44783cb672e8612a6109ec742fad8a8c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 SOPS: The Science Operations Planning System for the first ESA Lunar Mission SMART-1
SOPS: The Science Operations Planning System for the first ESA Lunar Mission SMART-1
 System Level View Targe t s ic entif Sci goals s POR Miss al tion ra ion O C Ope bjec tives ts train ons Po int ing Payload Pr ofi l e? What is a Science Operation Planning System? Sche ts dulin Oper g cipal Prin I or tigat nves ation Time indow nce Opportunity W Scie Line s o nvir E l. C enta nm Simu n strai on latio n
System Level View Targe t s ic entif Sci goals s POR Miss al tion ra ion O C Ope bjec tives ts train ons Po int ing Payload Pr ofi l e? What is a Science Operation Planning System? Sche ts dulin Oper g cipal Prin I or tigat nves ation Time indow nce Opportunity W Scie Line s o nvir E l. C enta nm Simu n strai on latio n
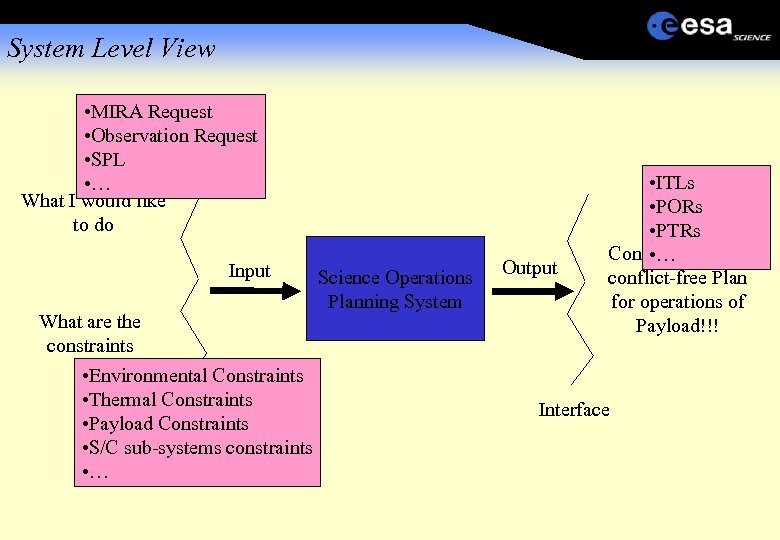 System Level View • MIRA Request • Observation Request • SPL • … What I would like to do Input What are the constraints • Environmental Constraints • Thermal Constraints Interface • Payload Constraints • S/C sub-systems constraints • … Science Operations Planning System Output • ITLs • PORs • PTRs Consolidated and • … conflict-free Plan for operations of Payload!!! Interface
System Level View • MIRA Request • Observation Request • SPL • … What I would like to do Input What are the constraints • Environmental Constraints • Thermal Constraints Interface • Payload Constraints • S/C sub-systems constraints • … Science Operations Planning System Output • ITLs • PORs • PTRs Consolidated and • … conflict-free Plan for operations of Payload!!! Interface
 System Level View Input: What I want - Concrete request including required Execution Time: Take an image of Target YYY in Orbit ZZZ Perform a dust particle analyse as long as possible in the time window XXX - Generic Input without concrete execution time: Take an Image of Target XXX, whenever the distance is YYY and the local solar elevation angle is ZZZ and …. Perform a dust particle analyse as long as possible, whenever the concentration of particles is higher than XXX and S/C Thrusters are off and …
System Level View Input: What I want - Concrete request including required Execution Time: Take an image of Target YYY in Orbit ZZZ Perform a dust particle analyse as long as possible in the time window XXX - Generic Input without concrete execution time: Take an Image of Target XXX, whenever the distance is YYY and the local solar elevation angle is ZZZ and …. Perform a dust particle analyse as long as possible, whenever the concentration of particles is higher than XXX and S/C Thrusters are off and …
 System Level View Input: What are the constraints - Environmental Constraints: Local Solar Elevation and Azimuth angles, distances, phase angles, particle concentration, target visibilities, … -Thermal Constraints: Max illumination of panel XXX shall be YYY for max duration of ZZZ, pre-defined Thermal profiles for operational phases -Resource Constraints: Power consumption, Data generation, Satellite Orientation -S/C and Sub-System Constraints: Reaction wheels saturation, Star tracker blindings, Slew times between two satellite orientations, . . -Payload Constraints: Interference between different Payloads and S/C, Internal payload constraints, Mode level constraints
System Level View Input: What are the constraints - Environmental Constraints: Local Solar Elevation and Azimuth angles, distances, phase angles, particle concentration, target visibilities, … -Thermal Constraints: Max illumination of panel XXX shall be YYY for max duration of ZZZ, pre-defined Thermal profiles for operational phases -Resource Constraints: Power consumption, Data generation, Satellite Orientation -S/C and Sub-System Constraints: Reaction wheels saturation, Star tracker blindings, Slew times between two satellite orientations, . . -Payload Constraints: Interference between different Payloads and S/C, Internal payload constraints, Mode level constraints
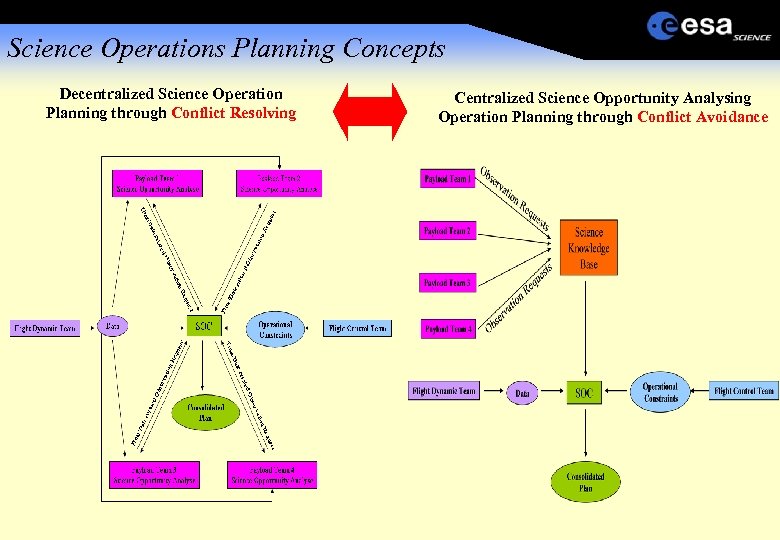 Science Operations Planning Concepts Decentralized Science Operation Planning through Conflict Resolving Centralized Science Opportunity Analysing Operation Planning through Conflict Avoidance
Science Operations Planning Concepts Decentralized Science Operation Planning through Conflict Resolving Centralized Science Opportunity Analysing Operation Planning through Conflict Avoidance
 System Requirements Management of all relevant operational Data Performing environmental and sub/system level simulations Analysing the simulation results and identifying available science opportunity windows Selecting some of available science opportunities Resource management and conflict resolution Prioritising and selecting among overlapping science opportunity windows Preparation of the final, consolidated science operations planning products Detailed operational Timeline files Detailed S/C orientation/pointing request files Tracking of all performed observations and achieved scientific objectives of the mission.
System Requirements Management of all relevant operational Data Performing environmental and sub/system level simulations Analysing the simulation results and identifying available science opportunity windows Selecting some of available science opportunities Resource management and conflict resolution Prioritising and selecting among overlapping science opportunity windows Preparation of the final, consolidated science operations planning products Detailed operational Timeline files Detailed S/C orientation/pointing request files Tracking of all performed observations and achieved scientific objectives of the mission.
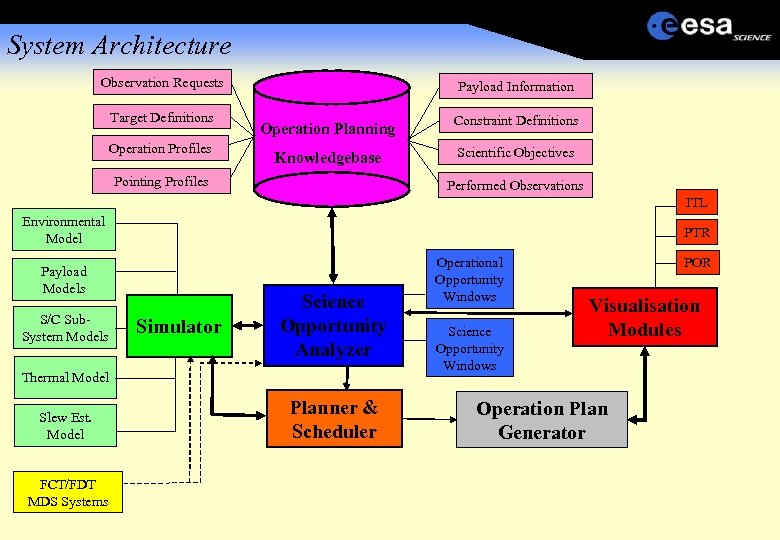 System Architecture Observation Requests Target Definitions Operation Profiles Payload Information Operation Planning Knowledgebase Pointing Profiles Constraint Definitions Scientific Objectives Performed Observations ITL Environmental Model PTR Payload Models S/C Sub. System Models Simulator Science Opportunity Analyzer Thermal Model Slew Est. Model FCT/FDT MDS Systems Planner & Scheduler Operational Opportunity Windows Science Opportunity Windows POR Visualisation Modules Operation Plan Generator
System Architecture Observation Requests Target Definitions Operation Profiles Payload Information Operation Planning Knowledgebase Pointing Profiles Constraint Definitions Scientific Objectives Performed Observations ITL Environmental Model PTR Payload Models S/C Sub. System Models Simulator Science Opportunity Analyzer Thermal Model Slew Est. Model FCT/FDT MDS Systems Planner & Scheduler Operational Opportunity Windows Science Opportunity Windows POR Visualisation Modules Operation Plan Generator
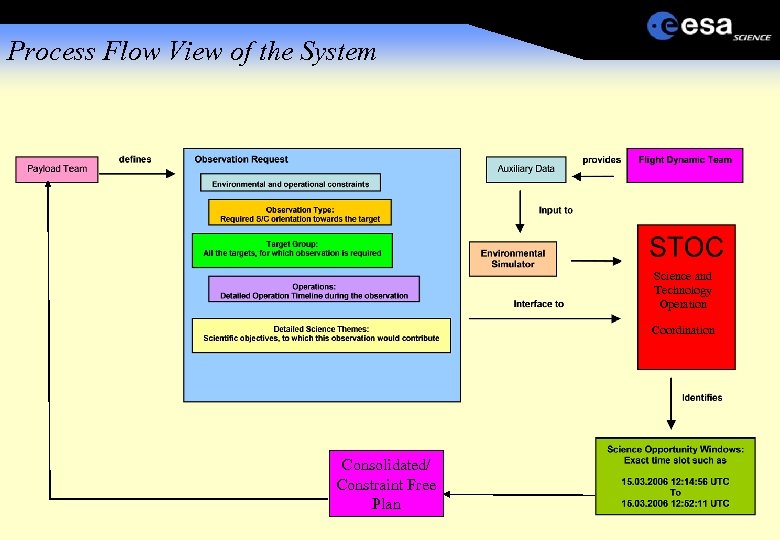 Process Flow View of the System Science and Technology Operation Coordination Consolidated/ Constraint Free Plan
Process Flow View of the System Science and Technology Operation Coordination Consolidated/ Constraint Free Plan
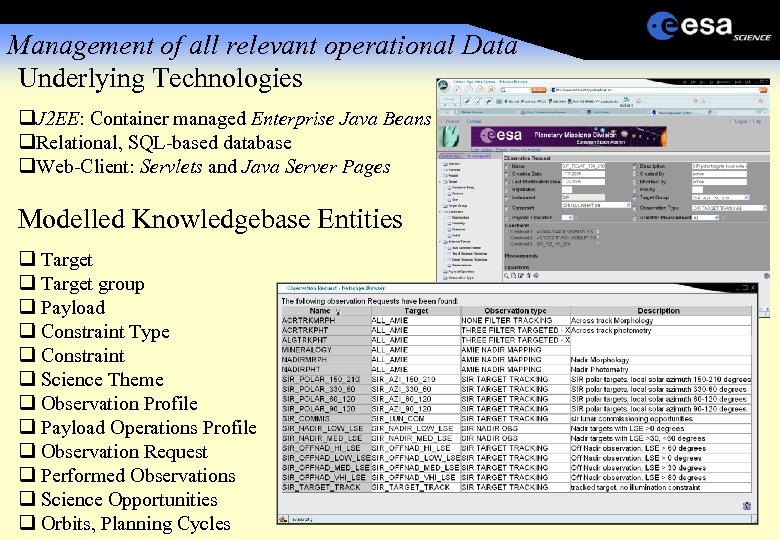 Management of all relevant operational Data Underlying Technologies J 2 EE: Container managed Enterprise Java Beans Relational, SQL-based database Web-Client: Servlets and Java Server Pages Modelled Knowledgebase Entities Target group Payload Constraint Type Constraint Science Theme Observation Profile Payload Operations Profile Observation Request Performed Observations Science Opportunities Orbits, Planning Cycles
Management of all relevant operational Data Underlying Technologies J 2 EE: Container managed Enterprise Java Beans Relational, SQL-based database Web-Client: Servlets and Java Server Pages Modelled Knowledgebase Entities Target group Payload Constraint Type Constraint Science Theme Observation Profile Payload Operations Profile Observation Request Performed Observations Science Opportunities Orbits, Planning Cycles
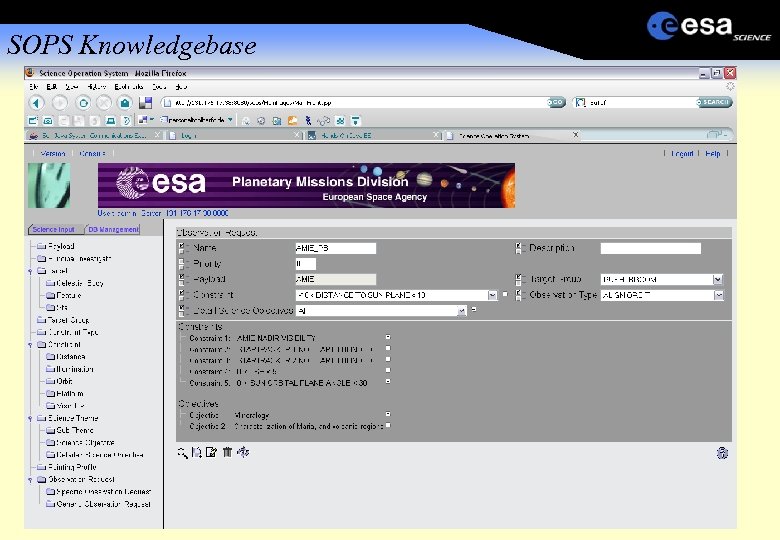 SOPS Knowledgebase
SOPS Knowledgebase
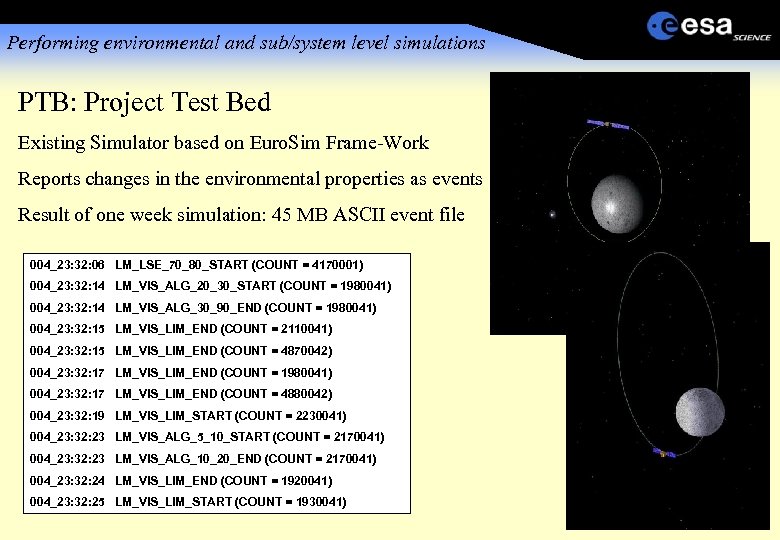 Performing environmental and sub/system level simulations PTB: Project Test Bed Existing Simulator based on Euro. Sim Frame-Work Reports changes in the environmental properties as events Result of one week simulation: 45 MB ASCII event file 004_23: 32: 06 LM_LSE_70_80_START (COUNT = 4170001) 004_23: 32: 14 LM_VIS_ALG_20_30_START (COUNT = 1980041) 004_23: 32: 14 LM_VIS_ALG_30_90_END (COUNT = 1980041) 004_23: 32: 15 LM_VIS_LIM_END (COUNT = 2110041) 004_23: 32: 15 LM_VIS_LIM_END (COUNT = 4870042) 004_23: 32: 17 LM_VIS_LIM_END (COUNT = 1980041) 004_23: 32: 17 LM_VIS_LIM_END (COUNT = 4880042) 004_23: 32: 19 LM_VIS_LIM_START (COUNT = 2230041) 004_23: 32: 23 LM_VIS_ALG_5_10_START (COUNT = 2170041) 004_23: 32: 23 LM_VIS_ALG_10_20_END (COUNT = 2170041) 004_23: 32: 24 LM_VIS_LIM_END (COUNT = 1920041) 004_23: 32: 25 LM_VIS_LIM_START (COUNT = 1930041)
Performing environmental and sub/system level simulations PTB: Project Test Bed Existing Simulator based on Euro. Sim Frame-Work Reports changes in the environmental properties as events Result of one week simulation: 45 MB ASCII event file 004_23: 32: 06 LM_LSE_70_80_START (COUNT = 4170001) 004_23: 32: 14 LM_VIS_ALG_20_30_START (COUNT = 1980041) 004_23: 32: 14 LM_VIS_ALG_30_90_END (COUNT = 1980041) 004_23: 32: 15 LM_VIS_LIM_END (COUNT = 2110041) 004_23: 32: 15 LM_VIS_LIM_END (COUNT = 4870042) 004_23: 32: 17 LM_VIS_LIM_END (COUNT = 1980041) 004_23: 32: 17 LM_VIS_LIM_END (COUNT = 4880042) 004_23: 32: 19 LM_VIS_LIM_START (COUNT = 2230041) 004_23: 32: 23 LM_VIS_ALG_5_10_START (COUNT = 2170041) 004_23: 32: 23 LM_VIS_ALG_10_20_END (COUNT = 2170041) 004_23: 32: 24 LM_VIS_LIM_END (COUNT = 1920041) 004_23: 32: 25 LM_VIS_LIM_START (COUNT = 1930041)
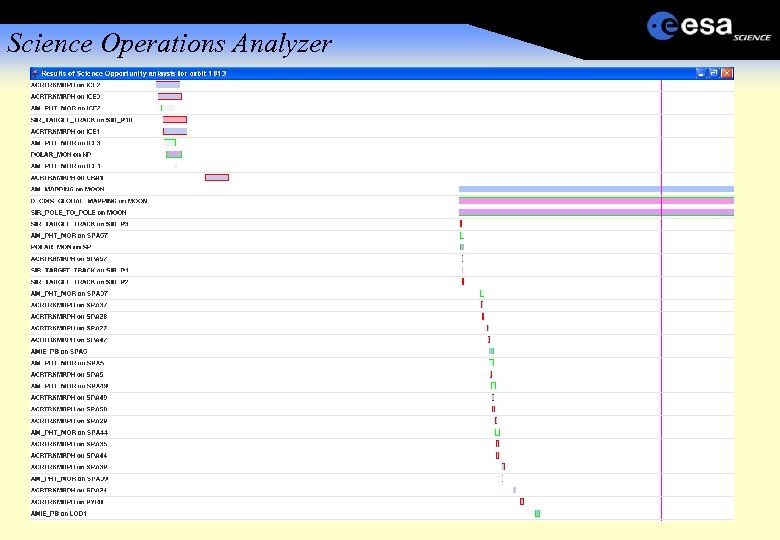
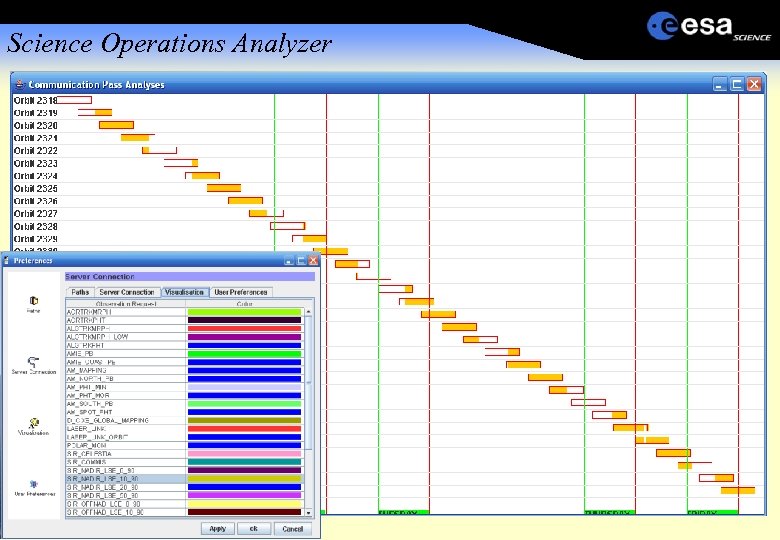
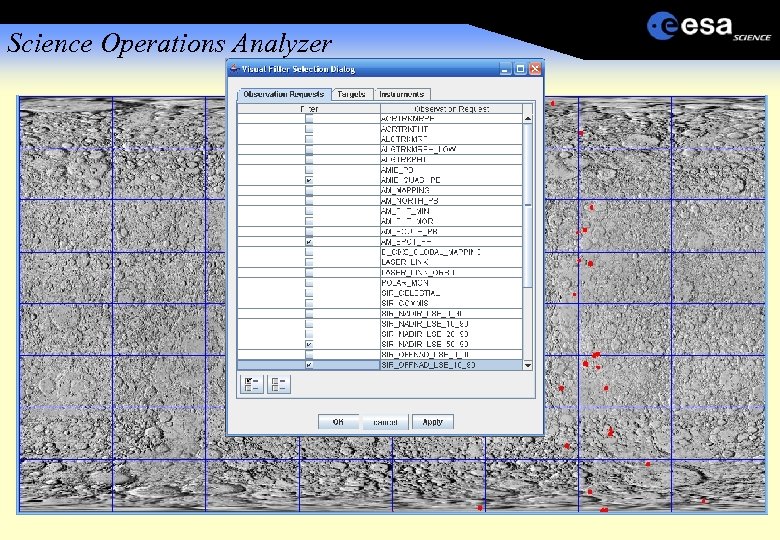
 Science Operations Analyzer 100 s of opportunities per week Visibility and geometry constraints Different pointing modes nadir, cross-track, tracking, inertial Conflicting pointing Platform thermal constraints Payload geometric constraints e. g Sun in Fo. V. Payload maintenance No ground station schedule
Science Operations Analyzer 100 s of opportunities per week Visibility and geometry constraints Different pointing modes nadir, cross-track, tracking, inertial Conflicting pointing Platform thermal constraints Payload geometric constraints e. g Sun in Fo. V. Payload maintenance No ground station schedule
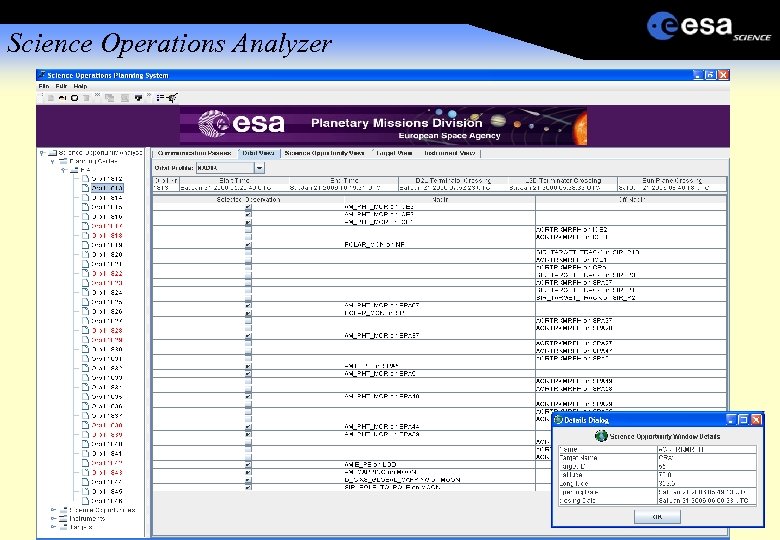 Science Operations Analyzer
Science Operations Analyzer
 Science Operations Analyzer
Science Operations Analyzer
 Science Operations Analyzer
Science Operations Analyzer
 Science Operations Analyzer
Science Operations Analyzer
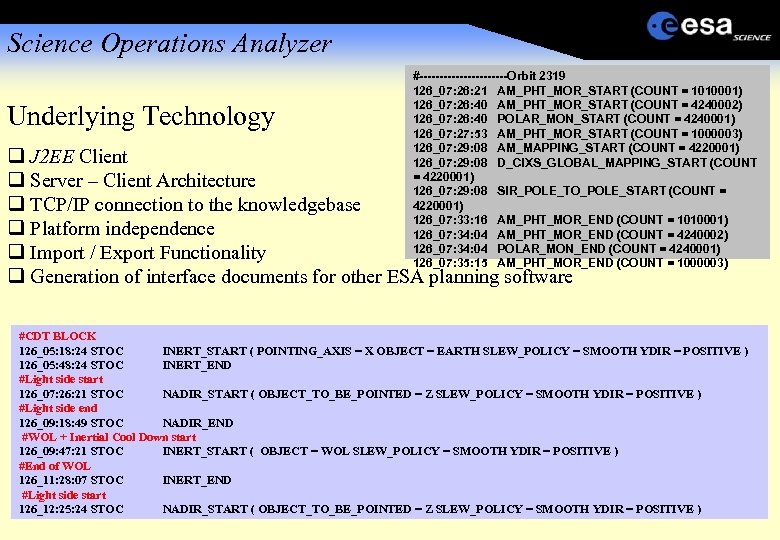 Science Operations Analyzer Underlying Technology #-----------Orbit 2319 126_07: 26: 21 AM_PHT_MOR_START (COUNT = 1010001) 126_07: 26: 40 AM_PHT_MOR_START (COUNT = 4240002) 126_07: 26: 40 POLAR_MON_START (COUNT = 4240001) 126_07: 27: 53 AM_PHT_MOR_START (COUNT = 1000003) 126_07: 29: 08 AM_MAPPING_START (COUNT = 4220001) 126_07: 29: 08 D_CIXS_GLOBAL_MAPPING_START (COUNT = 4220001) 126_07: 29: 08 SIR_POLE_TO_POLE_START (COUNT = 4220001) 126_07: 33: 16 AM_PHT_MOR_END (COUNT = 1010001) 126_07: 34: 04 AM_PHT_MOR_END (COUNT = 4240002) 126_07: 34: 04 POLAR_MON_END (COUNT = 4240001) 126_07: 35: 15 AM_PHT_MOR_END (COUNT = 1000003) J 2 EE Client Server – Client Architecture TCP/IP connection to the knowledgebase Platform independence Import / Export Functionality Generation of interface documents for other ESA planning software #CDT BLOCK 126_05: 18: 24 STOC INERT_START ( POINTING_AXIS = X OBJECT = EARTH SLEW_POLICY = SMOOTH YDIR = POSITIVE ) 126_05: 48: 24 STOC INERT_END #Light side start 126_07: 26: 21 STOC NADIR_START ( OBJECT_TO_BE_POINTED = Z SLEW_POLICY = SMOOTH YDIR = POSITIVE ) #Light side end 126_09: 18: 49 STOC NADIR_END #WOL + Inertial Cool Down start 126_09: 47: 21 STOC INERT_START ( OBJECT = WOL SLEW_POLICY = SMOOTH YDIR = POSITIVE ) #End of WOL 126_11: 28: 07 STOC INERT_END #Light side start 126_12: 25: 24 STOC NADIR_START ( OBJECT_TO_BE_POINTED = Z SLEW_POLICY = SMOOTH YDIR = POSITIVE )
Science Operations Analyzer Underlying Technology #-----------Orbit 2319 126_07: 26: 21 AM_PHT_MOR_START (COUNT = 1010001) 126_07: 26: 40 AM_PHT_MOR_START (COUNT = 4240002) 126_07: 26: 40 POLAR_MON_START (COUNT = 4240001) 126_07: 27: 53 AM_PHT_MOR_START (COUNT = 1000003) 126_07: 29: 08 AM_MAPPING_START (COUNT = 4220001) 126_07: 29: 08 D_CIXS_GLOBAL_MAPPING_START (COUNT = 4220001) 126_07: 29: 08 SIR_POLE_TO_POLE_START (COUNT = 4220001) 126_07: 33: 16 AM_PHT_MOR_END (COUNT = 1010001) 126_07: 34: 04 AM_PHT_MOR_END (COUNT = 4240002) 126_07: 34: 04 POLAR_MON_END (COUNT = 4240001) 126_07: 35: 15 AM_PHT_MOR_END (COUNT = 1000003) J 2 EE Client Server – Client Architecture TCP/IP connection to the knowledgebase Platform independence Import / Export Functionality Generation of interface documents for other ESA planning software #CDT BLOCK 126_05: 18: 24 STOC INERT_START ( POINTING_AXIS = X OBJECT = EARTH SLEW_POLICY = SMOOTH YDIR = POSITIVE ) 126_05: 48: 24 STOC INERT_END #Light side start 126_07: 26: 21 STOC NADIR_START ( OBJECT_TO_BE_POINTED = Z SLEW_POLICY = SMOOTH YDIR = POSITIVE ) #Light side end 126_09: 18: 49 STOC NADIR_END #WOL + Inertial Cool Down start 126_09: 47: 21 STOC INERT_START ( OBJECT = WOL SLEW_POLICY = SMOOTH YDIR = POSITIVE ) #End of WOL 126_11: 28: 07 STOC INERT_END #Light side start 126_12: 25: 24 STOC NADIR_START ( OBJECT_TO_BE_POINTED = Z SLEW_POLICY = SMOOTH YDIR = POSITIVE )
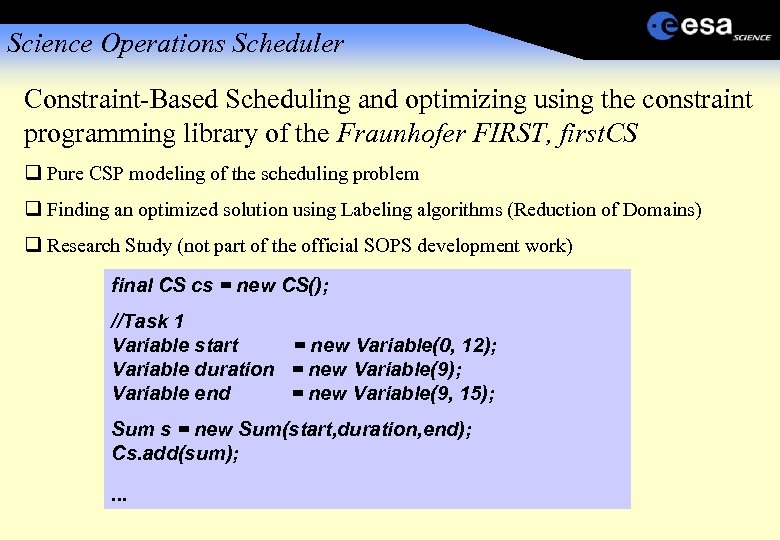 Science Operations Scheduler Constraint-Based Scheduling and optimizing using the constraint programming library of the Fraunhofer FIRST, first. CS Pure CSP modeling of the scheduling problem Finding an optimized solution using Labeling algorithms (Reduction of Domains) Research Study (not part of the official SOPS development work) final CS cs = new CS(); //Task 1 Variable start = new Variable(0, 12); Variable duration = new Variable(9); Variable end = new Variable(9, 15); Sum s = new Sum(start, duration, end); Cs. add(sum); . . .
Science Operations Scheduler Constraint-Based Scheduling and optimizing using the constraint programming library of the Fraunhofer FIRST, first. CS Pure CSP modeling of the scheduling problem Finding an optimized solution using Labeling algorithms (Reduction of Domains) Research Study (not part of the official SOPS development work) final CS cs = new CS(); //Task 1 Variable start = new Variable(0, 12); Variable duration = new Variable(9); Variable end = new Variable(9, 15); Sum s = new Sum(start, duration, end); Cs. add(sum); . . .
 Tracking and Analysing of Performed Observations The results of analysing/planning sessions are feed back into the same knowledgebase: - Planning Cycles - Orbits - Communication Opportunities - Science Opportunities - Performed Observations - All entities are time-taged and inter-related. - Any kind of queries (SQL or prepared Masks) can be carried out to perform detailed scientific analysis. - Closing the loop in the planning by taking the planning history and future into account.
Tracking and Analysing of Performed Observations The results of analysing/planning sessions are feed back into the same knowledgebase: - Planning Cycles - Orbits - Communication Opportunities - Science Opportunities - Performed Observations - All entities are time-taged and inter-related. - Any kind of queries (SQL or prepared Masks) can be carried out to perform detailed scientific analysis. - Closing the loop in the planning by taking the planning history and future into account.
 SOPS Features Summary Single Repository for all relevant information about science operations in a knowledgebase Web-based and easy access via the Internet to the knowledgebase Platform independent Java client for analyzing, scheduling, visualizing and planning Identification of all available science opportunity windows in a planning cycle Several visualization forms of analyzing results Partly automated scheduling of the identified science opportunity windows Generating interface files for other ESA planning software and the flight control team Reporting and Tracking functionality for all performed observations
SOPS Features Summary Single Repository for all relevant information about science operations in a knowledgebase Web-based and easy access via the Internet to the knowledgebase Platform independent Java client for analyzing, scheduling, visualizing and planning Identification of all available science opportunity windows in a planning cycle Several visualization forms of analyzing results Partly automated scheduling of the identified science opportunity windows Generating interface files for other ESA planning software and the flight control team Reporting and Tracking functionality for all performed observations
 SMART-1 Results, achieved using SOPS Target Coverage during the Push Broom 1 Phase of the Mission Coverage Image from the ESA MAPPS tool
SMART-1 Results, achieved using SOPS Target Coverage during the Push Broom 1 Phase of the Mission Coverage Image from the ESA MAPPS tool
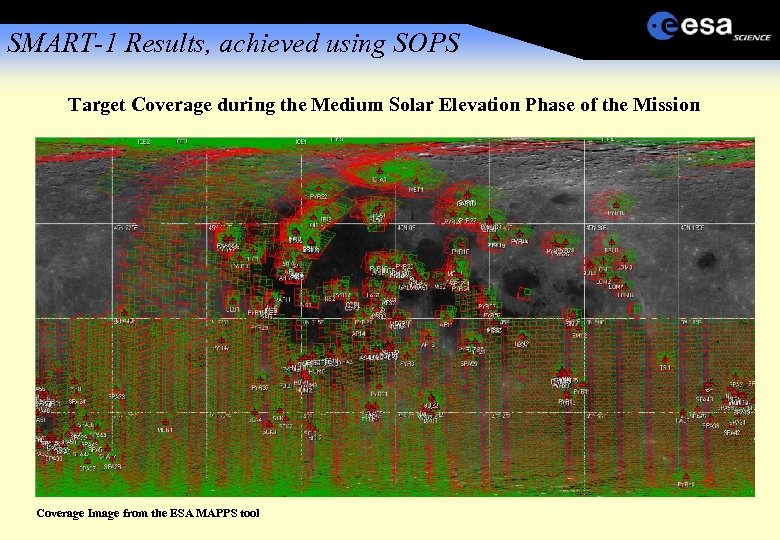 SMART-1 Results, achieved using SOPS Target Coverage during the Medium Solar Elevation Phase of the Mission Coverage Image from the ESA MAPPS tool
SMART-1 Results, achieved using SOPS Target Coverage during the Medium Solar Elevation Phase of the Mission Coverage Image from the ESA MAPPS tool
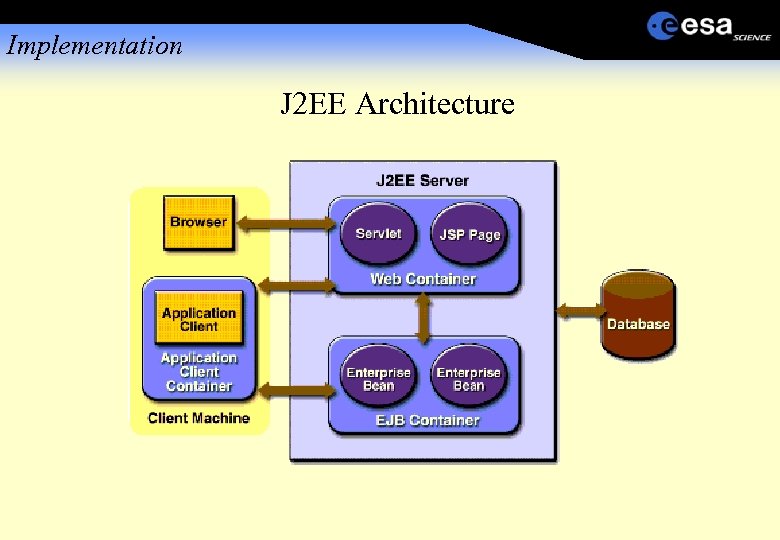 Implementation J 2 EE Architecture
Implementation J 2 EE Architecture
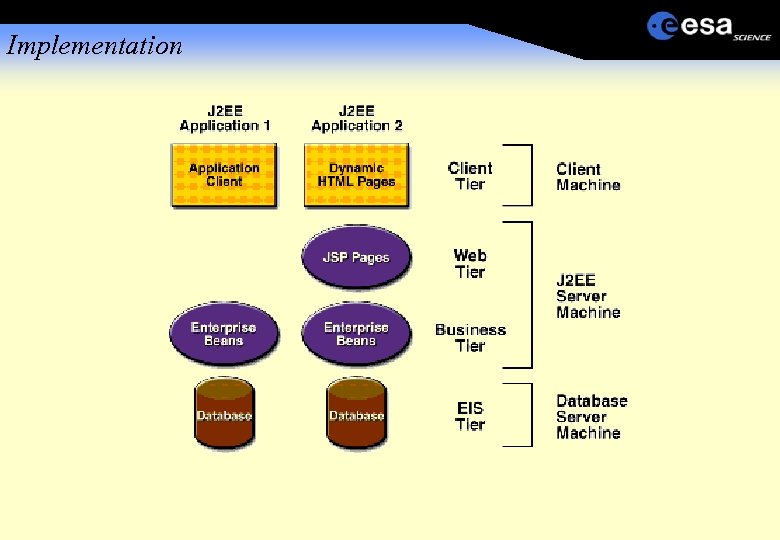 Implementation
Implementation
 Implementation Services Provided by the J 2 EE Server: • The J 2 EE security model lets you configure a web component or enterprise bean so that system resources are accessed only by authorized users. • The J 2 EE transaction model lets you specify relationships among methods that make up a single transaction so that all methods in one transaction are treated as a single unit. • JNDI lookup services provide a unified interface to multiple naming and directory services in the enterprise so that application components can access naming and directory services. • The J 2 EE remote connectivity model manages low-level communications between clients and enterprise beans. After an enterprise bean is created, a client invokes methods on it as if it were in the same virtual machine.
Implementation Services Provided by the J 2 EE Server: • The J 2 EE security model lets you configure a web component or enterprise bean so that system resources are accessed only by authorized users. • The J 2 EE transaction model lets you specify relationships among methods that make up a single transaction so that all methods in one transaction are treated as a single unit. • JNDI lookup services provide a unified interface to multiple naming and directory services in the enterprise so that application components can access naming and directory services. • The J 2 EE remote connectivity model manages low-level communications between clients and enterprise beans. After an enterprise bean is created, a client invokes methods on it as if it were in the same virtual machine.
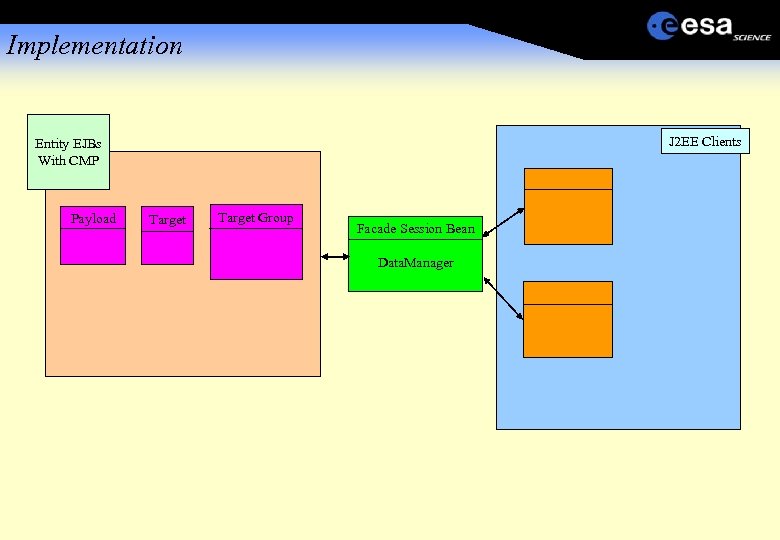 Implementation J 2 EE Clients Entity EJBs With CMP Payload Target Group Facade Session Bean Data. Manager
Implementation J 2 EE Clients Entity EJBs With CMP Payload Target Group Facade Session Bean Data. Manager
 Implementation
Implementation
 Implementation
Implementation
 Implementation
Implementation
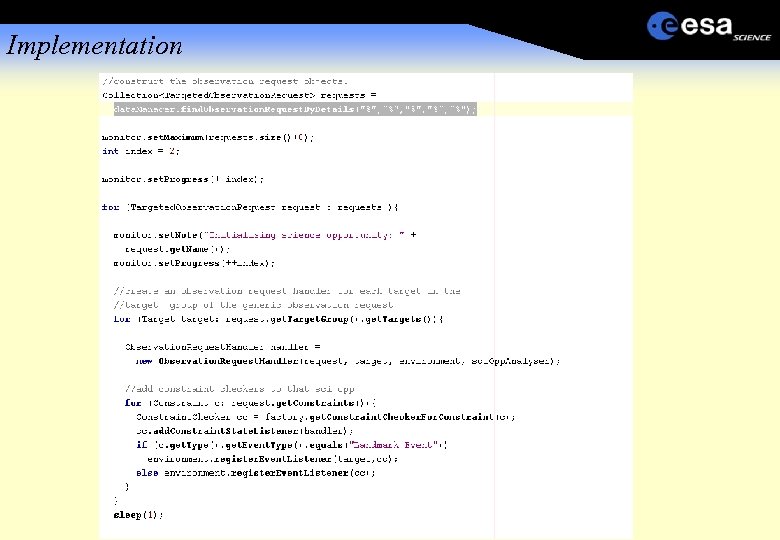 Implementation
Implementation
 Implementation
Implementation


