7078bee1e92aeffdf86ace4c91ae131d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 57
 South Asia – Past and Present Chapter 17 & 18
South Asia – Past and Present Chapter 17 & 18
 Bell Ringer Page 466 1. Why was Project Snow Leopard created? 2. Where is Mt. Everest? Why do so many people want to climb it? 3. Who built the Taj Mahal? Why? Where is it located? • Project Snow Leopard: created to save the endangered animal & boost the economy in Pakistan • Everest: located on the border of Nepal and China. It is the ultimate challenge because it is the tallest mountain in the world. • The Taj Mahal: located in India and was built by Emperor Shah Jahan as a memorial to his wife.
Bell Ringer Page 466 1. Why was Project Snow Leopard created? 2. Where is Mt. Everest? Why do so many people want to climb it? 3. Who built the Taj Mahal? Why? Where is it located? • Project Snow Leopard: created to save the endangered animal & boost the economy in Pakistan • Everest: located on the border of Nepal and China. It is the ultimate challenge because it is the tallest mountain in the world. • The Taj Mahal: located in India and was built by Emperor Shah Jahan as a memorial to his wife.
 Bell Ringer • Page 472 – 473 – Exploring the Himalayas 1. Why did people in Bhutan build most of their towns where they did? • Water source and lower elevation
Bell Ringer • Page 472 – 473 – Exploring the Himalayas 1. Why did people in Bhutan build most of their towns where they did? • Water source and lower elevation
 Bell Ringer • Page 489 – Map Lab 1. Which three countries disagree about their borders? 2. How does the presence of rivers factor into the cause of the conflict in Kashmir? • India, Pakistan, and China • The rivers are a valuable resource
Bell Ringer • Page 489 – Map Lab 1. Which three countries disagree about their borders? 2. How does the presence of rivers factor into the cause of the conflict in Kashmir? • India, Pakistan, and China • The rivers are a valuable resource
 Bell Ringer • Page 502 -503 1. How do movies and music unify the people of South Asia? 2. Do movies and music bring people together in the United States? • Music keeps Indian traditions alive, and many movies are based on Hindu stories that most people know. • Differing subcultures within the U. S. relate to different movies & music
Bell Ringer • Page 502 -503 1. How do movies and music unify the people of South Asia? 2. Do movies and music bring people together in the United States? • Music keeps Indian traditions alive, and many movies are based on Hindu stories that most people know. • Differing subcultures within the U. S. relate to different movies & music
 South Asia • India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan, Sri Lanka, Maldives • Subcontinent: large landmass that is part of another continent but distinct from it.
South Asia • India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan, Sri Lanka, Maldives • Subcontinent: large landmass that is part of another continent but distinct from it.
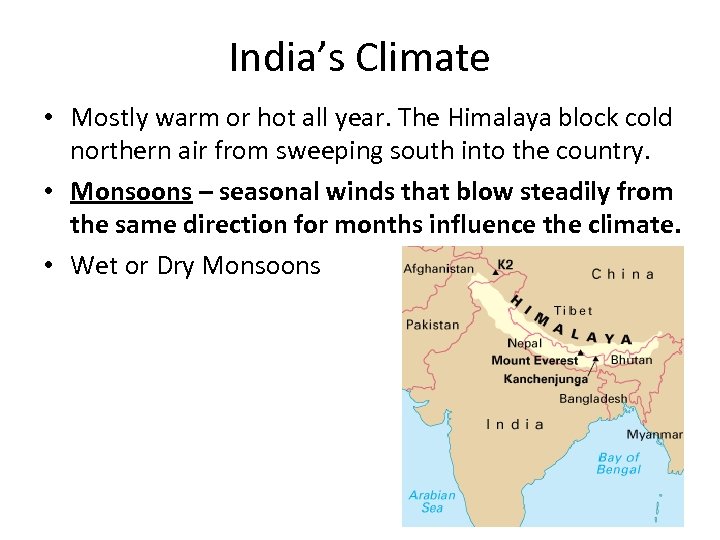 India’s Climate • Mostly warm or hot all year. The Himalaya block cold northern air from sweeping south into the country. • Monsoons – seasonal winds that blow steadily from the same direction for months influence the climate. • Wet or Dry Monsoons
India’s Climate • Mostly warm or hot all year. The Himalaya block cold northern air from sweeping south into the country. • Monsoons – seasonal winds that blow steadily from the same direction for months influence the climate. • Wet or Dry Monsoons
 Green Revolution • Bengal Famine: 1943 world’s worst recorded food disaster when UK ruled India, 4 million people died of starvation. • Green Revolution: effort to use modern techniques and science to increase production of food after India won its independence in 1947.
Green Revolution • Bengal Famine: 1943 world’s worst recorded food disaster when UK ruled India, 4 million people died of starvation. • Green Revolution: effort to use modern techniques and science to increase production of food after India won its independence in 1947.
 • Jute: a plant fiber used for making rope, burlap bags, and carpet backing. • India is the world’s second-largest rice producer, after China.
• Jute: a plant fiber used for making rope, burlap bags, and carpet backing. • India is the world’s second-largest rice producer, after China.
 • Cottage Industry: a home or village-based industry in which family members supply their own equipment to make goods.
• Cottage Industry: a home or village-based industry in which family members supply their own equipment to make goods.
 Pollution • Ganges River: one of the world’s most polluted rivers. • Raw Sewage is one source of pollution. India doesn’t have enough sewage plants for its population. • Pesticides: chemicals used to kill insects that destroy crops.
Pollution • Ganges River: one of the world’s most polluted rivers. • Raw Sewage is one source of pollution. India doesn’t have enough sewage plants for its population. • Pesticides: chemicals used to kill insects that destroy crops.
 You Do • Page 480 – 481 • How are China and India dealing with water pollution?
You Do • Page 480 – 481 • How are China and India dealing with water pollution?
 Essential Question • What is causing water scarcity in South Asia? • Pollution due to a growing population & poor waste disposal
Essential Question • What is causing water scarcity in South Asia? • Pollution due to a growing population & poor waste disposal
 South Asia’s Pollution • Pollution: making the environment dirty and contaminated. • Water pollution is just as bad in other parts of South Asia. • In Pakistan, 38. 5 million people do not have safe drinking water. • In Bangladesh, millions of wells have arsenic in the water. Experts believe that 20, 000 people die yearly in Bangladesh from poison in the water. • Contaminated water kills 500, 000 infants a year in South Asia.
South Asia’s Pollution • Pollution: making the environment dirty and contaminated. • Water pollution is just as bad in other parts of South Asia. • In Pakistan, 38. 5 million people do not have safe drinking water. • In Bangladesh, millions of wells have arsenic in the water. Experts believe that 20, 000 people die yearly in Bangladesh from poison in the water. • Contaminated water kills 500, 000 infants a year in South Asia.
 • Sanitation: measures, taken by people, to protect public health by cleanliness. • More than 50 million people lack proper sanitation in Pakistan, such as sewers. • Rivers in Nepal are so polluted that people cannot use the rivers for drinking water.
• Sanitation: measures, taken by people, to protect public health by cleanliness. • More than 50 million people lack proper sanitation in Pakistan, such as sewers. • Rivers in Nepal are so polluted that people cannot use the rivers for drinking water.
 • Aquifer: a layer beneath the surface of the earth that contains water. • Water is scarce for the 1. 5 billion people in South Asia because of growing population and climate change. • Also – they pollute the water they have. • India’s dams have reduced water flow into Bangladesh, forcing them to use water from aquifers. • According to some scientists, Glaciers are shrinking in the Himalayas, which supply water to rivers and lakes in Asia
• Aquifer: a layer beneath the surface of the earth that contains water. • Water is scarce for the 1. 5 billion people in South Asia because of growing population and climate change. • Also – they pollute the water they have. • India’s dams have reduced water flow into Bangladesh, forcing them to use water from aquifers. • According to some scientists, Glaciers are shrinking in the Himalayas, which supply water to rivers and lakes in Asia
 • Conservation: protection of the environment, including nature and animals. • In India, conservation of the rivers is a national issue. • The people cannot interact normally with their natural environment. The water is polluted, making people sick and marine life to die. • Ecosystem: a group of interacting organisms and their natural environment.
• Conservation: protection of the environment, including nature and animals. • In India, conservation of the rivers is a national issue. • The people cannot interact normally with their natural environment. The water is polluted, making people sick and marine life to die. • Ecosystem: a group of interacting organisms and their natural environment.
 Pollution Solution • In 1986, India’s government passed the Environmental Protection Act of India: It allows the government to stop industries from polluting.
Pollution Solution • In 1986, India’s government passed the Environmental Protection Act of India: It allows the government to stop industries from polluting.
 Essential Question 1. What are the main sources of pollution in the Ganges River ? • Poor waste disposal (trash & sewage) • Pollution from Industry (chemicals) 2. What is causing water scarcity in South Asia? • Increasing population • Climate change • India’s dams • Pollution
Essential Question 1. What are the main sources of pollution in the Ganges River ? • Poor waste disposal (trash & sewage) • Pollution from Industry (chemicals) 2. What is causing water scarcity in South Asia? • Increasing population • Climate change • India’s dams • Pollution
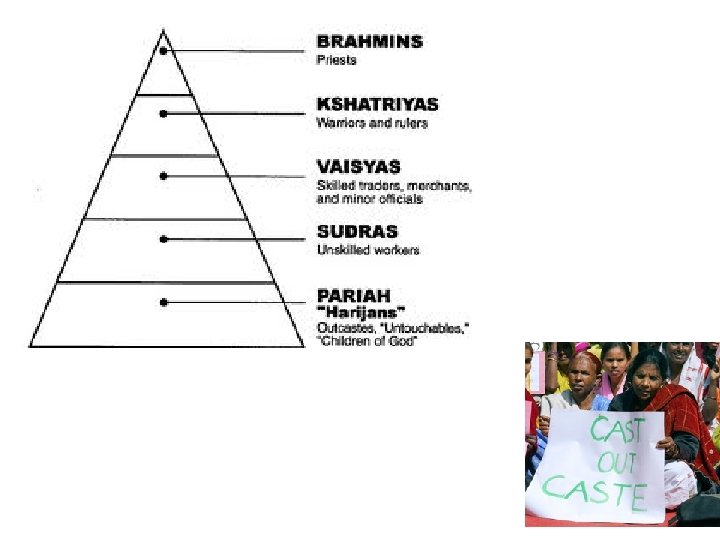
 History’s Influence • Caste: social class based on a person’s ancestry • Hinduism influenced a caste system where people are born into a particular caste, which determines the jobs they can hold and whom they can marry. • The caste system still influences Indian life, although laws now forbid unfair treatment of “lower” castes.
History’s Influence • Caste: social class based on a person’s ancestry • Hinduism influenced a caste system where people are born into a particular caste, which determines the jobs they can hold and whom they can marry. • The caste system still influences Indian life, although laws now forbid unfair treatment of “lower” castes.
 Religion in India – Mostly Hindu • Reincarnation: the belief that when a body dies, the soul is reborn, often in an animal or human form. • Karma: a soul’s actions during this life. • 80% of India’s people are Hindus. They honor many gods and goddesses.
Religion in India – Mostly Hindu • Reincarnation: the belief that when a body dies, the soul is reborn, often in an animal or human form. • Karma: a soul’s actions during this life. • 80% of India’s people are Hindus. They honor many gods and goddesses.
 India Seeks Independence • India became a colony of England 1800 s • Independence movement grew in the 1930 s under the leadership of lawyer Mohandas Gandhi. • Gandhi campaigned for civil disobedience. • Civil disobedience: nonviolent disobeying of laws.
India Seeks Independence • India became a colony of England 1800 s • Independence movement grew in the 1930 s under the leadership of lawyer Mohandas Gandhi. • Gandhi campaigned for civil disobedience. • Civil disobedience: nonviolent disobeying of laws.
 • India faced conflict between Hindus and Muslims. • India Independence Act of 1947: British India was divided into two countries: Majority-Hindu India and Majority-Muslim Pakistan, East & West. The part of Pakistan known as East Pakistan became Bangladesh in 1971
• India faced conflict between Hindus and Muslims. • India Independence Act of 1947: British India was divided into two countries: Majority-Hindu India and Majority-Muslim Pakistan, East & West. The part of Pakistan known as East Pakistan became Bangladesh in 1971
 Displaced: forced to leave their homes, August 1947 in India. • In 1948, Gandhi was assassinated. • The boundaries set by Partition have strained relations in South Asia to the present. https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=4 zq_JH_ux v. A
Displaced: forced to leave their homes, August 1947 in India. • In 1948, Gandhi was assassinated. • The boundaries set by Partition have strained relations in South Asia to the present. https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=4 zq_JH_ux v. A
 Essential Question • What challenges do you think the caste system caused? • Building trust between groups • Providing equality healthcare, education, and opportunities to all citizens.
Essential Question • What challenges do you think the caste system caused? • Building trust between groups • Providing equality healthcare, education, and opportunities to all citizens.
 South Asia Today Chapter 18 • Hindus believe that the Ganges River is sacred. • Millions of Hindus make pilgrimages to the city of Varanasi to worship on the ghats, or stone steps and platforms along the river. • They believe that bathing in the river gives them better Karma • Pilgrimage: a religious journey
South Asia Today Chapter 18 • Hindus believe that the Ganges River is sacred. • Millions of Hindus make pilgrimages to the city of Varanasi to worship on the ghats, or stone steps and platforms along the river. • They believe that bathing in the river gives them better Karma • Pilgrimage: a religious journey
 • In the last 50 years, rules of the Caste system have become less rigid. India’s constitution forbids discrimination. • Discrimination: unfair treatment
• In the last 50 years, rules of the Caste system have become less rigid. India’s constitution forbids discrimination. • Discrimination: unfair treatment
 Schools in South Asia • Most countries in South Asia offer some level of free public education. • India’s schools require attendance until age 14. • In Bhutan schools are set up wherever there is space. • Bangladesh Literacy Rate: 74% Maldives: 96%
Schools in South Asia • Most countries in South Asia offer some level of free public education. • India’s schools require attendance until age 14. • In Bhutan schools are set up wherever there is space. • Bangladesh Literacy Rate: 74% Maldives: 96%
 Clothing • Many people in South Asia wear clothes to adapt to the climate. • Shalwar-Kameez: long shirt with loose-fitting pants worn by Muslims and Hindus. • Sari: single piece of cloth (silk) wrapped to form a long dress. • Western clothes are increasingly popular.
Clothing • Many people in South Asia wear clothes to adapt to the climate. • Shalwar-Kameez: long shirt with loose-fitting pants worn by Muslims and Hindus. • Sari: single piece of cloth (silk) wrapped to form a long dress. • Western clothes are increasingly popular.
 Sports • Kabaddi: combination of wrestling and rugby existing in India for over 4000 years. • Cricket: team game similar to baseball • India has professional cricket and soccer leagues.
Sports • Kabaddi: combination of wrestling and rugby existing in India for over 4000 years. • Cricket: team game similar to baseball • India has professional cricket and soccer leagues.
 Popular Culture • Music and movies are a part of South Asia’s popular culture. • People in South Asia listen to Bollywood music, Indian rock, and Western pop. • Modern Indian musicians are fusing Indian and Western styles to create a new sound. • Bollywood: India’s film industry, producing more feature films than any other country in the world.
Popular Culture • Music and movies are a part of South Asia’s popular culture. • People in South Asia listen to Bollywood music, Indian rock, and Western pop. • Modern Indian musicians are fusing Indian and Western styles to create a new sound. • Bollywood: India’s film industry, producing more feature films than any other country in the world.
 Essential Question • How do South Asians mix old traditions with new traditions? • Many men and women wear traditional clothing and western clothing • Bollywood puts out new movies with Asian themes • Musicians mix Western music with Traditional Eastern music
Essential Question • How do South Asians mix old traditions with new traditions? • Many men and women wear traditional clothing and western clothing • Bollywood puts out new movies with Asian themes • Musicians mix Western music with Traditional Eastern music
 Bell Ringer May 8, 2017 • Page 505 – India’s Government Structure 1. Name two ways in which the gov’t of India is similar to the gov’t of the U. S. 2. Name one way they are different 3. Why does the Prime Minister have more power than the President? • Similarities: 3 branches of Gov’t, Legislative Branch has 2 houses • Different: India has a Prime Minister • PM is head of the Political party that has the most members in the Lok Sabba
Bell Ringer May 8, 2017 • Page 505 – India’s Government Structure 1. Name two ways in which the gov’t of India is similar to the gov’t of the U. S. 2. Name one way they are different 3. Why does the Prime Minister have more power than the President? • Similarities: 3 branches of Gov’t, Legislative Branch has 2 houses • Different: India has a Prime Minister • PM is head of the Political party that has the most members in the Lok Sabba
 The Largest Democracy India’s Parliament has two houses. Created a democracy in 1949. Government: 3 Branches Legislative Branch, along with the State Legislatures, elect the president. • The Prime Minister, head of the majority political party has the most power. • •
The Largest Democracy India’s Parliament has two houses. Created a democracy in 1949. Government: 3 Branches Legislative Branch, along with the State Legislatures, elect the president. • The Prime Minister, head of the majority political party has the most power. • •
 • Meira Kumar: 2009 first woman to become the Speaker of the House in India’s Parliament, promised to work toward a Casteless society.
• Meira Kumar: 2009 first woman to become the Speaker of the House in India’s Parliament, promised to work toward a Casteless society.
 Infrastructure • The government of India is working to accommodate for population growth. • Infrastructure: basic systems that a society needs, such as roads, bridge, and sewers.
Infrastructure • The government of India is working to accommodate for population growth. • Infrastructure: basic systems that a society needs, such as roads, bridge, and sewers.
 Old Delhi
Old Delhi
 New Delhi
New Delhi
 Bell Ringer • Page 509 1. How were sales of vehicles in India in 2007 different from sales in 2002? 2. How did the difference between Indian & U. S. sales change during the period on the graph? Why? 3. How would you explain the location of 3 of the 4 major cities connected by the GQ • More vehicles sold in 2007 than in 2002 • Decreased in the U. S. ; • Increased in India. More people need cars in India • 3 are Port Cities – Trade Centers
Bell Ringer • Page 509 1. How were sales of vehicles in India in 2007 different from sales in 2002? 2. How did the difference between Indian & U. S. sales change during the period on the graph? Why? 3. How would you explain the location of 3 of the 4 major cities connected by the GQ • More vehicles sold in 2007 than in 2002 • Decreased in the U. S. ; • Increased in India. More people need cars in India • 3 are Port Cities – Trade Centers
 Economic Growth in India • Bangalore: Where Companies handle support services for U. S. computer companies. • Outsourcing: the shifting of jobs to workers outside of a company, has been a big part of India’s economic growth.
Economic Growth in India • Bangalore: Where Companies handle support services for U. S. computer companies. • Outsourcing: the shifting of jobs to workers outside of a company, has been a big part of India’s economic growth.
 A Developing Nation • Developed Nations: Countries with a high per capita GDP • Developing Nations: Countries with a low per capita GDP • Developed nations: healthier, educated people, consume more goods, and employ more people in manufacturing and service industries. • Most South Asian countries are developing nations. • India is an emerging market, with a high growth rate and goods and services that compete in global trade.
A Developing Nation • Developed Nations: Countries with a high per capita GDP • Developing Nations: Countries with a low per capita GDP • Developed nations: healthier, educated people, consume more goods, and employ more people in manufacturing and service industries. • Most South Asian countries are developing nations. • India is an emerging market, with a high growth rate and goods and services that compete in global trade.
 The Golden Quadrilateral • Golden Quadrilateral: a 3, 633 - mile superhighway connecting four major cities: Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, and Kolkata. • Farmers can now use the GQ to sell their products in the larger cities at higher prices. • Indians are purchasing cars and trucks – a sign of economic growth. • For growth to continue – they will have to continue investing in their infrastructure.
The Golden Quadrilateral • Golden Quadrilateral: a 3, 633 - mile superhighway connecting four major cities: Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, and Kolkata. • Farmers can now use the GQ to sell their products in the larger cities at higher prices. • Indians are purchasing cars and trucks – a sign of economic growth. • For growth to continue – they will have to continue investing in their infrastructure.
 Urbanization Many people in India are moving to the cities. Push-pull factors are the reasons why people migrate. One key factor pushing people to leave the countryside is poverty. Factors pulling people to cities include job opportunities and better education. • India’s cities have gradually divided into small wealthy sections and vast slums. • Numbers of automobiles are creating traffic congestion and air pollution – causing thousands of deaths each year. • •
Urbanization Many people in India are moving to the cities. Push-pull factors are the reasons why people migrate. One key factor pushing people to leave the countryside is poverty. Factors pulling people to cities include job opportunities and better education. • India’s cities have gradually divided into small wealthy sections and vast slums. • Numbers of automobiles are creating traffic congestion and air pollution – causing thousands of deaths each year. • •
 Wealth in India
Wealth in India
 Essential Question • Why has India experienced an economic boom and what are some effects of rapid change? • Stable democratic gov’t • Improvements in infrastructure • Encourage foreign investment • Effects: urbanization, slums, clean water, electricity, healthcare, education
Essential Question • Why has India experienced an economic boom and what are some effects of rapid change? • Stable democratic gov’t • Improvements in infrastructure • Encourage foreign investment • Effects: urbanization, slums, clean water, electricity, healthcare, education
 Bell Ringer • Page 515 1. What natural resource appears most frequently on the Map? How would this contribute to building industries in Bangladesh? 2. How has a lack of education interfered with economic development in Bangladesh? 3. Why do you think the garment industry has grown so quickly in Bangladesh? • Natural Gas can provide energy to factories • The uneducated cannot compete in modern business • Clothing is needed worldwide – uneducated women can work in the clothing industry.
Bell Ringer • Page 515 1. What natural resource appears most frequently on the Map? How would this contribute to building industries in Bangladesh? 2. How has a lack of education interfered with economic development in Bangladesh? 3. Why do you think the garment industry has grown so quickly in Bangladesh? • Natural Gas can provide energy to factories • The uneducated cannot compete in modern business • Clothing is needed worldwide – uneducated women can work in the clothing industry.
 Chapter 17 -18 Review of South Asia 1. Where do many of South Asia’s major rivers begin? • Himalaya Mountains 2. What is a major element of domestic water pollution? • Raw sewage 3. Why are summer monsoons important to South Asia? • They bring heavy rains that provide water for crops
Chapter 17 -18 Review of South Asia 1. Where do many of South Asia’s major rivers begin? • Himalaya Mountains 2. What is a major element of domestic water pollution? • Raw sewage 3. Why are summer monsoons important to South Asia? • They bring heavy rains that provide water for crops
 4. What was the Green Revolution? • Agricultural experiments that increased the amount of crops 5. What is one cause of water scarcity in South Asia? • People are taking water too quickly from aquifers 6. What is the Indian government doing to clean up the rivers? • It passed a law setting standards for water quality
4. What was the Green Revolution? • Agricultural experiments that increased the amount of crops 5. What is one cause of water scarcity in South Asia? • People are taking water too quickly from aquifers 6. What is the Indian government doing to clean up the rivers? • It passed a law setting standards for water quality
 7. The belief that a soul can be reborn into a new body • Reincarnation 8. The nonviolent disobeying of laws • Civil disobedience 9. Control by one power over a dependent area or people • Colonialism
7. The belief that a soul can be reborn into a new body • Reincarnation 8. The nonviolent disobeying of laws • Civil disobedience 9. Control by one power over a dependent area or people • Colonialism
 10. A reddish powder that can be used as a dye, usually for skin or hair • Henna 11. The percentage of people who can read and write • Literacy rate 12. A traditional Indian garment for women worn wrapped around the body • Sari
10. A reddish powder that can be used as a dye, usually for skin or hair • Henna 11. The percentage of people who can read and write • Literacy rate 12. A traditional Indian garment for women worn wrapped around the body • Sari
 13. A journey to a holy place • Pilgrimage 14. A game played with a ball and bat between two teams with 11 players each popular in India • Cricket 15. The arts , music, and other elements of everyday life in a region • Popular culture
13. A journey to a holy place • Pilgrimage 14. A game played with a ball and bat between two teams with 11 players each popular in India • Cricket 15. The arts , music, and other elements of everyday life in a region • Popular culture
 16. The act of treating someone differently because of a certain factor, such as age, race, gender, or ethnicity • Discrimination 17. In Hinduism, the effects of a person’s actions in this life, which determine the person’s position in the next life • Karma 18. An Indian garment made up of a long shirt with loose pants • Shalwar-kameez
16. The act of treating someone differently because of a certain factor, such as age, race, gender, or ethnicity • Discrimination 17. In Hinduism, the effects of a person’s actions in this life, which determine the person’s position in the next life • Karma 18. An Indian garment made up of a long shirt with loose pants • Shalwar-kameez
 19. Describe the literacy rate in South Asia. • Steadily improving 20. What is true about the clothing worn in South Asia? • Clothing choices vary by region and weather conditions 21. What is one reason that music and movies foster a common culture among South Asians? • Music and movies are widely available to everyone
19. Describe the literacy rate in South Asia. • Steadily improving 20. What is true about the clothing worn in South Asia? • Clothing choices vary by region and weather conditions 21. What is one reason that music and movies foster a common culture among South Asians? • Music and movies are widely available to everyone
 22. What is a true statement about India’s film industry? • It produces more feature films than any other country 23. What describes South Asian culture? • It is a mix of ancient and modern practices 24. In the Indian caste system, which group of individuals was called the “Untouchables”? • Garbage collectors and animal skin tanners
22. What is a true statement about India’s film industry? • It produces more feature films than any other country 23. What describes South Asian culture? • It is a mix of ancient and modern practices 24. In the Indian caste system, which group of individuals was called the “Untouchables”? • Garbage collectors and animal skin tanners
 25. The basic systems that a society needs • Infrastructure 26. Nations with a high per capita Gross Domestic Product • Developed nations 27. The shifting of jobs to workers outside of a country • Outsourcing
25. The basic systems that a society needs • Infrastructure 26. Nations with a high per capita Gross Domestic Product • Developed nations 27. The shifting of jobs to workers outside of a country • Outsourcing
 28. Nations with a low per capita Gross Domestic Product • Developing nations 29. The acceptance and usage of new and current ways or ideas • Modernization 30. Why is it important for India’s government to improve the infrastructure? (roads, health, sanitation) • To support India’s growing population • To support economic growth by attracting large businesses to India
28. Nations with a low per capita Gross Domestic Product • Developing nations 29. The acceptance and usage of new and current ways or ideas • Modernization 30. Why is it important for India’s government to improve the infrastructure? (roads, health, sanitation) • To support India’s growing population • To support economic growth by attracting large businesses to India


