2a1edf3d43a97aa2d3798f6edb0b188c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37
 Solid waste and the environment Principles of the Kyoto Protocol 1. 2. : Clean Development Mechanism - Overview and Concepts
Solid waste and the environment Principles of the Kyoto Protocol 1. 2. : Clean Development Mechanism - Overview and Concepts
 Outline CDM Context within the Kyoto Protocol n Overview of CDM n Eligible Projects q Basic Rules & Processes q Baselines q Sustainable Development q CDM Concepts - Developing Projects q n What does the CDM mean for Indonesia? Opportunities q Reality and Issues with CDM q Next Steps q
Outline CDM Context within the Kyoto Protocol n Overview of CDM n Eligible Projects q Basic Rules & Processes q Baselines q Sustainable Development q CDM Concepts - Developing Projects q n What does the CDM mean for Indonesia? Opportunities q Reality and Issues with CDM q Next Steps q
 CDM Context (1) The Kyoto Protocol commits industrialized countries to legally binding GHG reduction targets during the period 2008 -2012 n Most countries have to reduce GHG emissions on ave 5% below their 1990 emission levels n q n results in a global target of ‘carbon’ reduction These countries can choose to reduce emissions ‘at home’ in their own country q in other countries q n Reducing emissions in Developing Countries is eligible – known as CDM
CDM Context (1) The Kyoto Protocol commits industrialized countries to legally binding GHG reduction targets during the period 2008 -2012 n Most countries have to reduce GHG emissions on ave 5% below their 1990 emission levels n q n results in a global target of ‘carbon’ reduction These countries can choose to reduce emissions ‘at home’ in their own country q in other countries q n Reducing emissions in Developing Countries is eligible – known as CDM
 CDM Context (2) Benefit of the CDM is n to help Annex 1 Parties to implement their commitment to reduce GHG emission in the most economical way and n To help developing countries (non Annex I Parties) in achieving sustainable development
CDM Context (2) Benefit of the CDM is n to help Annex 1 Parties to implement their commitment to reduce GHG emission in the most economical way and n To help developing countries (non Annex I Parties) in achieving sustainable development
 Overview of CDM – Clean Development Mechanism n A mechanism by which Industrialised Nations can achieve part of their reduction obligations through projects that reduce or fix/sequester carbon in Developing Countries. n The Certified Emission Reductions (CERs) are a unit of carbon that is reduced or sequestered. n Industrialised Nations can submit their CERs to meet their target in 2008 -2012. n there is a worldwide demand for projects and activities for ‘carbon’ reduction or fixation q Many of these projects will be in Developing Countries. q
Overview of CDM – Clean Development Mechanism n A mechanism by which Industrialised Nations can achieve part of their reduction obligations through projects that reduce or fix/sequester carbon in Developing Countries. n The Certified Emission Reductions (CERs) are a unit of carbon that is reduced or sequestered. n Industrialised Nations can submit their CERs to meet their target in 2008 -2012. n there is a worldwide demand for projects and activities for ‘carbon’ reduction or fixation q Many of these projects will be in Developing Countries. q
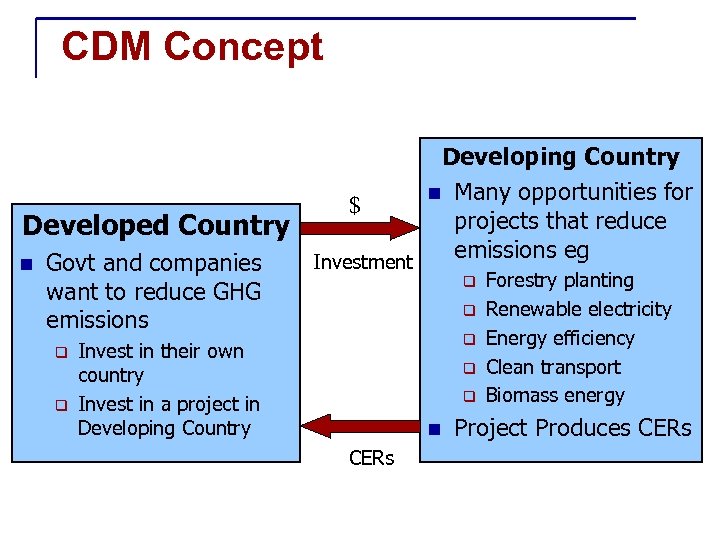 CDM Concept Developing Country n Many opportunities for $ projects that reduce Developed Country emissions eg Investment n Govt and companies q Forestry planting want to reduce GHG q Renewable electricity emissions q q q Invest in their own country Invest in a project in Developing Country q q n CERs Energy efficiency Clean transport Biomass energy Project Produces CERs
CDM Concept Developing Country n Many opportunities for $ projects that reduce Developed Country emissions eg Investment n Govt and companies q Forestry planting want to reduce GHG q Renewable electricity emissions q q q Invest in their own country Invest in a project in Developing Country q q n CERs Energy efficiency Clean transport Biomass energy Project Produces CERs
 Purpose of CDM to assist developing countries in achieving sustainable development 2. to assist developed countries in achieving compliance with part of their quantified emission reduction commitments. 1.
Purpose of CDM to assist developing countries in achieving sustainable development 2. to assist developed countries in achieving compliance with part of their quantified emission reduction commitments. 1.
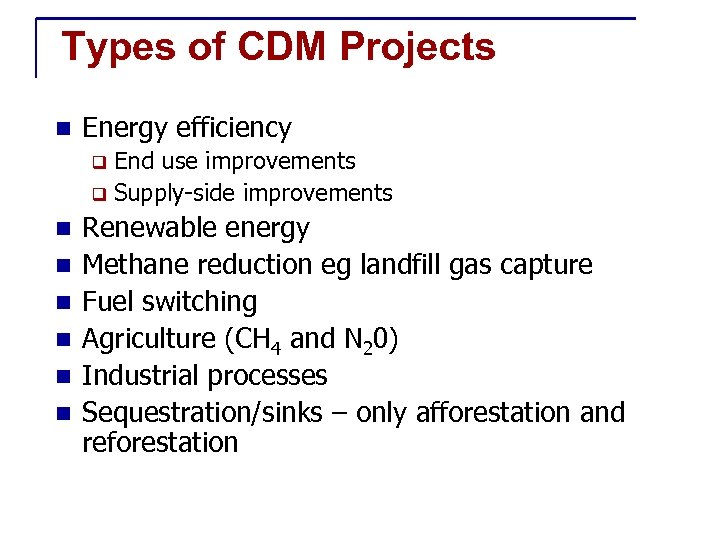 Types of CDM Projects n Energy efficiency End use improvements q Supply-side improvements q n n n Renewable energy Methane reduction eg landfill gas capture Fuel switching Agriculture (CH 4 and N 20) Industrial processes Sequestration/sinks – only afforestation and reforestation
Types of CDM Projects n Energy efficiency End use improvements q Supply-side improvements q n n n Renewable energy Methane reduction eg landfill gas capture Fuel switching Agriculture (CH 4 and N 20) Industrial processes Sequestration/sinks – only afforestation and reforestation
 CDM Project Examples End-use energy efficiency Supply-side energy efficiency Renewable energy High efficient lighting; efficient cook stoves; vehicle efficiency High efficiency turbine replacement; combine cycle Biomass; Solar; Wind; Hydro Fuel switching Gas conversion Biofuels replace fossil fuels Afforestration; Reforestation Community forestry Intermittent ricefield irrigation Forestry Agriculture
CDM Project Examples End-use energy efficiency Supply-side energy efficiency Renewable energy High efficient lighting; efficient cook stoves; vehicle efficiency High efficiency turbine replacement; combine cycle Biomass; Solar; Wind; Hydro Fuel switching Gas conversion Biofuels replace fossil fuels Afforestration; Reforestation Community forestry Intermittent ricefield irrigation Forestry Agriculture
 Summary of basic CDM Rules
Summary of basic CDM Rules
 Baseline Concepts The baseline is a measure of emissions that would have occurred in absence of project n Used to estimate emission reductions for project – basis for CERs n q n On a project by project basis Standard baselines for small scale projects 20 MW renewable energy q 20 GWh energy efficiency q
Baseline Concepts The baseline is a measure of emissions that would have occurred in absence of project n Used to estimate emission reductions for project – basis for CERs n q n On a project by project basis Standard baselines for small scale projects 20 MW renewable energy q 20 GWh energy efficiency q
 Baseline (PDD) Contents (1) A. General description of project activity B. Description of baseline methodology C. Timeline Project D. Monitoring methodology and Plan E. Calculation of GHG emission by sources F. Assessment of Environmental impacts G. Stakeholder’s comments
Baseline (PDD) Contents (1) A. General description of project activity B. Description of baseline methodology C. Timeline Project D. Monitoring methodology and Plan E. Calculation of GHG emission by sources F. Assessment of Environmental impacts G. Stakeholder’s comments
 Baseline (PDD) Contents (2) Annex I: Information of the parties participating in the project Annex II: Information of public investment Annex III: New methodology to calculate baseline Annex IV: New monitoring methodology Annex V: Baseline data
Baseline (PDD) Contents (2) Annex I: Information of the parties participating in the project Annex II: Information of public investment Annex III: New methodology to calculate baseline Annex IV: New monitoring methodology Annex V: Baseline data
 Baseline Methodologies n Approximately 50 baseline methodologies were approved on the basis of: Business as usual (“BAU”) - future emissions would been the same as current/historic emissions and “Additionality”, meaning that the project would otherwise not have occurred q Market Conditions - the technology used in the market is the baseline and market barriers prevent new technology being adopted q Best Available Technology - for markets where conditions are changing, historic emissions are less relevant – assume emissions for the technology that would have been installed q
Baseline Methodologies n Approximately 50 baseline methodologies were approved on the basis of: Business as usual (“BAU”) - future emissions would been the same as current/historic emissions and “Additionality”, meaning that the project would otherwise not have occurred q Market Conditions - the technology used in the market is the baseline and market barriers prevent new technology being adopted q Best Available Technology - for markets where conditions are changing, historic emissions are less relevant – assume emissions for the technology that would have been installed q
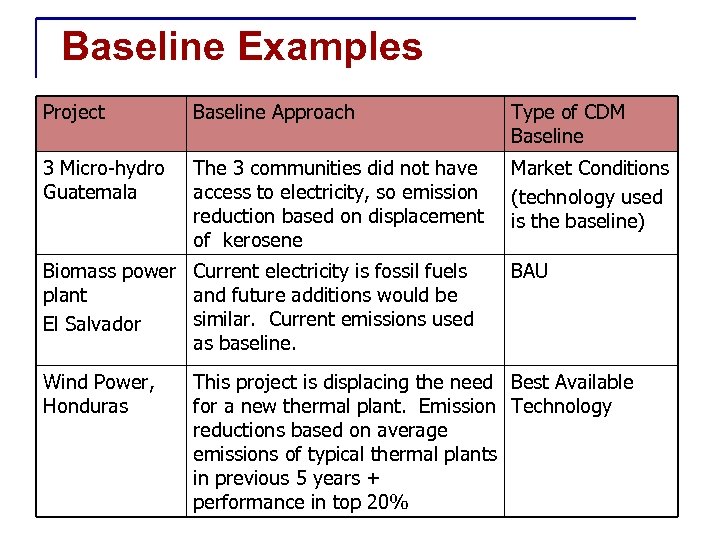 Baseline Examples Project Baseline Approach Type of CDM Baseline 3 Micro-hydro Guatemala The 3 communities did not have access to electricity, so emission reduction based on displacement of kerosene Market Conditions (technology used is the baseline) Biomass power Current electricity is fossil fuels plant and future additions would be similar. Current emissions used El Salvador as baseline. Wind Power, Honduras BAU This project is displacing the need Best Available for a new thermal plant. Emission Technology reductions based on average emissions of typical thermal plants in previous 5 years + performance in top 20%
Baseline Examples Project Baseline Approach Type of CDM Baseline 3 Micro-hydro Guatemala The 3 communities did not have access to electricity, so emission reduction based on displacement of kerosene Market Conditions (technology used is the baseline) Biomass power Current electricity is fossil fuels plant and future additions would be similar. Current emissions used El Salvador as baseline. Wind Power, Honduras BAU This project is displacing the need Best Available for a new thermal plant. Emission Technology reductions based on average emissions of typical thermal plants in previous 5 years + performance in top 20%
 Basic Rules for CDM Emission reductions from CDM project must be additional in developing country n Use of CERs can only supplement emission reduction at home in developed countries n CDM projects must: n be approved by the host country q lead to sustainable development in host country q result in real, measurable and long-term benefits in terms of climate change q Money for CDM projects not divert Official Development Assistance (ODA) n Nuclear power projects are not eligible n Only afforestation and reforestation allowed n
Basic Rules for CDM Emission reductions from CDM project must be additional in developing country n Use of CERs can only supplement emission reduction at home in developed countries n CDM projects must: n be approved by the host country q lead to sustainable development in host country q result in real, measurable and long-term benefits in terms of climate change q Money for CDM projects not divert Official Development Assistance (ODA) n Nuclear power projects are not eligible n Only afforestation and reforestation allowed n
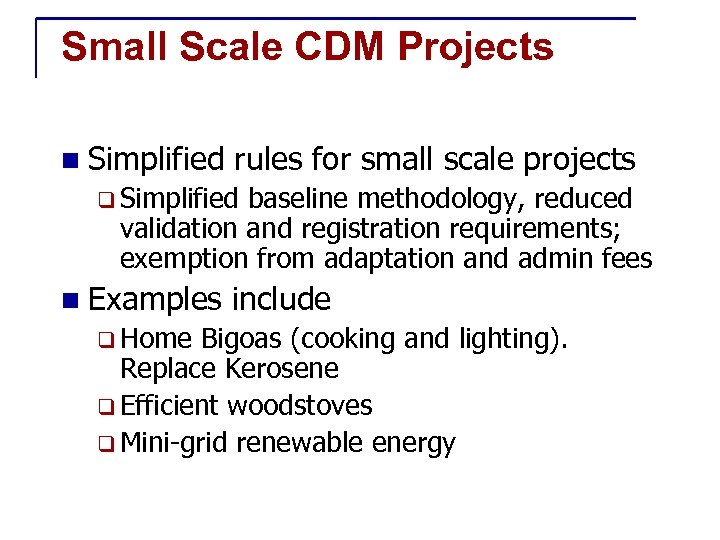 Small Scale CDM Projects n Simplified rules for small scale projects q Simplified baseline methodology, reduced validation and registration requirements; exemption from adaptation and admin fees n Examples q Home include Bigoas (cooking and lighting). Replace Kerosene q Efficient woodstoves q Mini-grid renewable energy
Small Scale CDM Projects n Simplified rules for small scale projects q Simplified baseline methodology, reduced validation and registration requirements; exemption from adaptation and admin fees n Examples q Home include Bigoas (cooking and lighting). Replace Kerosene q Efficient woodstoves q Mini-grid renewable energy
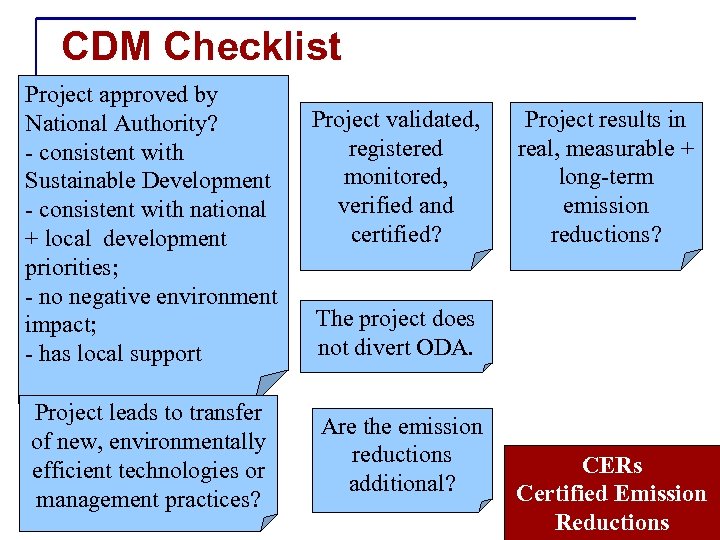 CDM Checklist Project approved by National Authority? - consistent with Sustainable Development - consistent with national + local development priorities; - no negative environment impact; - has local support Project leads to transfer of new, environmentally efficient technologies or management practices? Project validated, registered monitored, verified and certified? Project results in real, measurable + long-term emission reductions? The project does not divert ODA. Are the emission reductions additional? CERs Certified Emission Reductions
CDM Checklist Project approved by National Authority? - consistent with Sustainable Development - consistent with national + local development priorities; - no negative environment impact; - has local support Project leads to transfer of new, environmentally efficient technologies or management practices? Project validated, registered monitored, verified and certified? Project results in real, measurable + long-term emission reductions? The project does not divert ODA. Are the emission reductions additional? CERs Certified Emission Reductions
 Sustainable Development Criteria n Social Criteria Improves quality of life q Alleviates poverty q Improves Equity q n Economic Criteria Provides financial returns to local entities q Results in new investments q Transfers new technology q n Environmental Criteria Reduces GHG and use of fossil fuels q Conserves local resources q Reduces pressure on local environments q Provides health and environmental benefits q
Sustainable Development Criteria n Social Criteria Improves quality of life q Alleviates poverty q Improves Equity q n Economic Criteria Provides financial returns to local entities q Results in new investments q Transfers new technology q n Environmental Criteria Reduces GHG and use of fossil fuels q Conserves local resources q Reduces pressure on local environments q Provides health and environmental benefits q
 How does CDM work in practice?
How does CDM work in practice?
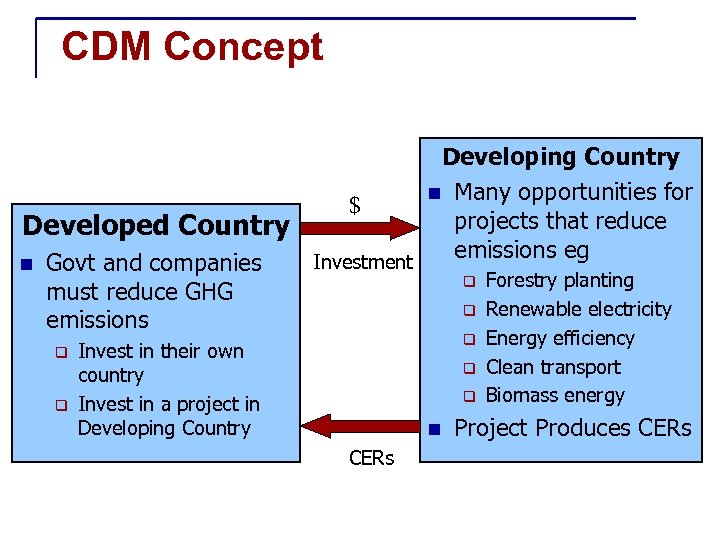 CDM Concept Developing Country n Many opportunities for $ projects that reduce Developed Country emissions eg Investment n Govt and companies q Forestry planting must reduce GHG q Renewable electricity emissions q q q Invest in their own country Invest in a project in Developing Country q q n CERs Energy efficiency Clean transport Biomass energy Project Produces CERs
CDM Concept Developing Country n Many opportunities for $ projects that reduce Developed Country emissions eg Investment n Govt and companies q Forestry planting must reduce GHG q Renewable electricity emissions q q q Invest in their own country Invest in a project in Developing Country q q n CERs Energy efficiency Clean transport Biomass energy Project Produces CERs
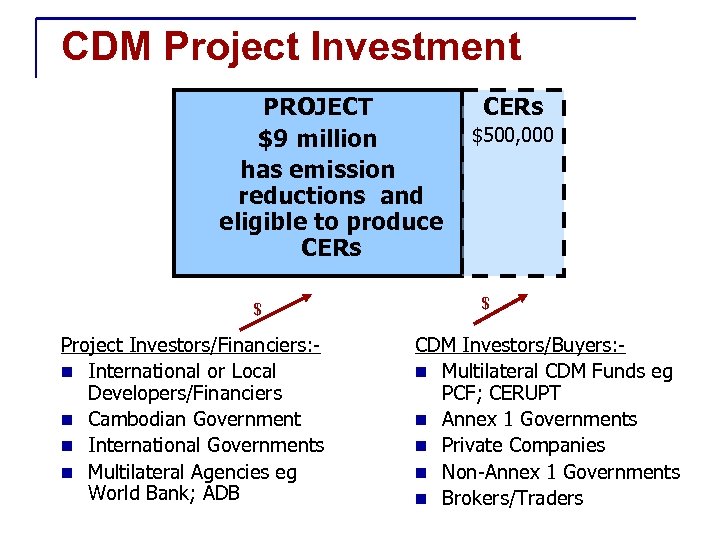 CDM Project Investment PROJECT $9 million has emission reductions and eligible to produce CERs $ Project Investors/Financiers: n International or Local Developers/Financiers n Cambodian Government n International Governments n Multilateral Agencies eg World Bank; ADB CERs $500, 000 $ CDM Investors/Buyers: n Multilateral CDM Funds eg PCF; CERUPT n Annex 1 Governments n Private Companies n Non-Annex 1 Governments n Brokers/Traders
CDM Project Investment PROJECT $9 million has emission reductions and eligible to produce CERs $ Project Investors/Financiers: n International or Local Developers/Financiers n Cambodian Government n International Governments n Multilateral Agencies eg World Bank; ADB CERs $500, 000 $ CDM Investors/Buyers: n Multilateral CDM Funds eg PCF; CERUPT n Annex 1 Governments n Private Companies n Non-Annex 1 Governments n Brokers/Traders
 CDM Investment Structures n Full or partial equity in project CER ownership becomes annex to the normal financing agreement q Usually investing for more than just CERs q n Financial contribution Usually upfront payment and takes ‘rights’ to CERs as they are produced q Normally not more than 10% project cost q n Loan q n Company provides loan at concessional rates in return for CERs eg payment of interest in CERs CER Purchase Agreement Company buys CERs as they are produced q Becomes additional income stream to project finance q
CDM Investment Structures n Full or partial equity in project CER ownership becomes annex to the normal financing agreement q Usually investing for more than just CERs q n Financial contribution Usually upfront payment and takes ‘rights’ to CERs as they are produced q Normally not more than 10% project cost q n Loan q n Company provides loan at concessional rates in return for CERs eg payment of interest in CERs CER Purchase Agreement Company buys CERs as they are produced q Becomes additional income stream to project finance q
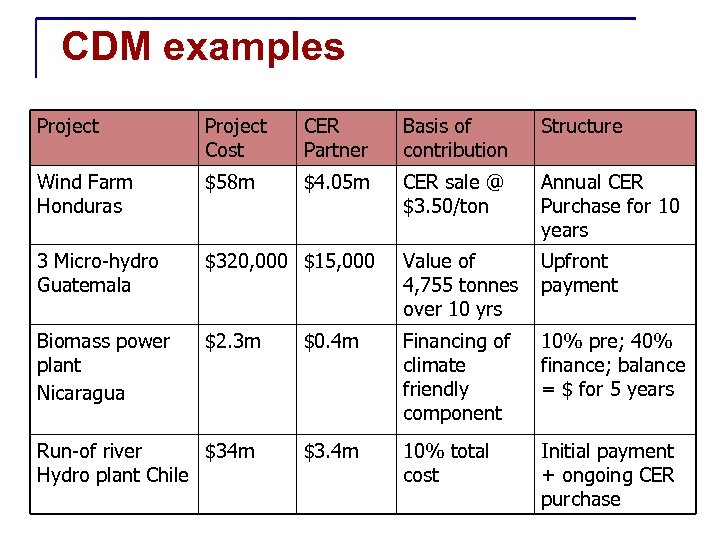 CDM examples Project Cost CER Partner Basis of contribution Structure Wind Farm Honduras $58 m $4. 05 m CER sale @ $3. 50/ton Annual CER Purchase for 10 years 3 Micro-hydro Guatemala $320, 000 $15, 000 Value of 4, 755 tonnes over 10 yrs Upfront payment Biomass power plant Nicaragua $2. 3 m $0. 4 m Financing of climate friendly component 10% pre; 40% finance; balance = $ for 5 years $3. 4 m 10% total cost Initial payment + ongoing CER purchase Run-of river $34 m Hydro plant Chile
CDM examples Project Cost CER Partner Basis of contribution Structure Wind Farm Honduras $58 m $4. 05 m CER sale @ $3. 50/ton Annual CER Purchase for 10 years 3 Micro-hydro Guatemala $320, 000 $15, 000 Value of 4, 755 tonnes over 10 yrs Upfront payment Biomass power plant Nicaragua $2. 3 m $0. 4 m Financing of climate friendly component 10% pre; 40% finance; balance = $ for 5 years $3. 4 m 10% total cost Initial payment + ongoing CER purchase Run-of river $34 m Hydro plant Chile
 Case Study n n n 3. 65 MW micro hydro project Indonesia Project offsetting diesel generation – 18, 500 t $9. 89 m capital cost; $0. 4 m operating costs Project executed by a local institute 16. 5% IRR without CDM; 18. 2% w CER @$5 Investment plan: Up to 70% of project capital through long term loan from financial institution; rest through equity q CDM investor options: q - Long term CER purchase agreement - Equity (JV partner) + commitment to buy CERs - Soft loan against realisation of CERs
Case Study n n n 3. 65 MW micro hydro project Indonesia Project offsetting diesel generation – 18, 500 t $9. 89 m capital cost; $0. 4 m operating costs Project executed by a local institute 16. 5% IRR without CDM; 18. 2% w CER @$5 Investment plan: Up to 70% of project capital through long term loan from financial institution; rest through equity q CDM investor options: q - Long term CER purchase agreement - Equity (JV partner) + commitment to buy CERs - Soft loan against realisation of CERs
 CDM Case Study Any Country looking for CDM Project n CDM Project Partner q Long term CER purchase agreement q Equity in project q Soft loan upfront in return for CERs later $ Investment Indonesia CDM Project n n n CERs 3. 65 MW hydro $9. 89 m capital cost $0. 4 m operating costs Project offsetting diesel emissions Likely 18, 500 CERs basic CER value $92, 500 looking for CDM Partner
CDM Case Study Any Country looking for CDM Project n CDM Project Partner q Long term CER purchase agreement q Equity in project q Soft loan upfront in return for CERs later $ Investment Indonesia CDM Project n n n CERs 3. 65 MW hydro $9. 89 m capital cost $0. 4 m operating costs Project offsetting diesel emissions Likely 18, 500 CERs basic CER value $92, 500 looking for CDM Partner
 Choosing a Host Country what do investors want? 1. Clear CDM Policy q q q Willingness for investment in CDM projects Transparent and clear processes, Quick and smooth government approval Time, effort and resources to complete deal 2. Secure investor climate q Political and economically stability What could occur that could affect investment? 3. Sound Techno-Economic potential Based on report conducted by Point Carbon www. pointcarbon. com
Choosing a Host Country what do investors want? 1. Clear CDM Policy q q q Willingness for investment in CDM projects Transparent and clear processes, Quick and smooth government approval Time, effort and resources to complete deal 2. Secure investor climate q Political and economically stability What could occur that could affect investment? 3. Sound Techno-Economic potential Based on report conducted by Point Carbon www. pointcarbon. com
 What does CDM mean for Indonesia?
What does CDM mean for Indonesia?
 Opportunities of CDM n CDM encourages developed countries to undertake GHG reduction projects in developing countries. Increased investment flows q Attract capital for less carbon-intensive projects q Technology transfer q n Assist in development priorities and sustainable development goals Create new industries in environmentally sustainable technologies q Poverty alleviation through income and employment q Assist in improving current and future environment (including air quality) q
Opportunities of CDM n CDM encourages developed countries to undertake GHG reduction projects in developing countries. Increased investment flows q Attract capital for less carbon-intensive projects q Technology transfer q n Assist in development priorities and sustainable development goals Create new industries in environmentally sustainable technologies q Poverty alleviation through income and employment q Assist in improving current and future environment (including air quality) q
 CDM in Cambodia Governments, Project Developers and Investors are seeking out CERs and emission reduction projects. n Emission reduction projects exist in Indonesia in many sectors: n Transport – establish intercity/intra-city transport q Forestry – community forestry, replanting q Energy – q - renewable energy (particularly in rural areas) - Installation of cleaner technology (cogeneration) - Energy usage – energy efficient technologies; building design q Waste management – capture of methane
CDM in Cambodia Governments, Project Developers and Investors are seeking out CERs and emission reduction projects. n Emission reduction projects exist in Indonesia in many sectors: n Transport – establish intercity/intra-city transport q Forestry – community forestry, replanting q Energy – q - renewable energy (particularly in rural areas) - Installation of cleaner technology (cogeneration) - Energy usage – energy efficient technologies; building design q Waste management – capture of methane
 Reality + Issues w CDM n CDM may tend towards large CDM Projects q High transaction costs with CDM projects BGP experience = $100, 000 – 150, 000 per project q transaction costs similar for small or large projects Solution - bundle small projects together eg association of community forestry; many small scale hydro projects n Larger developing countries more attractive infrastructure & institution to deal with large projects q Larger market = ability to do many similar projects q Spreads the upfront cost in learning local conditions; securing suppliers, local management, financial, legal and contractual processes q
Reality + Issues w CDM n CDM may tend towards large CDM Projects q High transaction costs with CDM projects BGP experience = $100, 000 – 150, 000 per project q transaction costs similar for small or large projects Solution - bundle small projects together eg association of community forestry; many small scale hydro projects n Larger developing countries more attractive infrastructure & institution to deal with large projects q Larger market = ability to do many similar projects q Spreads the upfront cost in learning local conditions; securing suppliers, local management, financial, legal and contractual processes q
 CDM Transaction Costs Preparation and review of the Project completion • Upstream Due Diligence, carbon risk assessment and documentation: $ 40 K 3 m ont Up to 21 ye ars hs ths 1 -3 2 m on ths rs yea • Verification: $10 -25 K • Supervision: $10 -20 K 2 mon All expenses $100 -150 K Periodic verification & certification • Baseline : $20 K • Monitoring Plan: $10 K Validation process • Contract, Processing • and documentation: $30 k 3 months Construction and start up • Initial verification at start-up: $15 K Project Appraisal and Negotiation Total through Negotiations
CDM Transaction Costs Preparation and review of the Project completion • Upstream Due Diligence, carbon risk assessment and documentation: $ 40 K 3 m ont Up to 21 ye ars hs ths 1 -3 2 m on ths rs yea • Verification: $10 -25 K • Supervision: $10 -20 K 2 mon All expenses $100 -150 K Periodic verification & certification • Baseline : $20 K • Monitoring Plan: $10 K Validation process • Contract, Processing • and documentation: $30 k 3 months Construction and start up • Initial verification at start-up: $15 K Project Appraisal and Negotiation Total through Negotiations
 Reality + Issues w CDM (2) n CDM will be a competitive market q Restricted without the US q Limit on amount of CERs developed countries can use towards target (~20%) q larger projects with low risk and smooth approval/transaction procedures will be preferred q May limit opportunities in least developed countries
Reality + Issues w CDM (2) n CDM will be a competitive market q Restricted without the US q Limit on amount of CERs developed countries can use towards target (~20%) q larger projects with low risk and smooth approval/transaction procedures will be preferred q May limit opportunities in least developed countries
 Reality + Issues w CDM (3) n Preparation of developing countries q poor co-ordination among Ministries q internal conflict over approvals Only 12 National Authorities registered n Capacity q Weak of developing countries knowledge of CDM at all levels policy -makers, businesses, finance + legal institutions, NGOs
Reality + Issues w CDM (3) n Preparation of developing countries q poor co-ordination among Ministries q internal conflict over approvals Only 12 National Authorities registered n Capacity q Weak of developing countries knowledge of CDM at all levels policy -makers, businesses, finance + legal institutions, NGOs
 Summary n CDM presents an opportunity for Indonesia developing energy infrastructure; q forestry is significant activity q n worldwide increased demand for projects that reduce emissions q n win-win situation for both parties Indonesia must be prepared Functioning approval body + smooth and transparent approval process q need a ‘pipeline’ of projects for investors when they come investigating q Need to improve investor climate q
Summary n CDM presents an opportunity for Indonesia developing energy infrastructure; q forestry is significant activity q n worldwide increased demand for projects that reduce emissions q n win-win situation for both parties Indonesia must be prepared Functioning approval body + smooth and transparent approval process q need a ‘pipeline’ of projects for investors when they come investigating q Need to improve investor climate q
 Acronymns CDM – Clean Development Mechanism n CER – Certified Emission Reductions n q n PCF – Prototype Carbon Fund q n A standard unit of greenhouse reduction or sink World Bank CER Fund ODA – Official Development Assistance q Part of 0. 07% govt aid IRR – Internal Rate of Return n DNA – Designated National Authority n q The national body who assess +/or approves CDM projects
Acronymns CDM – Clean Development Mechanism n CER – Certified Emission Reductions n q n PCF – Prototype Carbon Fund q n A standard unit of greenhouse reduction or sink World Bank CER Fund ODA – Official Development Assistance q Part of 0. 07% govt aid IRR – Internal Rate of Return n DNA – Designated National Authority n q The national body who assess +/or approves CDM projects
 Acronyms n Annex 1 countries q n Approx. 40 industrialised countries and economies in transitions listed in Annex 1 of the convention who can invest in CDM projects. These countries have emission reduction obligations. Non - Annex 1 countries q The countries who are not listed in Annex 1 of the Convention and who can host CDM projects
Acronyms n Annex 1 countries q n Approx. 40 industrialised countries and economies in transitions listed in Annex 1 of the convention who can invest in CDM projects. These countries have emission reduction obligations. Non - Annex 1 countries q The countries who are not listed in Annex 1 of the Convention and who can host CDM projects


