0eef196f66ec3dece4220228e1627a00.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 Sopron, 31. 10. 03 ERA, its future and beyond From Lisbon to Barcelona linking R&D to innovation and competitiveness The Regional Path 31/10/03 Mr Richard ESCRITT, Director ERA Coordination of Community Activities European Commission DG Research
Sopron, 31. 10. 03 ERA, its future and beyond From Lisbon to Barcelona linking R&D to innovation and competitiveness The Regional Path 31/10/03 Mr Richard ESCRITT, Director ERA Coordination of Community Activities European Commission DG Research
 The Knowledge-based economy is here - with a price • • • Today’s advanced economies are knowledge-based. This stresses even more the relevance of R&D for their development: increasingly higher S&T content embedded in products and services need for more and better qualified human resources; ICT Global Networks Increasing pace of trade liberalisation and flows of goods and services, pushing world economies to focus on more knowledge-intensive activities Under such pressures whole areas risk to become redundant globalisation tends to increase regional disparities 31/10/03 2
The Knowledge-based economy is here - with a price • • • Today’s advanced economies are knowledge-based. This stresses even more the relevance of R&D for their development: increasingly higher S&T content embedded in products and services need for more and better qualified human resources; ICT Global Networks Increasing pace of trade liberalisation and flows of goods and services, pushing world economies to focus on more knowledge-intensive activities Under such pressures whole areas risk to become redundant globalisation tends to increase regional disparities 31/10/03 2
 Globalisation challenges • Location choices for higher value economic investment are increasingly determined by market considerations (accessibility and economic framework conditions) rather than by public inducements and subsidies • Regional policies need to understand the process by which international business functions spill over to lever up competitiveness in the indigenous business base 31/10/03 3
Globalisation challenges • Location choices for higher value economic investment are increasingly determined by market considerations (accessibility and economic framework conditions) rather than by public inducements and subsidies • Regional policies need to understand the process by which international business functions spill over to lever up competitiveness in the indigenous business base 31/10/03 3
 Bridging the Technology and Innovation Gap (Building RTDI Capacity) • Unique experience makes the EU a world leader in the field: combined efforts by the Structural Funds and the RTD Framework Programme • EUR 17, 5 Billion earmarked for collaborative research in Europe by FP 6 (2002 -2006) on a competitive basis, geared to S&T excellence, without geographic restrictions • EUR 135 Billion earmarked for Objective 1 regions from the STRF (2000 -2006). Out of the 218 BEUR allocated for all regions under the STRF, 9 BEUR are effectively allocated to RTDI actions (2000 -2006). For 2004 -2006, EUR 24 Billion earmarked for the New Member States • Despite successful cases, significant delivery problems remain at regional and local level, as the operational routes to the knowledge economy are unclear or not sufficiently understood 31/10/03 4
Bridging the Technology and Innovation Gap (Building RTDI Capacity) • Unique experience makes the EU a world leader in the field: combined efforts by the Structural Funds and the RTD Framework Programme • EUR 17, 5 Billion earmarked for collaborative research in Europe by FP 6 (2002 -2006) on a competitive basis, geared to S&T excellence, without geographic restrictions • EUR 135 Billion earmarked for Objective 1 regions from the STRF (2000 -2006). Out of the 218 BEUR allocated for all regions under the STRF, 9 BEUR are effectively allocated to RTDI actions (2000 -2006). For 2004 -2006, EUR 24 Billion earmarked for the New Member States • Despite successful cases, significant delivery problems remain at regional and local level, as the operational routes to the knowledge economy are unclear or not sufficiently understood 31/10/03 4
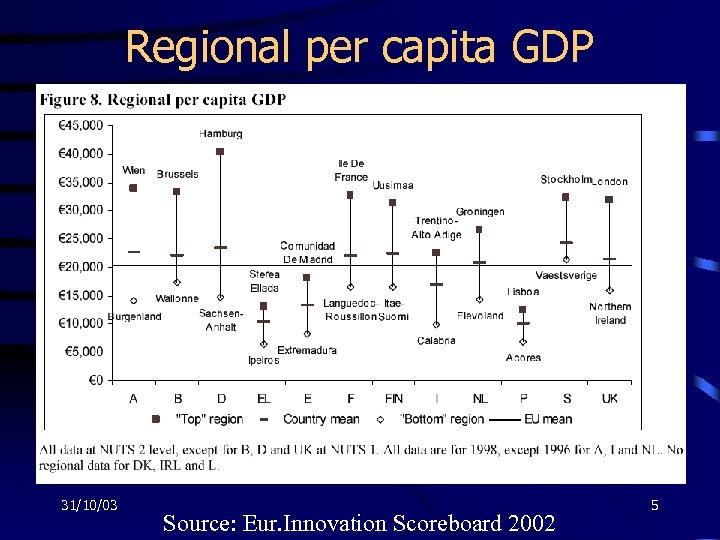 Regional per capita GDP 31/10/03 Source: Eur. Innovation Scoreboard 2002 5
Regional per capita GDP 31/10/03 Source: Eur. Innovation Scoreboard 2002 5
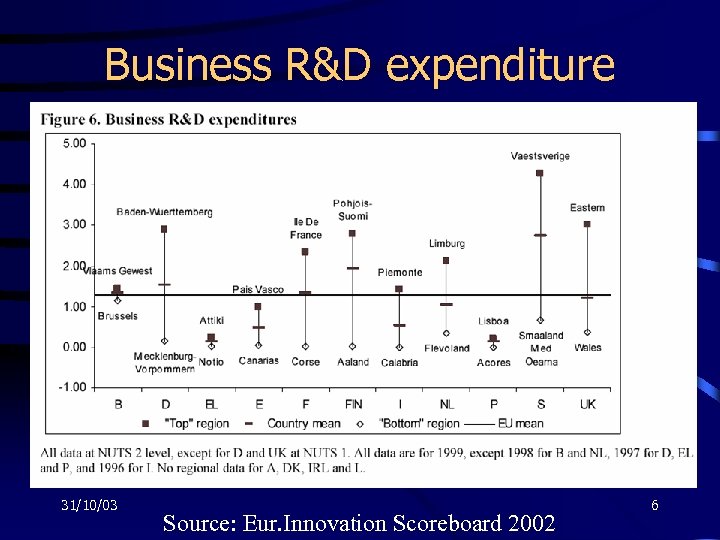 Business R&D expenditure 31/10/03 Source: Eur. Innovation Scoreboard 2002 6
Business R&D expenditure 31/10/03 Source: Eur. Innovation Scoreboard 2002 6
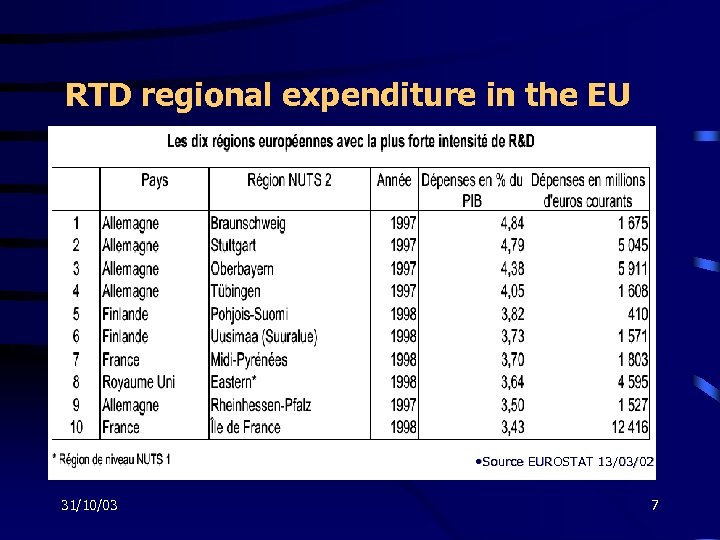 RTD regional expenditure in the EU • Source EUROSTAT 13/03/02 31/10/03 7
RTD regional expenditure in the EU • Source EUROSTAT 13/03/02 31/10/03 7
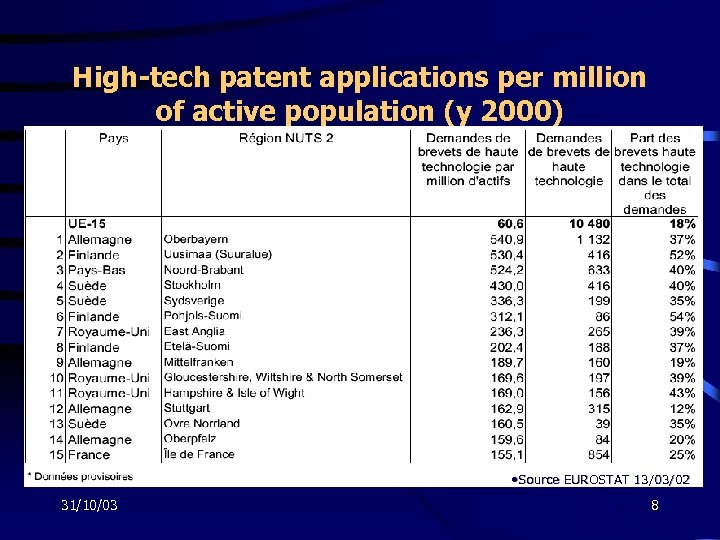 High-tech patent applications per million of active population (y 2000) • Source EUROSTAT 13/03/02 31/10/03 8
High-tech patent applications per million of active population (y 2000) • Source EUROSTAT 13/03/02 31/10/03 8
 The road from Lisbon to Barcelona goes through the regional path • Central government efforts alone are not enough to guarantee a successful take-up of the ERA process • Regions need to play an active role in creating and using knowledge: they need to be supportive, pro-active; cultivate public-private partnerships, strengthen actors, provide infrastructure and means, and more generally, find ways to bridge the gap between knowledge creators and knowledge users 31/10/03 9
The road from Lisbon to Barcelona goes through the regional path • Central government efforts alone are not enough to guarantee a successful take-up of the ERA process • Regions need to play an active role in creating and using knowledge: they need to be supportive, pro-active; cultivate public-private partnerships, strengthen actors, provide infrastructure and means, and more generally, find ways to bridge the gap between knowledge creators and knowledge users 31/10/03 9
 The concept of the Regional Dimension of the ERA • Concept identified in all ERA related Communications as important / Special Communication on the Regional Dimension adopted 03/10/01 (COM(2001)549) • Need to paying more attention to local and regional factors and operators, when thinking about research policy - a message primarily addressed to the Member States • Involve more the Member States and the regions in a European Policy context 31/10/03 10
The concept of the Regional Dimension of the ERA • Concept identified in all ERA related Communications as important / Special Communication on the Regional Dimension adopted 03/10/01 (COM(2001)549) • Need to paying more attention to local and regional factors and operators, when thinking about research policy - a message primarily addressed to the Member States • Involve more the Member States and the regions in a European Policy context 31/10/03 10
 What can be done to enhance regional capacity in the knowledge economy • Transform the economy into a learning one • Establish coherent development strategies based on local comparative advantage / regional foresight • Set up the appropriate framework conditions for R&D and innovation • Stimulate the take-up of new technologies • Local partnerships emerge as leaders in this process. Universities may play there an important role 31/10/03 11
What can be done to enhance regional capacity in the knowledge economy • Transform the economy into a learning one • Establish coherent development strategies based on local comparative advantage / regional foresight • Set up the appropriate framework conditions for R&D and innovation • Stimulate the take-up of new technologies • Local partnerships emerge as leaders in this process. Universities may play there an important role 31/10/03 11
 A strategy for integrating regions in the ERA • Integrating research policy and regional policy • building research capacity in the regions. Implementation of this strategy is based on a wide range of Community instruments: – The Sixth Framework Programme for RTD (2002 -2006), providing trans-regional co-operation opportunities – Innovation activities undertaken at regional level under the Framework Programme, in conjunction with the Mainstream Activities as well as the Innovative Actions of the Structural Funds – Longer-term structuring activities – Use of New Initiatives (ex. The Regions of Knowledge pilot action, introduced in 2003 by the European Parliament) 31/10/03 12
A strategy for integrating regions in the ERA • Integrating research policy and regional policy • building research capacity in the regions. Implementation of this strategy is based on a wide range of Community instruments: – The Sixth Framework Programme for RTD (2002 -2006), providing trans-regional co-operation opportunities – Innovation activities undertaken at regional level under the Framework Programme, in conjunction with the Mainstream Activities as well as the Innovative Actions of the Structural Funds – Longer-term structuring activities – Use of New Initiatives (ex. The Regions of Knowledge pilot action, introduced in 2003 by the European Parliament) 31/10/03 12
 The Regions of Knowledge Pilot Action (Know. REG) • introduced in the 2003 Community Budget by the European Parliament (heading B 5 -513) • implemented outside of the 6 th FP, it has a budget of EUR 2, 5 million and aspires to develop experimental activities involving networks of European regions (with the active involvement of universities, research centres, and the business community) to create "Knowledge regions", able to provide model regional implementations of the Lisbon strategy, that is, demonstrate the central role of knowledge in driving regional development. 31/10/03 13
The Regions of Knowledge Pilot Action (Know. REG) • introduced in the 2003 Community Budget by the European Parliament (heading B 5 -513) • implemented outside of the 6 th FP, it has a budget of EUR 2, 5 million and aspires to develop experimental activities involving networks of European regions (with the active involvement of universities, research centres, and the business community) to create "Knowledge regions", able to provide model regional implementations of the Lisbon strategy, that is, demonstrate the central role of knowledge in driving regional development. 31/10/03 13
 Regions of Knowledge (ii) • launched formally with a Call for Proposals • Covered two (2) basic strands: (1) Integrated Regional Technology Initiatives (IRTI) and (2) Supporting activities (workshops and conferences). – – IRTI sub-divided in three (3) parts: (a) Technology audits and Regional Foresight (b) University Driven Actions for Regional Development (c) Mentoring Initiatives, where technologically advanced regions would co-operate with less advanced regions (Objective 1) in a kind of "mentoring" partnership, for a more efficient innovation and technology transfer process. – Projects had to have at least 3 partners coming from 3 different Member States. 31/10/03 14
Regions of Knowledge (ii) • launched formally with a Call for Proposals • Covered two (2) basic strands: (1) Integrated Regional Technology Initiatives (IRTI) and (2) Supporting activities (workshops and conferences). – – IRTI sub-divided in three (3) parts: (a) Technology audits and Regional Foresight (b) University Driven Actions for Regional Development (c) Mentoring Initiatives, where technologically advanced regions would co-operate with less advanced regions (Objective 1) in a kind of "mentoring" partnership, for a more efficient innovation and technology transfer process. – Projects had to have at least 3 partners coming from 3 different Member States. 31/10/03 14
 Implementing the regional dimension through specific measures in FP 6 (2002 -2006) • • Regions as direct or indirect partners in the major new instruments (No. E or IP) Structuring the ERA: Research and Innovation ò encouragement and validation of local and regional initiatives ò encouraging trans-regional co-operation ò experimenting with new tools and approaches • • Strengthening the ERA foundations: the ERA-NET scheme: support for coordination measures at national or regional level / and also regional tech. foresight, benchmarking) SMES (collective / cooperative research) Human Potential: special grants favouring participants coming from less developed regions, in particular host driven technology transfer fellowships Possibility of complementing the Framework Programme funding for Objective 1 partners in successfully selected proposals. Money would come from the Structural Funds (ERDF). BUT: NOT COMPULSORY for ERDF / Respecting fully the scientific excellence criteria when selecting projects for funding; WITHIN THE LIMITS of the State Aids regulations. 31/10/03 15
Implementing the regional dimension through specific measures in FP 6 (2002 -2006) • • Regions as direct or indirect partners in the major new instruments (No. E or IP) Structuring the ERA: Research and Innovation ò encouragement and validation of local and regional initiatives ò encouraging trans-regional co-operation ò experimenting with new tools and approaches • • Strengthening the ERA foundations: the ERA-NET scheme: support for coordination measures at national or regional level / and also regional tech. foresight, benchmarking) SMES (collective / cooperative research) Human Potential: special grants favouring participants coming from less developed regions, in particular host driven technology transfer fellowships Possibility of complementing the Framework Programme funding for Objective 1 partners in successfully selected proposals. Money would come from the Structural Funds (ERDF). BUT: NOT COMPULSORY for ERDF / Respecting fully the scientific excellence criteria when selecting projects for funding; WITHIN THE LIMITS of the State Aids regulations. 31/10/03 15
 Towards a Mutual Learning Platform for the Regions • The Barcelona 3% Action Plan establishes the concept of the Mutual Learning Platform (MLP) – – building on existing activities to produce a typology of RTDI growth patterns to measure regional RTDI performance to stimulate a better use of regional foresight for more efficient planning – to stimulate a learning process 31/10/03 16
Towards a Mutual Learning Platform for the Regions • The Barcelona 3% Action Plan establishes the concept of the Mutual Learning Platform (MLP) – – building on existing activities to produce a typology of RTDI growth patterns to measure regional RTDI performance to stimulate a better use of regional foresight for more efficient planning – to stimulate a learning process 31/10/03 16
 Net links • http: //www. cordis. lu/era/knowreg. htm (The Regions of knowledge Web page) • http: //www. cordis. lu/era/regions. htm (Regional Dimension of the ERA) • http: //www. innovating-regions. org/ (The IRE Network, Innovating regions in Europe) • http: //europa. eu. int/comm/regional_policy/themes/resear_en. htm (Structural Funds and Research / Innovation) • http: //europa. eu. int/comm/research/index_en. html (DG Research official home page) • http: //europa. eu. int/comm/research/nfp. html (The 6 th Framework Programme (2002 -2006) 31/10/03 17
Net links • http: //www. cordis. lu/era/knowreg. htm (The Regions of knowledge Web page) • http: //www. cordis. lu/era/regions. htm (Regional Dimension of the ERA) • http: //www. innovating-regions. org/ (The IRE Network, Innovating regions in Europe) • http: //europa. eu. int/comm/regional_policy/themes/resear_en. htm (Structural Funds and Research / Innovation) • http: //europa. eu. int/comm/research/index_en. html (DG Research official home page) • http: //europa. eu. int/comm/research/nfp. html (The 6 th Framework Programme (2002 -2006) 31/10/03 17


