eb33e8b59eab1ec3b83fcc69ffb1d084.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 57

Social Security Administration

SSA Disability Benefit Programs Social Security Supplemental Security Income (SSI) • Based on a No work requirement; income, resources are factors • Family members Only for individual, not family worker’s earnings possibly entitled

Definition of Disability Same for Both Programs • Physical/mental impairment expected to last (or has lasted) 12 months & • Impairment prevents worker from engaging in “Substantial Gainful Activity” (SGA)

What is “SGA”? • “Gainful activity” is work • To be considered “substantial, ” gross earnings must be at least $940* monthly * $1, 570 for blind

Disability “Onset Date” • Refers to earliest date condition meets medical requirements & • Person was not working above SGA level ($940 monthly)

Who Qualifies for Social Security Disability Benefits? • Worker - filing on own work record • Disabled widow(er) - filing on deceased spouse’s record; minimum age 50 • Disabled Adult Child - filing on parent’s record; over age 18, disabled before 22

To be Insured, Workers need “Credits” • $1, 050 earnings = one credit • Can earn maximum of four per year

For Worker, Age at Onset Dictates Credits Required • Age 31 or older: 20 credits in 40 -credit period pre-onset • Age 24 to 30 credits for half the time from 21 -onset • Under Age 24 - 6 credits in three-year period pre-onset

Who Qualifies for SSI Benefits? • Categories of recipients - aged (65 and older) - blind - disabled adults and children • Receive cash benefits, Medicaid

SSI Income Limits • Federal maximum monthly payment, no other income: - $637 for individual - $956 for couple (both on SSI) • If other income, $20 exclusion applies - e. g. , $500 Social Security results in $157 federal SSI

SSI State Supplement – Penna. • State adds up to $27. 40 or $48. 30 in separate check exception: residents of Medicaid facility only due federal payment of $30

SSI - Resource Limits • Resources: cash, bank accounts, bonds, stocks, non-home property • Limits: $2, 000 individual $3, 000 couple

Filing Disability Application – Online at www. socialsecurity. gov • For Social Security disability, both medical and non-medical portions can be completed online • For SSI, only the medical portion can be completed online; non-medical must be completed in-person or by telephone

Filing Disability Application – By Telephone or In-Office • Call 1 -800 -772 -1213, weekdays 7: 00 a. m. to 7: 00 p. m. • Set up telephone/in-office appointment; will be sent “Disability Starter Kit” in advance

Speeding Up Application • Average processing time: 92 days • Applicant can help by supplying: - names, dates, etc. , of doctors, hospitals, clinics, & institutions - names of medications - medical records, lab tests - summary of jobs, type of work

Who Makes Decision? • Medical information sent to Disability Determination Services (DDS) • Disability evaluation specialist, physician review evidence, make determination

If Social Security Claim Approved… • Benefits due after 5 -month waiting period e. g. , onset date - March 10, 2008 entitlement begins - September 2008 paid October 2008 • Medicare begins after 24 months of entitlement: September 2010

If SSI Claim Approved… • Benefits usually retroactive to effective date of application • Medicaid entitlement coincides with benefit entitlement

If Claim Denied… • Upon receipt of denial notice, 60 days to file hearing • If hearing denied, other appeals remain: - Appeals Council Review - Federal court review

Medicare • Federal health insurance program administered by Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) • SSA makes eligibility determinations, enrolls people, gets card issued

Medicare – Who Gets It? • 65 or older - eligible for Soc. Sec. benefits, or - worked 10 years for government entity, paid Medicare tax • Under 65 - entitled to Soc. Sec. disab. 24 months (no waiting period for ALS) or kidney failure (& insured for benefits)

Traditional Parts of Medicare • Part A - Hospital Insurance - covers inpatient care in hospital, skilled nursing facility, some health care, hospice; but. . long-term care limited - length of in-patient stay dictates amount of coverage - no premium, but financed by worker’s 1. 45% tax
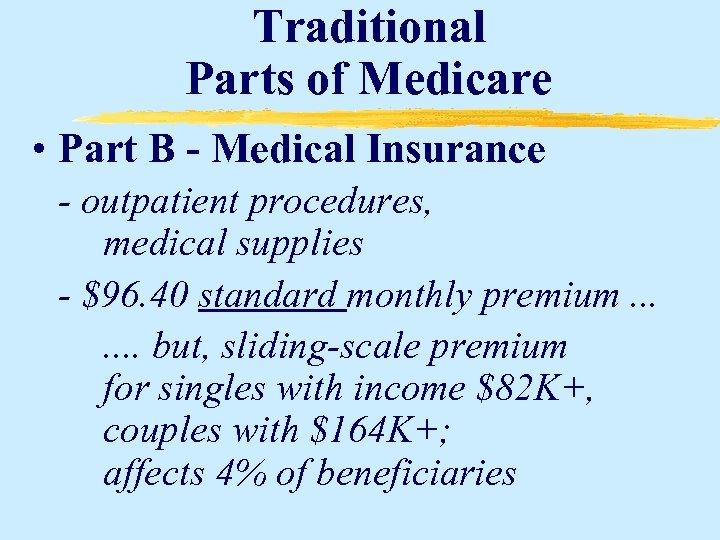
Traditional Parts of Medicare • Part B - Medical Insurance - outpatient procedures, medical supplies - $96. 40 standard monthly premium. . . . but, sliding-scale premium for singles with income $82 K+, couples with $164 K+; affects 4% of beneficiaries

Another “Part” of Medicare • Part C – Medicare Advantage Plan - health plan option, like Medigap plan; receive all health care services thru provider organization - includes HMOs, PPOs, special needs plans, private fee-for-service plans - pay Part B premium & plan premium; lower out-of-pocket costs, more covered services

Newest Part of Medicare – Part D Prescription Drug Plan • Began 2006, CMS responsible - open to all Medicare recipients - choose from plans of private companies - important: compare current plan - enroll soon after applying for Medicare; later, can only enroll Nov. 15 – Dec. 31

Part D “Extra Help” • SSA responsible • People of limited means can get help with: - premium, deductible, co-pays • Must apply, unless in “deemed” category • Apply online or use paper application

Work Incentives Social Security & Supplemental Security Income (SSI)

Social Security Beneficiary Returning to Work • Trial Work Period - can work in nine months - regardless of earnings, benefit paid - to count as TWP month, earnings at least $670 - nine months can be scattered over 60 -month period

At conclusion of TWP, ongoing work evaluated • If work “not substantial” (under $940), benefit continues • If work “substantial” ($940+), benefit paid months 10 -12, then suspended

Months #13 through #45. . Extended Period of Eligibility • After 12 -months TWP & grace months, “EPE” runs 33 months, to month 45 • Benefit unpaid for months #13 -45 whenever SGA ($940+) performed • Likewise, benefit paid for EPE months under $940

Impairment-Related Work Expenses • After TWP completed, the costs of some impairment-related items, services needed to work can be deducted from earnings in determining SGA. . . $1100 earnings - $165 IRWE $935 = no SGA • Individual must not be reimbursed for item, cost must be “reasonable, ” and item paid for in a work month

What about Work after EPE? • Month #45 is last EPE month * SGA in month 46 or later terminates eligibility * But. . .

“Expedited Reinstatement” * If earnings fall below SGA, benefit reinstated. . . no new application needed * Request must be made within 60 months of termination * Must have same disability * Can receive up to six months of benefits, including Medicare
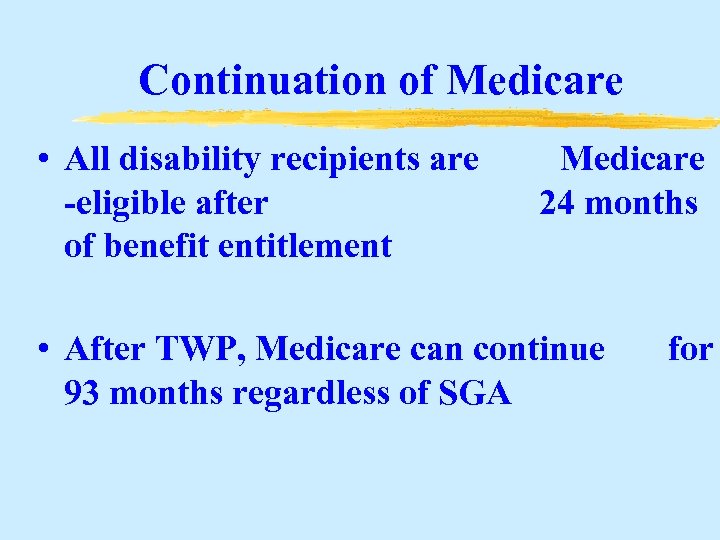
Continuation of Medicare • All disability recipients are -eligible after of benefit entitlement Medicare 24 months • After TWP, Medicare can continue 93 months regardless of SGA for

SSI Recipient Returning to Work • No TWP, no EPE • SGA not an issue • Earnings reduce payments, but benefits continue as long as income, resource limits not exceeded

How Earnings Reduce SSI • Unlike unearned income, earnings don’t reduce SSI dollar-for-dollar • Subtract $65 ($85) from monthly gross earnings; half of remainder counts against SSI • $600 earnings -$85 exclusion $515 remainder Half of $515 = $257. 50 SSI reduction

Monthly Earnings Cut-off • Earnings of $1, 359+ results in no SSI payable • $1359 earnings -$85 exclusion $1274 remainder • SSI limit: Half of $1274 is $637. 00 - $606. 40 countable income 0 = no SSI payable

Impairment-Related Work Expenses • Remember, SGA not an issue for SSI once on; but IRWE reduces countable earnings • $1267. 80 earnings -$85. 00 exclusion $1182. 80 - $52. 00 IRWE $1130. 80 Half of $1130. 80 = $565. 40 countable earnings • SSI limit $637. 00 - $565. 40 countable income $71. 60 SSI payable

Continuation of Medicaid • If earnings too high to allow SSI payment, Medicaid still continues if. . . . yearly earnings don’t exceed Pennsylvania threshold: $28, 554
Work Exclusion for Students • Must be under age 22 and in regular school attendance • Up to $1, 550 earnings excluded per month • Maximum $6, 240 excluded yearly

Plan for Achieving Self-Support (PASS) • Use or setting aside of income, resources to achieve work goal, increase prospects for self-support * Excluded income, resources don’t count against SSI, thereby increasing payment * Must be in writing, estimate time period for attaining goal

Ticket to Work • Gives disabled choice in obtaining free rehabilitation & vocational services • Provides more incentives for disabled to work & lessen dependence on public benefits • Removes barriers that make people choose between medical coverage and work

The Ticket Itself • New disability recipients, age 18 -64, will be sent Ticket, letter, & booklet • Ticket certificate can be “used” to obtain free vocational, employment services from organizations called “Employment Networks” - ENs are paid, but only if disabled individuals work • Ticket program is voluntary!


Upon Ticket receipt. . . • Recipient not required to do anything; remember. . voluntary program • But. . if interested in receiving services, call Program Manager (Maximus, Inc. ) • Later. . . take Ticket to an Employment Network (EN) to obtain services

Employment Network (EN) • Any agency or instrument of the state, or a private entity responsible for the coordination or actual delivery of services can become EN • Can be single entity, consortium, or association of organizations collaborating to combine resources to serve Ticket holders

Examples of ENs • State VR agencies • Any public/private entity providing appropriate services (job readiness, placement, voc. rehab. , training, etc. ) • Employers offering job training, voc. rehab. , support, retention, or other types of jobrelated services and/or assistance for the disabled

ENs Serving Philadelphia • Currently, 34 ENs signed up • Seven are based in city

How do People reach ENs? • SSA contracted with a Program Manager – Maximus, Inc. • Maximus recruits, monitors ENs; also facilitates access to ENs • When Ticket sent, people referred to Maximus toll-free number & www. yourtickettowork. com

Assigning a Ticket • Before “assigning” Ticket, person first discusses services, etc. , with EN • EN can refuse to accept the Ticket • If agreement is reached, individual work plan which details desired employment goals is written • After plan drawn up, Ticket considered assigned and “in use”

What’s in It for Disabled Individual? • Ticket-users not subject to medical Continuing Disability Reviews as long as making “timely progress” • “Timely progress” assumed in first two years of Ticket use - in third year, 3 of 12 months must be SGA ($940) - in fourth year, 6 of 12 months SGA - in fifth year, 6 of 12 months must be non-pay

What’s in It for ENs? • ENs paid when Ticket users either: have earnings which result in no cash benefit, or. . have earnings at or above SGA • ENs, therefore, have vested interest in getting people back to work

The National Numbers So Far. . • • 10. 4 million Tickets sent 192, 000 Tickets assigned One of every 54 Tickets sent out assigned 93% of assigned Tickets have gone to state VRs, 7% to new ENs • Note that pre-Ticket, state VRs “rehabbed” 10, 000 people yearly

Another Ticket Partner: WIPA • SSA awarded contracts to organizations; called Work Incentives Planning and Assistance (WIPA) organizations • They conduct outreach efforts re work incentives, provide planning and assistance, can also provide one-on-one counseling, advice, etc. • Disability Rights Network serves Philadelphia

Another Ticket Partner: Protection & Advocacy Program • SSA awarded contracts to legally -based disability rights agencies to provide legal representation & other advocacy services • In Pennsylvania, Disability Rights Network has the contract
eb33e8b59eab1ec3b83fcc69ffb1d084.ppt