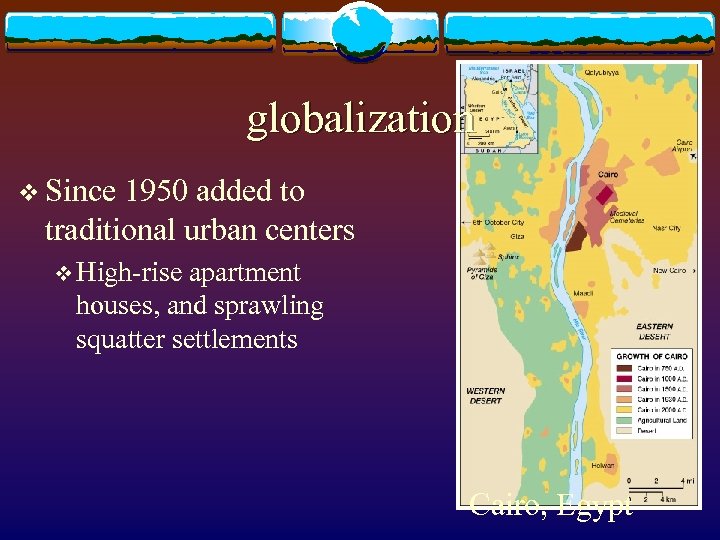 globalization v Since 1950 added to traditional urban centers v High-rise apartment houses, and sprawling squatter settlements Cairo, Egypt
globalization v Since 1950 added to traditional urban centers v High-rise apartment houses, and sprawling squatter settlements Cairo, Egypt
 globalization v Since 1970 oil-rich states of the Persian Gulf v Modern Western urban design, futuristic architecture, and new transportation infrastructure Abu Dhabi, UAE
globalization v Since 1970 oil-rich states of the Persian Gulf v Modern Western urban design, futuristic architecture, and new transportation infrastructure Abu Dhabi, UAE
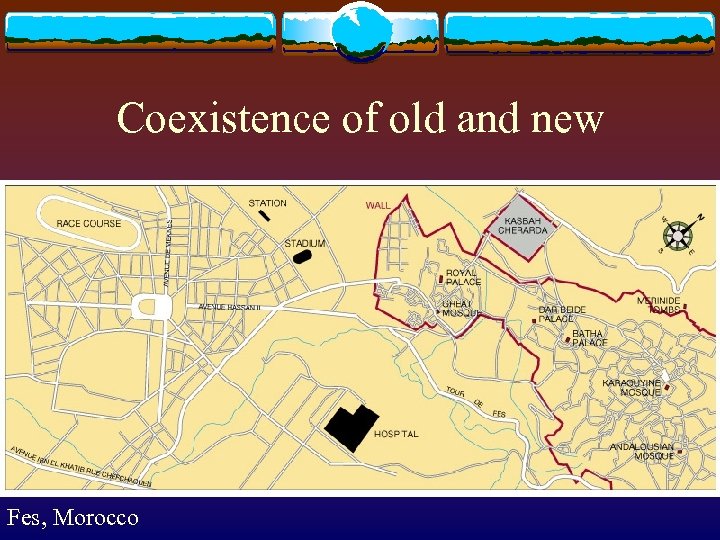 Coexistence of old and new Fes, Morocco
Coexistence of old and new Fes, Morocco
 Migration patterns v Rural-to-urban shift v v Migration within the region v v Saudi Arabian: 18% (1950) 83% (2000) To oil-rich states such as Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, UAE Migration between the region v Job Germany v Algerian, Moroccan France v Turkish v Political forces Lebanese, Iranian western Europe, North America v Jewish Israel v
Migration patterns v Rural-to-urban shift v v Migration within the region v v Saudi Arabian: 18% (1950) 83% (2000) To oil-rich states such as Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, UAE Migration between the region v Job Germany v Algerian, Moroccan France v Turkish v Political forces Lebanese, Iranian western Europe, North America v Jewish Israel v
 Cultural Coherence and Diversity
Cultural Coherence and Diversity
 Religion v Which religion has originated in Southwest Asia? v. Judaism (4000 years ago) v. Christianity v. Islam (622) (2000 years ago)
Religion v Which religion has originated in Southwest Asia? v. Judaism (4000 years ago) v. Christianity v. Islam (622) (2000 years ago)
 Geographies of religion v Judaism BC 2000 Mesopotamia to Canaan AD 70 Jewish Diaspora v Christianity v Outgrowth of Judaism v Emerged 2000 years ago near Israel 1948 Jew’s return to Israel
Geographies of religion v Judaism BC 2000 Mesopotamia to Canaan AD 70 Jewish Diaspora v Christianity v Outgrowth of Judaism v Emerged 2000 years ago near Israel 1948 Jew’s return to Israel
 Geographies of religion v Islam v Originated in Makkah (or Mecca) in AD 622 v Follows Quran (or Koran) v Divided into Shiites and Sunnis v Diffused to Persia (656), North Africa & Iberian Peninsula (750), Central/South Asia, and Southeast Asia
Geographies of religion v Islam v Originated in Makkah (or Mecca) in AD 622 v Follows Quran (or Koran) v Divided into Shiites and Sunnis v Diffused to Persia (656), North Africa & Iberian Peninsula (750), Central/South Asia, and Southeast Asia
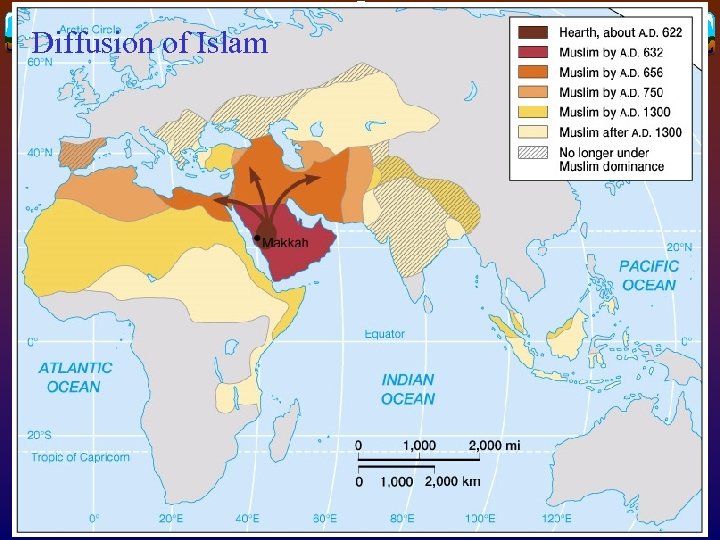 Diffusion of Islam
Diffusion of Islam
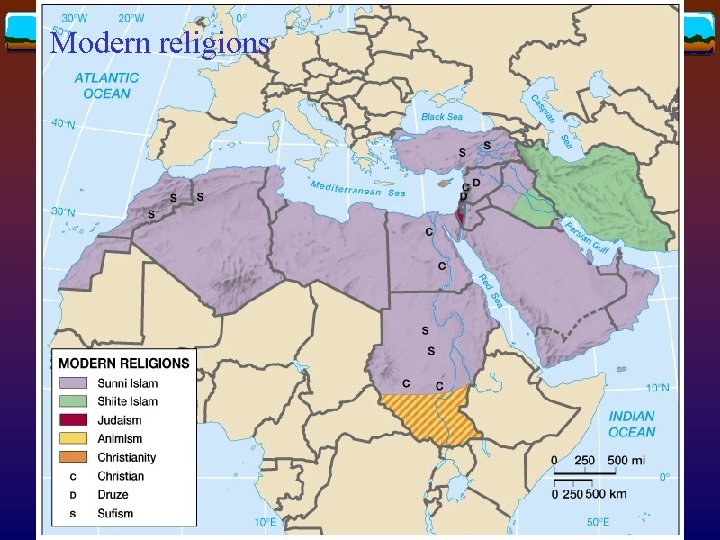 Modern religions
Modern religions
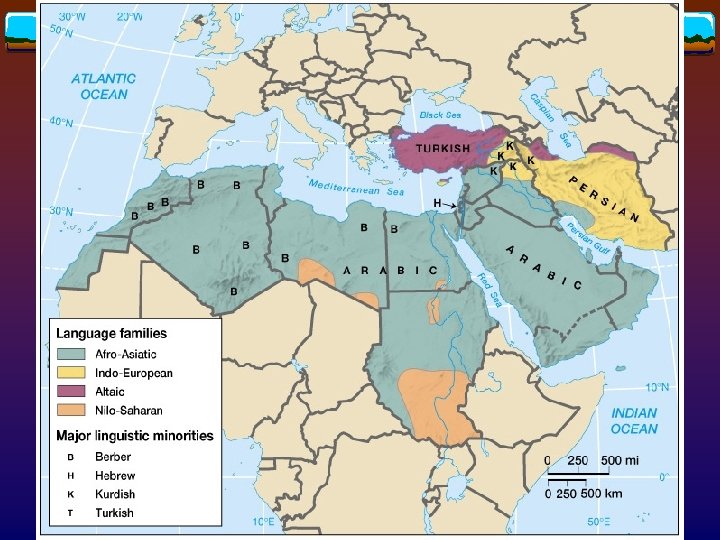
 Geographies of language v Afro-Asiatic v Semitic language v Arabic v Hebrew v v Berber language Indo-European v Indo-Iranian language v Persian v Kurdish v Altaic v Turkish language
Geographies of language v Afro-Asiatic v Semitic language v Arabic v Hebrew v v Berber language Indo-European v Indo-Iranian language v Persian v Kurdish v Altaic v Turkish language
 Geopolitical Framework
Geopolitical Framework
 Colonial legacy v When? v Late arrival because of Turkish Ottoman Empire v Began after WWI (1918) v Ended by the 1950 s
Colonial legacy v When? v Late arrival because of Turkish Ottoman Empire v Began after WWI (1918) v Ended by the 1950 s
 Colonial power - France v Maghreb v Algeria (1830 s) v Tunisia (1881) v Morocco (1912) v After WWI v Syria (1918) v Lebanon (1918)
Colonial power - France v Maghreb v Algeria (1830 s) v Tunisia (1881) v Morocco (1912) v After WWI v Syria (1918) v Lebanon (1918)
 Colonial power - Great Britain v British Protectorate before 1900 v Kuwait, v Suez Canal (1869) v Egypt v After Bahrain, Qatar, UAE, and Aden (1882), Sudan (1896) WWI v Palestine, Transjordan, Iraq
Colonial power - Great Britain v British Protectorate before 1900 v Kuwait, v Suez Canal (1869) v Egypt v After Bahrain, Qatar, UAE, and Aden (1882), Sudan (1896) WWI v Palestine, Transjordan, Iraq
 v So which countries have NOT been occupied by European powers? v Turkey v Saudi Arabia
v So which countries have NOT been occupied by European powers? v Turkey v Saudi Arabia
 Decolonization and independence v North Africa v Egypt, Sudan, Libya, Tunisia, Morocco (1950 s) v Algeria (1962) v Southwest v Iraq Asia (1932), Lebanon (1946), Syria (1946), etc… while containing the cultural seeds of its later trouble
Decolonization and independence v North Africa v Egypt, Sudan, Libya, Tunisia, Morocco (1950 s) v Algeria (1962) v Southwest v Iraq Asia (1932), Lebanon (1946), Syria (1946), etc… while containing the cultural seeds of its later trouble
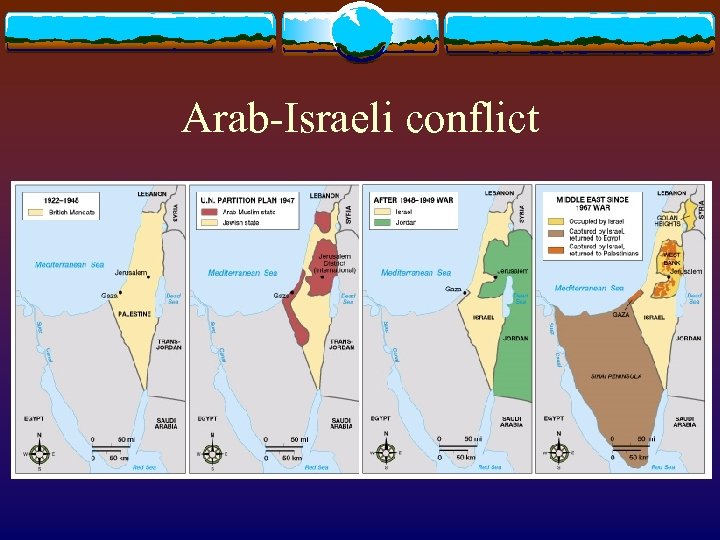 Arab-Israeli conflict
Arab-Israeli conflict
 Arab-Israeli conflict v “Intifada” (1987) v Demonstration, led by Palestinian, against the rule of Israel in Gaza Strip and the West Bank v Agreements v Potential between the PLO and Israel (1990 s) control of the ruling Palestinian Authority (PA) in the Gaza Strip and West Bank
Arab-Israeli conflict v “Intifada” (1987) v Demonstration, led by Palestinian, against the rule of Israel in Gaza Strip and the West Bank v Agreements v Potential between the PLO and Israel (1990 s) control of the ruling Palestinian Authority (PA) in the Gaza Strip and West Bank
 Islamic fundamentalism v Khomeni took power in Iran (1979) v “Rule the country by the Islamic law” v Sudan (1989) v Algeria (1992~) v Egypt, Turkey, and Saudi Arabia…
Islamic fundamentalism v Khomeni took power in Iran (1979) v “Rule the country by the Islamic law” v Sudan (1989) v Algeria (1992~) v Egypt, Turkey, and Saudi Arabia…
 Conflicts within states v Lebanon (1975 -95) v Discord among Christian and Muslim communities v Spillover of Arab-Israeli conflict v Iraq v South: Shiites v North: Kurds v Cyprus v Northern third: Islamic Turkish v South: Greek Orthodox
Conflicts within states v Lebanon (1975 -95) v Discord among Christian and Muslim communities v Spillover of Arab-Israeli conflict v Iraq v South: Shiites v North: Kurds v Cyprus v Northern third: Islamic Turkish v South: Greek Orthodox
 Conflicts between states Sahara Morocco (late 1970 s) v Libya Israel, Western Europe, U. S…. (1969~) v Sudan Egypt (1995) v Iran-Iraq war (1980 -88) v Persian Gulf war (1990 -91) v Western
Conflicts between states Sahara Morocco (late 1970 s) v Libya Israel, Western Europe, U. S…. (1969~) v Sudan Egypt (1995) v Iran-Iraq war (1980 -88) v Persian Gulf war (1990 -91) v Western
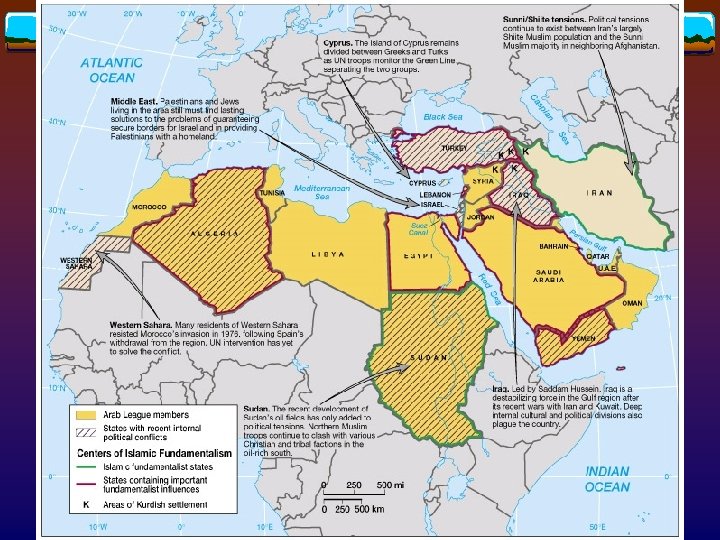
 Geopolitical issues v What v is the destablizing force after WWII? Creation of Israel v. Rise v. Cold of Islamic fundamentalism war (eg. Libya) v. Ethnic differences (eg. Kurds) v. Political/religious divide (eg. Sudan, Labanon)
Geopolitical issues v What v is the destablizing force after WWII? Creation of Israel v. Rise v. Cold of Islamic fundamentalism war (eg. Libya) v. Ethnic differences (eg. Kurds) v. Political/religious divide (eg. Sudan, Labanon)
 Relations with the U. S. v Strong allies Israel, and Turkey v Strongly opposed Iran, Iraq, Syria, Libya v Ambiguous relations Saudi Arabia
Relations with the U. S. v Strong allies Israel, and Turkey v Strongly opposed Iran, Iraq, Syria, Libya v Ambiguous relations Saudi Arabia
 Economic and Social Development
Economic and Social Development
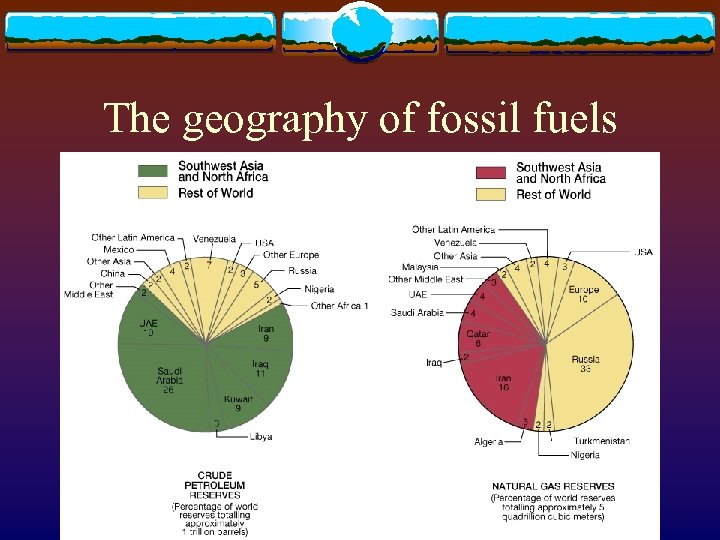 The geography of fossil fuels
The geography of fossil fuels
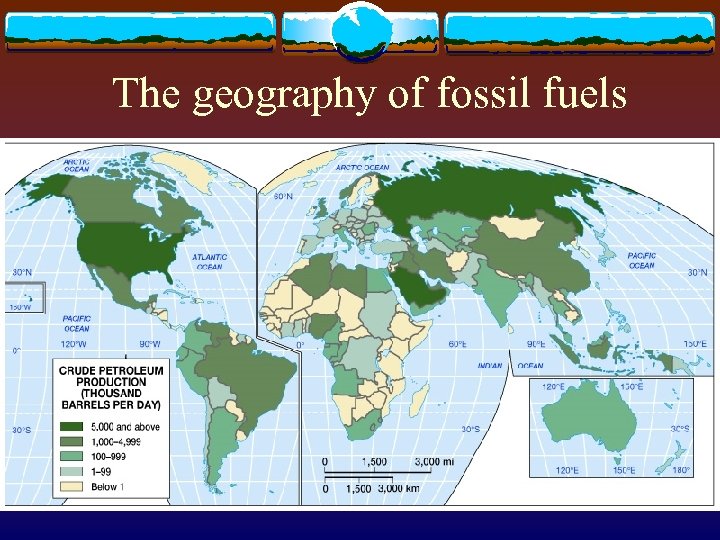 The geography of fossil fuels
The geography of fossil fuels
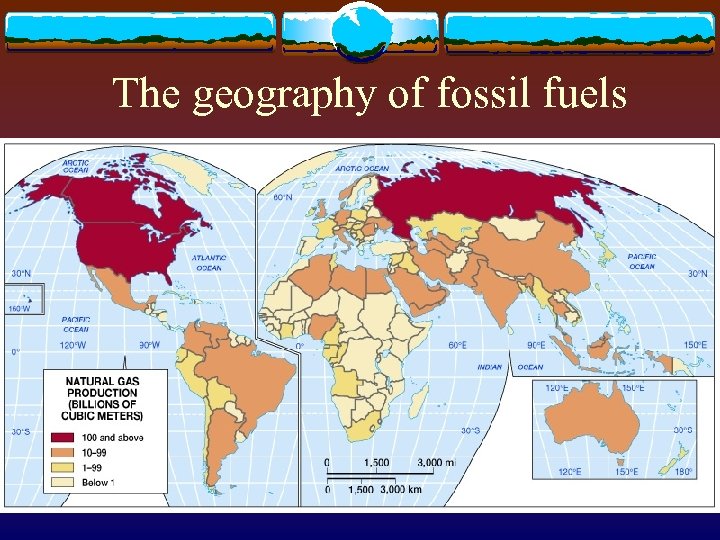 The geography of fossil fuels
The geography of fossil fuels
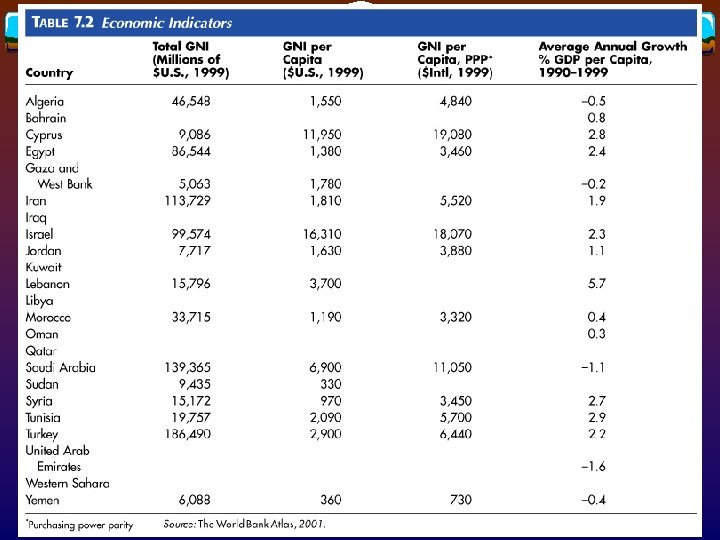
 Regional economic patterns v Higher-income v Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Qatar, Bahrain, and UAE v Lowe-income v Algeria, oil exporters Libya, Iraq, and Iran v Prospering v Israel, oil exporters without oil Turkey, Tunisia, and Cyprus
Regional economic patterns v Higher-income v Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Qatar, Bahrain, and UAE v Lowe-income v Algeria, oil exporters Libya, Iraq, and Iran v Prospering v Israel, oil exporters without oil Turkey, Tunisia, and Cyprus
 Regional patterns of poverty v Sudan v v Civil war Morocco Berber communities v Brain drain v v Egypt v v Population growth Yemen v Civil unrest
Regional patterns of poverty v Sudan v v Civil war Morocco Berber communities v Brain drain v v Egypt v v Population growth Yemen v Civil unrest
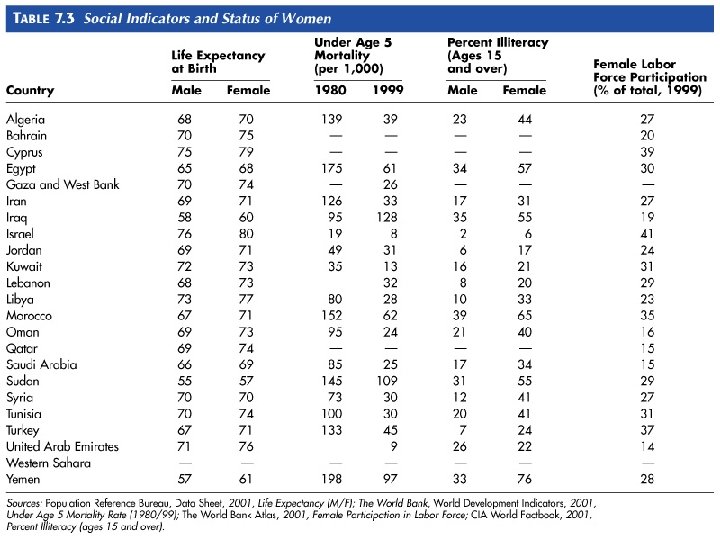
 The role of women v Is major social issues v Lowest female labor participation rates v Large gap between male and female literacy v But is changing v Iran v Libya v Israel
The role of women v Is major social issues v Lowest female labor participation rates v Large gap between male and female literacy v But is changing v Iran v Libya v Israel
 Connections with global economy v Oil economy v Influences oil price v Outflow of capital v Economic integration v E. U. , AFTA, Union of the Arab Maghreb v Role of Saudi Arabia v Tourism v Ancient historical sites; significant religious localities
Connections with global economy v Oil economy v Influences oil price v Outflow of capital v Economic integration v E. U. , AFTA, Union of the Arab Maghreb v Role of Saudi Arabia v Tourism v Ancient historical sites; significant religious localities
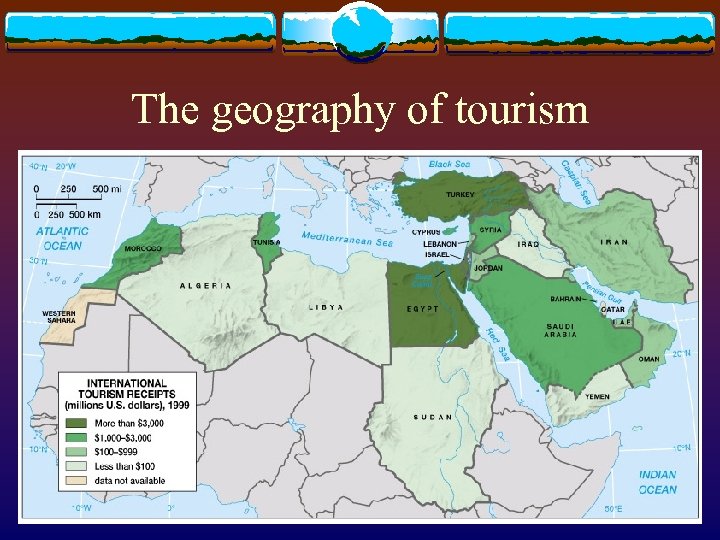 The geography of tourism
The geography of tourism


