0c344991c2d7251f014e175396b96b1b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 81
 Social Welfare The Impact of Crime on Society Llad Phillips 1
Social Welfare The Impact of Crime on Society Llad Phillips 1
 Your students have the option to order their course materials from our online store to be either shipped to them or reserved in store for pick up. We have assigned a unique username & password for ordering your class reader. Your course reader is now available for students to order online. Please inform your students that they can place their reader order by: 1) Logging on to www. alternativecopy. com 2) Clicking on the 'Order Readers' link in the top right corner of our home page 3) Entering your class username & password below: Username: ucsbecon 160 r Password: votey 29 **Please note that both username and password are lowercase** As before, we continue to sell the readers at our store as well. Thank you again for choosing the Alternative. Llad Phillips 2
Your students have the option to order their course materials from our online store to be either shipped to them or reserved in store for pick up. We have assigned a unique username & password for ordering your class reader. Your course reader is now available for students to order online. Please inform your students that they can place their reader order by: 1) Logging on to www. alternativecopy. com 2) Clicking on the 'Order Readers' link in the top right corner of our home page 3) Entering your class username & password below: Username: ucsbecon 160 r Password: votey 29 **Please note that both username and password are lowercase** As before, we continue to sell the readers at our store as well. Thank you again for choosing the Alternative. Llad Phillips 2
 Two Issues Today: What is it worth to the average student to not have their bicycle stolen? n What is the impact of crime on society? n Llad Phillips 3
Two Issues Today: What is it worth to the average student to not have their bicycle stolen? n What is the impact of crime on society? n Llad Phillips 3
 Preview of Coming Attractions n Evaluate public sector activities in terms of benefits and costs u Costs: $ u Benefits ? How do we value public safety? There is not a “market” for public safety u Benefit cost ratio: benefits/costs u benefits/costs = crime*price/costs Crime: How much crime is there? Crime: Does society focus on the right types of crime? Llad Phillips 4
Preview of Coming Attractions n Evaluate public sector activities in terms of benefits and costs u Costs: $ u Benefits ? How do we value public safety? There is not a “market” for public safety u Benefit cost ratio: benefits/costs u benefits/costs = crime*price/costs Crime: How much crime is there? Crime: Does society focus on the right types of crime? Llad Phillips 4
 Who is this guy? Llad Phillips 5
Who is this guy? Llad Phillips 5
 Llad Phillips 6
Llad Phillips 6
 Preview of Coming Attractions n Why is the Public Provision of Goods and Services in Crisis? u Costs are out of line with benefits u The management of the public provision of goods and services is out of the control of the public What we will learn in econ 160 also has application to other public sector goods such as health care and education. We will focus on public safety for our story and examples Llad Phillips 7
Preview of Coming Attractions n Why is the Public Provision of Goods and Services in Crisis? u Costs are out of line with benefits u The management of the public provision of goods and services is out of the control of the public What we will learn in econ 160 also has application to other public sector goods such as health care and education. We will focus on public safety for our story and examples Llad Phillips 7
 Outline and Issues Course logistics: http: //www. econ. ucsb. edu n Criminal Justice System (CJS) & economic paradigm: where do the values (prices) come from to evaluate the states (outcomes) of the CJS? n How much crime is there? How do we know? n Crime has two effects: n u Redistribution of welfare from the victim to the perpetrator u Opportunity cost or waste of resources for defense Llad Phillips 8
Outline and Issues Course logistics: http: //www. econ. ucsb. edu n Criminal Justice System (CJS) & economic paradigm: where do the values (prices) come from to evaluate the states (outcomes) of the CJS? n How much crime is there? How do we know? n Crime has two effects: n u Redistribution of welfare from the victim to the perpetrator u Opportunity cost or waste of resources for defense Llad Phillips 8



 SERIOUSNESS SURVEY RATE THE SERIOUSNESS OF EACH OF THE FOLLOWING BEHAVIORS ON A SCALE FROM ZERO( LEAST SERIOUS) TO TEN( MOST SERIOUS): 1. HOMICIDE ___ 2. MASS POISONING ( e. g. TYLENOL) 3. FORCIBLE RAPE 4. ARSON: SET FIRE TO A GARAGE 5. SELLING HEROIN 6. AUTO THEFT 7. EMBEZZLEMENT OF $1, 000 8. PROSTITUTE IN A HOUSE OF PROSTITUTION 9. POSSESSION OF MARIJUANA 10. SNIFFING GLUE ___ ___ ___
SERIOUSNESS SURVEY RATE THE SERIOUSNESS OF EACH OF THE FOLLOWING BEHAVIORS ON A SCALE FROM ZERO( LEAST SERIOUS) TO TEN( MOST SERIOUS): 1. HOMICIDE ___ 2. MASS POISONING ( e. g. TYLENOL) 3. FORCIBLE RAPE 4. ARSON: SET FIRE TO A GARAGE 5. SELLING HEROIN 6. AUTO THEFT 7. EMBEZZLEMENT OF $1, 000 8. PROSTITUTE IN A HOUSE OF PROSTITUTION 9. POSSESSION OF MARIJUANA 10. SNIFFING GLUE ___ ___ ___
 A Theme for this Course n Criminal Justice System is in crisis. u Courts told former Governor Schwarzenegger to find housing for prisoners or release them early u City and County jails are overflowing and a revolving door policy is in effect. Repeat offenders clog the system u Not enough judges and prosecutors Llad Phillips 13
A Theme for this Course n Criminal Justice System is in crisis. u Courts told former Governor Schwarzenegger to find housing for prisoners or release them early u City and County jails are overflowing and a revolving door policy is in effect. Repeat offenders clog the system u Not enough judges and prosecutors Llad Phillips 13
 Llad Phillips 14
Llad Phillips 14
 We have met the enemy and he is us Llad Phillips 15
We have met the enemy and he is us Llad Phillips 15
 Llad Phillips 16
Llad Phillips 16
 2006 Llad Phillips 17
2006 Llad Phillips 17
 Llad Phillips 18
Llad Phillips 18
 It Has Not Always Been This Way The Criminal Justice System had been relatively stable in the decade after World War II n What happened? That is the story of this course. n We will review the history of criminal justice in the 60 years since WW II. n We will suggest policies that will help turn things around now. In brief, what is needed is triage, i. e. to use scarce resources that will improve public safety the most. n Llad Phillips 19
It Has Not Always Been This Way The Criminal Justice System had been relatively stable in the decade after World War II n What happened? That is the story of this course. n We will review the history of criminal justice in the 60 years since WW II. n We will suggest policies that will help turn things around now. In brief, what is needed is triage, i. e. to use scarce resources that will improve public safety the most. n Llad Phillips 19
 Social Welfare The Impact of Crime on Society Llad Phillips 20
Social Welfare The Impact of Crime on Society Llad Phillips 20
 Questions about crime Is crime a real problem or a media induced problem? n Is crime an economic problem? n Are we getting our money’s worth for the dollars we spend on police, jails, and prisons? n Llad Phillips 21
Questions about crime Is crime a real problem or a media induced problem? n Is crime an economic problem? n Are we getting our money’s worth for the dollars we spend on police, jails, and prisons? n Llad Phillips 21
 Taking Crimes Robbery n Burglary n Auto Theft n Larceny n Llad Phillips 22
Taking Crimes Robbery n Burglary n Auto Theft n Larceny n Llad Phillips 22
 How is Crime Measured n Victimization Surveys of Households u U S Dept of Justice, Bureau of Justice Statistics, Criminal Victimization n Citizen (Victim) Reports to Police u U S Dept of Justice, FBI, Uniform Crime Reports Llad Phillips 23
How is Crime Measured n Victimization Surveys of Households u U S Dept of Justice, Bureau of Justice Statistics, Criminal Victimization n Citizen (Victim) Reports to Police u U S Dept of Justice, FBI, Uniform Crime Reports Llad Phillips 23
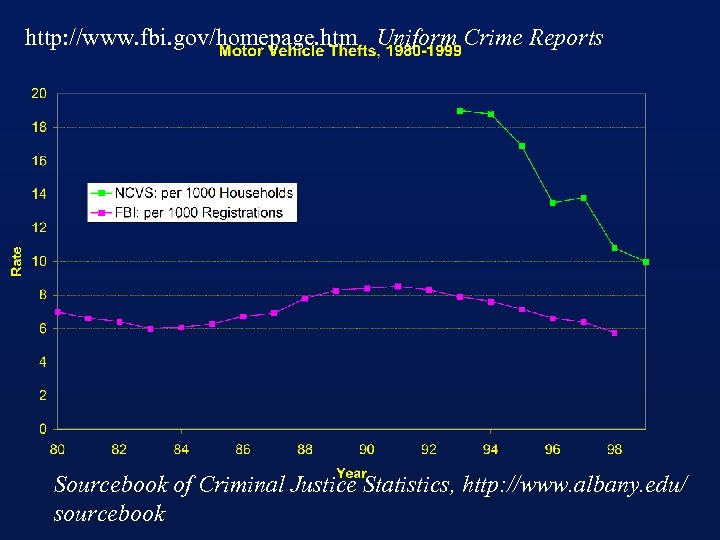 http: //www. fbi. gov/homepage. htm Uniform Crime Reports Sourcebook of Criminal Justice Statistics, http: //www. albany. edu/ sourcebook
http: //www. fbi. gov/homepage. htm Uniform Crime Reports Sourcebook of Criminal Justice Statistics, http: //www. albany. edu/ sourcebook
 Measures of Crime: Offense Rates n Thefts per 1000 registrations(FBI) = registrations per household * thefts per 1000 households(NCVS) u if registrations per household were growing in the 90’s then thefts per 1000 registrations would not fall as fast as thefts per 1000 households Llad Phillips 25
Measures of Crime: Offense Rates n Thefts per 1000 registrations(FBI) = registrations per household * thefts per 1000 households(NCVS) u if registrations per household were growing in the 90’s then thefts per 1000 registrations would not fall as fast as thefts per 1000 households Llad Phillips 25
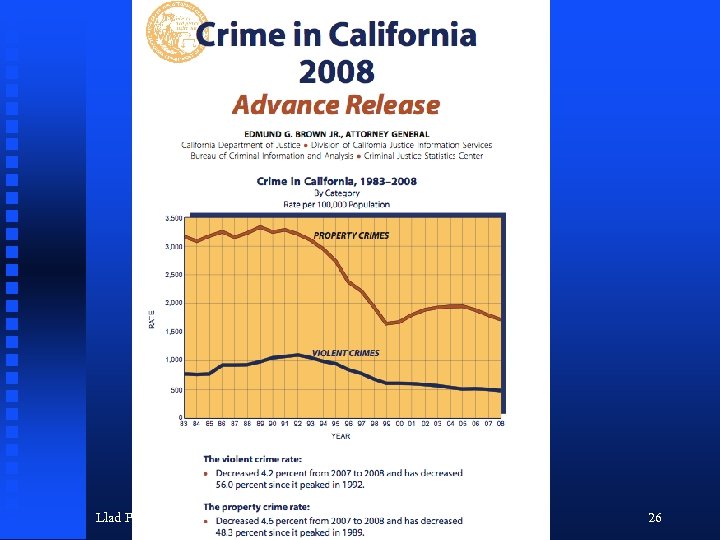 Llad Phillips 26
Llad Phillips 26
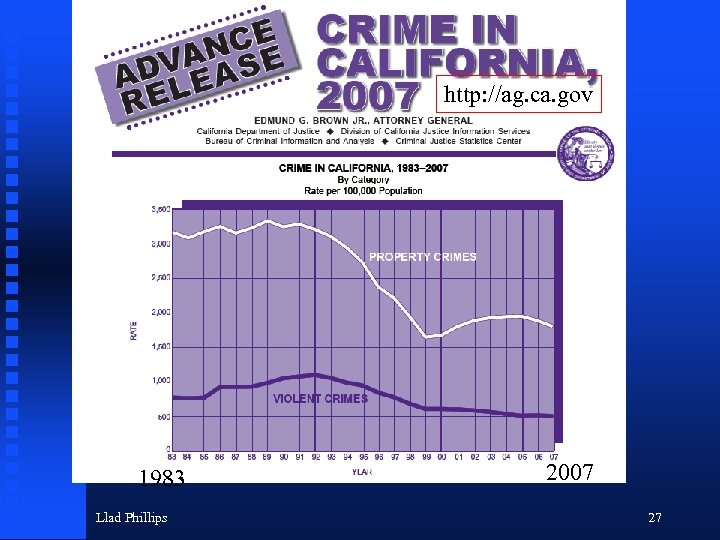 http: //ag. ca. gov 1983 Llad Phillips 2007 27
http: //ag. ca. gov 1983 Llad Phillips 2007 27
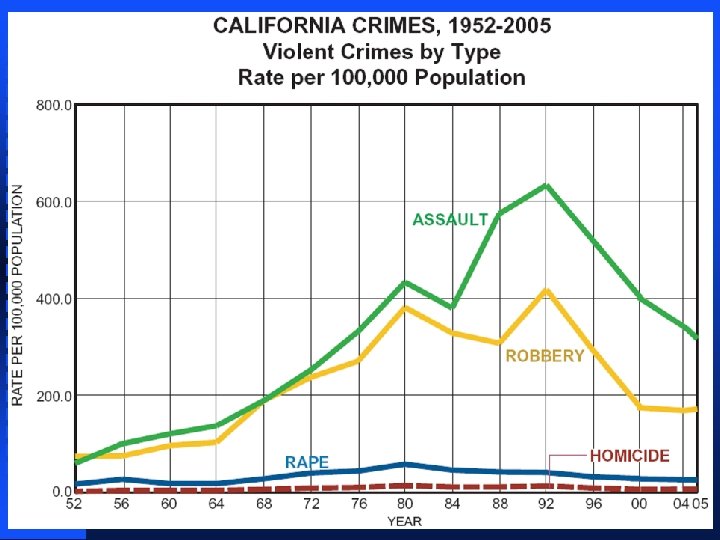 Llad Phillips 28
Llad Phillips 28
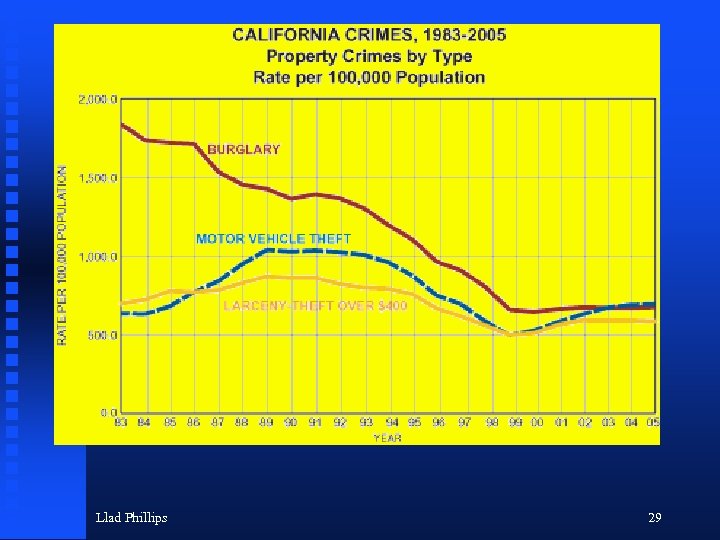 Llad Phillips 29
Llad Phillips 29
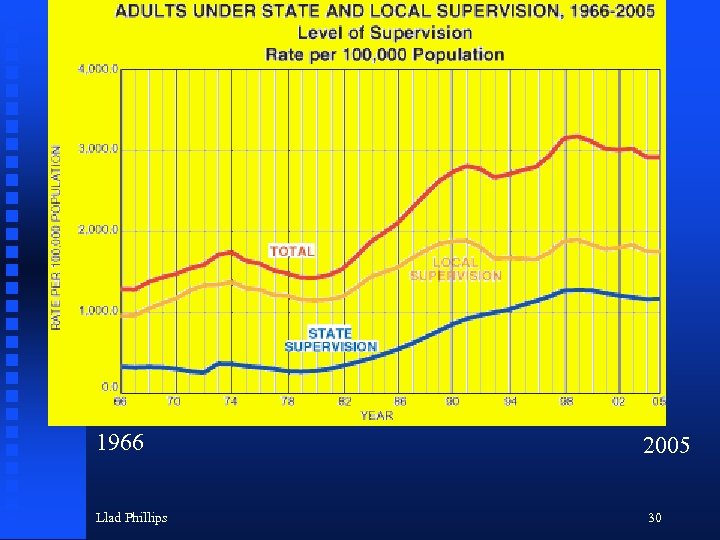 1966 Llad Phillips 2005 30
1966 Llad Phillips 2005 30
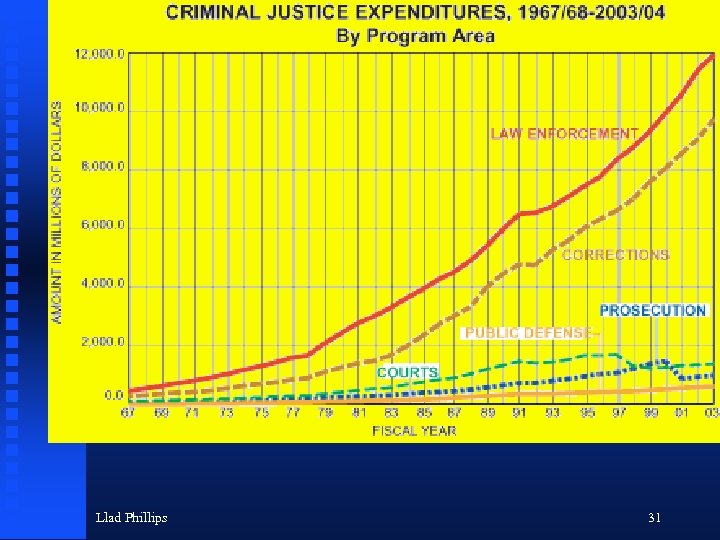 Llad Phillips 31
Llad Phillips 31
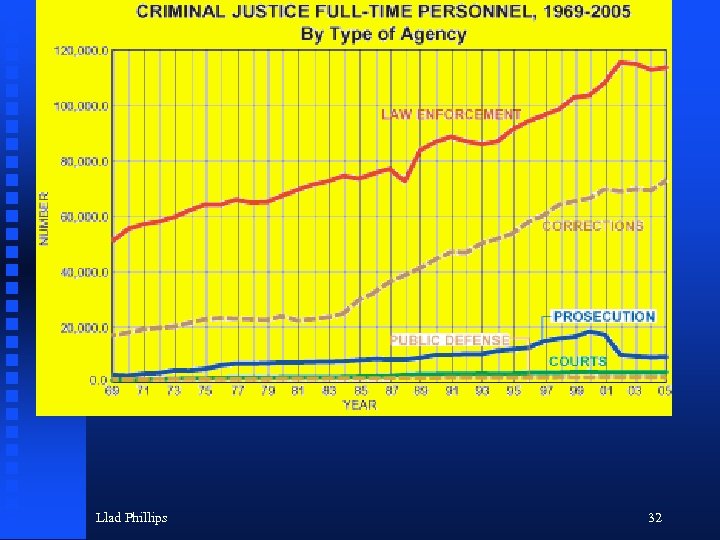 Llad Phillips 32
Llad Phillips 32
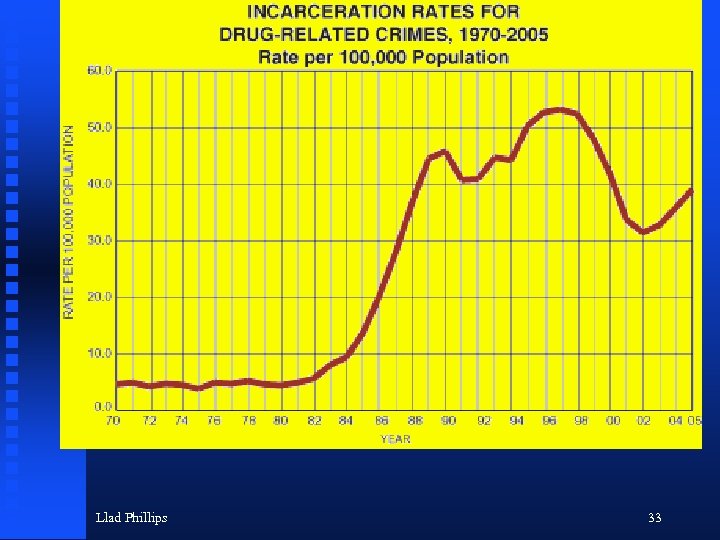 Llad Phillips 33
Llad Phillips 33
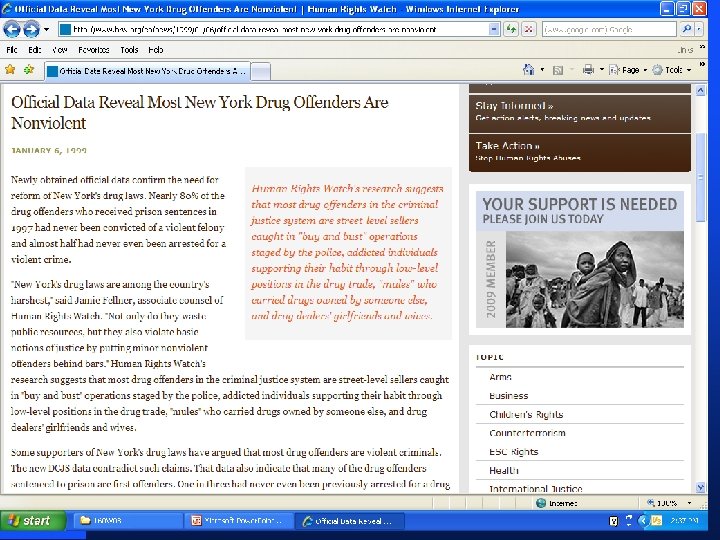 Llad Phillips 34
Llad Phillips 34
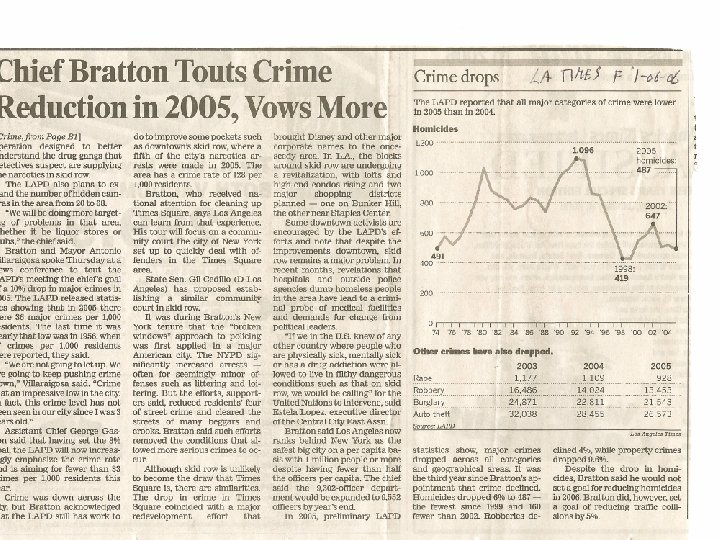 Llad Phillips 35
Llad Phillips 35
 Questions about the Operation of CJS If crime is going down, why are we devoting more resources to its control? n If drug offenders are mostly non-violent, why do we send them to state prison instead of rehabilitation? n Llad Phillips 36
Questions about the Operation of CJS If crime is going down, why are we devoting more resources to its control? n If drug offenders are mostly non-violent, why do we send them to state prison instead of rehabilitation? n Llad Phillips 36
 Sources of Criminal Justice Information On the Internet Sourcebook of Criminal Justice Statistics: http: //www. albany. edu/sourcebook/ Uniform Crime Reports, Crime in the United States, http: //www. fbi. gov/ucr/03 cius. htm Bureau of Justice Statistics: http: //www. ojp. usdoj. gov/bjs/ Crime in California, http: //caag. state. ca. us/cjsc/pubs. htm California Department of Corrections, http: //www. corr. ca. gov/ Llad Phillips 37
Sources of Criminal Justice Information On the Internet Sourcebook of Criminal Justice Statistics: http: //www. albany. edu/sourcebook/ Uniform Crime Reports, Crime in the United States, http: //www. fbi. gov/ucr/03 cius. htm Bureau of Justice Statistics: http: //www. ojp. usdoj. gov/bjs/ Crime in California, http: //caag. state. ca. us/cjsc/pubs. htm California Department of Corrections, http: //www. corr. ca. gov/ Llad Phillips 37
 Two Perspectives On Crime No Problem n It’s Bad n Llad Phillips 38
Two Perspectives On Crime No Problem n It’s Bad n Llad Phillips 38
 Crime as Income Redistribution n The Robin Hood Myth u Take from the rich and give to the poor n The impact on social welfare u depends on your views or values F socialist versus a capitalist Llad Phillips 39
Crime as Income Redistribution n The Robin Hood Myth u Take from the rich and give to the poor n The impact on social welfare u depends on your views or values F socialist versus a capitalist Llad Phillips 39
 41 Robin Hood Movies Silent film in 1908
41 Robin Hood Movies Silent film in 1908
 Llad Phillips 41
Llad Phillips 41
 Llad Phillips 42
Llad Phillips 42
 Llad Phillips 43
Llad Phillips 43
 Crime as a dead weight loss n Loss of resouces spent on defense u protection of homes u protection of cars u protection of bicycles n Resources spent on defense u could be spent on goods and services F in the absence of crime n The impact on social welfare u Unambiguously bad Llad Phillips 44
Crime as a dead weight loss n Loss of resouces spent on defense u protection of homes u protection of cars u protection of bicycles n Resources spent on defense u could be spent on goods and services F in the absence of crime n The impact on social welfare u Unambiguously bad Llad Phillips 44
 What is the nature of crime? Income redistribution? n or dead-weight loss? n Llad Phillips 45
What is the nature of crime? Income redistribution? n or dead-weight loss? n Llad Phillips 45
 Economists Assume You Know What You Like n Lingo: economists call these consumer tastes or consumer preferences Llad Phillips 46
Economists Assume You Know What You Like n Lingo: economists call these consumer tastes or consumer preferences Llad Phillips 46
 Thief’s Income Victim’s Income
Thief’s Income Victim’s Income
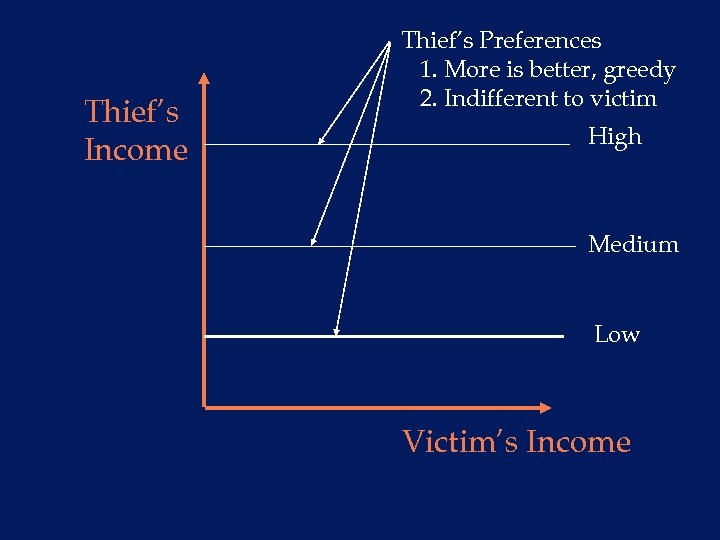 Thief’s Income Thief’s Preferences 1. More is better, greedy 2. Indifferent to victim High Medium Low Victim’s Income
Thief’s Income Thief’s Preferences 1. More is better, greedy 2. Indifferent to victim High Medium Low Victim’s Income
 Economists Assume You Can make Comparisons n For example: the thief can compare a high level of his income and a low level of the victim’s income with a high level of his income and a high level of the victim’s income u in the case just illustrated, the thief values these the same since his income stays the same F the thief does not care whether the victim’s income is high or low, i. e. he is indifferent Llad Phillips 49
Economists Assume You Can make Comparisons n For example: the thief can compare a high level of his income and a low level of the victim’s income with a high level of his income and a high level of the victim’s income u in the case just illustrated, the thief values these the same since his income stays the same F the thief does not care whether the victim’s income is high or low, i. e. he is indifferent Llad Phillips 49
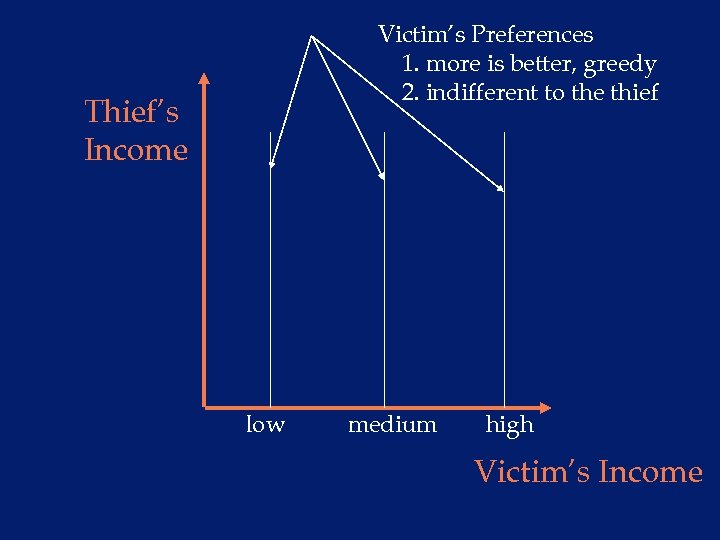 Victim’s Preferences 1. more is better, greedy 2. indifferent to the thief Thief’s Income low medium high Victim’s Income
Victim’s Preferences 1. more is better, greedy 2. indifferent to the thief Thief’s Income low medium high Victim’s Income
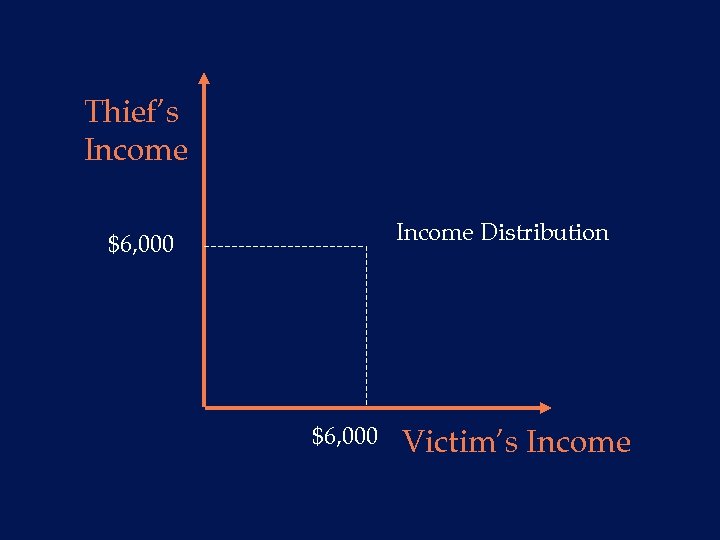 Thief’s Income Distribution $6, 000 Victim’s Income
Thief’s Income Distribution $6, 000 Victim’s Income
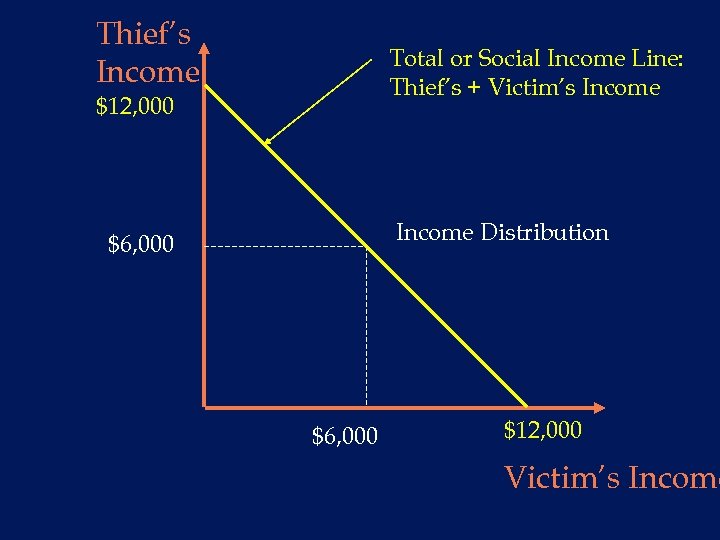 Thief’s Income Total or Social Income Line: Thief’s + Victim’s Income $12, 000 Income Distribution $6, 000 $12, 000 Victim’s Income
Thief’s Income Total or Social Income Line: Thief’s + Victim’s Income $12, 000 Income Distribution $6, 000 $12, 000 Victim’s Income
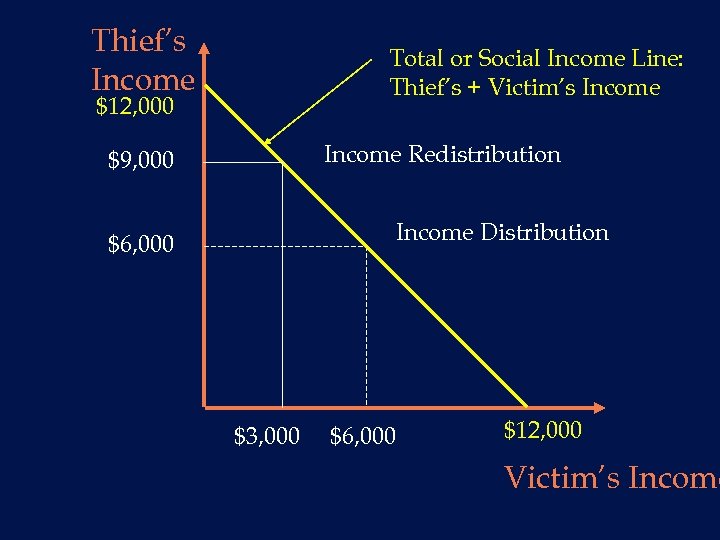 Thief’s Income Total or Social Income Line: Thief’s + Victim’s Income $12, 000 Income Redistribution $9, 000 Income Distribution $6, 000 $3, 000 $6, 000 $12, 000 Victim’s Income
Thief’s Income Total or Social Income Line: Thief’s + Victim’s Income $12, 000 Income Redistribution $9, 000 Income Distribution $6, 000 $3, 000 $6, 000 $12, 000 Victim’s Income
 Bad effects from taking crimes Victim has less incentive to be productive n Victim has more incentive to spend time and money on defense n Analogous to war: guns vs. butter n What is society going to produce? n u defense against crime? u or goods and services? Llad Phillips 54
Bad effects from taking crimes Victim has less incentive to be productive n Victim has more incentive to spend time and money on defense n Analogous to war: guns vs. butter n What is society going to produce? n u defense against crime? u or goods and services? Llad Phillips 54
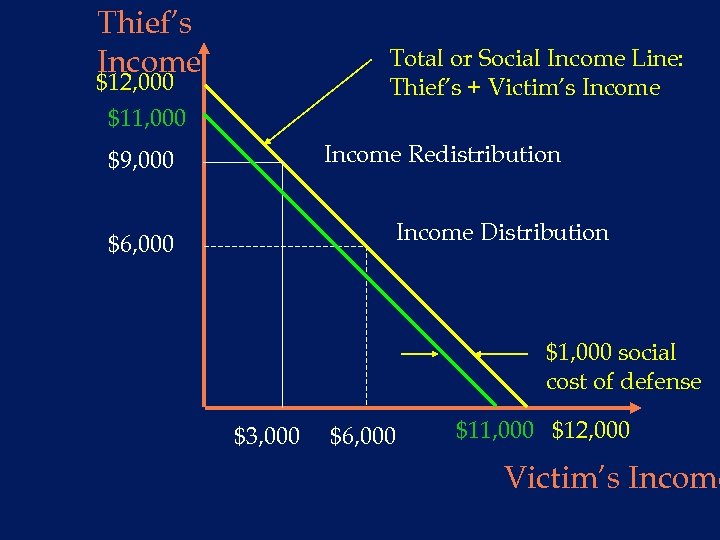 Thief’s Income Total or Social Income Line: Thief’s + Victim’s Income $12, 000 $11, 000 Income Redistribution $9, 000 Income Distribution $6, 000 $1, 000 social cost of defense $3, 000 $6, 000 $11, 000 $12, 000 Victim’s Income
Thief’s Income Total or Social Income Line: Thief’s + Victim’s Income $12, 000 $11, 000 Income Redistribution $9, 000 Income Distribution $6, 000 $1, 000 social cost of defense $3, 000 $6, 000 $11, 000 $12, 000 Victim’s Income
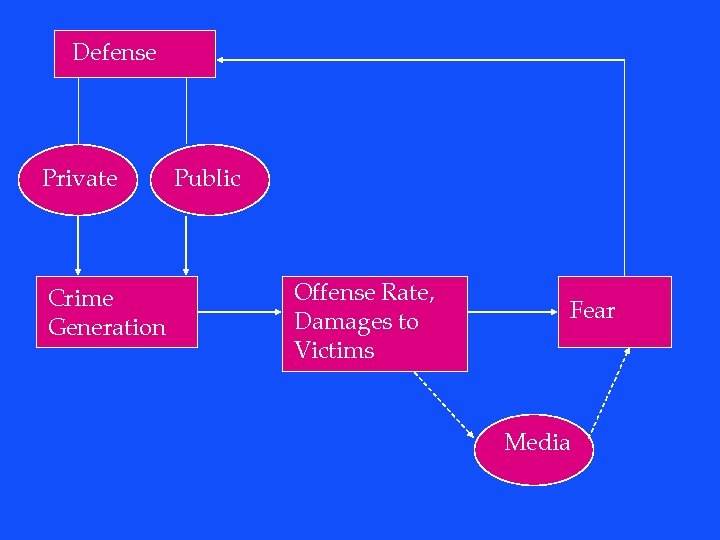 Defense Private Crime Generation Public Offense Rate, Damages to Victims Fear Media
Defense Private Crime Generation Public Offense Rate, Damages to Victims Fear Media
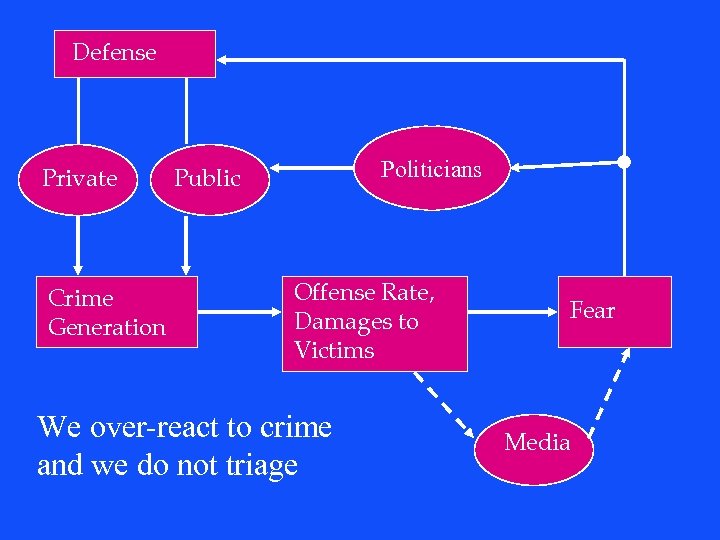 Defense Private Crime Generation Politicians Public Offense Rate, Damages to Victims We over-react to crime and we do not triage Fear Media
Defense Private Crime Generation Politicians Public Offense Rate, Damages to Victims We over-react to crime and we do not triage Fear Media
 Cost to Victims in US, 1993 Source: National Institute of Justice, Victim Costs and Consequences (1996) Llad Phillips 58
Cost to Victims in US, 1993 Source: National Institute of Justice, Victim Costs and Consequences (1996) Llad Phillips 58
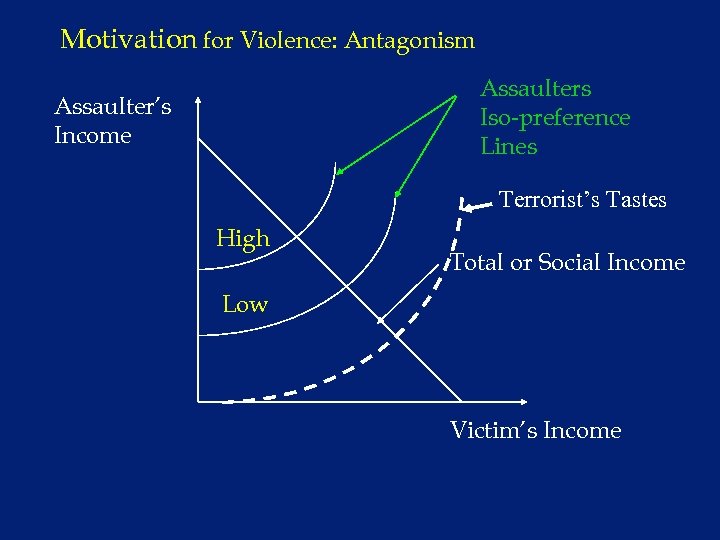 Motivation for Violence: Antagonism Assaulters Iso-preference Lines Assaulter’s Income Terrorist’s Tastes High Total or Social Income Low Victim’s Income
Motivation for Violence: Antagonism Assaulters Iso-preference Lines Assaulter’s Income Terrorist’s Tastes High Total or Social Income Low Victim’s Income
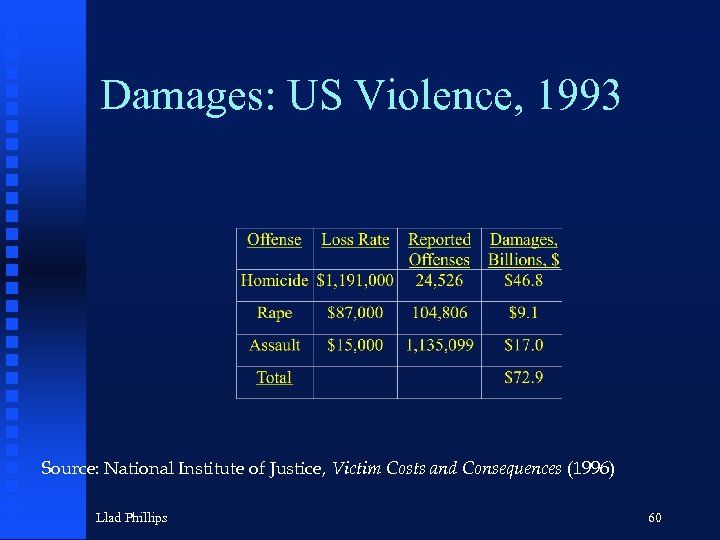 Damages: US Violence, 1993 Source: National Institute of Justice, Victim Costs and Consequences (1996) Llad Phillips 60
Damages: US Violence, 1993 Source: National Institute of Justice, Victim Costs and Consequences (1996) Llad Phillips 60
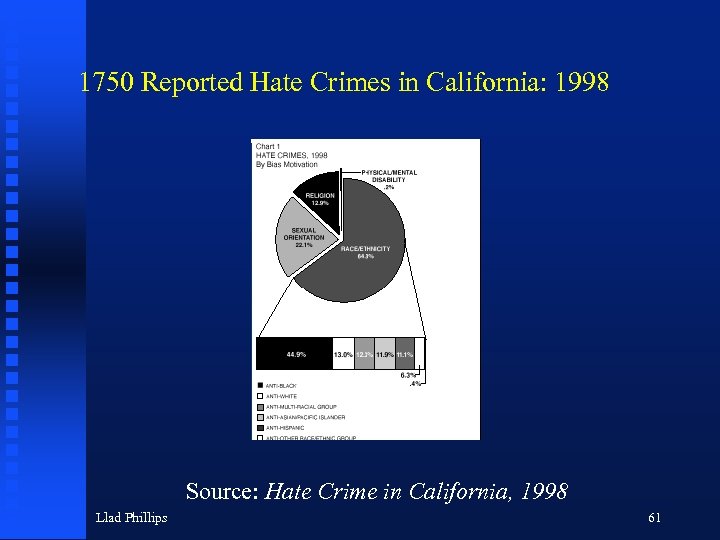 1750 Reported Hate Crimes in California: 1998 Source: Hate Crime in California, 1998 Llad Phillips 61
1750 Reported Hate Crimes in California: 1998 Source: Hate Crime in California, 1998 Llad Phillips 61
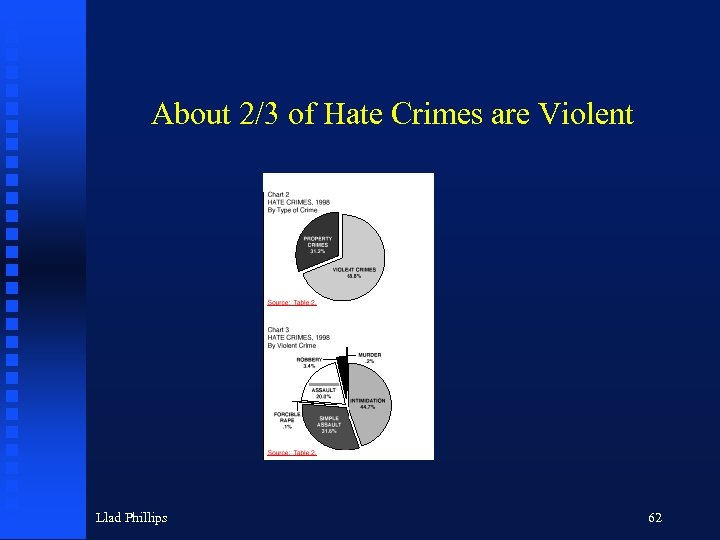 About 2/3 of Hate Crimes are Violent Llad Phillips 62
About 2/3 of Hate Crimes are Violent Llad Phillips 62
 Types of Crime n Motivation: self-interest, greed u Street Crimes: robbery, burglary, auto theft, larceny u White Collar: embezzlement, tax evasion, investment fraud, check fraud, telephone fraud u Status Offenses: runaway, truant, vagrant, beyond control of parents u Black Market: gambling, prostitution, drugs Llad Phillips 63
Types of Crime n Motivation: self-interest, greed u Street Crimes: robbery, burglary, auto theft, larceny u White Collar: embezzlement, tax evasion, investment fraud, check fraud, telephone fraud u Status Offenses: runaway, truant, vagrant, beyond control of parents u Black Market: gambling, prostitution, drugs Llad Phillips 63
 Types of Crime n Motivation: Hate, Rage u Street Crimes: homicide, aggravated assault, rape u Crimes Against Public Order: vandalism, terrorism u Hate Crimes F Columbine High F James Byrd: dragging death in Texas F Jewish Community Center in Granada Hills Llad Phillips 64
Types of Crime n Motivation: Hate, Rage u Street Crimes: homicide, aggravated assault, rape u Crimes Against Public Order: vandalism, terrorism u Hate Crimes F Columbine High F James Byrd: dragging death in Texas F Jewish Community Center in Granada Hills Llad Phillips 64
 CA Descriptive Statistics Llad Phillips 65
CA Descriptive Statistics Llad Phillips 65
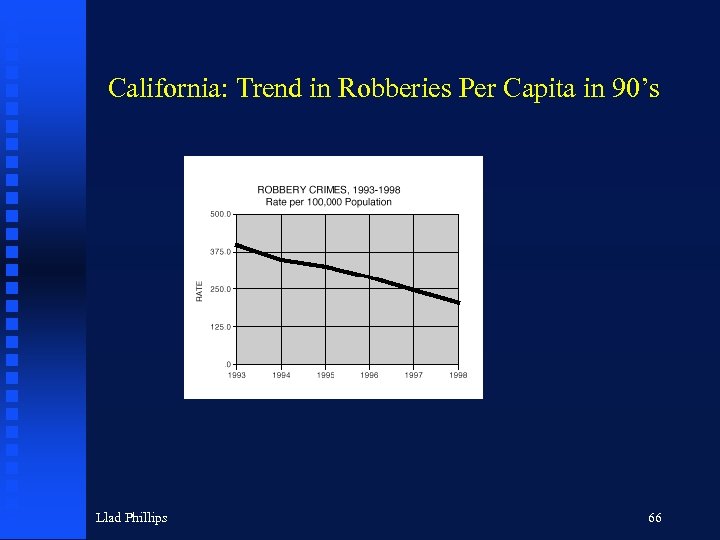 California: Trend in Robberies Per Capita in 90’s Llad Phillips 66
California: Trend in Robberies Per Capita in 90’s Llad Phillips 66
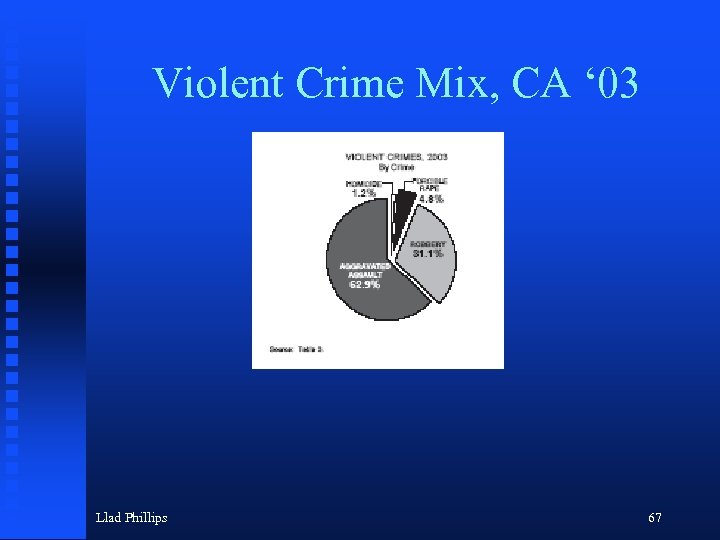 Violent Crime Mix, CA ‘ 03 Llad Phillips 67
Violent Crime Mix, CA ‘ 03 Llad Phillips 67
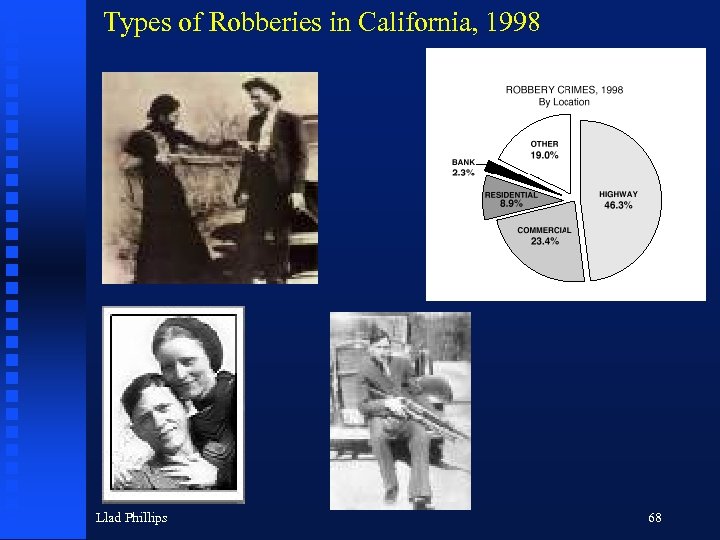 Types of Robberies in California, 1998 Llad Phillips 68
Types of Robberies in California, 1998 Llad Phillips 68
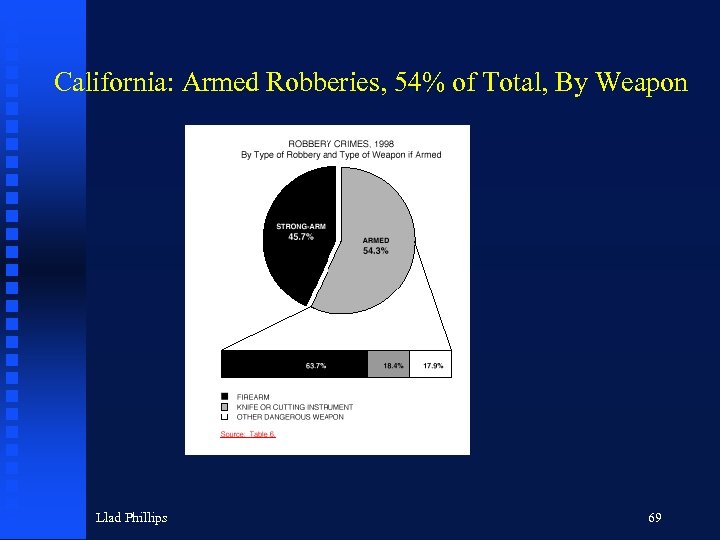 California: Armed Robberies, 54% of Total, By Weapon Llad Phillips 69
California: Armed Robberies, 54% of Total, By Weapon Llad Phillips 69
 Homicide by Weapon, CA ‘ 03 Llad Phillips 70
Homicide by Weapon, CA ‘ 03 Llad Phillips 70
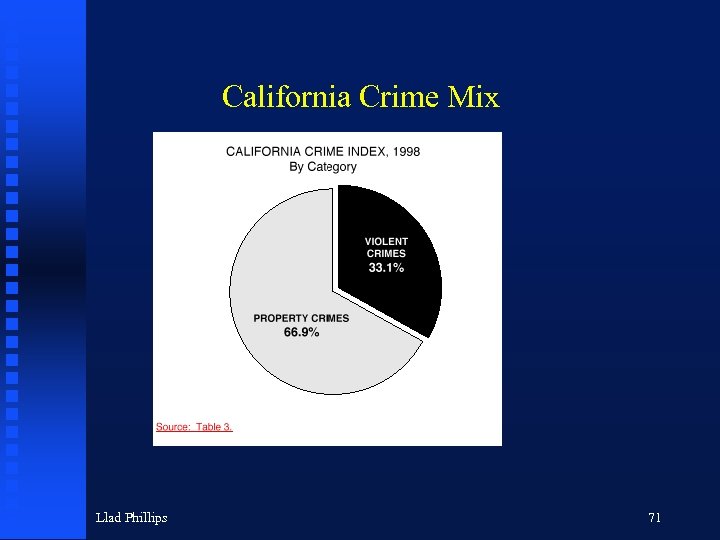 California Crime Mix Llad Phillips 71
California Crime Mix Llad Phillips 71
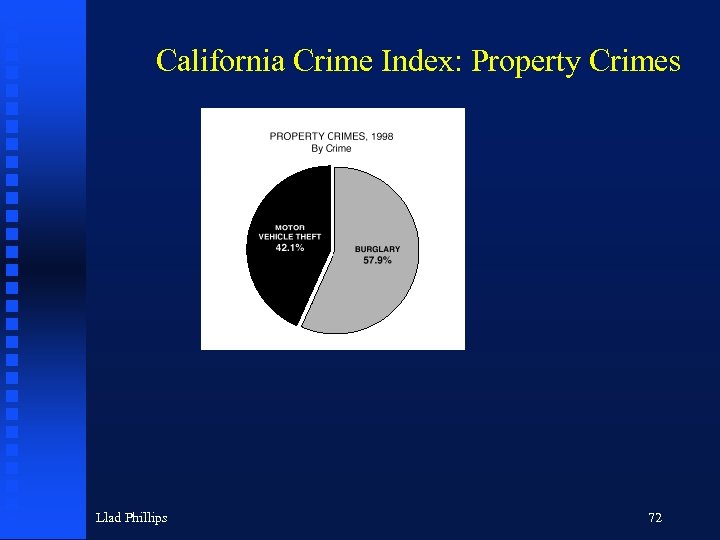 California Crime Index: Property Crimes Llad Phillips 72
California Crime Index: Property Crimes Llad Phillips 72
 Sources of Information p. of syllabus n US Data u Sourcebook of Criminal Justice Statistics F http: //www. albany. edu/sourcebook/ u Bureau of Justice Statistics F http: //www. ojp. usdoj. gov/bjs/welcome. html Llad Phillips 73
Sources of Information p. of syllabus n US Data u Sourcebook of Criminal Justice Statistics F http: //www. albany. edu/sourcebook/ u Bureau of Justice Statistics F http: //www. ojp. usdoj. gov/bjs/welcome. html Llad Phillips 73
 Summary n Crime is an economic problem u loss of resources(dead weight loss) from private and public defense n Damages to victims are 3 times as high for crimes against persons compared to crimes against property u Total for 7 FBI Index Crimes: $ 95 Billion Shouldn’t society focus more on big ticket fraud: Enron, World. Com, Bernard Madoff Investment Securities LLC? Llad Phillips 74
Summary n Crime is an economic problem u loss of resources(dead weight loss) from private and public defense n Damages to victims are 3 times as high for crimes against persons compared to crimes against property u Total for 7 FBI Index Crimes: $ 95 Billion Shouldn’t society focus more on big ticket fraud: Enron, World. Com, Bernard Madoff Investment Securities LLC? Llad Phillips 74
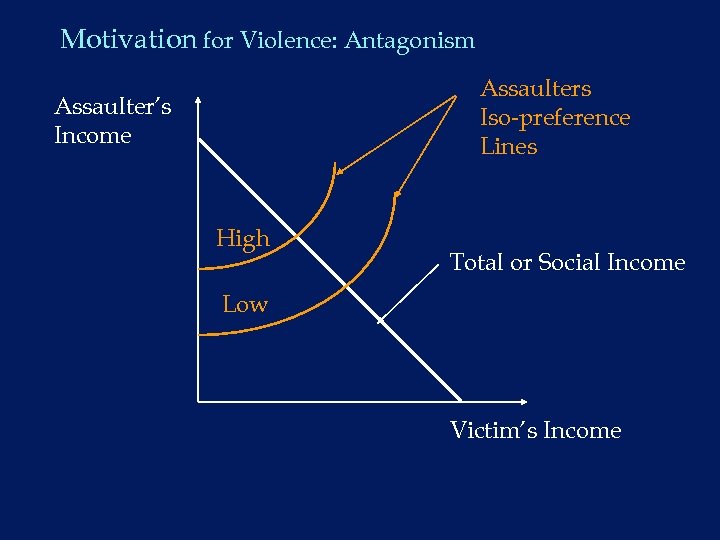 Motivation for Violence: Antagonism Assaulters Iso-preference Lines Assaulter’s Income High Total or Social Income Low Victim’s Income
Motivation for Violence: Antagonism Assaulters Iso-preference Lines Assaulter’s Income High Total or Social Income Low Victim’s Income
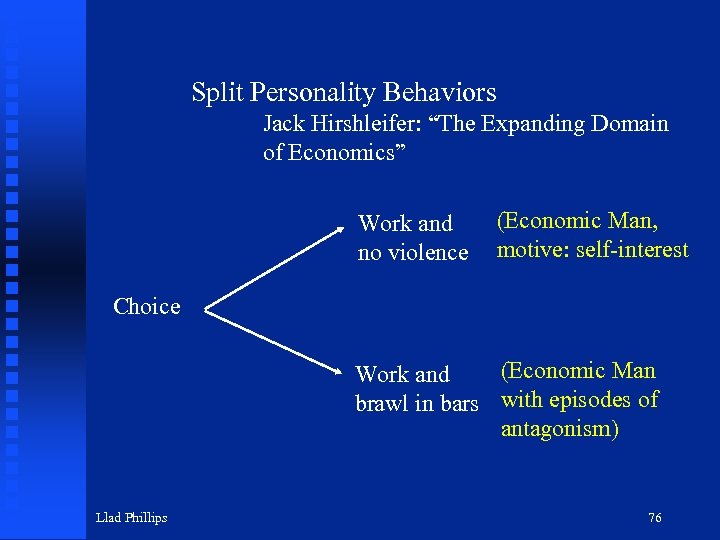 Split Personality Behaviors Jack Hirshleifer: “The Expanding Domain of Economics” Work and no violence (Economic Man, motive: self-interest) Choice (Economic Man Work and brawl in bars with episodes of antagonism) Llad Phillips 76
Split Personality Behaviors Jack Hirshleifer: “The Expanding Domain of Economics” Work and no violence (Economic Man, motive: self-interest) Choice (Economic Man Work and brawl in bars with episodes of antagonism) Llad Phillips 76
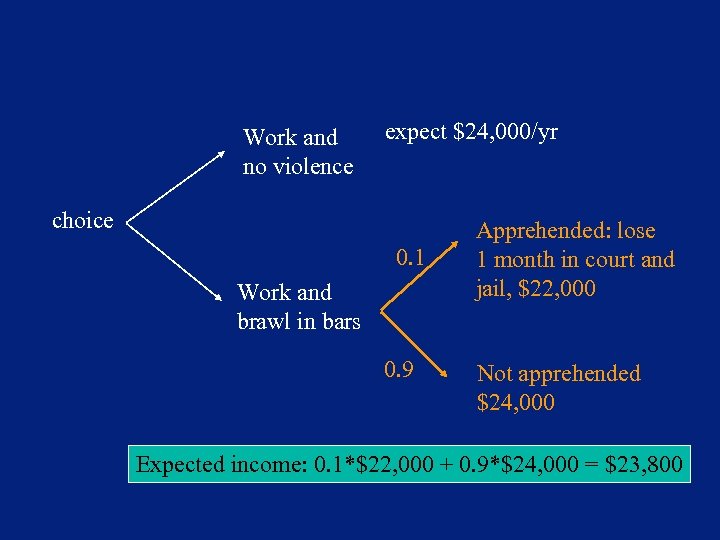 Work and no violence expect $24, 000/yr choice 0. 1 Work and brawl in bars 0. 9 Apprehended: lose 1 month in court and jail, $22, 000 Not apprehended $24, 000 Expected income: 0. 1*$22, 000 + 0. 9*$24, 000 = $23, 800
Work and no violence expect $24, 000/yr choice 0. 1 Work and brawl in bars 0. 9 Apprehended: lose 1 month in court and jail, $22, 000 Not apprehended $24, 000 Expected income: 0. 1*$22, 000 + 0. 9*$24, 000 = $23, 800

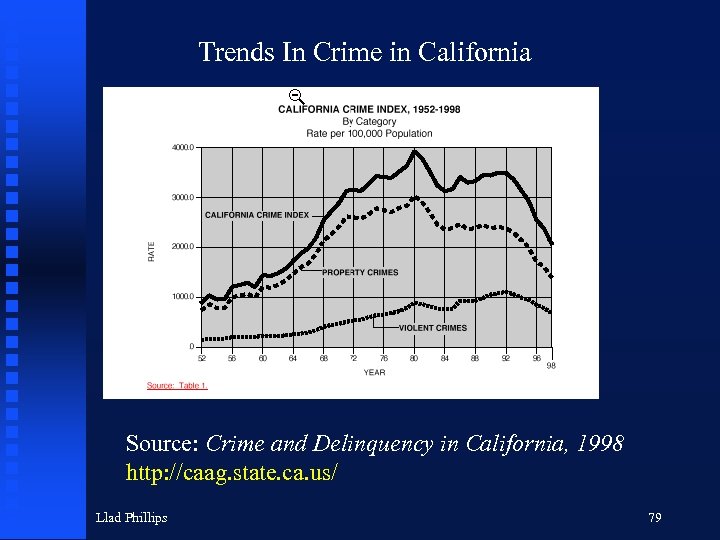 Trends In Crime in California Source: Crime and Delinquency in California, 1998 http: //caag. state. ca. us/ Llad Phillips 79
Trends In Crime in California Source: Crime and Delinquency in California, 1998 http: //caag. state. ca. us/ Llad Phillips 79
 Llad Phillips 80
Llad Phillips 80
 Llad Phillips 81
Llad Phillips 81


