40a85fed2758ead473ae80c7c81cf24b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 62

 Smells are surer than sounds and sights to make your heart-strings crack. - Rudyard Kipling
Smells are surer than sounds and sights to make your heart-strings crack. - Rudyard Kipling
 Olfactory system n Conveys specific visceral sensation (smell) via n. olfactorius. n Does not relay in the thalamus. n Connections with thalamus, hypothalamus, amygdaloid complex & hippocampal formation.
Olfactory system n Conveys specific visceral sensation (smell) via n. olfactorius. n Does not relay in the thalamus. n Connections with thalamus, hypothalamus, amygdaloid complex & hippocampal formation.
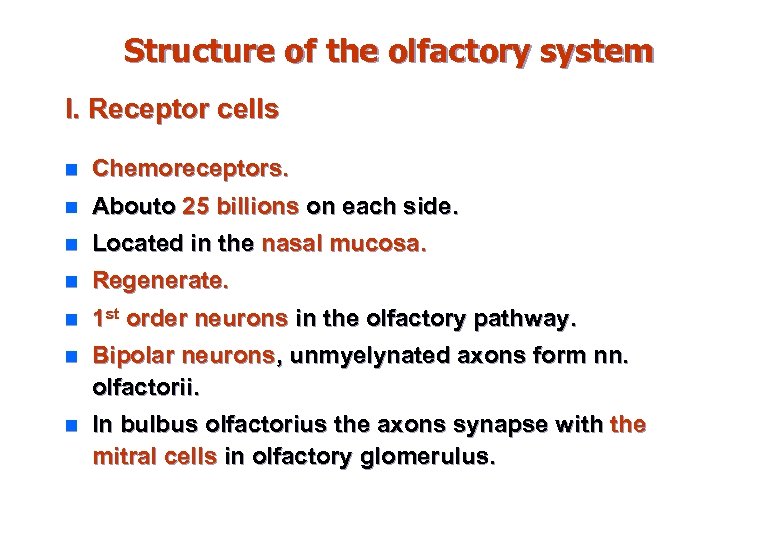 Structure of the olfactory system І. Receptor cells n Chemoreceptors. n Aboutо 25 billions on each side. n Located in the nasal mucosa. n Regenerate. n 1 st order neurons in the olfactory pathway. n Bipolar neurons, unmyelynated axons form nn. оlfactоrii. n In bulbus olfactorius the axons synapse with the mitral cells in olfactory glomerulus.
Structure of the olfactory system І. Receptor cells n Chemoreceptors. n Aboutо 25 billions on each side. n Located in the nasal mucosa. n Regenerate. n 1 st order neurons in the olfactory pathway. n Bipolar neurons, unmyelynated axons form nn. оlfactоrii. n In bulbus olfactorius the axons synapse with the mitral cells in olfactory glomerulus.
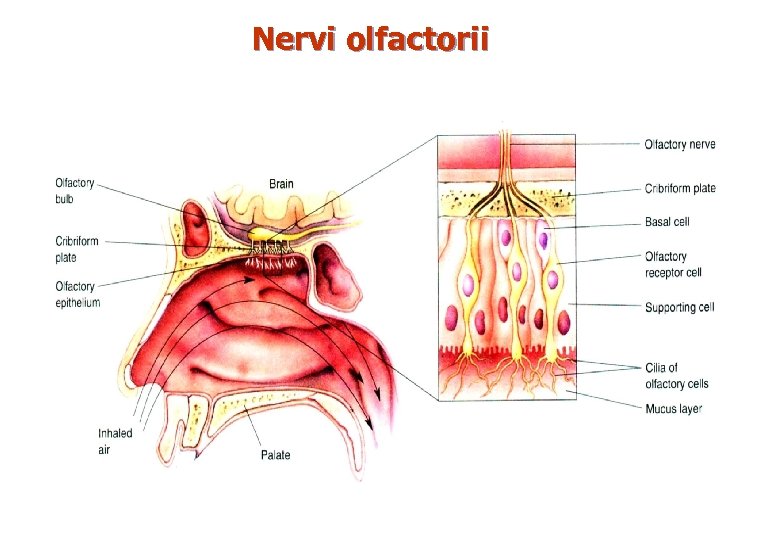 Nervi olfactorii
Nervi olfactorii
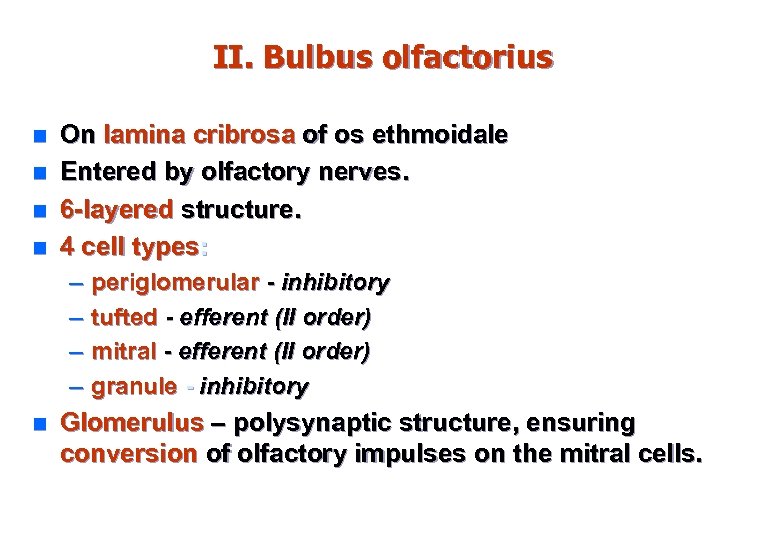 II. Bulbus olfactorius n n On lamina cribrosa of os ethmoidale Entered by olfactory nerves. 6 -layered structure. 4 cell types: – – n periglomerular - inhibitory tufted - efferent (ІІ order) mitral - efferent (ІІ order) granule - inhibitory Glomerulus – polysynaptic structure, ensuring conversion of olfactory impulses on the mitral cells.
II. Bulbus olfactorius n n On lamina cribrosa of os ethmoidale Entered by olfactory nerves. 6 -layered structure. 4 cell types: – – n periglomerular - inhibitory tufted - efferent (ІІ order) mitral - efferent (ІІ order) granule - inhibitory Glomerulus – polysynaptic structure, ensuring conversion of olfactory impulses on the mitral cells.
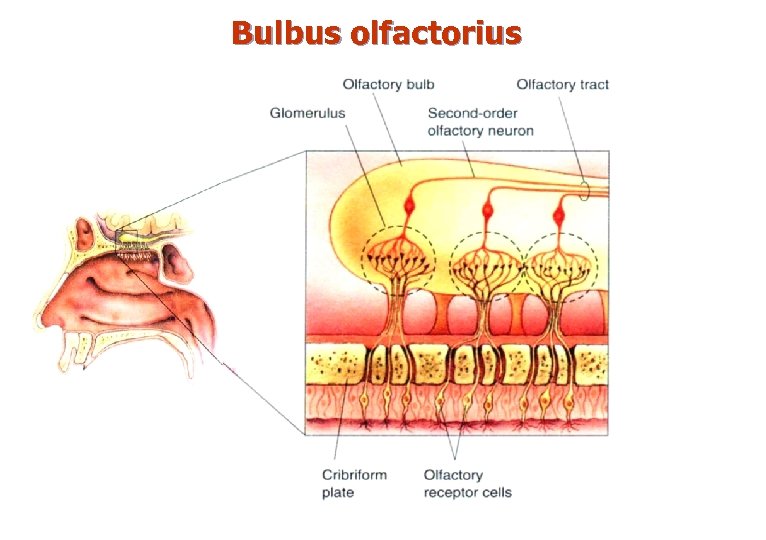 Bulbus olfactorius
Bulbus olfactorius
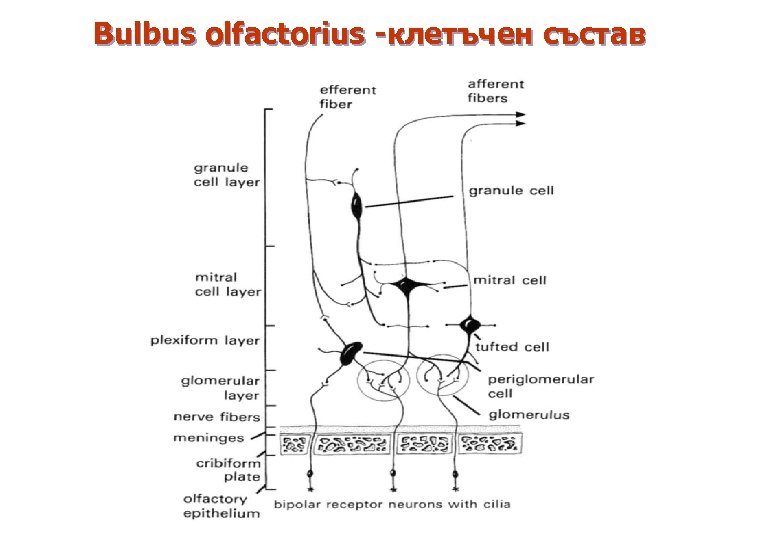 Bulbus olfactorius -клетъчен състав
Bulbus olfactorius -клетъчен състав
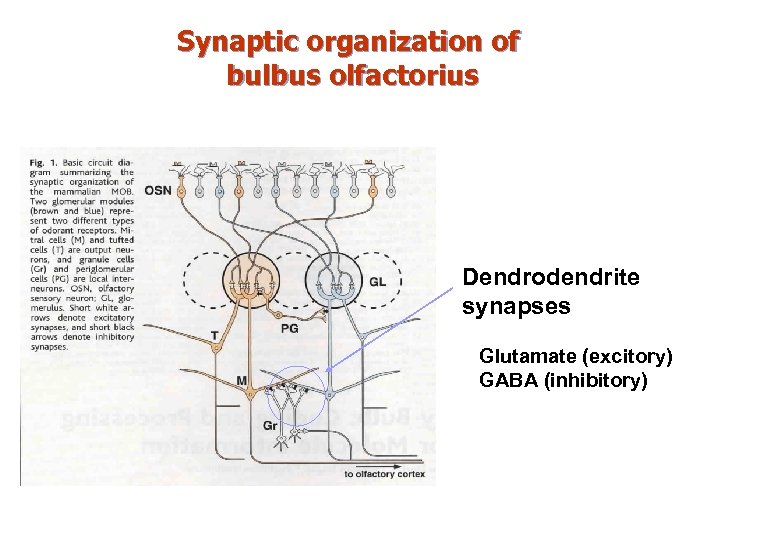 Synaptic organization of bulbus olfactorius Dendrodendrite synapses Glutamate (excitory) GABA (inhibitory)
Synaptic organization of bulbus olfactorius Dendrodendrite synapses Glutamate (excitory) GABA (inhibitory)
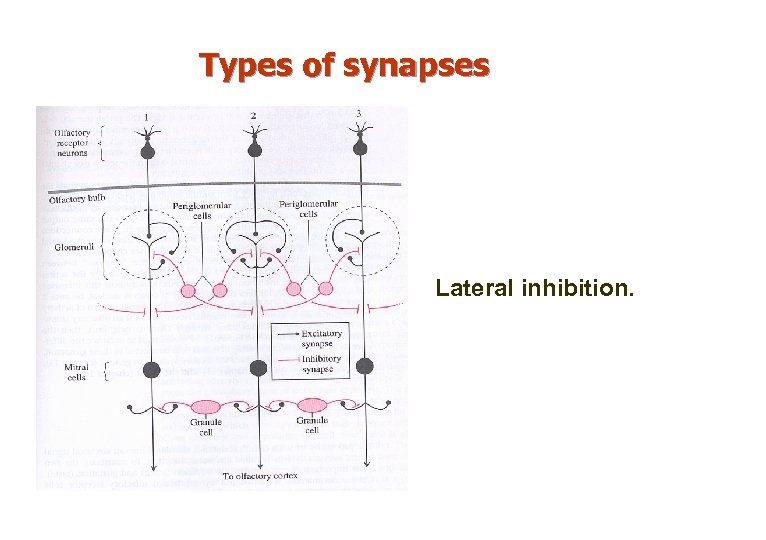 Types of synapses Lateral inhibition.
Types of synapses Lateral inhibition.
 ІІІ. Tractus olfactorius: – – in sulcus olfactorius. Axons of mitral and tufted cells. nucl. olfactorius anterior (modulator): terminates in trigonum olfactorium. ІV. Stria olfactoria lateralis – to primary olfactory cortex through limen insulae V. Stria olfactoria medialis – to area subcalosa and gyrus paraterminalis
ІІІ. Tractus olfactorius: – – in sulcus olfactorius. Axons of mitral and tufted cells. nucl. olfactorius anterior (modulator): terminates in trigonum olfactorium. ІV. Stria olfactoria lateralis – to primary olfactory cortex through limen insulae V. Stria olfactoria medialis – to area subcalosa and gyrus paraterminalis
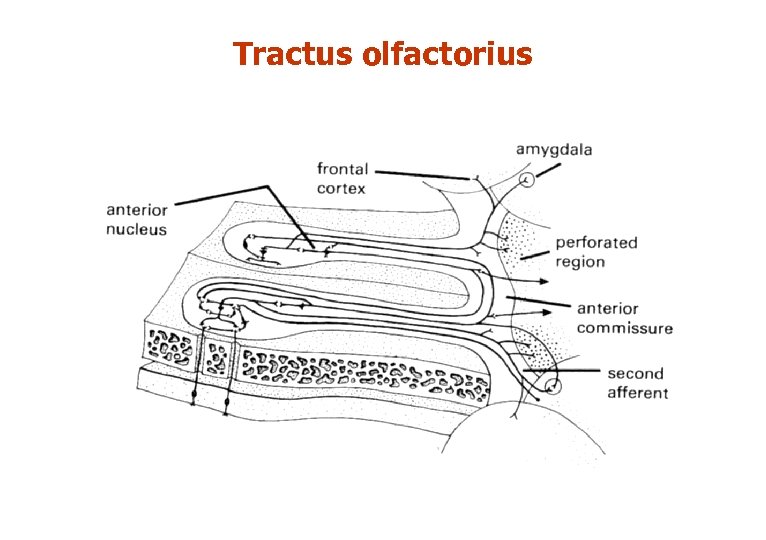 Tractus olfactorius
Tractus olfactorius
 VІ. Olfactory corex n Primary – – n Secondary – – – n on uncus (area 34 after Brodmann). fibers from stria olfactoria lateralis. contains prepiriform & periamygdaloid areas. connectins with nucl. medialis dorsalis of thalamus, hypothalamus, hipocampal formation. entorhinal area of gyrus parahippocampalis (area 28). Impulses from primary areas. efferents to hippocampus. Orbitofrontal cortex – Impulses from nucl. medialis dorsalis thalami – conscious preception of smell.
VІ. Olfactory corex n Primary – – n Secondary – – – n on uncus (area 34 after Brodmann). fibers from stria olfactoria lateralis. contains prepiriform & periamygdaloid areas. connectins with nucl. medialis dorsalis of thalamus, hypothalamus, hipocampal formation. entorhinal area of gyrus parahippocampalis (area 28). Impulses from primary areas. efferents to hippocampus. Orbitofrontal cortex – Impulses from nucl. medialis dorsalis thalami – conscious preception of smell.
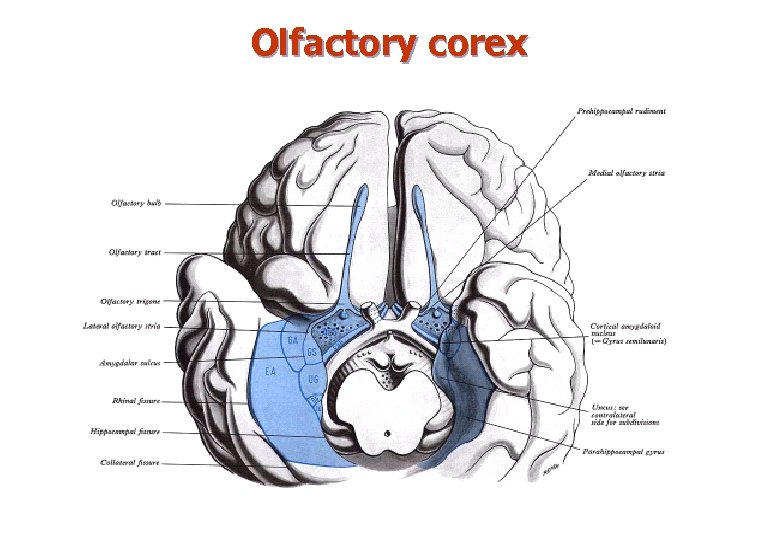 Olfactory corex
Olfactory corex
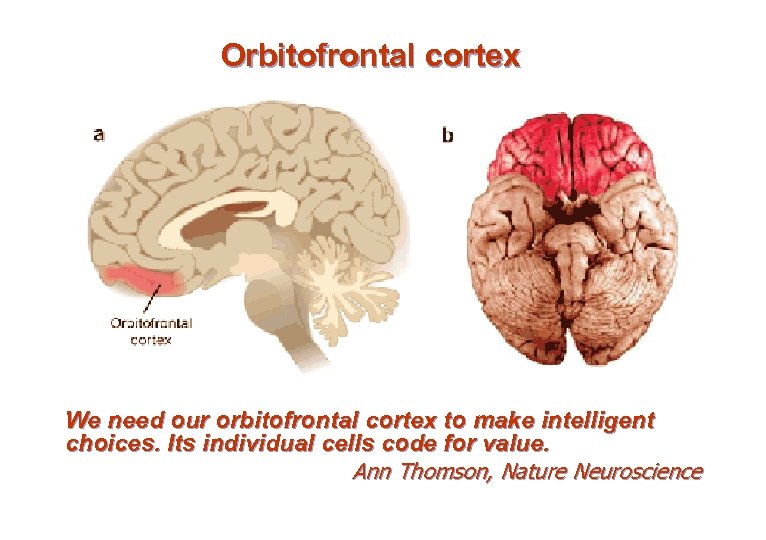 Orbitofrontal cortex We need our orbitofrontal cortex to make intelligent choices. Its individual cells code for value. Ann Thomson, Nature Neuroscience
Orbitofrontal cortex We need our orbitofrontal cortex to make intelligent choices. Its individual cells code for value. Ann Thomson, Nature Neuroscience
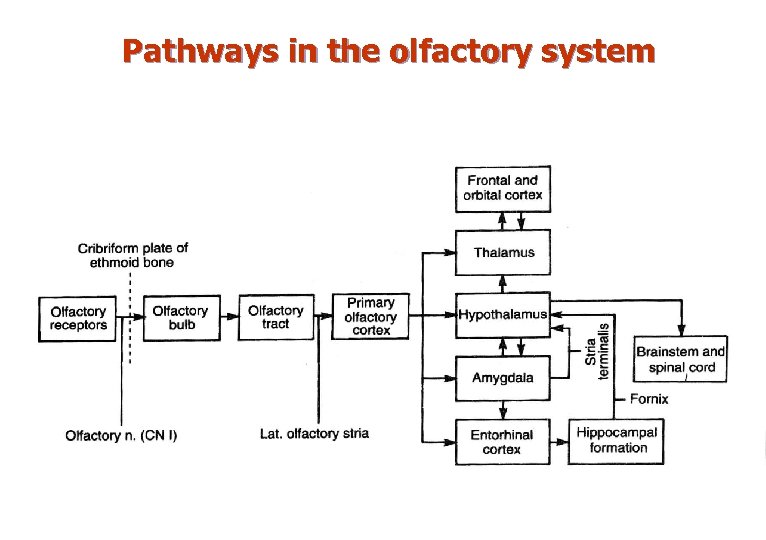 Pathways in the olfactory system
Pathways in the olfactory system
 Limbic system
Limbic system
 Limbic system n Morphological substrate of emotions and behaviour. n Role in emotional behavior, feeding, defensive reaction, sexual behaviour, memory and learning. n Functions mediated through hypothalamus and autonomic system. n Contains cortical & subcortical (nuclei) structures.
Limbic system n Morphological substrate of emotions and behaviour. n Role in emotional behavior, feeding, defensive reaction, sexual behaviour, memory and learning. n Functions mediated through hypothalamus and autonomic system. n Contains cortical & subcortical (nuclei) structures.
 Affective behavior Emotion Happiness and Grief
Affective behavior Emotion Happiness and Grief
 Introduction Concept Broca (1877) - ‘La Grand Lobe Limbique’ Papez (1937) - ‘Limbic Circuit’ - emotion Mac. Lean (1952) - ‘Limbic System’ – visceral brain Nauta (1972) - ‘Septo-hypothalamo-mesencephalic continuum’
Introduction Concept Broca (1877) - ‘La Grand Lobe Limbique’ Papez (1937) - ‘Limbic Circuit’ - emotion Mac. Lean (1952) - ‘Limbic System’ – visceral brain Nauta (1972) - ‘Septo-hypothalamo-mesencephalic continuum’
 PAUL BROCA (1824 -1880) JAMES PAPEZ (1883 -1958)
PAUL BROCA (1824 -1880) JAMES PAPEZ (1883 -1958)
 Limbic system - Term of Paul Mac. Lean (1952) - Visceral brain -Triple concept of brain evolution Hypothalamus Nucleus accumbens Nucleus amygdaloideus Cortex orbitofrontalis Some psychiatric implications on physiological studies on frontotemporal portions of limbic system (visceral brain). Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 4: 407 -418, 1952 Paul D. Mac. Lean (1913 - )
Limbic system - Term of Paul Mac. Lean (1952) - Visceral brain -Triple concept of brain evolution Hypothalamus Nucleus accumbens Nucleus amygdaloideus Cortex orbitofrontalis Some psychiatric implications on physiological studies on frontotemporal portions of limbic system (visceral brain). Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 4: 407 -418, 1952 Paul D. Mac. Lean (1913 - )
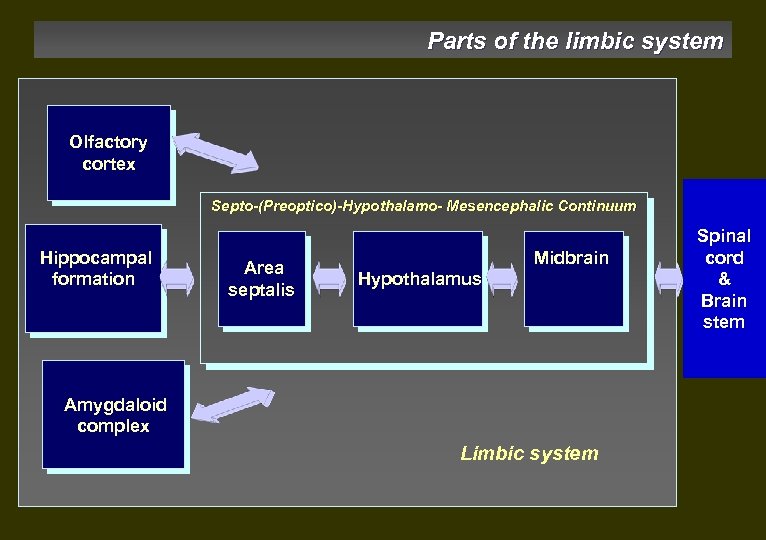 Parts of the limbic system Olfactory cortex Septo-(Preoptico)-Hypothalamo- Mesencephalic Continuum Hippocampal formation Area septalis Midbrain Hypothalamus Amygdaloid complex Limbic system Spinal cord & Brain stem
Parts of the limbic system Olfactory cortex Septo-(Preoptico)-Hypothalamo- Mesencephalic Continuum Hippocampal formation Area septalis Midbrain Hypothalamus Amygdaloid complex Limbic system Spinal cord & Brain stem
 Expression of emotion Septohypothalamomesencephalic continuum
Expression of emotion Septohypothalamomesencephalic continuum
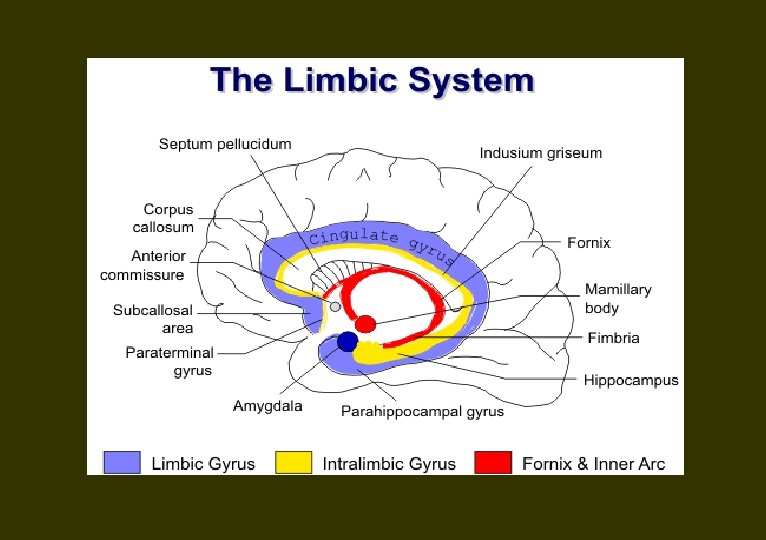
 Parts of the limbic system TELENCEPHALON Lobus Limbicus Gyrus Fornicatus Gyrus Cingulatus Gyrus Parahippocampalis Hippocampal Formation Hippocampus Gyrus Dentatus Subiculum Hippocampal Rudiments Gyrus Fasciolaris Indusium Griseum Cortex Olfactorius (Rhinencephalon) - Lobus Piriformis Cortex Prepiriformis Cortex Periamygdaloideus Cortex Entorhinalis Basal forebrain Substantia Innominata Nucleus Basalis на Meynert Pallidum Ventralis Nucleus Accumbens (Septi) Regio Septalis Area Septalis Gyrus Paraterminalis Gyrus Subcallosus Nuclei Septalis Dorsal, lateral and medial Nuclei Septalis Nucleus Stria Diagonalis Broca Nucleus Stria Terminalis Corpus Amygdaloideum Pars Corticomedialis Pars Basolateralis Nucleus Centralis
Parts of the limbic system TELENCEPHALON Lobus Limbicus Gyrus Fornicatus Gyrus Cingulatus Gyrus Parahippocampalis Hippocampal Formation Hippocampus Gyrus Dentatus Subiculum Hippocampal Rudiments Gyrus Fasciolaris Indusium Griseum Cortex Olfactorius (Rhinencephalon) - Lobus Piriformis Cortex Prepiriformis Cortex Periamygdaloideus Cortex Entorhinalis Basal forebrain Substantia Innominata Nucleus Basalis на Meynert Pallidum Ventralis Nucleus Accumbens (Septi) Regio Septalis Area Septalis Gyrus Paraterminalis Gyrus Subcallosus Nuclei Septalis Dorsal, lateral and medial Nuclei Septalis Nucleus Stria Diagonalis Broca Nucleus Stria Terminalis Corpus Amygdaloideum Pars Corticomedialis Pars Basolateralis Nucleus Centralis
 Lobus Limbicus Gyrus Fornicatus Gyrus Cinguli Gyrus Parahippocampalis Area Entorhinalis Isthmus Hippocampal Formation Hippocampus Proper (Ammon’s horn) Gyrus Dentatus Subiculum Hippocampal Rudiments Gyrus Fasciolaris Indusium Griseum Класификация на кората Isocortex - Neocortex Allocortex Archicortex Hippocampus Gyrus Dentatus Paleocortex Bulbus Olfactorius Lobus Piriformis Mesocortex (Juxtallocortex, Periallocortex, Mesallocortex) Gyrus Cinguli
Lobus Limbicus Gyrus Fornicatus Gyrus Cinguli Gyrus Parahippocampalis Area Entorhinalis Isthmus Hippocampal Formation Hippocampus Proper (Ammon’s horn) Gyrus Dentatus Subiculum Hippocampal Rudiments Gyrus Fasciolaris Indusium Griseum Класификация на кората Isocortex - Neocortex Allocortex Archicortex Hippocampus Gyrus Dentatus Paleocortex Bulbus Olfactorius Lobus Piriformis Mesocortex (Juxtallocortex, Periallocortex, Mesallocortex) Gyrus Cinguli
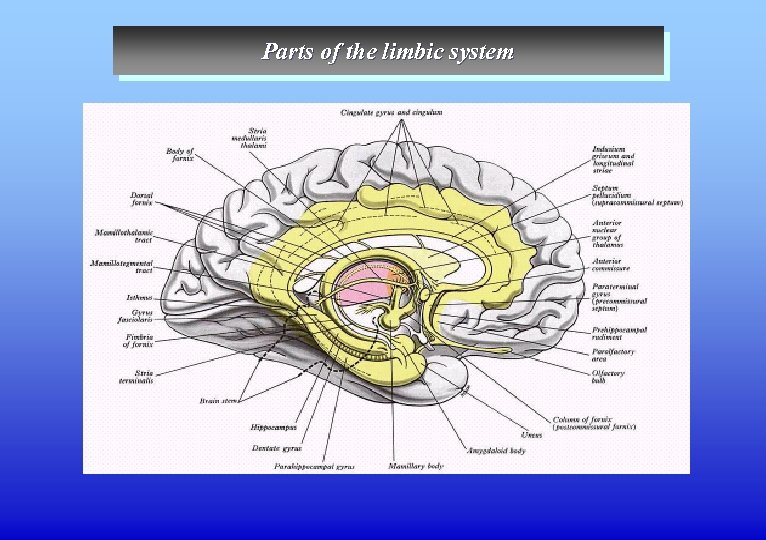 Parts of the limbic system
Parts of the limbic system
 Limbic cortex n On medial aspect of the hemispheres n Archicortex – In some parts paleo- & neocortex. n External ring n Internal ring
Limbic cortex n On medial aspect of the hemispheres n Archicortex – In some parts paleo- & neocortex. n External ring n Internal ring
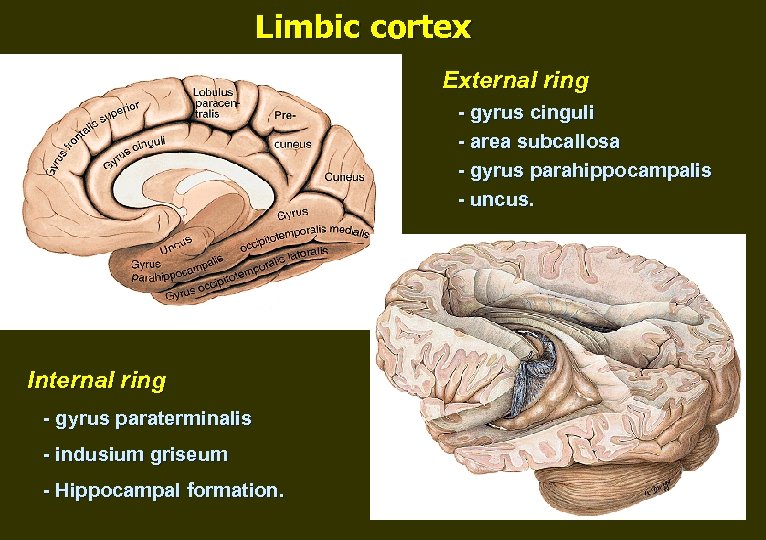 Limbic cortex External ring - gyrus cinguli - area subcallosa - gyrus parahippocampalis - uncus. Internal ring - gyrus paraterminalis - indusium griseum - Hippocampal formation.
Limbic cortex External ring - gyrus cinguli - area subcallosa - gyrus parahippocampalis - uncus. Internal ring - gyrus paraterminalis - indusium griseum - Hippocampal formation.
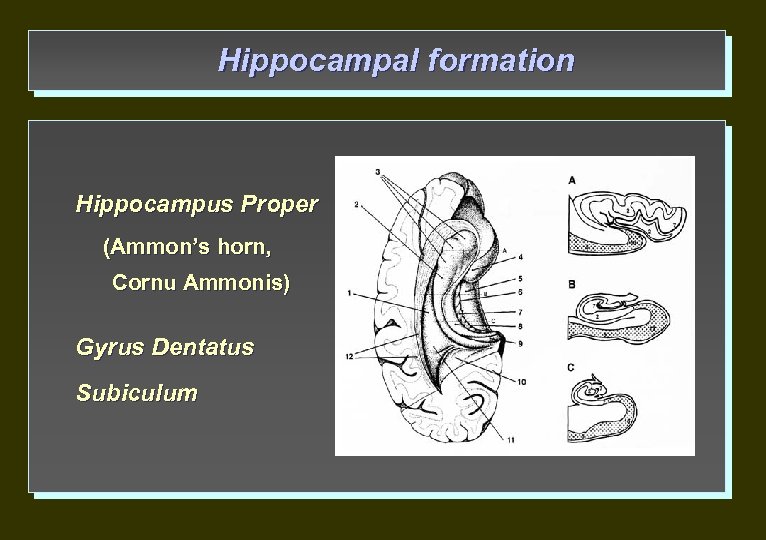 Hippocampal formation Hippocampus Proper (Ammon’s horn, Cornu Ammonis) Gyrus Dentatus Subiculum
Hippocampal formation Hippocampus Proper (Ammon’s horn, Cornu Ammonis) Gyrus Dentatus Subiculum
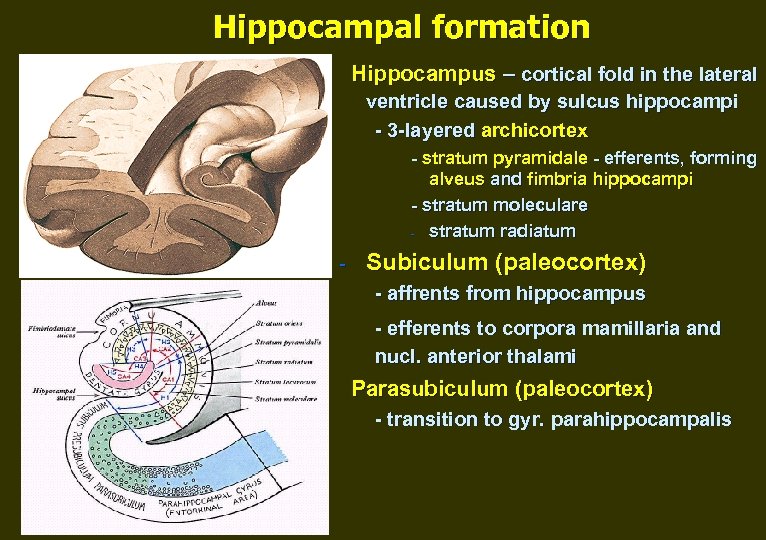 Hippocampal formation Hippocampus – cortical fold in the lateral ventricle caused by sulcus hippocampi - 3 -layered archicortex - stratum pyramidale - efferents, forming alveus and fimbria hippocampi - stratum moleculare - stratum radiatum - Subiculum (paleocortex) - affrents from hippocampus - efferents to corpora mamillaria and nucl. anterior thalami Parasubiculum (paleocortex) - transition to gyr. parahippocampalis
Hippocampal formation Hippocampus – cortical fold in the lateral ventricle caused by sulcus hippocampi - 3 -layered archicortex - stratum pyramidale - efferents, forming alveus and fimbria hippocampi - stratum moleculare - stratum radiatum - Subiculum (paleocortex) - affrents from hippocampus - efferents to corpora mamillaria and nucl. anterior thalami Parasubiculum (paleocortex) - transition to gyr. parahippocampalis
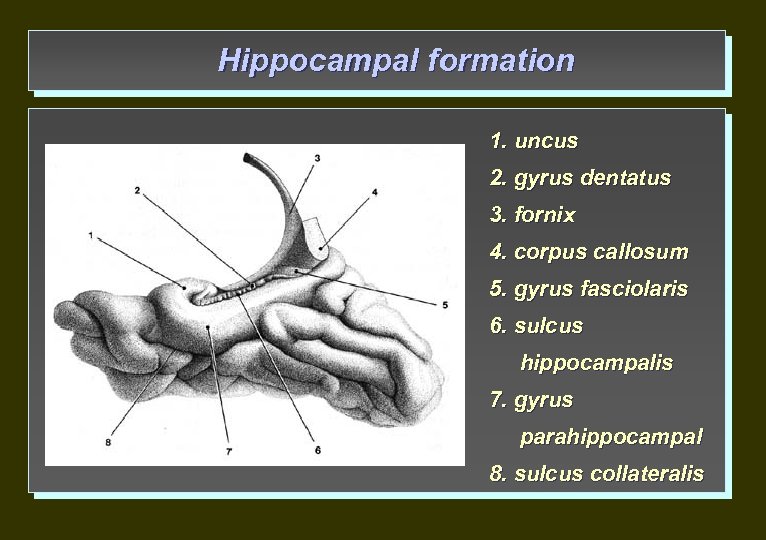 Hippocampal formation 1. uncus 2. gyrus dentatus 3. fornix 4. corpus callosum 5. gyrus fasciolaris 6. sulcus hippocampalis 7. gyrus parahippocampal 8. sulcus collateralis
Hippocampal formation 1. uncus 2. gyrus dentatus 3. fornix 4. corpus callosum 5. gyrus fasciolaris 6. sulcus hippocampalis 7. gyrus parahippocampal 8. sulcus collateralis
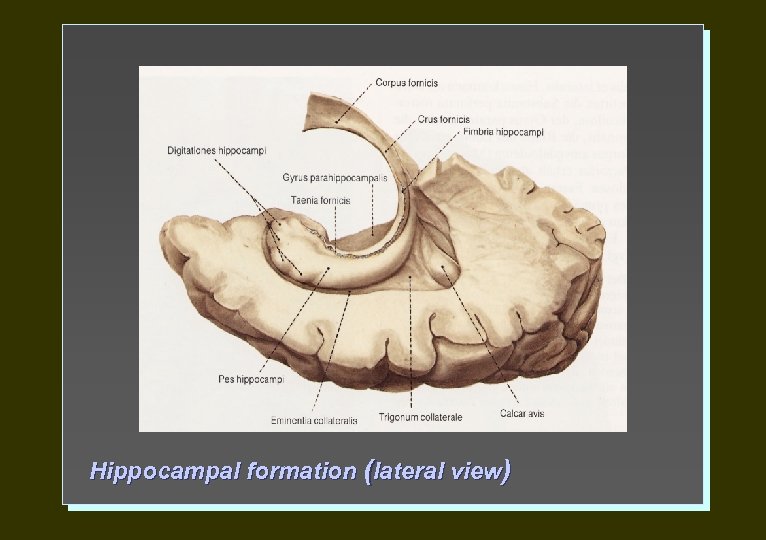 Hippocampal formation (lateral view)
Hippocampal formation (lateral view)
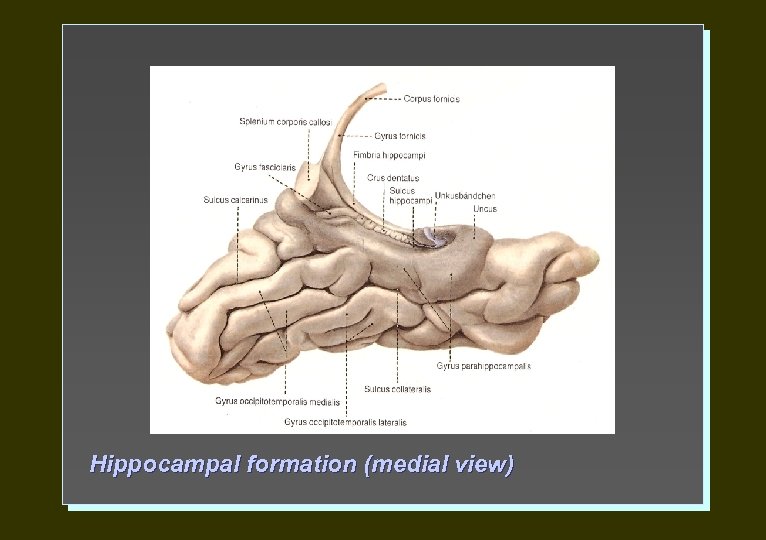 Hippocampal formation (medial view)
Hippocampal formation (medial view)
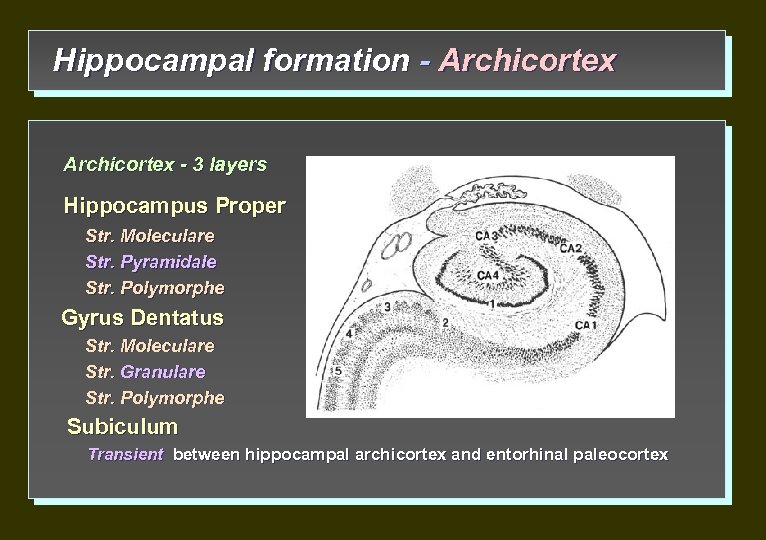 Hippocampal formation - Archicortex - 3 layers Hippocampus Proper Str. Moleculare Str. Pyramidale Str. Polymorphe Gyrus Dentatus Str. Moleculare Str. Granulare Str. Polymorphe Subiculum Transient between hippocampal archicortex and entorhinal paleocortex
Hippocampal formation - Archicortex - 3 layers Hippocampus Proper Str. Moleculare Str. Pyramidale Str. Polymorphe Gyrus Dentatus Str. Moleculare Str. Granulare Str. Polymorphe Subiculum Transient between hippocampal archicortex and entorhinal paleocortex
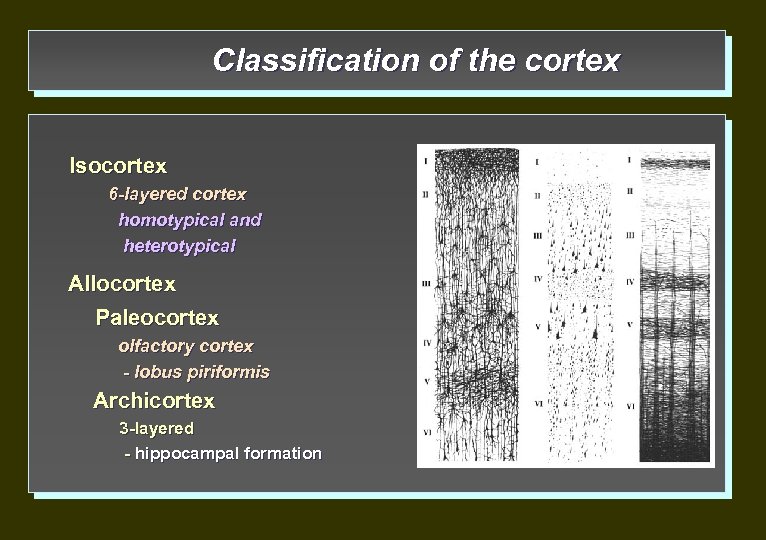 Classification of the cortex Isocortex 6 -layered cortex homotypical and heterotypical Allocortex Paleocortex olfactory cortex - lobus piriformis Archicortex 3 -layered - hippocampal formation
Classification of the cortex Isocortex 6 -layered cortex homotypical and heterotypical Allocortex Paleocortex olfactory cortex - lobus piriformis Archicortex 3 -layered - hippocampal formation
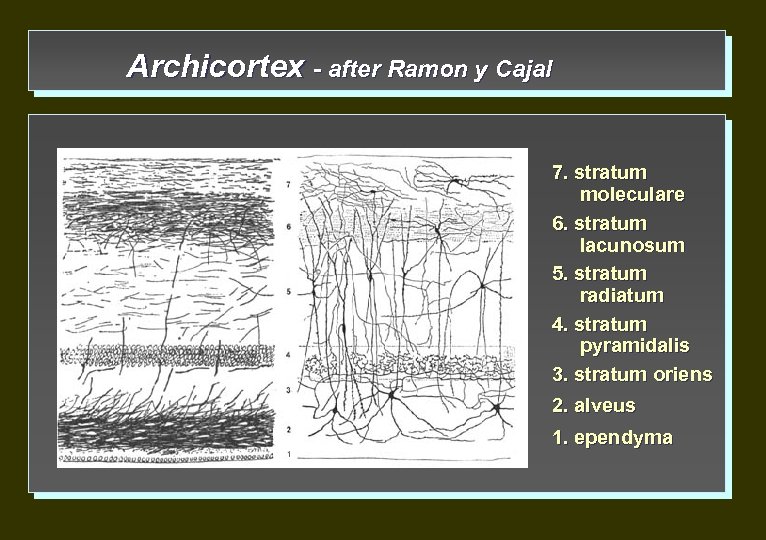 Archicortex - after Ramon y Cajal 7. stratum moleculare 6. stratum lacunosum 5. stratum radiatum 4. stratum pyramidalis 3. stratum oriens 2. alveus 1. ependyma
Archicortex - after Ramon y Cajal 7. stratum moleculare 6. stratum lacunosum 5. stratum radiatum 4. stratum pyramidalis 3. stratum oriens 2. alveus 1. ependyma
 Hippocampus and memory Х. M. - пациент с антеградна и ретроградна амнезия, възникнала след мозъчна операция за лечение на епилептични припадъци.
Hippocampus and memory Х. M. - пациент с антеградна и ретроградна амнезия, възникнала след мозъчна операция за лечение на епилептични припадъци.
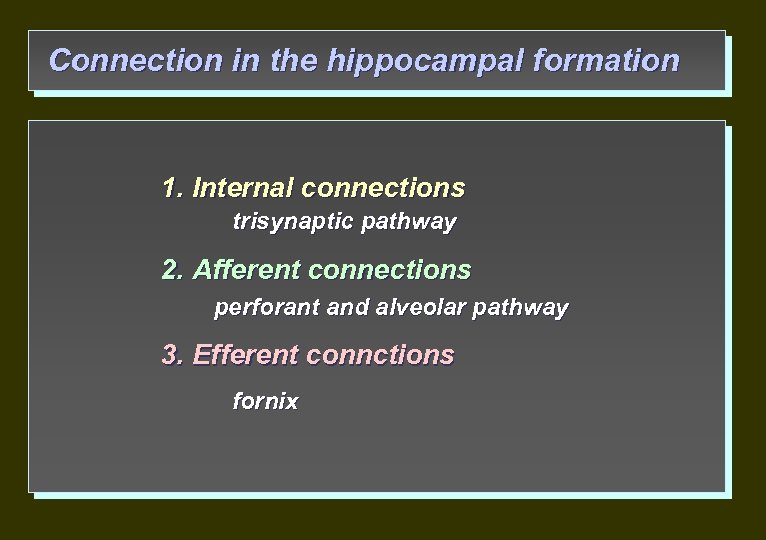 Connection in the hippocampal formation 1. Internal connections trisynaptic pathway 2. Afferent connections perforant and alveolar pathway 3. Efferent connctions fornix
Connection in the hippocampal formation 1. Internal connections trisynaptic pathway 2. Afferent connections perforant and alveolar pathway 3. Efferent connctions fornix
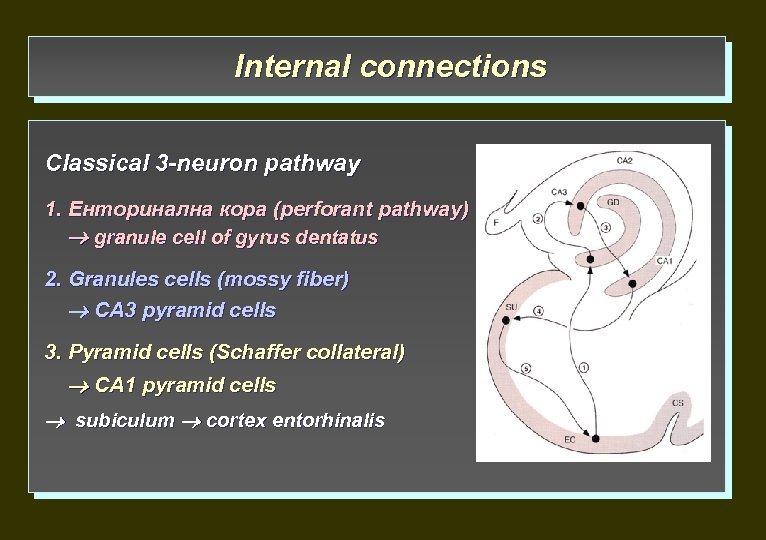 Internal connections Classical 3 -neuron pathway 1. Енторинална кора (perforant pathway) granule cell of gyrus dentatus 2. Granules cells (mossy fiber) CA 3 pyramid cells 3. Pyramid cells (Schaffer collateral) CA 1 pyramid cells subiculum cortex entorhinalis
Internal connections Classical 3 -neuron pathway 1. Енторинална кора (perforant pathway) granule cell of gyrus dentatus 2. Granules cells (mossy fiber) CA 3 pyramid cells 3. Pyramid cells (Schaffer collateral) CA 1 pyramid cells subiculum cortex entorhinalis
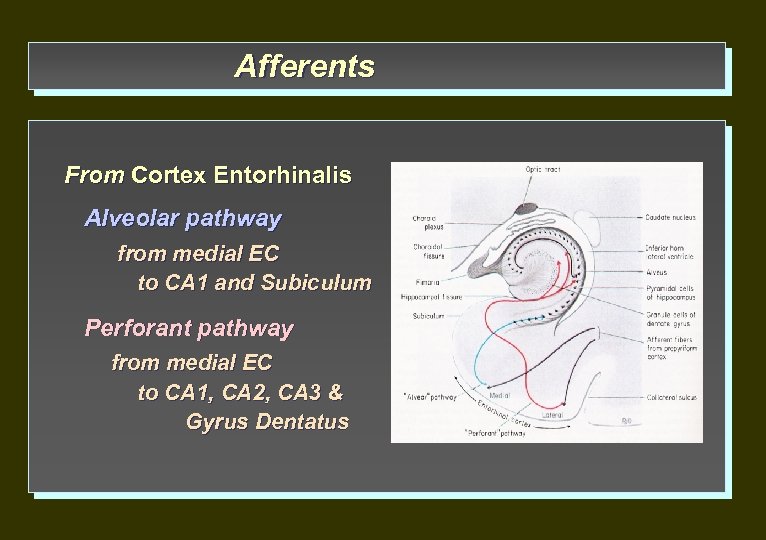 Afferents From Cortex Entorhinalis Alveolar pathway from medial EC to CA 1 and Subiculum Perforant pathway from medial EC to CA 1, CA 2, CA 3 & Gyrus Dentatus
Afferents From Cortex Entorhinalis Alveolar pathway from medial EC to CA 1 and Subiculum Perforant pathway from medial EC to CA 1, CA 2, CA 3 & Gyrus Dentatus
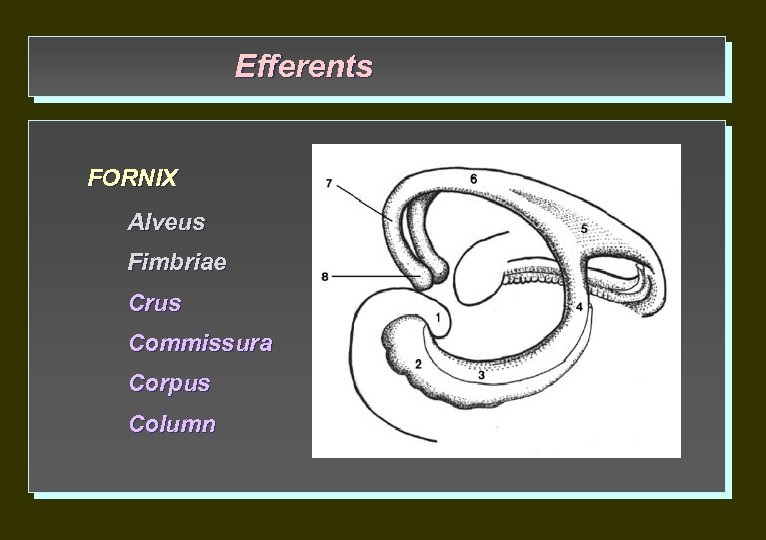 Efferents FORNIX Alveus Fimbriae Crus Commissurа Corpus Column
Efferents FORNIX Alveus Fimbriae Crus Commissurа Corpus Column
 Efferents Fornix - from pyramid cells of hippocampus & subiculum - 1. 2 million fibers Postcommissiral Fornix – basic bundle to Corpus Mammillare Thalamus Anterior Nuclei Septi Lateralis Hypothalamus Tegmentum of midbrain
Efferents Fornix - from pyramid cells of hippocampus & subiculum - 1. 2 million fibers Postcommissiral Fornix – basic bundle to Corpus Mammillare Thalamus Anterior Nuclei Septi Lateralis Hypothalamus Tegmentum of midbrain
 Efferents Precommissural Fornix – smaller - mainly from hippocampus proper to Nuclei Septi Area Preoptica Lateralis Area Hypothalamica Anterior Nucleus Striae Diagonalis Broca Nucleus Accumbens Medial aspect of frontal lobe Nucleus Caudatus & Putamen Amygdala & Claustrum
Efferents Precommissural Fornix – smaller - mainly from hippocampus proper to Nuclei Septi Area Preoptica Lateralis Area Hypothalamica Anterior Nucleus Striae Diagonalis Broca Nucleus Accumbens Medial aspect of frontal lobe Nucleus Caudatus & Putamen Amygdala & Claustrum
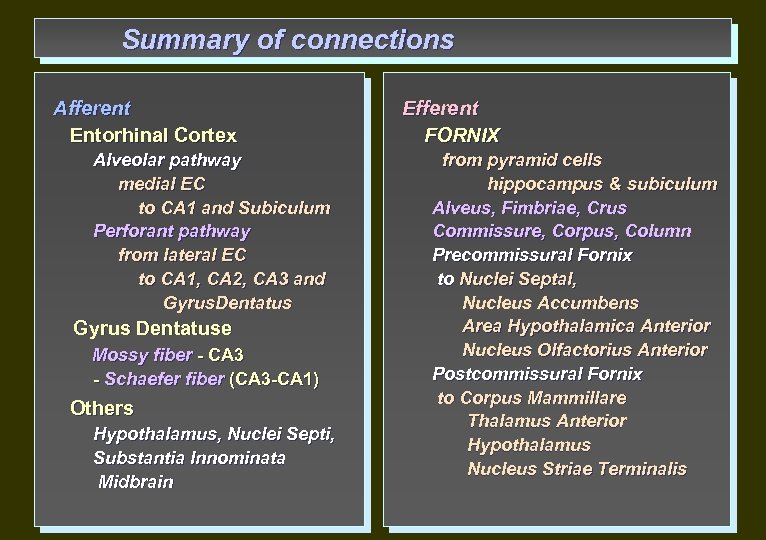 Summary of connections Afferent Entorhinal Cortex Alveolar pathway medial EC to CA 1 and Subiculum Perforant pathway from lateral EC to CA 1, CA 2, CA 3 and Gyrus. Dentatus Gyrus Dentatuse Mossy fiber - CA 3 - Schaefer fiber (CA 3 -CA 1) Others Hypothalamus, Nuclei Septi, Substantia Innominata Midbrain Efferent FORNIX from pyramid cells hippocampus & subiculum Alveus, Fimbriae, Crus Commissure, Corpus, Column Precommissural Fornix to Nuclei Septal, Nucleus Accumbens Area Hypothalamica Anterior Nucleus Olfactorius Anterior Postcommissural Fornix to Corpus Mammillare Thalamus Anterior Hypothalamus Nucleus Striaе Terminalis
Summary of connections Afferent Entorhinal Cortex Alveolar pathway medial EC to CA 1 and Subiculum Perforant pathway from lateral EC to CA 1, CA 2, CA 3 and Gyrus. Dentatus Gyrus Dentatuse Mossy fiber - CA 3 - Schaefer fiber (CA 3 -CA 1) Others Hypothalamus, Nuclei Septi, Substantia Innominata Midbrain Efferent FORNIX from pyramid cells hippocampus & subiculum Alveus, Fimbriae, Crus Commissure, Corpus, Column Precommissural Fornix to Nuclei Septal, Nucleus Accumbens Area Hypothalamica Anterior Nucleus Olfactorius Anterior Postcommissural Fornix to Corpus Mammillare Thalamus Anterior Hypothalamus Nucleus Striaе Terminalis
 Subcortical limbic structures 1. Amygdaloid complex 2. Mammillary body 3. Septal area 4. Nucleus anterior, nucleus medialis dorsalis & nuclei intralaminares thalami 5. Nucleus accumbems 6. Substantia innominata 7. Nuclei habenulae 8. Hypothalamus 9. Midbrain limbic nuclei
Subcortical limbic structures 1. Amygdaloid complex 2. Mammillary body 3. Septal area 4. Nucleus anterior, nucleus medialis dorsalis & nuclei intralaminares thalami 5. Nucleus accumbems 6. Substantia innominata 7. Nuclei habenulae 8. Hypothalamus 9. Midbrain limbic nuclei
 Amygdala L. almond K. F. Burdach’s term
Amygdala L. almond K. F. Burdach’s term
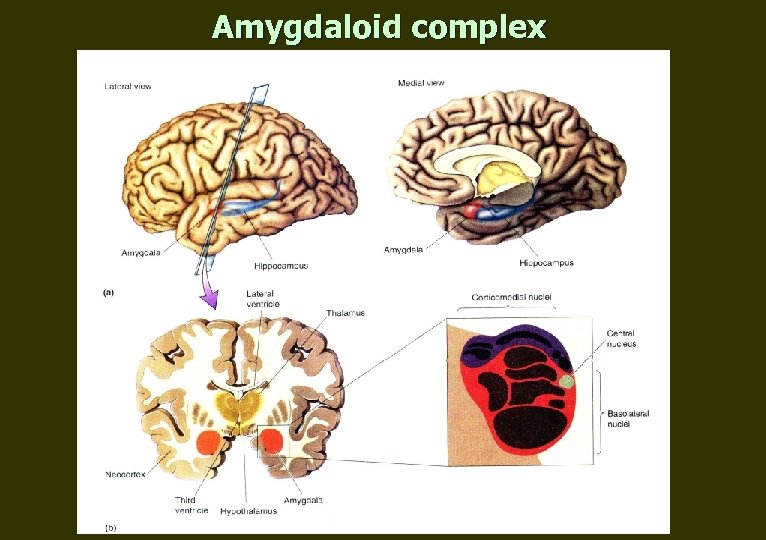 Amygdaloid complex
Amygdaloid complex
 Amygdaloid complex n Within uncus n Process sensory information n Determines emotional level, especially negative n Modulates affective expression n Autonomic, endocrine and affective reactions – Aggression when stimulated – Calm, fearless in damage
Amygdaloid complex n Within uncus n Process sensory information n Determines emotional level, especially negative n Modulates affective expression n Autonomic, endocrine and affective reactions – Aggression when stimulated – Calm, fearless in damage
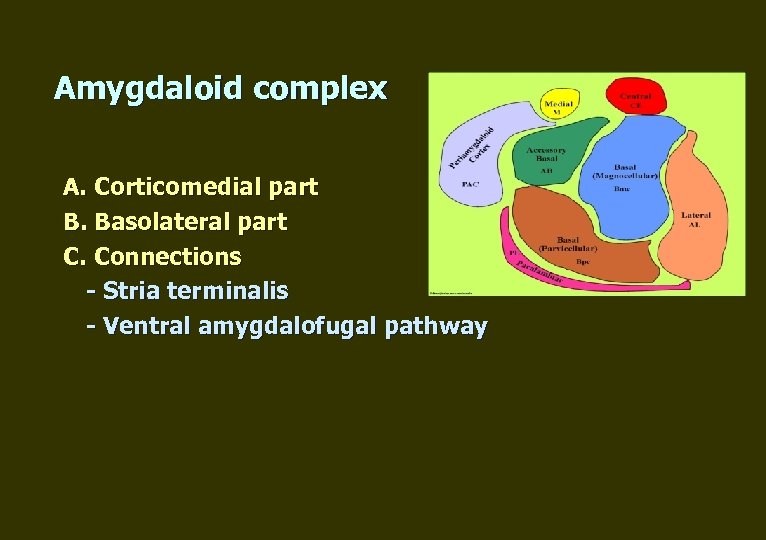 Amygdaloid complex А. Corticomedial part B. Basolateral part C. Connections - Stria terminalis - Ventral amygdalofugal pathway
Amygdaloid complex А. Corticomedial part B. Basolateral part C. Connections - Stria terminalis - Ventral amygdalofugal pathway
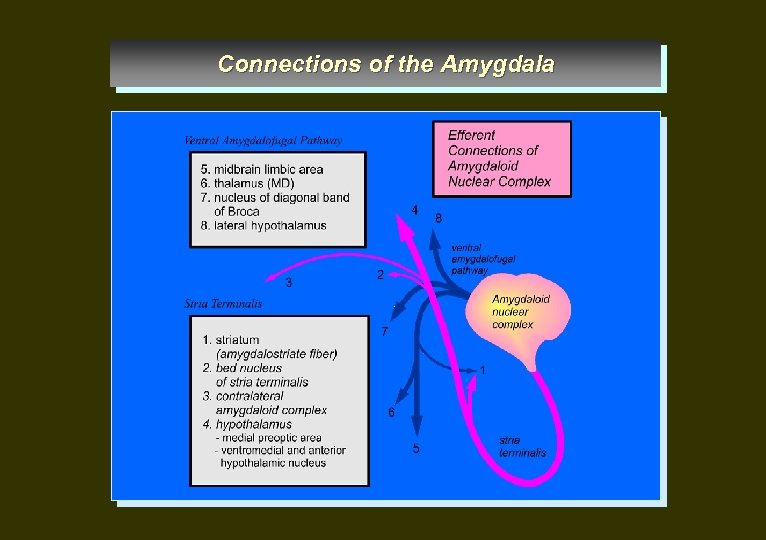 Connections of the Amygdala
Connections of the Amygdala
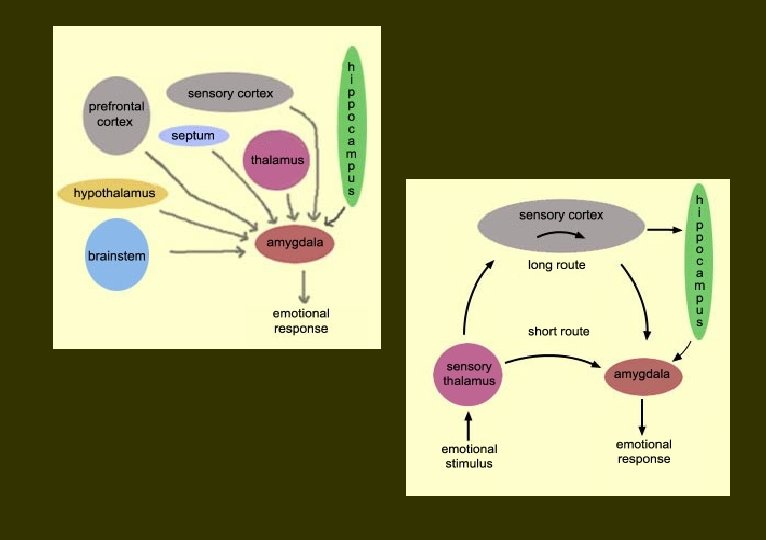
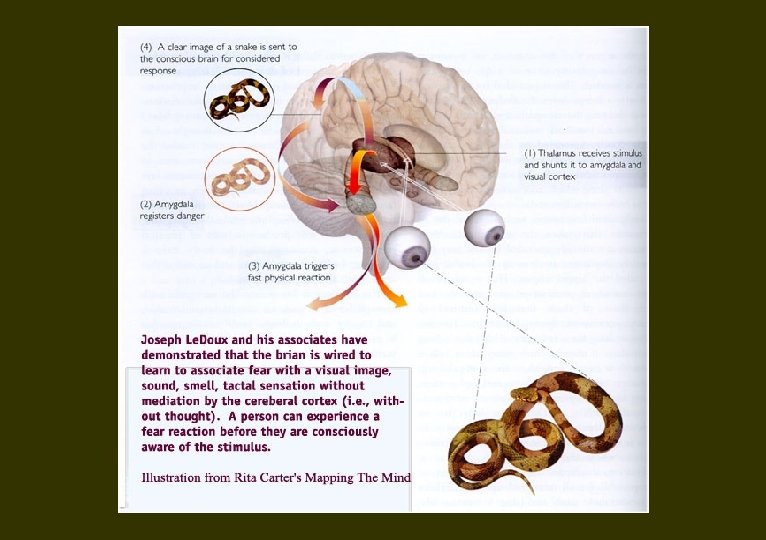
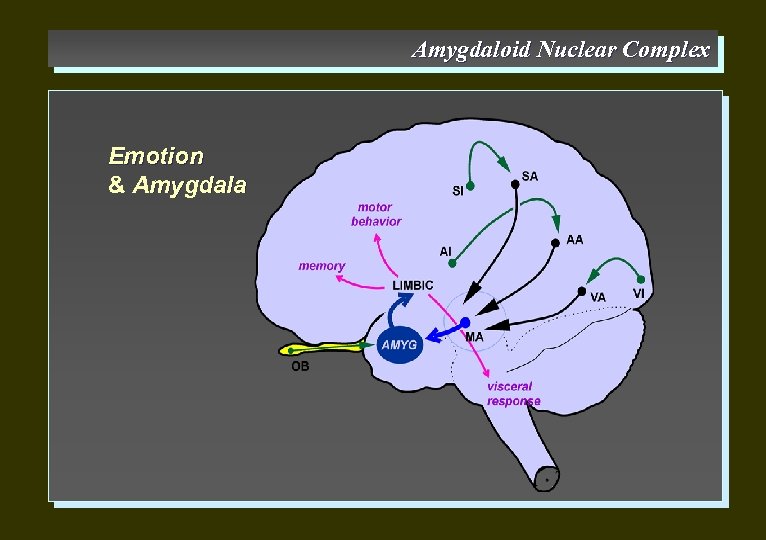 Amygdaloid Nuclear Complex Emotion & Amygdala
Amygdaloid Nuclear Complex Emotion & Amygdala
 Autism Dysfunction of amygdala Mercury Rising
Autism Dysfunction of amygdala Mercury Rising
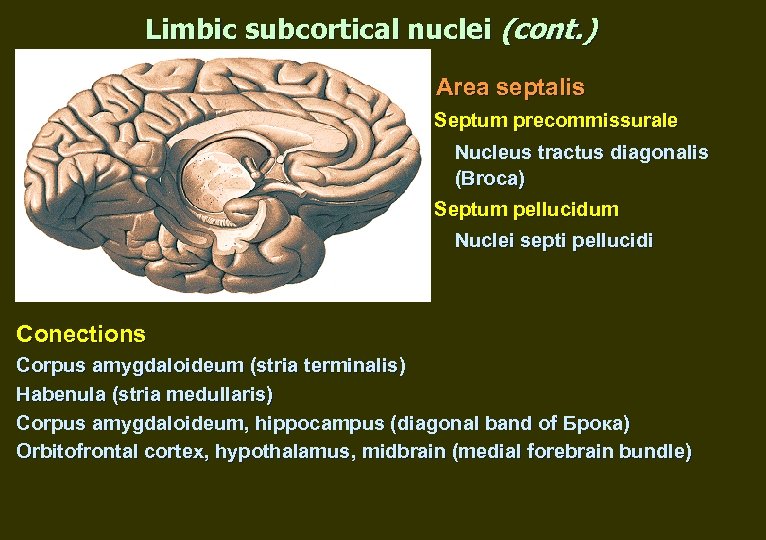 Limbic subcortical nuclei (cont. ) Area septalis Septum precommissurale Nucleus tractus diagonalis (Broca) Septum pellucidum Nuclei septi pellucidi Conections Corpus amygdaloideum (stria terminalis) Habenula (stria medullaris) Corpus amygdaloideum, hippocampus (diagonal band of Брока) Orbitofrontal cortex, hypothalamus, midbrain (medial forebrain bundle)
Limbic subcortical nuclei (cont. ) Area septalis Septum precommissurale Nucleus tractus diagonalis (Broca) Septum pellucidum Nuclei septi pellucidi Conections Corpus amygdaloideum (stria terminalis) Habenula (stria medullaris) Corpus amygdaloideum, hippocampus (diagonal band of Брока) Orbitofrontal cortex, hypothalamus, midbrain (medial forebrain bundle)
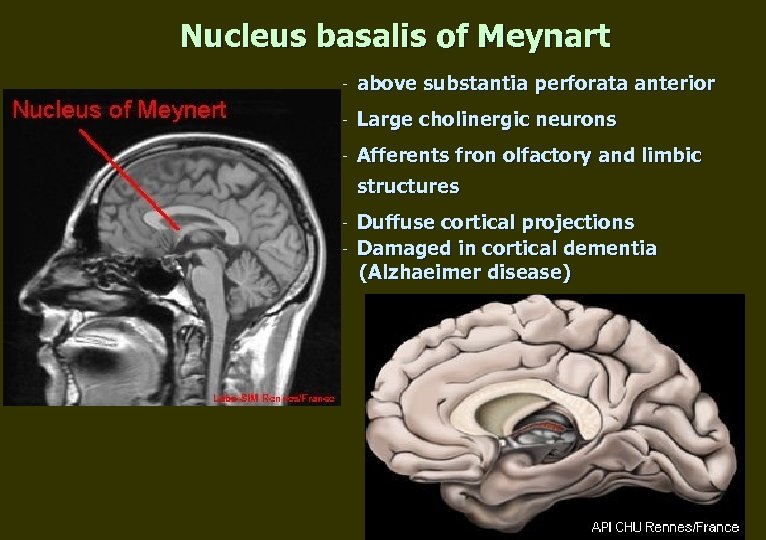 Nucleus basalis of Meynart - above substantia perforata anterior - Large cholinergic neurons - Afferents fron olfactory and limbic structures - Duffuse cortical projections Damaged in cortical dementia (Alzhaeimer disease)
Nucleus basalis of Meynart - above substantia perforata anterior - Large cholinergic neurons - Afferents fron olfactory and limbic structures - Duffuse cortical projections Damaged in cortical dementia (Alzhaeimer disease)
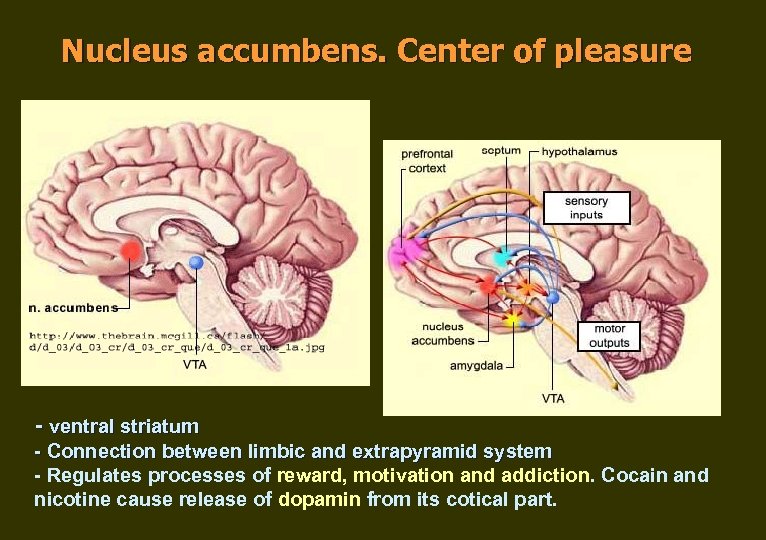 Nucleus accumbens. Center of pleasure - ventral striatum - Connection between limbic and extrapyramid system - Regulates processes of reward, motivation and addiction. Cocain and nicotine cause release of dopamin from its cotical part.
Nucleus accumbens. Center of pleasure - ventral striatum - Connection between limbic and extrapyramid system - Regulates processes of reward, motivation and addiction. Cocain and nicotine cause release of dopamin from its cotical part.
 Pathways 1. Fornix 2. Stria terminalis 3. Ventral amygdalofugal pathway 4. Stria medullaris thalami 5. Diagonal band of Broca 6. Fasciculus retroflexus
Pathways 1. Fornix 2. Stria terminalis 3. Ventral amygdalofugal pathway 4. Stria medullaris thalami 5. Diagonal band of Broca 6. Fasciculus retroflexus
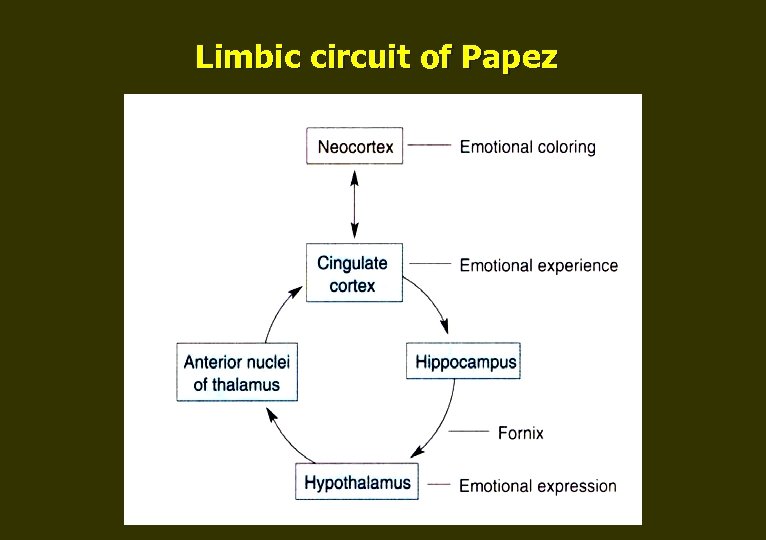 Limbic circuit of Papez
Limbic circuit of Papez


