Social influence 1 lecture.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 32
 Social influence 1
Social influence 1
 Social influence is one of the major topics in social psychology; It looks at how individual thoughts, actions and feelings are influenced by social groups 2
Social influence is one of the major topics in social psychology; It looks at how individual thoughts, actions and feelings are influenced by social groups 2
 What is conformity? 3
What is conformity? 3
 Conformity is when a person changes his/her behavior or opinion in order to fit in with a group 4
Conformity is when a person changes his/her behavior or opinion in order to fit in with a group 4
 This change is in response to real (involving the physical presence of others) or imagined (involving the pressure of social norms/expectations) group pressure 5
This change is in response to real (involving the physical presence of others) or imagined (involving the pressure of social norms/expectations) group pressure 5
 Why do people conform? 6
Why do people conform? 6
 3 types of conformity: Normative - a desire to ‘fit in’ or be liked; Informational – a desire to be correct; Identification – a desire to conform to a social role 7
3 types of conformity: Normative - a desire to ‘fit in’ or be liked; Informational – a desire to be correct; Identification – a desire to conform to a social role 7
 Normative conformity This type of influence often comes from peer pressure; wanting to be viewed as “normal” i. e. wanting approval for fear of rejection 8
Normative conformity This type of influence often comes from peer pressure; wanting to be viewed as “normal” i. e. wanting approval for fear of rejection 8
 Informational conformity This influence comes from the fear of appearing stupid, believing others know more than you 9
Informational conformity This influence comes from the fear of appearing stupid, believing others know more than you 9
 Identification This type of conformity occurs when people conform to what is expected of them based upon their social roles 10
Identification This type of conformity occurs when people conform to what is expected of them based upon their social roles 10
 What studies on conformity do you remember? 11
What studies on conformity do you remember? 11
 Jennes (1932) was the first psychologist to study conformity. His experiment involved a glass bottle filled with beans. 12
Jennes (1932) was the first psychologist to study conformity. His experiment involved a glass bottle filled with beans. 12
 However, perhaps the most famous conformity experiment was by Solomon Asch (1951) and his line judgment experiment 13
However, perhaps the most famous conformity experiment was by Solomon Asch (1951) and his line judgment experiment 13
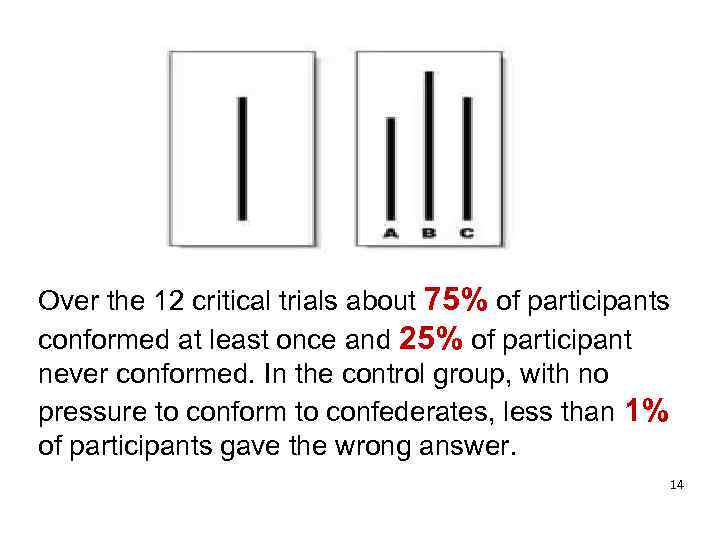 Over the 12 critical trials about 75% of participants conformed at least once and 25% of participant never conformed. In the control group, with no pressure to conform to confederates, less than 1% of participants gave the wrong answer. 14
Over the 12 critical trials about 75% of participants conformed at least once and 25% of participant never conformed. In the control group, with no pressure to conform to confederates, less than 1% of participants gave the wrong answer. 14
 Why did the participants conform so readily? 15
Why did the participants conform so readily? 15
 Limitations Biased sample Low ecological validity Ethical issues Reliability 16
Limitations Biased sample Low ecological validity Ethical issues Reliability 16
 Factors Increasing Conformity Size of the group Higher conformity Lower conformity 17
Factors Increasing Conformity Size of the group Higher conformity Lower conformity 17
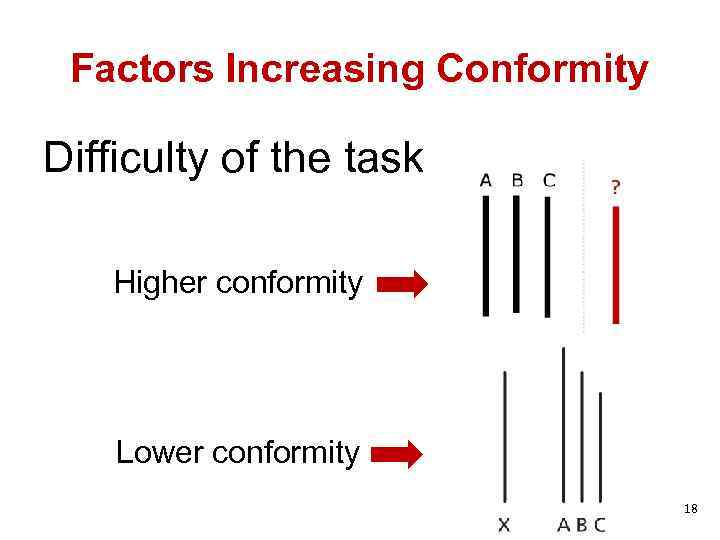 Factors Increasing Conformity Difficulty of the task Higher conformity Lower conformity 18
Factors Increasing Conformity Difficulty of the task Higher conformity Lower conformity 18
 Factors Increasing Conformity Status of Majority Group Higher conformity Lower conformity 19
Factors Increasing Conformity Status of Majority Group Higher conformity Lower conformity 19
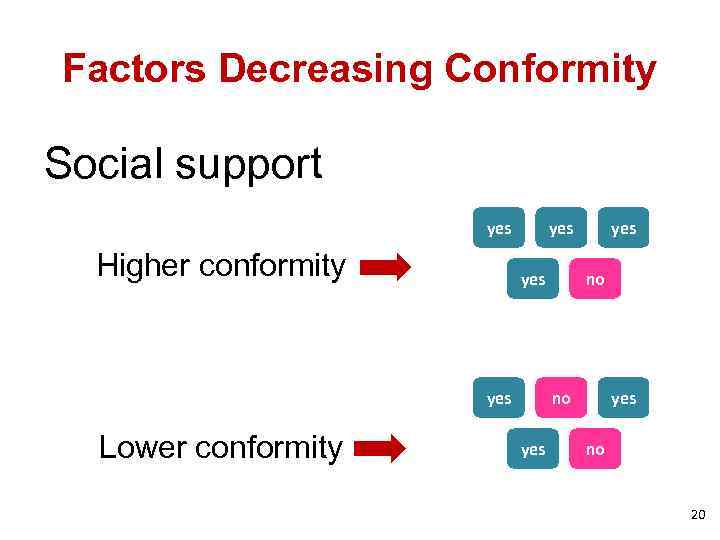 Factors Decreasing Conformity Social support yes Higher conformity yes yes Lower conformity yes no no yes no 20
Factors Decreasing Conformity Social support yes Higher conformity yes yes Lower conformity yes no no yes no 20
 Factors Decreasing Conformity Answer in private Higher conformity Lower conformity 21
Factors Decreasing Conformity Answer in private Higher conformity Lower conformity 21
 What is obedience? 22
What is obedience? 22
 Obedience is a form of social influence where an individual acts in response to a direct order from another individual, who is usually an authority figure It is assumed that without such an order the person would not have acted in this way 23
Obedience is a form of social influence where an individual acts in response to a direct order from another individual, who is usually an authority figure It is assumed that without such an order the person would not have acted in this way 23
 Why do people obey? 24
Why do people obey? 24
 25
25
 One of the most famous studies of obedience in psychology was carried out by Stanley Milgram (1963) 26
One of the most famous studies of obedience in psychology was carried out by Stanley Milgram (1963) 26
 Milgram (1963) wanted to investigate whether Germans were particularly obedient to authority figures as this was a common explanation for the Nazi killings in World War II 27
Milgram (1963) wanted to investigate whether Germans were particularly obedient to authority figures as this was a common explanation for the Nazi killings in World War II 27
 The results of the experiment Two-thirds (65%) of participants (i. e. teachers) continued to the highest level of 450 volts All the participants continued to 300 volts 28
The results of the experiment Two-thirds (65%) of participants (i. e. teachers) continued to the highest level of 450 volts All the participants continued to 300 volts 28
 So the question is this… What is the personal responsibility we have to each other to protect ourselves from the negative effects of conformity and blind obedience? 29
So the question is this… What is the personal responsibility we have to each other to protect ourselves from the negative effects of conformity and blind obedience? 29
 ЦКДЖ
ЦКДЖ
 Thank you for your attention!
Thank you for your attention!
 • Mc. Leod, S. A. (2007). What is Conformity? Retrieved from http: //www. simplypsychology. org/conformity. html • Mc. Leod, S. A. (2007). Milgram Experiment. Retrieved from http: //www. simplypsychology. org
• Mc. Leod, S. A. (2007). What is Conformity? Retrieved from http: //www. simplypsychology. org/conformity. html • Mc. Leod, S. A. (2007). Milgram Experiment. Retrieved from http: //www. simplypsychology. org


