e9ced8ebd981dea5945bfff010efd2ce.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 89
 Software Testing at Florida A&M University: Perspective, Direction and Opportunities Dr. Edward L. Jones CIS Department Florida A&M University Tallahassee, FL 3/19/20025/21/2001 Testing at FAMU 18 th ITCS 2001
Software Testing at Florida A&M University: Perspective, Direction and Opportunities Dr. Edward L. Jones CIS Department Florida A&M University Tallahassee, FL 3/19/20025/21/2001 Testing at FAMU 18 th ITCS 2001
 In 25 Words or Less z. FAMU a major player z. Vision -- software quality institute z. Technology transfer mission z. Incremental research expansion z. Collaboration opportunities z. Faculty & student recruitment z. A work in progress. . . 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 2
In 25 Words or Less z. FAMU a major player z. Vision -- software quality institute z. Technology transfer mission z. Incremental research expansion z. Collaboration opportunities z. Faculty & student recruitment z. A work in progress. . . 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 2
 Outline z. Part I -- Introduction z. Part II -- Technology Transfer z. Part III -- Research z. Part IV -- Conclusion 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 3
Outline z. Part I -- Introduction z. Part II -- Technology Transfer z. Part III -- Research z. Part IV -- Conclusion 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 3
 Part I INTRODUCTION 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 4
Part I INTRODUCTION 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 4
 Part I - Introduction z. Where I’m Coming From z. Where We Are z. What Can Academics Do? 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 5
Part I - Introduction z. Where I’m Coming From z. Where We Are z. What Can Academics Do? 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 5
 Where I’m Coming From 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 6
Where I’m Coming From 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 6
 My Institution z 11, 000 students total z 600+ CIS majors z 15 Faculty z. Heavy teaching z. Graduate program (20 students) z. Increasing research 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 7
My Institution z 11, 000 students total z 600+ CIS majors z 15 Faculty z. Heavy teaching z. Graduate program (20 students) z. Increasing research 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 7
 My Experience z 13 years Harris Corporation z. Software engineering technology z$200 M+ NASA project ymethodology expert ysoftware inspections, testing yprocess training z 20+ years university teaching z 3 years focusing on testing 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 8
My Experience z 13 years Harris Corporation z. Software engineering technology z$200 M+ NASA project ymethodology expert ysoftware inspections, testing yprocess training z 20+ years university teaching z 3 years focusing on testing 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 8
 Faculty Research Interests z. High-Performance Computing y. Harmon, Tseng, Chandra z. Databases and Data Engineering y. Chandra, Humphries z. Software Engineering y. Jones, Humphries -- testing, object database y. Evans -- cryptograhy, compression z. Intelligent Systems y. Allen, Riggs, Granville -- speech/natural language, IR, data mining, fuzzy systems 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 9
Faculty Research Interests z. High-Performance Computing y. Harmon, Tseng, Chandra z. Databases and Data Engineering y. Chandra, Humphries z. Software Engineering y. Jones, Humphries -- testing, object database y. Evans -- cryptograhy, compression z. Intelligent Systems y. Allen, Riggs, Granville -- speech/natural language, IR, data mining, fuzzy systems 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 9
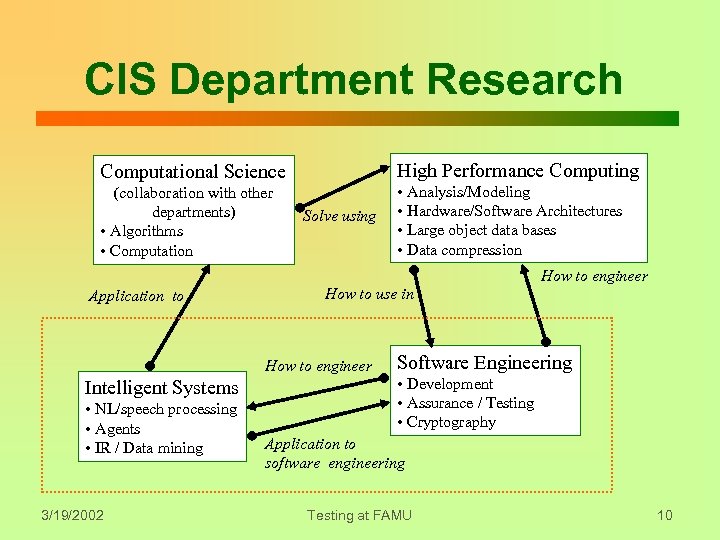 CIS Department Research High Performance Computing Computational Science (collaboration with other departments) • Algorithms • Computation Solve using • Analysis/Modeling • Hardware/Software Architectures • Large object data bases • Data compression How to engineer Application to How to use in How to engineer Intelligent Systems • NL/speech processing • Agents • IR / Data mining 3/19/2002 Software Engineering • Development • Assurance / Testing • Cryptography Application to software engineering Testing at FAMU 10
CIS Department Research High Performance Computing Computational Science (collaboration with other departments) • Algorithms • Computation Solve using • Analysis/Modeling • Hardware/Software Architectures • Large object data bases • Data compression How to engineer Application to How to use in How to engineer Intelligent Systems • NL/speech processing • Agents • IR / Data mining 3/19/2002 Software Engineering • Development • Assurance / Testing • Cryptography Application to software engineering Testing at FAMU 10
 My Perspective z. Testing is not just for testers! z. In ideal world, fewer testers required y. Verification vs testing y. More skilled developers z. No silver bullet … just bricks y. Simple things provide leverage y. Testing in-the-small -- classroom the lab z. Technology transfer crucial 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 11
My Perspective z. Testing is not just for testers! z. In ideal world, fewer testers required y. Verification vs testing y. More skilled developers z. No silver bullet … just bricks y. Simple things provide leverage y. Testing in-the-small -- classroom the lab z. Technology transfer crucial 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 11
 Where We Are 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 12
Where We Are 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 12
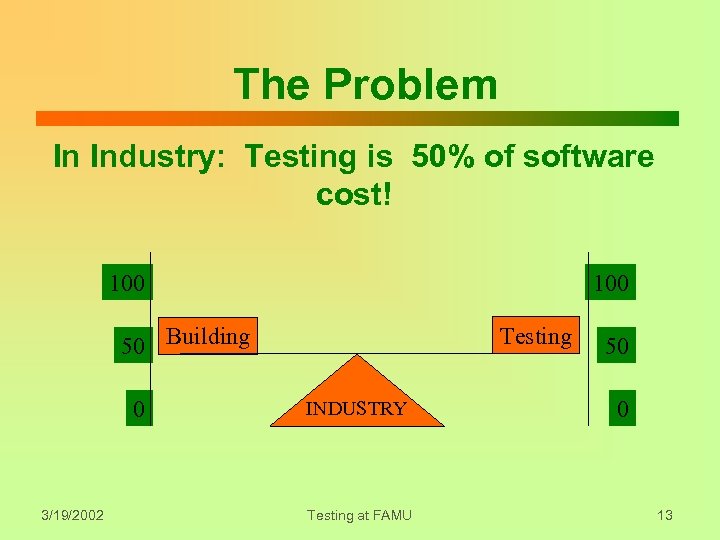 The Problem In Industry: Testing is 50% of software cost! 100 Testing 50 Building 0 3/19/2002 INDUSTRY Testing at FAMU 50 0 13
The Problem In Industry: Testing is 50% of software cost! 100 Testing 50 Building 0 3/19/2002 INDUSTRY Testing at FAMU 50 0 13
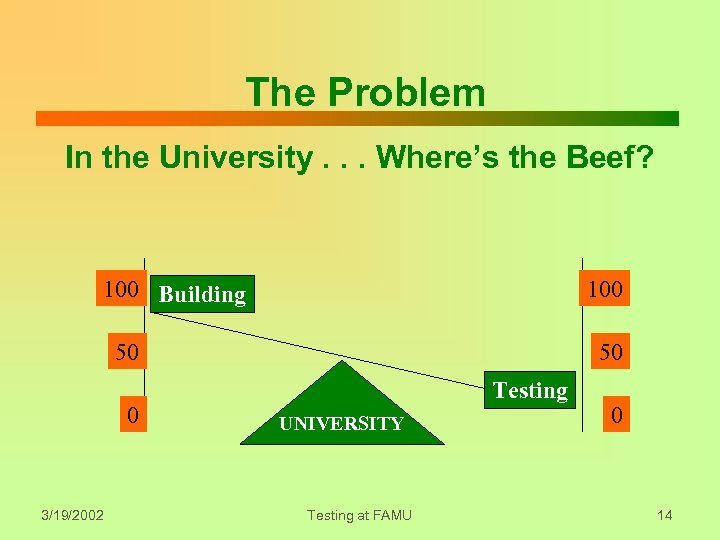 The Problem In the University. . . Where’s the Beef? 100 Building 100 50 0 3/19/2002 50 Testing UNIVERSITY Testing at FAMU 0 14
The Problem In the University. . . Where’s the Beef? 100 Building 100 50 0 3/19/2002 50 Testing UNIVERSITY Testing at FAMU 0 14
 Why So Little Testing? z. Heredity -- teachers not trained z. Priority -- no room in curriculum z. Attitude y. Digression from the fun part y. Testing a necessary evil y. Not the creative part z. Testing is HARD to teach! 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 15
Why So Little Testing? z. Heredity -- teachers not trained z. Priority -- no room in curriculum z. Attitude y. Digression from the fun part y. Testing a necessary evil y. Not the creative part z. Testing is HARD to teach! 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 15
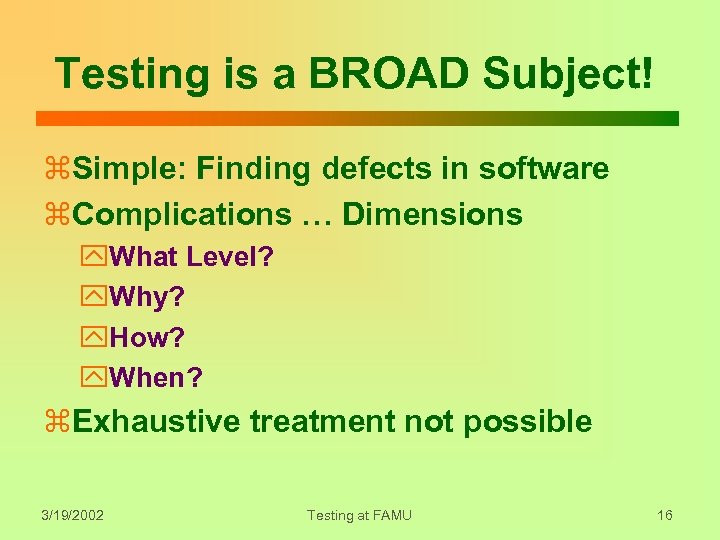 Testing is a BROAD Subject! z. Simple: Finding defects in software z. Complications … Dimensions y. What Level? y. Why? y. How? y. When? z. Exhaustive treatment not possible 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 16
Testing is a BROAD Subject! z. Simple: Finding defects in software z. Complications … Dimensions y. What Level? y. Why? y. How? y. When? z. Exhaustive treatment not possible 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 16
 SPRAE Experience Framework S pecification – no spec, no test P remeditation – follow a process R epeatability – tester independence A ccountability – documentation E conomy – cost effectiveness 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 17
SPRAE Experience Framework S pecification – no spec, no test P remeditation – follow a process R epeatability – tester independence A ccountability – documentation E conomy – cost effectiveness 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 17
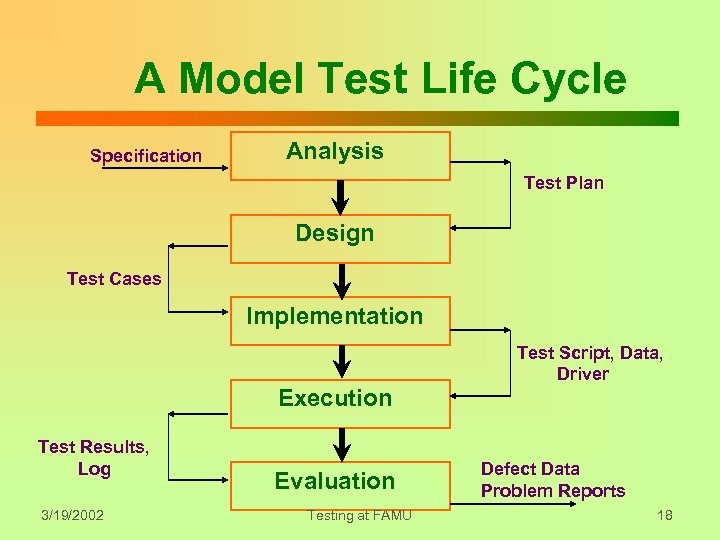 A Model Test Life Cycle Specification Analysis Test Plan Design Test Cases Implementation Test Script, Data, Driver Execution Test Results, Log 3/19/2002 Evaluation Testing at FAMU Defect Data Problem Reports 18
A Model Test Life Cycle Specification Analysis Test Plan Design Test Cases Implementation Test Script, Data, Driver Execution Test Results, Log 3/19/2002 Evaluation Testing at FAMU Defect Data Problem Reports 18
 What Can Academics Do? (Besides Teaching A Course? ) 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 19
What Can Academics Do? (Besides Teaching A Course? ) 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 19
 The Vision z. Quality Awareness in Curriculum z. Solid Framework z. Enhanced Student Skill Set z. Expanded Student Opportunities z. Industry Partnerships z. Dissemination 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 20
The Vision z. Quality Awareness in Curriculum z. Solid Framework z. Enhanced Student Skill Set z. Expanded Student Opportunities z. Industry Partnerships z. Dissemination 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 20
 A Software Testing Course z 80% practice, 20% theory z 2/3 fine-grained testing (functions) z 1/3 object and application testing z. Test cases, drivers, and scripts z. Decision tables the "formalism" z. Function, boundary, white-box testing z. Effectiveness: Coverage & error seeding 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 21
A Software Testing Course z 80% practice, 20% theory z 2/3 fine-grained testing (functions) z 1/3 object and application testing z. Test cases, drivers, and scripts z. Decision tables the "formalism" z. Function, boundary, white-box testing z. Effectiveness: Coverage & error seeding 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 21
 Course -- Lessons Learned z. Advantages y. A ”taste" of how hard testing really is y. Preparation for advanced study y. Rounds out analytical & programming skills z. Deficiencies y. Course not available to all students y. Students compartmentalize knowledge 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 22
Course -- Lessons Learned z. Advantages y. A ”taste" of how hard testing really is y. Preparation for advanced study y. Rounds out analytical & programming skills z. Deficiencies y. Course not available to all students y. Students compartmentalize knowledge 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 22
 Testing in Action -Automated Program Grading z. Shock & outrage at exactness z. Important -- grade at stake z. Teacher overhead y. Testable specification y. Test automation up-front costs z. Benefits y. Better, objective grading process y. Students begin to … think like testers!! 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 23
Testing in Action -Automated Program Grading z. Shock & outrage at exactness z. Important -- grade at stake z. Teacher overhead y. Testable specification y. Test automation up-front costs z. Benefits y. Better, objective grading process y. Students begin to … think like testers!! 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 23
 Technology Transfer Program Grading Services z. Provided by Test. Lab students y. Experience designing automated tests y. Shell programming z. Instructor plays active part y. Refines specification y. Creates grading plan z. Benefits y. Faculty more inclined to incorporate testing course insert 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 24
Technology Transfer Program Grading Services z. Provided by Test. Lab students y. Experience designing automated tests y. Shell programming z. Instructor plays active part y. Refines specification y. Creates grading plan z. Benefits y. Faculty more inclined to incorporate testing course insert 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 24
 Testing in Action -Plagiarism Deterrent z. Mutation analysis/error seeding applied to suspicious student program z. Student must debug modified program z. Test. Lab project y. Tunable error seeding y. Goal: debugging training (environment) z. Benefits y. Less plagiarism … or … more skilled programmers 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 25
Testing in Action -Plagiarism Deterrent z. Mutation analysis/error seeding applied to suspicious student program z. Student must debug modified program z. Test. Lab project y. Tunable error seeding y. Goal: debugging training (environment) z. Benefits y. Less plagiarism … or … more skilled programmers 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 25
 Other Notable Approaches z. Florida Tech Center for Software Engineering Research y. Industry sponsored projects y. Cem Kaner NSF project -- artifacts/modules z. Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University y. SEI Personal/Team Processes -- qualitycentric curriculum z. USF Software Testing Center 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 26
Other Notable Approaches z. Florida Tech Center for Software Engineering Research y. Industry sponsored projects y. Cem Kaner NSF project -- artifacts/modules z. Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University y. SEI Personal/Team Processes -- qualitycentric curriculum z. USF Software Testing Center 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 26
 Part II TECHNOLOGY TRANSFER 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 27
Part II TECHNOLOGY TRANSFER 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 27
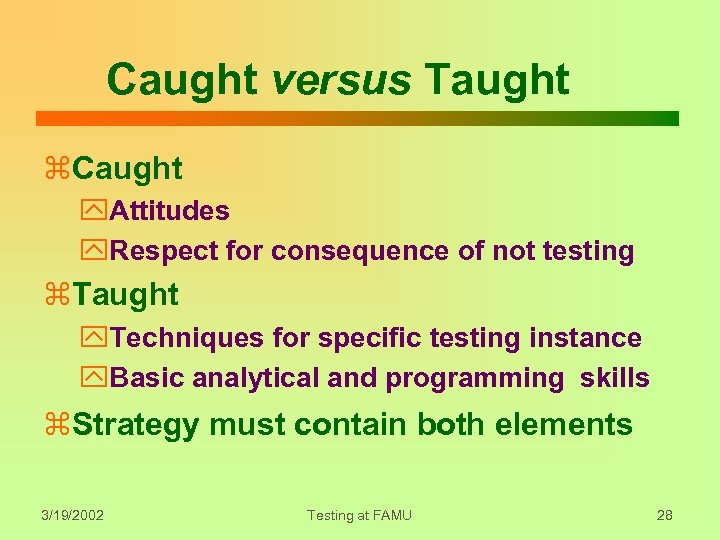 Caught versus Taught z. Caught y. Attitudes y. Respect for consequence of not testing z. Taught y. Techniques for specific testing instance y. Basic analytical and programming skills z. Strategy must contain both elements 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 28
Caught versus Taught z. Caught y. Attitudes y. Respect for consequence of not testing z. Taught y. Techniques for specific testing instance y. Basic analytical and programming skills z. Strategy must contain both elements 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 28
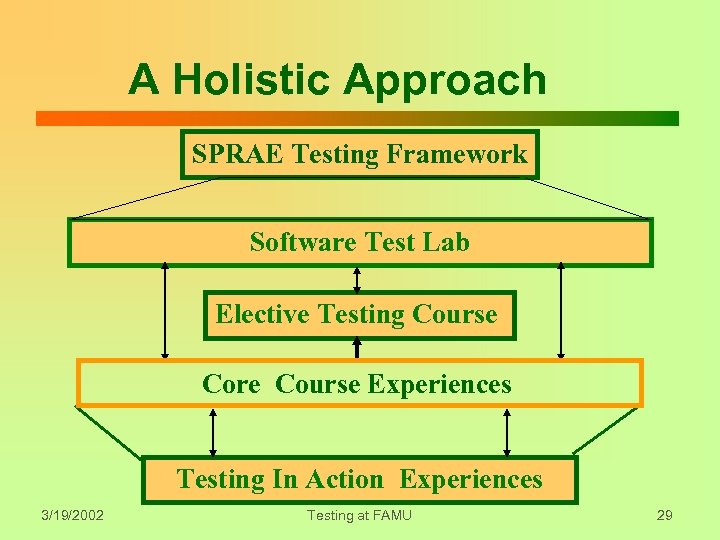 A Holistic Approach SPRAE Testing Framework Software Test Lab Elective Testing Course Core Course Experiences Testing In Action Experiences 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 29
A Holistic Approach SPRAE Testing Framework Software Test Lab Elective Testing Course Core Course Experiences Testing In Action Experiences 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 29
 What Is Meant By “Holistic”? z. Testing an integral part of curriculum z. Multiple test experiences z. Experiences in each course z. Repetition and reinforcement z. Accumulation of experiences z. Experiences cover test lifecycle z. Holistic, NOT Exhaustive! 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 30
What Is Meant By “Holistic”? z. Testing an integral part of curriculum z. Multiple test experiences z. Experiences in each course z. Repetition and reinforcement z. Accumulation of experiences z. Experiences cover test lifecycle z. Holistic, NOT Exhaustive! 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 30
 Why SPRAE? z. SPRAE = essential values for practice of testing z. Explains the “what” and “why” z. Sets goals for test experiences z. Value system reinforced with each new experience z. A framework for life-long learning. 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 31
Why SPRAE? z. SPRAE = essential values for practice of testing z. Explains the “what” and “why” z. Sets goals for test experiences z. Value system reinforced with each new experience z. A framework for life-long learning. 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 31
 Core Course Experiences z. Grade another student's program z. Treasure Hunt -- find seeded errors z. Write test cases before coding z. Develop and certify components z. Blind test -- develop specification for a working program. 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 32
Core Course Experiences z. Grade another student's program z. Treasure Hunt -- find seeded errors z. Write test cases before coding z. Develop and certify components z. Blind test -- develop specification for a working program. 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 32
 The Software Test. Lab z. Environment for discovery & learning y. Basic testing skills y. Mentoring / Competency based training z. Evolving Laboratory y. Tools & tutorials y. Staffed by students and faculty y. Problems/solutions test bed z. Dissemination Strategy 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 33
The Software Test. Lab z. Environment for discovery & learning y. Basic testing skills y. Mentoring / Competency based training z. Evolving Laboratory y. Tools & tutorials y. Staffed by students and faculty y. Problems/solutions test bed z. Dissemination Strategy 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 33
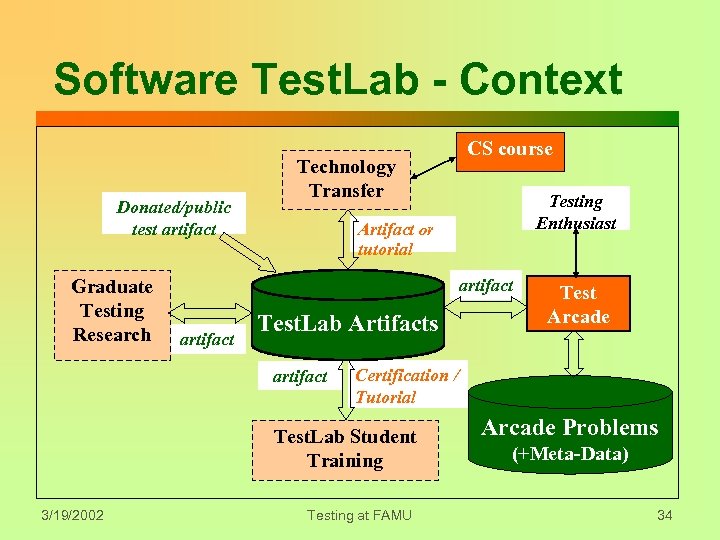 Software Test. Lab - Context Donated/public test artifact Graduate Testing Research Technology Transfer Testing Enthusiast Artifact or tutorial artifact Test. Lab Artifacts artifact Test Arcade Certification / Tutorial Test. Lab Student Training 3/19/2002 CS course Testing at FAMU Arcade Problems (+Meta-Data) 34
Software Test. Lab - Context Donated/public test artifact Graduate Testing Research Technology Transfer Testing Enthusiast Artifact or tutorial artifact Test. Lab Artifacts artifact Test Arcade Certification / Tutorial Test. Lab Student Training 3/19/2002 CS course Testing at FAMU Arcade Problems (+Meta-Data) 34
 Student Mentorship Model z. Managed skill development z. Clear achievement goals z. Key Practices x Competency Levels z. Progress certification z. Student-Student mentoring z. Recognition Program 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 35
Student Mentorship Model z. Managed skill development z. Clear achievement goals z. Key Practices x Competency Levels z. Progress certification z. Student-Student mentoring z. Recognition Program 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 35
 Key Practices z. Practitioner -- performs defined test z. Builder -- constructs test “machinery” z. Designer -- designs test cases z. Analyst -- sets test goals, strategy z. Inspector -- verifies process/results z. Environmentalist -- maintains test tools & environment z. Specialist -- performs test life cycle. 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 36
Key Practices z. Practitioner -- performs defined test z. Builder -- constructs test “machinery” z. Designer -- designs test cases z. Analyst -- sets test goals, strategy z. Inspector -- verifies process/results z. Environmentalist -- maintains test tools & environment z. Specialist -- performs test life cycle. 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 36
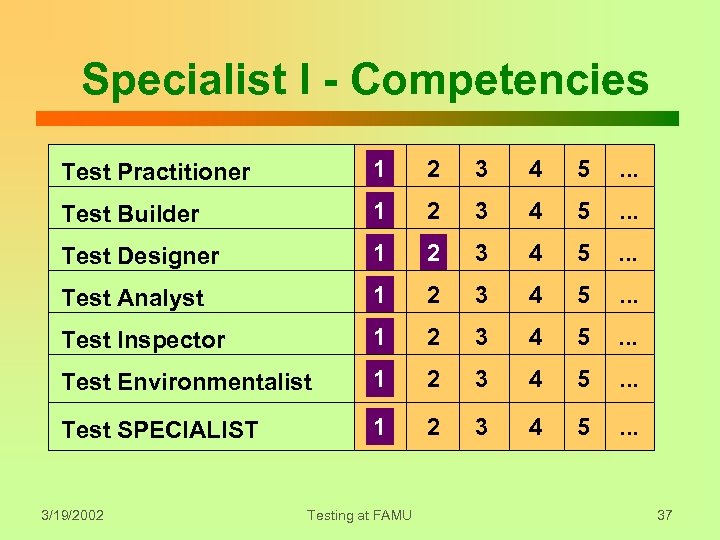 Specialist I - Competencies Practitioner Test Practitioner 1 2 3 4 5 . . . Test Builder 1 2 3 4 5 . . . Test Designer 1 2 3 4 5 . . . Test Analyst 1 2 3 4 5 . . . Test Inspector 1 2 3 4 5 . . . Test Environmentalist 1 2 3 4 5 . . . Test SPECIALIST 1 2 3 4 5 . . . 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 37
Specialist I - Competencies Practitioner Test Practitioner 1 2 3 4 5 . . . Test Builder 1 2 3 4 5 . . . Test Designer 1 2 3 4 5 . . . Test Analyst 1 2 3 4 5 . . . Test Inspector 1 2 3 4 5 . . . Test Environmentalist 1 2 3 4 5 . . . Test SPECIALIST 1 2 3 4 5 . . . 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 37
 Test Specialist I z Practitioner I - Run function test script & document test results. z Builder I - Develop function test driver. z Designer II - Develop functional and boundary test cases from decision table. z Analyst I - Develop decision table from functional specification. z Inspector I - Verify adherence to function test process and standards. 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 38
Test Specialist I z Practitioner I - Run function test script & document test results. z Builder I - Develop function test driver. z Designer II - Develop functional and boundary test cases from decision table. z Analyst I - Develop decision table from functional specification. z Inspector I - Verify adherence to function test process and standards. 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 38
 Training Topics • Test. Lab Environment Basic Training • Black-Box Function (unit) Testing • Black-Box Object Testing • White-Box Function Testing • Clear-Box Object Testing. . . 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 39
Training Topics • Test. Lab Environment Basic Training • Black-Box Function (unit) Testing • Black-Box Object Testing • White-Box Function Testing • Clear-Box Object Testing. . . 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 39
 Problems/Solutions Testbed z. Repository of testing problems z. Repository of student test artifacts z. Best in class solutions testbed z. Deficient solutions “almost” testbed z. Testbed used for tester certification 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 40
Problems/Solutions Testbed z. Repository of testing problems z. Repository of student test artifacts z. Best in class solutions testbed z. Deficient solutions “almost” testbed z. Testbed used for tester certification 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 40
 The Test Arcade z. Fun & Games approach z. Players compete solving testing problem y. Scored on time and accuracy y. Ranked list of players by score y. HELP facility provides a "teaching" mode z. Supports testing contests, certification z. NSF Funding requested 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 41
The Test Arcade z. Fun & Games approach z. Players compete solving testing problem y. Scored on time and accuracy y. Ranked list of players by score y. HELP facility provides a "teaching" mode z. Supports testing contests, certification z. NSF Funding requested 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 41
 Part III TESTLAB RESEARCH 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 42
Part III TESTLAB RESEARCH 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 42
 Research Obstacles z. Search for the silver bullet z. All eggs in one basket, i. e. , testing z. In-the-large empirical studies z. Graduate/research student pool z. Critical mass of faculty 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 43
Research Obstacles z. Search for the silver bullet z. All eggs in one basket, i. e. , testing z. In-the-large empirical studies z. Graduate/research student pool z. Critical mass of faculty 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 43
 Research Funding z$85 K Corporate support y$50 K from Dell Star Program (Test. Lab) y$35 K for student / travel z. Task on $1. 5 M NSF MII grant z$500 K NSF ITR proposal submitted 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 44
Research Funding z$85 K Corporate support y$50 K from Dell Star Program (Test. Lab) y$35 K for student / travel z. Task on $1. 5 M NSF MII grant z$500 K NSF ITR proposal submitted 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 44
 Seminal Projects z. Decision-based test methods z. Reliability testing training simulator z. Test arcade z. Testing via design mutation z. Test patterns/verification agents z. Other Ideas 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 45
Seminal Projects z. Decision-based test methods z. Reliability testing training simulator z. Test arcade z. Testing via design mutation z. Test patterns/verification agents z. Other Ideas 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 45
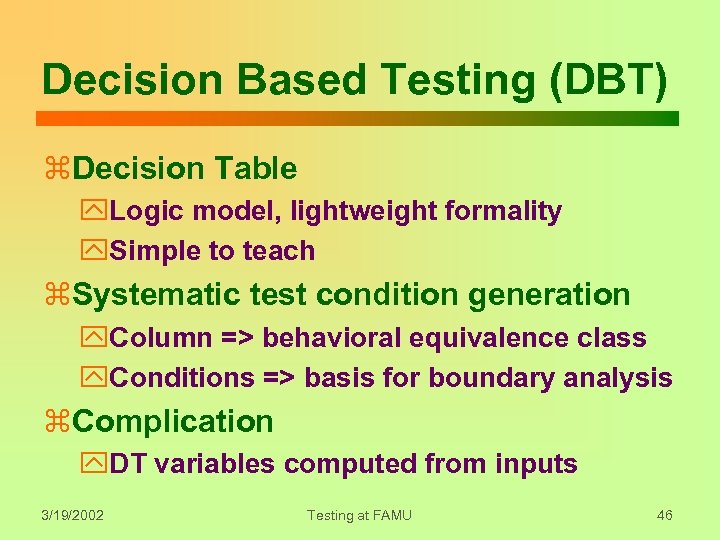 Decision Based Testing (DBT) z. Decision Table y. Logic model, lightweight formality y. Simple to teach z. Systematic test condition generation y. Column => behavioral equivalence class y. Conditions => basis for boundary analysis z. Complication y. DT variables computed from inputs 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 46
Decision Based Testing (DBT) z. Decision Table y. Logic model, lightweight formality y. Simple to teach z. Systematic test condition generation y. Column => behavioral equivalence class y. Conditions => basis for boundary analysis z. Complication y. DT variables computed from inputs 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 46
 Simple Example DBT & SPRAE z. Compute pay with overtime calculation based on employee classification z. Example illustrates y. SPRAE principles y. Test case design y. Opportunities for automation 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 47
Simple Example DBT & SPRAE z. Compute pay with overtime calculation based on employee classification z. Example illustrates y. SPRAE principles y. Test case design y. Opportunities for automation 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 47
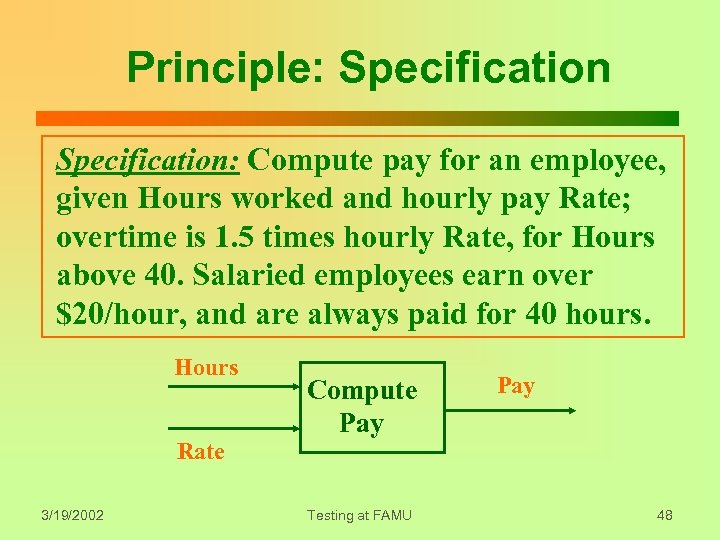 Principle: Specification: Compute pay for an employee, given Hours worked and hourly pay Rate; overtime is 1. 5 times hourly Rate, for Hours above 40. Salaried employees earn over $20/hour, and are always paid for 40 hours. Hours Rate 3/19/2002 Compute Pay Testing at FAMU Pay 48
Principle: Specification: Compute pay for an employee, given Hours worked and hourly pay Rate; overtime is 1. 5 times hourly Rate, for Hours above 40. Salaried employees earn over $20/hour, and are always paid for 40 hours. Hours Rate 3/19/2002 Compute Pay Testing at FAMU Pay 48
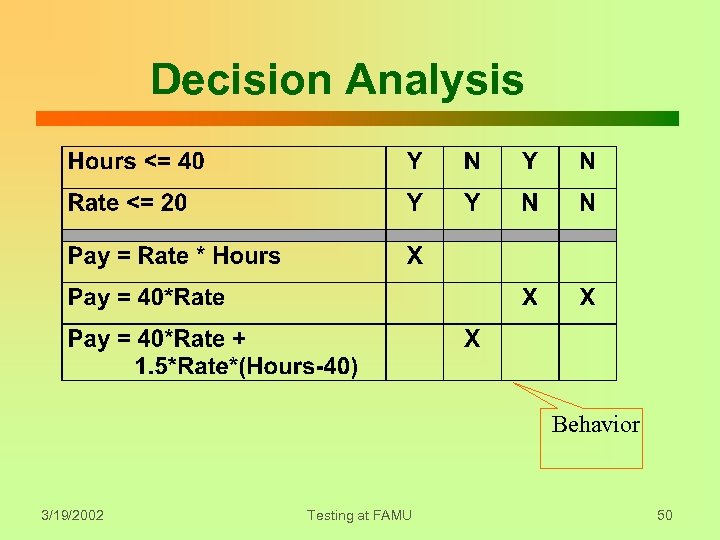
 Principle: Premeditation Use a systematic process to devise test cases based on the specification. Functional testing: • Decision rule (column) => behaviors • One test case per behavior • Determine expected result. 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 49
Principle: Premeditation Use a systematic process to devise test cases based on the specification. Functional testing: • Decision rule (column) => behaviors • One test case per behavior • Determine expected result. 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 49
 Decision Analysis Behavior 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 50
Decision Analysis Behavior 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 50
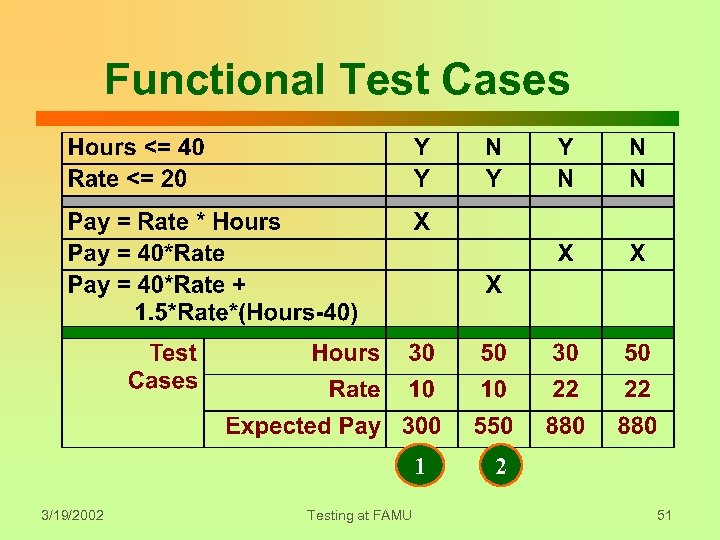 Functional Test Cases 1 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 2 51
Functional Test Cases 1 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 2 51
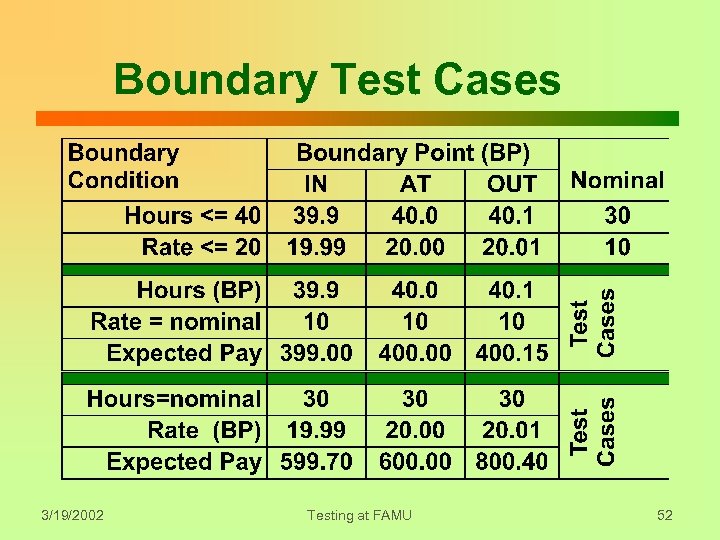 Boundary Test Cases 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 52
Boundary Test Cases 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 52
 Principle: Repeatability Processes for test case creation and test execution must yield equivalent results, independently of the tester. z. Systematic processes for deriving y. Functional test cases y. Boundary test cases z. Processes can be automated 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 53
Principle: Repeatability Processes for test case creation and test execution must yield equivalent results, independently of the tester. z. Systematic processes for deriving y. Functional test cases y. Boundary test cases z. Processes can be automated 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 53
 Principle: Accountability Keep records that document test process and artifacts. z. Documentation answers: y. What tests were planned? y. Which tests were conducted? y. Who did what testing, and when? y. What were the results? y. How were the results interpreted? 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 54
Principle: Accountability Keep records that document test process and artifacts. z. Documentation answers: y. What tests were planned? y. Which tests were conducted? y. Who did what testing, and when? y. What were the results? y. How were the results interpreted? 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 54
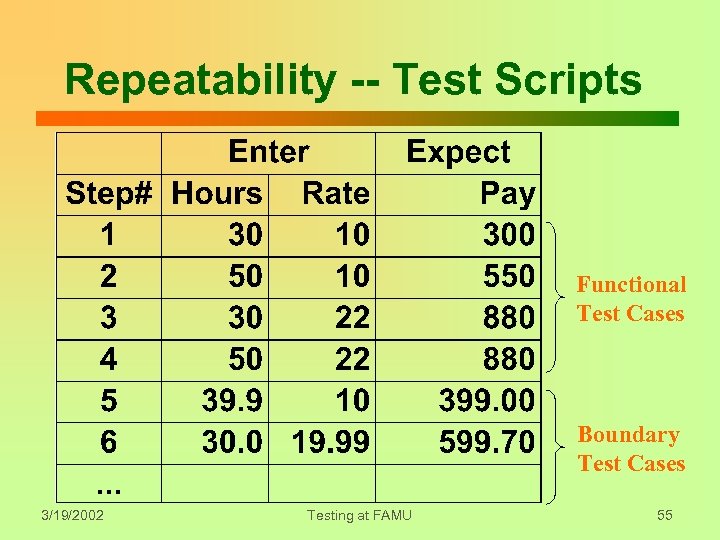 Repeatability -- Test Scripts Functional Test Cases Boundary Test Cases 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 55
Repeatability -- Test Scripts Functional Test Cases Boundary Test Cases 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 55
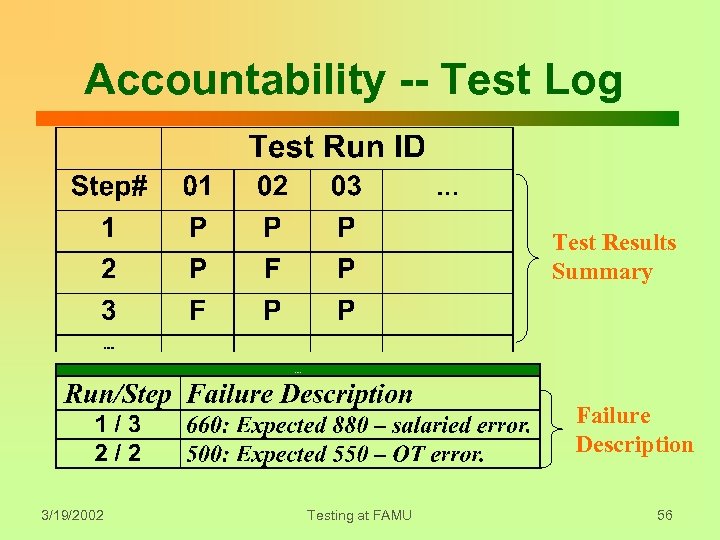 Accountability -- Test Log Test Results Summary Failure Description 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 56
Accountability -- Test Log Test Results Summary Failure Description 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 56
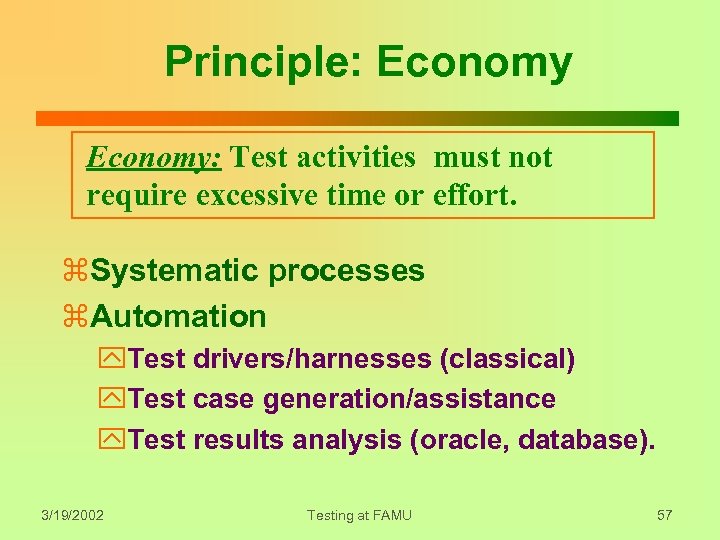 Principle: Economy: Test activities must not require excessive time or effort. z. Systematic processes z. Automation y. Test drivers/harnesses (classical) y. Test case generation/assistance y. Test results analysis (oracle, database). 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 57
Principle: Economy: Test activities must not require excessive time or effort. z. Systematic processes z. Automation y. Test drivers/harnesses (classical) y. Test case generation/assistance y. Test results analysis (oracle, database). 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 57
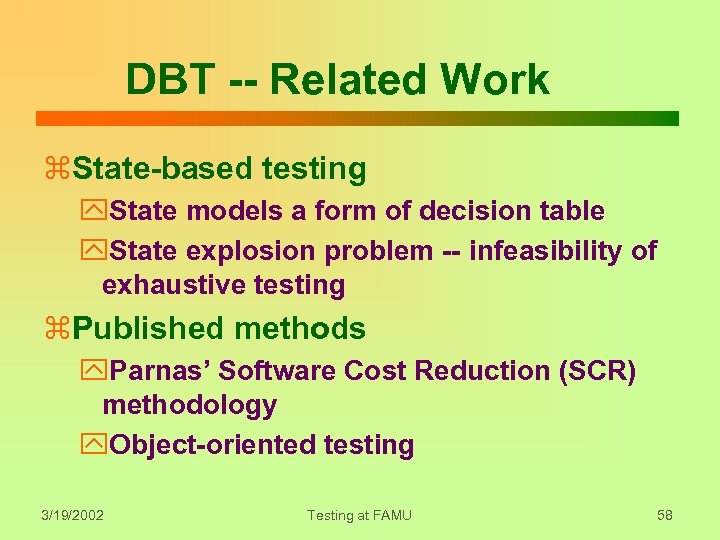 DBT -- Related Work z. State-based testing y. State models a form of decision table y. State explosion problem -- infeasibility of exhaustive testing z. Published methods y. Parnas’ Software Cost Reduction (SCR) methodology y. Object-oriented testing 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 58
DBT -- Related Work z. State-based testing y. State models a form of decision table y. State explosion problem -- infeasibility of exhaustive testing z. Published methods y. Parnas’ Software Cost Reduction (SCR) methodology y. Object-oriented testing 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 58
 Commercial/Research Decision Table Tool z. Prologa (PROcedural Logic Analyzer) y. Interactive, rule-based y. Table construction and manipulation y. Facilitates tasks such as checking, adding or reordering conditions. z. Reference y. Robbin, F. , Vanthienen, J. , “Developing Legal Knowledge Based Systems Using Decision Tables, ” Communications of the ACM, 1993. 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 59
Commercial/Research Decision Table Tool z. Prologa (PROcedural Logic Analyzer) y. Interactive, rule-based y. Table construction and manipulation y. Facilitates tasks such as checking, adding or reordering conditions. z. Reference y. Robbin, F. , Vanthienen, J. , “Developing Legal Knowledge Based Systems Using Decision Tables, ” Communications of the ACM, 1993. 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 59
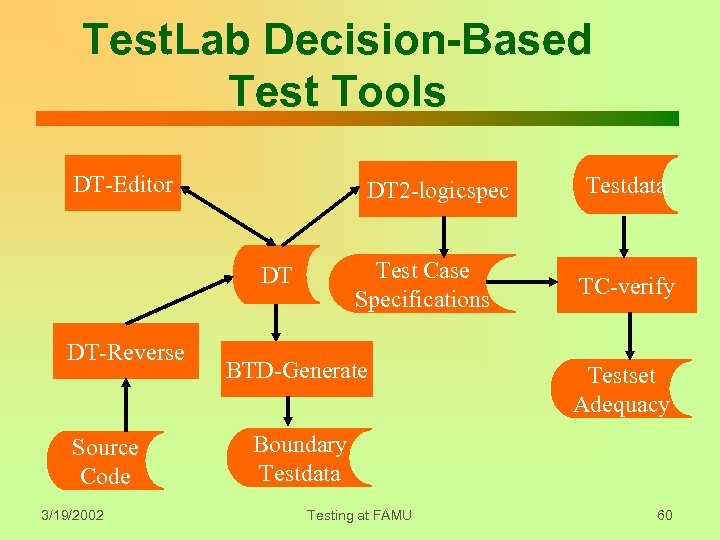 Test. Lab Decision-Based Test Tools DT-Editor DT 2 -logicspec Test Case Specifications DT DT-Reverse Source Code 3/19/2002 BTD-Generate Testdata TC-verify Testset Adequacy Boundary Testdata Testing at FAMU 60
Test. Lab Decision-Based Test Tools DT-Editor DT 2 -logicspec Test Case Specifications DT DT-Reverse Source Code 3/19/2002 BTD-Generate Testdata TC-verify Testset Adequacy Boundary Testdata Testing at FAMU 60
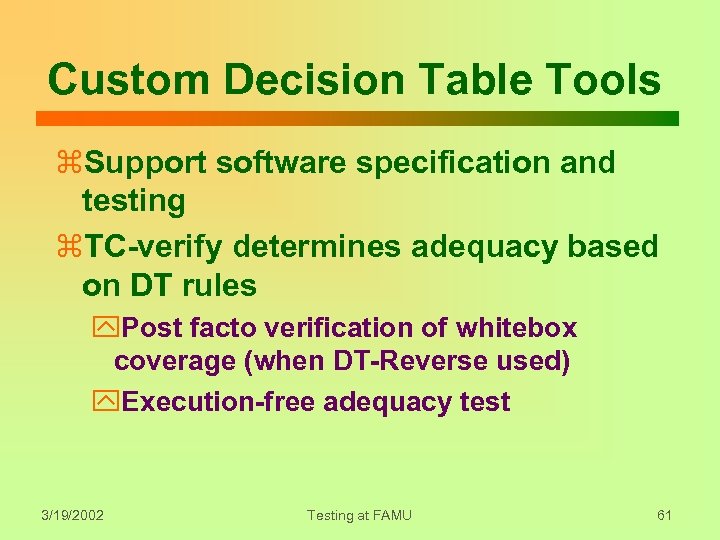 Custom Decision Table Tools z. Support software specification and testing z. TC-verify determines adequacy based on DT rules y. Post facto verification of whitebox coverage (when DT-Reverse used) y. Execution-free adequacy test 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 61
Custom Decision Table Tools z. Support software specification and testing z. TC-verify determines adequacy based on DT rules y. Post facto verification of whitebox coverage (when DT-Reverse used) y. Execution-free adequacy test 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 61
 Seminal Projects z. Decision-based test methods z. Reliability testing training simulator z. Test arcade z. Testing via design mutation z. Test patterns / verification agents z. Other Ideas 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 62
Seminal Projects z. Decision-based test methods z. Reliability testing training simulator z. Test arcade z. Testing via design mutation z. Test patterns / verification agents z. Other Ideas 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 62
 Reliability Test Simulator z. Prototype from Graduate IV&V Course z. Published in ISSRE 2001 Proceedings z. Excerpts from Presentation 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 63
Reliability Test Simulator z. Prototype from Graduate IV&V Course z. Published in ISSRE 2001 Proceedings z. Excerpts from Presentation 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 63
 Reliability Simulation -- TBDs z. Simulation for experimentation y. Imperfect defect removal (ref …) y. Operational testing z. Thesis topic(s) y. Model validation vs. published/industry results y. Management decision-support via simulation 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 64
Reliability Simulation -- TBDs z. Simulation for experimentation y. Imperfect defect removal (ref …) y. Operational testing z. Thesis topic(s) y. Model validation vs. published/industry results y. Management decision-support via simulation 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 64
 Seminal Projects z. Decision-based test methods z. Reliability testing training simulator z. Test arcade z. Testing via design mutation z. Test patterns / verification agents z. Other Ideas 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 65
Seminal Projects z. Decision-based test methods z. Reliability testing training simulator z. Test arcade z. Testing via design mutation z. Test patterns / verification agents z. Other Ideas 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 65
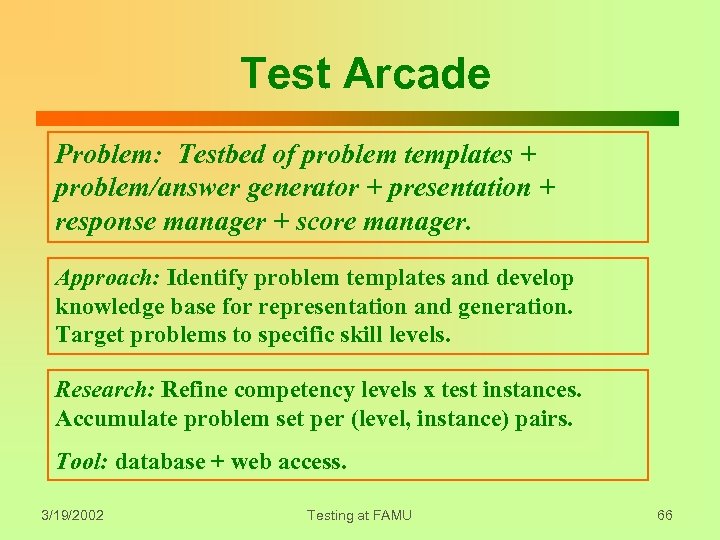 Test Arcade Problem: Testbed of problem templates + problem/answer generator + presentation + response manager + score manager. Approach: Identify problem templates and develop knowledge base for representation and generation. Target problems to specific skill levels. Research: Refine competency levels x test instances. Accumulate problem set per (level, instance) pairs. Tool: database + web access. 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 66
Test Arcade Problem: Testbed of problem templates + problem/answer generator + presentation + response manager + score manager. Approach: Identify problem templates and develop knowledge base for representation and generation. Target problems to specific skill levels. Research: Refine competency levels x test instances. Accumulate problem set per (level, instance) pairs. Tool: database + web access. 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 66
 Seminal Projects z. Decision-based test methods z. Reliability testing training simulator z. Test arcade z. Testing via design mutation z. Test patterns / verification agents z. Other Ideas 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 67
Seminal Projects z. Decision-based test methods z. Reliability testing training simulator z. Test arcade z. Testing via design mutation z. Test patterns / verification agents z. Other Ideas 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 67
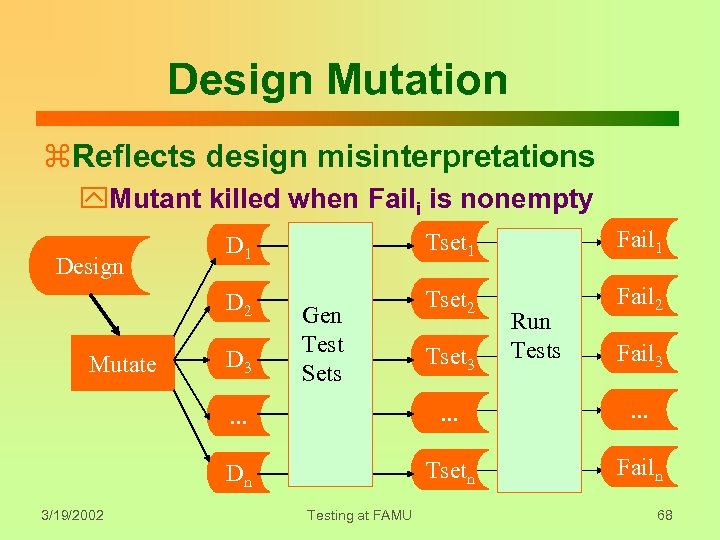 Design Mutation z. Reflects design misinterpretations y. Mutant killed when Faili is nonempty Mutate Tset 1 Fail 1 D 2 Design D 1 Tset 2 Fail 2 D 3 Gen Test Sets Tset 3 Run Tests Fail 3 . . . Dn 3/19/2002 . . . Tsetn Failn Testing at FAMU 68
Design Mutation z. Reflects design misinterpretations y. Mutant killed when Faili is nonempty Mutate Tset 1 Fail 1 D 2 Design D 1 Tset 2 Fail 2 D 3 Gen Test Sets Tset 3 Run Tests Fail 3 . . . Dn 3/19/2002 . . . Tsetn Failn Testing at FAMU 68
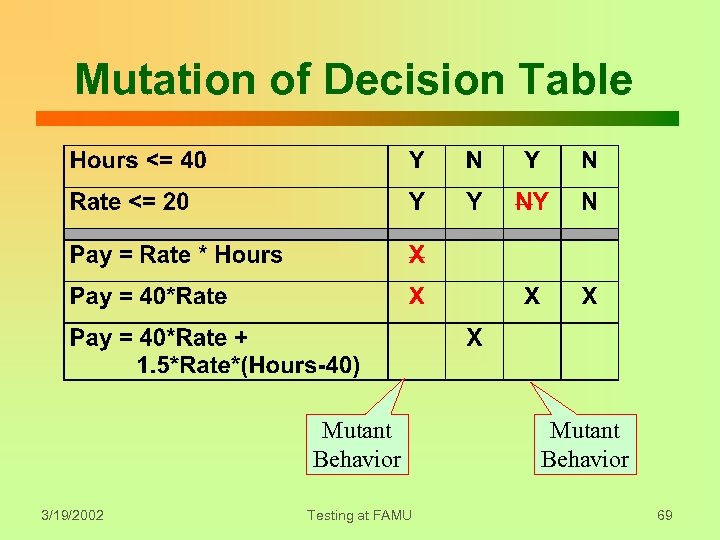 Mutation of Decision Table Mutant Behavior 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU Mutant Behavior 69
Mutation of Decision Table Mutant Behavior 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU Mutant Behavior 69
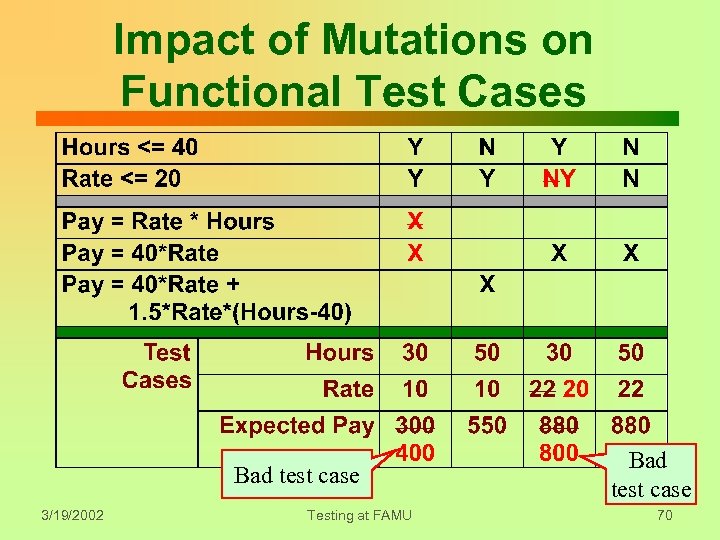 Impact of Mutations on Functional Test Cases Bad test case 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU Bad test case 70
Impact of Mutations on Functional Test Cases Bad test case 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU Bad test case 70
 Design Mutation -- Prospectus z. Application y. Requirements/design models y. Guided inspection -- ensure mutants not being created y. Testing: creation of BAD test cases z. Practical if automated y. Facilitated by formal representation 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 71
Design Mutation -- Prospectus z. Application y. Requirements/design models y. Guided inspection -- ensure mutants not being created y. Testing: creation of BAD test cases z. Practical if automated y. Facilitated by formal representation 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 71
 Seminal Projects z. Decision-based test methods z. Reliability testing training simulator z. Test arcade z. Testing via design mutation z. Test patterns / verification agents z. Other Ideas 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 72
Seminal Projects z. Decision-based test methods z. Reliability testing training simulator z. Test arcade z. Testing via design mutation z. Test patterns / verification agents z. Other Ideas 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 72
 Test Patterns (Example) z. GUI input controls z. Properties determine required testing z. Derive black-box test patterns for GUI input controls z. Propose automated test agents knowledgeable about specific test pattern 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 73
Test Patterns (Example) z. GUI input controls z. Properties determine required testing z. Derive black-box test patterns for GUI input controls z. Propose automated test agents knowledgeable about specific test pattern 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 73
 Test Patterns (Continued) z. Test patterns for design patterns z. Empirical test patterns reflecting organizational practices y. Reverse engineer practices into patterns y. Forward engineer patterns into practice 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 74
Test Patterns (Continued) z. Test patterns for design patterns z. Empirical test patterns reflecting organizational practices y. Reverse engineer practices into patterns y. Forward engineer patterns into practice 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 74
 Test Agents z. Properties of Agents y. Responsibility y. Knowledge y. Autonomy z. Scope of Agents y. Functional Unit (F) y. Architectural Component (A) y. System (S) 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 75
Test Agents z. Properties of Agents y. Responsibility y. Knowledge y. Autonomy z. Scope of Agents y. Functional Unit (F) y. Architectural Component (A) y. System (S) 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 75
 Test Agents -- Prospectus z. Intelligence y. Generator of checklist / procedure for human tester y. Watch-dog and status reporter y. Reminder to complete test action y. Performer of test action y. Coordinator of test agents 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 76
Test Agents -- Prospectus z. Intelligence y. Generator of checklist / procedure for human tester y. Watch-dog and status reporter y. Reminder to complete test action y. Performer of test action y. Coordinator of test agents 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 76
 Seminal Projects z. Decision-based test methods z. Reliability testing training simulator z. Test arcade z. Testing via design mutation z. Test patterns / verification agents z. Other Ideas 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 77
Seminal Projects z. Decision-based test methods z. Reliability testing training simulator z. Test arcade z. Testing via design mutation z. Test patterns / verification agents z. Other Ideas 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 77
 Testing: A State of Practice Study Problem: Develop a method for characterizing the state of practice in software testing. Approach: Use frameworks like the Test Maturity Model and SPRAE to characterize/assess state of practice. Research: Relate attributes of testing practice to qualitative and quantitative indicators of effectiveness and satisfaction. Devise easy to use evaluation system that identifies areas needing improvement, and which provide insightful measures of performance. 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 78
Testing: A State of Practice Study Problem: Develop a method for characterizing the state of practice in software testing. Approach: Use frameworks like the Test Maturity Model and SPRAE to characterize/assess state of practice. Research: Relate attributes of testing practice to qualitative and quantitative indicators of effectiveness and satisfaction. Devise easy to use evaluation system that identifies areas needing improvement, and which provide insightful measures of performance. 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 78
 Adaptive Operational Testing Problem: Perfecting software by OT is biased by expected feature usage. Even when errors are flushed out for one feature, the test emphasis remains the same. OT leads to slow rate of error discovery in other features. Approach: Given features A, B, C with probabilities p. A, p. B, p. C, and MTBF of t. A, t. B, t. C. Shift feature probability as feature reliability increases. Research: Determine criteria for shifting p’s so that feature starvation does not occur. Tool: Reliability simulator to prototype solutions. 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 79
Adaptive Operational Testing Problem: Perfecting software by OT is biased by expected feature usage. Even when errors are flushed out for one feature, the test emphasis remains the same. OT leads to slow rate of error discovery in other features. Approach: Given features A, B, C with probabilities p. A, p. B, p. C, and MTBF of t. A, t. B, t. C. Shift feature probability as feature reliability increases. Research: Determine criteria for shifting p’s so that feature starvation does not occur. Tool: Reliability simulator to prototype solutions. 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 79
 Speech Support for Intuitive Testing Problem: Intuitive testing exploits tester expertise and experience but lacks the formality which ensures repeatability and documentation of the test and results. Approach: Use speech input to capture test cases, test results, and error reports. Generate test artifacts: (1) test script; (2) test log; and (3) problem reports. Research: Develop dialog model. Experiment with student system testing. 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 80
Speech Support for Intuitive Testing Problem: Intuitive testing exploits tester expertise and experience but lacks the formality which ensures repeatability and documentation of the test and results. Approach: Use speech input to capture test cases, test results, and error reports. Generate test artifacts: (1) test script; (2) test log; and (3) problem reports. Research: Develop dialog model. Experiment with student system testing. 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 80
 Specification-Driven Testing of Speech Based Systems Problem. Use a formal dialogue model as the basis for test case design and test adequacy evaluation. Approach. Given the graphical dialogue model used by the FAMU JSBB tool (1) define dialogue coverage adequacy criteria; (2) extend the JSBB code generation to include coverage instrumentation; (3) design a test case generator based on the dialogue model; (4) implement coverage analyzer. Research. Evaluate effectiveness of model-based test cases using control-flow and dialogue-model coverage measures. 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 81
Specification-Driven Testing of Speech Based Systems Problem. Use a formal dialogue model as the basis for test case design and test adequacy evaluation. Approach. Given the graphical dialogue model used by the FAMU JSBB tool (1) define dialogue coverage adequacy criteria; (2) extend the JSBB code generation to include coverage instrumentation; (3) design a test case generator based on the dialogue model; (4) implement coverage analyzer. Research. Evaluate effectiveness of model-based test cases using control-flow and dialogue-model coverage measures. 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 81
![Testability via Self-Diagnostics in Objects Problem: Lack of observability [Voas] in O-O software complicates Testability via Self-Diagnostics in Objects Problem: Lack of observability [Voas] in O-O software complicates](https://present5.com/presentation/e9ced8ebd981dea5945bfff010efd2ce/image-82.jpg) Testability via Self-Diagnostics in Objects Problem: Lack of observability [Voas] in O-O software complicates testability. Encapsulation prevents error propagation to outside. Approach: Design in self diagnostics along with means of propagation to outside. Use multiple techniques such as assertions for state verification. Research: Research observability problem in objectbased testing. Apply and extend frameworks/methods like JUnit to implement self-diagnostics. 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 83
Testability via Self-Diagnostics in Objects Problem: Lack of observability [Voas] in O-O software complicates testability. Encapsulation prevents error propagation to outside. Approach: Design in self diagnostics along with means of propagation to outside. Use multiple techniques such as assertions for state verification. Research: Research observability problem in objectbased testing. Apply and extend frameworks/methods like JUnit to implement self-diagnostics. 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 83
 Part IV CONCLUSION 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 84
Part IV CONCLUSION 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 84
 Acknowledgments z. Lucent z. NSF (EIA-9906590) Technologies z. Lockheed Martin z. Dell Computer z. Abbott Laboratories z 3 M z. Eli Lilly and Company z. Telcordia z. Students z. Software Research, Inc. 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 85
Acknowledgments z. Lucent z. NSF (EIA-9906590) Technologies z. Lockheed Martin z. Dell Computer z. Abbott Laboratories z 3 M z. Eli Lilly and Company z. Telcordia z. Students z. Software Research, Inc. 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 85
 Future z. Evolve Test. Lab Mentorship Model z. Transfer to Selected Courses y. Test. Lab students == transfer agents z. Disseminate Results y. Web site, newsletter, conferences z. Procure Funding for Research z. Find Research Collaborators 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 86
Future z. Evolve Test. Lab Mentorship Model z. Transfer to Selected Courses y. Test. Lab students == transfer agents z. Disseminate Results y. Web site, newsletter, conferences z. Procure Funding for Research z. Find Research Collaborators 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 86
 Who Wins? • Students -- expanded career options • Academic Departments • Departmental Faculty • Corporate Employers • The State of Florida • The Software Industry 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 87
Who Wins? • Students -- expanded career options • Academic Departments • Departmental Faculty • Corporate Employers • The State of Florida • The Software Industry 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 87
 Opportunities To PAR T NER 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 88
Opportunities To PAR T NER 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 88
 Opportunities to Partner USF-FAMU z. Artifacts testbed development z. Test. Lab student exchange z. Student/Faculty Internship(s) z. State-of-Practice studies z. Thesis committee participation z. Scholar in residence 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 89
Opportunities to Partner USF-FAMU z. Artifacts testbed development z. Test. Lab student exchange z. Student/Faculty Internship(s) z. State-of-Practice studies z. Thesis committee participation z. Scholar in residence 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 89
 Questions? 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 90
Questions? 3/19/2002 Testing at FAMU 90


