4165affd4bd2dbb3800a31c78f2219a4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15
 Social Entrepreneurship: Challenges and Promises for the Next Decade Mirjam Schöning, Schwab Foundation for Social Entrepreneurship “Social Innovation” Conference Rome, 7 -8 October 2009
Social Entrepreneurship: Challenges and Promises for the Next Decade Mirjam Schöning, Schwab Foundation for Social Entrepreneurship “Social Innovation” Conference Rome, 7 -8 October 2009
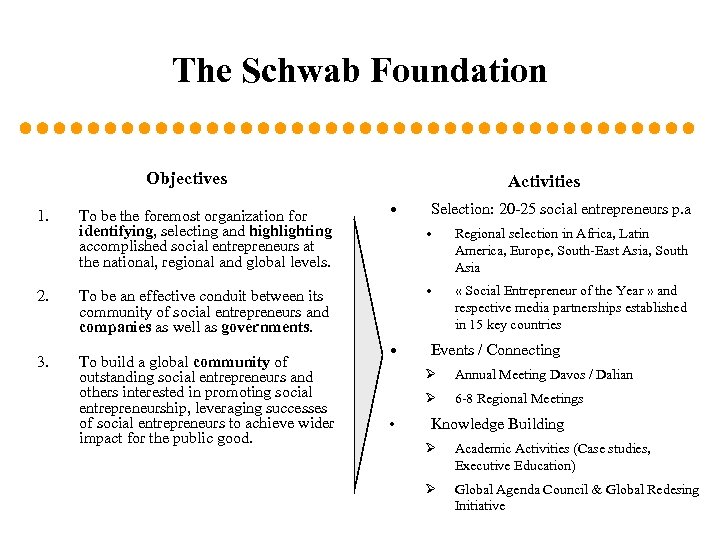 The Schwab Foundation Objectives 1. 2. 3. To be the foremost organization for identifying, selecting and highlighting accomplished social entrepreneurs at the national, regional and global levels. To be an effective conduit between its community of social entrepreneurs and companies as well as governments. To build a global community of outstanding social entrepreneurs and others interested in promoting social entrepreneurship, leveraging successes of social entrepreneurs to achieve wider impact for the public good. Activities • Selection: 20 -25 social entrepreneurs p. a • • • Regional selection in Africa, Latin America, Europe, South-East Asia, South Asia « Social Entrepreneur of the Year » and respective media partnerships established in 15 key countries Events / Connecting Ø Ø • Annual Meeting Davos / Dalian 6 -8 Regional Meetings Knowledge Building Ø Academic Activities (Case studies, Executive Education) Ø Global Agenda Council & Global Redesing Initiative
The Schwab Foundation Objectives 1. 2. 3. To be the foremost organization for identifying, selecting and highlighting accomplished social entrepreneurs at the national, regional and global levels. To be an effective conduit between its community of social entrepreneurs and companies as well as governments. To build a global community of outstanding social entrepreneurs and others interested in promoting social entrepreneurship, leveraging successes of social entrepreneurs to achieve wider impact for the public good. Activities • Selection: 20 -25 social entrepreneurs p. a • • • Regional selection in Africa, Latin America, Europe, South-East Asia, South Asia « Social Entrepreneur of the Year » and respective media partnerships established in 15 key countries Events / Connecting Ø Ø • Annual Meeting Davos / Dalian 6 -8 Regional Meetings Knowledge Building Ø Academic Activities (Case studies, Executive Education) Ø Global Agenda Council & Global Redesing Initiative
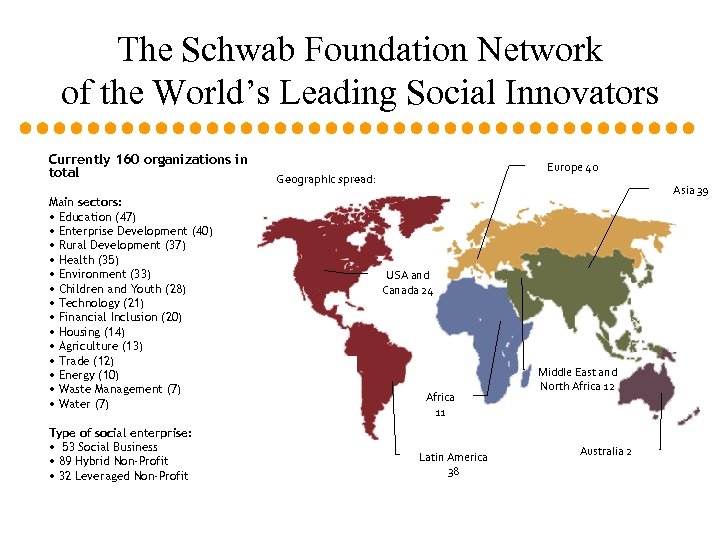 The Schwab Foundation Network of the World’s Leading Social Innovators Currently 160 organizations in total Main sectors: • Education (47) • Enterprise Development (40) • Rural Development (37) • Health (35) • Environment (33) • Children and Youth (28) • Technology (21) • Financial Inclusion (20) • Housing (14) • Agriculture (13) • Trade (12) • Energy (10) • Waste Management (7) • Water (7) Type of social enterprise: • 53 Social Business • 89 Hybrid Non-Profit • 32 Leveraged Non-Profit Europe 40 Geographic spread: Asia 39 USA and Canada 24 Africa 11 Latin America 38 Middle East and North Africa 12 Australia 2
The Schwab Foundation Network of the World’s Leading Social Innovators Currently 160 organizations in total Main sectors: • Education (47) • Enterprise Development (40) • Rural Development (37) • Health (35) • Environment (33) • Children and Youth (28) • Technology (21) • Financial Inclusion (20) • Housing (14) • Agriculture (13) • Trade (12) • Energy (10) • Waste Management (7) • Water (7) Type of social enterprise: • 53 Social Business • 89 Hybrid Non-Profit • 32 Leveraged Non-Profit Europe 40 Geographic spread: Asia 39 USA and Canada 24 Africa 11 Latin America 38 Middle East and North Africa 12 Australia 2
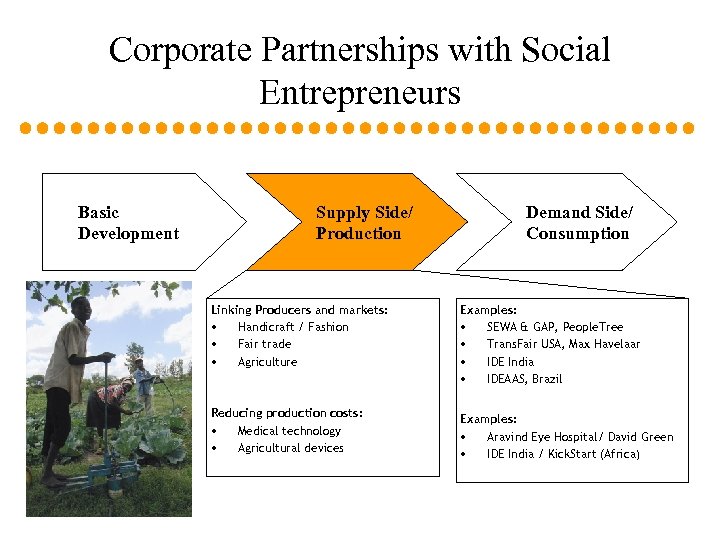 Corporate Partnerships with Social Entrepreneurs Basic Development Supply Side/ Production Demand Side/ Consumption Linking Producers and markets: • Handicraft / Fashion • Fair trade • Agriculture Examples: • SEWA & GAP, People. Tree • Trans. Fair USA, Max Havelaar • IDE India • IDEAAS, Brazil Reducing production costs: • Medical technology • Agricultural devices Examples: • Aravind Eye Hospital/ David Green • IDE India / Kick. Start (Africa)
Corporate Partnerships with Social Entrepreneurs Basic Development Supply Side/ Production Demand Side/ Consumption Linking Producers and markets: • Handicraft / Fashion • Fair trade • Agriculture Examples: • SEWA & GAP, People. Tree • Trans. Fair USA, Max Havelaar • IDE India • IDEAAS, Brazil Reducing production costs: • Medical technology • Agricultural devices Examples: • Aravind Eye Hospital/ David Green • IDE India / Kick. Start (Africa)
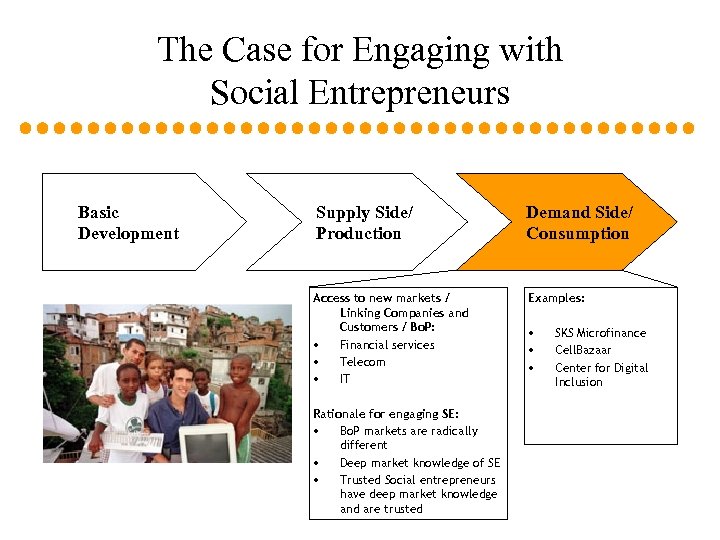 The Case for Engaging with Social Entrepreneurs Basic Development Supply Side/ Production Demand Side/ Consumption Access to new markets / Linking Companies and Customers / Bo. P: • Financial services • Telecom • IT Examples: Rationale for engaging SE: • Bo. P markets are radically different • Deep market knowledge of SE • Trusted Social entrepreneurs have deep market knowledge and are trusted • • • SKS Microfinance Cell. Bazaar Center for Digital Inclusion
The Case for Engaging with Social Entrepreneurs Basic Development Supply Side/ Production Demand Side/ Consumption Access to new markets / Linking Companies and Customers / Bo. P: • Financial services • Telecom • IT Examples: Rationale for engaging SE: • Bo. P markets are radically different • Deep market knowledge of SE • Trusted Social entrepreneurs have deep market knowledge and are trusted • • • SKS Microfinance Cell. Bazaar Center for Digital Inclusion
 What is a Social Entrepreneur? Entrepreneurial Founder of for-profit or not-for-profit organization Social Mission-driven Employs business methods, but aims at maximizing social or ecological impact. Financial return is optimized. Innovative New products, services or approaches driving social transformation. Sustainable Revenue through fees, sales of products and services Practical Visionary Focus on implementation
What is a Social Entrepreneur? Entrepreneurial Founder of for-profit or not-for-profit organization Social Mission-driven Employs business methods, but aims at maximizing social or ecological impact. Financial return is optimized. Innovative New products, services or approaches driving social transformation. Sustainable Revenue through fees, sales of products and services Practical Visionary Focus on implementation
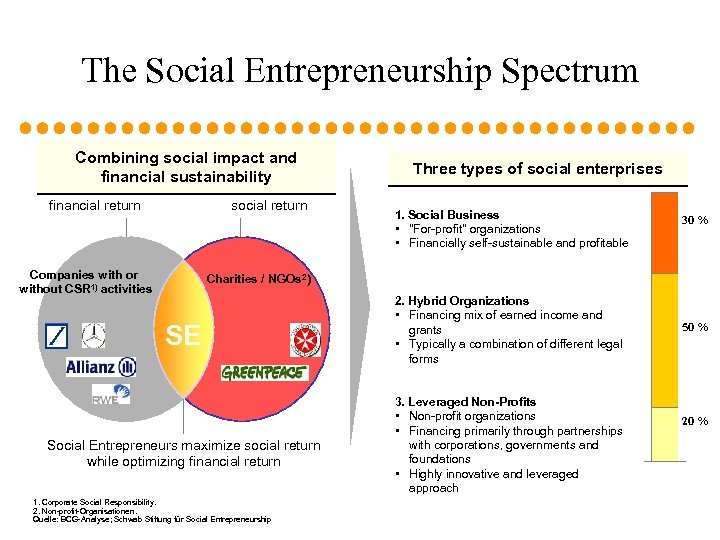 The Social Entrepreneurship Spectrum Combining social impact and financial sustainability financial return social return Companies with or without CSR 1) activities Three types of social enterprises 1. Social Business • "For-profit" organizations • Financially self-sustainable and profitable 30 % Charities / NGOs 2) SE Social Entrepreneurs maximize social return while optimizing financial return 1. Corporate Social Responsibility. 2. Non-profit-Organisationen. Quelle: BCG-Analyse; Schwab Stiftung für Social Entrepreneurship 2. Hybrid Organizations • Financing mix of earned income and grants • Typically a combination of different legal forms 3. Leveraged Non-Profits • Non-profit organizations • Financing primarily through partnerships with corporations, governments and foundations • Highly innovative and leveraged approach 50 % 20 %
The Social Entrepreneurship Spectrum Combining social impact and financial sustainability financial return social return Companies with or without CSR 1) activities Three types of social enterprises 1. Social Business • "For-profit" organizations • Financially self-sustainable and profitable 30 % Charities / NGOs 2) SE Social Entrepreneurs maximize social return while optimizing financial return 1. Corporate Social Responsibility. 2. Non-profit-Organisationen. Quelle: BCG-Analyse; Schwab Stiftung für Social Entrepreneurship 2. Hybrid Organizations • Financing mix of earned income and grants • Typically a combination of different legal forms 3. Leveraged Non-Profits • Non-profit organizations • Financing primarily through partnerships with corporations, governments and foundations • Highly innovative and leveraged approach 50 % 20 %
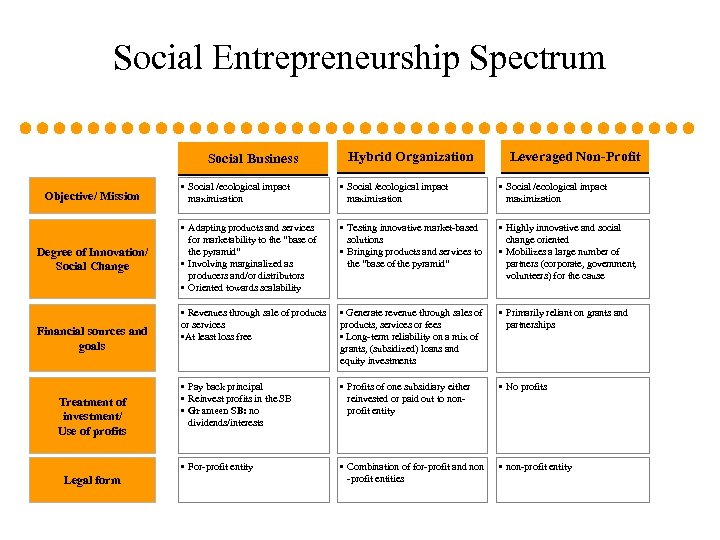 Social Entrepreneurship Spectrum Social Business Hybrid Organization Leveraged Non-Profit Degree of Innovation/ Social Change Financial sources and goals Treatment of investment/ Use of profits Legal form • Social /ecological impact maximization • Adapting products and services for marketability to the “base of the pyramid” • Involving marginalized as producers and/or distributors • Oriented towards scalability • Testing innovative market-based solutions • Bringing products and services to the “base of the pyramid” • Highly innovative and social change oriented • Mobilizes a large number of partners (corporate, government, volunteers) for the cause • Revenues through sale of products or services • At least loss free • Generate revenue through sales of products, services or fees • Long-term reliability on a mix of grants, (subsidized) loans and equity investments • Primarily reliant on grants and partnerships • Pay back principal • Reinvest profits in the SB • Grameen SB: no dividends/interests • Profits of one subsidiary either reinvested or paid out to nonprofit entity • No profits • For-profit entity Objective/ Mission • Combination of for-profit and non -profit entities • non-profit entity
Social Entrepreneurship Spectrum Social Business Hybrid Organization Leveraged Non-Profit Degree of Innovation/ Social Change Financial sources and goals Treatment of investment/ Use of profits Legal form • Social /ecological impact maximization • Adapting products and services for marketability to the “base of the pyramid” • Involving marginalized as producers and/or distributors • Oriented towards scalability • Testing innovative market-based solutions • Bringing products and services to the “base of the pyramid” • Highly innovative and social change oriented • Mobilizes a large number of partners (corporate, government, volunteers) for the cause • Revenues through sale of products or services • At least loss free • Generate revenue through sales of products, services or fees • Long-term reliability on a mix of grants, (subsidized) loans and equity investments • Primarily reliant on grants and partnerships • Pay back principal • Reinvest profits in the SB • Grameen SB: no dividends/interests • Profits of one subsidiary either reinvested or paid out to nonprofit entity • No profits • For-profit entity Objective/ Mission • Combination of for-profit and non -profit entities • non-profit entity
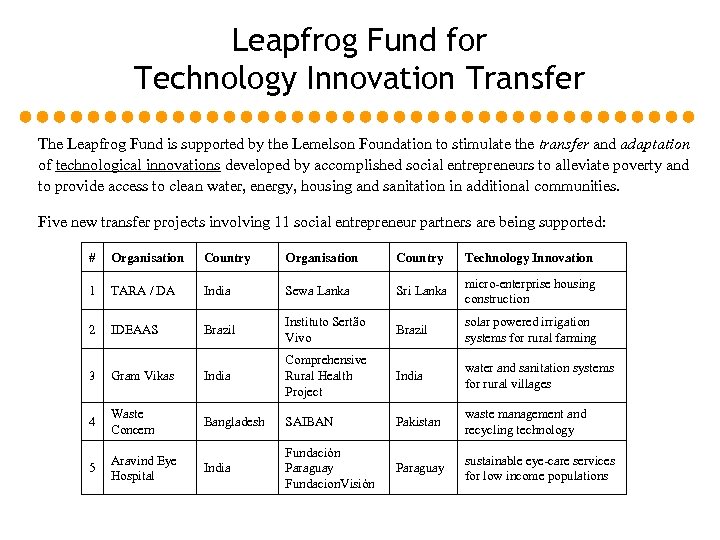 Leapfrog Fund for Technology Innovation Transfer The Leapfrog Fund is supported by the Lemelson Foundation to stimulate the transfer and adaptation of technological innovations developed by accomplished social entrepreneurs to alleviate poverty and to provide access to clean water, energy, housing and sanitation in additional communities. Five new transfer projects involving 11 social entrepreneur partners are being supported: # Organisation Country Technology Innovation 1 TARA / DA India Sewa Lanka Sri Lanka micro-enterprise housing construction 2 IDEAAS Brazil Instituto Sertão Vivo Brazil solar powered irrigation systems for rural farming India water and sanitation systems for rural villages 3 Gram Vikas India Comprehensive Rural Health Project 4 Waste Concern Bangladesh SAIBAN Pakistan waste management and recycling technology 5 Aravind Eye Hospital India Fundación Paraguay Fundacion. Visión Paraguay sustainable eye-care services for low income populations
Leapfrog Fund for Technology Innovation Transfer The Leapfrog Fund is supported by the Lemelson Foundation to stimulate the transfer and adaptation of technological innovations developed by accomplished social entrepreneurs to alleviate poverty and to provide access to clean water, energy, housing and sanitation in additional communities. Five new transfer projects involving 11 social entrepreneur partners are being supported: # Organisation Country Technology Innovation 1 TARA / DA India Sewa Lanka Sri Lanka micro-enterprise housing construction 2 IDEAAS Brazil Instituto Sertão Vivo Brazil solar powered irrigation systems for rural farming India water and sanitation systems for rural villages 3 Gram Vikas India Comprehensive Rural Health Project 4 Waste Concern Bangladesh SAIBAN Pakistan waste management and recycling technology 5 Aravind Eye Hospital India Fundación Paraguay Fundacion. Visión Paraguay sustainable eye-care services for low income populations
 BACK UP
BACK UP
 Examples of Leading Social Entrepreneurs Hybrid Organisation Social Business Leveraged Non-Profit Organization: Sekem Group Founder: Helmy Abouleish Country: Egypt Organization: Job Factory Basel Founder: Robert Roth Country: Schweiz Organization: Teach for America Founder: Wendy Kopp Country: USA Focus Landwirtschaftsbildung, Unternehmensentwicklung, Umwelt Focus Arbeitslosigkeit, Jugendarbeitsbedingungen Focus Bildung Innovation Entwicklung innovativer biodynam. Landwirtschaftsmethoden, Weiterbildung & Qualifizierung Innovation Zweite Job-Chance für Jugendliche mittels speziellem Praktikum mit effizientem Coaching Innovation Hervorragende Graduierte bilden für die Bildungsgleichberechtigung aller Einkommensschichten Strategie 15 profit- und marktorientierte Ausbildungszentren mit unterschiedl. Fokus (Informationstechnologien, Gastronomie, Gitarrenbau etc. ) zur Berufsfindung und -qualifizierung Strategie Ausbildung von exzellenten Graduierten zu bezahlten Lehrern von öffentl. Schulen mit Aktionsfokus in sozial schwächeren Regionen Strategie Anwendung "grüner" Leitlinien und Technologien in Farms Berücksichtigung sozialer & kultureller Aspekte in Gesundheits- und Bildungseinrichtungen Quelle: Schwab Stiftung für Social Entrepreneurship, BCG-Analyse
Examples of Leading Social Entrepreneurs Hybrid Organisation Social Business Leveraged Non-Profit Organization: Sekem Group Founder: Helmy Abouleish Country: Egypt Organization: Job Factory Basel Founder: Robert Roth Country: Schweiz Organization: Teach for America Founder: Wendy Kopp Country: USA Focus Landwirtschaftsbildung, Unternehmensentwicklung, Umwelt Focus Arbeitslosigkeit, Jugendarbeitsbedingungen Focus Bildung Innovation Entwicklung innovativer biodynam. Landwirtschaftsmethoden, Weiterbildung & Qualifizierung Innovation Zweite Job-Chance für Jugendliche mittels speziellem Praktikum mit effizientem Coaching Innovation Hervorragende Graduierte bilden für die Bildungsgleichberechtigung aller Einkommensschichten Strategie 15 profit- und marktorientierte Ausbildungszentren mit unterschiedl. Fokus (Informationstechnologien, Gastronomie, Gitarrenbau etc. ) zur Berufsfindung und -qualifizierung Strategie Ausbildung von exzellenten Graduierten zu bezahlten Lehrern von öffentl. Schulen mit Aktionsfokus in sozial schwächeren Regionen Strategie Anwendung "grüner" Leitlinien und Technologien in Farms Berücksichtigung sozialer & kultureller Aspekte in Gesundheits- und Bildungseinrichtungen Quelle: Schwab Stiftung für Social Entrepreneurship, BCG-Analyse
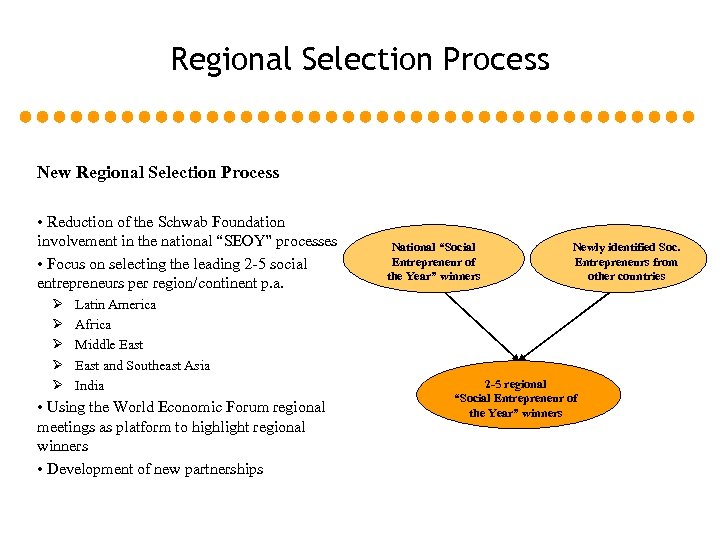 Regional Selection Process New Regional Selection Process • Reduction of the Schwab Foundation involvement in the national “SEOY” processes • Focus on selecting the leading 2 -5 social entrepreneurs per region/continent p. a. Ø Ø Ø Latin America Africa Middle East and Southeast Asia India • Using the World Economic Forum regional meetings as platform to highlight regional winners • Development of new partnerships National “Social Entrepreneur of the Year” winners Newly identified Soc. Entrepreneurs from other countries 2 -5 regional “Social Entrepreneur of the Year” winners
Regional Selection Process New Regional Selection Process • Reduction of the Schwab Foundation involvement in the national “SEOY” processes • Focus on selecting the leading 2 -5 social entrepreneurs per region/continent p. a. Ø Ø Ø Latin America Africa Middle East and Southeast Asia India • Using the World Economic Forum regional meetings as platform to highlight regional winners • Development of new partnerships National “Social Entrepreneur of the Year” winners Newly identified Soc. Entrepreneurs from other countries 2 -5 regional “Social Entrepreneur of the Year” winners
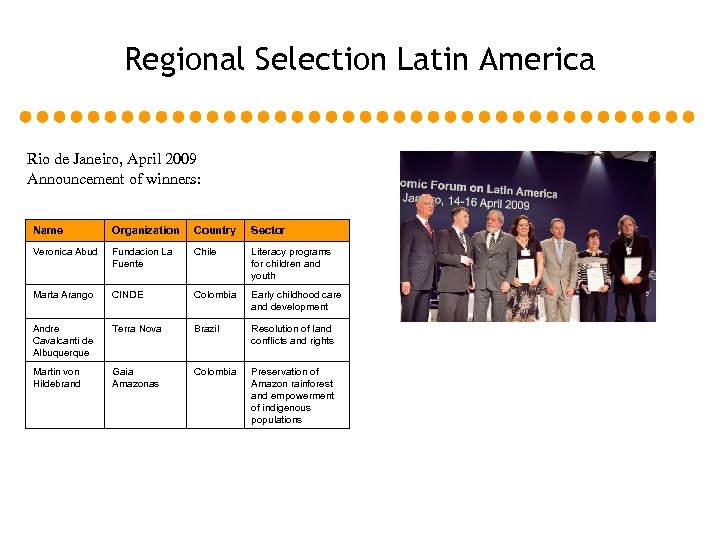 Regional Selection Latin America Rio de Janeiro, April 2009 Announcement of winners: Name Organization Country Sector Veronica Abud Fundacion La Fuente Chile Literacy programs for children and youth Marta Arango CINDE Colombia Early childhood care and development Andre Cavalcanti de Albuquerque Terra Nova Brazil Resolution of land conflicts and rights Martin von Hildebrand Gaia Amazonas Colombia Preservation of Amazon rainforest and empowerment of indigenous populations
Regional Selection Latin America Rio de Janeiro, April 2009 Announcement of winners: Name Organization Country Sector Veronica Abud Fundacion La Fuente Chile Literacy programs for children and youth Marta Arango CINDE Colombia Early childhood care and development Andre Cavalcanti de Albuquerque Terra Nova Brazil Resolution of land conflicts and rights Martin von Hildebrand Gaia Amazonas Colombia Preservation of Amazon rainforest and empowerment of indigenous populations
 Abbreviated List of Social Entrepreneurs submitting GRI case studies Poverty Eradication/ Rural Development • Agriculture risk insurance, BASIX • Low-cost energy solutions, Freeplay/SELCO • Land ownership reform, Rural Development Institute • Solving the water scarcity crisis, IDE India • Investment fund for start-up social enterprises, Kick. Start • Reversing the urban distress migration, Gram Vikras • Unleashing the power of the SME sector, Techno. Serve • Universal access to credit, Kashf Foundation Education/Human rights • Global literacy, Fundacion La Fuente • Universal socio-financial education for children, Aflatoun • Creating an enabling environment for girls, CAMFED/Fundacion Paraguaya Health • Making medical technology affordable, PATH/Aravind/David Green • Improving access to health services, Riders for Health • Improving child nutrition, Un Kilo de Ayuda • Neglected diseases, One. World Health • International patent reform, CAMBIA
Abbreviated List of Social Entrepreneurs submitting GRI case studies Poverty Eradication/ Rural Development • Agriculture risk insurance, BASIX • Low-cost energy solutions, Freeplay/SELCO • Land ownership reform, Rural Development Institute • Solving the water scarcity crisis, IDE India • Investment fund for start-up social enterprises, Kick. Start • Reversing the urban distress migration, Gram Vikras • Unleashing the power of the SME sector, Techno. Serve • Universal access to credit, Kashf Foundation Education/Human rights • Global literacy, Fundacion La Fuente • Universal socio-financial education for children, Aflatoun • Creating an enabling environment for girls, CAMFED/Fundacion Paraguaya Health • Making medical technology affordable, PATH/Aravind/David Green • Improving access to health services, Riders for Health • Improving child nutrition, Un Kilo de Ayuda • Neglected diseases, One. World Health • International patent reform, CAMBIA
 Leapfrog Fund (2) Phase I completed: • Site visits, training of staff and beneficiaries, stakeholder consultations and buy-in, purchases of equipment and project assessments and planning by the "importing" social entrepreneur. • INSEAD initiated research of all 16 Leapfrog finalists discovered that 14 of the 16 replication proposals stimulated by the Leapfrog Fund are in progress (despite not receiving Leapfrog funding). Phase II in progress: • The final 50% of the grants has been disbursed to facilitate the purchase of equipment and employment of staff to implement and apply the new technologies. • Some initial outcomes: Ø Construction of sanitation facilities throughout all households in 2 villages in Jamkhed, Rajasthan. Ø Construction of compost plant for solid waste management and recycling programs in low cost housing development in Karachi, Pakistan Ø Research & development of best low-cost solar irrigation model for rural agriculture in Brazil Ø Production centre with equipment and trained staff established for production of earth blocks, roofing and flooring tiles and certificate training of micro-entrepreneur builders in Batticaloa, Sri Lanka.
Leapfrog Fund (2) Phase I completed: • Site visits, training of staff and beneficiaries, stakeholder consultations and buy-in, purchases of equipment and project assessments and planning by the "importing" social entrepreneur. • INSEAD initiated research of all 16 Leapfrog finalists discovered that 14 of the 16 replication proposals stimulated by the Leapfrog Fund are in progress (despite not receiving Leapfrog funding). Phase II in progress: • The final 50% of the grants has been disbursed to facilitate the purchase of equipment and employment of staff to implement and apply the new technologies. • Some initial outcomes: Ø Construction of sanitation facilities throughout all households in 2 villages in Jamkhed, Rajasthan. Ø Construction of compost plant for solid waste management and recycling programs in low cost housing development in Karachi, Pakistan Ø Research & development of best low-cost solar irrigation model for rural agriculture in Brazil Ø Production centre with equipment and trained staff established for production of earth blocks, roofing and flooring tiles and certificate training of micro-entrepreneur builders in Batticaloa, Sri Lanka.


