c832ad3540be6cf958406f7942390b99.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 14
 ™ Software Assurance Ecosystem and its Applications Djenana Campara Chief Executive Officer, KDM Analytics Board Director, Object Management Group (OMG) Co-Chair Software Assurance and Architecture Driven Modernization, OMG ™
™ Software Assurance Ecosystem and its Applications Djenana Campara Chief Executive Officer, KDM Analytics Board Director, Object Management Group (OMG) Co-Chair Software Assurance and Architecture Driven Modernization, OMG ™
 Agenda n Software Assurance n n n Software Assurance Ecosystem n n n Definition - OMG and Government Initiative The Assurance Case Introduction and Current State Enabling Technologies ISO/OMG Tooling Standards Detailed View of the Ecosystem Software Assurance Ecosystem in Action ™ © 2007, KDM Analytics
Agenda n Software Assurance n n n Software Assurance Ecosystem n n n Definition - OMG and Government Initiative The Assurance Case Introduction and Current State Enabling Technologies ISO/OMG Tooling Standards Detailed View of the Ecosystem Software Assurance Ecosystem in Action ™ © 2007, KDM Analytics
 Software Assurance ™ © 2007, KDM Analytics
Software Assurance ™ © 2007, KDM Analytics
 Software Assurance n Definition n The justified confidence that the system functions as intended and is free of exploitable vulnerabilities, either intentionally or unintentionally designed or inserted as part of the system at any time during the lifecycle” n n [National Defense Industrial Association -NDIA]. Basic Principals n For each software artifact of interest, there exist a set of claims (generally related to safety and security) about the software artifact, a set of facts (collectively called evidence) about the software artifact, and a set of assurance arguments that use the evidence to show that the software artifact does, in fact, satisfy the claims. The Justified Confidence is presented through Assurance Case: set of auditable claims, arguments and evidence created to support the contention that a defined system/service will satisfy the particular requirements through supporting arguments and evidence ™ © 2007, KDM Analytics
Software Assurance n Definition n The justified confidence that the system functions as intended and is free of exploitable vulnerabilities, either intentionally or unintentionally designed or inserted as part of the system at any time during the lifecycle” n n [National Defense Industrial Association -NDIA]. Basic Principals n For each software artifact of interest, there exist a set of claims (generally related to safety and security) about the software artifact, a set of facts (collectively called evidence) about the software artifact, and a set of assurance arguments that use the evidence to show that the software artifact does, in fact, satisfy the claims. The Justified Confidence is presented through Assurance Case: set of auditable claims, arguments and evidence created to support the contention that a defined system/service will satisfy the particular requirements through supporting arguments and evidence ™ © 2007, KDM Analytics
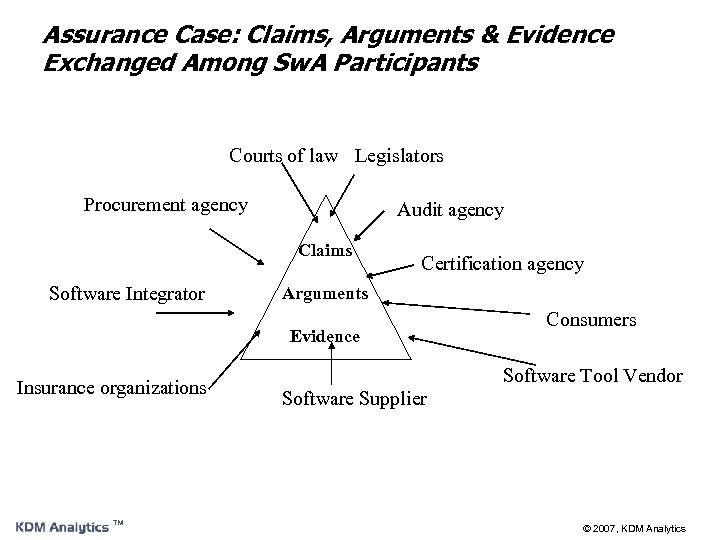 Assurance Case: Claims, Arguments & Evidence Exchanged Among Sw. A Participants Courts of law Legislators Procurement agency Audit agency Claims Software Integrator Certification agency Arguments Evidence Insurance organizations ™ Consumers Software Tool Vendor Software Supplier © 2007, KDM Analytics
Assurance Case: Claims, Arguments & Evidence Exchanged Among Sw. A Participants Courts of law Legislators Procurement agency Audit agency Claims Software Integrator Certification agency Arguments Evidence Insurance organizations ™ Consumers Software Tool Vendor Software Supplier © 2007, KDM Analytics
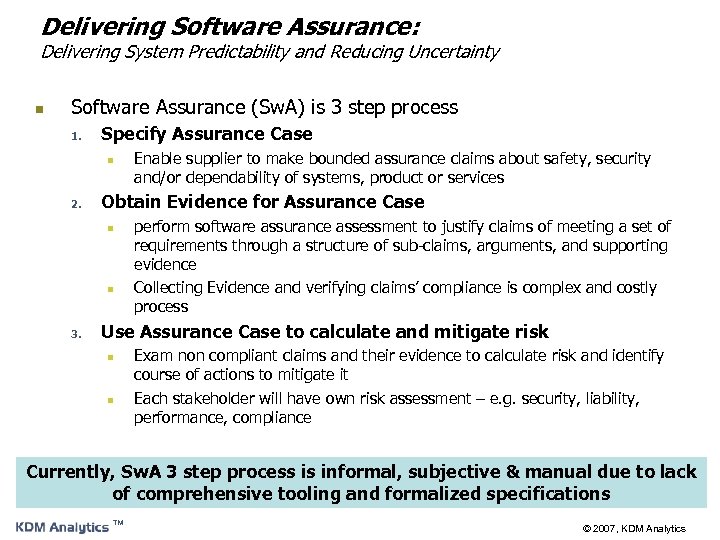 Delivering Software Assurance: Delivering System Predictability and Reducing Uncertainty n Software Assurance (Sw. A) is 3 step process 1. Specify Assurance Case n 2. Obtain Evidence for Assurance Case n n 3. Enable supplier to make bounded assurance claims about safety, security and/or dependability of systems, product or services perform software assurance assessment to justify claims of meeting a set of requirements through a structure of sub-claims, arguments, and supporting evidence Collecting Evidence and verifying claims’ compliance is complex and costly process Use Assurance Case to calculate and mitigate risk n n Exam non compliant claims and their evidence to calculate risk and identify course of actions to mitigate it Each stakeholder will have own risk assessment – e. g. security, liability, performance, compliance Currently, Sw. A 3 step process is informal, subjective & manual due to lack of comprehensive tooling and formalized specifications ™ © 2007, KDM Analytics
Delivering Software Assurance: Delivering System Predictability and Reducing Uncertainty n Software Assurance (Sw. A) is 3 step process 1. Specify Assurance Case n 2. Obtain Evidence for Assurance Case n n 3. Enable supplier to make bounded assurance claims about safety, security and/or dependability of systems, product or services perform software assurance assessment to justify claims of meeting a set of requirements through a structure of sub-claims, arguments, and supporting evidence Collecting Evidence and verifying claims’ compliance is complex and costly process Use Assurance Case to calculate and mitigate risk n n Exam non compliant claims and their evidence to calculate risk and identify course of actions to mitigate it Each stakeholder will have own risk assessment – e. g. security, liability, performance, compliance Currently, Sw. A 3 step process is informal, subjective & manual due to lack of comprehensive tooling and formalized specifications ™ © 2007, KDM Analytics
 The Software Assurance Ecosystem – achieving more objectivity and automation ™ © 2007, KDM Analytics
The Software Assurance Ecosystem – achieving more objectivity and automation ™ © 2007, KDM Analytics
 The Software Assurance Ecosystem: Turning Challenge into Solution n Sw. A Ecosystem is a formal framework for analysis and exchange of information related to software security and trustworthiness Provides a technical environment where formalized claims, arguments and evidence can be brought together with formalized and abstracted software system representations to support high automation and high fidelity analysis. Based entirely on ISO/OMG Open Standards n n n Semantics of Business Vocabulary and Rules (SBVR) Knowledge Discovery Meta-model (KDM) Software Assurance Meta-model (SAM) – work in progress n n n Software Assurance Evidence Metamodel submissions received Software Assurance Claims & Arguments Metamodel RFP in progress Architected with a focus on providing fundamental improvements in analysis ™ © 2007, KDM Analytics
The Software Assurance Ecosystem: Turning Challenge into Solution n Sw. A Ecosystem is a formal framework for analysis and exchange of information related to software security and trustworthiness Provides a technical environment where formalized claims, arguments and evidence can be brought together with formalized and abstracted software system representations to support high automation and high fidelity analysis. Based entirely on ISO/OMG Open Standards n n n Semantics of Business Vocabulary and Rules (SBVR) Knowledge Discovery Meta-model (KDM) Software Assurance Meta-model (SAM) – work in progress n n n Software Assurance Evidence Metamodel submissions received Software Assurance Claims & Arguments Metamodel RFP in progress Architected with a focus on providing fundamental improvements in analysis ™ © 2007, KDM Analytics
 Leveraging what we already have through Sw. A Ecosystem n n Software Assurance Ecosystem enables industry and government to leverage and connect existing policies, practices, processes and tools, in an affordable and efficient manner The key enabler is the Software Assurance (Sw. A) Ecosystem Infrastructure n an open standard-based integrated tooling environment that dramatically reduces the cost of software assurance activities n n n ™ Integrates 3+1 different communities: Formal Methods, Reverse Engineering and Static Analysis, and Dynamic Analysis for a Sw. A solution Enables different tool types to interoperate Introduces many new vendors to ecosystem because they each leverage parts of the tool chain © 2007, KDM Analytics
Leveraging what we already have through Sw. A Ecosystem n n Software Assurance Ecosystem enables industry and government to leverage and connect existing policies, practices, processes and tools, in an affordable and efficient manner The key enabler is the Software Assurance (Sw. A) Ecosystem Infrastructure n an open standard-based integrated tooling environment that dramatically reduces the cost of software assurance activities n n n ™ Integrates 3+1 different communities: Formal Methods, Reverse Engineering and Static Analysis, and Dynamic Analysis for a Sw. A solution Enables different tool types to interoperate Introduces many new vendors to ecosystem because they each leverage parts of the tool chain © 2007, KDM Analytics
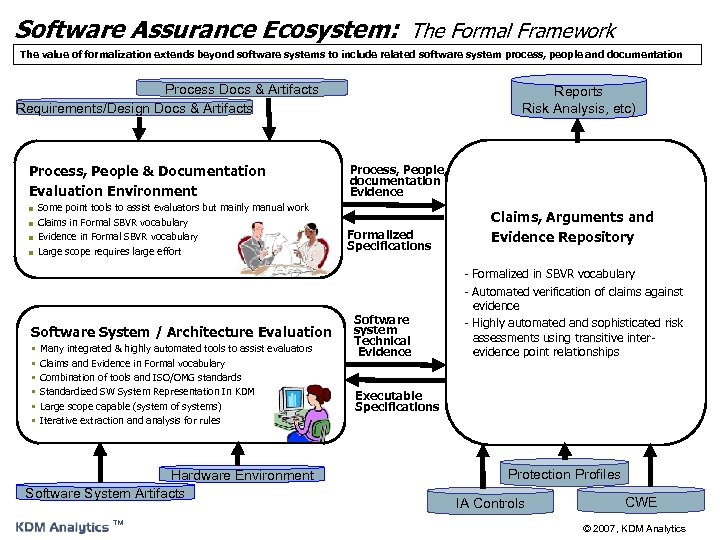 Software Assurance Ecosystem: The Formal Framework The value of formalization extends beyond software systems to include related software system process, people and documentation Process Docs & Artifacts Requirements/Design Docs & Artifacts Process, People & Documentation Evaluation Environment n n Some point tools to assist evaluators but mainly manual work Claims in Formal SBVR vocabulary Evidence in Formal SBVR vocabulary Large scope requires large effort Software System / Architecture Evaluation § § § Many integrated & highly automated tools to assist evaluators Claims and Evidence in Formal vocabulary Combination of tools and ISO/OMG standards Standardized SW System Representation In KDM Large scope capable (system of systems) Iterative extraction and analysis for rules Hardware Environment Software System Artifacts ™ Reports Risk Analysis, etc) Process, People, documentation Evidence Formalized Specifications Software system Technical Evidence Claims, Arguments and Evidence Repository - Formalized in SBVR vocabulary - Automated verification of claims against evidence - Highly automated and sophisticated risk assessments using transitive interevidence point relationships Executable Specifications Protection Profiles IA Controls CWE © 2007, KDM Analytics
Software Assurance Ecosystem: The Formal Framework The value of formalization extends beyond software systems to include related software system process, people and documentation Process Docs & Artifacts Requirements/Design Docs & Artifacts Process, People & Documentation Evaluation Environment n n Some point tools to assist evaluators but mainly manual work Claims in Formal SBVR vocabulary Evidence in Formal SBVR vocabulary Large scope requires large effort Software System / Architecture Evaluation § § § Many integrated & highly automated tools to assist evaluators Claims and Evidence in Formal vocabulary Combination of tools and ISO/OMG standards Standardized SW System Representation In KDM Large scope capable (system of systems) Iterative extraction and analysis for rules Hardware Environment Software System Artifacts ™ Reports Risk Analysis, etc) Process, People, documentation Evidence Formalized Specifications Software system Technical Evidence Claims, Arguments and Evidence Repository - Formalized in SBVR vocabulary - Automated verification of claims against evidence - Highly automated and sophisticated risk assessments using transitive interevidence point relationships Executable Specifications Protection Profiles IA Controls CWE © 2007, KDM Analytics
 The Software Assurance Ecosystem in Action ™ © 2007, KDM Analytics
The Software Assurance Ecosystem in Action ™ © 2007, KDM Analytics
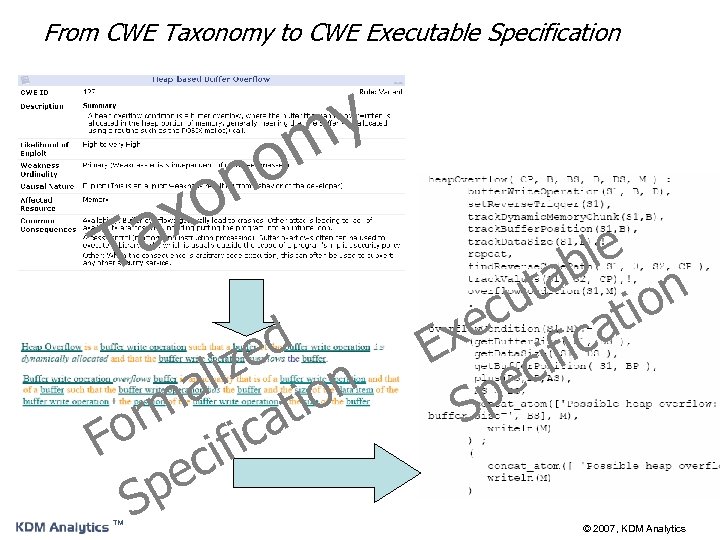 From CWE Taxonomy to CWE Executable Specification o x a T y m ed liz on a m ti or ifica F ec Sp ™ le ab t u on ec icati x E if ec p S © 2007, KDM Analytics
From CWE Taxonomy to CWE Executable Specification o x a T y m ed liz on a m ti or ifica F ec Sp ™ le ab t u on ec icati x E if ec p S © 2007, KDM Analytics
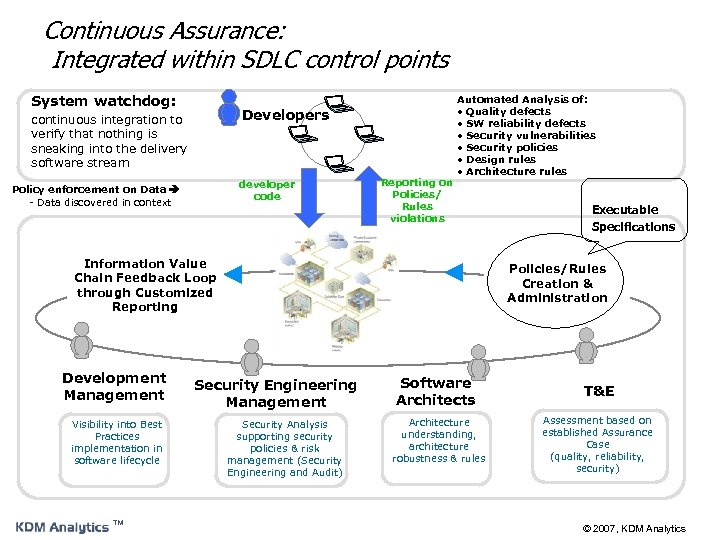 Continuous Assurance: Integrated within SDLC control points System watchdog: Developers continuous integration to verify that nothing is sneaking into the delivery software stream developer code Policy enforcement on Data - Data discovered in context Reporting on Policies/ Rules violations Automated Analysis of: • Quality defects • SW reliability defects • Security vulnerabilities • Security policies • Design rules • Architecture rules Information Value Chain Feedback Loop through Customized Reporting Development Management Visibility into Best Practices implementation in software lifecycle ™ Executable Specifications Policies/Rules Creation & Administration Security Engineering Management Security Analysis supporting security policies & risk management (Security Engineering and Audit) Software Architects Architecture understanding, architecture robustness & rules T&E Assessment based on established Assurance Case (quality, reliability, security) © 2007, KDM Analytics
Continuous Assurance: Integrated within SDLC control points System watchdog: Developers continuous integration to verify that nothing is sneaking into the delivery software stream developer code Policy enforcement on Data - Data discovered in context Reporting on Policies/ Rules violations Automated Analysis of: • Quality defects • SW reliability defects • Security vulnerabilities • Security policies • Design rules • Architecture rules Information Value Chain Feedback Loop through Customized Reporting Development Management Visibility into Best Practices implementation in software lifecycle ™ Executable Specifications Policies/Rules Creation & Administration Security Engineering Management Security Analysis supporting security policies & risk management (Security Engineering and Audit) Software Architects Architecture understanding, architecture robustness & rules T&E Assessment based on established Assurance Case (quality, reliability, security) © 2007, KDM Analytics
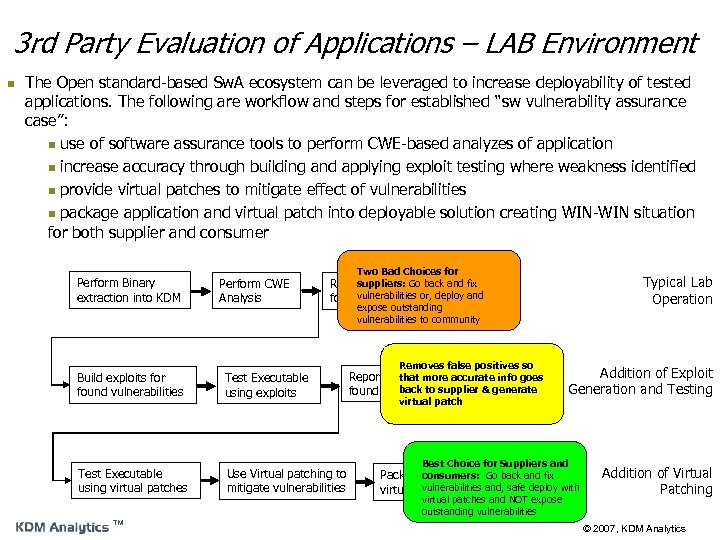 3 rd Party Evaluation of Applications – LAB Environment n The Open standard-based Sw. A ecosystem can be leveraged to increase deployability of tested applications. The following are workflow and steps for established “sw vulnerability assurance case”: n use of software assurance tools to perform CWE-based analyzes of application n increase accuracy through building and applying exploit testing where weakness identified n provide virtual patches to mitigate effect of vulnerabilities n package application and virtual patch into deployable solution creating WIN-WIN situation for both supplier and consumer Perform Binary extraction into KDM Perform CWE Analysis Two Bad Choices for suppliers: Go back Report Vulnerabilities and fix vulnerabilities or, deploy and found expose outstanding vulnerabilities to community Build exploits for found vulnerabilities Test Executable using exploits Test Executable using virtual patches Use Virtual patching to mitigate vulnerabilities ™ Removes false positives so Report Vulnerabilities that more accurate info goes back to supplier & generate found virtual patch Typical Lab Operation Addition of Exploit Generation and Testing Best Choice for Suppliers and Packageconsumers: Go back and fix Executable with vulnerabilities and, safe deploy with virtual patches for deployment virtual patches and NOT expose outstanding vulnerabilities Addition of Virtual Patching © 2007, KDM Analytics
3 rd Party Evaluation of Applications – LAB Environment n The Open standard-based Sw. A ecosystem can be leveraged to increase deployability of tested applications. The following are workflow and steps for established “sw vulnerability assurance case”: n use of software assurance tools to perform CWE-based analyzes of application n increase accuracy through building and applying exploit testing where weakness identified n provide virtual patches to mitigate effect of vulnerabilities n package application and virtual patch into deployable solution creating WIN-WIN situation for both supplier and consumer Perform Binary extraction into KDM Perform CWE Analysis Two Bad Choices for suppliers: Go back Report Vulnerabilities and fix vulnerabilities or, deploy and found expose outstanding vulnerabilities to community Build exploits for found vulnerabilities Test Executable using exploits Test Executable using virtual patches Use Virtual patching to mitigate vulnerabilities ™ Removes false positives so Report Vulnerabilities that more accurate info goes back to supplier & generate found virtual patch Typical Lab Operation Addition of Exploit Generation and Testing Best Choice for Suppliers and Packageconsumers: Go back and fix Executable with vulnerabilities and, safe deploy with virtual patches for deployment virtual patches and NOT expose outstanding vulnerabilities Addition of Virtual Patching © 2007, KDM Analytics


