
SOCIAL PROTECTION FOR THE AGED 1 CONTRIBUTORY LEGAL PROVISIONS FOR THE AGED, COVERAGE AND REFORMS SOCIAL PROTECTION WEEK GOVERNMENT COMPLEX 29 TH NOVEMBER 2017 JOSEPH BANDA SOCIAL SECURITY DEPARTMENT MINISTRY OF LABOUR AND SOCIAL SECURITY

OUTLINE 2 1. OBJECTIVE OF SOCIAL SECURITY PROVISIONS FOR THE AGED 2. CONTRIBUTORY LEGAL PROVISION FOR THE AGED 3. COVERAGE AND FINANCING 4. PENSIONS REFORMS 5. EXPECTED OUTCOME OF THE REFORMS

3 OBJECTIVE OF SOCIAL SECURITY PROVISIONS FOR THE AGED

OBJECTIVE OF SOCIAL SECURITY PROVISIONS FOR THE AGED 4 The Social Security Programmes are financed through contributions (payroll deductions) SS schemes are important institutional solutions to guarantee income security in old age; Old-age pensions from mandatory public social insurance and/or voluntary occupational or other private pension schemes; Income distribution and providing adequate benefits for minimum well-being and the fullfillment of basic needs; Provides prevention measures and protection for individuals against life-course risks;

5 CONTRIBUTORY LEGAL PROVISION FOR THE AGED

CONTRIBUTORY LEGAL PROVISION FOR THE AGED 6 Contributory Social Security Schemes include; 1) NAPSA, National Pension Scheme Act no. 40 of 1996 2) LASF, Local Authorities Superannuation Fund Act Chapter 284 3) PSPF; the Public Service Pensions Act, Chapter 260 4) WCFCB; the Workers’ Compensation Act No. 10 of 1999 of the Laws of Zambia; and 5) Occupational Pension Schemes; the Pension Scheme Regulation Act, 1996
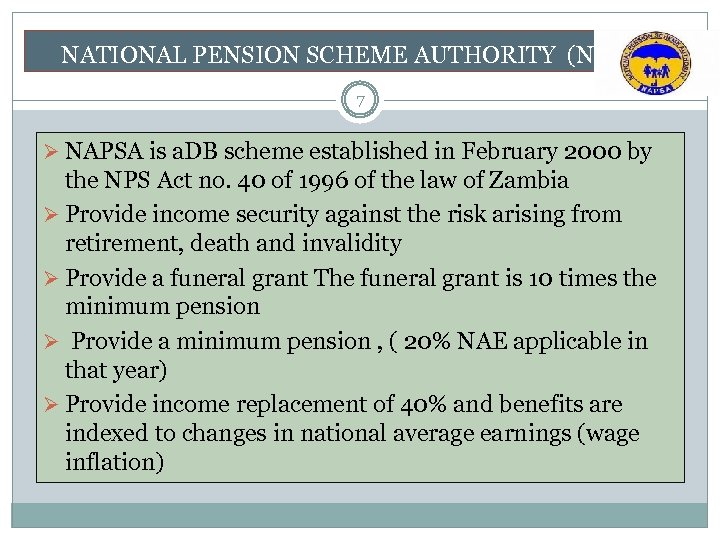
NATIONAL PENSION SCHEME AUTHORITY (NAPSA) 7 Ø NAPSA is a. DB scheme established in February 2000 by the NPS Act no. 40 of 1996 of the law of Zambia Ø Provide income security against the risk arising from retirement, death and invalidity Ø Provide a funeral grant The funeral grant is 10 times the minimum pension Ø Provide a minimum pension , ( 20% NAE applicable in that year) Ø Provide income replacement of 40% and benefits are indexed to changes in national average earnings (wage inflation)

PUBLIC SERVICE PENSION FUND (PSPF) 8 Ø PSPF is established to provide pensions and other benefits for persons employed in the Public Service; Ø DB Pension scheme; Ø Members who exit the scheme through early retirement, on medical grounds, National Interest and deceased cases are paid through the Government; Ø A member who is eligible for full retirement benefits can elect to commute one-third or twothirds;

LOCAL AUTHORITIES SUPERANNUATION FUND 9 Ø LASF established to provide pensions and other benefits for employees of the local authorities and utility companies Ø Employer Members: Councils, ZESCO, NHA, LWSC, EWSC Ø LASF is a DB scheme Ø A member who is eligible for full retirement benefits can elect to commute one-third or twothirds

WORKERS’ COMPENSATION FUND CONTROL BOARD (WCFCB) 10 Ø WCFCB is a social security scheme establish under the Workers’ Compensation Act No. 10 of 1999; Ø The scheme covers employers in the public and private sector except the state ; Ø the scheme compensate workers for disability suffered or disease contracted during the course of employment and pay compensation to dependants of workers who die as a result of occupation accidents or disease ; Ø Employers liability; Ø Invest surplus fund to generate additional income to ensure the growth of the fund; and Ø Scheme provide benefits both cash and in kind benefits: lump sum, pension, rehab, medical items, back to work etc
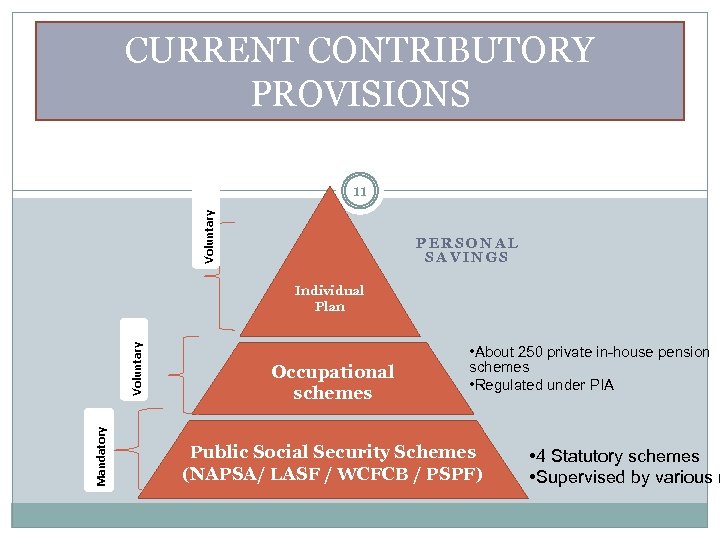
CURRENT CONTRIBUTORY PROVISIONS Voluntary 11 PERSONAL SAVINGS Mandatory Voluntary Individual Plan Occupational schemes • About 250 private in-house pension schemes • Regulated under PIA Public Social Security Schemes (NAPSA/ LASF / WCFCB / PSPF) • 4 Statutory schemes • Supervised by various m

12 COVERAGE AND FINANCING
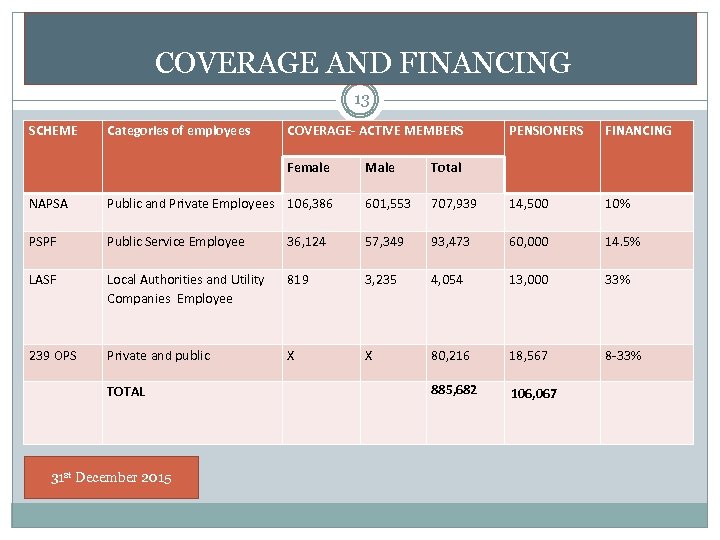
COVERAGE AND FINANCING 13 SCHEME Categories of employees COVERAGE- ACTIVE MEMBERS Female Male PENSIONERS FINANCING Total NAPSA Public and Private Employees 106, 386 601, 553 707, 939 14, 500 10% PSPF Public Service Employee 36, 124 57, 349 93, 473 60, 000 14. 5% LASF Local Authorities and Utility Companies Employee 819 3, 235 4, 054 13, 000 33% 239 OPS Private and public X X 80, 216 18, 567 8 -33% 885, 682 106, 067 TOTAL 31 st December 2015

14 REFORMS

OBJECTIVE OF THE REFORMS 15 Reforms are aimed at establishing a comprehensive and responsive social protection system that would: 1. Adequately address the plight of workers, retirees, Pensioners and beneficiaries; 2. Address the long term financial sustainability of the social security system 3. Create a three tier pension system - 4. Introduce new benefits – MP 5. Provide legal framework to facilitate transition from informal to formal economy

REFORMS SOCIAL SECURITY- MULTI TIER SYSTEM 16 Establish a three tier Social Security System to provided a minimum income replacement Ratio (IRR) of 60%: Tier 1: Mandatory National Basic Scheme – NSSA providing 40% IRR (or More), Cover - Private and Public employees, DB scheme, no lump sum Tier 2: Mandatory Occupational Pension schemes (MOPS) providing a minimum of 20% IRR - mixed DC and DB schemes, restructure LASF, PSPF into MOPS for public employees (10% lump sum) Tier 3: Voluntary Private Pension Scheme – providing an additional minimum IRR of up to 20% (individual plans) v v IRR is the percentage of working income that an individual would receive to maintain the same standard of living in retirement. E. g. income K 1, 000 in retirement u will get K 600/m
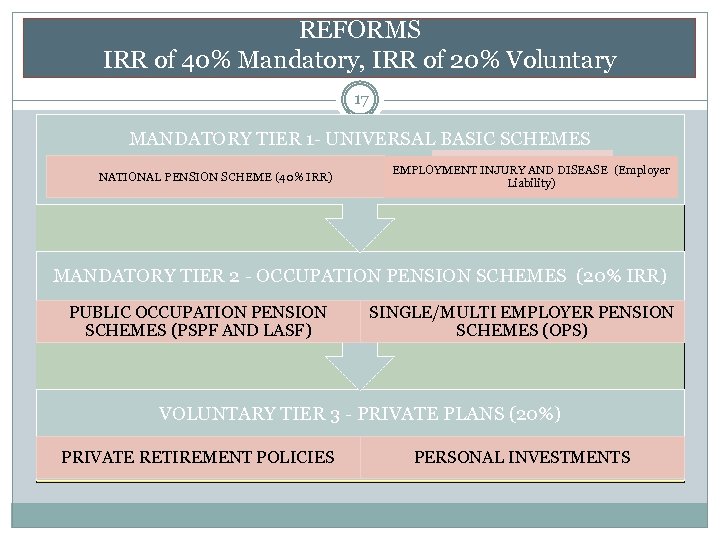
REFORMS IRR of 40% Mandatory, IRR of 20% Voluntary 17 MANDATORY TIER 1 - UNIVERSAL BASIC SCHEMES NATIONAL PENSION SCHEME (40% IRR) EMPLOYMENT INJURY AND DISEASE (Employer Liability) MANDATORY TIER 2 - OCCUPATION PENSION SCHEMES (20% IRR) PUBLIC OCCUPATION PENSION SCHEMES (PSPF AND LASF) SINGLE/MULTI EMPLOYER PENSION SCHEMES (OPS) VOLUNTARY TIER 3 - PRIVATE PLANS (20%) PRIVATE RETIREMENT POLICIES PERSONAL INVESTMENTS

REFORMS Cont…. Revision of the retirement age: - • FOR employees employed BEFORE the enactment of a new law shall elect to retire on the following : – Can retire in accordance with law before the amendment or retire at 60 years or retire at 65 years but with the employer’s approval • For employees employed AFTER the enactment of a new law the retirement age will be as follows : – 55 years. Early Retirement – 60 Years. Normal Retirement Age – 65 Years late retirement (employer’s spproval)

EXPECTED OUTCOMES OF THE REFORMS 19 1. Decent retirement benefits - Providing a minimum 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. combined IRR of 60%; Make parametric changes to make the SP system sustainable; Introduction of Minimum Pension Increase portability of benefits and Providing for annual pension indexation Reducing the allowed share of accrued rights that could be taken as lump sum to half (10%) (meaningful monthly pension); Embedding homeownership in the system; Private sector participation in investment and management of public pension funds;
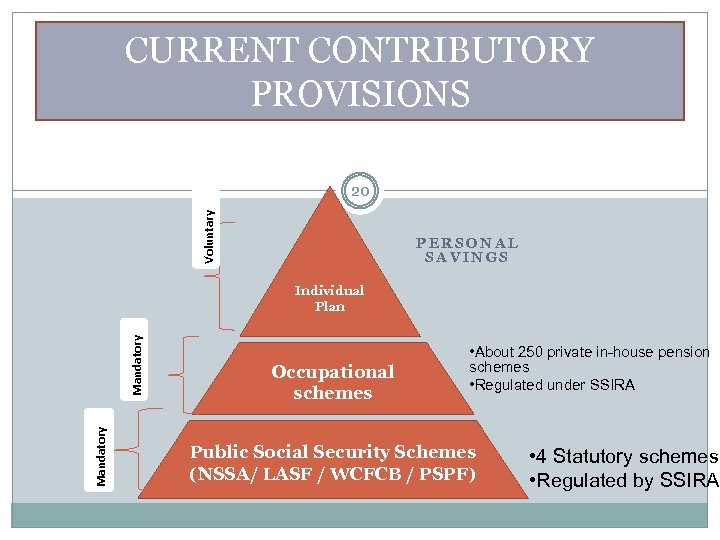
CURRENT CONTRIBUTORY PROVISIONS Voluntary 20 PERSONAL SAVINGS Mandatory Individual Plan Occupational schemes • About 250 private in-house pension schemes • Regulated under SSIRA Public Social Security Schemes (NSSA/ LASF / WCFCB / PSPF) • 4 Statutory schemes • Regulated by SSIRA

THE END 21 THANK YOU