b026d260d3d6d6774aff84be6c9a106a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39
 Software Overview 1) Installation 2) Scanning Procedure 3) File organization 4) Segmentation 5) Unfolding 6) Importing data into HFM toolbox 7) Demarcation 8) Analysis in Flat Space
Software Overview 1) Installation 2) Scanning Procedure 3) File organization 4) Segmentation 5) Unfolding 6) Importing data into HFM toolbox 7) Demarcation 8) Analysis in Flat Space
 Before you begin. . . Read all of the following: • Zeineh et. al. Neuro. Image 11(6): 668 -83, 2000 • Zeineh et. al. The Anatom. Record: New Anatomist 265: 111 -120, 2001 • Zeineh et. al. Science Jan 24: 299(5606) 577 -80, 2003 • Amaral & Insausti 1990. Hippocampal formation. In The Human Nervous System (G. Praxinos, Ed. ), pp. 711– 755. Academic Press, San Diego • Duvernoy, H. M. 1998. The Human Hippocampus: Springer, Berlin. • Insausti et. al. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 19: 659– 671.
Before you begin. . . Read all of the following: • Zeineh et. al. Neuro. Image 11(6): 668 -83, 2000 • Zeineh et. al. The Anatom. Record: New Anatomist 265: 111 -120, 2001 • Zeineh et. al. Science Jan 24: 299(5606) 577 -80, 2003 • Amaral & Insausti 1990. Hippocampal formation. In The Human Nervous System (G. Praxinos, Ed. ), pp. 711– 755. Academic Press, San Diego • Duvernoy, H. M. 1998. The Human Hippocampus: Springer, Berlin. • Insausti et. al. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 19: 659– 671.
 Instructions http: //airto. loni. ucla. edu/BMCweb/How. To/Hippocampus/
Instructions http: //airto. loni. ucla. edu/BMCweb/How. To/Hippocampus/
 Requirements • PC: segmentation • UNIX: MATLAB • patience, forttude, + computer skills
Requirements • PC: segmentation • UNIX: MATLAB • patience, forttude, + computer skills
 I. Installation • PC: download mr. Gray - segmentation program. http: //white. stanford. edu/~brian/mri/segment. Unfold. htm
I. Installation • PC: download mr. Gray - segmentation program. http: //white. stanford. edu/~brian/mri/segment. Unfold. htm
 I. Installation • UNIX: download, gunzip, and untar 5 files http: //sourceforge. net/projects/mtl-unfolding/ – HFM Main Module – Stanford Unfolding Code (Brian Wandell) – Stanford mr. Load. Ret Visualization Utility – Image utilities – Example data
I. Installation • UNIX: download, gunzip, and untar 5 files http: //sourceforge. net/projects/mtl-unfolding/ – HFM Main Module – Stanford Unfolding Code (Brian Wandell) – Stanford mr. Load. Ret Visualization Utility – Image utilities – Example data
 I. Installation • UNIX: download updated image utilities – Automated Image Registration (AIR) http: //bishopw. loni. ucla. edu/ – imconvert (UCLA image conversion utility) http: //airto. loni. ucla. edu/BMCweb/Shared. Code/Img. Lib/imconvert. c. html http: //airto. loni. ucla. edu/BMCweb/Shared. Code/Shared. Software. html#Anchor-UCLA-35829 • Compile everything • Make data directories and links • Test with the sample data
I. Installation • UNIX: download updated image utilities – Automated Image Registration (AIR) http: //bishopw. loni. ucla. edu/ – imconvert (UCLA image conversion utility) http: //airto. loni. ucla. edu/BMCweb/Shared. Code/Img. Lib/imconvert. c. html http: //airto. loni. ucla. edu/BMCweb/Shared. Code/Shared. Software. html#Anchor-UCLA-35829 • Compile everything • Make data directories and links • Test with the sample data
 I. Installation • Sign up for the mailing list! http: //lists. sourceforge. net/mailman/listinfo/mtlunfolding-help
I. Installation • Sign up for the mailing list! http: //lists. sourceforge. net/mailman/listinfo/mtlunfolding-help
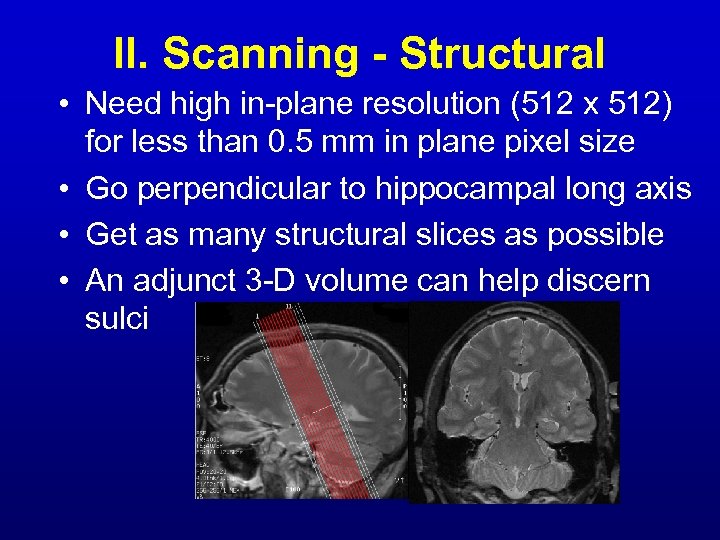 II. Scanning - Structural • Need high in-plane resolution (512 x 512) for less than 0. 5 mm in plane pixel size • Go perpendicular to hippocampal long axis • Get as many structural slices as possible • An adjunct 3 -D volume can help discern sulci
II. Scanning - Structural • Need high in-plane resolution (512 x 512) for less than 0. 5 mm in plane pixel size • Go perpendicular to hippocampal long axis • Get as many structural slices as possible • An adjunct 3 -D volume can help discern sulci
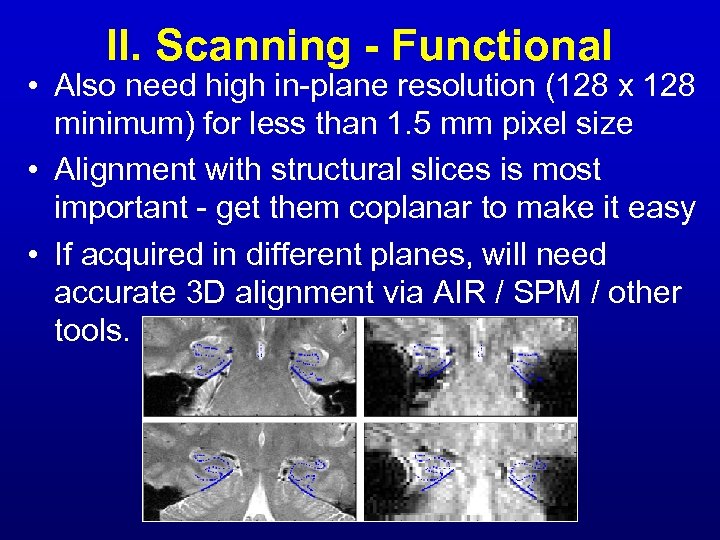 II. Scanning - Functional • Also need high in-plane resolution (128 x 128 minimum) for less than 1. 5 mm pixel size • Alignment with structural slices is most important - get them coplanar to make it easy • If acquired in different planes, will need accurate 3 D alignment via AIR / SPM / other tools.
II. Scanning - Functional • Also need high in-plane resolution (128 x 128 minimum) for less than 1. 5 mm pixel size • Alignment with structural slices is most important - get them coplanar to make it easy • If acquired in different planes, will need accurate 3 D alignment via AIR / SPM / other tools.
 III. File Organization • For each subject, 4 main directories – raw - all fxnal aw data goes in here – segment - all structural data for segmentation – air - motion correction for fxnal data – loadret - it all gets synthesized here
III. File Organization • For each subject, 4 main directories – raw - all fxnal aw data goes in here – segment - all structural data for segmentation – air - motion correction for fxnal data – loadret - it all gets synthesized here
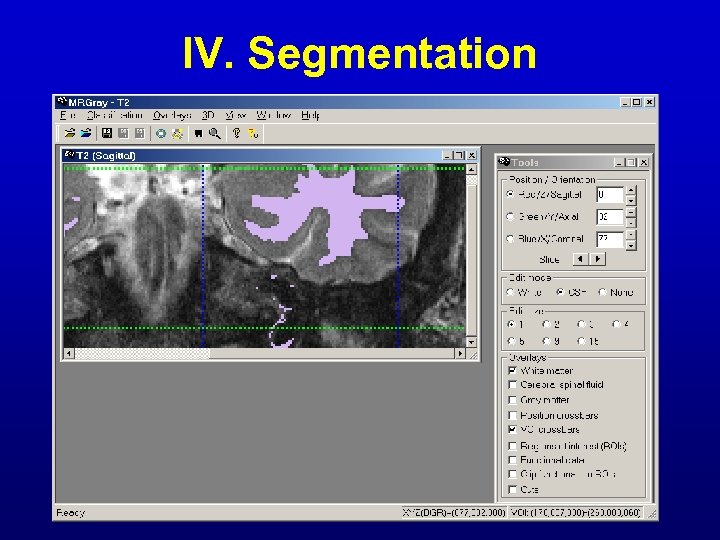 IV. Segmentation
IV. Segmentation
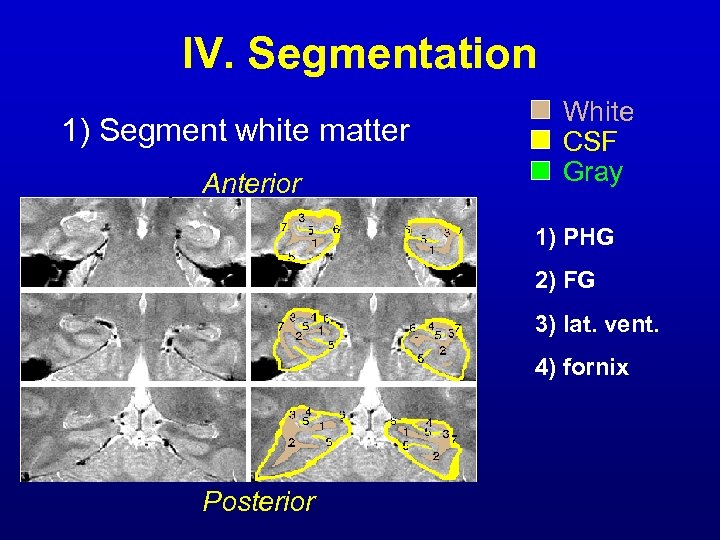 IV. Segmentation 1) Segment white matter Anterior White CSF Gray 1) PHG 2) FG 3) lat. vent. 4) fornix Posterior
IV. Segmentation 1) Segment white matter Anterior White CSF Gray 1) PHG 2) FG 3) lat. vent. 4) fornix Posterior
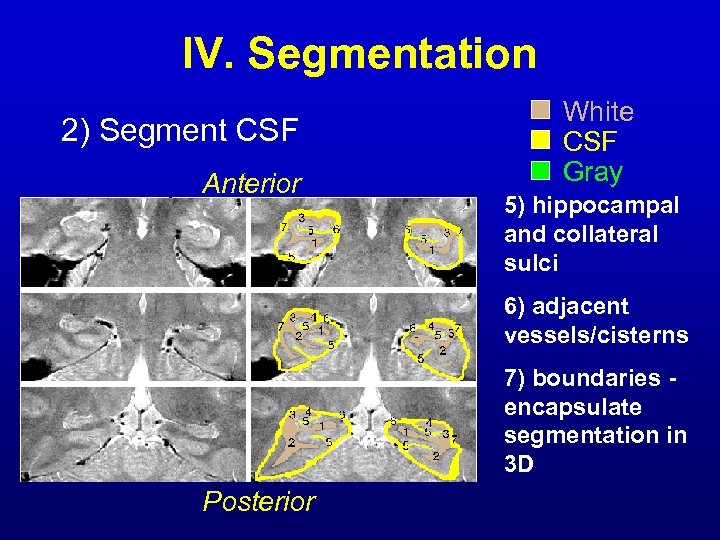 IV. Segmentation 2) Segment CSF Anterior White CSF Gray 5) hippocampal and collateral sulci 6) adjacent vessels/cisterns 7) boundaries encapsulate segmentation in 3 D Posterior
IV. Segmentation 2) Segment CSF Anterior White CSF Gray 5) hippocampal and collateral sulci 6) adjacent vessels/cisterns 7) boundaries encapsulate segmentation in 3 D Posterior
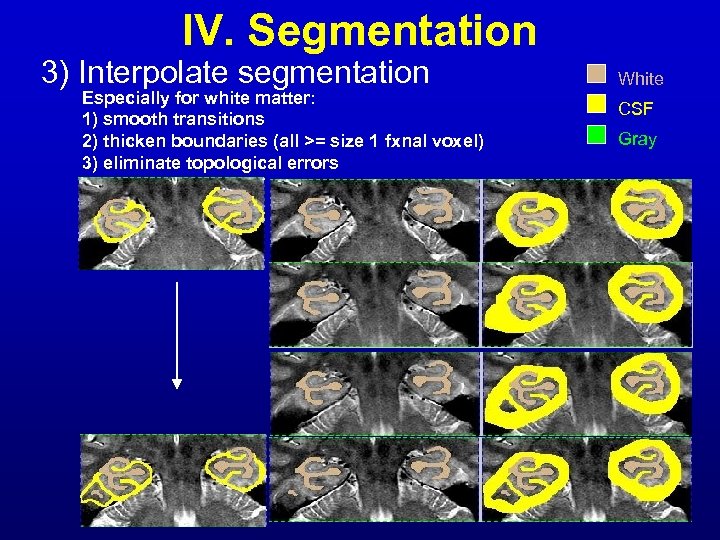 IV. Segmentation 3) Interpolate segmentation Especially for white matter: 1) smooth transitions 2) thicken boundaries (all >= size 1 fxnal voxel) 3) eliminate topological errors White CSF Gray
IV. Segmentation 3) Interpolate segmentation Especially for white matter: 1) smooth transitions 2) thicken boundaries (all >= size 1 fxnal voxel) 3) eliminate topological errors White CSF Gray
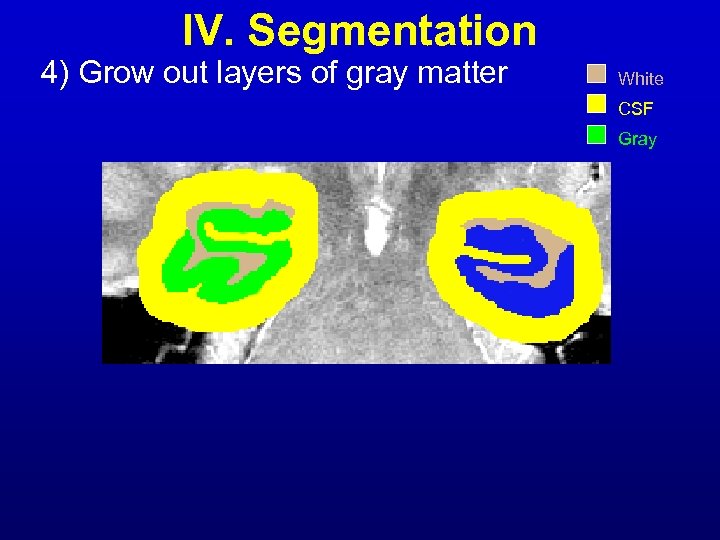 IV. Segmentation 4) Grow out layers of gray matter White CSF Gray
IV. Segmentation 4) Grow out layers of gray matter White CSF Gray
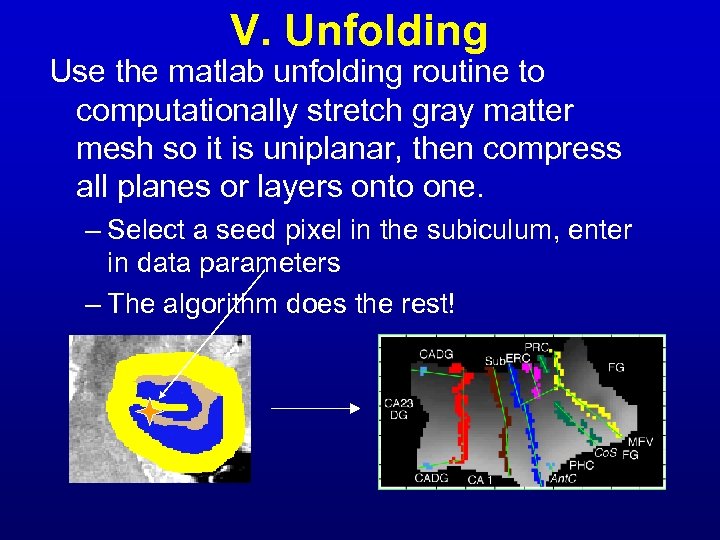 V. Unfolding Use the matlab unfolding routine to computationally stretch gray matter mesh so it is uniplanar, then compress all planes or layers onto one. – Select a seed pixel in the subiculum, enter in data parameters – The algorithm does the rest!
V. Unfolding Use the matlab unfolding routine to computationally stretch gray matter mesh so it is uniplanar, then compress all planes or layers onto one. – Select a seed pixel in the subiculum, enter in data parameters – The algorithm does the rest!
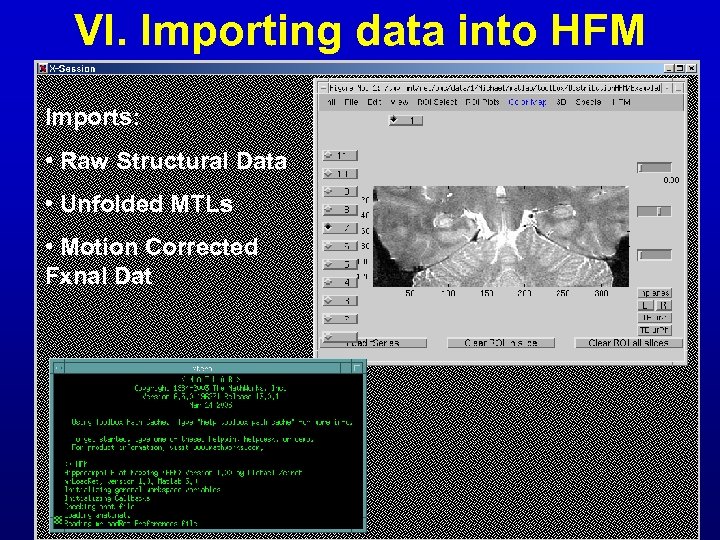 VI. Importing data into HFM Imports: • Raw Structural Data • Unfolded MTLs • Motion Corrected Fxnal Dat
VI. Importing data into HFM Imports: • Raw Structural Data • Unfolded MTLs • Motion Corrected Fxnal Dat
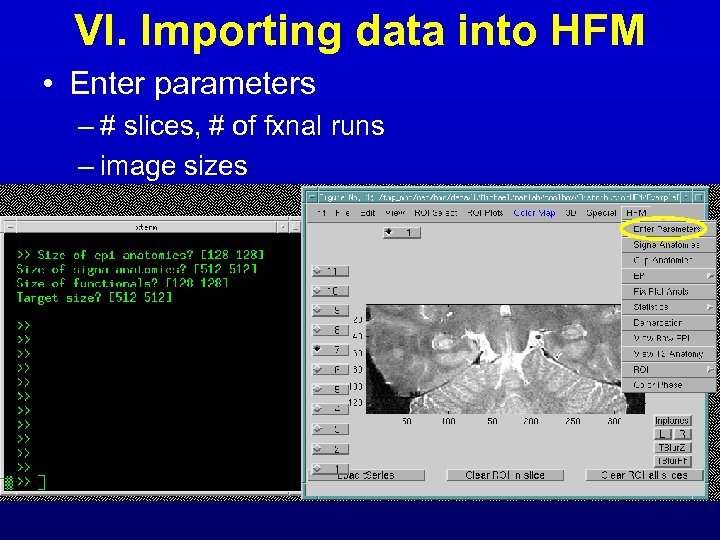 VI. Importing data into HFM • Enter parameters – # slices, # of fxnal runs – image sizes
VI. Importing data into HFM • Enter parameters – # slices, # of fxnal runs – image sizes
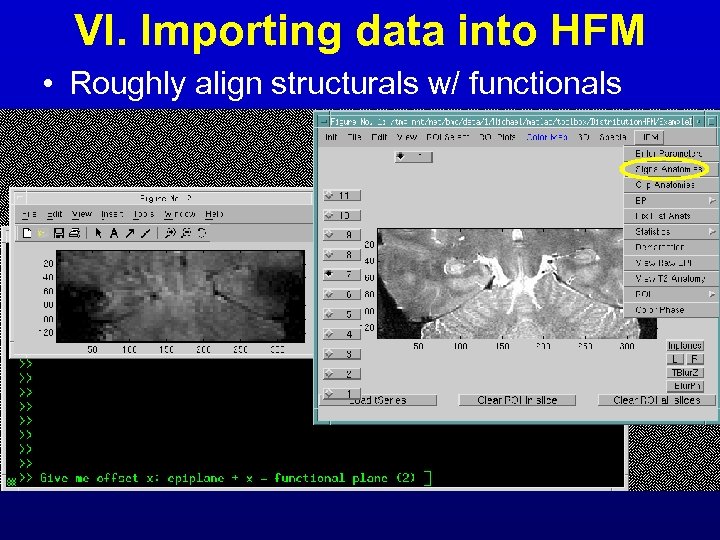 VI. Importing data into HFM • Roughly align structurals w/ functionals
VI. Importing data into HFM • Roughly align structurals w/ functionals
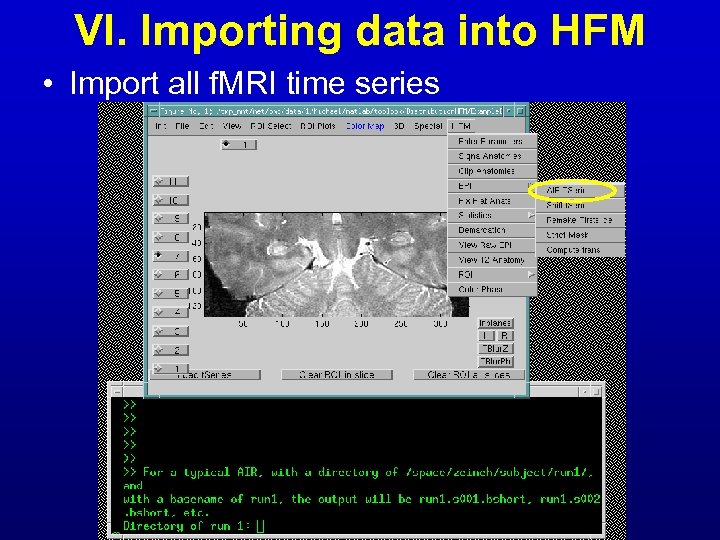 VI. Importing data into HFM • Import all f. MRI time series
VI. Importing data into HFM • Import all f. MRI time series
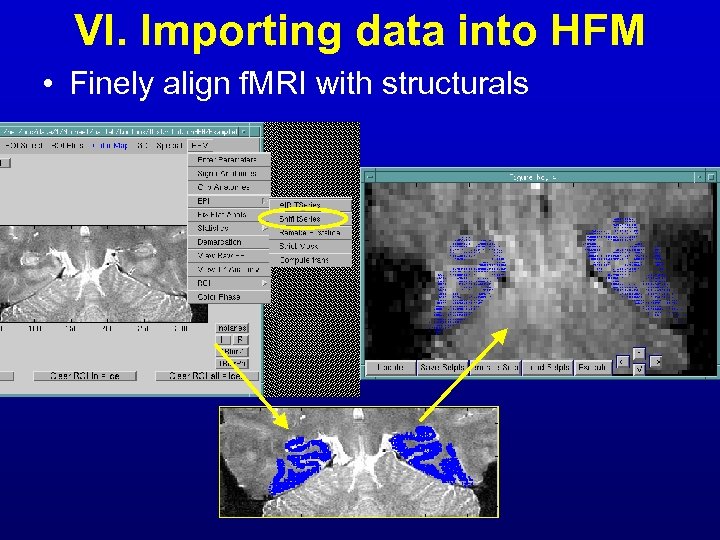 VI. Importing data into HFM • Finely align f. MRI with structurals
VI. Importing data into HFM • Finely align f. MRI with structurals
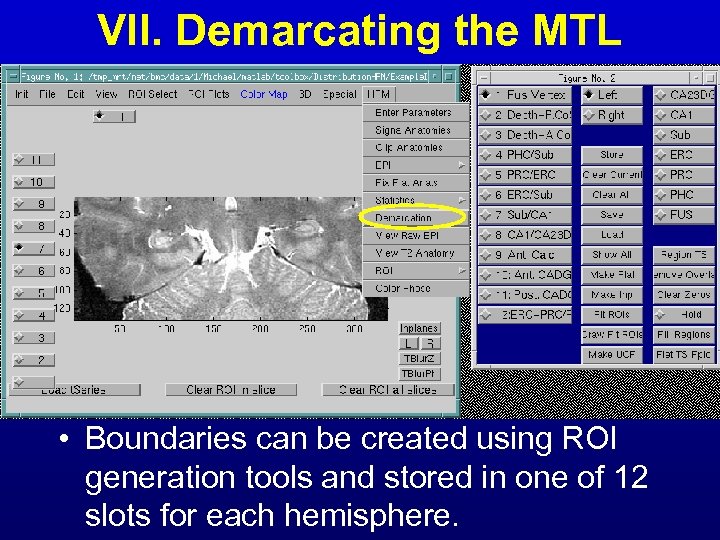 VII. Demarcating the MTL • Boundaries can be created using ROI generation tools and stored in one of 12 slots for each hemisphere.
VII. Demarcating the MTL • Boundaries can be created using ROI generation tools and stored in one of 12 slots for each hemisphere.
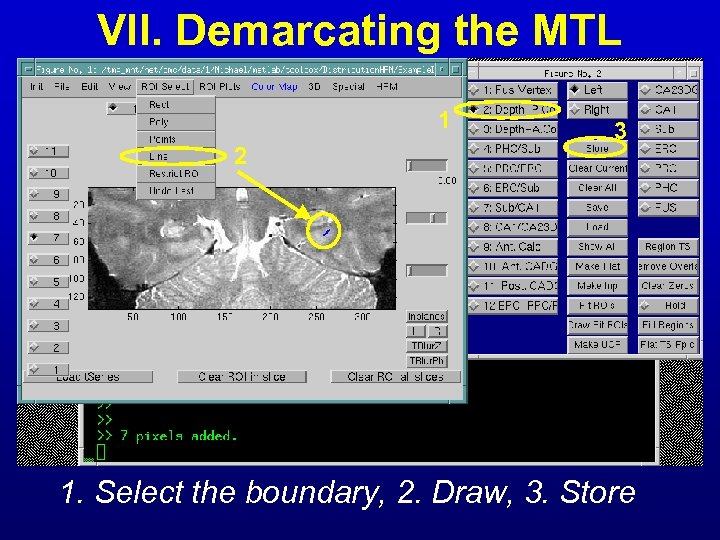 VII. Demarcating the MTL 1 2 3 1. Select the boundary, 2. Draw, 3. Store
VII. Demarcating the MTL 1 2 3 1. Select the boundary, 2. Draw, 3. Store
 VII. Demarcating the MTL • You can project the boundary to flat space (smaller projection is better).
VII. Demarcating the MTL • You can project the boundary to flat space (smaller projection is better).
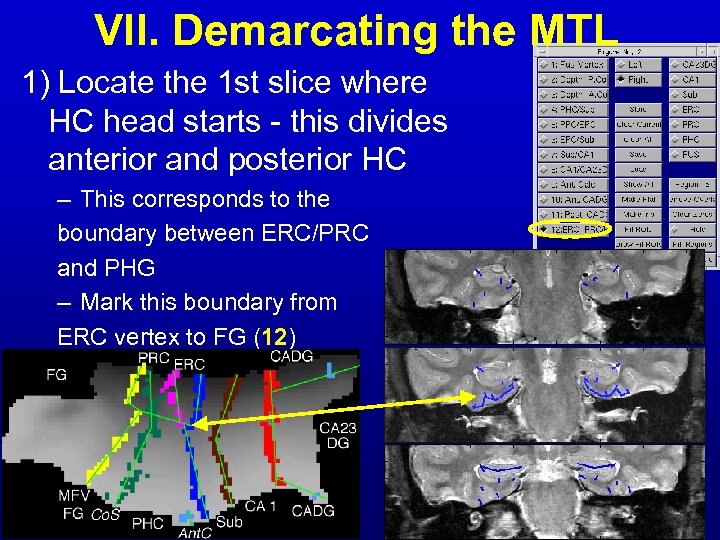 VII. Demarcating the MTL 1) Locate the 1 st slice where HC head starts - this divides anterior and posterior HC – This corresponds to the boundary between ERC/PRC and PHG – Mark this boundary from ERC vertex to FG (12)
VII. Demarcating the MTL 1) Locate the 1 st slice where HC head starts - this divides anterior and posterior HC – This corresponds to the boundary between ERC/PRC and PHG – Mark this boundary from ERC vertex to FG (12)
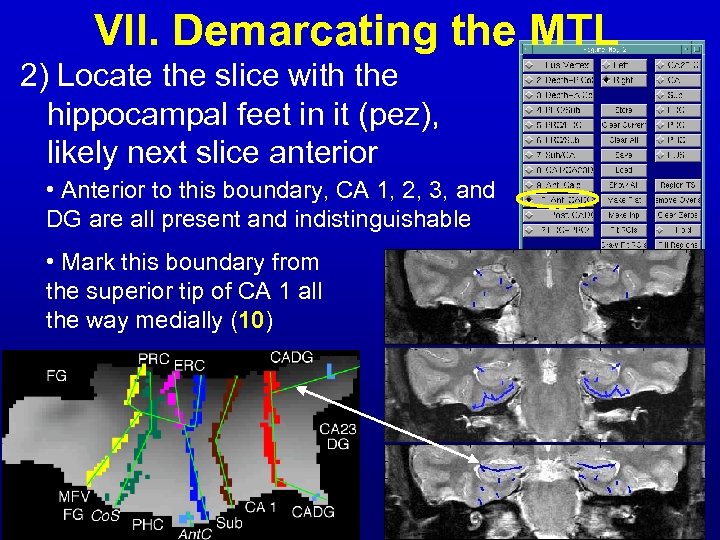 VII. Demarcating the MTL 2) Locate the slice with the hippocampal feet in it (pez), likely next slice anterior • Anterior to this boundary, CA 1, 2, 3, and DG are all present and indistinguishable • Mark this boundary from the superior tip of CA 1 all the way medially (10)
VII. Demarcating the MTL 2) Locate the slice with the hippocampal feet in it (pez), likely next slice anterior • Anterior to this boundary, CA 1, 2, 3, and DG are all present and indistinguishable • Mark this boundary from the superior tip of CA 1 all the way medially (10)
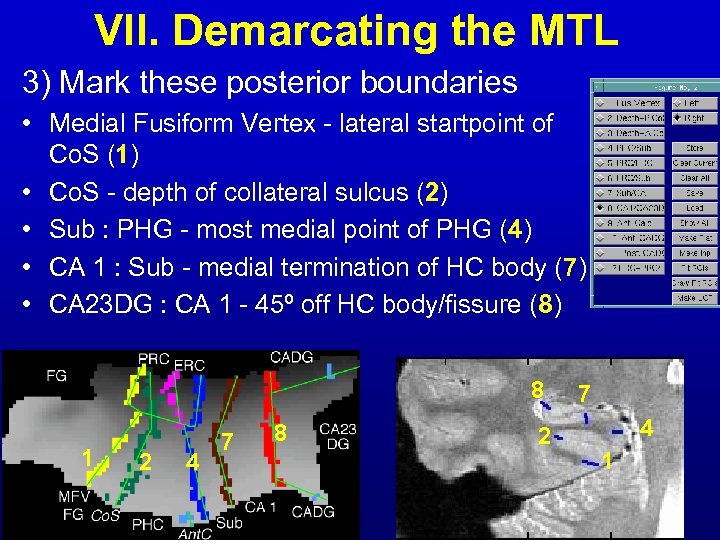 VII. Demarcating the MTL 3) Mark these posterior boundaries • Medial Fusiform Vertex - lateral startpoint of Co. S (1) • Co. S - depth of collateral sulcus (2) • Sub : PHG - most medial point of PHG (4) • CA 1 : Sub - medial termination of HC body (7) • CA 23 DG : CA 1 - 45º off HC body/fissure (8) 8 1 2 4 7 8 2 7 4 1
VII. Demarcating the MTL 3) Mark these posterior boundaries • Medial Fusiform Vertex - lateral startpoint of Co. S (1) • Co. S - depth of collateral sulcus (2) • Sub : PHG - most medial point of PHG (4) • CA 1 : Sub - medial termination of HC body (7) • CA 23 DG : CA 1 - 45º off HC body/fissure (8) 8 1 2 4 7 8 2 7 4 1
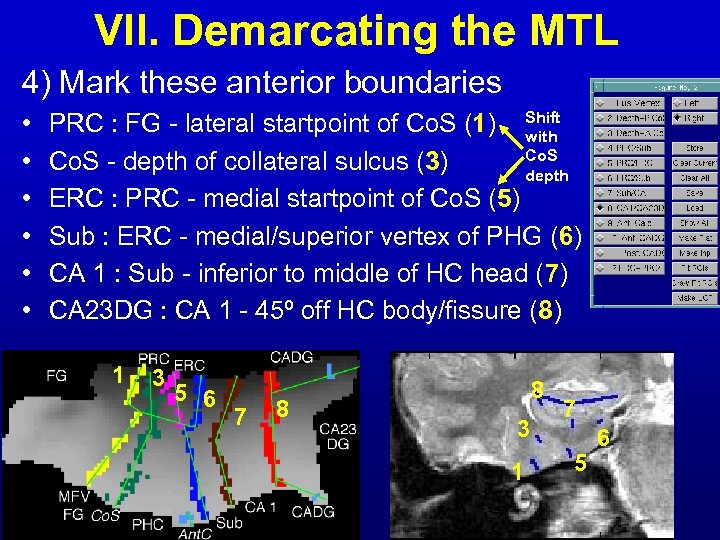 VII. Demarcating the MTL 4) Mark these anterior boundaries • • • PRC : FG - lateral startpoint of Co. S (1) Shift with Co. S - depth of collateral sulcus (3) depth ERC : PRC - medial startpoint of Co. S (5) Sub : ERC - medial/superior vertex of PHG (6) CA 1 : Sub - inferior to middle of HC head (7) CA 23 DG : CA 1 - 45º off HC body/fissure (8) 1 3 5 6 7 8 8 3 1 7 5 6
VII. Demarcating the MTL 4) Mark these anterior boundaries • • • PRC : FG - lateral startpoint of Co. S (1) Shift with Co. S - depth of collateral sulcus (3) depth ERC : PRC - medial startpoint of Co. S (5) Sub : ERC - medial/superior vertex of PHG (6) CA 1 : Sub - inferior to middle of HC head (7) CA 23 DG : CA 1 - 45º off HC body/fissure (8) 1 3 5 6 7 8 8 3 1 7 5 6
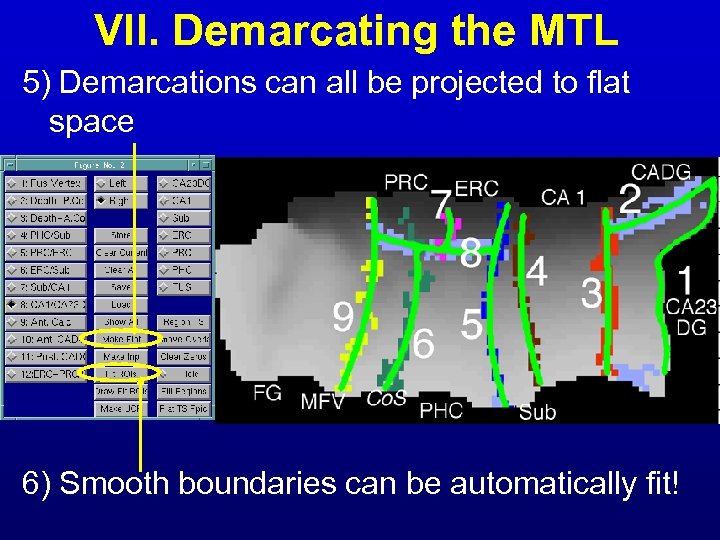 VII. Demarcating the MTL 5) Demarcations can all be projected to flat space 6) Smooth boundaries can be automatically fit!
VII. Demarcating the MTL 5) Demarcations can all be projected to flat space 6) Smooth boundaries can be automatically fit!
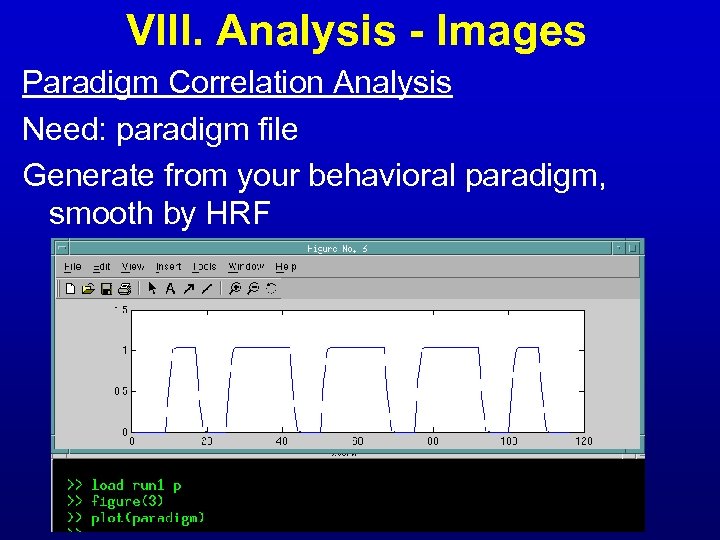 VIII. Analysis - Images Paradigm Correlation Analysis Need: paradigm file Generate from your behavioral paradigm, smooth by HRF
VIII. Analysis - Images Paradigm Correlation Analysis Need: paradigm file Generate from your behavioral paradigm, smooth by HRF
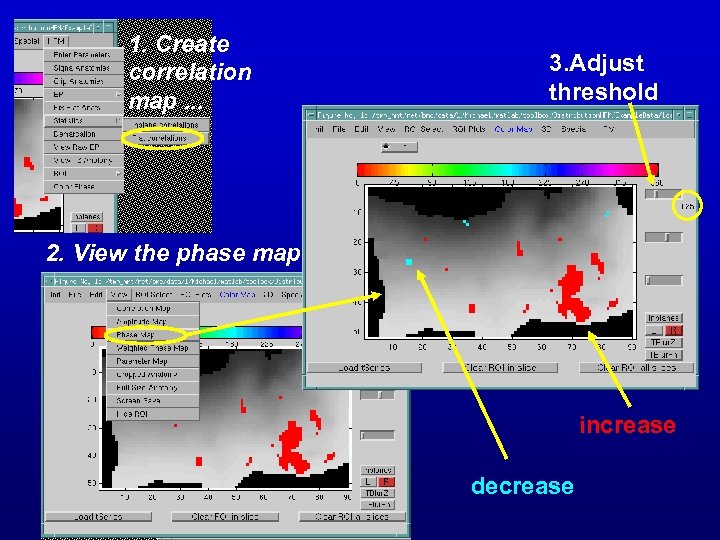 1. Create correlation map. . . 3. Adjust threshold 2. View the phase map increase decrease
1. Create correlation map. . . 3. Adjust threshold 2. View the phase map increase decrease
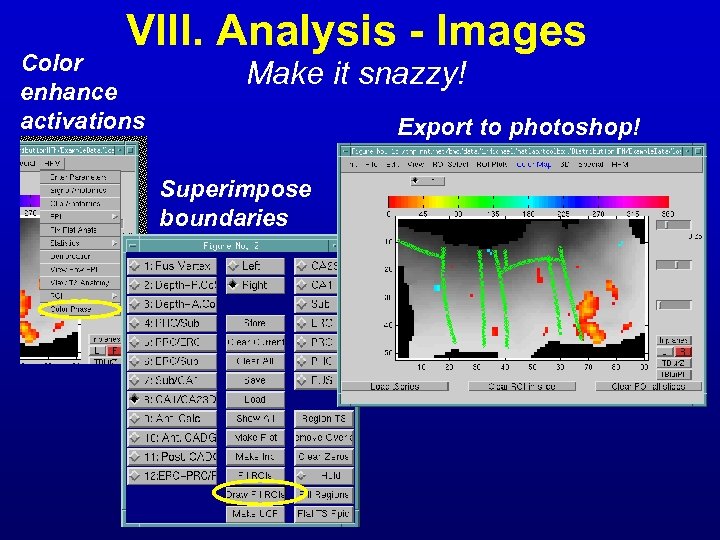 VIII. Analysis - Images Color enhance activations Make it snazzy! Export to photoshop! Superimpose boundaries
VIII. Analysis - Images Color enhance activations Make it snazzy! Export to photoshop! Superimpose boundaries
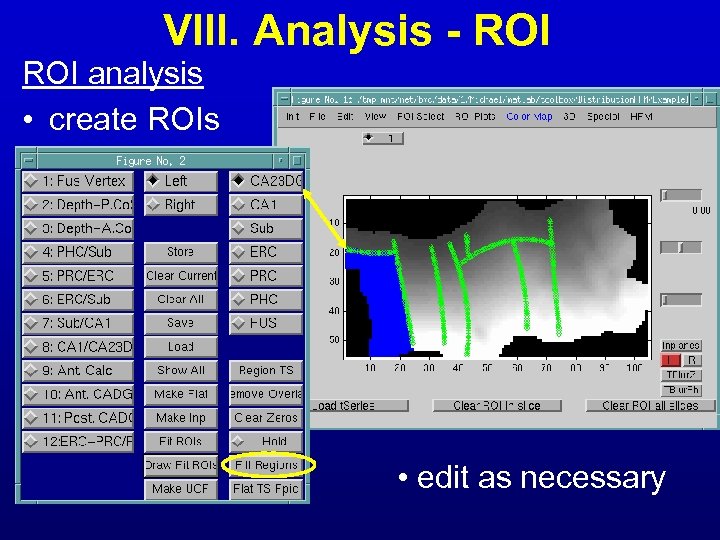 VIII. Analysis - ROI analysis • create ROIs • edit as necessary
VIII. Analysis - ROI analysis • create ROIs • edit as necessary
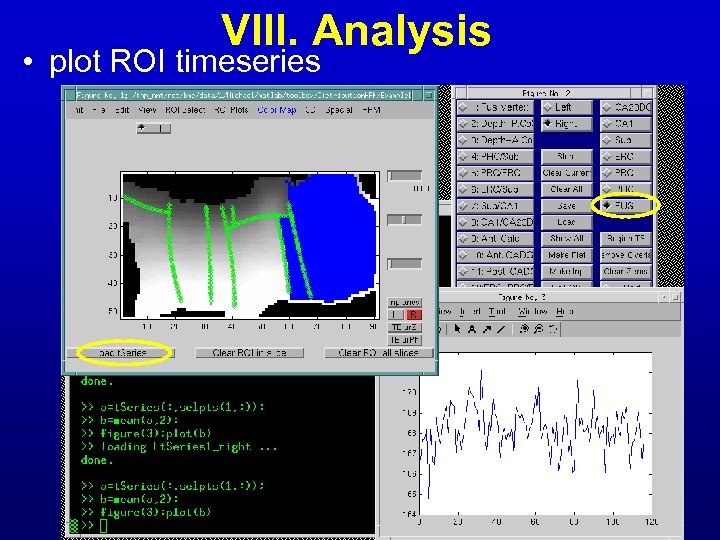 VIII. Analysis • plot ROI timeseries
VIII. Analysis • plot ROI timeseries
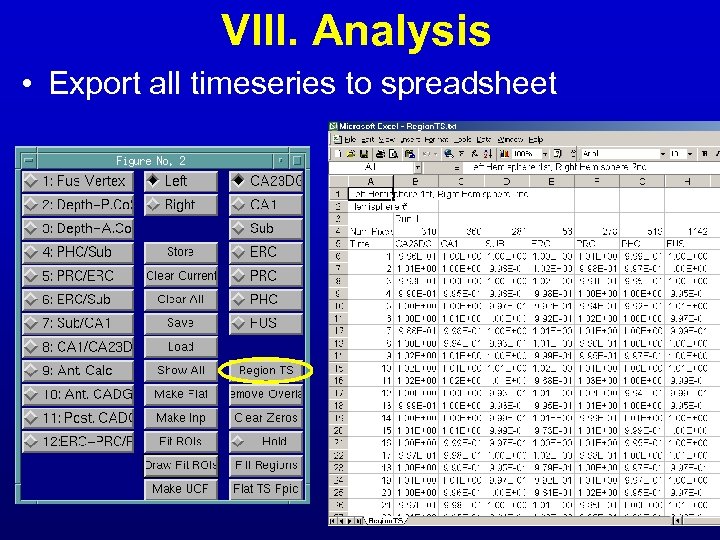 VIII. Analysis • Export all timeseries to spreadsheet
VIII. Analysis • Export all timeseries to spreadsheet
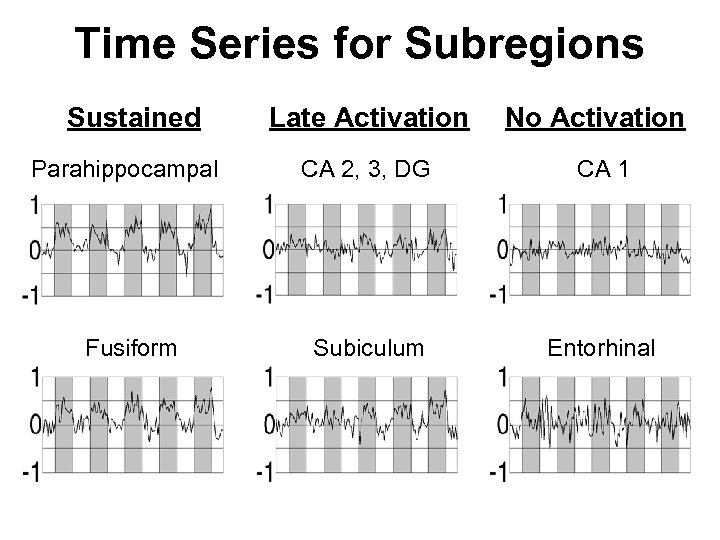 Time Series for Subregions Sustained Parahippocampal Fusiform Late Activation No Activation CA 2, 3, DG CA 1 Subiculum Entorhinal
Time Series for Subregions Sustained Parahippocampal Fusiform Late Activation No Activation CA 2, 3, DG CA 1 Subiculum Entorhinal
 Future Releases • Hippocampal Flat Template • Warping • Automated Segmentation
Future Releases • Hippocampal Flat Template • Warping • Automated Segmentation
 Acknowledgements UCLA Medical Scientist Training Program NIH National Research Service Award Ahmanson Foundation Pierson-Lovelace Foundation Brain Mapping Medical Research Organization Tamkin Foundation Alma and Nick Robson Norma and Lyn Lear Jennifer Jones-Simon UCLA School of Medicine Neuropsychiatric Institute Department of Neurology Susan Bookheimer Stephen Engel John Mazziotta Barbara Knowlton Joaquin Fuster Itzhak Fried Charles Wilson Mark Cohen Paul Thompson Bernice Wenzel Gary Small Roger Woods Arthur Toga Russ Poldrack Paul Rodriguez
Acknowledgements UCLA Medical Scientist Training Program NIH National Research Service Award Ahmanson Foundation Pierson-Lovelace Foundation Brain Mapping Medical Research Organization Tamkin Foundation Alma and Nick Robson Norma and Lyn Lear Jennifer Jones-Simon UCLA School of Medicine Neuropsychiatric Institute Department of Neurology Susan Bookheimer Stephen Engel John Mazziotta Barbara Knowlton Joaquin Fuster Itzhak Fried Charles Wilson Mark Cohen Paul Thompson Bernice Wenzel Gary Small Roger Woods Arthur Toga Russ Poldrack Paul Rodriguez


