0018069271bde1c8164aab64844152d7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30

Solutions to the Problem Gambling and Crime Connection Henry R. Lesieur, Ph. D. Brown University and Rhode Island Hospital

Crime Rates Among Pathological Gamblers l GA & treatment Studies -- 50 -67% l Helpline Study of Problem Gamblers -20% admitted crime and 11. 5% arrested l NORC study -- general population -- 32% of PGs arrested for any crime
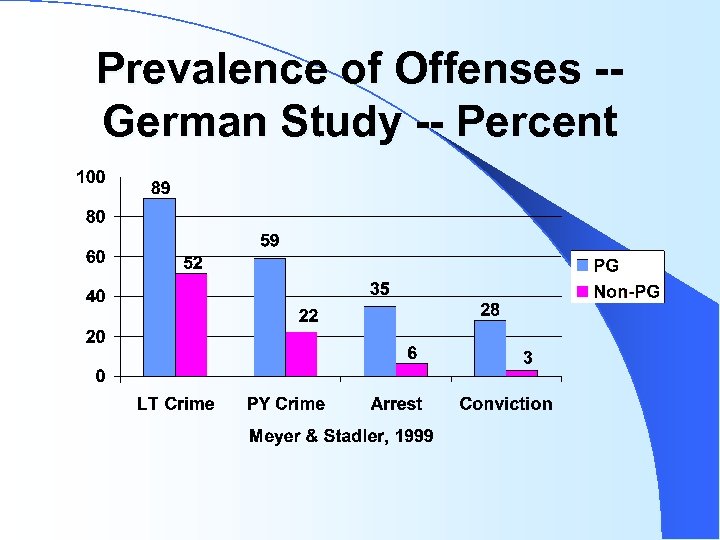
Prevalence of Offenses -German Study -- Percent

Crime Types Among Pathological Gamblers l Forgery, Fraud, Theft, Embezzlement l Tax violations (fraud & evasion) l Illegal Gambling operation l Less common: Burglary, Armed robbery, Drug Sales, Fencing Stolen Goods, Prostitution, Extortion

Psychologist as Expert Witness l Reviews Materials from Court l Interviews Offender and others l Evaluates Mental Status l Evaluates for Mental Disorders l Conducts Psychological Tests l Writes Report

Psychologist as Expert Witness - 2 l Examines issues not covered by presentence investigation l -- Emotional Issues l -- Family Dysfunction l -- Co-occurring Disorders l -- Coping Skills

Psychologist as Expert Witness - 3 l Examines work history (positives as well as negatives) l Social supports l Gambling Progression l Cognitive Distortions l Personality Disorder (especially ASPD)

Action/Escape Phase l ACTION -- become involved; good at it; exciting; early success; bolster self-esteem by gambling; wins=internally produced; losses=externally produced l ESCAPE -- gambling to escape from problems, loneliness, depression, anxiety, trauma; gambling = time out, time away from problems

Losing/Chasing Phase l ACTION gambler finds losing intolerable; CHASE after bad beats & serious losses l ESCAPE gambler finds “time out” is expensive l BOTH use up options for obtaining money as their involvement increases l New Money = Big Win

Cycles in the Spiral of Options and Involvement 1. Get Money 2. “Moving, ” “Manipulating, ” or “Juggling” Money 3. Tightening of Resources (Closure) and Need to Make Moral Decision

Desperation Phase l Job & Family Disaster Areas l Illegal Activities (CG Spiral) l Obsession with Getting Out of Trouble Overtakes Excitement l Escapes into Gambling Yet No Relief l Serious bouts with Depression l Suicide Attempts

Hopeless Phase l Getting Even Not Possible l No Longer Care l Know They Will Lose l Continual State of Depression l Playing for Action is All That Matters

Considerations Before Turning To Crime 1. Opportunity 2. External Agents of Social Control (Police, Family) 3. Beliefs & Justifications 4. Closing of Available Options 5. Threat (to self-esteem, financial threat, Physical threat)

CRIME AND STRESS Stress of Gambling l Stress of Financial Pressures l Stress of Impact on Family l Work-related Stress l l Produce: Anxiety, Depression, and Cognitive Distortions that Impair Judgment and Decision -Making

Moral Justifications and Illegal Activity

Social Attachment (Meyer & Stadler) l Change in Living Condition l Relationship to Parents l Parental Education Methods l Emotional & Social Attachment l Involvement in Conventional Activities l Belief in Social Rules

Addiction Pressures for Crime (Meyer & Stadler) l Severity of Pathological Gambling l Cravings to Gamble l Duration of Gambling l Debt & Income/Loss Ratio l Emotional & Family Problems l Type and Frequency of Gambling

Personality and Crime (Meyer & Stadler) l Aggressiveness l Extroversion l Impulsivity; Risk-Motivation l Antisocial Personality l Frankness; Emotionality l Global Mental Status
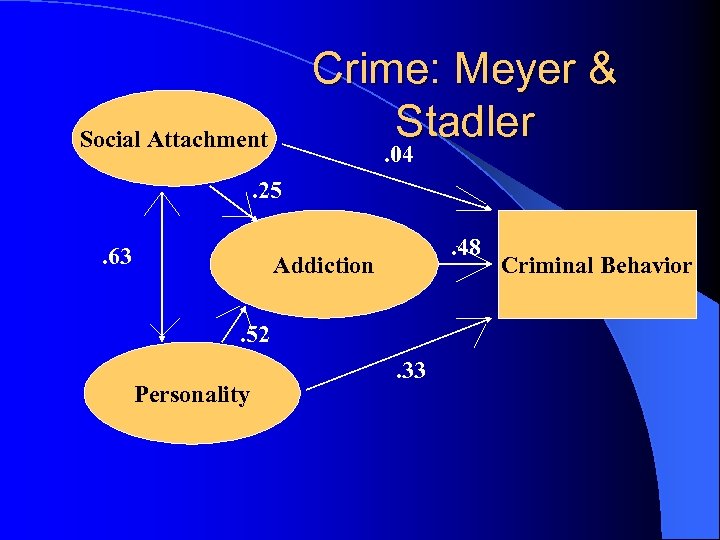
Crime: Meyer & Stadler Social Attachment . 04 . 25. 63 . 48 Addiction. 52 Personality . 33 Criminal Behavior

The Five “R”s l l l Remorse – evidence of feelings Repentance – evidence of lifestyle changes. What is different? Job situation, marriage, etc. Restitution plan. Is it realistic? Recovery – treatment plan for recovery. Give details and dates. Evidence of compliance Rehabilitation – evidence of change in attitude. Volunteer work, community service, spiritual life style change

US Courts & Pathological Gambling l Insanity Defense Argued in 1980 s (PG does not apply) l Federal Sentencing Guidelines l Diminished Capacity and Downward Departure l “Significantly Reduced Mental Capacity”

Minnesota Rule 82 Pathological Gambling l Offenders Convicted of Felony Theft, Embezzlement & Forgery l PO Screens using SOGS l 17% SOGS 5+ l Sent for Gambling Assessment

Conditions of Probation for Pathological Gamblers l l l Abstinence from Gambling Attendance at GA Community Service Gambling Counseling Restitution Orders How about Exclusion?

Gambling Court l Modeled after Drug Courts l Buffalo, New York l 26 th Judicial Court in Louisiana l Proposed in Florida

Gambling Court - 2 l l l Eligibility Criteria Pathological Gamblers First Offenders Non-violent No drug dealers No sex offenders

Gambling Court - 5 l l l Recommendations possible depend on what treatment is available Inpatient treatment (Louisiana only) Intensive Outpatient day treatment Halfway House Outpatient treatment Gamblers Anonymous

Gambling Court - 8 l No Evaluations of gambling courts conducted to date l Drug Courts show 45 -50% graduation rates l Drug Courts show reduced recidivism in two-thirds of the courts evaluated

Pathological Gambling among Prisoners l Conducted a Meta-analysis of 10 Studies l 19. 6% of prisoners level 3 gamblers (probable PGs) l Gamblers higher criminality l Higher rate of psychopathy l Higher rate of Depression l Higher Rate of SUD

Gambling in Prisons l Play Cards for Cigarettes l Bet on Horses with prison bookies l Sports Betting l -- Sell drugs to pay for gambling l -- Bet with $$ on outside l -- Get into Fights l -- Provide services to pay gambling

Recommendations for CJS and Pathological Gambling 1. Educate & train CJS personnel 2. Explore Gambling Courts 3. Evaluate and Assess Offenders on Pre-trial basis 4. GA meetings in Prisons 5. PG Treatment with trained counselors 6. Community Service by ex-prisoners at prison GA meetings
0018069271bde1c8164aab64844152d7.ppt