05efb109542baebd1e7fb35e88123ac7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27

Software Engineering at Faculty of EE in Belgrade Prof. Dr Miroslav Bojovic Baile Herculane, August 2005.

Instead of Introduction -1 l Where we a month before (Jun 2004. )?

Instead of Introduction - 2 l Where are we now (August 2004. )?

Instead of Introduction - 3 l What we have to reach until the October 1 st 2004. ?
Environment l University of Belgrade – – – l 30 faculties About 70. 000 students About 5. 000 professors and assistants Faculty of Electrical Engineering – – 10 departments 7 profiles (divisions, degree programs, different curricula) 4. 000 students 145 full-time and 77 part-time professors and assistants

History l l l l l 1894: First lectures in electrical engineering at “Great School” 1905: Great School becomes University of Belgrade 1922: First degrees in EE 1935: Mechanical-electrical engineering department 1946: Electrical engineering department 1948: Faculty of Electrical engineering 1971: Department for data processing at faculty of EE 1981: Department for computer engineering and informatics 1986: 1(common) + 4(specialised) years of studies in CEI 2004: established profile of Software engineering
Faculty of EE l From 1948: – – – 14. 846 students received BSEE degree 1. 687 graduate students received MSEE degree 450 candidates received Ph. D degree About 3. 500 engineers work abroad About 600 students enrolls Faculty of EE per year About 45 students enrolled SE this year

Background l Department for Computer Engineering and Informatics (CEI) – – l Profile CEI – – – l 12 professors (full-time) 6 teaching assistants (full-time) Reformed curriculum last year About 100 students on state budget per year About 30 self-financing students per year Profile SE – Up to 100 self-financing students per year

Motivation l Probable the ultimate way to survive for EE – – Decreased candidate interests for traditional EE Attractive studies and future jobs in SE field Good opportunities for employment Competition l l l Some CS/IT departments at state faculties (Uo. B) Faculty of computing – private faculty Faculty for information systems and technology - private

CEI Profile l Number of subjects: – l Number of CEI subjects: 54 38 Four sub-profiles (the last 3 semesters): – – Computer Architecture and Networks Software Development Internet Technologies Information Systems
SE Profile l l l Number of exams: No sub-profiles Curriculum base – – – 44 IEEE CS & ACM suggestions Professors’ experience Available human resources
SE Profile - Conditions l 8 semesters studies >BS. SE (dipl. ing. ) 240 ECTS credits – l l Subject duration: 1 semester (with no exception) Classes per week: – l l 2 (lectures) + 2 (exercises) + 1 (laboratory) Number of – l “side exit”: engineer degree after 3 years compulsory subjects and practicums: 22+5=27 elective subjects and practicums: 14+3=17 (from 34) Up to 50 students per group for lectures Up to 25 students per lab-group Power Point presentations & handouts
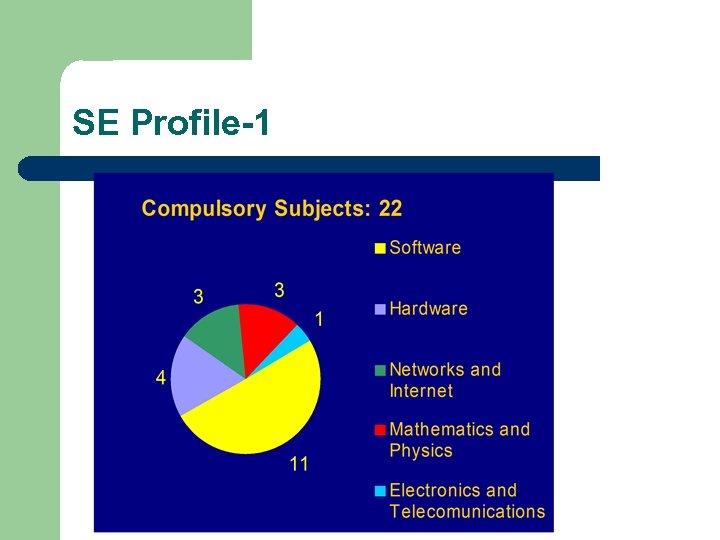
SE Profile-1
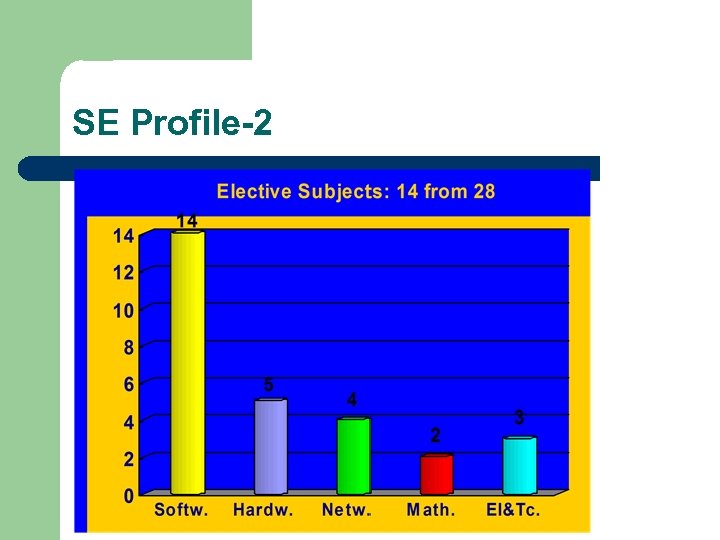
SE Profile-2
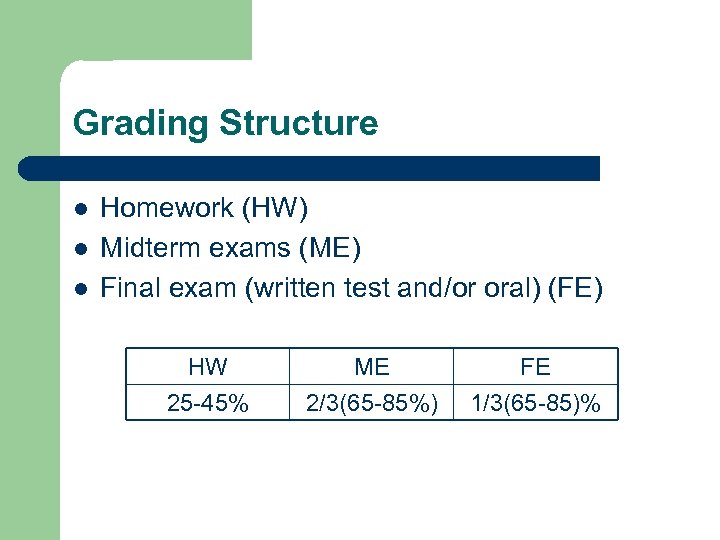
Grading Structure l l l Homework (HW) Midterm exams (ME) Final exam (written test and/or oral) (FE) HW 25 -45% ME 2/3(65 -85%) FE 1/3(65 -85)%
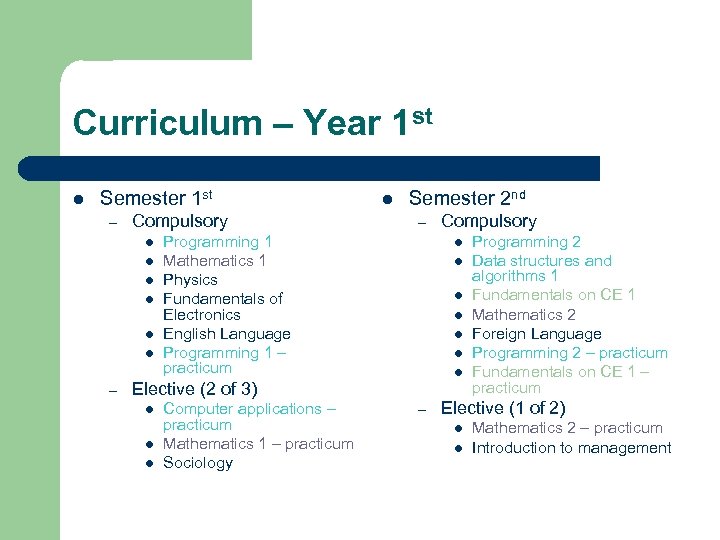
Curriculum – Year 1 st l Semester 1 st – Compulsory l l l – l Semester 2 nd – Programming 1 Mathematics 1 Physics Fundamentals of Electronics English Language Programming 1 – practicum l l l l Elective (2 of 3) l l l Computer applications – practicum Mathematics 1 – practicum Sociology Compulsory – Programming 2 Data structures and algorithms 1 Fundamentals on CE 1 Mathematics 2 Foreign Language Programming 2 – practicum Fundamentals on CE 1 – practicum Elective (1 of 2) l l Mathematics 2 – practicum Introduction to management
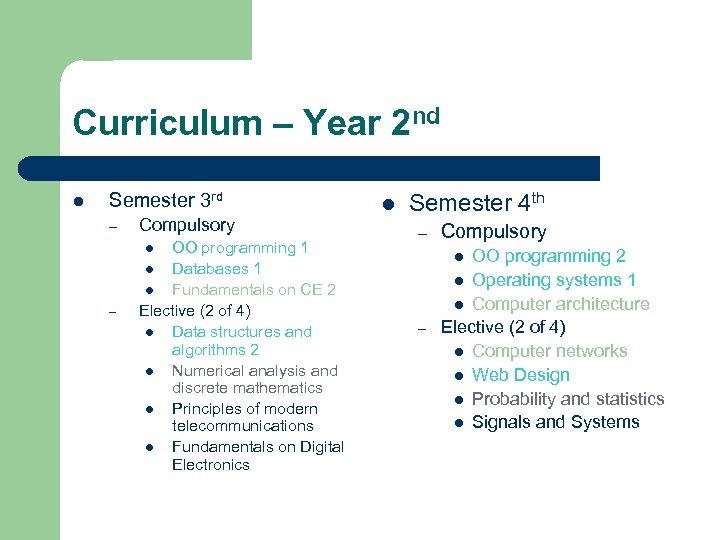
Curriculum – Year 2 nd l Semester 3 rd – Compulsory OO programming 1 l Databases 1 l Fundamentals on CE 2 Elective (2 of 4) l Data structures and algorithms 2 l Numerical analysis and discrete mathematics l Principles of modern telecommunications l Fundamentals on Digital Electronics l Semester 4 th – l – Compulsory OO programming 2 l Operating systems 1 l Computer architecture Elective (2 of 4) l Computer networks l Web Design l Probability and statistics l Signals and Systems l –
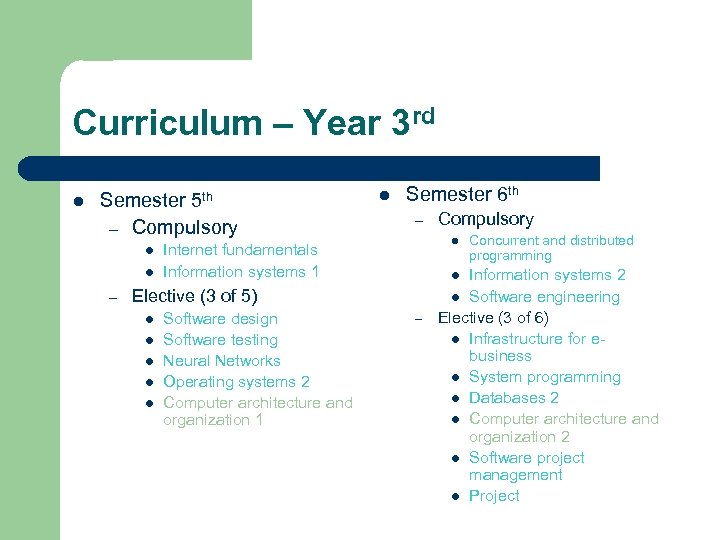
Curriculum – Year 3 rd l Semester 5 th – Compulsory l l – l Semester 6 th – l Internet fundamentals Information systems 1 l l Software design Software testing Neural Networks Operating systems 2 Computer architecture and organization 1 – Concurrent and distributed programming Information systems 2 l Software engineering Elective (3 of 6) l Infrastructure for ebusiness l System programming l Databases 2 l Computer architecture and organization 2 l Software project management l Project l Elective (3 of 5) l Compulsory
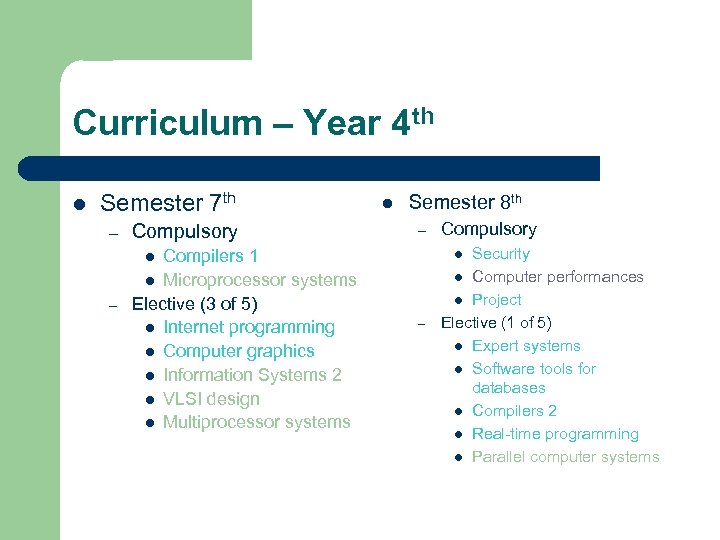
Curriculum – Year 4 th l Semester 7 th – Compulsory Compilers 1 l Microprocessor systems Elective (3 of 5) l Internet programming l Computer graphics l Information Systems 2 l VLSI design l Multiprocessor systems l Semester 8 th – Security l Computer performances l Project Elective (1 of 5) l Expert systems l Software tools for databases l Compilers 2 l Real-time programming l Parallel computer systems l l – Compulsory –

Where are we now?
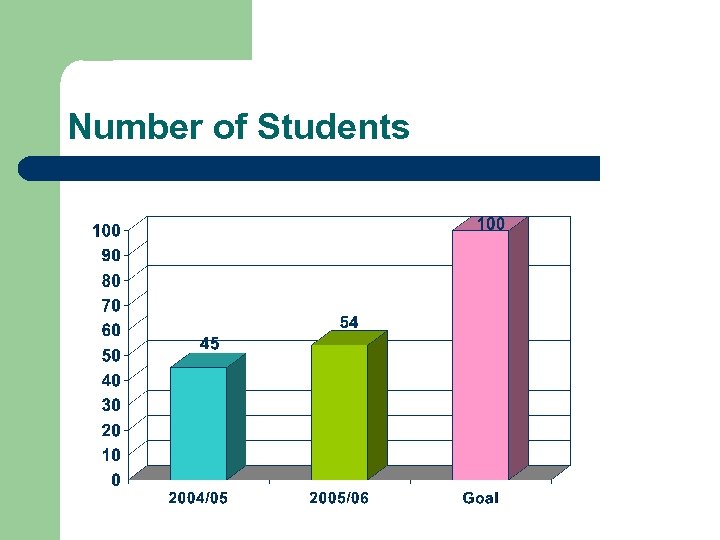
Number of Students

Results – Semester 1 st 2004/05 l Semester 1 st – 5 classes per week l l – Programming 1 Mathematics 1 Physics Fundamentals of Electronics 2 classes per week l l l Programming 1 – practicum Computer applications – practicum Mathematics 1 – practicum English Language Sociology
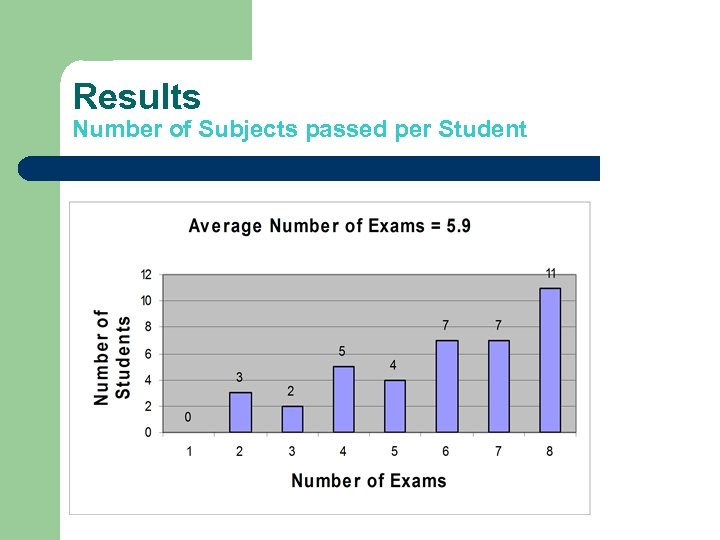
Results Number of Subjects passed per Student
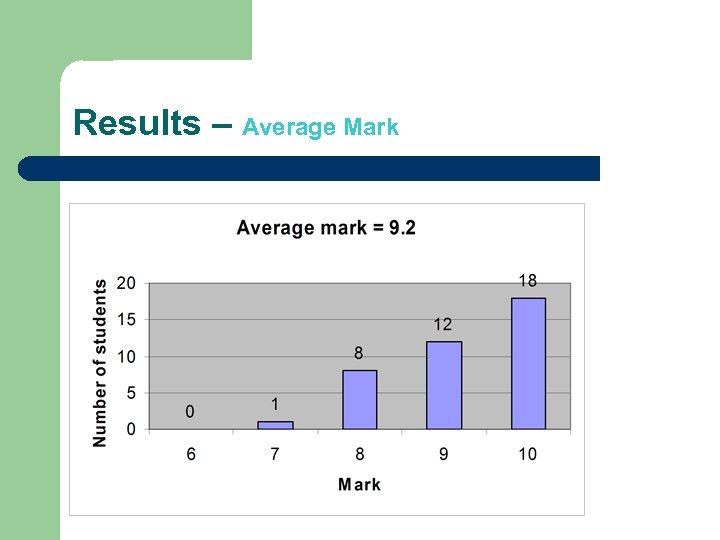
Results – Average Mark
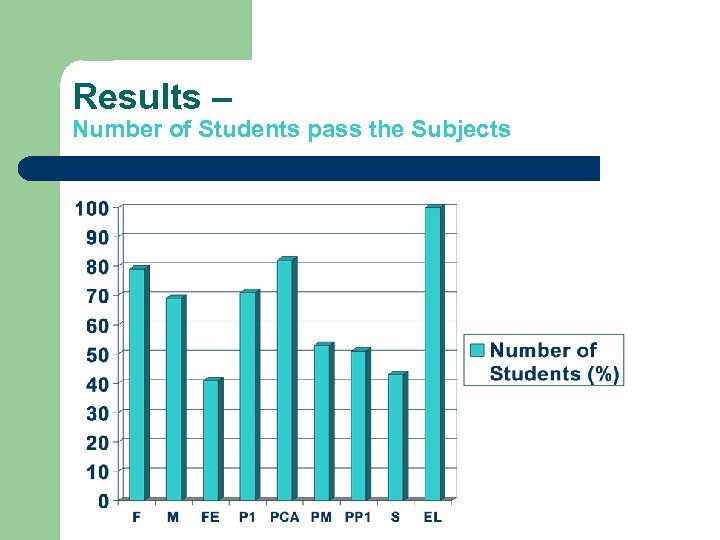
Results – Number of Students pass the Subjects
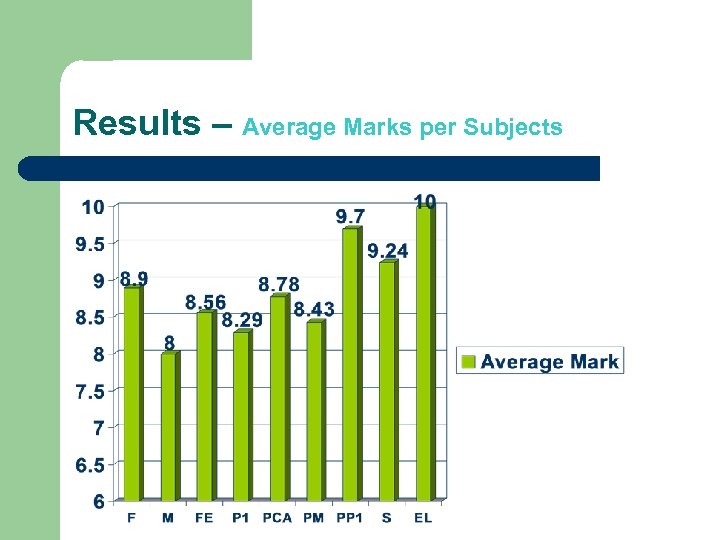
Results – Average Marks per Subjects

CONCLUSION l Number of Students: 20% increase l Promising Results l SE at EE: “BEST BUY” l Information: si. etf. bg. ac. yu
05efb109542baebd1e7fb35e88123ac7.ppt