88b48cbf6ec06728f210e6fb538707ea.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 SNOW Spoke Server Implementation on SHRINE 1. 20. 1 Greater Plains Collaborative Hackathon Four Keith M. Wanta January 17, 2017
SNOW Spoke Server Implementation on SHRINE 1. 20. 1 Greater Plains Collaborative Hackathon Four Keith M. Wanta January 17, 2017
 What is the SNOW Network? • SNOW stands for SHRINE Network of Wisconsin • Research network formed by Marshfield Clinic Research Foundation, Medical College of Wisconsin & University of Wisconsin in 2012 • Goal of establishing a shared ontology • Umberto Tachinardi, Tom Mish
What is the SNOW Network? • SNOW stands for SHRINE Network of Wisconsin • Research network formed by Marshfield Clinic Research Foundation, Medical College of Wisconsin & University of Wisconsin in 2012 • Goal of establishing a shared ontology • Umberto Tachinardi, Tom Mish
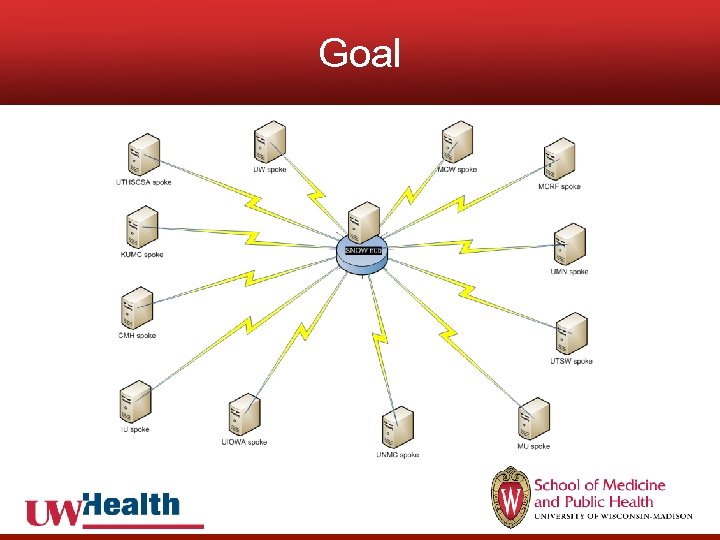 Goal
Goal
 How to Achieve this Goal • Use the SNOW wiki administered by George Kowalski from MCW – – • Use the Harvard SHRINE install wiki as a reference: – • https: //wiki. ctri. mcw. edu/display/SNOW+Spoke+Implementation+on+Cent. OS This will require two shrine. keystore files for each spoke server you build – – • https: //open. med. harvard. edu/wiki/display/SHRINE/Documentation Follow these instructions – • https: //wiki. ctri. mcw. edu/pages/viewpage. action? page. Id=44991731 Ask George for credentials to access the wiki One for your spoke(s) connecting to the SNOW TEST HUB One for your site’s spoke(s) connecting to the SNOW PROD HUB Use tips and tricks in this presentation!
How to Achieve this Goal • Use the SNOW wiki administered by George Kowalski from MCW – – • Use the Harvard SHRINE install wiki as a reference: – • https: //wiki. ctri. mcw. edu/display/SNOW+Spoke+Implementation+on+Cent. OS This will require two shrine. keystore files for each spoke server you build – – • https: //open. med. harvard. edu/wiki/display/SHRINE/Documentation Follow these instructions – • https: //wiki. ctri. mcw. edu/pages/viewpage. action? page. Id=44991731 Ask George for credentials to access the wiki One for your spoke(s) connecting to the SNOW TEST HUB One for your site’s spoke(s) connecting to the SNOW PROD HUB Use tips and tricks in this presentation!
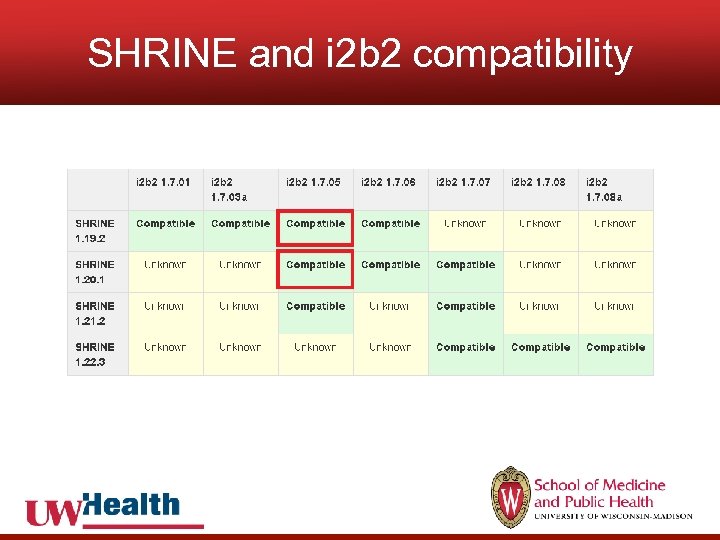 SHRINE and i 2 b 2 compatibility
SHRINE and i 2 b 2 compatibility
 System Architecture • • • Operating System (administrator’s choice) – Cent. OS 6. 6 – tested and approved! – Windows Database Management System (administrator’s choice) – My. SQL, Postgre. SQL, Oracle, MSSQL Linux Services – JBoss, Tomcat, Apache, My. SQL, shrine Software Frameworks in SHRINE application server – Java, J 2 EE, Scala, Slick, JAX-RS, github. com/typesafehub Software frameworks for SHRINE web client – PHP, Curl, YUI, Fast. CGI (on Windows) Software frameworks in i 2 b 2 – Java, J 2 EE, Spring Web Framework
System Architecture • • • Operating System (administrator’s choice) – Cent. OS 6. 6 – tested and approved! – Windows Database Management System (administrator’s choice) – My. SQL, Postgre. SQL, Oracle, MSSQL Linux Services – JBoss, Tomcat, Apache, My. SQL, shrine Software Frameworks in SHRINE application server – Java, J 2 EE, Scala, Slick, JAX-RS, github. com/typesafehub Software frameworks for SHRINE web client – PHP, Curl, YUI, Fast. CGI (on Windows) Software frameworks in i 2 b 2 – Java, J 2 EE, Spring Web Framework
 Client/Server Model (1) • • Request: Many based on i 2 b 2 framework Response: Many based on i 2 b 2 framework Client: SHRINE web client Java. Script app in browser (spoke) Authentication: Java Key Store (JKS) SSL certificate – “shrine-client-signed. pem” & PM cell username/password • Server: /opt/shrine/tomcat/webapps/shrine-webclient (spoke) • Topology: Hub and Spoke • Configuration: lst. Domains. url. Cell. PM /opt/shrine/tomcat/webapps/shrine-webclient/i 2 b 2_config_data. js • Port: 6443 – outbound port 6443 from internal network browser to DMZ firewall – inbound port 6443 from DMZ firewall to internal network browser
Client/Server Model (1) • • Request: Many based on i 2 b 2 framework Response: Many based on i 2 b 2 framework Client: SHRINE web client Java. Script app in browser (spoke) Authentication: Java Key Store (JKS) SSL certificate – “shrine-client-signed. pem” & PM cell username/password • Server: /opt/shrine/tomcat/webapps/shrine-webclient (spoke) • Topology: Hub and Spoke • Configuration: lst. Domains. url. Cell. PM /opt/shrine/tomcat/webapps/shrine-webclient/i 2 b 2_config_data. js • Port: 6443 – outbound port 6443 from internal network browser to DMZ firewall – inbound port 6443 from DMZ firewall to internal network browser
 Client/Server Model (2) • Request: Example: Send marshalled XML from SHRINE web client cohort and send to hub broadcaster • Response: Example: Receive aggregated counts for each downstream node defined on broadcaster • Client: SHRINE adapter forward proxy (spoke) • Authentication: Java Key Store (JKS) SSL certificate – “{site domain}-https. pem” • • Server: SHRINE broadcaster reverse proxy (hub) Topology: Hub and Spoke Configuration: shrine. query. Entry. Point. broadcaster. Service. Endpoint Port: 6443 – outbound port 6443 on firewall in which spoke resides – inbound port 6443 on firewall in which hub resides
Client/Server Model (2) • Request: Example: Send marshalled XML from SHRINE web client cohort and send to hub broadcaster • Response: Example: Receive aggregated counts for each downstream node defined on broadcaster • Client: SHRINE adapter forward proxy (spoke) • Authentication: Java Key Store (JKS) SSL certificate – “{site domain}-https. pem” • • Server: SHRINE broadcaster reverse proxy (hub) Topology: Hub and Spoke Configuration: shrine. query. Entry. Point. broadcaster. Service. Endpoint Port: 6443 – outbound port 6443 on firewall in which spoke resides – inbound port 6443 on firewall in which hub resides
 Client/Server Models (3) • Request: QEP requests. Example: Send marshalled XML request from initiating spoke adapter off to all spoke server adapters defined • Response: QEP responses. Example: Receive counts for each downstream node • Client: SHRINE broadcaster forward proxy (hub QEPs) • Authentication: Java Key Store (JKS) SSL certificate • - “shrine-hub-https. pem” • • Server: SHRINE adapter reverse proxy (spoke) Topology: Hub and Spoke Configuration: shrine. hub. downstream. Nodes Port: 6443 – outbound port 6443 on firewall with hub – inbound port 6443 on firewall with spoke
Client/Server Models (3) • Request: QEP requests. Example: Send marshalled XML request from initiating spoke adapter off to all spoke server adapters defined • Response: QEP responses. Example: Receive counts for each downstream node • Client: SHRINE broadcaster forward proxy (hub QEPs) • Authentication: Java Key Store (JKS) SSL certificate • - “shrine-hub-https. pem” • • Server: SHRINE adapter reverse proxy (spoke) Topology: Hub and Spoke Configuration: shrine. hub. downstream. Nodes Port: 6443 – outbound port 6443 on firewall with hub – inbound port 6443 on firewall with spoke
 Client/Server Model (4) • Request: Example: Send marshalled XML request from downstream spoke server adapter to i 2 b 2 • Response: Example: Receive count from i 2 b 2 based on cohort query • Client: SHRINE data steward • Authentication: i 2 b 2 authorization provider (PM, AD, Shibboleth) • Server: Apache HTTP Server (i 2 b 2 application server) • Topology: Hub and Spoke • Configuration: shrine. steward. pm. Cell. Endpoint (authorization), etc. . • Port: standard HTTP(s) ports – Port 443 if using https protocol in Apache via open_ssl • https: //wiki. centos. org/How. Tos/Https – Port 80 if using http protocol in Apache
Client/Server Model (4) • Request: Example: Send marshalled XML request from downstream spoke server adapter to i 2 b 2 • Response: Example: Receive count from i 2 b 2 based on cohort query • Client: SHRINE data steward • Authentication: i 2 b 2 authorization provider (PM, AD, Shibboleth) • Server: Apache HTTP Server (i 2 b 2 application server) • Topology: Hub and Spoke • Configuration: shrine. steward. pm. Cell. Endpoint (authorization), etc. . • Port: standard HTTP(s) ports – Port 443 if using https protocol in Apache via open_ssl • https: //wiki. centos. org/How. Tos/Https – Port 80 if using http protocol in Apache
 Install Non-Requirements • It is NOT required to run SHRINE and i 2 b 2 on the same server – SNOW wiki has instructions for implementation on the same server • It is NOT required to have SHRINE use My. SQL and Postgres – SNOW wiki has instructions to configure My. SQL and Postgres • It is NOT required to build a test spoke server – SNOW wiki asks you to build a shrine. keystore for the test hub on 1. 19. 2 and production hub on 1. 20. 1 for every site spoke server irregardless of whether you build a test spoke server • It is NOT required by Harvard to install SHRINE as root, but you will need to rewrite code if you try – You may run Tomcat as a user other than root
Install Non-Requirements • It is NOT required to run SHRINE and i 2 b 2 on the same server – SNOW wiki has instructions for implementation on the same server • It is NOT required to have SHRINE use My. SQL and Postgres – SNOW wiki has instructions to configure My. SQL and Postgres • It is NOT required to build a test spoke server – SNOW wiki asks you to build a shrine. keystore for the test hub on 1. 19. 2 and production hub on 1. 20. 1 for every site spoke server irregardless of whether you build a test spoke server • It is NOT required by Harvard to install SHRINE as root, but you will need to rewrite code if you try – You may run Tomcat as a user other than root
 Troubleshooting SHRINE Exceptions • SHRINE dashboard – New client application that checks diagnostics of SHRINE configuration – Is this tool helpful? You decide. • Alternate way of troubleshooting SHRINE exceptions? – Check the log files
Troubleshooting SHRINE Exceptions • SHRINE dashboard – New client application that checks diagnostics of SHRINE configuration – Is this tool helpful? You decide. • Alternate way of troubleshooting SHRINE exceptions? – Check the log files
 Troubleshooting SHRINE Exceptions Log Files: – – – /opt/shrine/tomcat/logs/catalina. out /opt/shrine/tomcat/logs/proxy. log /opt/shrine/tomcat/logs/shrine. log /opt/shrine/tomcat/logs/steward. log /opt/shrine/tomcat/logs/shrine-dashboard. log (wait a minute!) /opt/jboss-as-7. 1. 1. Final/standalone/log/server. log You are encouraged to email the University of Wisconsin SNOW hub team with your problems. You cannot test a spoke without a hub.
Troubleshooting SHRINE Exceptions Log Files: – – – /opt/shrine/tomcat/logs/catalina. out /opt/shrine/tomcat/logs/proxy. log /opt/shrine/tomcat/logs/shrine. log /opt/shrine/tomcat/logs/steward. log /opt/shrine/tomcat/logs/shrine-dashboard. log (wait a minute!) /opt/jboss-as-7. 1. 1. Final/standalone/log/server. log You are encouraged to email the University of Wisconsin SNOW hub team with your problems. You cannot test a spoke without a hub.
 Troubleshooting SHRINE Exceptions – Document exception • Add to SHRINE wiki – Make a copy of the file – Delete log file – Restart service • • • service mysqld restart (status/start/stop) service httpd restart (status/start/stop) service jboss restart (status/start/stop) /etc/init. d/postgresql-9. 1 restart (status/start/stop) shrine_shutdown / shrine_startup – Ask SNOW hub team for help at UW Health!
Troubleshooting SHRINE Exceptions – Document exception • Add to SHRINE wiki – Make a copy of the file – Delete log file – Restart service • • • service mysqld restart (status/start/stop) service httpd restart (status/start/stop) service jboss restart (status/start/stop) /etc/init. d/postgresql-9. 1 restart (status/start/stop) shrine_shutdown / shrine_startup – Ask SNOW hub team for help at UW Health!
 SHRINE Configuration Files – – – – – /opt/shrine. keystore /opt/shrine/tomcat/conf/server. xml /opt/shrine/tomcat/conf/Catalina/localhost/shrine. xml /opt/shrine/tomcat/conf/Catalina/localhost/steward. xml /opt/shrine/tomcat/lib/dashboard. conf /opt/shrine/tomcat/lib/shrine. conf /opt/shrine/tomcat/lib/steward. conf /opt/shrine/tomcat/lib/Adapter. Mappings. xml /opt/shrine/tomcat/webapps/shrine-webclient/i 2 b 2_config_data. js /opt/shrine/tomcat/bin/setenv. sh • Ignore line w/ shrine: shrine if Tomcat installed as root – /opt/shrine/tomcat/webapps/shrine-webclient/jsi 2 b 2/cells/SHRINE/cell_config_data. js
SHRINE Configuration Files – – – – – /opt/shrine. keystore /opt/shrine/tomcat/conf/server. xml /opt/shrine/tomcat/conf/Catalina/localhost/shrine. xml /opt/shrine/tomcat/conf/Catalina/localhost/steward. xml /opt/shrine/tomcat/lib/dashboard. conf /opt/shrine/tomcat/lib/shrine. conf /opt/shrine/tomcat/lib/steward. conf /opt/shrine/tomcat/lib/Adapter. Mappings. xml /opt/shrine/tomcat/webapps/shrine-webclient/i 2 b 2_config_data. js /opt/shrine/tomcat/bin/setenv. sh • Ignore line w/ shrine: shrine if Tomcat installed as root – /opt/shrine/tomcat/webapps/shrine-webclient/jsi 2 b 2/cells/SHRINE/cell_config_data. js
 Cent. OS Configuration Files – – – /etc/sysconfig/network /etc/hosts /etc/udev/rules. d/70 -persistent-net. rules /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth 0 (defined) /etc/resolve. conf /etc/nsswitch. conf
Cent. OS Configuration Files – – – /etc/sysconfig/network /etc/hosts /etc/udev/rules. d/70 -persistent-net. rules /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth 0 (defined) /etc/resolve. conf /etc/nsswitch. conf
 Nuances on Cent. OS • JBoss expects localhost. localdomain by default – /etc/sysconfig/network, /etc/hosts or method is defined in /etc/nsswitch. conf • Postgre. SQL 9. 1 expects localhost as the hostname in its default configuration – /etc/hosts or method is defined in /etc/nsswitch. conf • shrine_shutdown command can cause error “Could not contact localhost” – Be patient after calling shrine_startup before calling shrine_shutdown
Nuances on Cent. OS • JBoss expects localhost. localdomain by default – /etc/sysconfig/network, /etc/hosts or method is defined in /etc/nsswitch. conf • Postgre. SQL 9. 1 expects localhost as the hostname in its default configuration – /etc/hosts or method is defined in /etc/nsswitch. conf • shrine_shutdown command can cause error “Could not contact localhost” – Be patient after calling shrine_startup before calling shrine_shutdown
 Hub Connectivity
Hub Connectivity
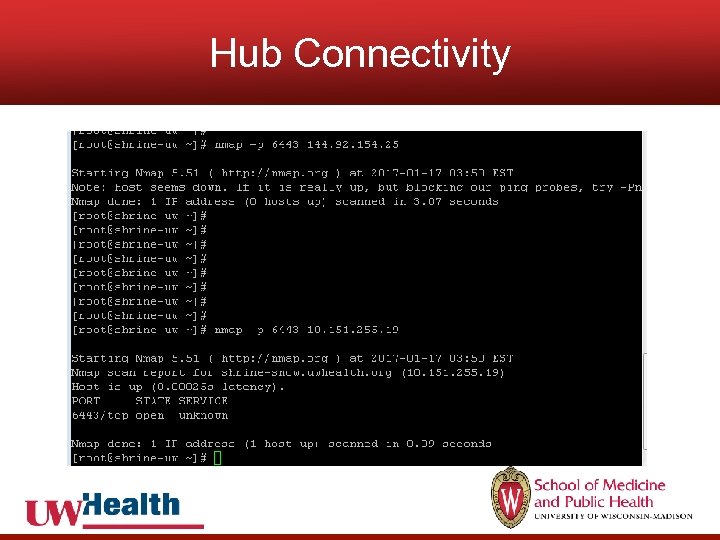 Hub Connectivity
Hub Connectivity
 SHRINE web client login
SHRINE web client login
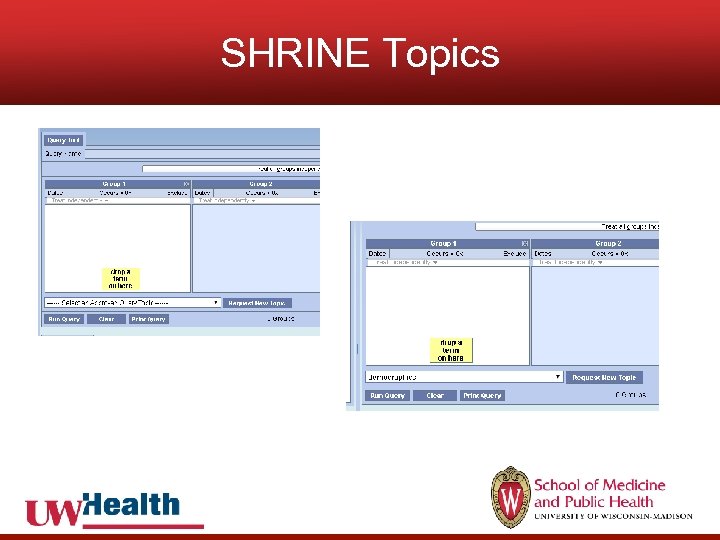 SHRINE Topics
SHRINE Topics
 SHRINE Data Steward
SHRINE Data Steward
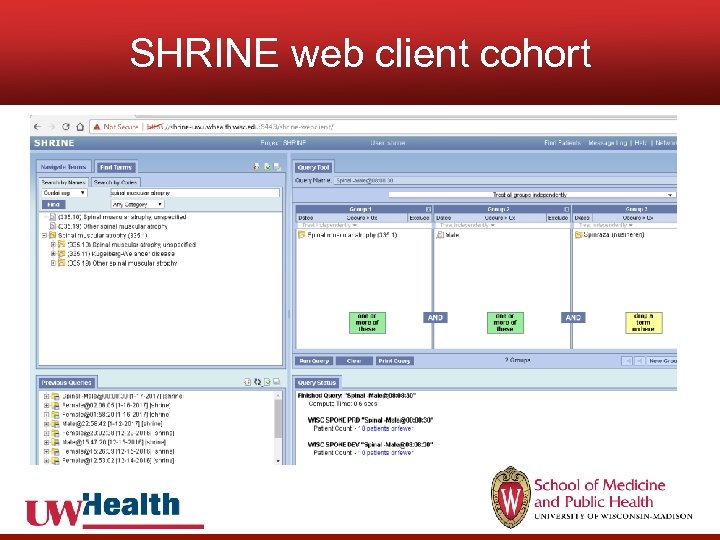 SHRINE web client cohort
SHRINE web client cohort
 SHRINE Topics • Pending - new topics start in the Pending state; researchers must wait for the Steward to approve them • Approved - new topics start in the Approved state; researchers can use them immediately • Topics. Ignored. Just. Log - all queries are logged and approved; researchers don't need to create topics
SHRINE Topics • Pending - new topics start in the Pending state; researchers must wait for the Steward to approve them • Approved - new topics start in the Approved state; researchers can use them immediately • Topics. Ignored. Just. Log - all queries are logged and approved; researchers don't need to create topics
 Q&A
Q&A


