 Sources of failures in Mergers and Acquisitions. The effects of employee identity. By Kateryna Herman 1
Sources of failures in Mergers and Acquisitions. The effects of employee identity. By Kateryna Herman 1
 Definitions Mergers and acquisitions (M&Asare important ) mechanisms for the growth and internationalization of firms (Weber & Fried, 2011). Merger means the combination of two or more companies in creation of a new entity (Hoang, Thuy Vu Nga Lapumnuaypon, Kamolrat, 2007). Acquisition, when one company takes over another and clearly established itself as the new owner, the purchase is called an acquisition (Yaakov Weber, Shlomo Y. Tarba, Christina´Öberg, 2013). 2
Definitions Mergers and acquisitions (M&Asare important ) mechanisms for the growth and internationalization of firms (Weber & Fried, 2011). Merger means the combination of two or more companies in creation of a new entity (Hoang, Thuy Vu Nga Lapumnuaypon, Kamolrat, 2007). Acquisition, when one company takes over another and clearly established itself as the new owner, the purchase is called an acquisition (Yaakov Weber, Shlomo Y. Tarba, Christina´Öberg, 2013). 2
 Research question Why employees' social identity may lead the companies to unsuccessful performance during Mergers and Acquisitions? 3
Research question Why employees' social identity may lead the companies to unsuccessful performance during Mergers and Acquisitions? 3
 Motives For M&A (Bower, 2001) to deal with overcapacity through consolidation in mature industries to roll-up competitors in geographically fragmented industries to extend into new products or markets as a substitute for R&D to exploit eroding industry boundaries by inventing an industry 4
Motives For M&A (Bower, 2001) to deal with overcapacity through consolidation in mature industries to roll-up competitors in geographically fragmented industries to extend into new products or markets as a substitute for R&D to exploit eroding industry boundaries by inventing an industry 4
 Why M&A’s fail Action is not based on the corporate strategy ( Marks and Mirvis, 2011). Managerial self-interest 5
Why M&A’s fail Action is not based on the corporate strategy ( Marks and Mirvis, 2011). Managerial self-interest 5
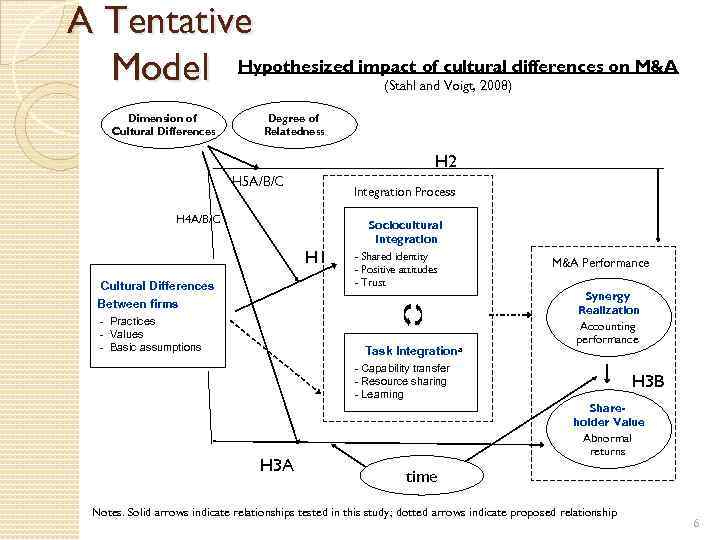 A Tentative Model Hypothesized impact of cultural differences on M&A (Stahl and Voigt, 2008) Dimension of Cultural Differences Degree of Relatedness H 2 H 5 A/B/C Integration Process H 4 A/B/C Sociocultural Integration H 1 Cultural Differences - Shared identity - Positive attitudes - Trust Between firms - Practices - Values - Basic assumptions Task Integrationa M&A Performance Synergy Realization Accounting performance - Capability transfer - Resource sharing - Learning H 3 A H 3 B Shareholder Value Abnormal returns time Notes. Solid arrows indicate relationships tested in this study; dotted arrows indicate proposed relationship 6
A Tentative Model Hypothesized impact of cultural differences on M&A (Stahl and Voigt, 2008) Dimension of Cultural Differences Degree of Relatedness H 2 H 5 A/B/C Integration Process H 4 A/B/C Sociocultural Integration H 1 Cultural Differences - Shared identity - Positive attitudes - Trust Between firms - Practices - Values - Basic assumptions Task Integrationa M&A Performance Synergy Realization Accounting performance - Capability transfer - Resource sharing - Learning H 3 A H 3 B Shareholder Value Abnormal returns time Notes. Solid arrows indicate relationships tested in this study; dotted arrows indicate proposed relationship 6
 Hypothesis H 1 Differences in culture between merging firms are negatively associated with sociocultural integration outcomes. H 2 Differences in culture between merging firms are negatively associated with synergy realization H 3 A Cultural differences are negatively associated with acquisition announcement returns for the acquiring firm’s shareholders H 3 B Cultural differences are negatively associated with postacquisition stock returns for the acquiring firm’s shareholders H 4 A/B/C Differences in national culture between merging firms are less negatively associated with sociocultural integration outcomes/ synergy realization/ shareholder value than are organizational cultural differences. H 5 A/B/C Cultural differences are more negatively associated with sociocultural integration/ synergy realization/ shareholder value when the degree of relatedness is high than when it is low. 7
Hypothesis H 1 Differences in culture between merging firms are negatively associated with sociocultural integration outcomes. H 2 Differences in culture between merging firms are negatively associated with synergy realization H 3 A Cultural differences are negatively associated with acquisition announcement returns for the acquiring firm’s shareholders H 3 B Cultural differences are negatively associated with postacquisition stock returns for the acquiring firm’s shareholders H 4 A/B/C Differences in national culture between merging firms are less negatively associated with sociocultural integration outcomes/ synergy realization/ shareholder value than are organizational cultural differences. H 5 A/B/C Cultural differences are more negatively associated with sociocultural integration/ synergy realization/ shareholder value when the degree of relatedness is high than when it is low. 7
 Main formulas 8
Main formulas 8
 Conclusion 9
Conclusion 9