1f8f72dece877a396a7510c5b8e136e3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 Source & Courtesy: Jing Zou
Source & Courtesy: Jing Zou
 Reasons for Unified Process 1. Software becomes more complex and is updated fast. 2. Software developers uses methods that are as old as 25 years ago. 3. Development process is diverse
Reasons for Unified Process 1. Software becomes more complex and is updated fast. 2. Software developers uses methods that are as old as 25 years ago. 3. Development process is diverse
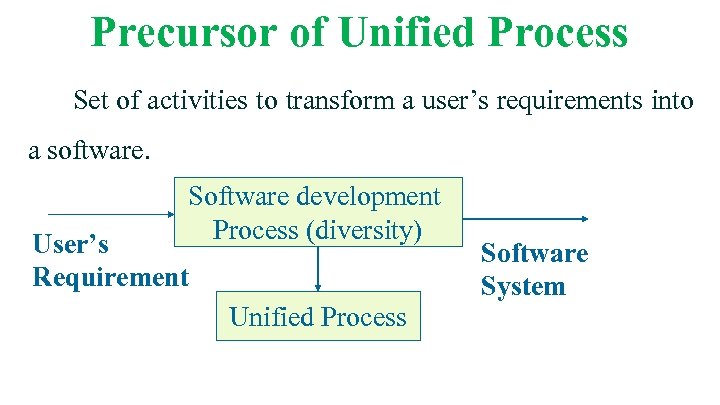 Precursor of Unified Process Set of activities to transform a user’s requirements into a software. Software development Process (diversity) User’s Requirement Unified Process Software System
Precursor of Unified Process Set of activities to transform a user’s requirements into a software. Software development Process (diversity) User’s Requirement Unified Process Software System
 What does Unified Process do? 1. Provides guidance to the order of team’s activities 2. Integrates team’s work and individual’s work 3. Specifies artifacts 4. Offers criteria for monitoring and measuring
What does Unified Process do? 1. Provides guidance to the order of team’s activities 2. Integrates team’s work and individual’s work 3. Specifies artifacts 4. Offers criteria for monitoring and measuring
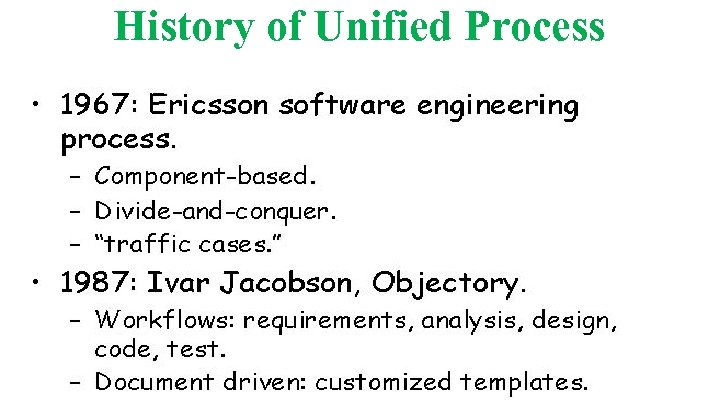 History of Unified Process
History of Unified Process
 History of Unified Process
History of Unified Process
 3 Key Aspects of Unified Process 1. Use-case driven 2. Architecture-centric 3. Iterative and incremental
3 Key Aspects of Unified Process 1. Use-case driven 2. Architecture-centric 3. Iterative and incremental
 Use-Case Driven Use-Case driven means: Development process proceeds through a series of workflows that derive from use cases.
Use-Case Driven Use-Case driven means: Development process proceeds through a series of workflows that derive from use cases.
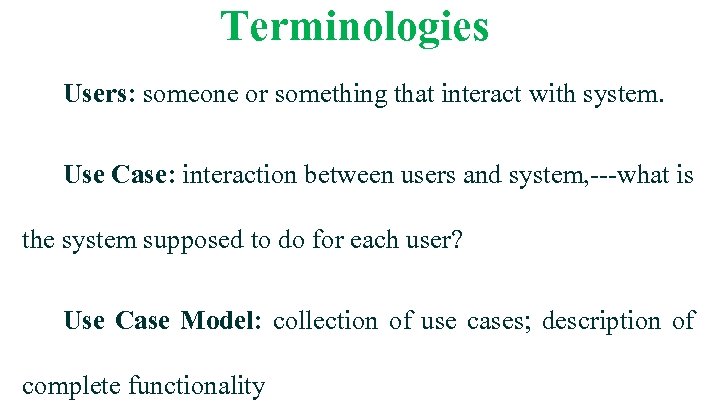 Terminologies Users: someone or something that interact with system. Use Case: interaction between users and system, ---what is the system supposed to do for each user? Use Case Model: collection of use cases; description of complete functionality
Terminologies Users: someone or something that interact with system. Use Case: interaction between users and system, ---what is the system supposed to do for each user? Use Case Model: collection of use cases; description of complete functionality
 Initiate AND bind 1. Tool for specifying requirements 2. Driving design 3. Source for testing
Initiate AND bind 1. Tool for specifying requirements 2. Driving design 3. Source for testing
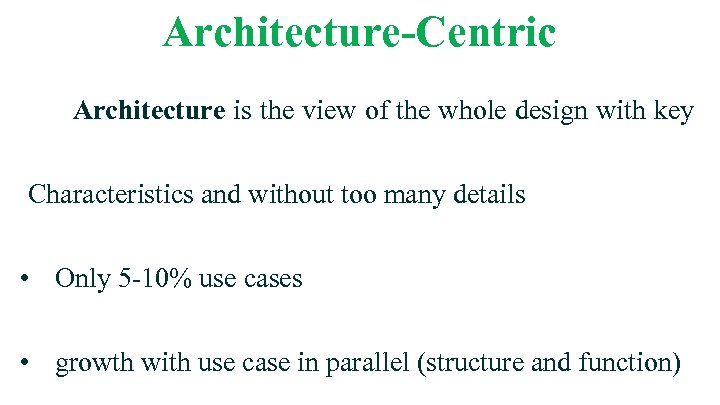 Architecture-Centric Architecture is the view of the whole design with key Characteristics and without too many details • Only 5 -10% use cases • growth with use case in parallel (structure and function)
Architecture-Centric Architecture is the view of the whole design with key Characteristics and without too many details • Only 5 -10% use cases • growth with use case in parallel (structure and function)
 Simplified Process 1. Rough outline (use case independent) 2. Subset of the identified use cases (5 -10%) 3. More use cases specified, more architecture discovered
Simplified Process 1. Rough outline (use case independent) 2. Subset of the identified use cases (5 -10%) 3. More use cases specified, more architecture discovered
 Use case & Architecture Use case drive influence System architecture
Use case & Architecture Use case drive influence System architecture
 Iterative and Incremental ? ? Iteration: Steps in the workflow (mini-project) Ø Create a design for relevant use cases Ø Implement with components Ø Required iteration in logical order for economy Increments: Growth in the product (might not be additive)
Iterative and Incremental ? ? Iteration: Steps in the workflow (mini-project) Ø Create a design for relevant use cases Ø Implement with components Ø Required iteration in logical order for economy Increments: Growth in the product (might not be additive)
 Benefits to controlled iteration 1. Reduce the cost risk to the expenditures on a single increment 2. Reduce the risk of delayed product delivery (find the risks earlier) 3. Speed up the tempo of the whole development effort 4. Easier to adapt to the requirement modification
Benefits to controlled iteration 1. Reduce the cost risk to the expenditures on a single increment 2. Reduce the risk of delayed product delivery (find the risks earlier) 3. Speed up the tempo of the whole development effort 4. Easier to adapt to the requirement modification
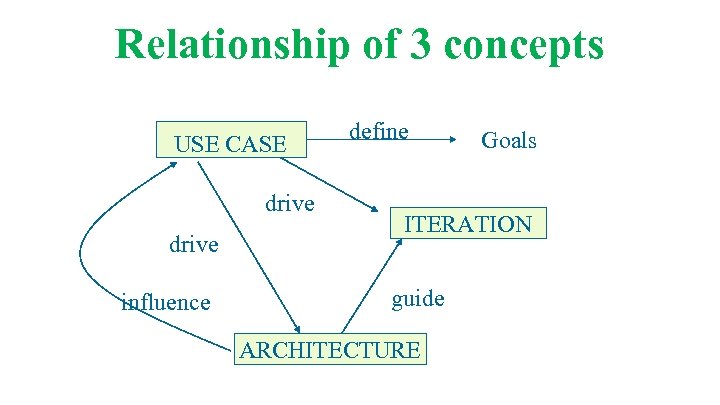 Relationship of 3 concepts USE CASE drive influence define Goals ITERATION guide ARCHITECTURE
Relationship of 3 concepts USE CASE drive influence define Goals ITERATION guide ARCHITECTURE
 Lifecycle of Unified Process Ø Each cycle concludes with a product release to customers. Ø Each cycle consists of 4 phases: 1. Inception 2. Elaboration 3. Construction 4. Transition
Lifecycle of Unified Process Ø Each cycle concludes with a product release to customers. Ø Each cycle consists of 4 phases: 1. Inception 2. Elaboration 3. Construction 4. Transition
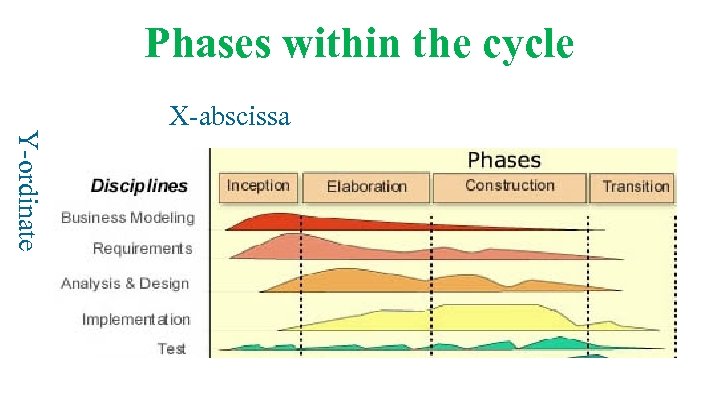 Phases within the cycle Y-ordinate X-abscissa
Phases within the cycle Y-ordinate X-abscissa
 End of a Cycle At the end, a software product is releasable Finished product includes 1. requirements 2. use cases 3. nonfunctional requirements 4. test cases 5. artifacts modeled by the UML
End of a Cycle At the end, a software product is releasable Finished product includes 1. requirements 2. use cases 3. nonfunctional requirements 4. test cases 5. artifacts modeled by the UML
 For New Cycle For every new cycle, we need • Use-case model • Analysis model • Design model • Implementation Model • Deployment model • Test model • Representation of the architecture
For New Cycle For every new cycle, we need • Use-case model • Analysis model • Design model • Implementation Model • Deployment model • Test model • Representation of the architecture
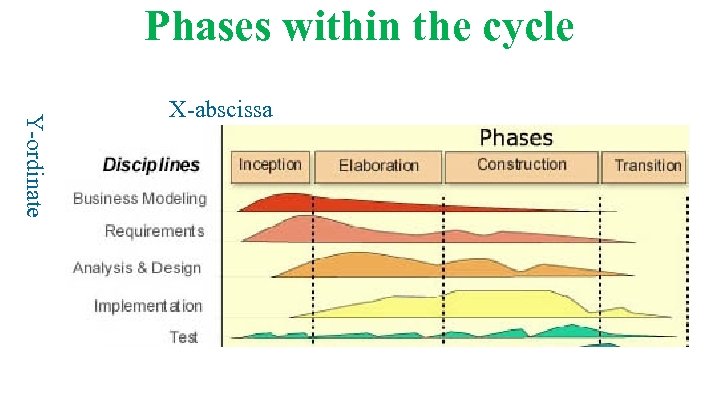 Phases within the cycle Y-ordinate X-abscissa
Phases within the cycle Y-ordinate X-abscissa
 Phase I --> Inception Ø Develop a good idea into a vision of the end product Ø Business case for the product is presented • Establish goals • Build business case • Identify essential system requirement • Initiate risk management (cost, time, political environment)
Phase I --> Inception Ø Develop a good idea into a vision of the end product Ø Business case for the product is presented • Establish goals • Build business case • Identify essential system requirement • Initiate risk management (cost, time, political environment)
 Phase II --> Elaboration Here, architecture is expressed as a view of different models • Develop architecture • Capture functional requirements as use cases • Identify non-functional requirements • Plan the construction • Continue risk management
Phase II --> Elaboration Here, architecture is expressed as a view of different models • Develop architecture • Capture functional requirements as use cases • Identify non-functional requirements • Plan the construction • Continue risk management
 Phase III --> Construction Muscle built : software added to the architecture • - Build the System • Maintain architectural integrity (Architecture is stable but might has minor changes) • Iterative, Incremental • However, is it sufficient to take early delivery?
Phase III --> Construction Muscle built : software added to the architecture • - Build the System • Maintain architectural integrity (Architecture is stable but might has minor changes) • Iterative, Incremental • However, is it sufficient to take early delivery?
 Phase IV --> Transition Products move to beta release. Trial Defects and deficiencies are reported. Corrections and improvements • Final testing( system, acceptance, beta ) • Training customer personnel • Documentation, installation and consultation • Perform postmortem review
Phase IV --> Transition Products move to beta release. Trial Defects and deficiencies are reported. Corrections and improvements • Final testing( system, acceptance, beta ) • Training customer personnel • Documentation, installation and consultation • Perform postmortem review
 Modeling Disciplines of Unified Process Business Modeling: Model the business context, the scope, of the system. Requirement: Engineer the requirements for the project, Analysis and Design: Evolve a robust architecture for the system Enterprise Management: Encompasses activities that are outside of the scope of a single project,
Modeling Disciplines of Unified Process Business Modeling: Model the business context, the scope, of the system. Requirement: Engineer the requirements for the project, Analysis and Design: Evolve a robust architecture for the system Enterprise Management: Encompasses activities that are outside of the scope of a single project,
 RUP and UP UP is more of a philosophy of how to run development projects RUP is Rational commercial product
RUP and UP UP is more of a philosophy of how to run development projects RUP is Rational commercial product
 Rational Corporate Introduction Background Introduction Products Introduction: 1. Requirements & analysis Rational Suite® Analyst. Studio 2. Visual modeling & development Rational Suite® Development. Studio 3. Automated Testing Rational Suite® Test. Studio® 4. Project Management Rational Unified Process® 5. Configurable Process RUP
Rational Corporate Introduction Background Introduction Products Introduction: 1. Requirements & analysis Rational Suite® Analyst. Studio 2. Visual modeling & development Rational Suite® Development. Studio 3. Automated Testing Rational Suite® Test. Studio® 4. Project Management Rational Unified Process® 5. Configurable Process RUP
 UML and RUP UML: international standard for object-oriented modeling. RUP uses UML to prepare blueprints of the software How to build a use case diagram? “…We are making inroads into many corporations today, and it's our goal to get there. We don't think it would be an easy thing to make the Unified Process a standard; …And I think that everyone that looks at the Rational Unified Process will become convinced this is the way they've got to do it…. ”
UML and RUP UML: international standard for object-oriented modeling. RUP uses UML to prepare blueprints of the software How to build a use case diagram? “…We are making inroads into many corporations today, and it's our goal to get there. We don't think it would be an easy thing to make the Unified Process a standard; …And I think that everyone that looks at the Rational Unified Process will become convinced this is the way they've got to do it…. ”
 RUP strengths Strength of RUP: 1. Based on sound Sw. E principles 2. Mechanisms that provide management visibility into the development process 3. HTML-based description of the RUP
RUP strengths Strength of RUP: 1. Based on sound Sw. E principles 2. Mechanisms that provide management visibility into the development process 3. HTML-based description of the RUP
 RUP weaknesses Weaknesses of RUP: 1. Only developing process, not the entire software process 2. Not supporting multi-system infrastructure development efforts 3. Iterative nature foreign to experienced developers 4. Tool-driven approach, not sufficient for complex system
RUP weaknesses Weaknesses of RUP: 1. Only developing process, not the entire software process 2. Not supporting multi-system infrastructure development efforts 3. Iterative nature foreign to experienced developers 4. Tool-driven approach, not sufficient for complex system
 Conclusion 6 Best Practices 1. Iterative Software Deployment 2. Manage Requirements 3. Component-based architecture 4. Visually model software 5. Quality Control 6. Configuration Management
Conclusion 6 Best Practices 1. Iterative Software Deployment 2. Manage Requirements 3. Component-based architecture 4. Visually model software 5. Quality Control 6. Configuration Management
 • RUP is component based. • RUP uses visual modeling standard UML and rely on 3 aspects • Establishes a framework that integrates all different facets such as workflows, risk mitigation, quality control and etc. • Developers can build different models
• RUP is component based. • RUP uses visual modeling standard UML and rely on 3 aspects • Establishes a framework that integrates all different facets such as workflows, risk mitigation, quality control and etc. • Developers can build different models
 Thanks…
Thanks…


