607e399960aacea1fc210ce69d75d824.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37
 Software Engineering: A Practitioner’s Approach Chapter 25 Process and Project Metrics copyright © 1996, 2001, 2005 R. S. Pressman & Associates, Inc. For University Use Only May be reproduced ONLY for student use at the university level when used in conjunction with Software Engineering: A Practitioner's Approach. Any other reproduction or use is expressly prohibited. Coming up: Questions 1
Software Engineering: A Practitioner’s Approach Chapter 25 Process and Project Metrics copyright © 1996, 2001, 2005 R. S. Pressman & Associates, Inc. For University Use Only May be reproduced ONLY for student use at the university level when used in conjunction with Software Engineering: A Practitioner's Approach. Any other reproduction or use is expressly prohibited. Coming up: Questions 1
 Until you can measure something and express it in numbers, you have only the beginning of understanding. - Lord Kelvin Coming up: Questions 2
Until you can measure something and express it in numbers, you have only the beginning of understanding. - Lord Kelvin Coming up: Questions 2
 Until you can measure something and express it in numbers, you have only the beginning of understanding. - Lord Kelvin Non-software metrics you use everyday: - Gas tank scale - Speedometer - Thermostat in your house - Battery monitor in your laptop What would happen if instead these were not numeric? What other examples do you have? Coming up: Questions Gas Tank ☐A Lot ☐Some A little 3
Until you can measure something and express it in numbers, you have only the beginning of understanding. - Lord Kelvin Non-software metrics you use everyday: - Gas tank scale - Speedometer - Thermostat in your house - Battery monitor in your laptop What would happen if instead these were not numeric? What other examples do you have? Coming up: Questions Gas Tank ☐A Lot ☐Some A little 3
 Until you can measure something and express it in numbers, you have only the beginning of understanding. - Lord Kelvin The problem is non-numeric measurements are subjective… they mean different things to different people. Numbers are objective… they mean the same thing to everyone! When your friend says “oh yeah, John/Jane Doe is super attractive, you should go our with him/her”… that is a subjective measurement… so, you ask “Send me a photo”. Why? Because the subjective term “super attractive” has vastly different meanings for different people! Coming up: Metrics for software 4
Until you can measure something and express it in numbers, you have only the beginning of understanding. - Lord Kelvin The problem is non-numeric measurements are subjective… they mean different things to different people. Numbers are objective… they mean the same thing to everyone! When your friend says “oh yeah, John/Jane Doe is super attractive, you should go our with him/her”… that is a subjective measurement… so, you ask “Send me a photo”. Why? Because the subjective term “super attractive” has vastly different meanings for different people! Coming up: Metrics for software 4
 Metrics for software n When asked to measure something, always try to determine an objective measurement. If not possible, try to get as close as you can! Coming up: A Good Manager Measures 5
Metrics for software n When asked to measure something, always try to determine an objective measurement. If not possible, try to get as close as you can! Coming up: A Good Manager Measures 5
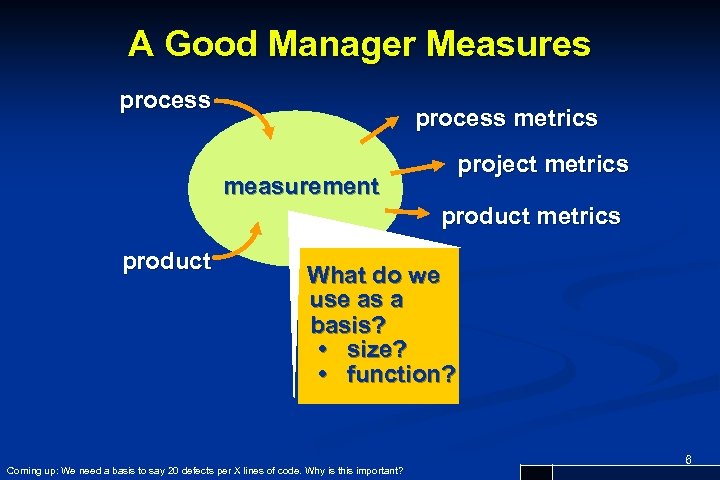 A Good Manager Measures process metrics project metrics measurement product metrics product What do we use as a basis? • size? • function? Coming up: We need a basis to say 20 defects per X lines of code. Why is this important? 6
A Good Manager Measures process metrics project metrics measurement product metrics product What do we use as a basis? • size? • function? Coming up: We need a basis to say 20 defects per X lines of code. Why is this important? 6
 n n We need a basis to say 20 defects per X lines of code. Why is this important? A Because lines of code equals cost B We want our metrics to be valid across projects of many sizes C Because you just caused me to die in Halo 3… stop asking these questions! D Because this helps up understand how big our program is Coming up: Why Do We Measure? 7
n n We need a basis to say 20 defects per X lines of code. Why is this important? A Because lines of code equals cost B We want our metrics to be valid across projects of many sizes C Because you just caused me to die in Halo 3… stop asking these questions! D Because this helps up understand how big our program is Coming up: Why Do We Measure? 7
 Why Do We Measure? n n n assess the status of an ongoing project track potential risks uncover problem areas before they go “critical, ” adjust work flow or tasks, evaluate the project team’s ability to control quality of software work products. Coming up: Process versus Project Metrics 8
Why Do We Measure? n n n assess the status of an ongoing project track potential risks uncover problem areas before they go “critical, ” adjust work flow or tasks, evaluate the project team’s ability to control quality of software work products. Coming up: Process versus Project Metrics 8
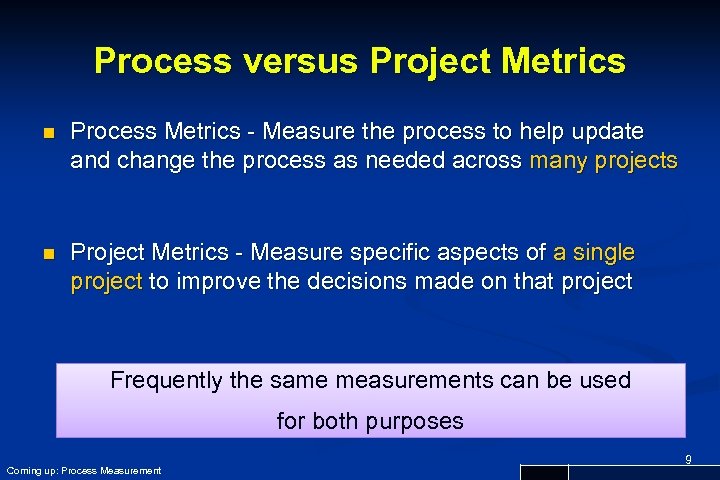 Process versus Project Metrics n Process Metrics - Measure the process to help update and change the process as needed across many projects n Project Metrics - Measure specific aspects of a single project to improve the decisions made on that project Frequently the same measurements can be used for both purposes Coming up: Process Measurement 9
Process versus Project Metrics n Process Metrics - Measure the process to help update and change the process as needed across many projects n Project Metrics - Measure specific aspects of a single project to improve the decisions made on that project Frequently the same measurements can be used for both purposes Coming up: Process Measurement 9
 Process Measurement n We measure the efficacy of a software process indirectly. n n n That is, we derive a set of metrics based on the outcomes of the process Outcomes include n measures of errors uncovered before release of the software n defects delivered to and reported by end-users n work products delivered (productivity) n human effort expended n calendar time expended n schedule conformance n many others… We also derive process metrics by measuring the characteristics of specific software engineering tasks. Coming up: Process Metrics Guidelines 10
Process Measurement n We measure the efficacy of a software process indirectly. n n n That is, we derive a set of metrics based on the outcomes of the process Outcomes include n measures of errors uncovered before release of the software n defects delivered to and reported by end-users n work products delivered (productivity) n human effort expended n calendar time expended n schedule conformance n many others… We also derive process metrics by measuring the characteristics of specific software engineering tasks. Coming up: Process Metrics Guidelines 10
 Process Metrics Guidelines n n n n Use common sense and organizational sensitivity when interpreting metrics data. Provide regular feedback to the individuals and teams who collect measures and metrics. Don’t use metrics to appraise individuals. Work with practitioners and teams to set clear goals and metrics that will be used to achieve them. Never use metrics to threaten individuals or teams. Metrics data that indicate a problem area should not be considered “negative. ” These data are merely an indicator for process improvement. Don’t obsess on a single metric to the exclusion of other important metrics. Coming up: If I calculate the number of defects per developer and rank them, then using that rank assign salary raises based on that. 11
Process Metrics Guidelines n n n n Use common sense and organizational sensitivity when interpreting metrics data. Provide regular feedback to the individuals and teams who collect measures and metrics. Don’t use metrics to appraise individuals. Work with practitioners and teams to set clear goals and metrics that will be used to achieve them. Never use metrics to threaten individuals or teams. Metrics data that indicate a problem area should not be considered “negative. ” These data are merely an indicator for process improvement. Don’t obsess on a single metric to the exclusion of other important metrics. Coming up: If I calculate the number of defects per developer and rank them, then using that rank assign salary raises based on that. 11
 If I calculate the number of defects per developer and rank them, then using that rank assign salary raises based on that. n n A. This is good B. This is bad Coming up: Software Process Improvement 12
If I calculate the number of defects per developer and rank them, then using that rank assign salary raises based on that. n n A. This is good B. This is bad Coming up: Software Process Improvement 12
 Software Process Improvement Process model Process improvement recommendations Improvement goals Process metrics SPI Make your metrics actionable! Coming up: Typical Process Metrics 13
Software Process Improvement Process model Process improvement recommendations Improvement goals Process metrics SPI Make your metrics actionable! Coming up: Typical Process Metrics 13
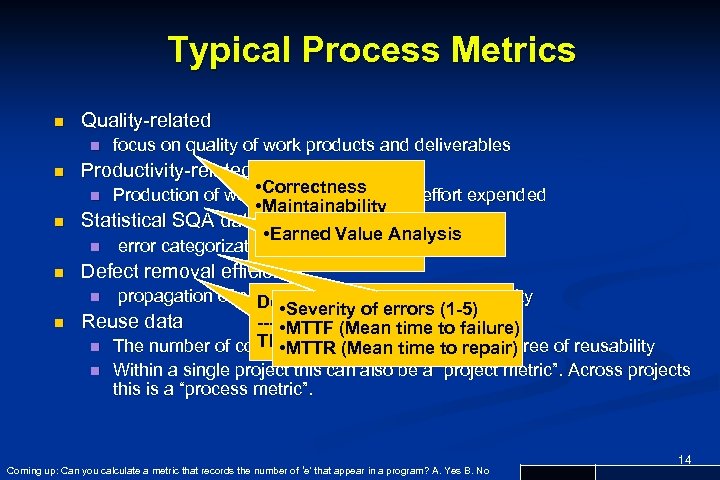 Typical Process Metrics n Quality-related n n focus on quality of work products and deliverables Productivity-related • Correctness Production of work-products related to effort expended • Maintainability n Statistical SQA data Integrity • • Earned Value Analysis • Usability n error categorization & analysis n n Defect removal efficiency propagation of errors from found in activity to activity Defects process this stage • Severity of errors (1 -5) n Reuse data ------------------- • MTTF (Mean time to failure) This Stage + Next Stage repair) n The number of components produced and their degree of reusability • MTTR (Mean time to n Within a single project this can also be a “project metric”. Across projects this is a “process metric”. n Coming up: Can you calculate a metric that records the number of ‘e’ that appear in a program? A. Yes B. No 14
Typical Process Metrics n Quality-related n n focus on quality of work products and deliverables Productivity-related • Correctness Production of work-products related to effort expended • Maintainability n Statistical SQA data Integrity • • Earned Value Analysis • Usability n error categorization & analysis n n Defect removal efficiency propagation of errors from found in activity to activity Defects process this stage • Severity of errors (1 -5) n Reuse data ------------------- • MTTF (Mean time to failure) This Stage + Next Stage repair) n The number of components produced and their degree of reusability • MTTR (Mean time to n Within a single project this can also be a “project metric”. Across projects this is a “process metric”. n Coming up: Can you calculate a metric that records the number of ‘e’ that appear in a program? A. Yes B. No 14
 Can you calculate a metric that records the number of ‘e’ that appear in a program? A. Yes B. No n n n Should you calculate the number of ‘e’ in a program? A. Yes B. No Coming up: Effective Metrics (ch 16) 15
Can you calculate a metric that records the number of ‘e’ that appear in a program? A. Yes B. No n n n Should you calculate the number of ‘e’ in a program? A. Yes B. No Coming up: Effective Metrics (ch 16) 15
 Effective Metrics (ch 16) n n n Simple and computable Empirically and intuitively persuasive Consistent and objective Consistent in use of units and dimensions Programming language independent Should be actionable Coming up: Actionable Metrics 16
Effective Metrics (ch 16) n n n Simple and computable Empirically and intuitively persuasive Consistent and objective Consistent in use of units and dimensions Programming language independent Should be actionable Coming up: Actionable Metrics 16
 Actionable Metrics Actionable metrics (or information in general) are metrics that guide change or decisions about something n Actionable: Measure the amount of human effort versus use cases completed. n n n Too high: more training, more design, etc… Very low: maybe we can shorten the schedule Not-Actionable: Measure the number of times the letter “e” appears in code Think before you measure. Don’t waste people’s time! Coming up: Project Metrics 17
Actionable Metrics Actionable metrics (or information in general) are metrics that guide change or decisions about something n Actionable: Measure the amount of human effort versus use cases completed. n n n Too high: more training, more design, etc… Very low: maybe we can shorten the schedule Not-Actionable: Measure the number of times the letter “e” appears in code Think before you measure. Don’t waste people’s time! Coming up: Project Metrics 17
 Project Metrics n n n used to minimize the development schedule by making the adjustments necessary to avoid delays and mitigate potential problems and risks used to assess product quality on an ongoing basis and, when necessary, modify the technical approach to improve quality. every project should measure: n n n Inputs —measures of the resources (e. g. , people, tools) required to do the work. Outputs —measures of the deliverables or work products created during the software engineering process. Results —measures that indicate the effectiveness of the deliverables. Coming up: Typical Project Metrics 18
Project Metrics n n n used to minimize the development schedule by making the adjustments necessary to avoid delays and mitigate potential problems and risks used to assess product quality on an ongoing basis and, when necessary, modify the technical approach to improve quality. every project should measure: n n n Inputs —measures of the resources (e. g. , people, tools) required to do the work. Outputs —measures of the deliverables or work products created during the software engineering process. Results —measures that indicate the effectiveness of the deliverables. Coming up: Typical Project Metrics 18
 Typical Project Metrics n n n Effort/time per software engineering task Errors uncovered per review hour Scheduled vs. actual milestone dates Changes (number) and their characteristics Distribution of effort on software engineering tasks Actionable: What do you do if it’s too high/low? Coming up: Metrics Guidelines 19
Typical Project Metrics n n n Effort/time per software engineering task Errors uncovered per review hour Scheduled vs. actual milestone dates Changes (number) and their characteristics Distribution of effort on software engineering tasks Actionable: What do you do if it’s too high/low? Coming up: Metrics Guidelines 19
 Metrics Guidelines n n n n Use common sense and organizational sensitivity when interpreting metrics data. Provide regular feedback to the individuals and teams who have worked to collect measures and metrics. Don’t use metrics to appraise individuals. Work with practitioners and teams to set clear goals and metrics that will be used to achieve them. Never use metrics to threaten individuals or teams. Metrics data that indicate a problem area should not be considered “negative. ” These data are merely an indicator for process improvement. Don’t obsess on a single metric to the exclusion of other important metrics. Same as process metrics guidelines Coming up: Typical Size-Oriented Metrics 20
Metrics Guidelines n n n n Use common sense and organizational sensitivity when interpreting metrics data. Provide regular feedback to the individuals and teams who have worked to collect measures and metrics. Don’t use metrics to appraise individuals. Work with practitioners and teams to set clear goals and metrics that will be used to achieve them. Never use metrics to threaten individuals or teams. Metrics data that indicate a problem area should not be considered “negative. ” These data are merely an indicator for process improvement. Don’t obsess on a single metric to the exclusion of other important metrics. Same as process metrics guidelines Coming up: Typical Size-Oriented Metrics 20
 Typical Size-Oriented Metrics n n n n errors per KLOC (thousand lines of code) defects per KLOC $ per LOC pages of documentation per KLOC errors person-month Errors per review hour LOC person-month $ per page of documentation Coming up: Typical Function-Oriented Metrics 21
Typical Size-Oriented Metrics n n n n errors per KLOC (thousand lines of code) defects per KLOC $ per LOC pages of documentation per KLOC errors person-month Errors per review hour LOC person-month $ per page of documentation Coming up: Typical Function-Oriented Metrics 21
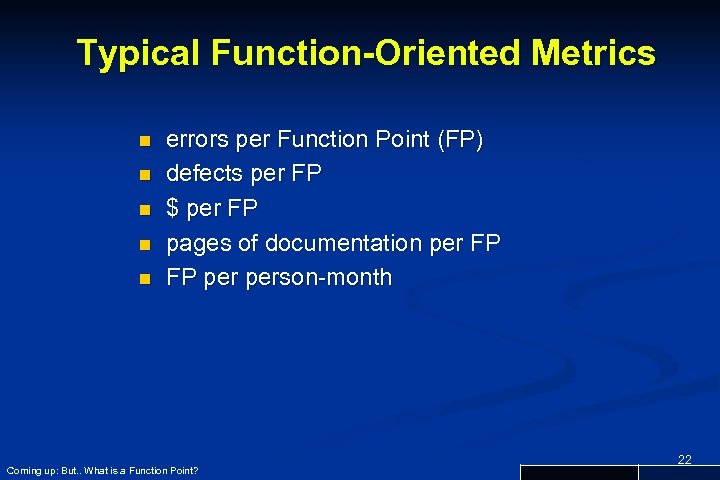 Typical Function-Oriented Metrics n n n errors per Function Point (FP) defects per FP $ per FP pages of documentation per FP FP person-month Coming up: But. . What is a Function Point? 22
Typical Function-Oriented Metrics n n n errors per Function Point (FP) defects per FP $ per FP pages of documentation per FP FP person-month Coming up: But. . What is a Function Point? 22
 But. . What is a Function Point? n n n See Book section 23. 2. 1 for more detail Function points (FP) are a unit measure for software size developed at IBM in 1979 by Richard Albrecht To determine your number of FPs, you classify a system’s features into five classes: n n Transactions - External Inputs, External Outputs, External Inquires Data storage - Internal Logical Files and External Interface Files Each class is then weighted by complexity as low/average/high Multiplied by a value adjustment factor (determined by asking questions based on 14 system characteristics Coming up: But. . What is a Function Point? 23
But. . What is a Function Point? n n n See Book section 23. 2. 1 for more detail Function points (FP) are a unit measure for software size developed at IBM in 1979 by Richard Albrecht To determine your number of FPs, you classify a system’s features into five classes: n n Transactions - External Inputs, External Outputs, External Inquires Data storage - Internal Logical Files and External Interface Files Each class is then weighted by complexity as low/average/high Multiplied by a value adjustment factor (determined by asking questions based on 14 system characteristics Coming up: But. . What is a Function Point? 23
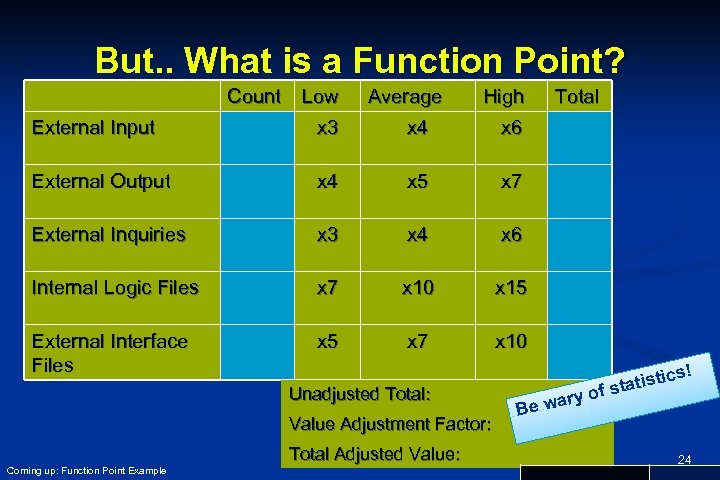 But. . What is a Function Point? Count Low Average High External Input x 3 x 4 x 6 External Output x 4 x 5 x 7 External Inquiries x 3 x 4 x 6 Internal Logic Files x 7 x 10 x 15 External Interface Files x 5 x 7 Total x 10 Unadjusted Total: Value Adjustment Factor: Total Adjusted Value: Coming up: Function Point Example cs! y ar Be w ti statis of 24
But. . What is a Function Point? Count Low Average High External Input x 3 x 4 x 6 External Output x 4 x 5 x 7 External Inquiries x 3 x 4 x 6 Internal Logic Files x 7 x 10 x 15 External Interface Files x 5 x 7 Total x 10 Unadjusted Total: Value Adjustment Factor: Total Adjusted Value: Coming up: Function Point Example cs! y ar Be w ti statis of 24
 Function Point Example http: //www. his. sunderland. ac. uk/~cs 0 mel/Alb_Example. doc Coming up: Comparing LOC and FP 25
Function Point Example http: //www. his. sunderland. ac. uk/~cs 0 mel/Alb_Example. doc Coming up: Comparing LOC and FP 25
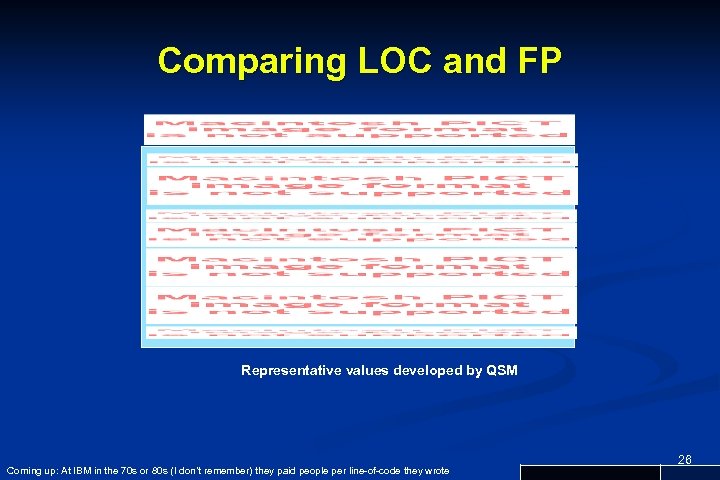 Comparing LOC and FP Representative values developed by QSM Coming up: At IBM in the 70 s or 80 s (I don’t remember) they paid people per line-of-code they wrote 26
Comparing LOC and FP Representative values developed by QSM Coming up: At IBM in the 70 s or 80 s (I don’t remember) they paid people per line-of-code they wrote 26
 At IBM in the 70 s or 80 s (I don’t remember) they paid people per lineof-code they wrote n n n What happened? A. The best programmers got paid the most B. The worst programmers got paid the most C. The sneakiest programmers, got paid the most D. The lawyers got paid the most Coming up: Why Opt against LOC? 27
At IBM in the 70 s or 80 s (I don’t remember) they paid people per lineof-code they wrote n n n What happened? A. The best programmers got paid the most B. The worst programmers got paid the most C. The sneakiest programmers, got paid the most D. The lawyers got paid the most Coming up: Why Opt against LOC? 27
 Why Opt against LOC? n n n Programming language independent Used readily countable characteristics that are determined early in the software process Does not “penalize” inventive (short) implementations that use fewer LOC that other more clumsy versions Makes it easier to measure the impact of reusable components Other options: COCOMO, Planning Poker, SLIM, Story Points (remember Scrum? ), many others… Coming up: Object-Oriented Metrics 28
Why Opt against LOC? n n n Programming language independent Used readily countable characteristics that are determined early in the software process Does not “penalize” inventive (short) implementations that use fewer LOC that other more clumsy versions Makes it easier to measure the impact of reusable components Other options: COCOMO, Planning Poker, SLIM, Story Points (remember Scrum? ), many others… Coming up: Object-Oriented Metrics 28
 Object-Oriented Metrics n n Number of scenario scripts (use-cases) Number of support classes (required to implement the system but are not immediately related to the problem domain) Average number of support classes per key class (analysis class) Number of subsystems (an aggregation of classes that support a function that is visible to the end-user of a system) Coming up: Web. Engineering Project Metrics 29
Object-Oriented Metrics n n Number of scenario scripts (use-cases) Number of support classes (required to implement the system but are not immediately related to the problem domain) Average number of support classes per key class (analysis class) Number of subsystems (an aggregation of classes that support a function that is visible to the end-user of a system) Coming up: Web. Engineering Project Metrics 29
 Web. Engineering Project Metrics n n n n Number of static Web pages (the end-user has no control over the content displayed on the page) Number of dynamic Web pages (end-user actions result in customized content displayed on the page) Number of internal page links (internal page links are pointers that provide a hyperlink to some other Web page within the Web. App) Number of persistent data objects Number of external systems interfaced Number of static content objects Number of dynamic content objects Number of executable functions Coming up: Measuring Quality 30
Web. Engineering Project Metrics n n n n Number of static Web pages (the end-user has no control over the content displayed on the page) Number of dynamic Web pages (end-user actions result in customized content displayed on the page) Number of internal page links (internal page links are pointers that provide a hyperlink to some other Web page within the Web. App) Number of persistent data objects Number of external systems interfaced Number of static content objects Number of dynamic content objects Number of executable functions Coming up: Measuring Quality 30
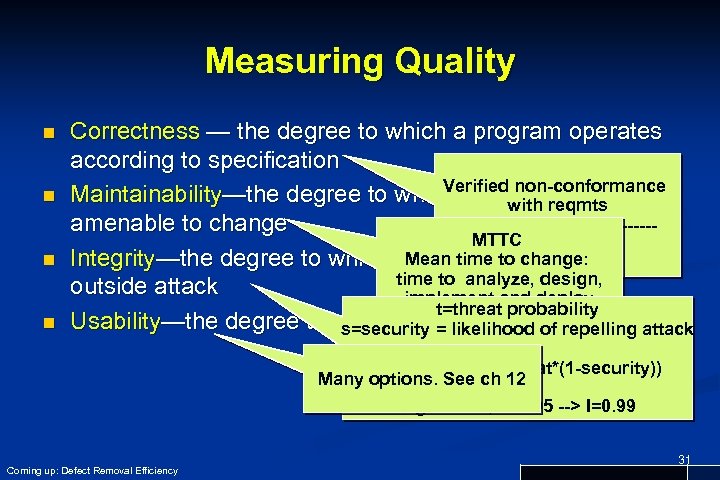 Measuring Quality n n Correctness — the degree to which a program operates according to specification Verified non-conformance Maintainability—the degree to which a program is with reqmts -----------------amenable to change MTTC KLOC Integrity—the degree to which a. Mean time tois impervious to program change: time to analyze, design, outside attack implement and deploy t=threat probability a change Usability—the degree to which a program is of repelling attack s=security = likelihood easy to use Integrity = 1 -(threat*(1 -security)) Many options. See ch 12 E. g. t=0. 25, s=0. 95 --> I=0. 99 Coming up: Defect Removal Efficiency 31
Measuring Quality n n Correctness — the degree to which a program operates according to specification Verified non-conformance Maintainability—the degree to which a program is with reqmts -----------------amenable to change MTTC KLOC Integrity—the degree to which a. Mean time tois impervious to program change: time to analyze, design, outside attack implement and deploy t=threat probability a change Usability—the degree to which a program is of repelling attack s=security = likelihood easy to use Integrity = 1 -(threat*(1 -security)) Many options. See ch 12 E. g. t=0. 25, s=0. 95 --> I=0. 99 Coming up: Defect Removal Efficiency 31
 Defect Removal Efficiency DRE = E /(E + D) E is the number of errors found before delivery of the software to the end-user D is the number of defects found after delivery. Coming up: Defect Removal Efficiency 32
Defect Removal Efficiency DRE = E /(E + D) E is the number of errors found before delivery of the software to the end-user D is the number of defects found after delivery. Coming up: Defect Removal Efficiency 32
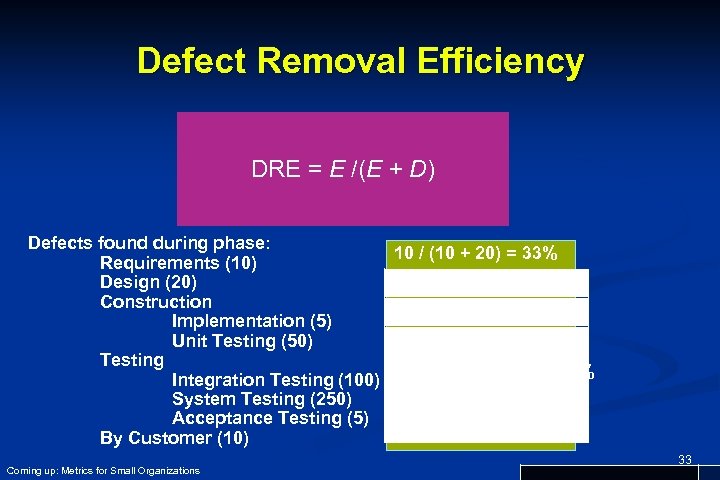 Defect Removal Efficiency DRE = E /(E + D) Defects found during phase: 10 (10 20) 33% 10 / /(10 ++20) ==33% Requirements (10) 20 / are 50) = 28% Design (20) What(20 +the rest? Construction 5 / (5 + 50) = 9% Implementation (5) Unit Testing (50) 50 / (50 + 100) = 33% Testing Integration Testing (100) 100 / (100 + 250) = 28% System Testing (250) 250 / (250 + 5) = 98% Acceptance Testing (5) 5 / (5 + 10) = 33% By Customer (10) Coming up: Metrics for Small Organizations 33
Defect Removal Efficiency DRE = E /(E + D) Defects found during phase: 10 (10 20) 33% 10 / /(10 ++20) ==33% Requirements (10) 20 / are 50) = 28% Design (20) What(20 +the rest? Construction 5 / (5 + 50) = 9% Implementation (5) Unit Testing (50) 50 / (50 + 100) = 33% Testing Integration Testing (100) 100 / (100 + 250) = 28% System Testing (250) 250 / (250 + 5) = 98% Acceptance Testing (5) 5 / (5 + 10) = 33% By Customer (10) Coming up: Metrics for Small Organizations 33
 Metrics for Small Organizations n n n n time (hours or days) elapsed from the time a request is made until evaluation is complete, tqueue. effort (person-hours) to perform the evaluation, Weval. time (hours or days) elapsed from completion of evaluation to assignment of change order to personnel, teval. effort (person-hours) required to make the change, Wchange. time required (hours or days) to make the change, tchange. errors uncovered during work to make change, Echange. defects uncovered after change is released to the customer base, Dchange. Coming up: Establishing a Metrics Program 34
Metrics for Small Organizations n n n n time (hours or days) elapsed from the time a request is made until evaluation is complete, tqueue. effort (person-hours) to perform the evaluation, Weval. time (hours or days) elapsed from completion of evaluation to assignment of change order to personnel, teval. effort (person-hours) required to make the change, Wchange. time required (hours or days) to make the change, tchange. errors uncovered during work to make change, Echange. defects uncovered after change is released to the customer base, Dchange. Coming up: Establishing a Metrics Program 34
 Establishing a Metrics Program n Set Goals n n n Determine indicators for goals n n n Identify your business goals. Identify what you want to know or learn. Identify your subgoals. Identify the entities and attributes related to your subgoals. Formalize your measurement goals. Identify quantifiable questions and the related indicators that you will use to help you achieve your measurement goals. Identify the data elements that you will collect to construct the indicators that help answer your questions. Define Measurements n n n Define the measures to be used, and make these definitions operational. Identify the actions that you will take to implement the measures. Prepare a plan for implementing the measures. Coming up: Metrics give you information! 35
Establishing a Metrics Program n Set Goals n n n Determine indicators for goals n n n Identify your business goals. Identify what you want to know or learn. Identify your subgoals. Identify the entities and attributes related to your subgoals. Formalize your measurement goals. Identify quantifiable questions and the related indicators that you will use to help you achieve your measurement goals. Identify the data elements that you will collect to construct the indicators that help answer your questions. Define Measurements n n n Define the measures to be used, and make these definitions operational. Identify the actions that you will take to implement the measures. Prepare a plan for implementing the measures. Coming up: Metrics give you information! 35
 Metrics give you information! n n n Metrics about your process help you determine if you need to make changes or if your process is working Metrics about your project do they same thing Metrics about your software can help you understand it better, and see where possible problems may lurk. Let’s see the complexity measurement (after a few questions…) Coming up: Questions 36
Metrics give you information! n n n Metrics about your process help you determine if you need to make changes or if your process is working Metrics about your project do they same thing Metrics about your software can help you understand it better, and see where possible problems may lurk. Let’s see the complexity measurement (after a few questions…) Coming up: Questions 36
 Questions n n n What are some reasons NOT to use lines of code to measure size? What do you expect the DRE rate will be for the implementation (or construction) phase of the software lifecycle? What about for testing? Give an example of a usability metric? According to the chart, Smalltalk is much more efficient than Java and C++. Why don’t we use it for everything? End of presentation 37
Questions n n n What are some reasons NOT to use lines of code to measure size? What do you expect the DRE rate will be for the implementation (or construction) phase of the software lifecycle? What about for testing? Give an example of a usability metric? According to the chart, Smalltalk is much more efficient than Java and C++. Why don’t we use it for everything? End of presentation 37


