ff8160170ebce804f28f73a9819bb1ef.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31

So you have been asked to submit a portfolio… Saleem Farook Associate Dean

Objectives of this session • Why a portfolio? • What is a portfolio in the context of PG medical education? • How to put together a portfolio? • Portfolio assessment • E-portfolios

Why a portfolio? • • Changes to postgraduate medicine Competency based curriculum Need to demonstrate competence Stress on ethical and professional practice • Continuing professional development • Licensing and revalidation

What is a portfolio? Is it a • Logbook? • Scrapbook? • Compilation of certificates? • Display album for your presentations? • Summary book of publications?

Portfolio in other professions • • Artist’s portfolio Company portfolio Educational portfolio (teachers) Educational portfolio (learners)

Company Portfolio • Is the company worth the investment? • What is the company’s track record? • How is it doing currently? – Profits – how will these be maintained? – Losses – how will these be addressed? • What are the company’s future plans?

Doctor’s portfolio • Are you worth investing in terms of – Training time and money? – Patient care? – Health Service? • What have you done in the past? – Strengths – how would you continue to excel? – Developmental needs – how will these be addressed? • What are you doing currently? • Where are you heading in the future?

What is a portfolio meant to demonstrate? • Knowledge • Skills • Attitude
What is a portfolio meant to demonstrate?
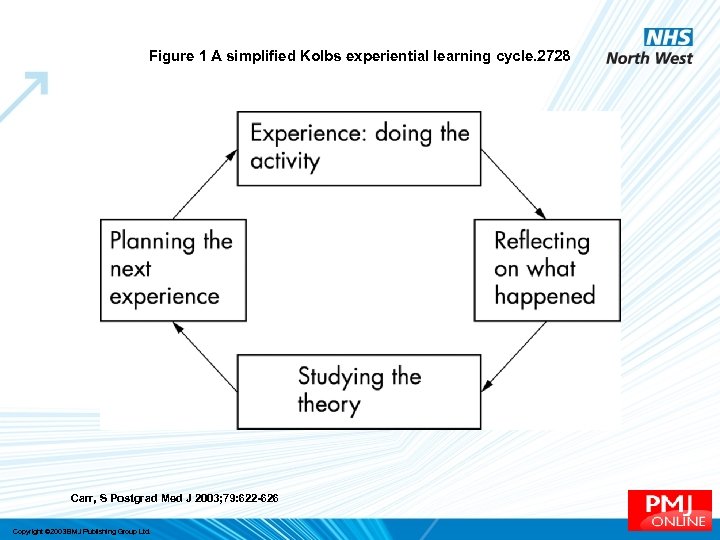
Figure 1 A simplified Kolbs experiential learning cycle. 2728 Carr, S Postgrad Med J 2003; 79: 622 -626 Copyright © 2003 BMJ Publishing Group Ltd.

Putting together a portfolio • Question 1 - What is it for? – ST selection – PMETB approval of competencies – Annual appraisal

Putting together a portfolio • Question 2 - Who is going to look at it? – Appraisers (colleagues) – Assessors (examiners) – Selectors (Trainers)

Putting together a portfolio • Question 3 – What are they looking for? – Curricular coverage – Dates – Evidence of achievement of specific competencies

Putting together a portfolio • Question 4 – What will your portfolio say about you? – What type of person are you? – What are your interests?

Putting together a portfolio • • C O R P Collect Organize Reflect Present

Collect Have an accessible file/ folder/drawer • • Emails Letters Certificates Interesting Cases Private study Reflective summary Presentations Publications

Organize Put them in order of • Chronology • Competencies – PMETB curriculum – GMC Good medical practice

Reflect • The most important element of a portfolio • Brings all the evidence together • Demonstrates capacity to learn • Reflect on both – Achievements – Developmental needs


Present • Presentable format • Tagged appropriately • Summaries where appropriate, especially – Audits – Research – Courses attended

Assessment of portfolio – ST selection • Wide variation • Assessment of achievement and excellence • Be ready to be quizzed on specifics • Know your way around the portfolio

Assessment of portfolio – PMETB • Evidence of curricular competencies • Evidence of generic skills • Evidence of professional development

Assessment of portfolio – annual NHS appraisal • • Meeting GMC requirements Demonstrate excellence Personal development plan Leading to revalidation

E -portfolios
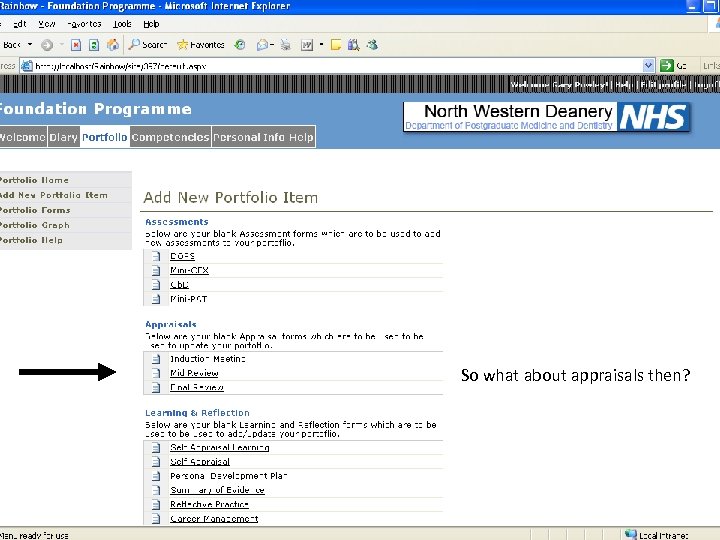
So what about appraisals then?
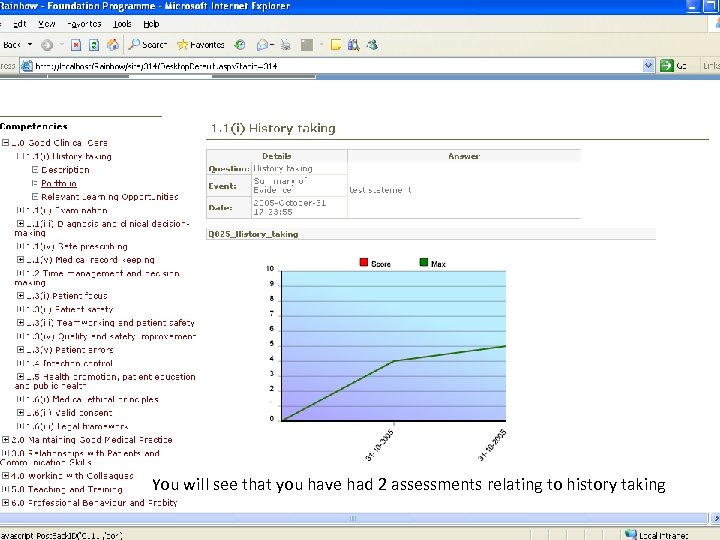
You will see that you have had 2 assessments relating to history taking
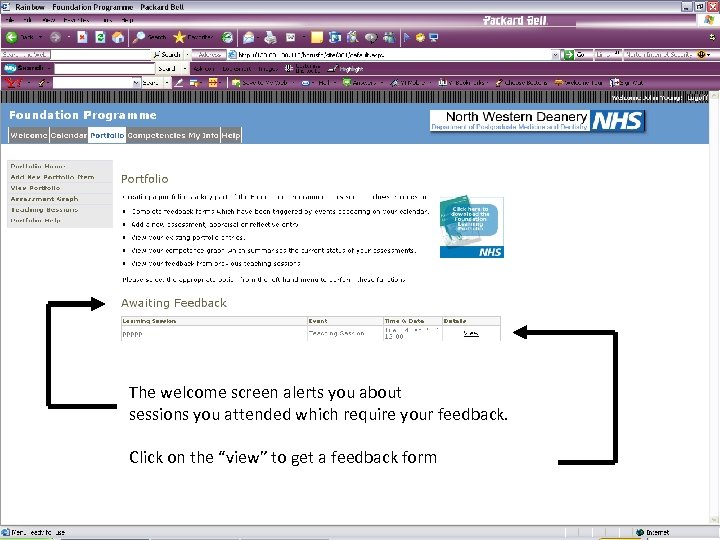
The welcome screen alerts you about sessions you attended which require your feedback. Click on the “view” to get a feedback form
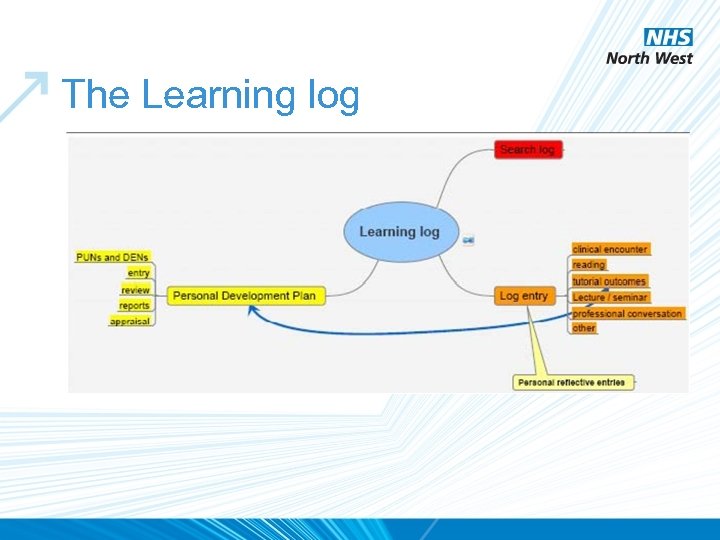
The Learning log
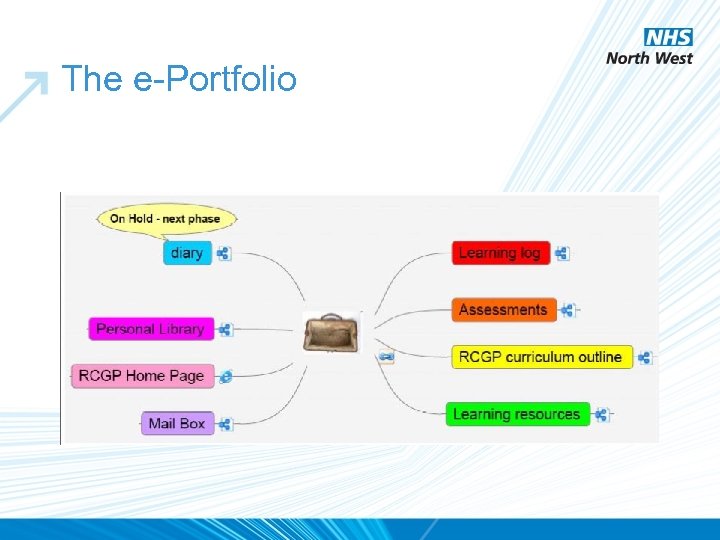
The e-Portfolio
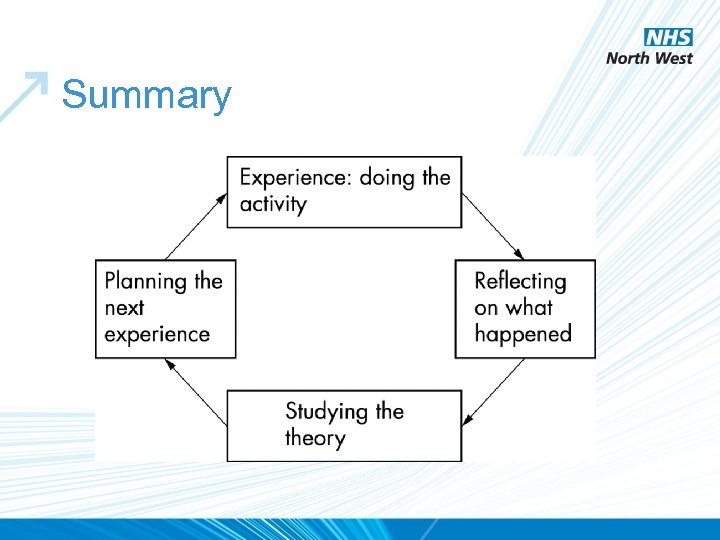
Summary

Summary • Portfolio is much more than a logbook • It is a record of educational progress on ALL fronts – Not just knowledge and clinical skills – Also Attitude and Professional skills • Cannot do it in one week or one month. . Portfolios are here to stay. . .
ff8160170ebce804f28f73a9819bb1ef.ppt