4f8dd0d970148d562be3084d2e540ac9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Social Protection Floor initiative Why progressively tending towards universal social protection matters: an international perspective Valerie Schmitt ILO Decent Work Team, Bangkok Development Cooperation Seminar Social Protection: Towards universal Coverage in Thailand Bangkok, 5 November 2010
Social Protection Floor initiative Why progressively tending towards universal social protection matters: an international perspective Valerie Schmitt ILO Decent Work Team, Bangkok Development Cooperation Seminar Social Protection: Towards universal Coverage in Thailand Bangkok, 5 November 2010
 Three points: • It is important to expand social protection • What is the SPF concept & approach? • The SPF approach is adapted to Thailand
Three points: • It is important to expand social protection • What is the SPF concept & approach? • The SPF approach is adapted to Thailand
 First point: It is important to expand social protection … Because: • Social security / social protection is a human right • Although it is a human right only 20% of the world’s population has access to adequate social protection • Social protection is a social and economic stabilizer and was included in many stimulus packages • It enhances productivity at enterprise level • It contributes to develop the domestic market • It is affordable and feasible to establish a basic set of social protection for all • It contributes to social peace
First point: It is important to expand social protection … Because: • Social security / social protection is a human right • Although it is a human right only 20% of the world’s population has access to adequate social protection • Social protection is a social and economic stabilizer and was included in many stimulus packages • It enhances productivity at enterprise level • It contributes to develop the domestic market • It is affordable and feasible to establish a basic set of social protection for all • It contributes to social peace
 It is important to expand social protection… • Social security / social protection is a human right … – Universal Declaration of Human Rights (1948), UN Member States have recognized social security as a basic human right : • Article 22: Everyone, as a member of society, has the right to social security • Article 25: Everyone has the right to a standard of living adequate for the health and well-being of himself and of his family
It is important to expand social protection… • Social security / social protection is a human right … – Universal Declaration of Human Rights (1948), UN Member States have recognized social security as a basic human right : • Article 22: Everyone, as a member of society, has the right to social security • Article 25: Everyone has the right to a standard of living adequate for the health and well-being of himself and of his family
 It is important to expand social protection… • Although it is a human right only 20% of the world’s population has access to adequate social protection – Social security schemes often target formal sector employees, leaving Informal economy workers with no protection at all – Effective coverage is even lower than legal coverage (delivery problems, enforcement problems)
It is important to expand social protection… • Although it is a human right only 20% of the world’s population has access to adequate social protection – Social security schemes often target formal sector employees, leaving Informal economy workers with no protection at all – Effective coverage is even lower than legal coverage (delivery problems, enforcement problems)
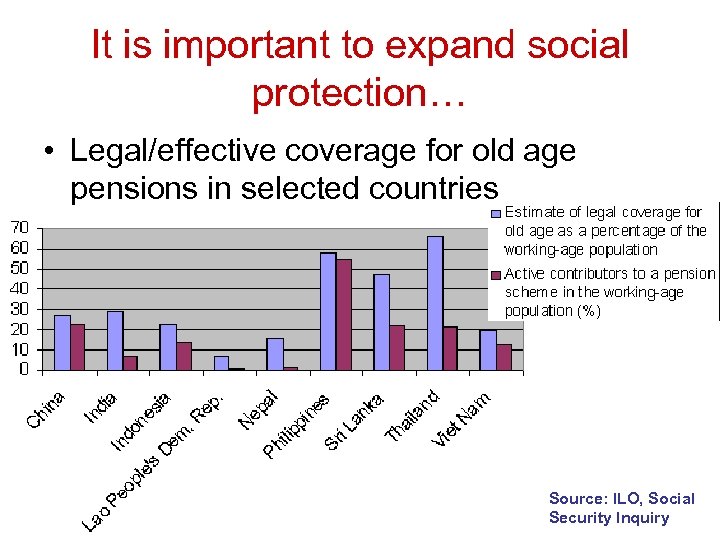 It is important to expand social protection… • Legal/effective coverage for old age pensions in selected countries Source: ILO, Social Security Inquiry
It is important to expand social protection… • Legal/effective coverage for old age pensions in selected countries Source: ILO, Social Security Inquiry
 It is important to expand social protection… • Social protection acts as a social and economic stabilizer and was included in many stimulus packages Increased support to low- income Bangladesh (destitute women and others), Nepal households (CCTs and social (children, elderly, deprived castes), Viet Nam, India assistance) (widows, disabled), Philippines (CCT, very poor) Employment programmes (PWP) Cambodia (small projects in rural areas), Viet Nam (infrastructure in poorest districts), Philippines, Pakistan, India Increased support to the elderly & old age pensions Bangladesh, Nepal, China Increasing coverage of unemployment benefits Viet Nam, China Measures to protect migrant workers Bangladesh, Nepal, Viet Nam India (Kerala), Philippines, Pakistan
It is important to expand social protection… • Social protection acts as a social and economic stabilizer and was included in many stimulus packages Increased support to low- income Bangladesh (destitute women and others), Nepal households (CCTs and social (children, elderly, deprived castes), Viet Nam, India assistance) (widows, disabled), Philippines (CCT, very poor) Employment programmes (PWP) Cambodia (small projects in rural areas), Viet Nam (infrastructure in poorest districts), Philippines, Pakistan, India Increased support to the elderly & old age pensions Bangladesh, Nepal, China Increasing coverage of unemployment benefits Viet Nam, China Measures to protect migrant workers Bangladesh, Nepal, Viet Nam India (Kerala), Philippines, Pakistan
 It is important to expand social protection… • Social protection has a positive impact on consumption & the development of domestic market – In China the development of reliable and universal social protection schemes was seen as a means to develop the domestic market – Because protected households would reduce their extraordinary high savings rate and consume more
It is important to expand social protection… • Social protection has a positive impact on consumption & the development of domestic market – In China the development of reliable and universal social protection schemes was seen as a means to develop the domestic market – Because protected households would reduce their extraordinary high savings rate and consume more
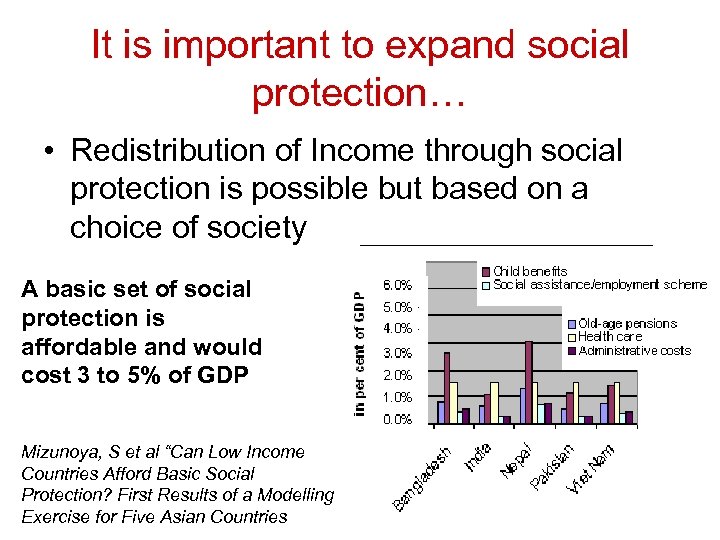 It is important to expand social protection… • Redistribution of Income through social protection is possible but based on a choice of society A basic set of social protection is affordable and would cost 3 to 5% of GDP Mizunoya, S et al “Can Low Income Countries Afford Basic Social Protection? First Results of a Modelling Exercise for Five Asian Countries
It is important to expand social protection… • Redistribution of Income through social protection is possible but based on a choice of society A basic set of social protection is affordable and would cost 3 to 5% of GDP Mizunoya, S et al “Can Low Income Countries Afford Basic Social Protection? First Results of a Modelling Exercise for Five Asian Countries
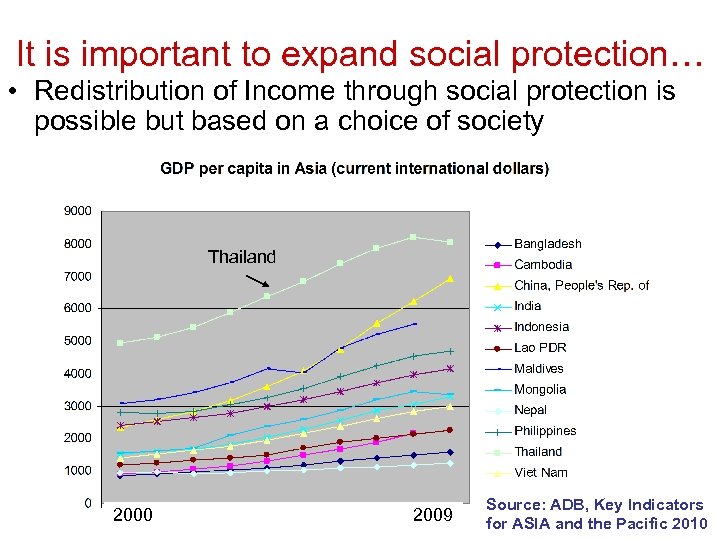 It is important to expand social protection… • Redistribution of Income through social protection is possible but based on a choice of society Thailand 2000 2009 Source: ADB, Key Indicators for ASIA and the Pacific 2010
It is important to expand social protection… • Redistribution of Income through social protection is possible but based on a choice of society Thailand 2000 2009 Source: ADB, Key Indicators for ASIA and the Pacific 2010
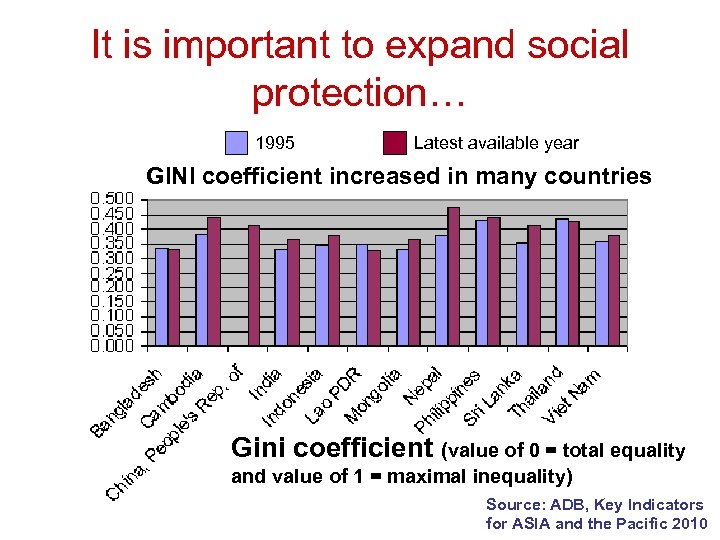 It is important to expand social protection… 1995 Latest available year GINI coefficient increased in many countries Gini coefficient (value of 0 = total equality and value of 1 = maximal inequality) Source: ADB, Key Indicators for ASIA and the Pacific 2010
It is important to expand social protection… 1995 Latest available year GINI coefficient increased in many countries Gini coefficient (value of 0 = total equality and value of 1 = maximal inequality) Source: ADB, Key Indicators for ASIA and the Pacific 2010
 It is important to expand social protection… • Social protection can be effective to prevent conflict and create politically stable societies • Poverty and gross inequities tend to generate intense social tensions and violent conflict • Social benefits ensure the political/ electoral support of citizens
It is important to expand social protection… • Social protection can be effective to prevent conflict and create politically stable societies • Poverty and gross inequities tend to generate intense social tensions and violent conflict • Social benefits ensure the political/ electoral support of citizens
 Second point: What is the Social protection floor concept & approach? • The social protection floor is a set of basic social rights, services and facilities that each member of society should enjoy • It is not a safety net • It is included in the social security staircase and is the 1 st step towards the development of a comprehensive system of social protection • It is a precondition to inclusion in labor market and can support ALMPs • It is recognized as a powerful approach to address low social protection coverage in Asia • Many countries in Asia have developed elements of the SPF
Second point: What is the Social protection floor concept & approach? • The social protection floor is a set of basic social rights, services and facilities that each member of society should enjoy • It is not a safety net • It is included in the social security staircase and is the 1 st step towards the development of a comprehensive system of social protection • It is a precondition to inclusion in labor market and can support ALMPs • It is recognized as a powerful approach to address low social protection coverage in Asia • Many countries in Asia have developed elements of the SPF
 What is the Social protection floor concept & approach? • The social protection floor initiative – One of the nine UN initiatives to confront the crisis – Many actors involved (UN agencies, ministries, civil society …) – Advisory group – Teams at country level – Conclusions of the 8 th ASEM meeting, 4 & 5 Oct. 2010 • Heads of States and of Governments of 46 Asian and European countries noted with interest the concept of SPF • Leaders called for further sharing of experiences and for technical assistance in implementing social welfare policies
What is the Social protection floor concept & approach? • The social protection floor initiative – One of the nine UN initiatives to confront the crisis – Many actors involved (UN agencies, ministries, civil society …) – Advisory group – Teams at country level – Conclusions of the 8 th ASEM meeting, 4 & 5 Oct. 2010 • Heads of States and of Governments of 46 Asian and European countries noted with interest the concept of SPF • Leaders called for further sharing of experiences and for technical assistance in implementing social welfare policies
 What is the Social protection floor concept & approach? • A set of basic social rights, services and facilities that each member of society should enjoy • A SPF should consist of: Availability of essential services: -Housing, WATSAN, -Education/skills, -Health care supply, -Food/Nutrition, … Accessibility of these services through basic transfers in cash or in kind: -Subsidized health insurance / health cards, -Scholarships & school buses, -Minimum income support to families (family/child benefits), the working poor (cash transfers and PWPs) and the elderly (minimum pensions) … • Notion of availability and accessibility – both work hand in hand, are articulated
What is the Social protection floor concept & approach? • A set of basic social rights, services and facilities that each member of society should enjoy • A SPF should consist of: Availability of essential services: -Housing, WATSAN, -Education/skills, -Health care supply, -Food/Nutrition, … Accessibility of these services through basic transfers in cash or in kind: -Subsidized health insurance / health cards, -Scholarships & school buses, -Minimum income support to families (family/child benefits), the working poor (cash transfers and PWPs) and the elderly (minimum pensions) … • Notion of availability and accessibility – both work hand in hand, are articulated
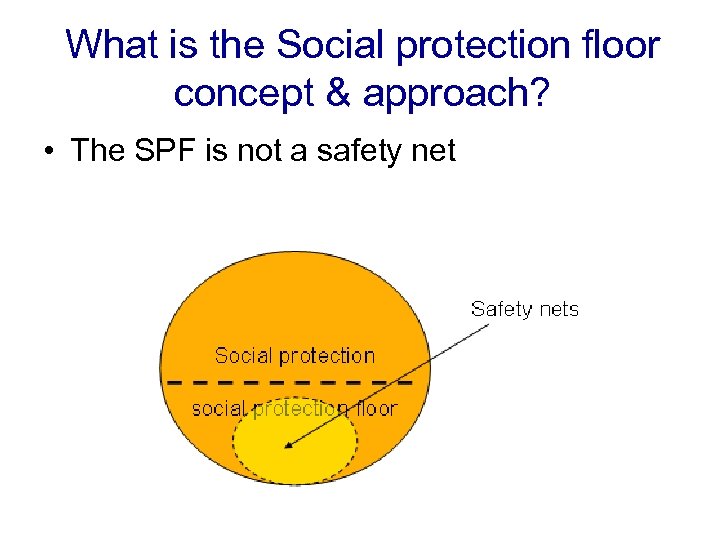 What is the Social protection floor concept & approach? • The SPF is not a safety net
What is the Social protection floor concept & approach? • The SPF is not a safety net
 What is the Social protection floor concept & approach? • The SPF is not a safety net Criteria Safety Nets Social Protection Floor Overall Objective Poverty reduction Giving effect to the Human Right to Social Security Type of interventions Targeted set of noncontributory transfers, depending on government priorities Universal entitlement to protection through a defined basic package for all in need Benefit levels Minimum National poverty lines Role SNs as transitory response measures/ short term (crisis, reforms) Rights-based, systemic “insurance” against poverty for all residents
What is the Social protection floor concept & approach? • The SPF is not a safety net Criteria Safety Nets Social Protection Floor Overall Objective Poverty reduction Giving effect to the Human Right to Social Security Type of interventions Targeted set of noncontributory transfers, depending on government priorities Universal entitlement to protection through a defined basic package for all in need Benefit levels Minimum National poverty lines Role SNs as transitory response measures/ short term (crisis, reforms) Rights-based, systemic “insurance” against poverty for all residents
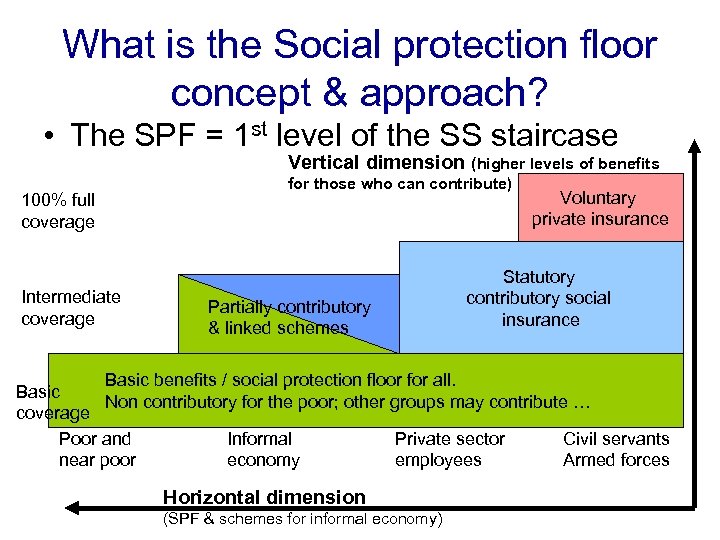 What is the Social protection floor concept & approach? • The SPF = 1 st level of the SS staircase Vertical dimension (higher levels of benefits 100% full coverage Intermediate coverage for those who can contribute) Partially contributory & linked schemes Voluntary private insurance Statutory contributory social insurance Basic benefits / social protection floor for all. Basic Non contributory for the poor; other groups may contribute … coverage Poor and Informal Private sector Civil servants near poor economy employees Armed forces Horizontal dimension (SPF & schemes for informal economy)
What is the Social protection floor concept & approach? • The SPF = 1 st level of the SS staircase Vertical dimension (higher levels of benefits 100% full coverage Intermediate coverage for those who can contribute) Partially contributory & linked schemes Voluntary private insurance Statutory contributory social insurance Basic benefits / social protection floor for all. Basic Non contributory for the poor; other groups may contribute … coverage Poor and Informal Private sector Civil servants near poor economy employees Armed forces Horizontal dimension (SPF & schemes for informal economy)
 What is the Social protection floor concept & approach? • Many countries in Asia have developed elements of the SPF : – nation wide non-contributory or highly subsidized social protection programs – national strategies to accelerate the implementation and scaling up of diverse and scattered basic social protection programs
What is the Social protection floor concept & approach? • Many countries in Asia have developed elements of the SPF : – nation wide non-contributory or highly subsidized social protection programs – national strategies to accelerate the implementation and scaling up of diverse and scattered basic social protection programs
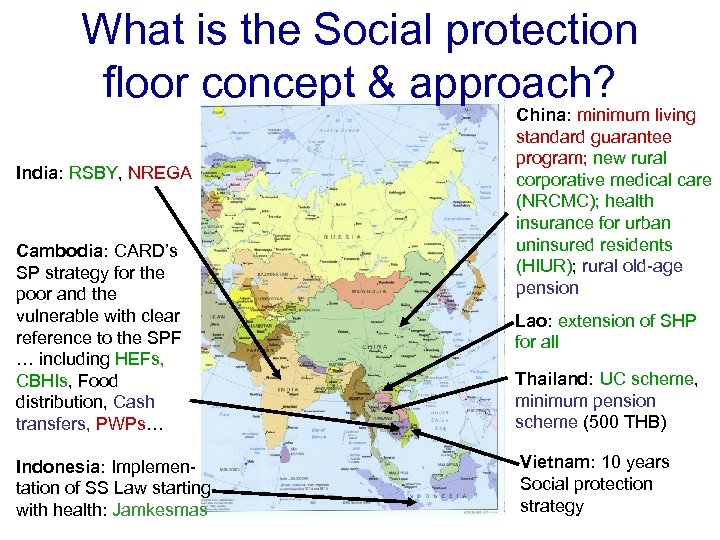 What is the Social protection floor concept & approach? India: RSBY, NREGA Cambodia: CARD’s SP strategy for the poor and the vulnerable with clear reference to the SPF … including HEFs, CBHIs, Food distribution, Cash transfers, PWPs… Indonesia: Implementation of SS Law starting with health: Jamkesmas China: minimum living standard guarantee program; new rural corporative medical care (NRCMC); health insurance for urban uninsured residents (HIUR); rural old-age pension Lao: extension of SHP for all Thailand: UC scheme, minimum pension scheme (500 THB) Vietnam: 10 years Social protection strategy
What is the Social protection floor concept & approach? India: RSBY, NREGA Cambodia: CARD’s SP strategy for the poor and the vulnerable with clear reference to the SPF … including HEFs, CBHIs, Food distribution, Cash transfers, PWPs… Indonesia: Implementation of SS Law starting with health: Jamkesmas China: minimum living standard guarantee program; new rural corporative medical care (NRCMC); health insurance for urban uninsured residents (HIUR); rural old-age pension Lao: extension of SHP for all Thailand: UC scheme, minimum pension scheme (500 THB) Vietnam: 10 years Social protection strategy
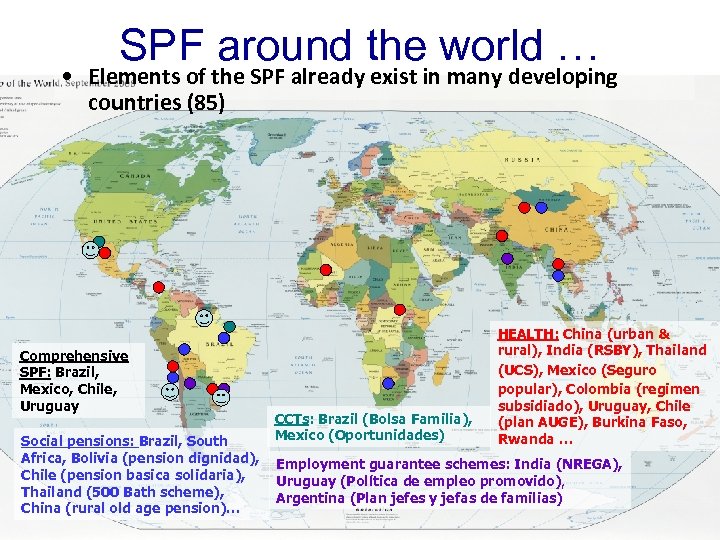 SPF around the world … • Elements of the SPF already exist in many developing countries (85) Comprehensive SPF: Brazil, Mexico, Chile, Uruguay Social pensions: Brazil, South Africa, Bolivia (pension dignidad), Chile (pension basica solidaria), Thailand (500 Bath scheme), China (rural old age pension)… CCTs: Brazil (Bolsa Familia), Mexico (Oportunidades) HEALTH: China (urban & rural), India (RSBY), Thailand (UCS), Mexico (Seguro popular), Colombia (regimen subsidiado), Uruguay, Chile (plan AUGE), Burkina Faso, Rwanda … Employment guarantee schemes: India (NREGA), Uruguay (Política de empleo promovido), Argentina (Plan jefes y jefas de familias)
SPF around the world … • Elements of the SPF already exist in many developing countries (85) Comprehensive SPF: Brazil, Mexico, Chile, Uruguay Social pensions: Brazil, South Africa, Bolivia (pension dignidad), Chile (pension basica solidaria), Thailand (500 Bath scheme), China (rural old age pension)… CCTs: Brazil (Bolsa Familia), Mexico (Oportunidades) HEALTH: China (urban & rural), India (RSBY), Thailand (UCS), Mexico (Seguro popular), Colombia (regimen subsidiado), Uruguay, Chile (plan AUGE), Burkina Faso, Rwanda … Employment guarantee schemes: India (NREGA), Uruguay (Política de empleo promovido), Argentina (Plan jefes y jefas de familias)
 Last point: The SPF approach is adapted to Thailand • The SPF approach relevant with: – The SS Staircase in Thailand & the objective of a welfare society • The SPF approach can be useful to: – Develop a consistent national social protection strategy – Bring more coherence at policy level – Enhance coordination at implementation level – Ensure a more efficient delivery
Last point: The SPF approach is adapted to Thailand • The SPF approach relevant with: – The SS Staircase in Thailand & the objective of a welfare society • The SPF approach can be useful to: – Develop a consistent national social protection strategy – Bring more coherence at policy level – Enhance coordination at implementation level – Ensure a more efficient delivery
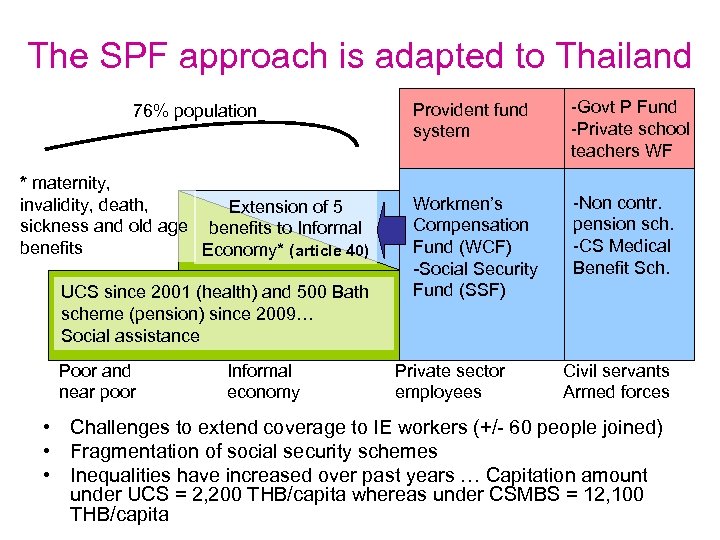 The SPF approach is adapted to Thailand 76% population * maternity, invalidity, death, Extension of 5 sickness and old age benefits to Informal benefits Economy* (article 40) UCS since 2001 (health) and 500 Bath scheme (pension) since 2009… Social assistance Poor and near poor Informal economy Provident fund system -Govt P Fund -Private school teachers WF Workmen’s Compensation Fund (WCF) -Social Security Fund (SSF) -Non contr. pension sch. -CS Medical Benefit Sch. Private sector employees Civil servants Armed forces • Challenges to extend coverage to IE workers (+/- 60 people joined) • Fragmentation of social security schemes • Inequalities have increased over past years … Capitation amount under UCS = 2, 200 THB/capita whereas under CSMBS = 12, 100 THB/capita
The SPF approach is adapted to Thailand 76% population * maternity, invalidity, death, Extension of 5 sickness and old age benefits to Informal benefits Economy* (article 40) UCS since 2001 (health) and 500 Bath scheme (pension) since 2009… Social assistance Poor and near poor Informal economy Provident fund system -Govt P Fund -Private school teachers WF Workmen’s Compensation Fund (WCF) -Social Security Fund (SSF) -Non contr. pension sch. -CS Medical Benefit Sch. Private sector employees Civil servants Armed forces • Challenges to extend coverage to IE workers (+/- 60 people joined) • Fragmentation of social security schemes • Inequalities have increased over past years … Capitation amount under UCS = 2, 200 THB/capita whereas under CSMBS = 12, 100 THB/capita
 The SPF approach is adapted to Thailand • The SPF approach can be useful to: – Develop a consistent national social protection strategy going beyond what is already in place (500 Bath, UCS) – Bring more coherence at policy level • Example: Lack of coordination between Min of Finance and Min of Labour in the design and implementation of the three existing/planned old age schemes for workers in the informal economy: – 500 Baht pension and National Saving Fund – Article 40 of Social Security Act
The SPF approach is adapted to Thailand • The SPF approach can be useful to: – Develop a consistent national social protection strategy going beyond what is already in place (500 Bath, UCS) – Bring more coherence at policy level • Example: Lack of coordination between Min of Finance and Min of Labour in the design and implementation of the three existing/planned old age schemes for workers in the informal economy: – 500 Baht pension and National Saving Fund – Article 40 of Social Security Act
 The SPF approach is adapted to Thailand • The SPF approach can be useful to: – Operationalize the concept of “Welfare Society” by increasing coordination between all actors involved in the social protection landscape: • Supply side and Demand side • National / local level (communities) – Make sure that the right to social protection is effective by systematically identifying and addressing delivery issues • Example: A number of delivery issues of the UCS limit the efficiency of this scheme such as lack of information on the UCS; Fear of stigma and discrimination; Perceived quality of health care facilities and reception of patients (under UCS) is low …
The SPF approach is adapted to Thailand • The SPF approach can be useful to: – Operationalize the concept of “Welfare Society” by increasing coordination between all actors involved in the social protection landscape: • Supply side and Demand side • National / local level (communities) – Make sure that the right to social protection is effective by systematically identifying and addressing delivery issues • Example: A number of delivery issues of the UCS limit the efficiency of this scheme such as lack of information on the UCS; Fear of stigma and discrimination; Perceived quality of health care facilities and reception of patients (under UCS) is low …
 More information on the SPF www. socialsecurityextension. org
More information on the SPF www. socialsecurityextension. org


