3da7a468e75cbe187c5d125fb54d5881.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36

Software Engineering Standards Book Series Deborah E. Plummer Group Manager, CS Press August 6 & 7 2001

Program Progress Financial Projections approved by Financial Committee u Negotiated 50% standard reuse terms of agreement w/ IEEE Standards group and a bulk sales agreement u Negotiated copyright terms of agreement with IEEE copyrights manager u Book 1 – telecon completed, revised schedule, manuscript in development u Book 2 - telecon date -TBD u Book 3 -telecon completed, revised schedule, manuscript in development-(ahead of schedule) u IEEE Computer Society Software Engineering Standards Book Series 2

Purpose Under leadership of Roger Fujii, Software Engineering Standards Book Series Editor: Ø Ø Ø Ø Recap mission & strategic focus Goals Manuscript Development Review Sponsorship Finding a Distribution Channel Conclude with action plan and assigned responsibilities for August –December 2001 Schedule next board meeting for 2002 IEEE Computer Society Software Engineering Standards Book Series 3

SWE Standards Book Series Mission Develop SE standards-based knowledge products to increase the use of the standards and benefit software engineering professionals and their organizations. u Objectives: u Increase awareness, influence, and sales of standards-based products for the IEEE Computer Society Ø Support the goals of all involved (IEEE Standards sales group, IEEE CS SESC, IEEE CS) Ø Make a significant contribution to the profession Ø IEEE Computer Society Software Engineering Standards Book Series 4

Organizational Meeting for the Software Engineering Standards Book Series Roger U. Fujii IEEE Computer Society Software Engineering Standards Book Series Editor Sheraton Reston Hotel 6& 7 August 2001 IEEE Computer Society Software Engineering Standards Book Series 5
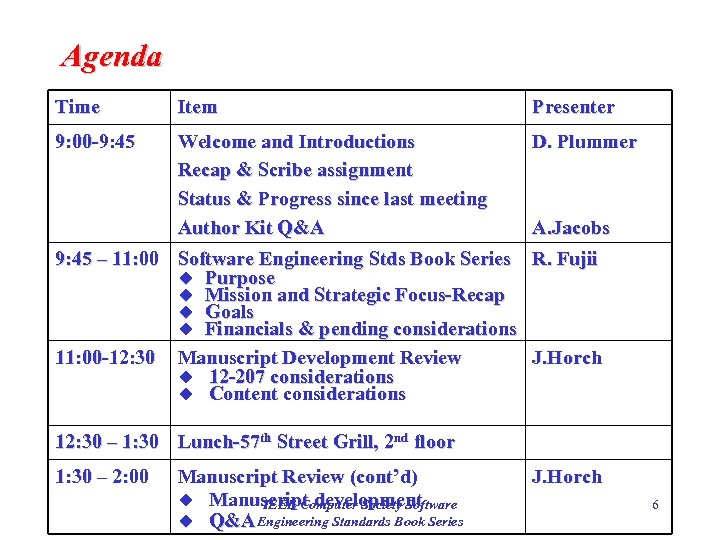
Agenda Time Item Presenter 9: 00 -9: 45 Welcome and Introductions Recap & Scribe assignment Status & Progress since last meeting Author Kit Q&A D. Plummer A. Jacobs 9: 45 – 11: 00 Software Engineering Stds Book Series R. Fujii u Purpose u Mission and Strategic Focus-Recap u Goals u Financials & pending considerations 11: 00 -12: 30 Manuscript Development Review J. Horch u 12 -207 considerations u Content considerations 12: 30 – 1: 30 Lunch-57 th Street Grill, 2 nd floor 1: 30 – 2: 00 Manuscript Review (cont’d) u Manuscript development IEEE Computer Society Software u Q&A Engineering Standards Book Series J. Horch 6
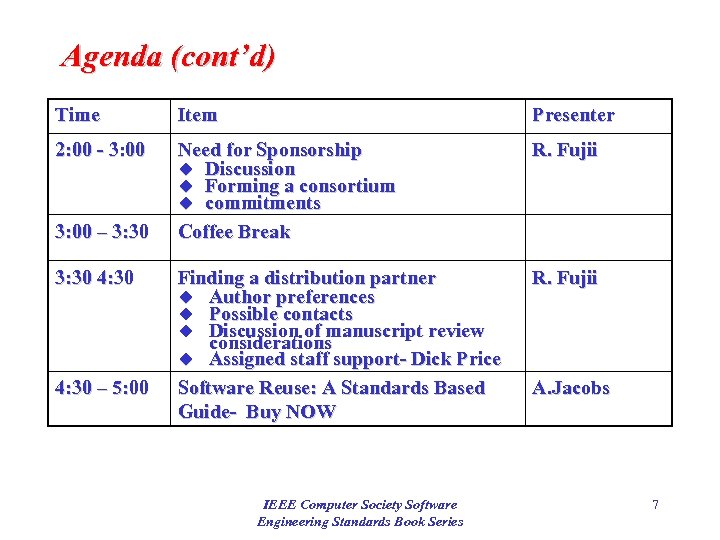
Agenda (cont’d) Time Item Presenter 2: 00 - 3: 00 Need for Sponsorship u Discussion u Forming a consortium u commitments Coffee Break R. Fujii Finding a distribution partner u Author preferences u Possible contacts u Discussion of manuscript review considerations u Assigned staff support- Dick Price Software Reuse: A Standards Based Guide- Buy NOW R. Fujii 3: 00 – 3: 30 4: 30 – 5: 00 IEEE Computer Society Software Engineering Standards Book Series A. Jacobs 7

Purpose u u Develop a series of books for the software engineering standards to serve as reference ‘companion books’ Using the book series products, develop related products and services including hypertext linked electronic books, book series seminars, and professional development and accreditation certificate programs. u Enhance the publication and sales of standards by developing a book series that helps the practitioner more effectively use the IEEE Computer Society software engineering standards. Answer typical questions from industry: “Explain 12207 and how SQA, V&V, project management, etc are implemented using 12207 for a specific project. ” IEEE Computer Society Software Engineering Standards Book Series 8

Mission Statement Provide products that promote the sale and development of IEEE Computer Society software engineering standards. u Establish an effective process to provide the correct product, at the right time and price, to the customer. This effective work process includes volunteers in vital roles (product development) and results in a revitalized CS Press. u Provide the computer science professional with standards related products and services to enable software developers with the knowledge and tools to produce software in compliance with 12207 and IEEE software standards. u IEEE Computer Society Software Engineering Standards Book Series 9

Goals u Complete (in pipeline) the initial set of the IEEE Computer Society software engineering standards book series by Q 4 2001. Ø Ø Ø Ø ISO/IEC 12207 Overview Software Project Management Software Quality Assurance Software Verification and Validation Software Testing Software Engineering Standards Roadmap Software Reuse Require first product in editing by Q 4 2001. u Establish distribution partner and sponsorship by November 1 2001. u IEEE Computer Society Software Engineering Standards Book Series 10

Basic Parameters to the Book Series Written as guidebooks following the 12207 process and IEEE Computer Society software engineering standards - Provide interpretation of the standards, describe the meaning/intent of the standard (examples for different industry sectors), provide techniques and methods to implement the standard process, provide examples, and supply sample exercise problems (optional) u All books will have the same look (cover) u Use 7 x 10 page size u Book size can be up to 500 or more sheets (1000 pages) u Bundling the standard with the book u IEEE Computer Society Software Engineering Standards Book Series 11

Book Series Categories Integrative (Overview) q q Roadmap to ISO/IEC 12207 Software Taxomony Core Standards q Software Quality Assurance q Software Verification and Validation q Software Project Management q Software Testing q Software Design Derivative Standards q q Software Reuse Software Risk Management IEEE Computer Society Software Engineering Standards Book Series 12
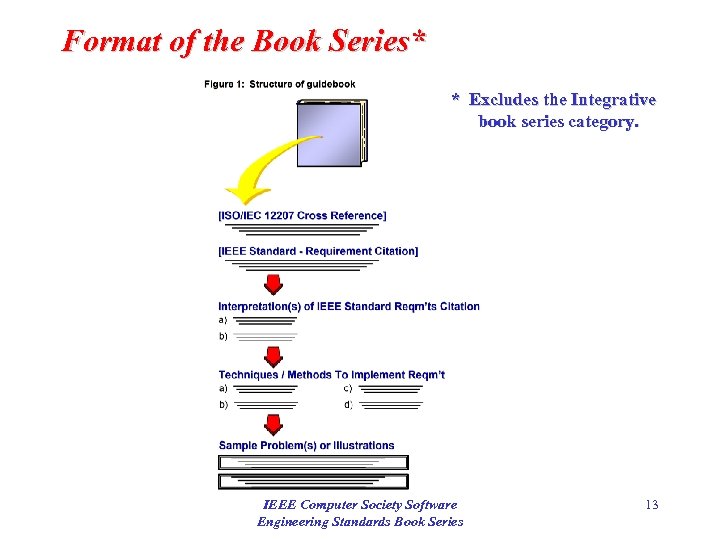
Format of the Book Series* * Excludes the Integrative book series category. IEEE Computer Society Software Engineering Standards Book Series 13
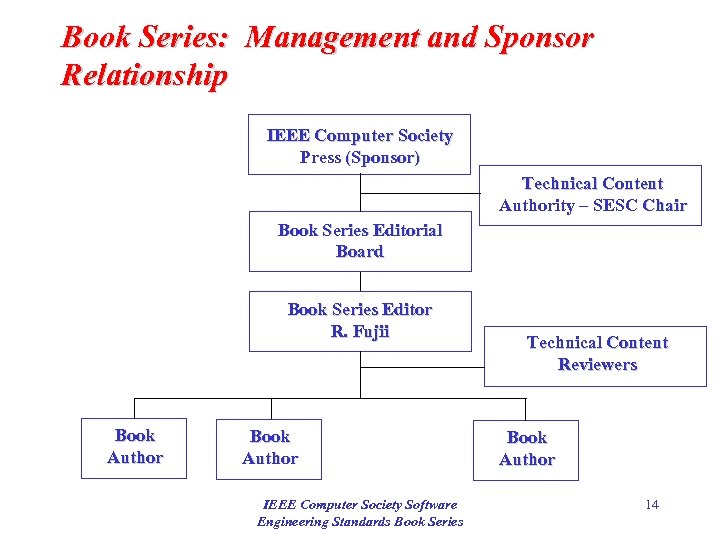
Book Series: Management and Sponsor Relationship IEEE Computer Society Press (Sponsor) Technical Content Authority – SESC Chair Book Series Editorial Board Book Series Editor R. Fujii Book Author IEEE Computer Society Software Engineering Standards Book Series Technical Content Reviewers Book Author 14

Members of the Editorial Board Roger U. Fujii (Chair) u Paul Croll u James Moore u Mark Christensen u Richard Thayer u CS Press (Angela Burgess, Deborah Plummer, Dick Price, Anne Jacobs, Bob Werner) u IEEE Computer Society Software Engineering Standards Book Series 15
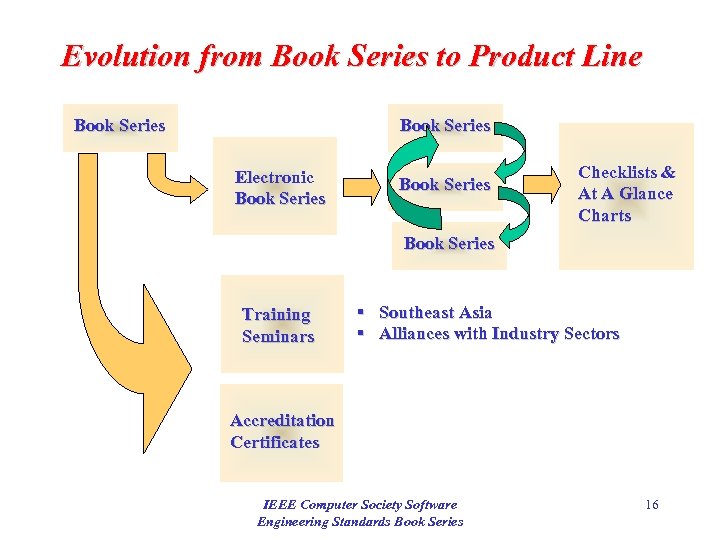
Evolution from Book Series to Product Line Book Series Electronic Book Series Checklists & At A Glance Charts Book Series Training Seminars § Southeast Asia § Alliances with Industry Sectors Accreditation Certificates IEEE Computer Society Software Engineering Standards Book Series 16

CS Press Support u u Facilitate achievement of goals set by the SWE Standards Book Series Board and the CS Press Publisher Establish an effective working process to produce knowledge products developed by the SWE Standards Book Series Partner with each volunteer author in their vital role as product developers Produce books according to the required schedule IEEE Computer Society Software Engineering Standards Book Series 17

Suggested Timing of Books for Availability to the Market Book 1 & 2: Authors complete manuscript by 1 October 2001; In print May 2002 u Book 3 & 4: Authors complete manuscript by 1 January 2002; In print August 2002 u Book 5, 6 & 7: Author completes manuscript by 1 April 2002; In print November 2002 u IEEE Computer Society Software Engineering Standards Book Series 18

Royalty Terms: Author meets mutually agreed upon schedules and facilitates CS Press process requirements to ensure the book is produced and in print on time. u 0 -2, 500 copies=12% royalty u 2, 500 -7, 000 copies = 15% royalty u 7000 -10, 000 copies=17. 5% royalty u 10, 000 & up copies = 20% royalty IEEE Computer Society Software Engineering Standards Book Series 19

Author Kit Contract u IEEE copyright form u Project Schedule u Standardized MS Word template u Copy of the appropriate standards (for author use only) u Author Marketing questionnaire u IEEE Computer Society Software Engineering Standards Book Series 20
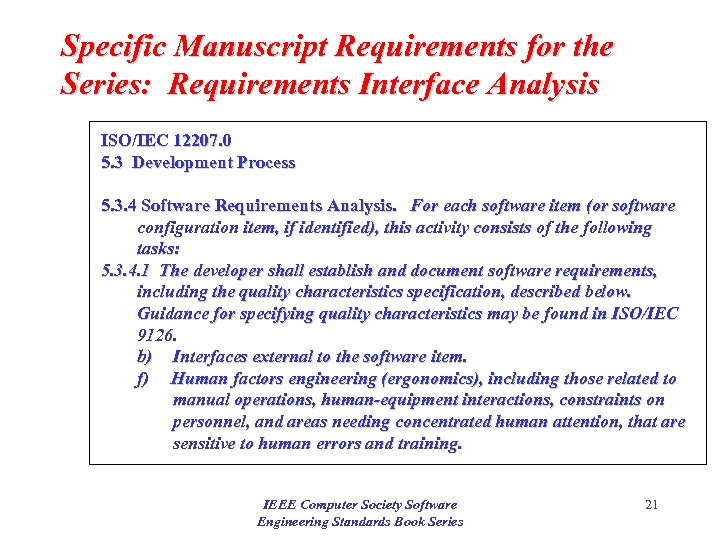
Specific Manuscript Requirements for the Series: Requirements Interface Analysis ISO/IEC 12207. 0 5. 3 Development Process 5. 3. 4 Software Requirements Analysis. For each software item (or software configuration item, if identified), this activity consists of the following tasks: 5. 3. 4. 1 The developer shall establish and document software requirements, including the quality characteristics specification, described below. Guidance for specifying quality characteristics may be found in ISO/IEC 9126. b) Interfaces external to the software item. f) Human factors engineering (ergonomics), including those related to manual operations, human-equipment interactions, constraints on personnel, and areas needing concentrated human attention, that are sensitive to human errors and training. IEEE Computer Society Software Engineering Standards Book Series 21

Specific Manuscript Requirements for the Series: Requirements Interface Analysis ISO/IEC 12207. 0 5. 3. 4. 2 The developer shall evaluate the software requirements considering the criteria listed below. The results of the evaluation shall be documented. b) External consistency with system requirements c) Internal consistency The role of software V&V is to provide objective evidence, analysis, or conclusions that the developer has complied with ISO/IEC 12207 processes. The IEEE Standard for Software Verification and Validation (IEEE Std 1012) addresses the ISO/IEC 12207 requirements in the following manner. IEEE Std 1012 -1998 5. 4. 2 Requirements V&V Activity (3) Interface Analysis. Verify and validate that the requirements for software interfaces with hardware, user, operator, and other systems are correct, consistent, complete, accurate, and testable. The task criteria are as follows: IEEE Computer Society Software Engineering Standards Book Series 22
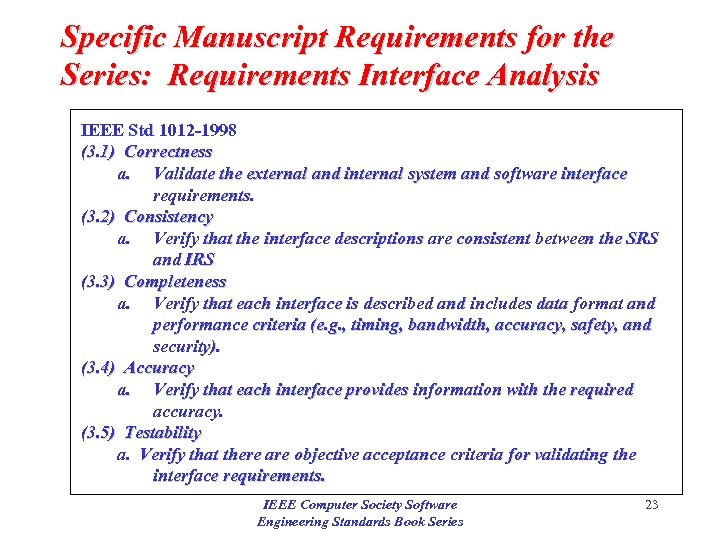
Specific Manuscript Requirements for the Series: Requirements Interface Analysis IEEE Std 1012 -1998 (3. 1) Correctness a. Validate the external and internal system and software interface requirements. (3. 2) Consistency a. Verify that the interface descriptions are consistent between the SRS and IRS (3. 3) Completeness a. Verify that each interface is described and includes data format and performance criteria (e. g. , timing, bandwidth, accuracy, safety, and security). (3. 4) Accuracy a. Verify that each interface provides information with the required accuracy. (3. 5) Testability a. Verify that there are objective acceptance criteria for validating the interface requirements. IEEE Computer Society Software Engineering Standards Book Series 23

Specific Manuscript Requirements for the Series: Requirements Interface Analysis Interpretation of the Standards. V&V must verify and validate all requirements originating from and sent to all interfaces of the software under examination. These interfaces include the user, operator, external and internal hardware components, external and internal software components, database systems, and environmental or physical laws that influence system behavior. The sources of the interface descriptions can be found in many documents and specifications including: 1. Software Requirements Specification (SRSs) 2. Interface Requirements Specifications (IRSs) 3. Concept Documentation 4. Interface Control Documents (ICDs) 5. Hardware Specifications 6. COTS Technical Specifications 7. User Documentation and Manuals 8. Operator Manuals 9. Database Manuals and Database Use Case Descriptions Figure 5. 3. 1 -1 is a system block diagram that illustrates the different types of interfaces existing in a system. The output of the interface analysis consist of IEEE Computer Society each analysis conducted. 24 anomaly reports and task summary reports for. Software Engineering Standards Book Series
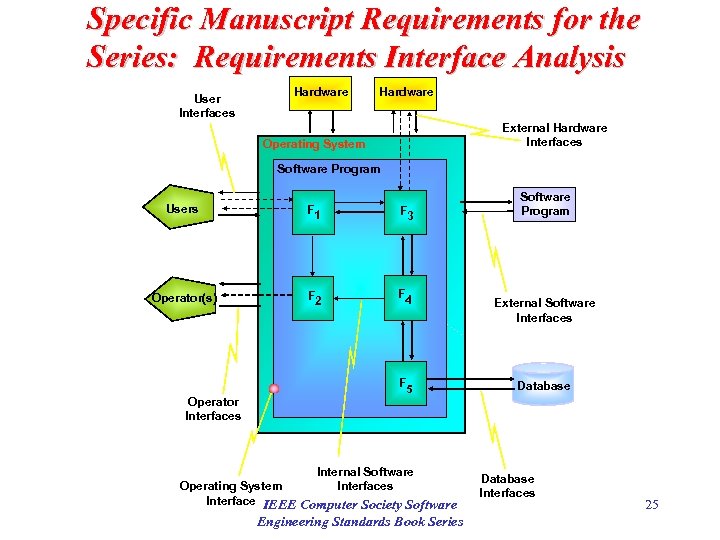
Specific Manuscript Requirements for the Series: Requirements Interface Analysis User Interfaces Hardware External Hardware Interfaces Operating System Software Program Users F 1 F 3 Operator(s) F 2 F 4 F 5 Software Program External Software Interfaces Database Operator Interfaces Internal Software Interfaces Operating System Interface IEEE Computer Society Software Engineering Standards Book Series Database Interfaces 25

Specific Manuscript Requirements for the Series: Requirements Interface Analysis An example of a task summary report is illustrated in Figure 5. 3. 1 -2. Techniques/Methods. The system block diagram showing each of the different interfaces is a good starting point to analyze the interface requirements. The most widely used techniques and methods for analyzing the interface requirements are: • Interface Input/Output Requirements Matrix • Interface Control Flow Diagrams • Interface Data Flow Diagrams • Hierarchical Input/Process/Output (HIPO) Charts A disciplined V&V approach is applied to analyze each interface shown in the system block diagram using an interface analysis technique such as the ones listed above. A detailed checklist of questions and analysis are applied to each interface as a rigorous method of verifying and validating the interfaces for correctness, consistency, completeness, accuracy, and testability. The sample checklist of questions and analysis to apply to each interface are listed in Figure 5. 3. 1 -3. IEEE Computer Society Software Engineering Standards Book Series 26
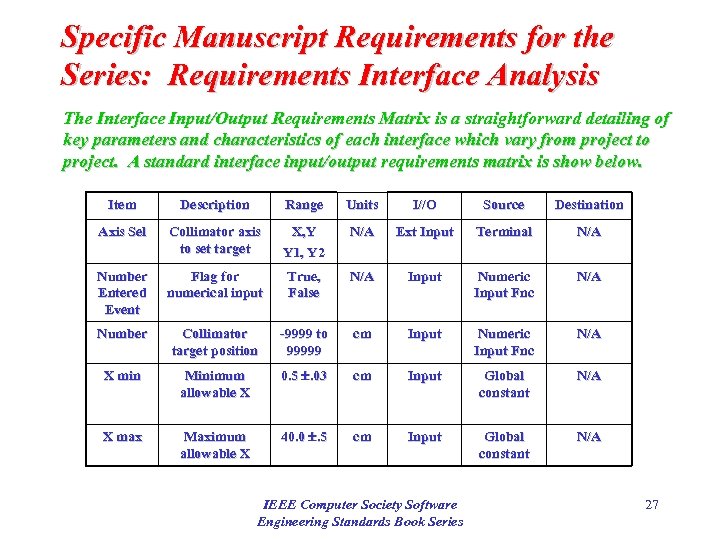
Specific Manuscript Requirements for the Series: Requirements Interface Analysis The Interface Input/Output Requirements Matrix is a straightforward detailing of key parameters and characteristics of each interface which vary from project to project. A standard interface input/output requirements matrix is show below. Item Description Range Units I//O Source Destination Axis Sel Collimator axis to set target X, Y Y 1, Y 2 N/A Ext Input Terminal N/A Number Entered Event Flag for numerical input True, False N/A Input Numeric Input Fnc N/A Number Collimator target position -9999 to 99999 cm Input Numeric Input Fnc N/A X min Minimum allowable X 0. 5 . 03 cm Input Global constant N/A X max Maximum allowable X 40. 0 . 5 cm Input Global constant N/A IEEE Computer Society Software Engineering Standards Book Series 27

Specific Manuscript Requirements for the Series: Requirements Interface Analysis The V&V analysis process of constructing the matrix (if not already provided in one of the development specifications) affords the V&V analyst the ability to question and analyze the data. For example, one can ask whether the precision and range of values listed for each item accurate and consistent with the performance of the software and system requirements. Does the precision of the values impose constraints on the accuracy of computations performed by program functions (double precision or precision to the correct decimal point). Are the units of measure consistent with the units of measure used by the software functions and system. Are the inputs and outputs correctly specified or are there missing input/outputs. Does the source of the interface have the same consistency of the interface as required by the software (for example, will any interfacing hardware or software system provide the data to the accuracy and precision as stated in the interface? ). Are any constraints identified by the source or destination consistent with the system requirements and are testing of such constraints feasible. By following an orderly process of analysis of each interface, a thorough V&V examination and analysis is achieved. Typical checklists of questions and analyses are shown in Figure 5. 3. 1 -3. IEEE Computer Society Software Engineering Standards Book Series 28

Specific Manuscript Requirements for the Series: Requirements Interface Analysis Sample Problems and Illustrations. IEEE Computer Society Software Engineering Standards Book Series 29

Summary Return appropriate forms from the author’s kit to CS Press u Work on book schedule with Book Series Editor and CS Press u Develop draft material with Book Series Editor and prepare a sample section/chapter for review. u Work with Book Series Editor, Assistant Publisher and Group Manager, Press to solicit Distribution partners and sponsorship for series. u Help evolve the concept of the software engineering standards book series product line u IEEE Computer Society Software Engineering Standards Book Series 30

V&V Book Outline u Chapter 1: Basic Principles of Verification and Validation History of V&V Ø V&V Objectives Ø Relationship of V&V to PM, QA, CM, Testing, and Development • Independent V&V • Audience/Field of Application Ø u Chapter 2: Relationship of V&V to Software Engineering Standards V&V to ISO/IEC 12207. 0 Ø V&V to IEEE Software Engineering Standards Ø Organization of Book to ISO/IEC 12207. 0 Life Cycle Processes Ø IEEE Computer Society Software Engineering Standards Book Series 31

V&V Book Outline u Chapter 3: Acquisition Process V&V Initiation Ø Request-for-proposal (tender) preparation Ø Supplier monitoring Ø Acceptance and completion Ø u Chapter 4: Supply Process V&V Ø Ø Ø Ø Initiation Preparation and Response (? ? ) Contract Planning Execution and Control Review and Evaluation Delivery and Completion (? ? ) IEEE Computer Society Software Engineering Standards Book Series 32

V&V Book Outline u Chapter 5: Development Process V&V Ø Ø Ø Process Implementation Systems Requirements Analysis System Architecture Design Software Requirements Analysis Software Architecture Design/Software Detailed Design Software Coding and Testing Software Integration Software Qualification Testing System Integration System Qualification Testing Software Installation Software Acceptance Support IEEE Computer Society Software Engineering Standards Book Series 33

V&V Book Outline u Chapter 6: Operation Process V&V Process Implementation Ø Operational Testing Ø System Operation (? ? ) Ø User Support Ø u Chapter 7: Maintenance Process V&V Ø Ø Ø Process Implementation Problems and Modification Analysis Modification Implementation Migration Software Retirement IEEE Computer Society Software Engineering Standards Book Series 34

V&V Book Outline Chapter 9: Management of V&V u Chapter 10: Support Life Cycle Processes V&V u Ø Ø Ø Documentation Process Configuration Process Quality Assurance Joint Review Process Audit Process Problem Resolution Process IEEE Computer Society Software Engineering Standards Book Series 35

3da7a468e75cbe187c5d125fb54d5881.ppt