c78fb57ca7ccfafe48abe407aa25f965.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 Software Project Planning
Software Project Planning
 Software Engineering Estimation n The SPM begins with a set of activities that are collectively called Project planning n Whenever estimates are made we look into future concern and so there is some degree of uncertainty in estimation n
Software Engineering Estimation n The SPM begins with a set of activities that are collectively called Project planning n Whenever estimates are made we look into future concern and so there is some degree of uncertainty in estimation n
 Software Engineering n n Observation on Estimation PM manager must have the ability to estimate PM with the ability to know what will go wrong before it actually does Estimation of resources, cost and schedule for a software requires experience of past projects and access to historical data
Software Engineering n n Observation on Estimation PM manager must have the ability to estimate PM with the ability to know what will go wrong before it actually does Estimation of resources, cost and schedule for a software requires experience of past projects and access to historical data
 Software Engineering Project complexity has a strong effect on uncertainty that is inherent in planning. n Complexity is affected by familiarity with past efforts n Real time projects are always complex n Project size also effect the accuracy of the estimates n
Software Engineering Project complexity has a strong effect on uncertainty that is inherent in planning. n Complexity is affected by familiarity with past efforts n Real time projects are always complex n Project size also effect the accuracy of the estimates n
 Software Engineering n If the requirements have been solidified estimation is easy but if the requirement are keep on changing estimation is affects
Software Engineering n If the requirements have been solidified estimation is easy but if the requirement are keep on changing estimation is affects
 Software Engineering Project Planning objectives n The objectives of software project planning is to provides the reasonable estimates of cost, effort and schedule n These estimates are made at the beginning of the project and must be updated wit the passage of time. n
Software Engineering Project Planning objectives n The objectives of software project planning is to provides the reasonable estimates of cost, effort and schedule n These estimates are made at the beginning of the project and must be updated wit the passage of time. n
 Software Engineering Software Scope n Estimation of scope n Functional, non functional requirements. Constraints n
Software Engineering Software Scope n Estimation of scope n Functional, non functional requirements. Constraints n
 Software Engineering Obtaining information necessary for scope n Things are always hazy at the start of the project n There must be some meeting between customer and analyst for obtaining the scope of project n
Software Engineering Obtaining information necessary for scope n Things are always hazy at the start of the project n There must be some meeting between customer and analyst for obtaining the scope of project n
 Software Engineering 1 st meeting question n 2 nd meeting question n 3 rd meeting question and so on n
Software Engineering 1 st meeting question n 2 nd meeting question n 3 rd meeting question and so on n
 Software Engineering n Resources n The 2 nd task of software planning is the estimation of resources required to accomplish the software development effort Pyramid The development environment-----Hardware and software tools, Reusable components and people n n
Software Engineering n Resources n The 2 nd task of software planning is the estimation of resources required to accomplish the software development effort Pyramid The development environment-----Hardware and software tools, Reusable components and people n n
 Software Engineering n n Human Resource: The no. of people required for a software project can be determined only after an estimate of development effort. Reusable Software component Off the shelf components Full experience components Partial experience components New components
Software Engineering n n Human Resource: The no. of people required for a software project can be determined only after an estimate of development effort. Reusable Software component Off the shelf components Full experience components Partial experience components New components
 Software Engineering n Guidelines
Software Engineering n Guidelines
 Software Engineering n Software Sizing Fuzzy logic sizing Function point sizing Standard component sizing
Software Engineering n Software Sizing Fuzzy logic sizing Function point sizing Standard component sizing
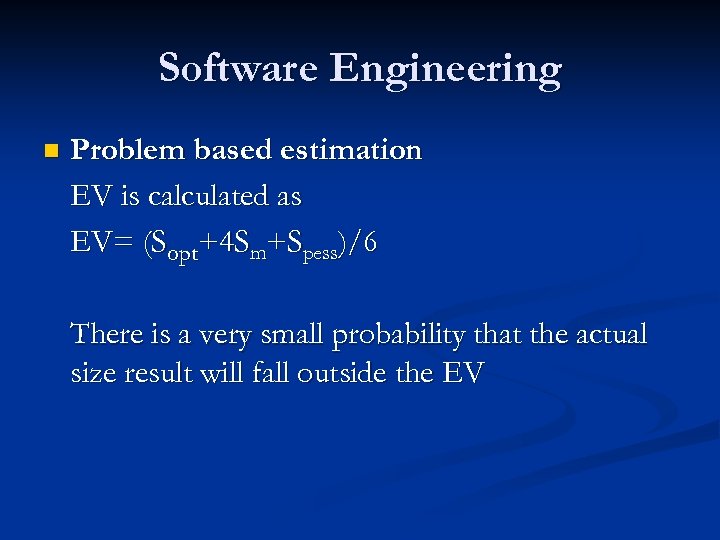 Software Engineering n Problem based estimation EV is calculated as EV= (Sopt+4 Sm+Spess)/6 There is a very small probability that the actual size result will fall outside the EV
Software Engineering n Problem based estimation EV is calculated as EV= (Sopt+4 Sm+Spess)/6 There is a very small probability that the actual size result will fall outside the EV
 Software Engineering n Example
Software Engineering n Example
 Software Engineering n COCOMO Model Constructive Cost model Three model Model 1 Model 2 Mode 3
Software Engineering n COCOMO Model Constructive Cost model Three model Model 1 Model 2 Mode 3
 Software Engineering Model 1 is called Basic COCOMO n It has three level Organic Semi-detached Embedded n
Software Engineering Model 1 is called Basic COCOMO n It has three level Organic Semi-detached Embedded n
 Software Engineering E= ab. KLOCbb n D= cb. Edd n N= E/D n Where E is the development effort in PM and D is the development effort time in months and N is the no of people
Software Engineering E= ab. KLOCbb n D= cb. Edd n N= E/D n Where E is the development effort in PM and D is the development effort time in months and N is the no of people
 Software Engineering n Make Buy decision: The software managers are often faced with the problem of make buy decision. In some cases it is cost effective to acquire rather than internal development
Software Engineering n Make Buy decision: The software managers are often faced with the problem of make buy decision. In some cases it is cost effective to acquire rather than internal development


