f195fc437c7b98cd691167e91e6ca58e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 Smart Manufacturing, Manufacturing Intelligence and Demand-Dynamic Performance Smart Manufacturing Leadership Coalition (SMLC) Jim Davis – UCLA; Tom Edgar – UT-Austin; Jim Porter – retired Du. Pont John Bernaden – Rockwell; Mike Sarli – retired Exxon. Mobil FOCAPO 2012/CPC VIII January 11, 2012
Smart Manufacturing, Manufacturing Intelligence and Demand-Dynamic Performance Smart Manufacturing Leadership Coalition (SMLC) Jim Davis – UCLA; Tom Edgar – UT-Austin; Jim Porter – retired Du. Pont John Bernaden – Rockwell; Mike Sarli – retired Exxon. Mobil FOCAPO 2012/CPC VIII January 11, 2012
 Smart Manufacturing Leadership Coalition (SMLC) It’s a business and technological journey not a technology
Smart Manufacturing Leadership Coalition (SMLC) It’s a business and technological journey not a technology
 SMLC Implementing 21 st Century Smart Manufacturing • • • • Air Liquide Alcoa Applied Materials CH 2 MHill Cisco Dow Du. Pont Eli Lilly Emerson Exxon. Mobil Ford General Dynamics General Mills, Inc. General Motors Honeywell International • Invensys • Kraft • Merck • Microsoft • Oakridge National Laboratory • Owens-Corning • Procter & Gamble • Pfizer • Praxair • Rockwell Automation • Sematech • Carnegie Mellon University • Purdue • Georgia Tech • RENCI/North Carolina Chapel Hill • UCLA • University of Texas Austin • American Council for an Energy Efficient Economy • American Institute of Chemical Engineers • Council on Competitiveness • Institute of Paper Science & Technology – Georgia Tech • Manufacturing Institute • National Center for Manufacturing Sciences • National Council for Advanced Manufacturing • Putman Media • Walt Boyes – Spitzer and Boyes • Jim Porter – President Sustainable Operations Solutions - Chief Engineer and Vice President Engineering and Operations Du. Pont Company (Retired)
SMLC Implementing 21 st Century Smart Manufacturing • • • • Air Liquide Alcoa Applied Materials CH 2 MHill Cisco Dow Du. Pont Eli Lilly Emerson Exxon. Mobil Ford General Dynamics General Mills, Inc. General Motors Honeywell International • Invensys • Kraft • Merck • Microsoft • Oakridge National Laboratory • Owens-Corning • Procter & Gamble • Pfizer • Praxair • Rockwell Automation • Sematech • Carnegie Mellon University • Purdue • Georgia Tech • RENCI/North Carolina Chapel Hill • UCLA • University of Texas Austin • American Council for an Energy Efficient Economy • American Institute of Chemical Engineers • Council on Competitiveness • Institute of Paper Science & Technology – Georgia Tech • Manufacturing Institute • National Center for Manufacturing Sciences • National Council for Advanced Manufacturing • Putman Media • Walt Boyes – Spitzer and Boyes • Jim Porter – President Sustainable Operations Solutions - Chief Engineer and Vice President Engineering and Operations Du. Pont Company (Retired)
 Smart Manufacturing Leadership Coalition (SMLC): Relevant Timelines https: //smart-process-manufacturing. ucla. edu/ Advocacy & National Alignment • Office of Science and Technology Policy and Whitehouse interactions (2010 -2011) • Interactions with DOE, NIST, DARPA, DOD, NSF (2010 -2011) • Council on Competitiveness (20102011) • Obama’s AMP Announcement (1/24/11) • Secretary of Commerce and Director of NEC White House of Manufacturing Policy 12/12/11 • AMP National Program Office to be in NIST (12/15/11) • NIST workshop on U. S. Competitiveness in CPS 3/13/12 Development & Funding • September, 2006: Cyberinfrastructure in Chemical and Biological Systems (NSF) • April, 2008: Workshop and Technology Roadmap (NSF grant) • SM Operations and Technology Report in November 2009 (NSF grant) • September, 2010: Implementing 21 st Century Smart Manufacturing Workshop (SMLC-DOE) • June 24, 2011 Implementing 21 st Century Smart Manufacturing Report (SMLC and DOE) • August 2011 Awarded NSF RCN: Sustainable Manufacturing Advances in Research and Technology (SMART) Coordination Network • October 2011 SM Public-Partnership Proposal at OSTP request • November 2011 SMLC DOE proposal emphasizing energy productivity • January 2012 DOE SBIR SMLC Platform for fossil fuel test bed 4
Smart Manufacturing Leadership Coalition (SMLC): Relevant Timelines https: //smart-process-manufacturing. ucla. edu/ Advocacy & National Alignment • Office of Science and Technology Policy and Whitehouse interactions (2010 -2011) • Interactions with DOE, NIST, DARPA, DOD, NSF (2010 -2011) • Council on Competitiveness (20102011) • Obama’s AMP Announcement (1/24/11) • Secretary of Commerce and Director of NEC White House of Manufacturing Policy 12/12/11 • AMP National Program Office to be in NIST (12/15/11) • NIST workshop on U. S. Competitiveness in CPS 3/13/12 Development & Funding • September, 2006: Cyberinfrastructure in Chemical and Biological Systems (NSF) • April, 2008: Workshop and Technology Roadmap (NSF grant) • SM Operations and Technology Report in November 2009 (NSF grant) • September, 2010: Implementing 21 st Century Smart Manufacturing Workshop (SMLC-DOE) • June 24, 2011 Implementing 21 st Century Smart Manufacturing Report (SMLC and DOE) • August 2011 Awarded NSF RCN: Sustainable Manufacturing Advances in Research and Technology (SMART) Coordination Network • October 2011 SM Public-Partnership Proposal at OSTP request • November 2011 SMLC DOE proposal emphasizing energy productivity • January 2012 DOE SBIR SMLC Platform for fossil fuel test bed 4
 Global Threshold Changes in Manufacturing • Innovation and customer demand-dynamics will be key to economics – Faster and more product transitions – Operating globally but responding to local markets with resiliency • Vertical organizations will give way to B 2 B interactions among small, medium and large enterprises • EH & S compliance will increase and risks of non-compliance will increase • Social conscientiousness will be heightened while demands of a growing world population increase • Pressure to manage risk and uncertainty and the need for radical improvements in energy and raw materials productivity will heighten • Energy, environment, sustainability and safety performance will Dynamic demands accelerating on manufacturing become significant economic and competitive advantages 5
Global Threshold Changes in Manufacturing • Innovation and customer demand-dynamics will be key to economics – Faster and more product transitions – Operating globally but responding to local markets with resiliency • Vertical organizations will give way to B 2 B interactions among small, medium and large enterprises • EH & S compliance will increase and risks of non-compliance will increase • Social conscientiousness will be heightened while demands of a growing world population increase • Pressure to manage risk and uncertainty and the need for radical improvements in energy and raw materials productivity will heighten • Energy, environment, sustainability and safety performance will Dynamic demands accelerating on manufacturing become significant economic and competitive advantages 5
 Global Threshold Changes in Manufacturing • Existing assets need to become globally competitive while installed based runs its investment life cycle • Capital and operating costs need to lowered • Performance will need to be responsive to multi-faceted objectives • Manufacturing workforce with advanced training and skills will be the key competitive advantage • Job growth will not be with unskilled, high labor oriented manufacturing Dynamic demands accelerating on manufacturing 6
Global Threshold Changes in Manufacturing • Existing assets need to become globally competitive while installed based runs its investment life cycle • Capital and operating costs need to lowered • Performance will need to be responsive to multi-faceted objectives • Manufacturing workforce with advanced training and skills will be the key competitive advantage • Job growth will not be with unskilled, high labor oriented manufacturing Dynamic demands accelerating on manufacturing 6
 Advanced Manufacturing 2011 -2012 Critical Issues Report Manufacturing Executive Board President’s Council of Advisors on Science and Technology • The Adaptive Organization • Global Value Chain Optimization • The Innovative Enterprise • Factories of the Future • Next Generation Leadership and Culture • The New Workforce • The Sustainability Imperative • Game-Changing • Advanced manufacturing refers to a family of activities that (a) depend on the use and coordination of information, automation, computation, software, sensing and networking and (b) make use of cutting edge materials and emerging capabilities enabled by physical and biological sciences. • AM involves both new ways to manufacture existing products and especially the manufacture of new products emerging from new advanced technologies.
Advanced Manufacturing 2011 -2012 Critical Issues Report Manufacturing Executive Board President’s Council of Advisors on Science and Technology • The Adaptive Organization • Global Value Chain Optimization • The Innovative Enterprise • Factories of the Future • Next Generation Leadership and Culture • The New Workforce • The Sustainability Imperative • Game-Changing • Advanced manufacturing refers to a family of activities that (a) depend on the use and coordination of information, automation, computation, software, sensing and networking and (b) make use of cutting edge materials and emerging capabilities enabled by physical and biological sciences. • AM involves both new ways to manufacture existing products and especially the manufacture of new products emerging from new advanced technologies.
 Raising the Level of Abstraction If Smart Manufacturing is such a smart idea why aren’t companies already doing it? Already Investing in Information Technology and Automation for 40 year
Raising the Level of Abstraction If Smart Manufacturing is such a smart idea why aren’t companies already doing it? Already Investing in Information Technology and Automation for 40 year
 What is Smart Manufacturing? Business (Collaboration, Broader Metrics Real-time Decisions) Organizational Mindset Technology (Horizontal & Vertical Pervasive) Workforce (Innovation & Broad-Based)
What is Smart Manufacturing? Business (Collaboration, Broader Metrics Real-time Decisions) Organizational Mindset Technology (Horizontal & Vertical Pervasive) Workforce (Innovation & Broad-Based)
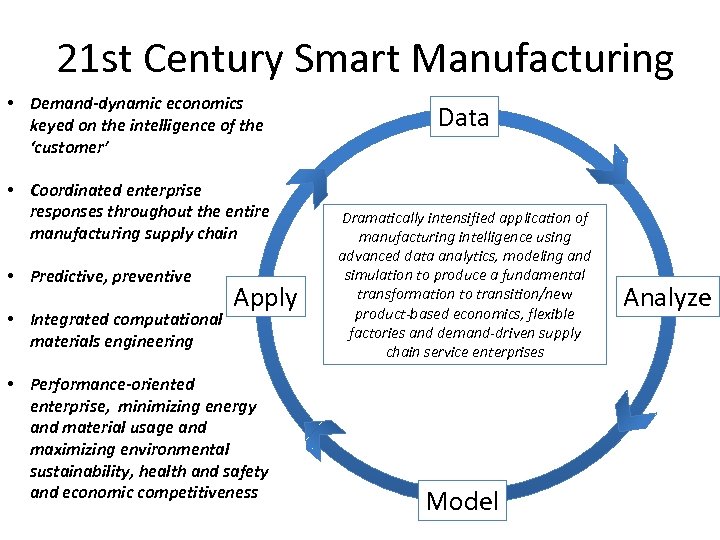 21 st Century Smart Manufacturing • Demand-dynamic economics keyed on the intelligence of the ‘customer’ • Coordinated enterprise responses throughout the entire manufacturing supply chain • Predictive, preventive Apply • Integrated computational materials engineering • Performance-oriented enterprise, minimizing energy and material usage and maximizing environmental sustainability, health and safety and economic competitiveness Data Dramatically intensified application of manufacturing intelligence using advanced data analytics, modeling and simulation to produce a fundamental transformation to transition/new product-based economics, flexible factories and demand-driven supply chain service enterprises Model Analyze
21 st Century Smart Manufacturing • Demand-dynamic economics keyed on the intelligence of the ‘customer’ • Coordinated enterprise responses throughout the entire manufacturing supply chain • Predictive, preventive Apply • Integrated computational materials engineering • Performance-oriented enterprise, minimizing energy and material usage and maximizing environmental sustainability, health and safety and economic competitiveness Data Dramatically intensified application of manufacturing intelligence using advanced data analytics, modeling and simulation to produce a fundamental transformation to transition/new product-based economics, flexible factories and demand-driven supply chain service enterprises Model Analyze
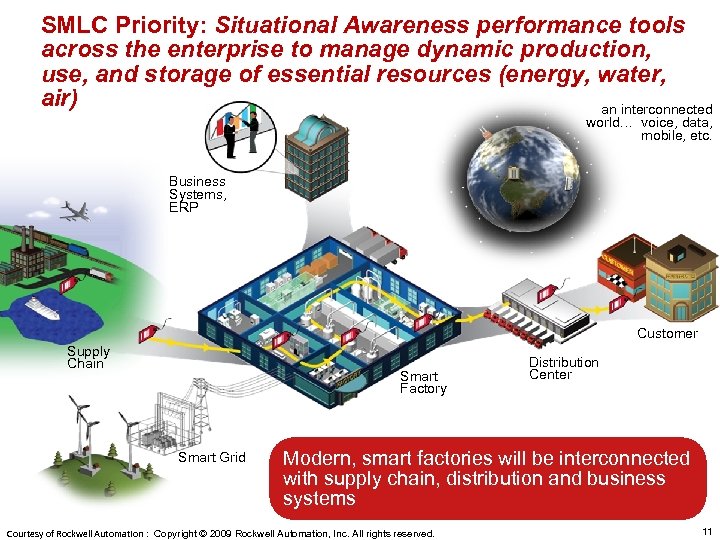 SMLC Priority: Situational Awareness performance tools across the enterprise to manage dynamic production, use, and storage of essential resources (energy, water, air) an interconnected world… voice, data, mobile, etc. Business Systems, ERP Customer Supply Chain Smart Factory Smart Grid Distribution Center Modern, smart factories will be interconnected with supply chain, distribution and business systems Courtesy of Rockwell Automation : Copyright © 2009 Rockwell Automation, Inc. All rights reserved. 11
SMLC Priority: Situational Awareness performance tools across the enterprise to manage dynamic production, use, and storage of essential resources (energy, water, air) an interconnected world… voice, data, mobile, etc. Business Systems, ERP Customer Supply Chain Smart Factory Smart Grid Distribution Center Modern, smart factories will be interconnected with supply chain, distribution and business systems Courtesy of Rockwell Automation : Copyright © 2009 Rockwell Automation, Inc. All rights reserved. 11
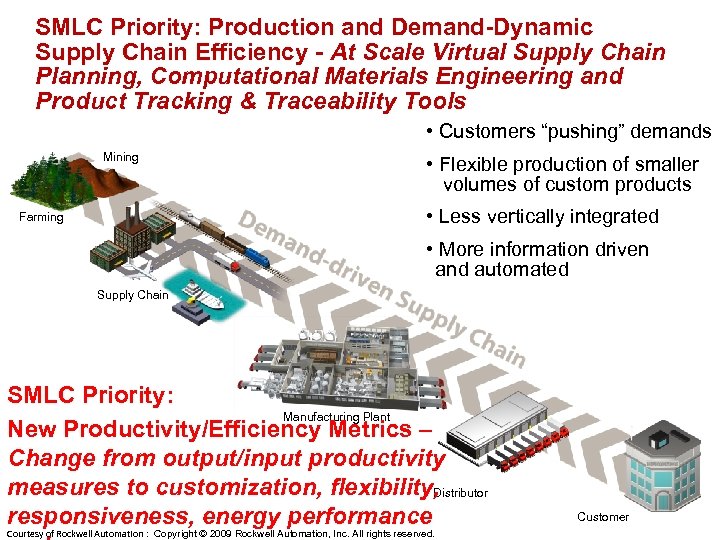 SMLC Priority: Production and Demand-Dynamic Supply Chain Efficiency - At Scale Virtual Supply Chain Planning, Computational Materials Engineering and Product Tracking & Traceability Tools • Customers “pushing” demands Mining • Flexible production of smaller volumes of custom products • Less vertically integrated Farming • More information driven and automated Supply Chain SMLC Priority: Manufacturing Plant New Productivity/Efficiency Metrics – Change from output/input productivity measures to customization, flexibility, Distributor responsiveness, energy performance Courtesy of Rockwell Automation : Copyright © 2009 Rockwell Automation, Inc. All rights reserved. Customer
SMLC Priority: Production and Demand-Dynamic Supply Chain Efficiency - At Scale Virtual Supply Chain Planning, Computational Materials Engineering and Product Tracking & Traceability Tools • Customers “pushing” demands Mining • Flexible production of smaller volumes of custom products • Less vertically integrated Farming • More information driven and automated Supply Chain SMLC Priority: Manufacturing Plant New Productivity/Efficiency Metrics – Change from output/input productivity measures to customization, flexibility, Distributor responsiveness, energy performance Courtesy of Rockwell Automation : Copyright © 2009 Rockwell Automation, Inc. All rights reserved. Customer
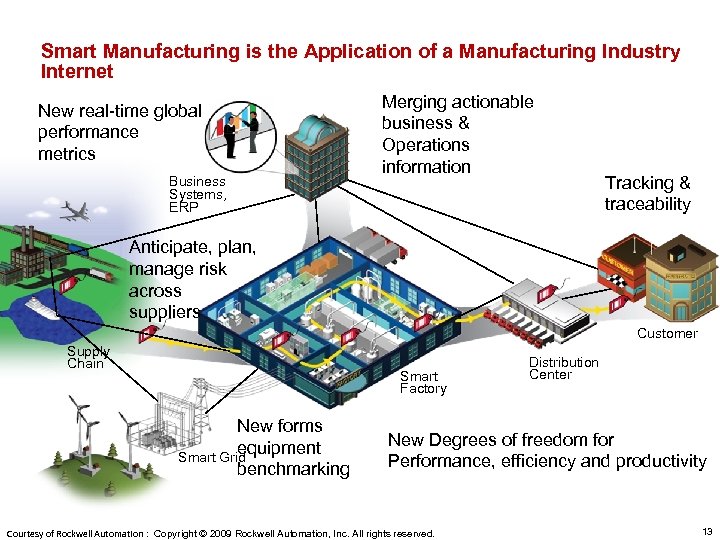 Smart Manufacturing is the Application of a Manufacturing Industry Internet New real-time global performance metrics Business Systems, ERP Merging actionable business & Operations information Tracking & traceability Anticipate, plan, manage risk across suppliers Customer Supply Chain Smart Factory New forms equipment Smart Grid benchmarking Distribution Center New Degrees of freedom for Performance, efficiency and productivity Courtesy of Rockwell Automation : Copyright © 2009 Rockwell Automation, Inc. All rights reserved. 13
Smart Manufacturing is the Application of a Manufacturing Industry Internet New real-time global performance metrics Business Systems, ERP Merging actionable business & Operations information Tracking & traceability Anticipate, plan, manage risk across suppliers Customer Supply Chain Smart Factory New forms equipment Smart Grid benchmarking Distribution Center New Degrees of freedom for Performance, efficiency and productivity Courtesy of Rockwell Automation : Copyright © 2009 Rockwell Automation, Inc. All rights reserved. 13
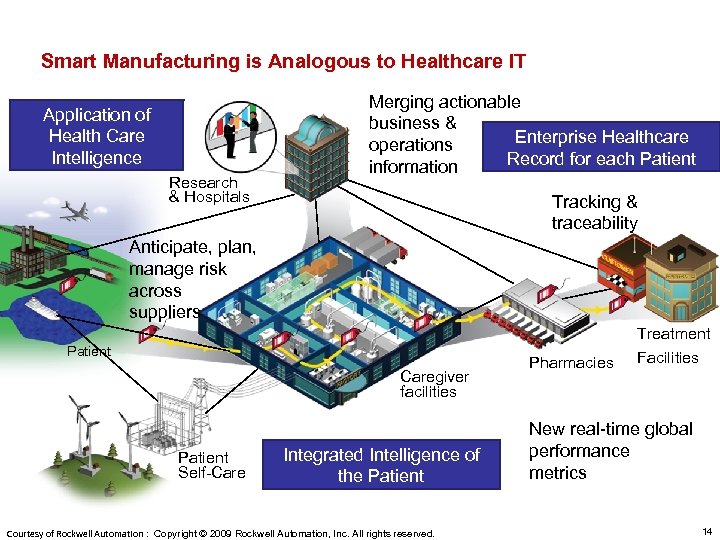 Smart Manufacturing is Analogous to Healthcare IT Application of Health Care Intelligence Research & Hospitals Merging actionable business & Enterprise Healthcare operations Record for each Patient information Tracking & traceability Anticipate, plan, manage risk across suppliers Treatment Patient Caregiver facilities Patient Self-Care Integrated Intelligence of the Patient Courtesy of Rockwell Automation : Copyright © 2009 Rockwell Automation, Inc. All rights reserved. Pharmacies Facilities New real-time global performance metrics 14
Smart Manufacturing is Analogous to Healthcare IT Application of Health Care Intelligence Research & Hospitals Merging actionable business & Enterprise Healthcare operations Record for each Patient information Tracking & traceability Anticipate, plan, manage risk across suppliers Treatment Patient Caregiver facilities Patient Self-Care Integrated Intelligence of the Patient Courtesy of Rockwell Automation : Copyright © 2009 Rockwell Automation, Inc. All rights reserved. Pharmacies Facilities New real-time global performance metrics 14
 How do we proceed?
How do we proceed?
 Excellent Work Underway
Excellent Work Underway
 Technology Roadmap Report (2009) 1. Motivating Smart Process Manufacturing 2. The Business Case and the Business Transformation 3. The Technical Transformation 4. The Smart Process Manufacturing Roadmap 5. The Path Forward 17
Technology Roadmap Report (2009) 1. Motivating Smart Process Manufacturing 2. The Business Case and the Business Transformation 3. The Technical Transformation 4. The Smart Process Manufacturing Roadmap 5. The Path Forward 17
 18
18
 SMLC Program Agenda Ø Lower the cost for applying advanced data analysis, modeling, and simulation in core manufacturing processes Ø Build pre-competitive infrastructure including network and information technology, interoperability, and shared business data Ø Establish an industry-shared, community-source platform and associated software that functions as an “apps” store and clearinghouse Ø Create and provide broad access to next-generation sensors, including low-cost sensing and sensor fusion technologies Ø Establish test beds for smart manufacturing concepts and make them available to companies of all sizes
SMLC Program Agenda Ø Lower the cost for applying advanced data analysis, modeling, and simulation in core manufacturing processes Ø Build pre-competitive infrastructure including network and information technology, interoperability, and shared business data Ø Establish an industry-shared, community-source platform and associated software that functions as an “apps” store and clearinghouse Ø Create and provide broad access to next-generation sensors, including low-cost sensing and sensor fusion technologies Ø Establish test beds for smart manufacturing concepts and make them available to companies of all sizes
 Achievable Meaningful Use Goals and Magnitude of Impact • Demand-driven efficient use of resources and supplies in more highly optimized plants and supply – – – 80% reduction in cost of implementing modeling and simulation 25% reduction in safety incidents 25% improvement in energy efficiency 10% improvement in overall operating efficiency 40% reduction in cycle times 40% reduction in water usage • Product safety – Product tracking and traceability throughout the supply • Sustainable production processes for current and future critical industries – 10 x improvement in time to market in target industries – 25% reduction in consumer packaging • Maintain and grow existing U. S. industrial base – Environment for broad innovation – 25% revenue in adjacent industries – 25% revenue in new products and services – 2 x current SME’s addressing total market – More highly skilled sustainable jobs created
Achievable Meaningful Use Goals and Magnitude of Impact • Demand-driven efficient use of resources and supplies in more highly optimized plants and supply – – – 80% reduction in cost of implementing modeling and simulation 25% reduction in safety incidents 25% improvement in energy efficiency 10% improvement in overall operating efficiency 40% reduction in cycle times 40% reduction in water usage • Product safety – Product tracking and traceability throughout the supply • Sustainable production processes for current and future critical industries – 10 x improvement in time to market in target industries – 25% reduction in consumer packaging • Maintain and grow existing U. S. industrial base – Environment for broad innovation – 25% revenue in adjacent industries – 25% revenue in new products and services – 2 x current SME’s addressing total market – More highly skilled sustainable jobs created
 Resilient Proactive Plant Operations Smart Plant Knowledgeenabled Workforce in Global Operation Smart Process 3/17/2018 Manufacturing 21
Resilient Proactive Plant Operations Smart Plant Knowledgeenabled Workforce in Global Operation Smart Process 3/17/2018 Manufacturing 21
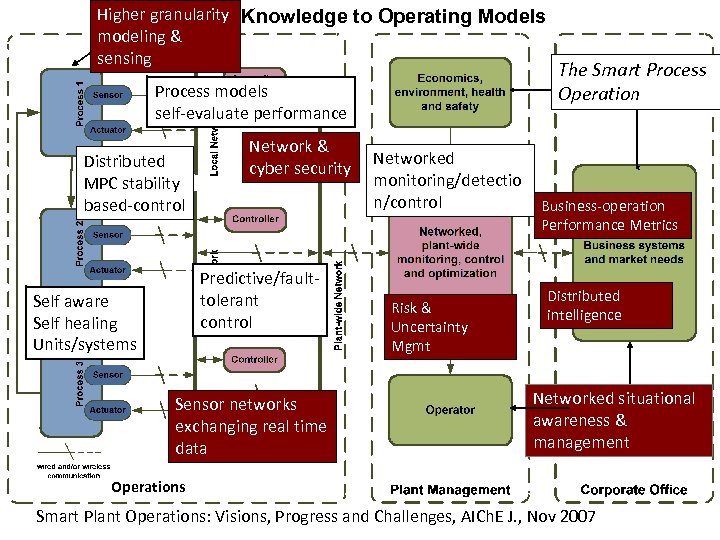 Higher granularity Knowledge to Operating Models modeling & sensing Process models self-evaluate performance Distributed MPC stability based-control Network & cyber security Predictive/faulttolerant control Self aware Self healing Units/systems Sensor networks exchanging real time data Networked monitoring/detectio n/control Risk & Uncertainty Mgmt The Smart Process Operation Business-operation Performance Metrics Distributed intelligence Networked situational awareness & management Operations Smart Plant Operations: Visions, Progress and Challenges, AICh. E J. , Nov 2007
Higher granularity Knowledge to Operating Models modeling & sensing Process models self-evaluate performance Distributed MPC stability based-control Network & cyber security Predictive/faulttolerant control Self aware Self healing Units/systems Sensor networks exchanging real time data Networked monitoring/detectio n/control Risk & Uncertainty Mgmt The Smart Process Operation Business-operation Performance Metrics Distributed intelligence Networked situational awareness & management Operations Smart Plant Operations: Visions, Progress and Challenges, AICh. E J. , Nov 2007
 Active Management and Innovation • Integrated performance metrics driving bottom up local and global decision making • Involved workforce making decisions that drive performance and objectives and not tasks • Explicit management of risk and uncertainty • Distributed business and operating intelligence through integrated information • Distributed intelligent manufacturing and innovation
Active Management and Innovation • Integrated performance metrics driving bottom up local and global decision making • Involved workforce making decisions that drive performance and objectives and not tasks • Explicit management of risk and uncertainty • Distributed business and operating intelligence through integrated information • Distributed intelligent manufacturing and innovation
 Let’s raise the level of abstraction Let’s define new, integrated and global performance metrics Let’s define the minimum data, analytics, and modeling, that produces new degrees of operational freedom s Let’s establish a process of building and applying Manufacturing Intelligence in increasing levels of sophistication
Let’s raise the level of abstraction Let’s define new, integrated and global performance metrics Let’s define the minimum data, analytics, and modeling, that produces new degrees of operational freedom s Let’s establish a process of building and applying Manufacturing Intelligence in increasing levels of sophistication
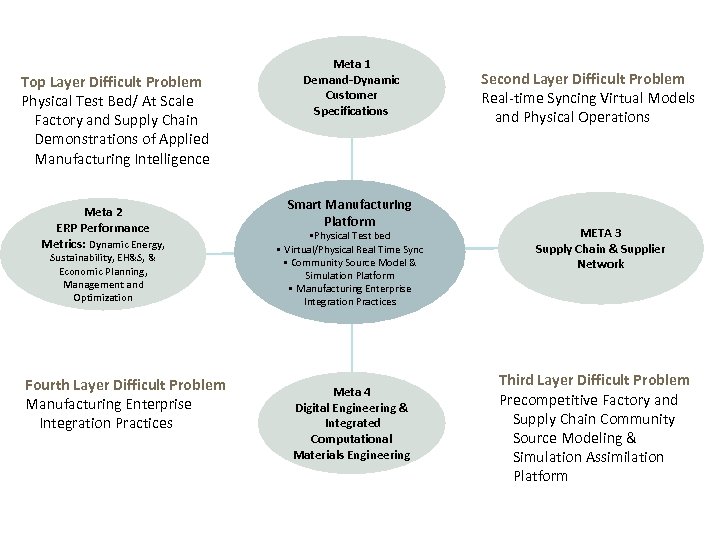 Top Layer Difficult Problem Physical Test Bed/ At Scale Factory and Supply Chain Demonstrations of Applied Manufacturing Intelligence Meta 2 ERP Performance Metrics: Dynamic Energy, Sustainability, EH&S, & Economic Planning, Management and Optimization Fourth Layer Difficult Problem Manufacturing Enterprise Integration Practices Meta 1 Demand-Dynamic Customer Specifications Smart Manufacturing Platform • Physical Test bed • Virtual/Physical Real Time Sync • Community Source Model & Simulation Platform • Manufacturing Enterprise Integration Practices Meta 4 Digital Engineering & Integrated Computational Materials Engineering Second Layer Difficult Problem Real-time Syncing Virtual Models and Physical Operations META 3 Supply Chain & Supplier Network Third Layer Difficult Problem Precompetitive Factory and Supply Chain Community Source Modeling & Simulation Assimilation Platform
Top Layer Difficult Problem Physical Test Bed/ At Scale Factory and Supply Chain Demonstrations of Applied Manufacturing Intelligence Meta 2 ERP Performance Metrics: Dynamic Energy, Sustainability, EH&S, & Economic Planning, Management and Optimization Fourth Layer Difficult Problem Manufacturing Enterprise Integration Practices Meta 1 Demand-Dynamic Customer Specifications Smart Manufacturing Platform • Physical Test bed • Virtual/Physical Real Time Sync • Community Source Model & Simulation Platform • Manufacturing Enterprise Integration Practices Meta 4 Digital Engineering & Integrated Computational Materials Engineering Second Layer Difficult Problem Real-time Syncing Virtual Models and Physical Operations META 3 Supply Chain & Supplier Network Third Layer Difficult Problem Precompetitive Factory and Supply Chain Community Source Modeling & Simulation Assimilation Platform
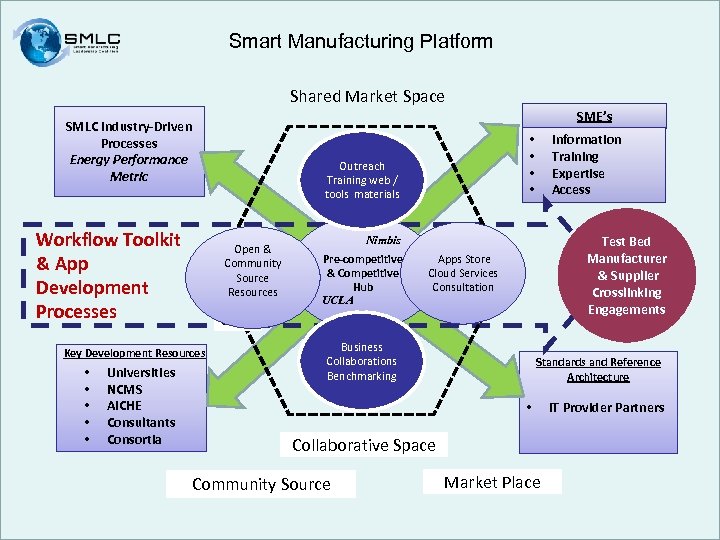 Smart Manufacturing Platform Shared Market Space SME’s SMLC Industry-Driven Processes Energy Performance Metric Workflow Toolkit & App Development Processes Universities NCMS AICHE Consultants Consortia Test Bed Manufacturer & Supplier Crosslinking Engagements Nimbis Pre-competitive & Competitive Hub UCLA Apps Store Cloud Services Consultation UCLA Key Development Resources • • • Outreach Training web / tools materials Open & Community Source Resources Information Training Expertise Access • • Business Collaborations Benchmarking Standards and Reference Architecture • IT Provider Partners Collaborative Space Community Source Market Place 26 11/1/11
Smart Manufacturing Platform Shared Market Space SME’s SMLC Industry-Driven Processes Energy Performance Metric Workflow Toolkit & App Development Processes Universities NCMS AICHE Consultants Consortia Test Bed Manufacturer & Supplier Crosslinking Engagements Nimbis Pre-competitive & Competitive Hub UCLA Apps Store Cloud Services Consultation UCLA Key Development Resources • • • Outreach Training web / tools materials Open & Community Source Resources Information Training Expertise Access • • Business Collaborations Benchmarking Standards and Reference Architecture • IT Provider Partners Collaborative Space Community Source Market Place 26 11/1/11
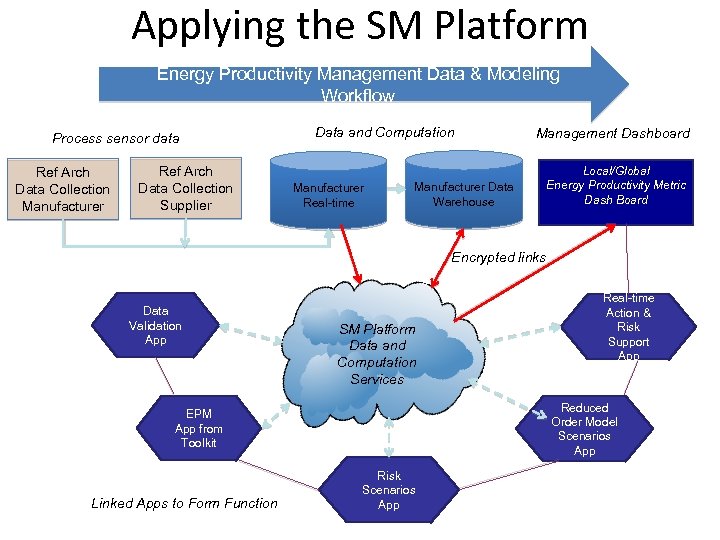 Applying the SM Platform Energy Productivity Management Data & Modeling Workflow Process sensor data Ref Arch Data Collection Manufacturer Ref Arch Data Collection Supplier Data and Computation Manufacturer Real-time Management Dashboard Manufacturer Data Warehouse Local/Global Energy Productivity Metric Dash Board Encrypted links Data Validation App SM Platform Data and Computation Services Reduced Order Model Scenarios App EPM App from Toolkit Linked Apps to Form Function Real-time Action & Risk Support App Risk Scenarios App
Applying the SM Platform Energy Productivity Management Data & Modeling Workflow Process sensor data Ref Arch Data Collection Manufacturer Ref Arch Data Collection Supplier Data and Computation Manufacturer Real-time Management Dashboard Manufacturer Data Warehouse Local/Global Energy Productivity Metric Dash Board Encrypted links Data Validation App SM Platform Data and Computation Services Reduced Order Model Scenarios App EPM App from Toolkit Linked Apps to Form Function Real-time Action & Risk Support App Risk Scenarios App
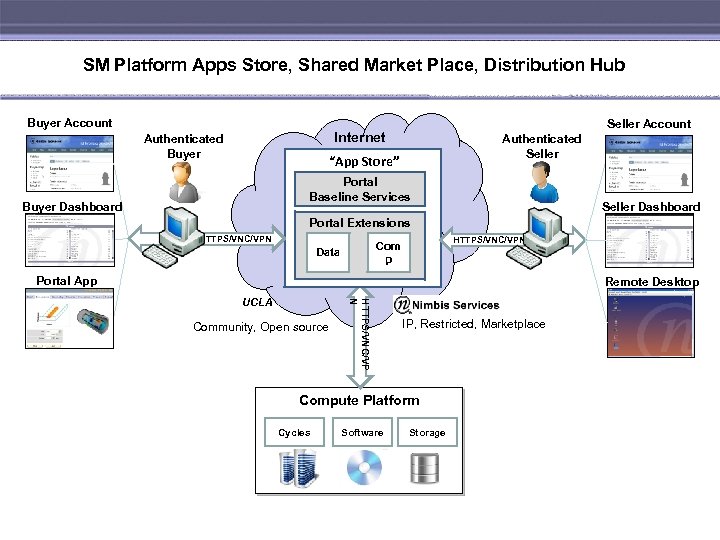 SM Platform Apps Store, Shared Market Place, Distribution Hub Buyer Account Seller Account Internet Authenticated Buyer Authenticated Seller “App Store” Portal Baseline Services Buyer Dashboard Seller Dashboard Portal Extensions HTTPS/VNC/VPN Com p Data Portal App Remote Desktop Community, Open source HTTPS/VNC/VP N UCLA IP, Restricted, Marketplace Compute Platform Cycles Software Storage
SM Platform Apps Store, Shared Market Place, Distribution Hub Buyer Account Seller Account Internet Authenticated Buyer Authenticated Seller “App Store” Portal Baseline Services Buyer Dashboard Seller Dashboard Portal Extensions HTTPS/VNC/VPN Com p Data Portal App Remote Desktop Community, Open source HTTPS/VNC/VP N UCLA IP, Restricted, Marketplace Compute Platform Cycles Software Storage
 New Technology R & D • Economic, business, performance collaboration models • Education and training aimed at science, engineering and operating practices for Smart Manufacturing • Static and real-time modeling architectures redesigned for apps store-like distribution, competitive and pre-competitive management and managed crowdsourcing • Richer lower cost sensing and actuation technologies combined with richer real-time analytics to build manufacturing intelligence • Tools and rapid evaluation procedures for the ‘right’ rigor and right ‘realtime’ for a model • Projection of global and local decision and/or action risk • Making control, optimization and planning indistinct while distributable • Accommodate modern processor architectures • Computer architectures for assured real-time actions with greater levels of active management • Real-time synchronization, verification and validation of enterprise data • Human centered dashboards with new expectations for decision-making
New Technology R & D • Economic, business, performance collaboration models • Education and training aimed at science, engineering and operating practices for Smart Manufacturing • Static and real-time modeling architectures redesigned for apps store-like distribution, competitive and pre-competitive management and managed crowdsourcing • Richer lower cost sensing and actuation technologies combined with richer real-time analytics to build manufacturing intelligence • Tools and rapid evaluation procedures for the ‘right’ rigor and right ‘realtime’ for a model • Projection of global and local decision and/or action risk • Making control, optimization and planning indistinct while distributable • Accommodate modern processor architectures • Computer architectures for assured real-time actions with greater levels of active management • Real-time synchronization, verification and validation of enterprise data • Human centered dashboards with new expectations for decision-making
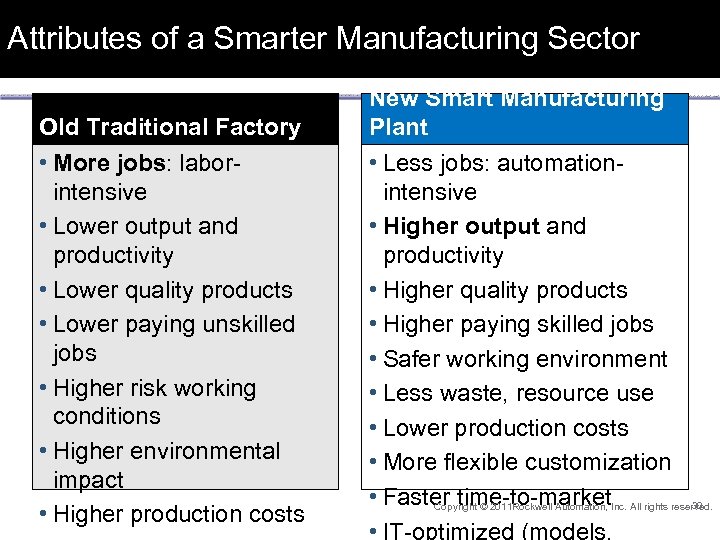 Attributes of a Smarter Manufacturing Sector Old Traditional Factory • More jobs: laborintensive • Lower output and productivity • Lower quality products • Lower paying unskilled jobs • Higher risk working conditions • Higher environmental impact • Higher production costs New Smart Manufacturing Plant • Less jobs: automationintensive • Higher output and productivity • Higher quality products • Higher paying skilled jobs • Safer working environment • Less waste, resource use • Lower production costs • More flexible customization • Faster time-to-market 30 Copyright © 2011 Rockwell Automation, Inc. All rights reserved. • IT-optimized (models,
Attributes of a Smarter Manufacturing Sector Old Traditional Factory • More jobs: laborintensive • Lower output and productivity • Lower quality products • Lower paying unskilled jobs • Higher risk working conditions • Higher environmental impact • Higher production costs New Smart Manufacturing Plant • Less jobs: automationintensive • Higher output and productivity • Higher quality products • Higher paying skilled jobs • Safer working environment • Less waste, resource use • Lower production costs • More flexible customization • Faster time-to-market 30 Copyright © 2011 Rockwell Automation, Inc. All rights reserved. • IT-optimized (models,
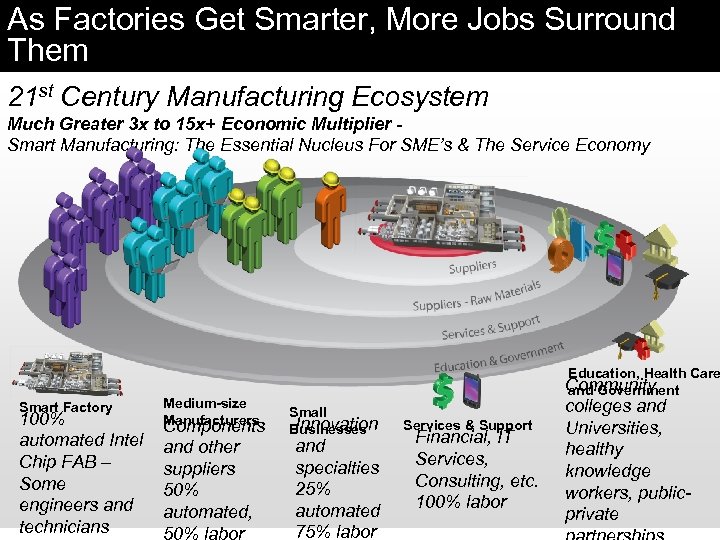 As Factories Get Smarter, More Jobs Surround Them 21 st Century Manufacturing Ecosystem Much Greater 3 x to 15 x+ Economic Multiplier Smart Manufacturing: The Essential Nucleus For SME’s & The Service Economy Education, Health Care Smart Factory 100% automated Intel Chip FAB – Some engineers and technicians Medium-size Manufacturers Components and other suppliers 50% automated, 50% labor Small Innovation Businesses and specialties 25% automated 75% labor Services & Support Financial, IT Services, Consulting, etc. 100% labor Community and Government colleges and Universities, healthy knowledge workers, publicprivate
As Factories Get Smarter, More Jobs Surround Them 21 st Century Manufacturing Ecosystem Much Greater 3 x to 15 x+ Economic Multiplier Smart Manufacturing: The Essential Nucleus For SME’s & The Service Economy Education, Health Care Smart Factory 100% automated Intel Chip FAB – Some engineers and technicians Medium-size Manufacturers Components and other suppliers 50% automated, 50% labor Small Innovation Businesses and specialties 25% automated 75% labor Services & Support Financial, IT Services, Consulting, etc. 100% labor Community and Government colleges and Universities, healthy knowledge workers, publicprivate
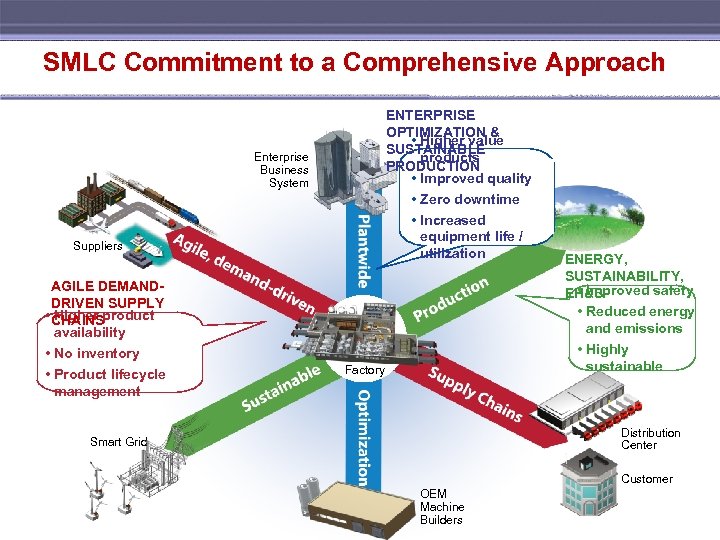 SMLC Commitment to a Comprehensive Approach ENTERPRISE OPTIMIZATION & • Higher value SUSTAINABLE products PRODUCTION • Improved quality • Zero downtime • Increased equipment life / utilization Enterprise Business System Suppliers AGILE DEMANDDRIVEN SUPPLY • CHAINS Higher product availability • No inventory • Product lifecycle management Factory ENERGY, SUSTAINABILITY, • Improved safety EH&S • Reduced energy and emissions • Highly sustainable Distribution Center Smart Grid Customer OEM Machine Builders
SMLC Commitment to a Comprehensive Approach ENTERPRISE OPTIMIZATION & • Higher value SUSTAINABLE products PRODUCTION • Improved quality • Zero downtime • Increased equipment life / utilization Enterprise Business System Suppliers AGILE DEMANDDRIVEN SUPPLY • CHAINS Higher product availability • No inventory • Product lifecycle management Factory ENERGY, SUSTAINABILITY, • Improved safety EH&S • Reduced energy and emissions • Highly sustainable Distribution Center Smart Grid Customer OEM Machine Builders
 Smart Manufacturing http: //smart-processmanufacturing. ucla. edu/
Smart Manufacturing http: //smart-processmanufacturing. ucla. edu/


