742e715c36cbc7df18b5021b0ac0b404.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25

Software Design Principles “Producing the software blueprint” TCS 2411 Software Engineering 1
Lecture Objectives z. To understand the importance of design in developing quality software z. To describe the translation from the requirements analysis model to the design model z. To understand the principles that guide proper design of software TCS 2411 Software Engineering 2
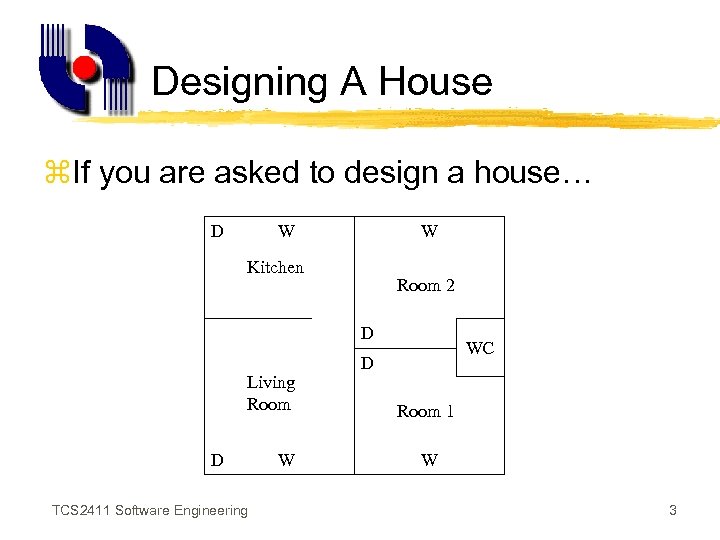
Designing A House z. If you are asked to design a house… D W W Kitchen Room 2 D Living Room D TCS 2411 Software Engineering W WC D Room 1 W 3
What Is Design? z. Explaining the idea/concept of something z. Usually with graphical diagrams z. With the intention to build from the explanation z. The design is a representation of a product or a system with sufficient detail for implementation TCS 2411 Software Engineering 4
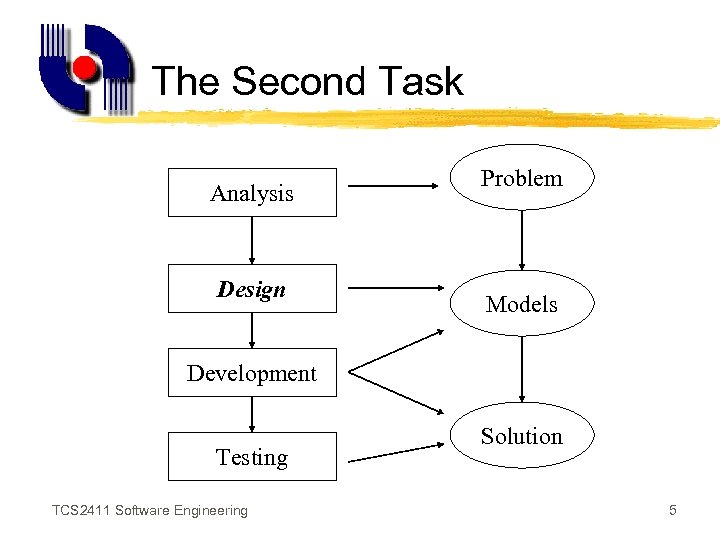
The Second Task Analysis Design Problem Models Development Testing TCS 2411 Software Engineering Solution 5

Designing Software z. From our understanding of the problem, we start building the software z. Translate the analysis model into the design model z. Map the information from the analysis model to the design representations - data design, architectural design, interface design, procedural design TCS 2411 Software Engineering 6
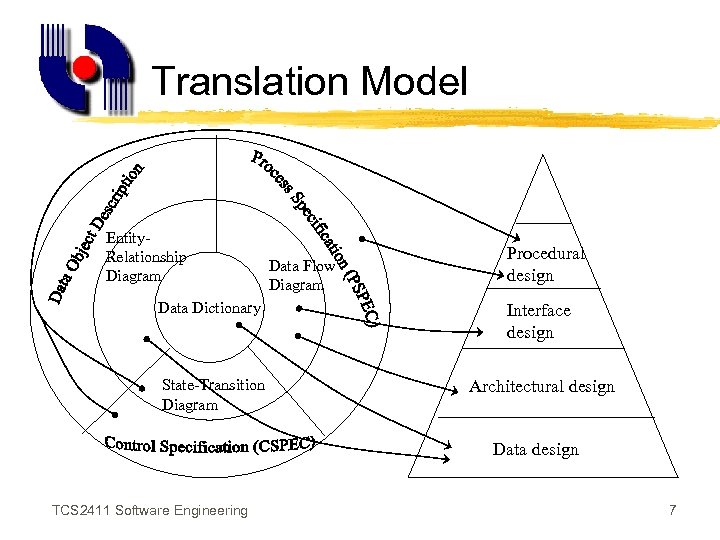
Translation Model Entity. Relationship Diagram Data Flow Diagram Procedural design Data Dictionary Interface design State-Transition Diagram Architectural design Data design TCS 2411 Software Engineering 7

Design Principles z. Design process should not suffer from “tunnel vision” z. The design should be traceable to the analysis model z. The design should not reinvent the wheel; Time is short z. The design should “minimize intellectual distance” between the software and the problem in the real world TCS 2411 Software Engineering 8

Design Principles (Continued) z. The design should exhibit uniformity and integration z. The design should be structured to accommodate change z. The design should be structured to degrade gently. TCS 2411 Software Engineering 9

Design Principles (Continued) z. Design is not coding, coding is not design z. The design should be assessed for quality as it is being created, not after the fact z. The design should be reviewed to minimize conceptual errors TCS 2411 Software Engineering 10
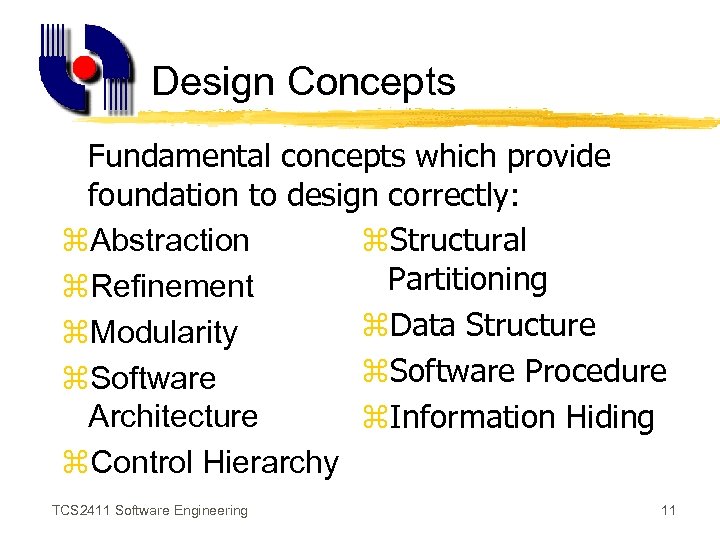
Design Concepts Fundamental concepts which provide foundation to design correctly: z. Abstraction z. Structural Partitioning z. Refinement z. Data Structure z. Modularity z. Software Procedure z. Software Architecture z. Information Hiding z. Control Hierarchy TCS 2411 Software Engineering 11

Abstraction z. Identifying important features for representation z. There are many levels of abstraction depending on how detailed the representation is required z. Data abstraction - representation of data objects z. Procedural abstraction - representation of instructions TCS 2411 Software Engineering 12

Refinement z. Stepwise refinement - top-down design strategy by Niklaus Wirth z. Starting at the highest level of abstraction, every step of refinement ‘decompose’ instructions into more detailed instructions z. Complementary to abstraction TCS 2411 Software Engineering 13

Modularity z. Software is divided into separately named and addressable modules z“Divide and conquer” approach - problem is broken into manageable pieces z. Solutions for the separate pieces then integrated into the whole system TCS 2411 Software Engineering 14
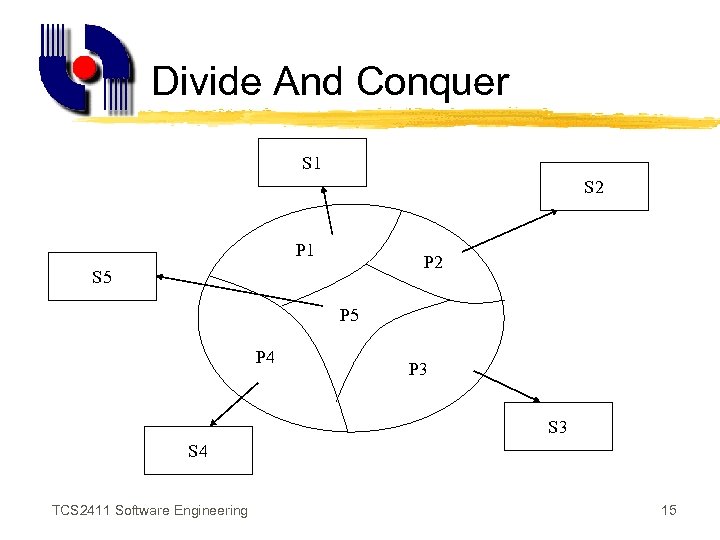
Divide And Conquer S 1 S 2 P 1 P 2 S 5 P 4 P 3 S 4 TCS 2411 Software Engineering 15

Software Architecture z. Modules can be integrated in many ways to produce the system z. Software architecture is the overall structure of the software z. The hierarchy of components and how they interact, and the structure of data used by the components z. Use of framework models, and possible reuse of architectural patterns TCS 2411 Software Engineering 16

Software Architecture Patterns z. Recurring pattern help designers reuse successful designs by basing new designs on prior experience. z. A designer who is familiar with such patterns can apply them immediately to design problems without having to rediscover them. TCS 2411 Software Engineering 17

Why use Design Patterns? z. Reuse successful practices. y. Not new – recognised that this is something that engineers have done for years. z. Improve communication z. Step towards a software engineer’s handbook TCS 2411 Software Engineering 18
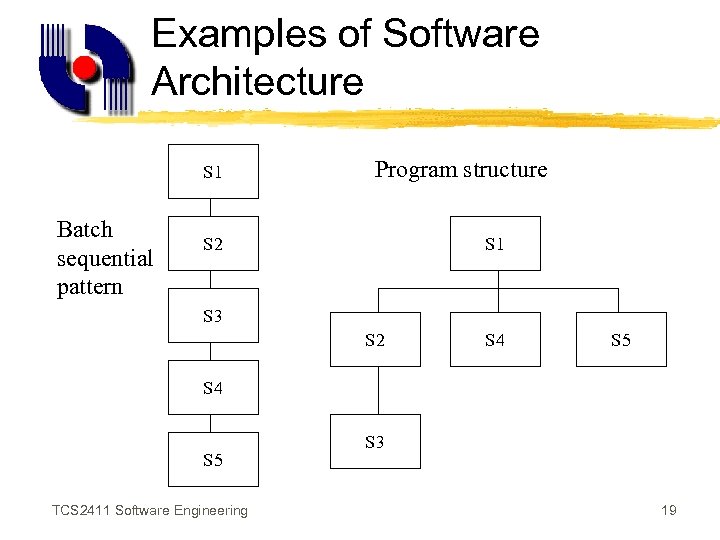
Examples of Software Architecture S 1 Batch sequential pattern Program structure S 2 S 1 S 3 S 2 S 4 S 5 TCS 2411 Software Engineering S 3 19
Control Hierarchy z. Hierarchy of modules representing the control relationships z. A super-ordinate module controls another module z. A subordinate module is controlled by another module z. Measures relevant to control hierarchy: depth, width, fan-in, fan-out TCS 2411 Software Engineering 20
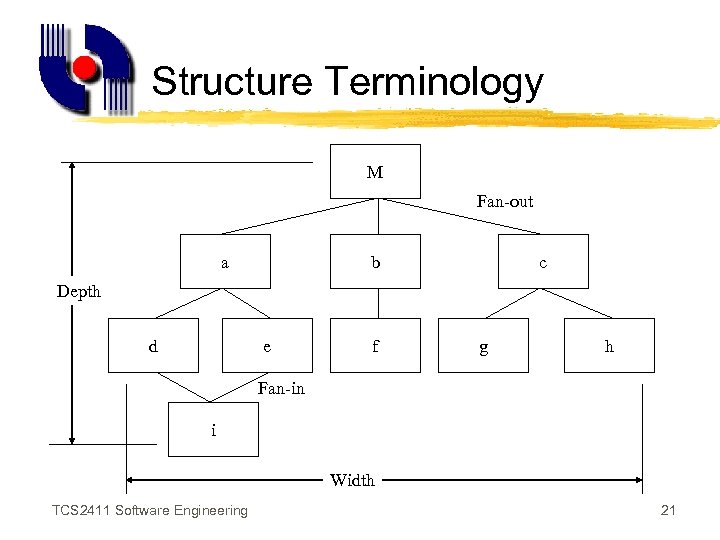
Structure Terminology M Fan-out a b c Depth d e f g h Fan-in i Width TCS 2411 Software Engineering 21

Structural Partitioning z. Program structure partitioned horizontally and vertically z. Horizontal partitioning defines separate branches for each major program function - input, process, output z. Vertical partitioning (aka factoring) defines control (decision-making) at the top and work at the bottom TCS 2411 Software Engineering 22
Software Procedure z. Processing details of individual modules z. Precise specification of processing, including sequence of events, exact decision points, repetitive operations, and data organization/structure z. Procedure is layered - subordinate modules must be referenced in processing details TCS 2411 Software Engineering 23

Information Hiding z. Information (procedure and data) contained within a module is inaccessible to other modules that have no need for such information z. Effective modularity is achieved by independent modules, that communicate only necessary information z. Ease of maintenance - testing, modification localized and less likely to propagate TCS 2411 Software Engineering 24

References z“Software Engineering: A Practitioner’s Approach” 5 th Ed. by Roger S. Pressman, Mc-Graw-Hill, 2001 z“Software Engineering” by Ian Sommerville, Addison-Wesley, 2001 TCS 2411 Software Engineering 25
742e715c36cbc7df18b5021b0ac0b404.ppt