86db901a06096fc4e6ea8a0084b6c855.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 54
 Smoke Alarm Installer Training
Smoke Alarm Installer Training
 Please Introduce Yourself Name Organization
Please Introduce Yourself Name Organization
 Course Objectives § Recognize the need for smoke alarms. § Describe the selection of single-station smoke alarms. § Differentiate between the smoke-sensing technologies of single-station smoke alarms.
Course Objectives § Recognize the need for smoke alarms. § Describe the selection of single-station smoke alarms. § Differentiate between the smoke-sensing technologies of single-station smoke alarms.
 Course Objectives § Determine the minimum number of smoke alarms needed to meet the requirements of NFPA® 72 for residential structures and HUD guidelines for mobile homes. . § Describe installation of alert devices for people with disabilities. § Recognize the opportunity to conduct fire and life safety education during smoke alarm installation.
Course Objectives § Determine the minimum number of smoke alarms needed to meet the requirements of NFPA® 72 for residential structures and HUD guidelines for mobile homes. . § Describe installation of alert devices for people with disabilities. § Recognize the opportunity to conduct fire and life safety education during smoke alarm installation.
 Modern furnishings and construction materials make smoke alarms vital to resident safety. [Click to play video. ]
Modern furnishings and construction materials make smoke alarms vital to resident safety. [Click to play video. ]
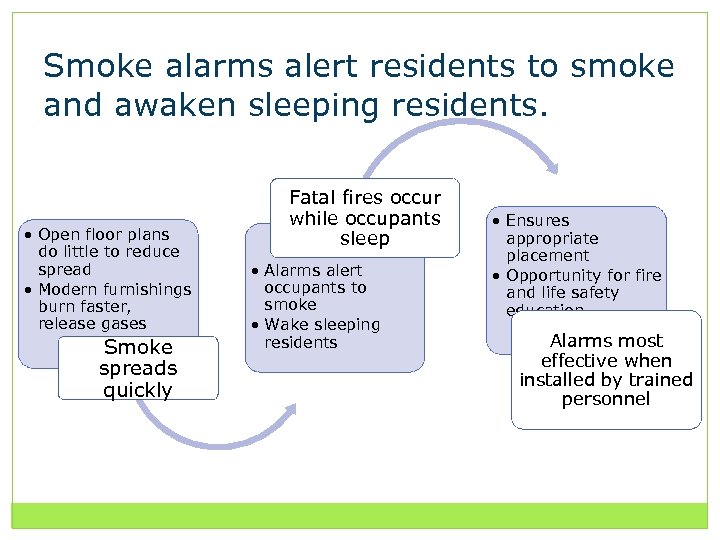 Smoke alarms alert residents to smoke and awaken sleeping residents. • Open floor plans do little to reduce spread • Modern furnishings burn faster, release gases Smoke spreads quickly Fatal fires occur while occupants sleep • Alarms alert occupants to smoke • Wake sleeping residents • Ensures appropriate placement • Opportunity for fire and life safety education Alarms most effective when installed by trained personnel
Smoke alarms alert residents to smoke and awaken sleeping residents. • Open floor plans do little to reduce spread • Modern furnishings burn faster, release gases Smoke spreads quickly Fatal fires occur while occupants sleep • Alarms alert occupants to smoke • Wake sleeping residents • Ensures appropriate placement • Opportunity for fire and life safety education Alarms most effective when installed by trained personnel
 Ensure alarms are approved by a nationally-recognized testing authority.
Ensure alarms are approved by a nationally-recognized testing authority.
 Single station smoke alarms are suited for residential installation. • With many alarms, activation of one does not activate all • Require battery, replacement • Require maintenance • Relatively inexpensive • Use same technology as hard-wired alarms • Easy to install • Do not require licensed electrician to install
Single station smoke alarms are suited for residential installation. • With many alarms, activation of one does not activate all • Require battery, replacement • Require maintenance • Relatively inexpensive • Use same technology as hard-wired alarms • Easy to install • Do not require licensed electrician to install
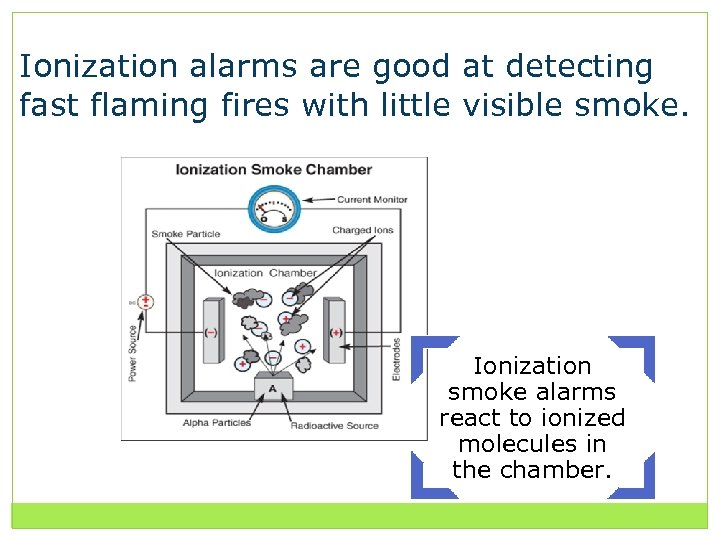 Ionization alarms are good at detecting fast flaming fires with little visible smoke. Ionization smoke alarms react to ionized molecules in the chamber.
Ionization alarms are good at detecting fast flaming fires with little visible smoke. Ionization smoke alarms react to ionized molecules in the chamber.
 Photoelectric alarms are more responsive to smoldering fires and dense smoke. A refractory smoke alarm detects smoke when light reaches a sensor after reflecting off smoke.
Photoelectric alarms are more responsive to smoldering fires and dense smoke. A refractory smoke alarm detects smoke when light reaches a sensor after reflecting off smoke.
 Combination ionization/photoelectric alarms combine the benefits of both technologies. Alarm can be activated by either of the sensors within the unit.
Combination ionization/photoelectric alarms combine the benefits of both technologies. Alarm can be activated by either of the sensors within the unit.
 Several smoke alarms are available through the Oklahoma Assistive Technology Foundation program. Ionization/ Photoelectric 9 V front loading battery Test button Hush feature 10 -year life Kidde PI 9000
Several smoke alarms are available through the Oklahoma Assistive Technology Foundation program. Ionization/ Photoelectric 9 V front loading battery Test button Hush feature 10 -year life Kidde PI 9000
 Several smoke alarms are available through the Oklahoma Assistive Technology Foundation program. Photoelectric Sealed lithium battery Automatic activation once the alarm is installed Test/Hush button for testing Kidde P 3010 L Alarm
Several smoke alarms are available through the Oklahoma Assistive Technology Foundation program. Photoelectric Sealed lithium battery Automatic activation once the alarm is installed Test/Hush button for testing Kidde P 3010 L Alarm
 Several smoke alarms are available through the Oklahoma Assistive Technology Foundation program. Photoelectric Plugs into wall outlet Lithium Battery included. 90 db alarm 177 candela strobe light Gentex Series 7139 LS
Several smoke alarms are available through the Oklahoma Assistive Technology Foundation program. Photoelectric Plugs into wall outlet Lithium Battery included. 90 db alarm 177 candela strobe light Gentex Series 7139 LS
 What are the two common smoke Review Questions sensing technologies used in single-station alarms? Which technology is most prone to false alarms from cooking? Which technology is best at detecting smoldering fires and dense smoke? Which technology is best at detecting fast flaming fires with little smoke? Which technology is most prone to false alarms from dust and insects?
What are the two common smoke Review Questions sensing technologies used in single-station alarms? Which technology is most prone to false alarms from cooking? Which technology is best at detecting smoldering fires and dense smoke? Which technology is best at detecting fast flaming fires with little smoke? Which technology is most prone to false alarms from dust and insects?
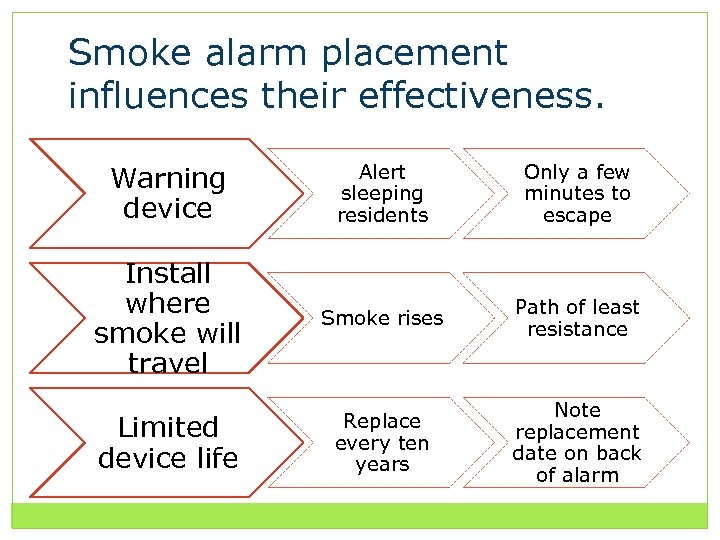 Smoke alarm placement influences their effectiveness. Warning device Alert sleeping residents Only a few minutes to escape Install where smoke will travel Smoke rises Path of least resistance Limited device life Replace every ten years Note replacement date on back of alarm
Smoke alarm placement influences their effectiveness. Warning device Alert sleeping residents Only a few minutes to escape Install where smoke will travel Smoke rises Path of least resistance Limited device life Replace every ten years Note replacement date on back of alarm
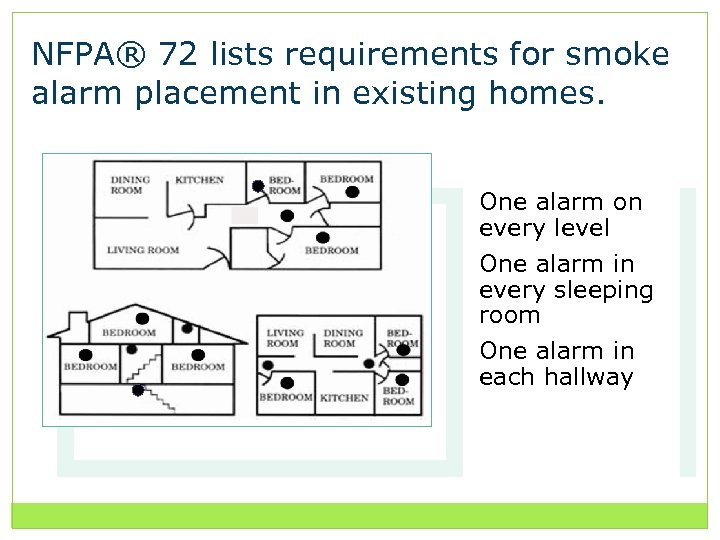 NFPA® 72 lists requirements for smoke alarm placement in existing homes. One alarm on every level One alarm in every sleeping room One alarm in each hallway
NFPA® 72 lists requirements for smoke alarm placement in existing homes. One alarm on every level One alarm in every sleeping room One alarm in each hallway
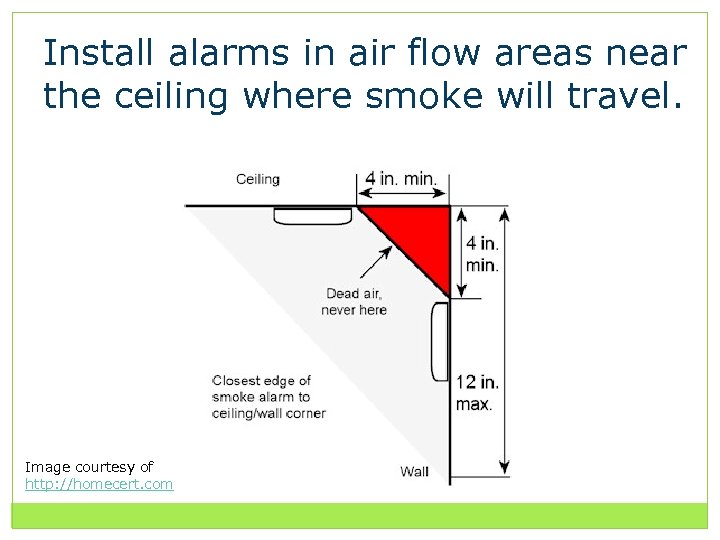 Install alarms in air flow areas near the ceiling where smoke will travel. Image courtesy of http: //homecert. com
Install alarms in air flow areas near the ceiling where smoke will travel. Image courtesy of http: //homecert. com
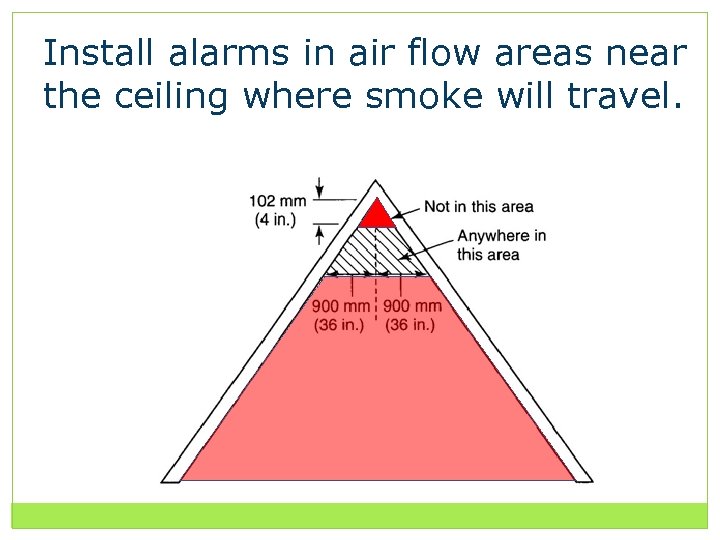 Install alarms in air flow areas near the ceiling where smoke will travel.
Install alarms in air flow areas near the ceiling where smoke will travel.
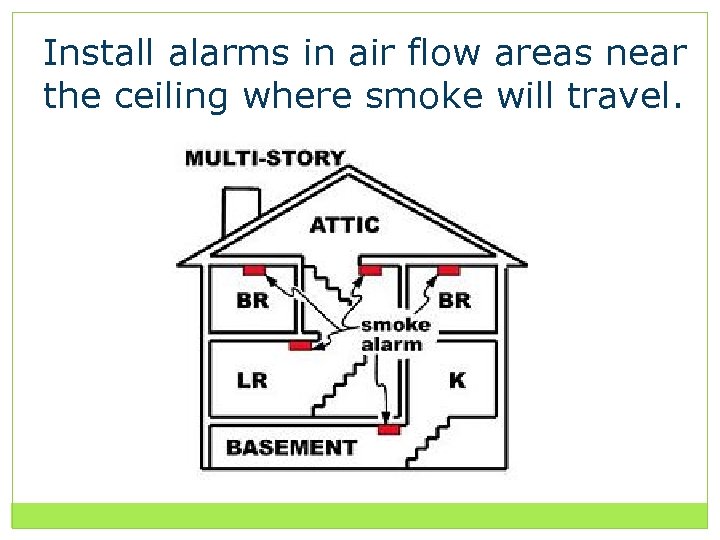 Install alarms in air flow areas near the ceiling where smoke will travel.
Install alarms in air flow areas near the ceiling where smoke will travel.
 Review Questions What are the minimum smoke alarm requirements in existing residential construction? In mobile homes? How far should wall-mounted smoke alarms be placed from the ceiling? Where should smoke alarms be placed on a sloped ceiling, relative to the peak?
Review Questions What are the minimum smoke alarm requirements in existing residential construction? In mobile homes? How far should wall-mounted smoke alarms be placed from the ceiling? Where should smoke alarms be placed on a sloped ceiling, relative to the peak?
 False alarms are more than an annoyance. Annoying noise Assume all alarms are false Disconnect battery or remove alarm to silence false alarms
False alarms are more than an annoyance. Annoying noise Assume all alarms are false Disconnect battery or remove alarm to silence false alarms
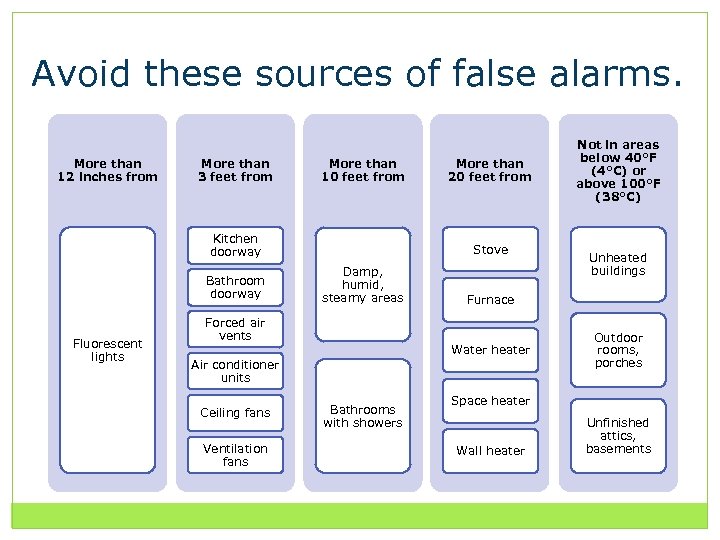 Avoid these sources of false alarms. More than 12 inches from More than 3 feet from More than 10 feet from Kitchen doorway Bathroom doorway Fluorescent lights Stove Damp, humid, steamy areas Forced air vents Ventilation fans Bathrooms with showers Unheated buildings Furnace Water heater Air conditioner units Ceiling fans More than 20 feet from Not in areas below 40°F (4°C) or above 100°F (38°C) Outdoor rooms, porches Space heater Wall heater Unfinished attics, basements
Avoid these sources of false alarms. More than 12 inches from More than 3 feet from More than 10 feet from Kitchen doorway Bathroom doorway Fluorescent lights Stove Damp, humid, steamy areas Forced air vents Ventilation fans Bathrooms with showers Unheated buildings Furnace Water heater Air conditioner units Ceiling fans More than 20 feet from Not in areas below 40°F (4°C) or above 100°F (38°C) Outdoor rooms, porches Space heater Wall heater Unfinished attics, basements
 Remember these placement guidelines. Use your best judgment Install the number of alarms needed Write the replacement date on the alarm Do not remove existing alarms
Remember these placement guidelines. Use your best judgment Install the number of alarms needed Write the replacement date on the alarm Do not remove existing alarms
 Learning Activity Identify the smoke alarms needed for residential structures and mobile homes.
Learning Activity Identify the smoke alarms needed for residential structures and mobile homes.
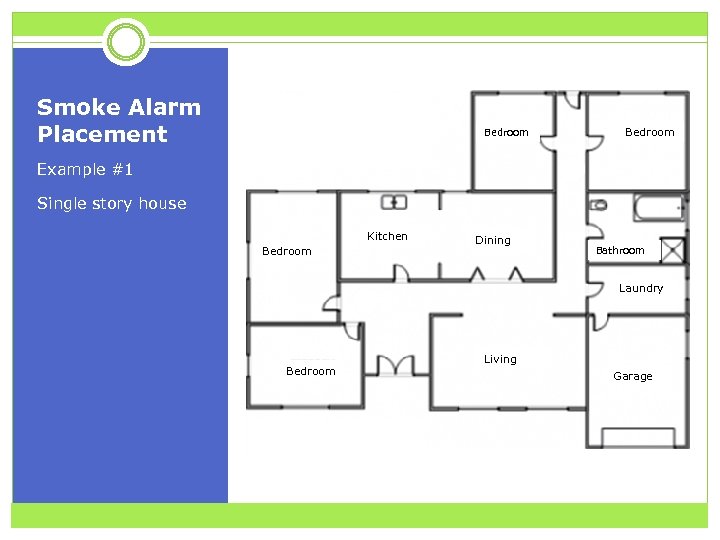 Smoke Alarm Placement Bedroom Example #1 Single story house Kitchen Bedroom Dining Bathroom Laundry Bedroom Living Garage
Smoke Alarm Placement Bedroom Example #1 Single story house Kitchen Bedroom Dining Bathroom Laundry Bedroom Living Garage
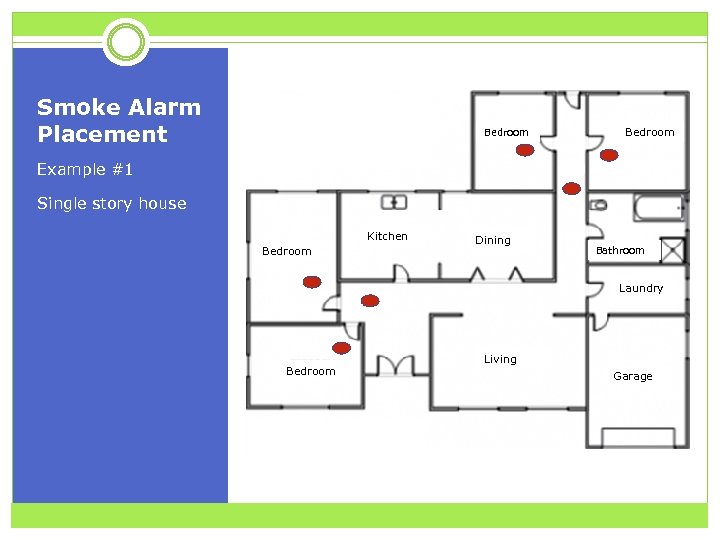 Smoke Alarm Placement Bedroom Example #1 Single story house Kitchen Bedroom Dining Bathroom Laundry Bedroom Living Garage
Smoke Alarm Placement Bedroom Example #1 Single story house Kitchen Bedroom Dining Bathroom Laundry Bedroom Living Garage
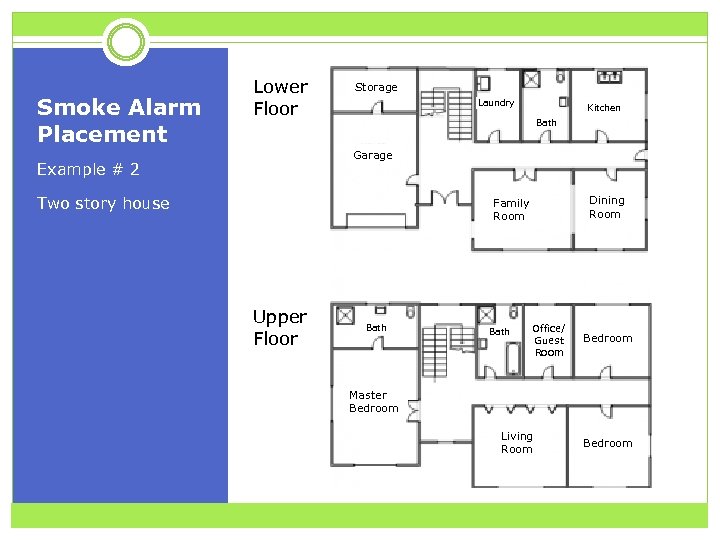 Smoke Alarm Placement Lower Floor Storage Laundry Kitchen Bath Garage Example # 2 Two story house Dining Room Family Room Upper Floor Bath Office/ Guest Room Bedroom Master Bedroom Living Room Bedroom
Smoke Alarm Placement Lower Floor Storage Laundry Kitchen Bath Garage Example # 2 Two story house Dining Room Family Room Upper Floor Bath Office/ Guest Room Bedroom Master Bedroom Living Room Bedroom
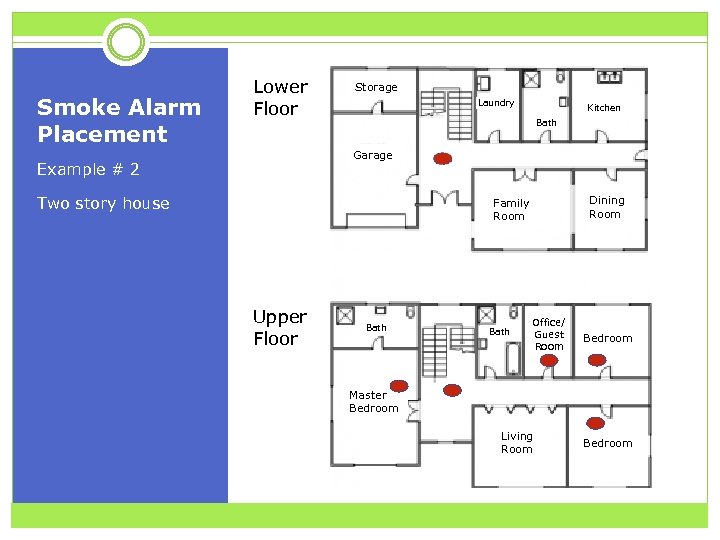 Smoke Alarm Placement Lower Floor Storage Laundry Kitchen Bath Garage Example # 2 Two story house Dining Room Family Room Upper Floor Bath Office/ Guest Room Bedroom Master Bedroom Living Room Bedroom
Smoke Alarm Placement Lower Floor Storage Laundry Kitchen Bath Garage Example # 2 Two story house Dining Room Family Room Upper Floor Bath Office/ Guest Room Bedroom Master Bedroom Living Room Bedroom
 Learning Activity Complete the rest of the floor plans on your own.
Learning Activity Complete the rest of the floor plans on your own.
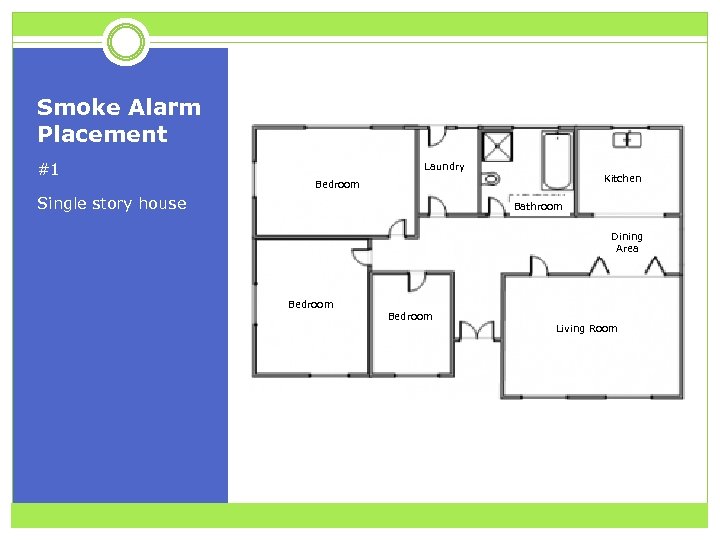 Smoke Alarm Placement #1 Laundry Kitchen Bedroom Single story house Bathroom Dining Area Bedroom Living Room
Smoke Alarm Placement #1 Laundry Kitchen Bedroom Single story house Bathroom Dining Area Bedroom Living Room
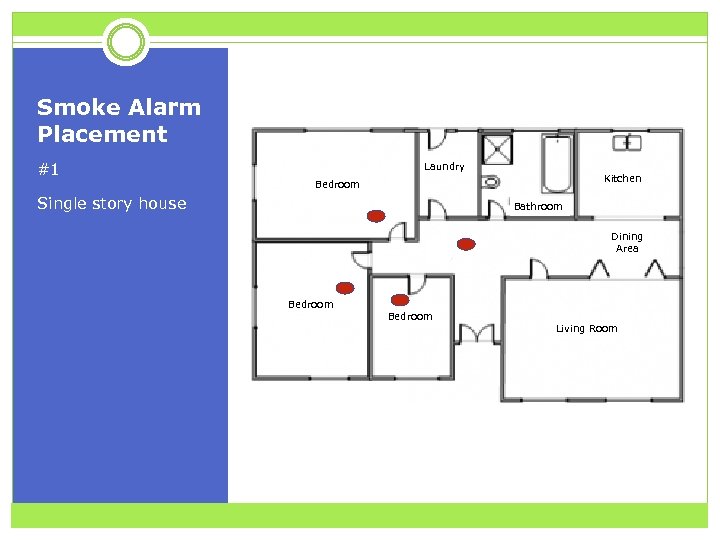 Smoke Alarm Placement #1 Laundry Kitchen Bedroom Single story house Bathroom Dining Area Bedroom Living Room
Smoke Alarm Placement #1 Laundry Kitchen Bedroom Single story house Bathroom Dining Area Bedroom Living Room
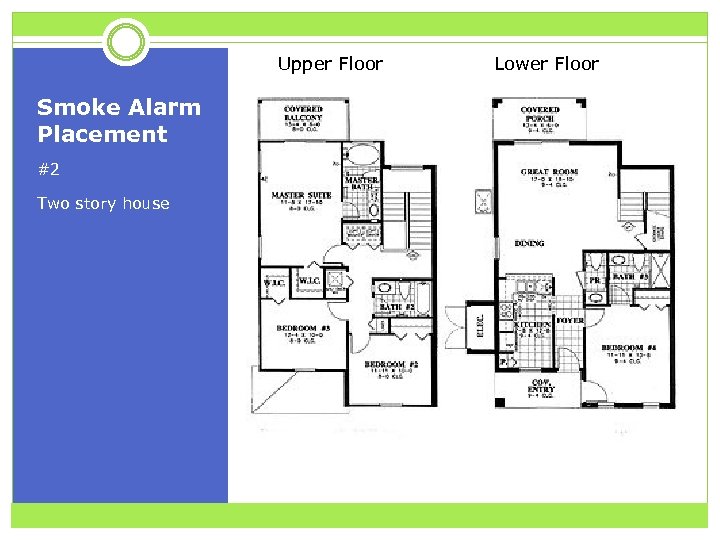 Upper Floor Smoke Alarm Placement #2 Two story house Lower Floor
Upper Floor Smoke Alarm Placement #2 Two story house Lower Floor
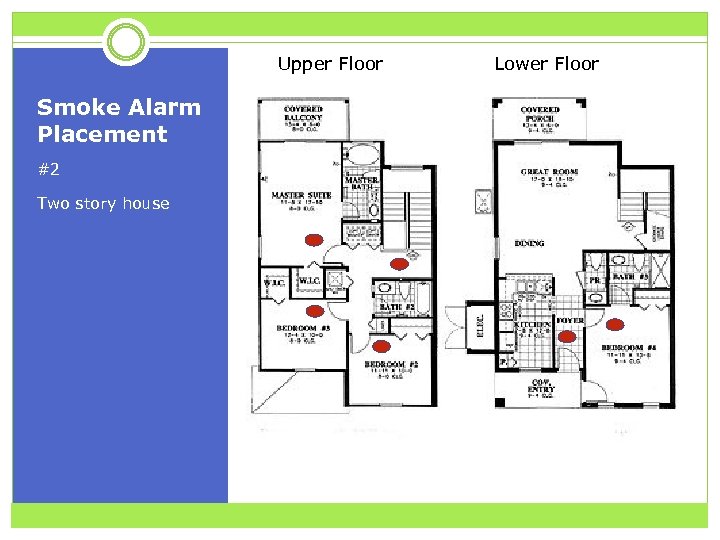 Upper Floor Smoke Alarm Placement #2 Two story house Lower Floor
Upper Floor Smoke Alarm Placement #2 Two story house Lower Floor
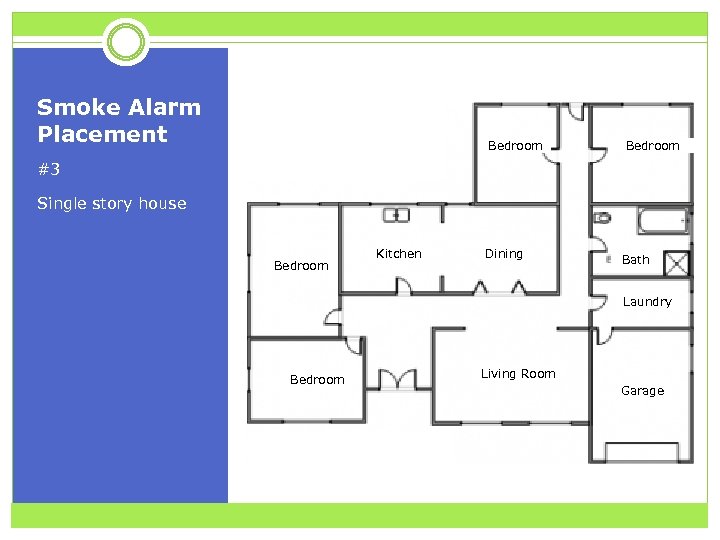 Smoke Alarm Placement Bedroom #3 Single story house Bedroom Kitchen Dining Bath Laundry Bedroom Living Room Garage
Smoke Alarm Placement Bedroom #3 Single story house Bedroom Kitchen Dining Bath Laundry Bedroom Living Room Garage
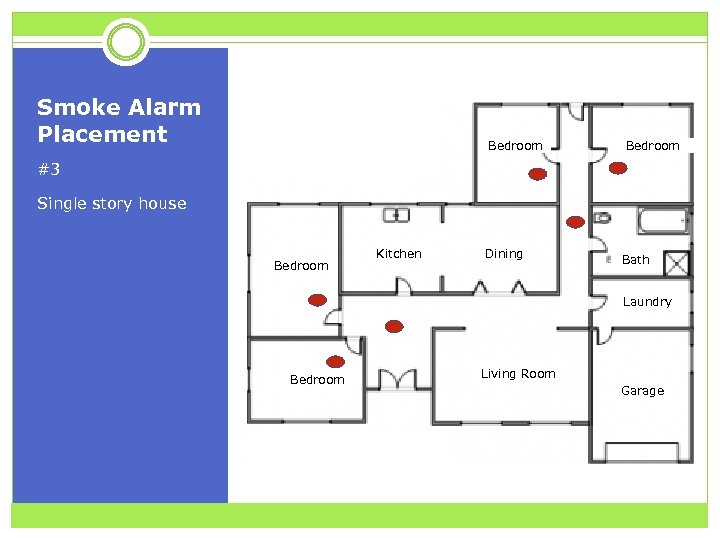 Smoke Alarm Placement Bedroom #3 Single story house Bedroom Kitchen Dining Bath Laundry Bedroom Living Room Garage
Smoke Alarm Placement Bedroom #3 Single story house Bedroom Kitchen Dining Bath Laundry Bedroom Living Room Garage
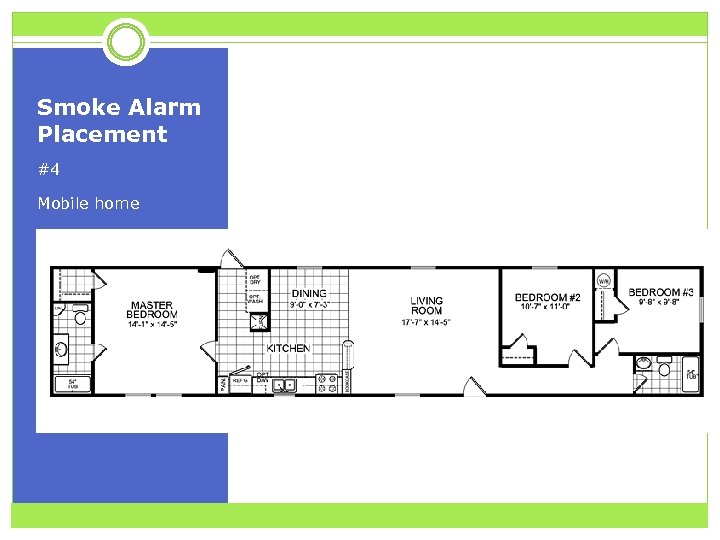 Smoke Alarm Placement #4 Mobile home
Smoke Alarm Placement #4 Mobile home
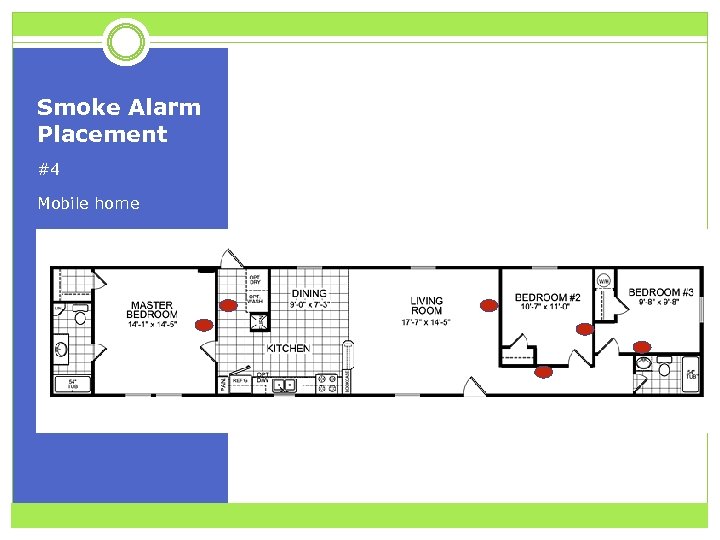 Smoke Alarm Placement #4 Mobile home
Smoke Alarm Placement #4 Mobile home
 Alert equipment supplements smoke alarms for people with disabilities. Lifetone alert device Listening device – not a smoke alarm “Hears” audio signal from smoke alarm Alerts by • 520 Hz audio signal • Displays “FIRE” • Shakes bed
Alert equipment supplements smoke alarms for people with disabilities. Lifetone alert device Listening device – not a smoke alarm “Hears” audio signal from smoke alarm Alerts by • 520 Hz audio signal • Displays “FIRE” • Shakes bed
 Alert equipment supplements smoke alarms for people with disabilities. Place at bedside, within six feet of bed Face screen, speaker toward bed Place bed shaker under mattress or pillow Power the unit • Insert batteries • Plug into wall outlet Lifetone alert device Test the unit • Press TEST button • Test smoke detector Set the Clock
Alert equipment supplements smoke alarms for people with disabilities. Place at bedside, within six feet of bed Face screen, speaker toward bed Place bed shaker under mattress or pillow Power the unit • Insert batteries • Plug into wall outlet Lifetone alert device Test the unit • Press TEST button • Test smoke detector Set the Clock
 Fire and life safety education focuses on four key messages. Fall prevention Poisoning prevention Home safety survey Family escape plan
Fire and life safety education focuses on four key messages. Fall prevention Poisoning prevention Home safety survey Family escape plan
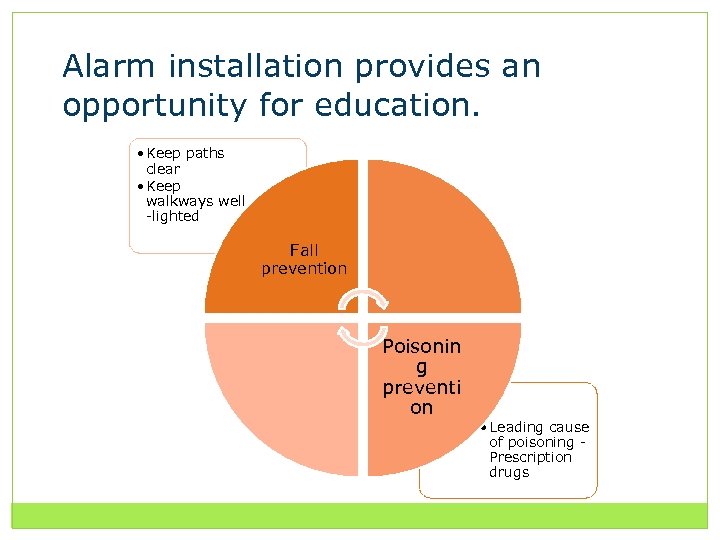 Alarm installation provides an opportunity for education. • Keep paths clear • Keep walkways well -lighted Fall prevention Poisonin g preventi on • Leading cause of poisoning Prescription drugs
Alarm installation provides an opportunity for education. • Keep paths clear • Keep walkways well -lighted Fall prevention Poisonin g preventi on • Leading cause of poisoning Prescription drugs
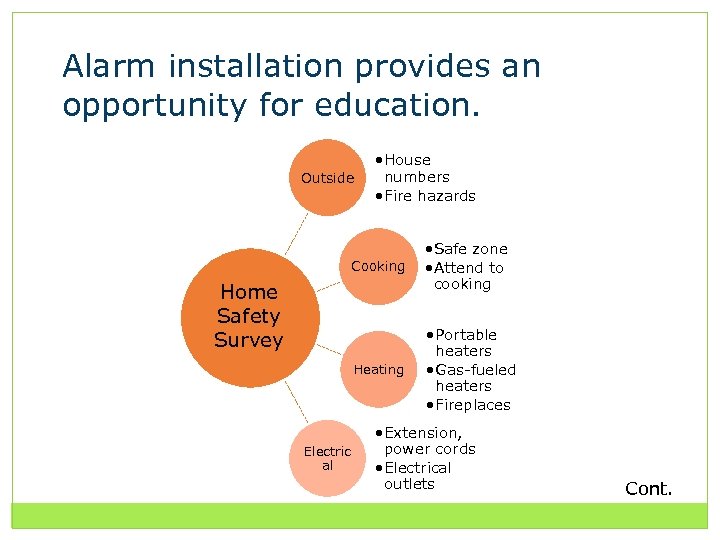 Alarm installation provides an opportunity for education. Outside • House numbers • Fire hazards Cooking • Safe zone • Attend to cooking Heating • Portable heaters • Gas-fueled heaters • Fireplaces Home Safety Survey Electric al • Extension, power cords • Electrical outlets Cont.
Alarm installation provides an opportunity for education. Outside • House numbers • Fire hazards Cooking • Safe zone • Attend to cooking Heating • Portable heaters • Gas-fueled heaters • Fireplaces Home Safety Survey Electric al • Extension, power cords • Electrical outlets Cont.
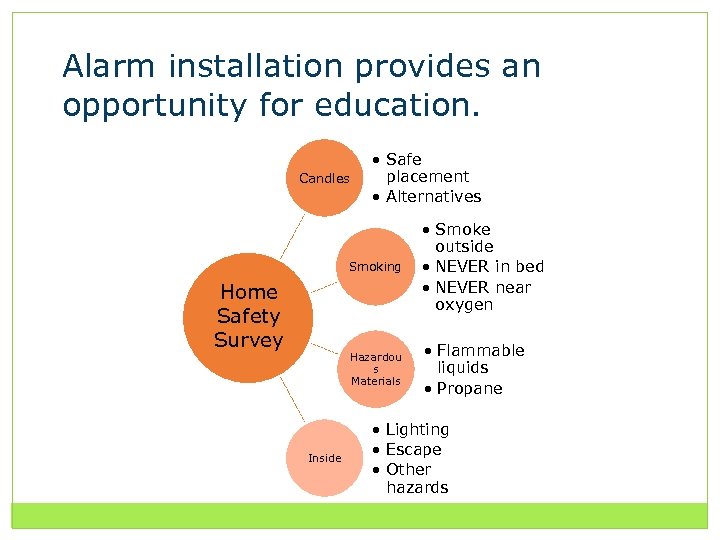 Alarm installation provides an opportunity for education. Candles • Safe placement • Alternatives Smoking Hazardou s Materials Home Safety Survey Inside • Smoke outside • NEVER in bed • NEVER near oxygen • Flammable liquids • Propane • Lighting • Escape • Other hazards
Alarm installation provides an opportunity for education. Candles • Safe placement • Alternatives Smoking Hazardou s Materials Home Safety Survey Inside • Smoke outside • NEVER in bed • NEVER near oxygen • Flammable liquids • Propane • Lighting • Escape • Other hazards
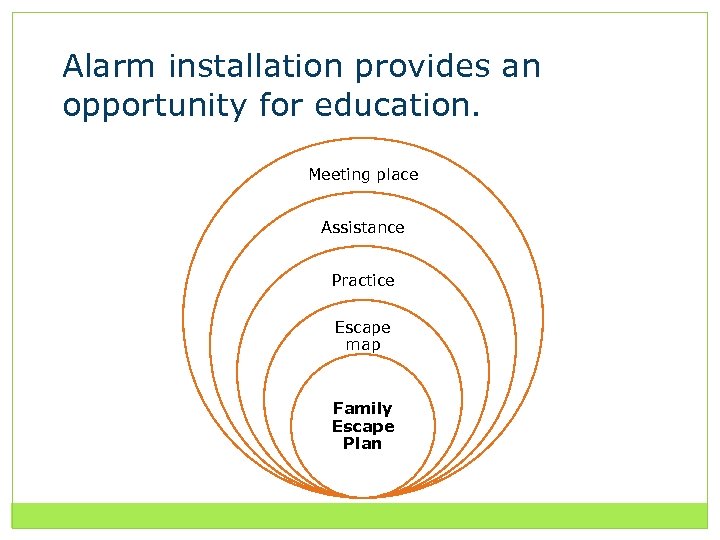 Alarm installation provides an opportunity for education. Meeting place Assistance Practice Escape map Family Escape Plan
Alarm installation provides an opportunity for education. Meeting place Assistance Practice Escape map Family Escape Plan
 Summary § Smoke alarms alert residents to smoke, allow time for residents to escape § Alarms are most effective when installed by trained personnel
Summary § Smoke alarms alert residents to smoke, allow time for residents to escape § Alarms are most effective when installed by trained personnel
 Summary § Single station smoke alarms are appropriate for existing residences because they are: § Relatively inexpensive § Easy to install – no electrician required § Smoke alarms do require maintenance and testing § Smoke alarms should be replaced after ten years
Summary § Single station smoke alarms are appropriate for existing residences because they are: § Relatively inexpensive § Easy to install – no electrician required § Smoke alarms do require maintenance and testing § Smoke alarms should be replaced after ten years
 Summary § Ionization smoke alarms react more quickly to fast flaming fires with little visible smoke. § Photoelectric smoke alarms are more responsive to smoldering fires and dense smoke. § Combination Ionization/Photoelectric smoke alarms give the benefit of both technologies.
Summary § Ionization smoke alarms react more quickly to fast flaming fires with little visible smoke. § Photoelectric smoke alarms are more responsive to smoldering fires and dense smoke. § Combination Ionization/Photoelectric smoke alarms give the benefit of both technologies.
 Summary § Residents have only a few minutes to escape –smoke alarms must be installed properly to alert at earliest opportunity. § Smoke alarms should be installed where smoke is most likely to go.
Summary § Residents have only a few minutes to escape –smoke alarms must be installed properly to alert at earliest opportunity. § Smoke alarms should be installed where smoke is most likely to go.
 Summary § NFPA® 72 established minimum smoke alarm requirements for existing residences. § One alarm on every level § One alarm in every sleeping area § One alarm in each hallway § Smoke alarms should be placed on ceilings or high on walls, out of dead air zones.
Summary § NFPA® 72 established minimum smoke alarm requirements for existing residences. § One alarm on every level § One alarm in every sleeping area § One alarm in each hallway § Smoke alarms should be placed on ceilings or high on walls, out of dead air zones.
 Summary § Proper placement of smoke alarms can reduce the number of false alarms § No home will perfectly match the guidelines – Installers should use their judgment when placing smoke alarms.
Summary § Proper placement of smoke alarms can reduce the number of false alarms § No home will perfectly match the guidelines – Installers should use their judgment when placing smoke alarms.
 Summary § Alert devices for people with disabilities supplement smoke alarms § Home visits to install smoke alarms present a good opportunity to provide fire and life safety education
Summary § Alert devices for people with disabilities supplement smoke alarms § Home visits to install smoke alarms present a good opportunity to provide fire and life safety education
 Summary § Fire and life safety visits should include four key messages § Fall Prevention § Poisoning prevention § Home safety survey § Family escape plan
Summary § Fire and life safety visits should include four key messages § Fall Prevention § Poisoning prevention § Home safety survey § Family escape plan
 Smoke Alarm Installation
Smoke Alarm Installation


