541dcdab32fc4819441231c5cad24984.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19

SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT IN GAZA STRIP PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS Dr. Abdul-Karim Jouda UNRWA-Gaza

SOLID WASTE • Definition. • Why to manage solid waste? • Who is doing what in Gaza Strip.
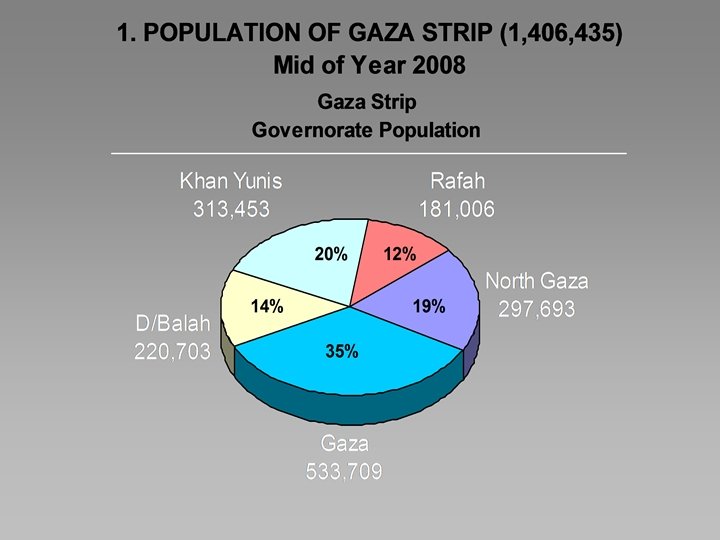

2. QUANTITIES (2007) • Gaza North : 207 tonne/day • Gaza City: 617 tonne/day • Deir al-Balah: 129 tonne/day • Khan Younis: 143 tonne/day • Rafah: 130 tonne/day • TOTAL: 1, 226 tonne/day Volume: 907 m 3/day • Required Area: 17, 500 m 2/year • 1 kg/capita/day

3. Equipment (Crane Truck and Tractors).

4. Solid Waste Disposal: GAZA CONTROLLED LANDFILL Serves Governorates of Gaza & North Gaza DEIR AL BALAH SANITARY LANDFILL Serves Governorates of Deir Al-Balah & Khan Younis RAFAH CONTROLLED LANDFILL Serves Governorate of Rafah
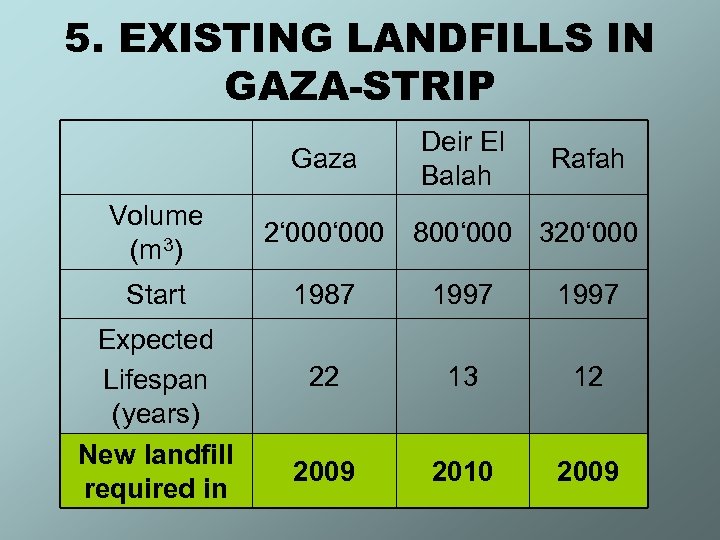
5. EXISTING LANDFILLS IN GAZA-STRIP Gaza Volume (m 3) Start Expected Lifespan (years) New landfill required in Deir El Balah Rafah 2‘ 000 800‘ 000 320‘ 000 1987 1997 22 13 12 2009 2010 2009
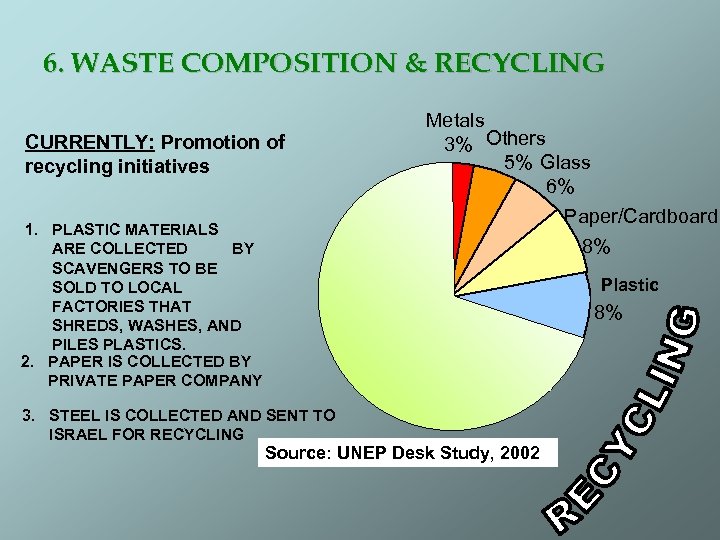
6. WASTE COMPOSITION & RECYCLING Metals 3% Others 5% Glass 6% Paper/Cardboard 8% CURRENTLY: Promotion of recycling initiatives 1. PLASTIC MATERIALS ARE COLLECTED BY SCAVENGERS TO BE SOLD TO LOCAL FACTORIES THAT SHREDS, WASHES, AND PILES PLASTICS. 2. PAPER IS COLLECTED BY PRIVATE PAPER COMPANY Plastic Organic Material Plastic 70% 3. STEEL IS COLLECTED AND SENT TO ISRAEL FOR RECYCLING Source: UNEP Desk Study, 2002 8%

What are the Problems?

1. Problems of garbage collection process First – Containers: – – Burning refuse inside containers. Lack of cleanliness around containers. Lack of maintenance of containers. Steeling and selling some refuse containers as scrap. Second – Vehicles: – – – Fleets are becoming old. No standby vehicles. Frequent breakdown of vehicles due to the use of rough roads.

2. Problems of Land fills : • Limited life span and scarcity of land. • The close proximity of landfill sites to the border with Israel. • Uncontrolled fires and damages by IDF. • Sieving plant of the Middle Area is not working because of the lack of coordination with the Israeli side

3. Problems due to the closure • Shortage or absence of spare parts and other supplies. • Specialists and technicians were unable to access Gaza. • Shortage of fuel • Donor funding problems. • Payment of salaries.

4. Waste Disposal / treatment 1. Absence of comprehensive hazardous and clinical waste management system. 2. Absence of alternate disposal options. 3. Land filling is the main option.

What are the Solutions?

1. DEVELOPMENT STRATEGY • Institutional development. • Sharing common database for decision making. • Contingency planning for emergencies • Private sector involvement. • Support extension of Solid waste councils. • Standardization of equipment.

2. PREREQUISITES FOR DEVELOPMENT A. Removing all obstacles to humanitarian access and enhancing cross-boarder cooperation. B. Applying appropriate technologies. C. Ensuring adequate and sustainable flow of financial and technical assistance by the international community D. Coordination of international aid efforts within major donors.

3. MEETING SWM INVESTMENT NEEDS A. Support projects for segregation, recycling and composting of solid waste. B. Support projects for mechanization of solid waste collection and disposal C. Support projects for hazardous and medical waste management D. Support the construction of high capacity incinerators to stop open burning and reduce the number of disposal sites

4. ENHANCING COOPERATION • Cooperation among municipalities, SWMC’s, PA departments and UNRWA. • Partnership with donors • Community involvement.

5. OTHER CONSIDERATIONS 1. How to improve willingness to pay. 2. Cost recovery. 3. Improving the work environment of personnel.
541dcdab32fc4819441231c5cad24984.ppt