95ab3aef1e924619ef9f8a0e7c3bd738.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35
 Software Engineering Chapter 16 User Interface Design Ku-Yaw Chang canseco@mail. dyu. edu. tw Assistant Professor Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering Da-Yeh University Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design
Software Engineering Chapter 16 User Interface Design Ku-Yaw Chang canseco@mail. dyu. edu. tw Assistant Professor Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering Da-Yeh University Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design
 Objectives Understand a number of user interface design principles Have been introduced to several interaction styles and understand when these are most appropriate Understand when to use graphical and textural presentation of information Know what is involved in the principal activities in the user interface design process Understand usability attributes and have been introduced to different approaches to interface evaluation Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 2
Objectives Understand a number of user interface design principles Have been introduced to several interaction styles and understand when these are most appropriate Understand when to use graphical and textural presentation of information Know what is involved in the principal activities in the user interface design process Understand usability attributes and have been introduced to different approaches to interface evaluation Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 2
 Preamble Software engineers often take responsibility for user interface design n Only large organizations employ specialist interface designers Focus on the design process for user interfaces n Graphical user interfaces Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 3
Preamble Software engineers often take responsibility for user interface design n Only large organizations employ specialist interface designers Focus on the design process for user interfaces n Graphical user interfaces Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 3
 Preamble Take into account the physical and mental capabilities of the people n People have a limited short-term memory Seven items of information n People make mistakes Warning messages and alarms put more stress on users n People have a diverse range of physical capabilities See better / color-blind n People have different interaction preferences Pictures or text Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 4
Preamble Take into account the physical and mental capabilities of the people n People have a limited short-term memory Seven items of information n People make mistakes Warning messages and alarms put more stress on users n People have a diverse range of physical capabilities See better / color-blind n People have different interaction preferences Pictures or text Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 4
 User Interface Design Principles Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 5
User Interface Design Principles Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 5
 Contents 16. 1 Design issues 16. 2 The UI design process 16. 3 User analysis 16. 4 User interface prototyping 16. 5 Interface evaluation Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 6
Contents 16. 1 Design issues 16. 2 The UI design process 16. 3 User analysis 16. 4 User interface prototyping 16. 5 Interface evaluation Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 6
 Design Issues Two key questions n n How should the user interact with the computer system? How should information from the computer system be presented to the user? Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 7
Design Issues Two key questions n n How should the user interact with the computer system? How should information from the computer system be presented to the user? Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 7
 User Interaction User interaction n Issue commands and associated data to the computer system Five primary styles n n n Direct manipulation Menu selection Form fill-in Command language Natural language Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 8
User Interaction User interaction n Issue commands and associated data to the computer system Five primary styles n n n Direct manipulation Menu selection Form fill-in Command language Natural language Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 8
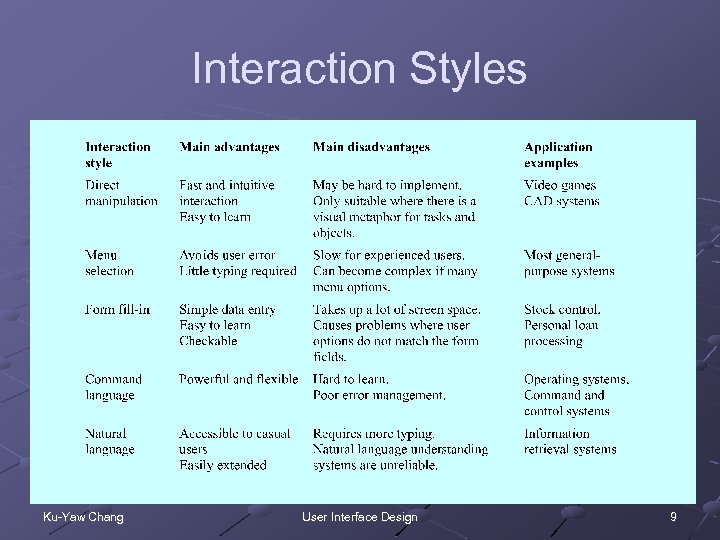 Interaction Styles Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 9
Interaction Styles Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 9
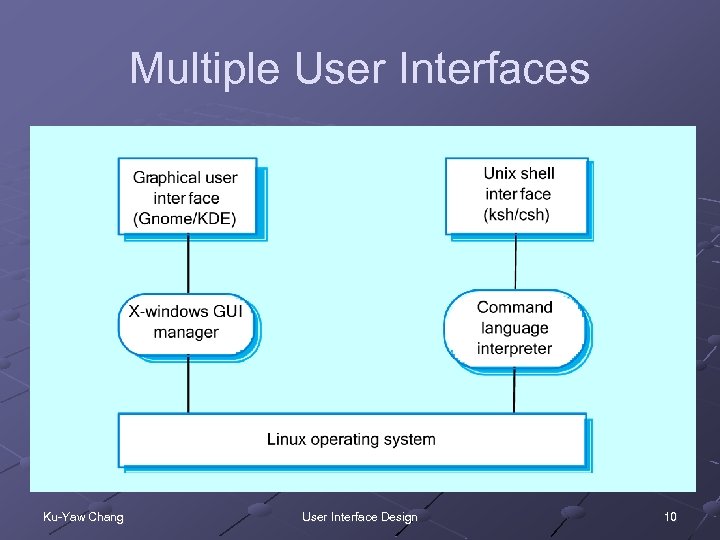 Multiple User Interfaces Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 10
Multiple User Interfaces Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 10
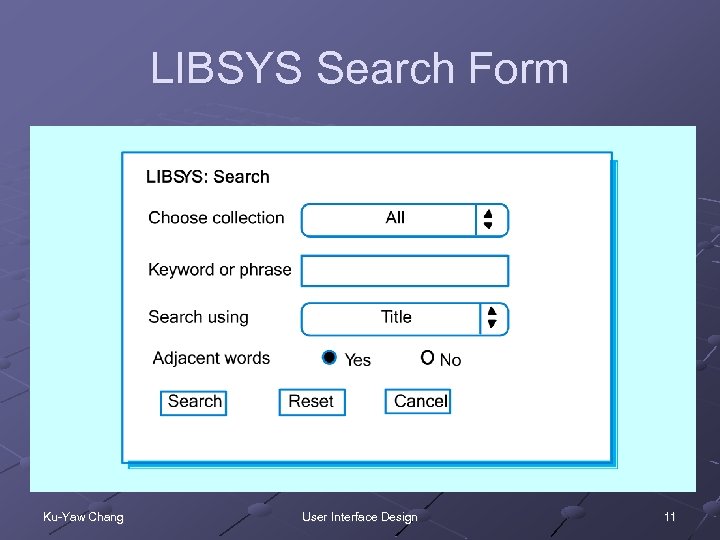 LIBSYS Search Form Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 11
LIBSYS Search Form Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 11
 Information Presentation A good design guideline n To keep the software required for information presentation separate from the information itself Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 12
Information Presentation A good design guideline n To keep the software required for information presentation separate from the information itself Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 12
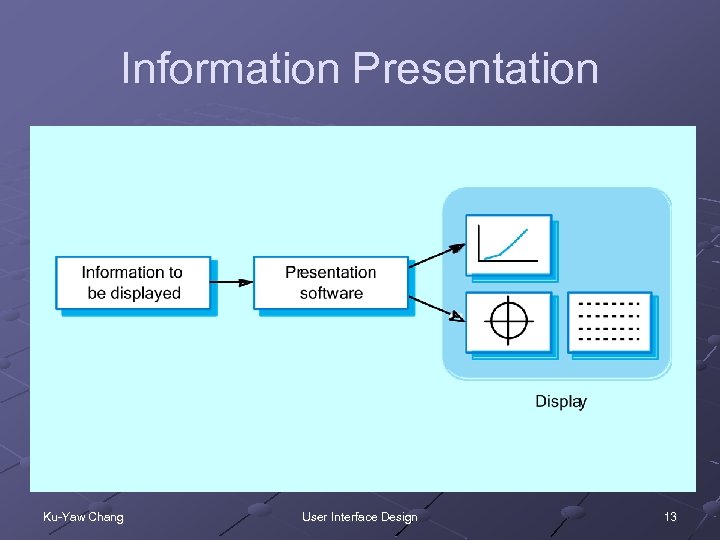 Information Presentation Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 13
Information Presentation Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 13
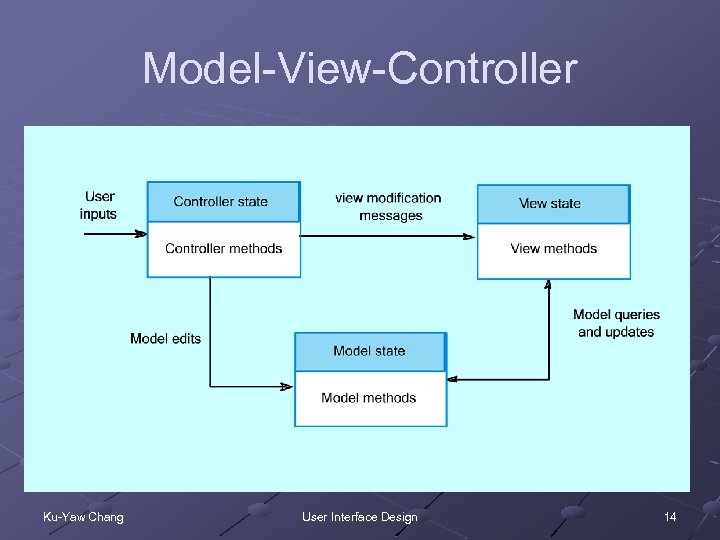 Model-View-Controller Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 14
Model-View-Controller Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 14
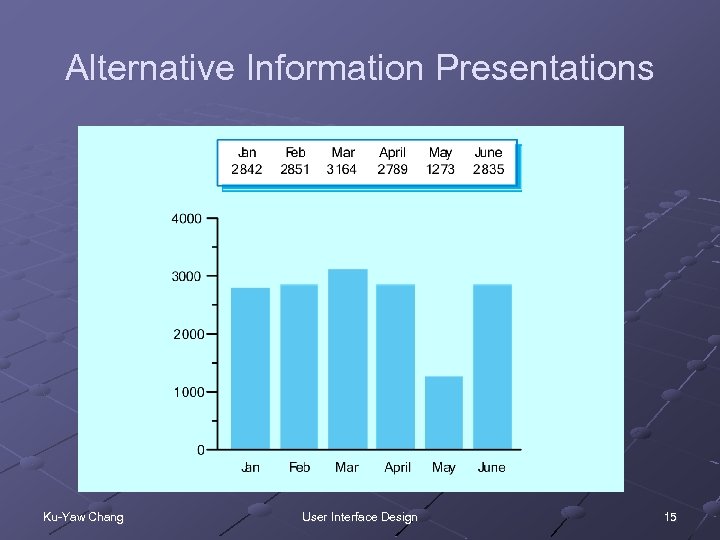 Alternative Information Presentations Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 15
Alternative Information Presentations Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 15
 Presentation Methods Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 16
Presentation Methods Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 16
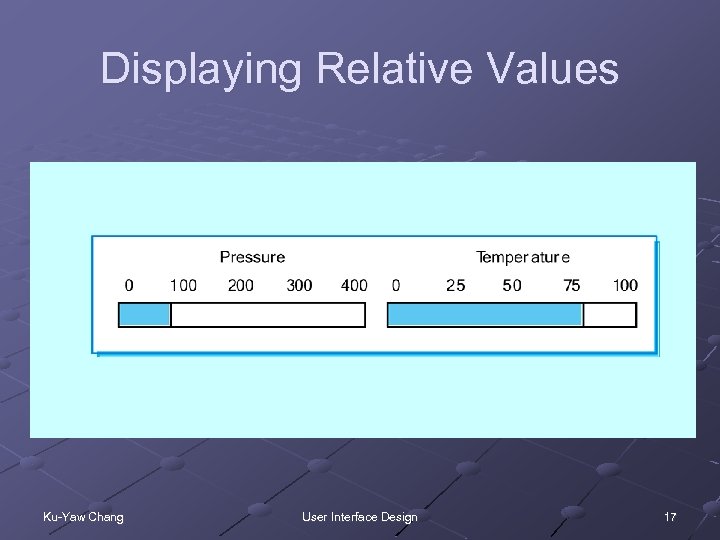 Displaying Relative Values Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 17
Displaying Relative Values Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 17
 Design Factors in Message Wording Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 18
Design Factors in Message Wording Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 18
 Color Displays Color adds an extra dimension to an interface and can help the user understand complex information structures. Color can be used to highlight exceptional events. Common mistakes in the use of color in interface design include: n n The use of color to communicate meaning; The over-use of color in the display. Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 19
Color Displays Color adds an extra dimension to an interface and can help the user understand complex information structures. Color can be used to highlight exceptional events. Common mistakes in the use of color in interface design include: n n The use of color to communicate meaning; The over-use of color in the display. Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 19
 Color Use Guidelines Limit the number of colors used and be conservative in their use. n n 4 to 5 in a window 7 in a system interface Use color change to show a change in system status. Use color coding to support the task that users are trying to perform. Use color coding in a thoughtful and consistent way. Be careful about color pairings. n Red and blue Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 20
Color Use Guidelines Limit the number of colors used and be conservative in their use. n n 4 to 5 in a window 7 in a system interface Use color change to show a change in system status. Use color coding to support the task that users are trying to perform. Use color coding in a thoughtful and consistent way. Be careful about color pairings. n Red and blue Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 20
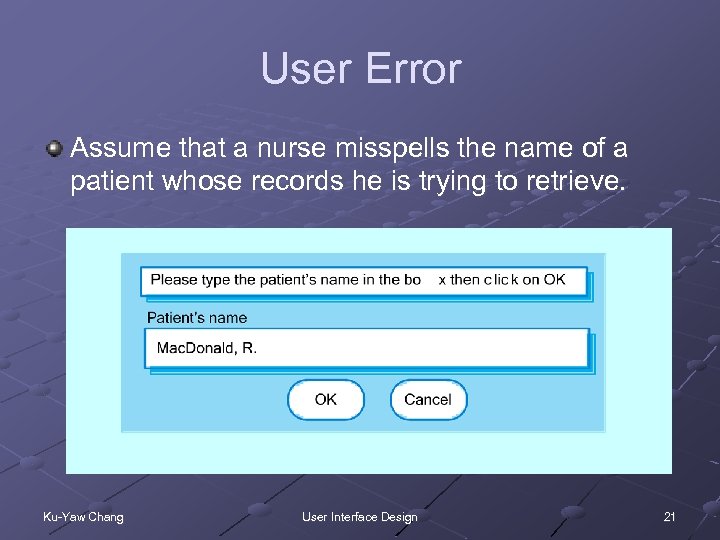 User Error Assume that a nurse misspells the name of a patient whose records he is trying to retrieve. Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 21
User Error Assume that a nurse misspells the name of a patient whose records he is trying to retrieve. Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 21
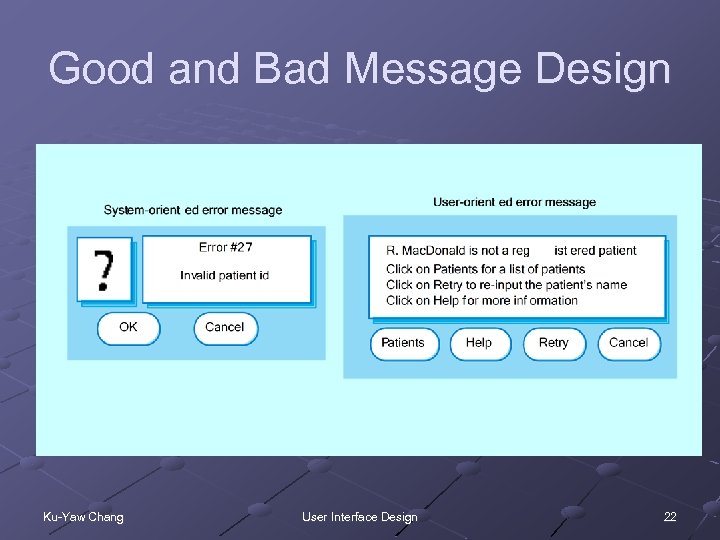 Good and Bad Message Design Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 22
Good and Bad Message Design Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 22
 Contents 16. 1 Design issues 16. 2 The UI design process 16. 3 User analysis 16. 4 User interface prototyping 16. 5 Interface evaluation Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 23
Contents 16. 1 Design issues 16. 2 The UI design process 16. 3 User analysis 16. 4 User interface prototyping 16. 5 Interface evaluation Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 23
 The UI Design Process An interactive process n User interact with designers and interface prototypes Three core activities n User analysis An understanding of the tasks that users do, their working environment, how they interact with other people and so on n System prototyping The evolution of the interface n Interface evaluation Collect information about users’ actual experience Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 24
The UI Design Process An interactive process n User interact with designers and interface prototypes Three core activities n User analysis An understanding of the tasks that users do, their working environment, how they interact with other people and so on n System prototyping The evolution of the interface n Interface evaluation Collect information about users’ actual experience Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 24
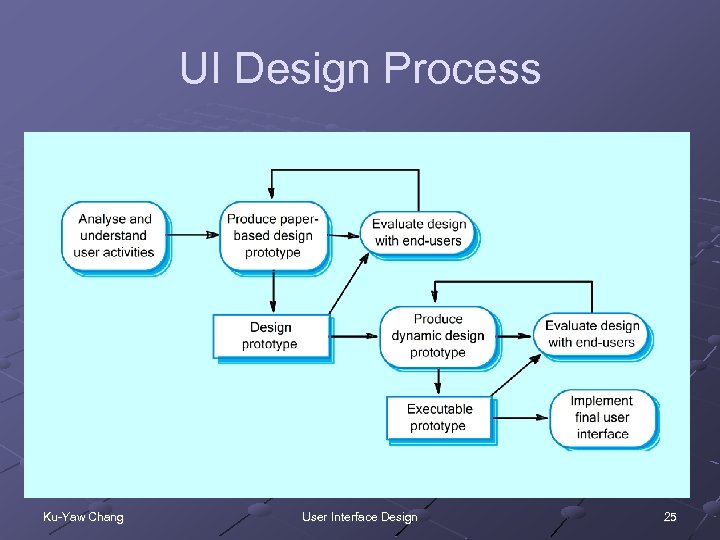 UI Design Process Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 25
UI Design Process Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 25
 Contents 16. 1 Design issues 16. 2 The UI design process 16. 3 User analysis 16. 4 User interface prototyping 16. 5 Interface evaluation Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 26
Contents 16. 1 Design issues 16. 2 The UI design process 16. 3 User analysis 16. 4 User interface prototyping 16. 5 Interface evaluation Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 26
 Analysis Techniques Task analysis n Models the steps involved in completing a task. Interviewing and questionnaires n Asks the users about the work they do. Ethnography n Observes the user at work Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 27
Analysis Techniques Task analysis n Models the steps involved in completing a task. Interviewing and questionnaires n Asks the users about the work they do. Ethnography n Observes the user at work Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 27
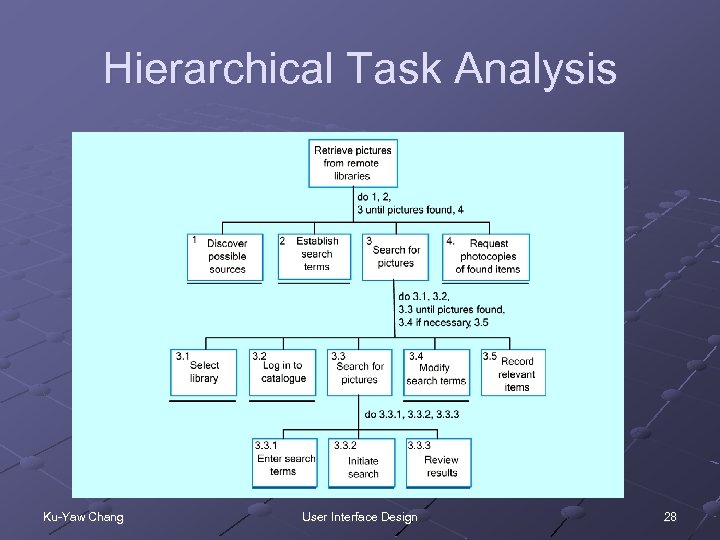 Hierarchical Task Analysis Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 28
Hierarchical Task Analysis Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 28
 Hierarchical Task Analysis A high-level task is broken down into subtasks Advantage n Force you to consider each of the tasks and to decide whether these should be decomposed Problem n Best suited to sequential processes only Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 29
Hierarchical Task Analysis A high-level task is broken down into subtasks Advantage n Force you to consider each of the tasks and to decide whether these should be decomposed Problem n Best suited to sequential processes only Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 29
 Contents 16. 1 Design issues 16. 2 The UI design process 16. 3 User analysis 16. 4 User interface prototyping 16. 5 Interface evaluation Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 30
Contents 16. 1 Design issues 16. 2 The UI design process 16. 3 User analysis 16. 4 User interface prototyping 16. 5 Interface evaluation Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 30
 User Interface Prototyping Aim n n Allow users to gain direct experience with the interface Judge the usability of an interface A two-stage process n n Early in the process, paper prototypes may be used; The design is then refined and increasingly sophisticated automated prototypes are then developed. Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 31
User Interface Prototyping Aim n n Allow users to gain direct experience with the interface Judge the usability of an interface A two-stage process n n Early in the process, paper prototypes may be used; The design is then refined and increasingly sophisticated automated prototypes are then developed. Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 31
 Prototyping Techniques Script-driven approach n Develop a set of scripts and screens using a tool such as Macromedia Director. When the user interacts with these, the screen changes to the next display. Visual programming languages n Use a language designed for rapid development such as Visual Basic Internet-based prototyping n Use a web browser and associated scripts. Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 32
Prototyping Techniques Script-driven approach n Develop a set of scripts and screens using a tool such as Macromedia Director. When the user interacts with these, the screen changes to the next display. Visual programming languages n Use a language designed for rapid development such as Visual Basic Internet-based prototyping n Use a web browser and associated scripts. Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 32
 Contents 16. 1 Design issues 16. 2 The UI design process 16. 3 User analysis 16. 4 User interface prototyping 16. 5 Interface evaluation Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 33
Contents 16. 1 Design issues 16. 2 The UI design process 16. 3 User analysis 16. 4 User interface prototyping 16. 5 Interface evaluation Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 33
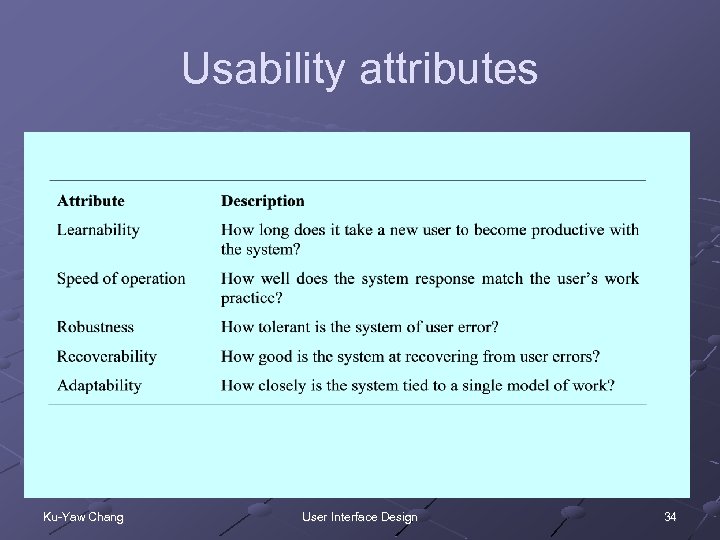 Usability attributes Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 34
Usability attributes Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design 34
 The End Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design
The End Ku-Yaw Chang User Interface Design


