334136c116e84928dc86ed1433fcca76.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 Software Engineering for Capstone Courses Richard Anderson CSE 481 b Winter 2007
Software Engineering for Capstone Courses Richard Anderson CSE 481 b Winter 2007
 Announcements n n HW 2, Due Thursday, Jan 19 Presentations, Tuesday Jan 23 n n n 15 minute presentation + 3 minutes discussion Power. Point slides Group order: A, B, C, D
Announcements n n HW 2, Due Thursday, Jan 19 Presentations, Tuesday Jan 23 n n n 15 minute presentation + 3 minutes discussion Power. Point slides Group order: A, B, C, D
 Today’s lecture n n Software Engineering vs. Computer Science Software Life Cycle Requirements Risk Analysis
Today’s lecture n n Software Engineering vs. Computer Science Software Life Cycle Requirements Risk Analysis
 Key aspects of software engineering n n n Large scale projects Long lasting projects External constraints n n E. g. , Make money, Support a business process, Don’t kill anyone Life cycle that includes many nonprogramming activities
Key aspects of software engineering n n n Large scale projects Long lasting projects External constraints n n E. g. , Make money, Support a business process, Don’t kill anyone Life cycle that includes many nonprogramming activities
 SE for Capstone Courses Computer Science n n Process Useful Partial Life Cycle Realistic Challenge Meet a Delivery Software Engineering
SE for Capstone Courses Computer Science n n Process Useful Partial Life Cycle Realistic Challenge Meet a Delivery Software Engineering
 Life Cycle
Life Cycle
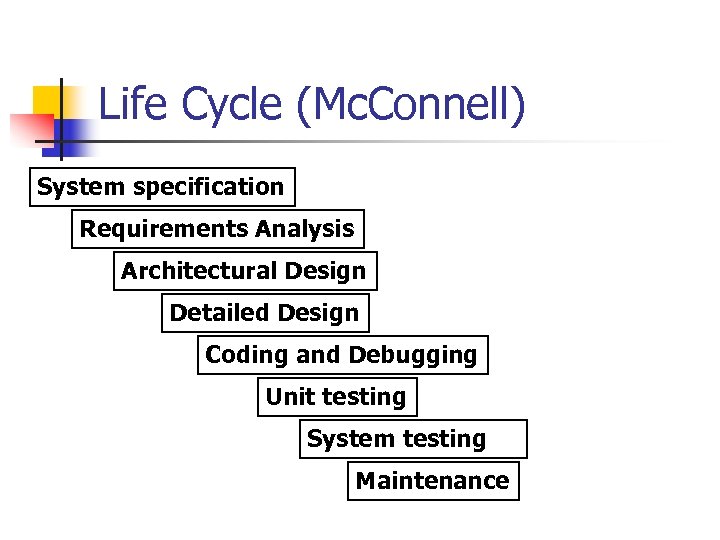 Life Cycle (Mc. Connell) System specification Requirements Analysis Architectural Design Detailed Design Coding and Debugging Unit testing System testing Maintenance
Life Cycle (Mc. Connell) System specification Requirements Analysis Architectural Design Detailed Design Coding and Debugging Unit testing System testing Maintenance
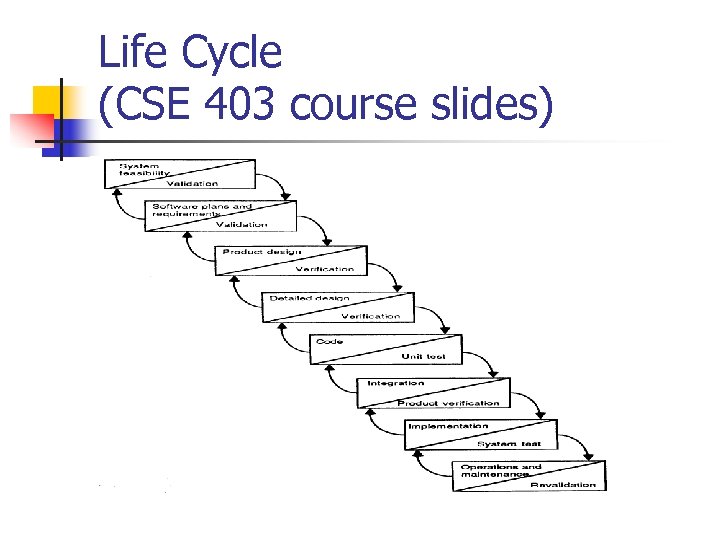 Life Cycle (CSE 403 course slides)
Life Cycle (CSE 403 course slides)
 Requirements on requirements n n Who are they for? What are they for? n n Pitch to management Fodder for market study Basis for legal contract Easy to understand, concise, complete, unambiguous, . . .
Requirements on requirements n n Who are they for? What are they for? n n Pitch to management Fodder for market study Basis for legal contract Easy to understand, concise, complete, unambiguous, . . .
 Requirements n n "Gather and document the functions that the application should perform for the users in the users' language and from the users' perspective" Requirements should neither constrain nor define methods of implementation
Requirements n n "Gather and document the functions that the application should perform for the users in the users' language and from the users' perspective" Requirements should neither constrain nor define methods of implementation
 Customers n n (Almost) every large software project has a customer who is paying the bills Project requirements driven by this customer
Customers n n (Almost) every large software project has a customer who is paying the bills Project requirements driven by this customer
 Approaches to requirements n n n Personas Scenarios Use cases
Approaches to requirements n n n Personas Scenarios Use cases
 Project Pitch n n What you are going to do value it delivers to the customer is the novelty are the risks
Project Pitch n n What you are going to do value it delivers to the customer is the novelty are the risks
 Is dog food good for you? n Dog food (verb), to use your own software
Is dog food good for you? n Dog food (verb), to use your own software
 Risk n Exposure to the chance of injury or loss n For a software project: n n n Failure to deliver on time Exceeding resource limits Not meeting quality threshold
Risk n Exposure to the chance of injury or loss n For a software project: n n n Failure to deliver on time Exceeding resource limits Not meeting quality threshold
 Risk analysis n Types of Risk n n n Code Development External Dependency Technology Personnel Requirements Change
Risk analysis n Types of Risk n n n Code Development External Dependency Technology Personnel Requirements Change
 Sources of Risk I n Development risks n n n Code harder to develop than thought Learning curve on new facilities Expected facilities not available Need to iterate on requirements / design Performance Issues Trigger other bugs
Sources of Risk I n Development risks n n n Code harder to develop than thought Learning curve on new facilities Expected facilities not available Need to iterate on requirements / design Performance Issues Trigger other bugs
 Sources of Risk II n Integration risks n n n Parts don't fit together Integration reveals bugs Integration reveals design errors Need to rewrite code after integration Code left out
Sources of Risk II n Integration risks n n n Parts don't fit together Integration reveals bugs Integration reveals design errors Need to rewrite code after integration Code left out
 Sources of Risk III n Testing risks n n n Bugs will be found Bugs won't be found Complexity of testing matrix Deployment beyond development machines Difficulties in test automation and test tools UI and Workflow feedback
Sources of Risk III n Testing risks n n n Bugs will be found Bugs won't be found Complexity of testing matrix Deployment beyond development machines Difficulties in test automation and test tools UI and Workflow feedback
 Sources of Risk IV n Requirements Risks n n n New requirements introduced Change in Specification Inconsistencies in requirements User feedback Market conditions Platform and technology changes
Sources of Risk IV n Requirements Risks n n n New requirements introduced Change in Specification Inconsistencies in requirements User feedback Market conditions Platform and technology changes
 Sources of Risk V n Deployment Risks n n n Packaging distributable Rights and licensing of components Legal signoff Marketing signoff Systems configuration
Sources of Risk V n Deployment Risks n n n Packaging distributable Rights and licensing of components Legal signoff Marketing signoff Systems configuration
 Sources of Risk VI n People risks n n n n Unexpected Loss of Personnel Illness Vacation Other demands on time Group friction Inaccurate evaluation of skills Drop in performance
Sources of Risk VI n People risks n n n n Unexpected Loss of Personnel Illness Vacation Other demands on time Group friction Inaccurate evaluation of skills Drop in performance
 What to do with risk analysis n n n Avoid the risk Transfer risk off the critical path Buy information n Publicize risk n n n Bring in outside help Prototype The sky is falling Schedule to accommodate some risk Monitor risks as project progresses
What to do with risk analysis n n n Avoid the risk Transfer risk off the critical path Buy information n Publicize risk n n n Bring in outside help Prototype The sky is falling Schedule to accommodate some risk Monitor risks as project progresses


