 Software Development For Correction of Gradient. Nonlinearity Distortions in MR Images T. S. Lee, K. E. Schubert Computer Science CSUSB R. W. Schulte Radiation Medicine LLUMC
Software Development For Correction of Gradient. Nonlinearity Distortions in MR Images T. S. Lee, K. E. Schubert Computer Science CSUSB R. W. Schulte Radiation Medicine LLUMC
 Functional Proton Radiosurgery n Functional – – – Trigeminal Neuralgia Parkinson’s Disease Brain regions (< 1 cm) n Proton – Radiosurgery Accurate to less than 1 mm n MRI – – Neurosurgery for target localization Distinguish tissue types 512 images 262, 144 pixels/study Gradient nonlinearity distortions (~2 mm)
Functional Proton Radiosurgery n Functional – – – Trigeminal Neuralgia Parkinson’s Disease Brain regions (< 1 cm) n Proton – Radiosurgery Accurate to less than 1 mm n MRI – – Neurosurgery for target localization Distinguish tissue types 512 images 262, 144 pixels/study Gradient nonlinearity distortions (~2 mm)
 Example MR Phantom Images Axial Plane Coronal Plane Sagittal Plane
Example MR Phantom Images Axial Plane Coronal Plane Sagittal Plane
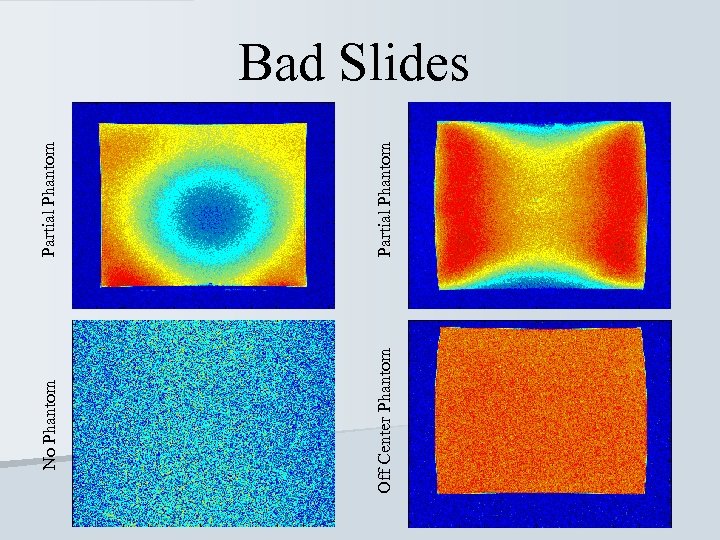 Partial Phantom No Phantom Off Center Phantom Bad Slides
Partial Phantom No Phantom Off Center Phantom Bad Slides
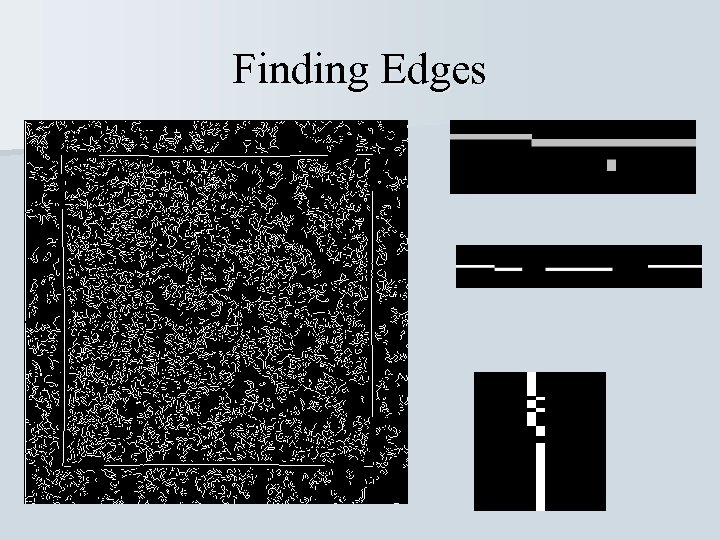 Finding Edges
Finding Edges
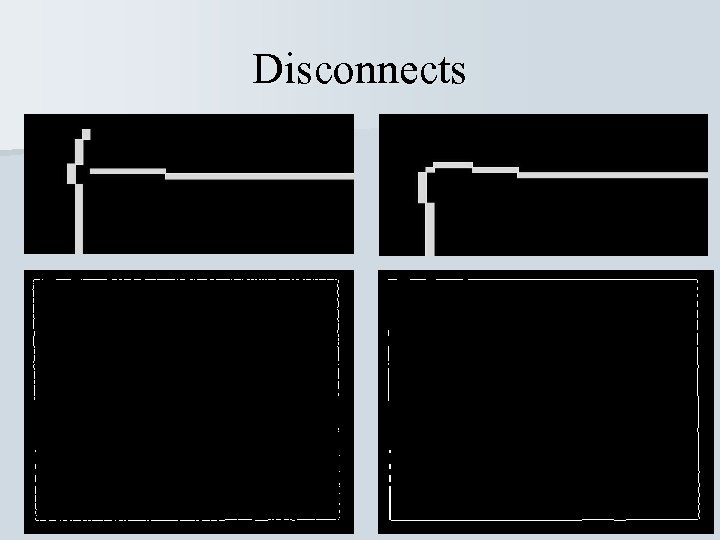 Disconnects
Disconnects
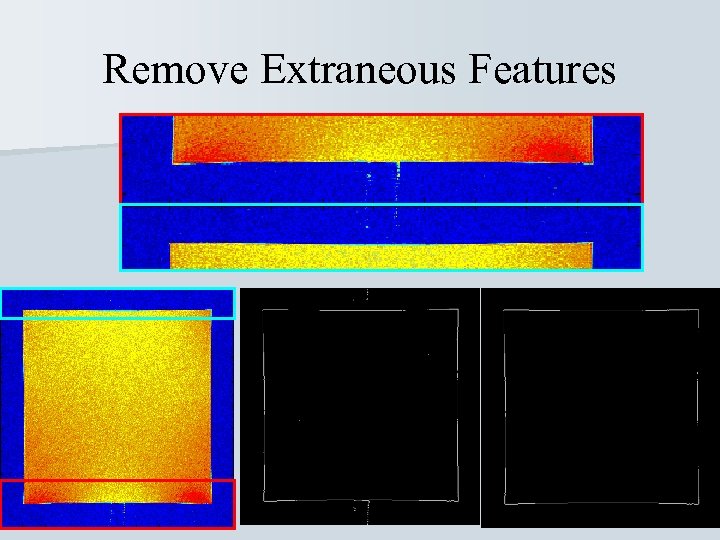 Remove Extraneous Features
Remove Extraneous Features
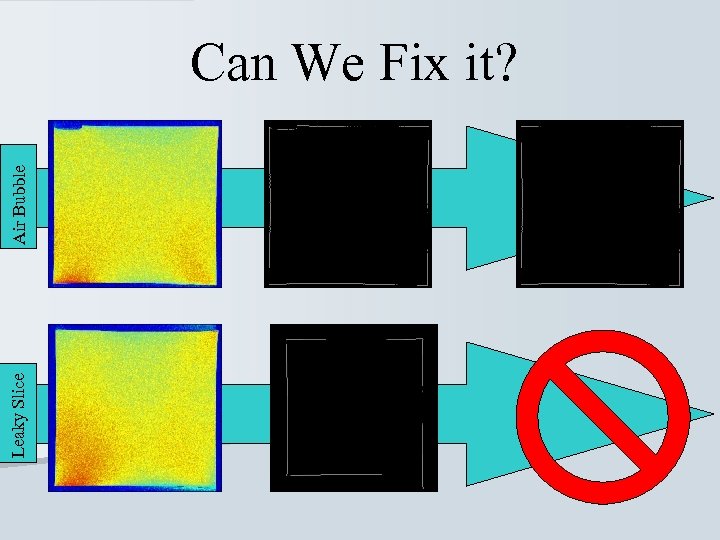 Leaky Slice Air Bubble Can We Fix it?
Leaky Slice Air Bubble Can We Fix it?
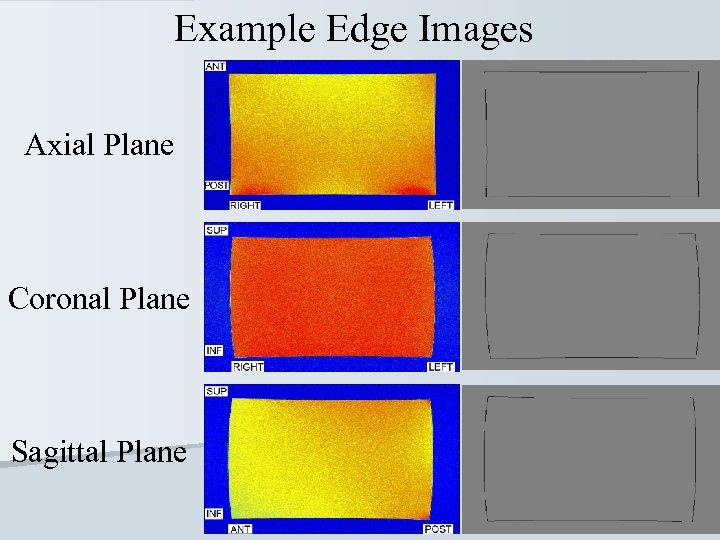 Example Edge Images Axial Plane Coronal Plane Sagittal Plane
Example Edge Images Axial Plane Coronal Plane Sagittal Plane
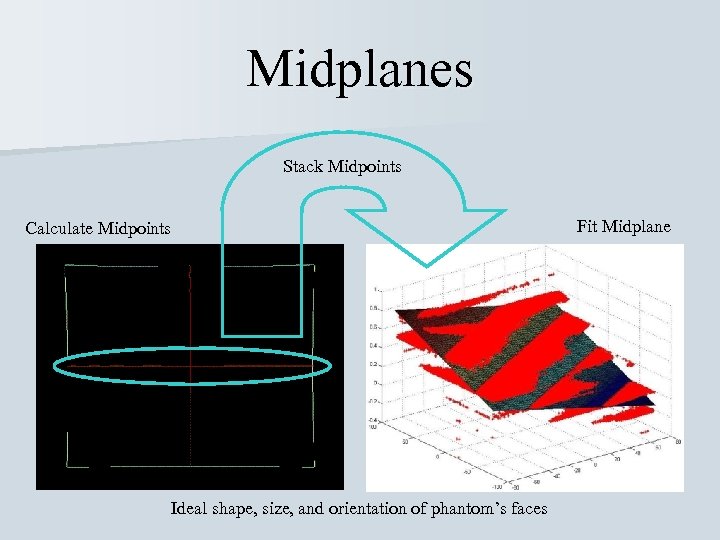 Midplanes Stack Midpoints Calculate Midpoints Ideal shape, size, and orientation of phantom’s faces Fit Midplane
Midplanes Stack Midpoints Calculate Midpoints Ideal shape, size, and orientation of phantom’s faces Fit Midplane
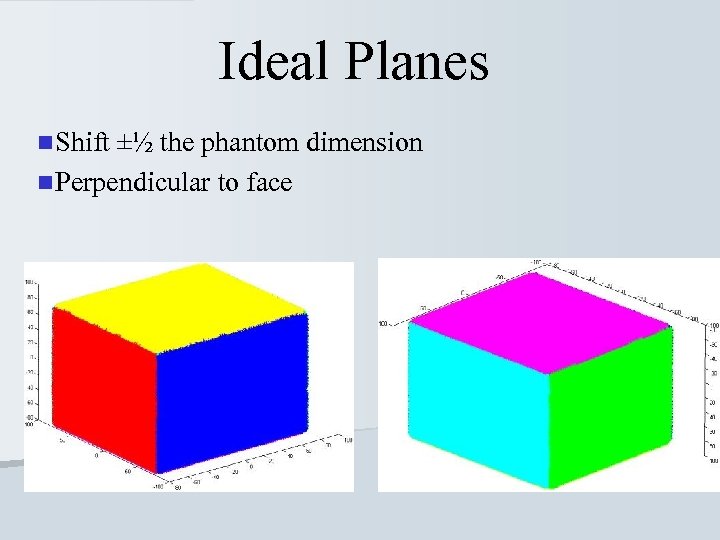 Ideal Planes n Shift ±½ the phantom dimension n Perpendicular to face
Ideal Planes n Shift ±½ the phantom dimension n Perpendicular to face
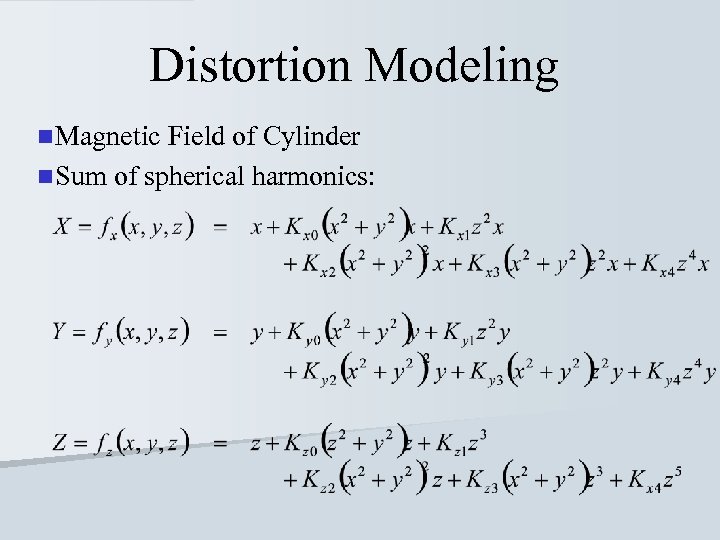 Distortion Modeling n Magnetic Field of Cylinder n Sum of spherical harmonics:
Distortion Modeling n Magnetic Field of Cylinder n Sum of spherical harmonics:
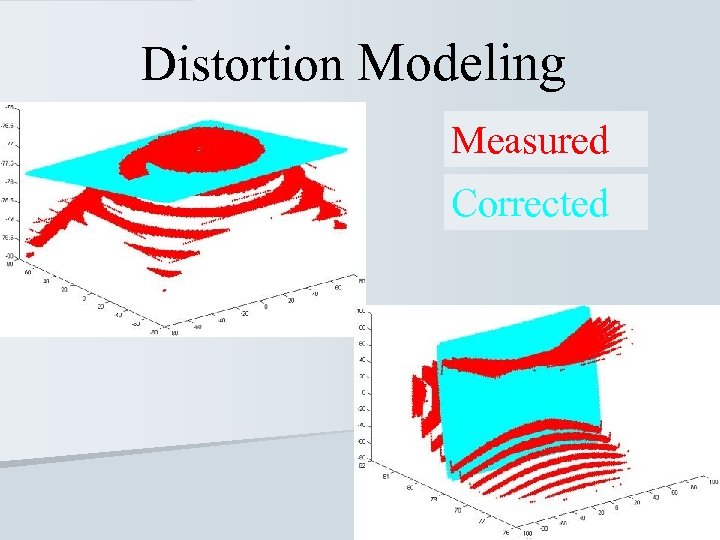 Distortion Modeling Measured Corrected
Distortion Modeling Measured Corrected
 Applying Distortion Correction Axial Plane
Applying Distortion Correction Axial Plane
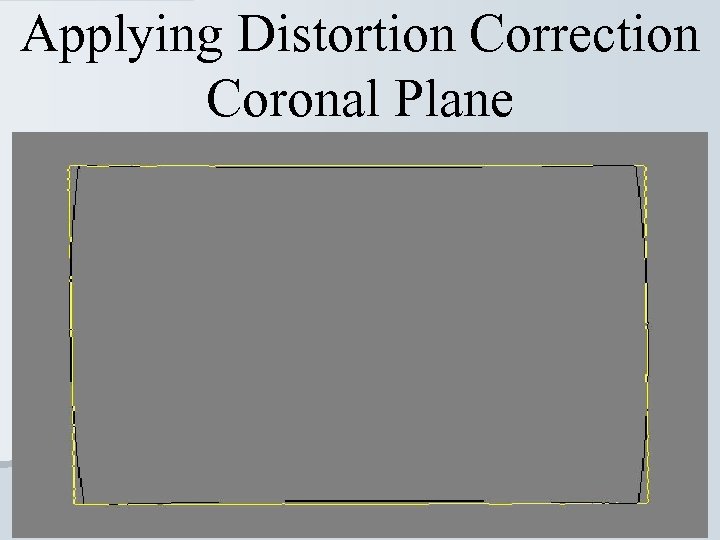 Applying Distortion Correction Coronal Plane
Applying Distortion Correction Coronal Plane
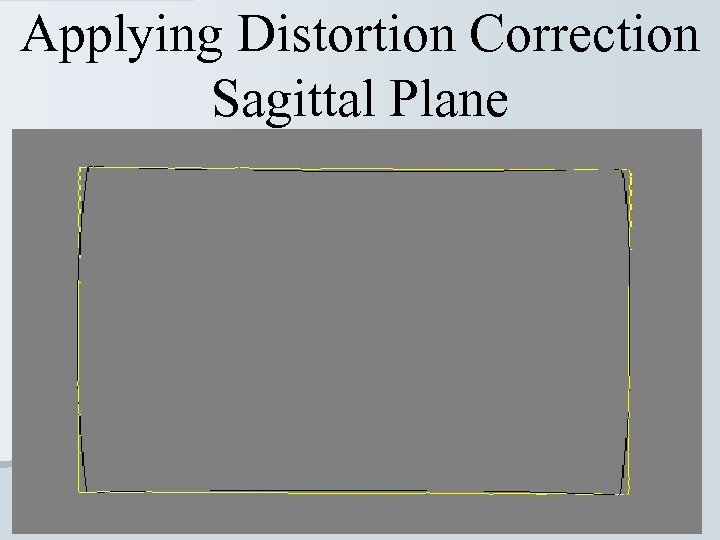 Applying Distortion Correction Sagittal Plane
Applying Distortion Correction Sagittal Plane
 Results n Theoretical undistorted points vs. corrected points n Standard deviations of correction +X face: Standard Deviation = 0. 23503 mm -X face: Standard Deviation = 0. 25168 mm +Y face: Standard Deviation = 0. 15322 mm -Y face: Standard Deviation = 0. 15823 mm +Z face: Standard Deviation = 0. 13548 mm -Z face: Standard Deviation = 0. 14173 mm
Results n Theoretical undistorted points vs. corrected points n Standard deviations of correction +X face: Standard Deviation = 0. 23503 mm -X face: Standard Deviation = 0. 25168 mm +Y face: Standard Deviation = 0. 15322 mm -Y face: Standard Deviation = 0. 15823 mm +Z face: Standard Deviation = 0. 13548 mm -Z face: Standard Deviation = 0. 14173 mm
 Conclusions n 3 s range 0. 4 – 0. 8 mm – 1 -2 pixels on each image –Originally 2 mm (5 -6 pixels) n. Accurate localization of anatomical targets
Conclusions n 3 s range 0. 4 – 0. 8 mm – 1 -2 pixels on each image –Originally 2 mm (5 -6 pixels) n. Accurate localization of anatomical targets
 Future Work n. Further verification and testing n. Clinical trials n. FDA approval n. Treatment on humans
Future Work n. Further verification and testing n. Clinical trials n. FDA approval n. Treatment on humans