646a33fb2a78004fef7d70128655be20.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 Smart Grid Utility Challenges in the 21 st Century Andrew Tang Smart Energy Web Pacific Gas and Electric Company September 18, 2009
Smart Grid Utility Challenges in the 21 st Century Andrew Tang Smart Energy Web Pacific Gas and Electric Company September 18, 2009
 Balancing Competing Priorities Environmental Sustainability Reasonable Cost Reliable Service Smart Grid 2
Balancing Competing Priorities Environmental Sustainability Reasonable Cost Reliable Service Smart Grid 2
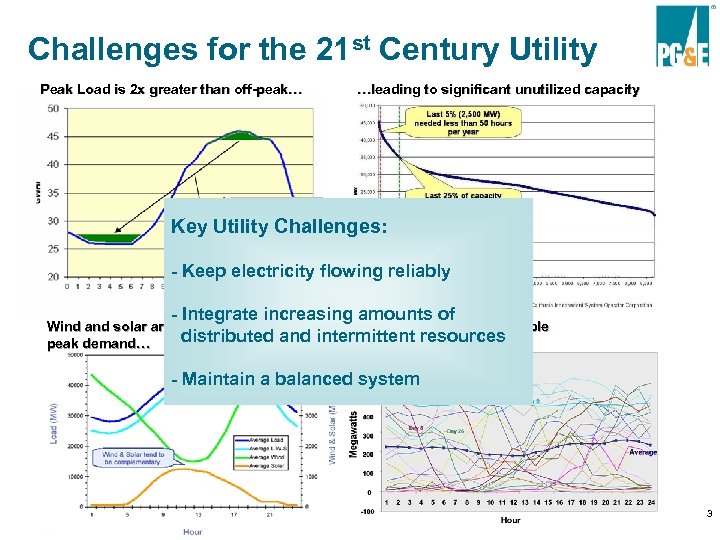 Challenges for the 21 st Century Utility Peak Load is 2 x greater than off-peak… …leading to significant unutilized capacity Key Utility Challenges: - Keep electricity flowing reliably - Integrate increasing amounts of … and they are unpredictable intermittent resources Wind and solar are non-coincident with distributed and peak demand… - Maintain a balanced system 3
Challenges for the 21 st Century Utility Peak Load is 2 x greater than off-peak… …leading to significant unutilized capacity Key Utility Challenges: - Keep electricity flowing reliably - Integrate increasing amounts of … and they are unpredictable intermittent resources Wind and solar are non-coincident with distributed and peak demand… - Maintain a balanced system 3
 Traditional End-to-end Utility Network Balances Supply and Demand Nuclear Power Plants Transmission Smart Grid functionality restores the Lines balance Natural Gas Generators Hydro power plants Distribution Substations Customers 4
Traditional End-to-end Utility Network Balances Supply and Demand Nuclear Power Plants Transmission Smart Grid functionality restores the Lines balance Natural Gas Generators Hydro power plants Distribution Substations Customers 4
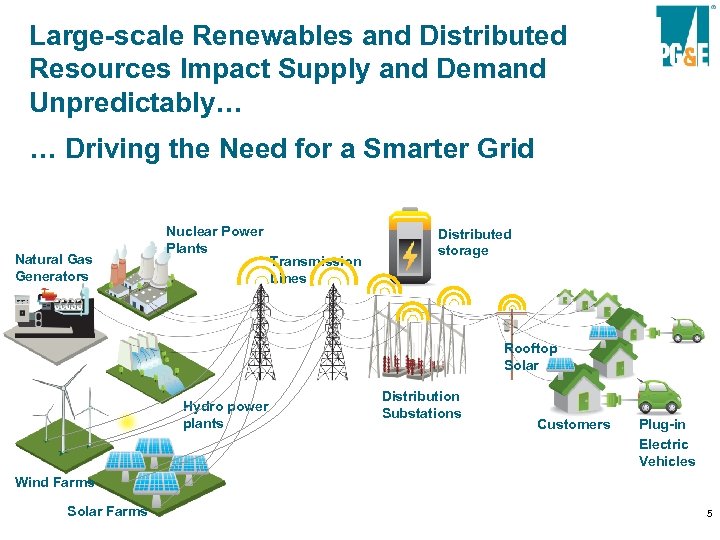 Large-scale Renewables and Distributed Resources Impact Supply and Demand Unpredictably… … Driving the Need for a Smarter Grid Natural Gas Generators Nuclear Power Plants Transmission Lines Distributed storage Smart Grid functionality restores the Rooftop balance Solar Hydro power plants Distribution Substations Customers Plug-in Electric Vehicles Wind Farms Solar Farms 5
Large-scale Renewables and Distributed Resources Impact Supply and Demand Unpredictably… … Driving the Need for a Smarter Grid Natural Gas Generators Nuclear Power Plants Transmission Lines Distributed storage Smart Grid functionality restores the Rooftop balance Solar Hydro power plants Distribution Substations Customers Plug-in Electric Vehicles Wind Farms Solar Farms 5
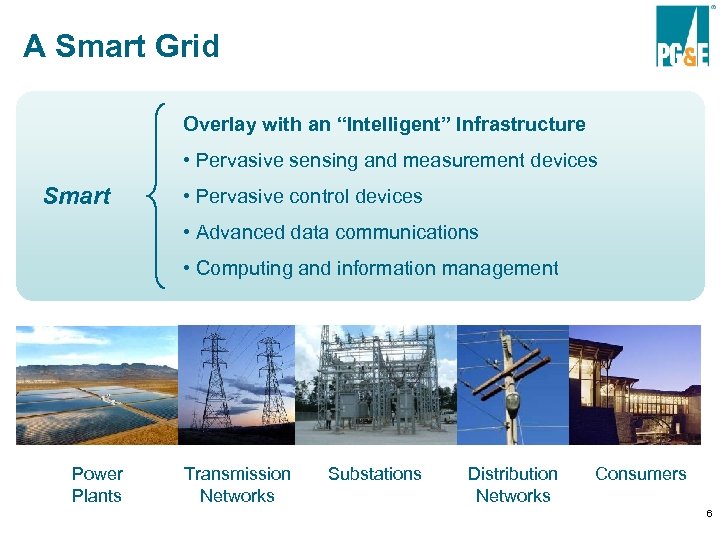 A Smart Grid Overlay with an “Intelligent” Infrastructure • Pervasive sensing and measurement devices Smart • Pervasive control devices • Advanced data communications • Computing and information management Power Plants Transmission Networks Substations Distribution Networks Consumers 6
A Smart Grid Overlay with an “Intelligent” Infrastructure • Pervasive sensing and measurement devices Smart • Pervasive control devices • Advanced data communications • Computing and information management Power Plants Transmission Networks Substations Distribution Networks Consumers 6
 Utility-scale Storage Resources Pumped Hydro Compressed Air Zinc Bromine Flow Batteries Sodium-Sulfur (NAS) Battery Flywheel 7
Utility-scale Storage Resources Pumped Hydro Compressed Air Zinc Bromine Flow Batteries Sodium-Sulfur (NAS) Battery Flywheel 7
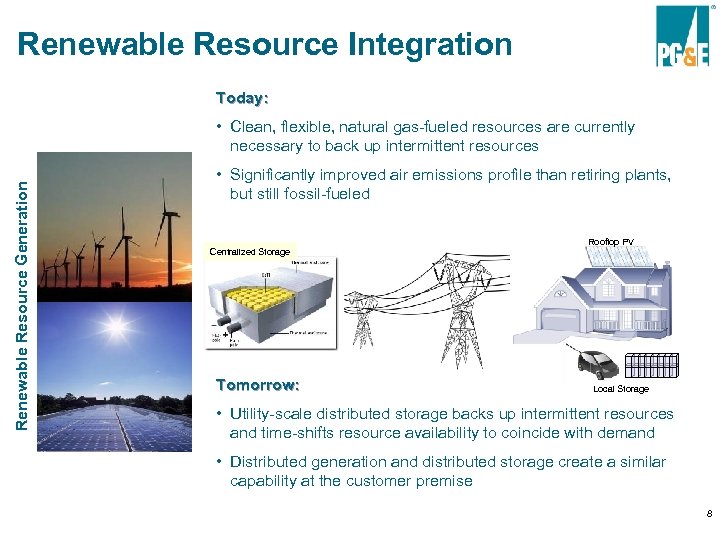 Renewable Resource Integration Today: Renewable Resource Generation • Clean, flexible, natural gas-fueled resources are currently necessary to back up intermittent resources • Significantly improved air emissions profile than retiring plants, but still fossil-fueled Centralized Storage CCGT Power Plant Tomorrow: Rooftop PV Local Storage • Utility-scale distributed storage backs up intermittent resources and time-shifts resource availability to coincide with demand • Distributed generation and distributed storage create a similar capability at the customer premise 8
Renewable Resource Integration Today: Renewable Resource Generation • Clean, flexible, natural gas-fueled resources are currently necessary to back up intermittent resources • Significantly improved air emissions profile than retiring plants, but still fossil-fueled Centralized Storage CCGT Power Plant Tomorrow: Rooftop PV Local Storage • Utility-scale distributed storage backs up intermittent resources and time-shifts resource availability to coincide with demand • Distributed generation and distributed storage create a similar capability at the customer premise 8
 Smart Grid Foundation: Largest US Smart Meter Deployment n Ubiquitous automated meter reading n 10 million meter upgrades by 2012 n 3. 5 million deployed to date n Frequent meter reads n daily for gas n hourly or 15 minute intervals for electric n Embedded in-premise network gateway device unlocks new opportunities n Customer energy management n Demand-side management n Smart. Charging for PEVs 9
Smart Grid Foundation: Largest US Smart Meter Deployment n Ubiquitous automated meter reading n 10 million meter upgrades by 2012 n 3. 5 million deployed to date n Frequent meter reads n daily for gas n hourly or 15 minute intervals for electric n Embedded in-premise network gateway device unlocks new opportunities n Customer energy management n Demand-side management n Smart. Charging for PEVs 9
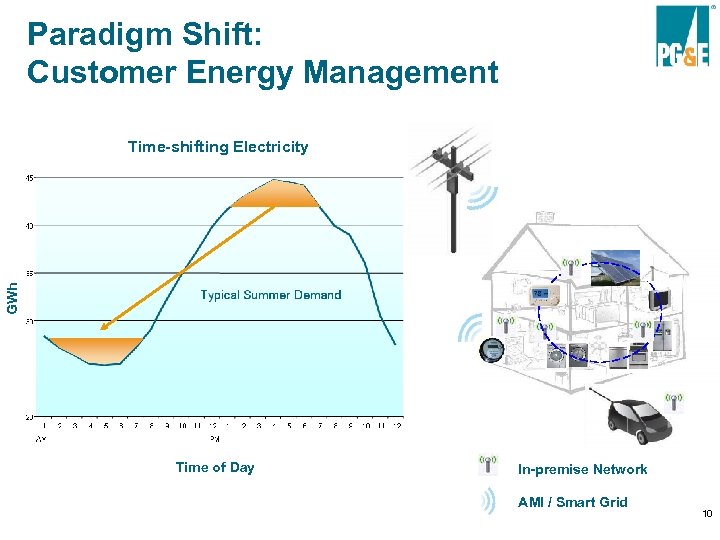 Paradigm Shift: Customer Energy Management GWh Time-shifting Electricity Time of Day In-premise Network AMI / Smart Grid 10
Paradigm Shift: Customer Energy Management GWh Time-shifting Electricity Time of Day In-premise Network AMI / Smart Grid 10
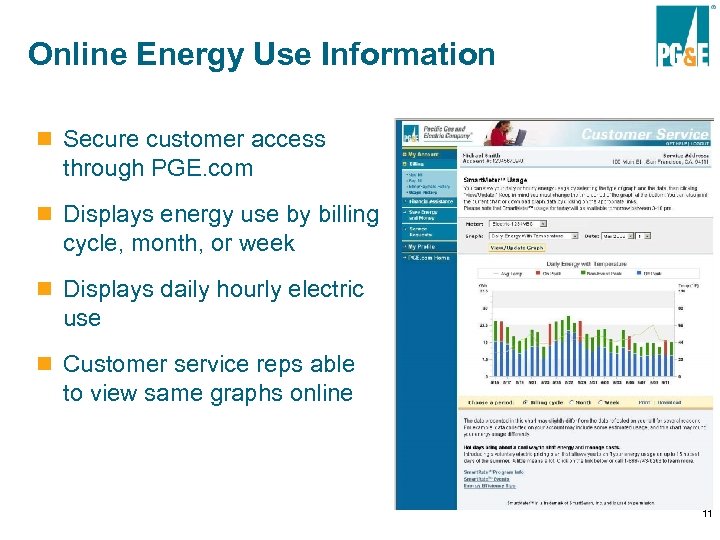 Online Energy Use Information n Secure customer access through PGE. com n Displays energy use by billing cycle, month, or week n Displays daily hourly electric use n Customer service reps able to view same graphs online 11
Online Energy Use Information n Secure customer access through PGE. com n Displays energy use by billing cycle, month, or week n Displays daily hourly electric use n Customer service reps able to view same graphs online 11
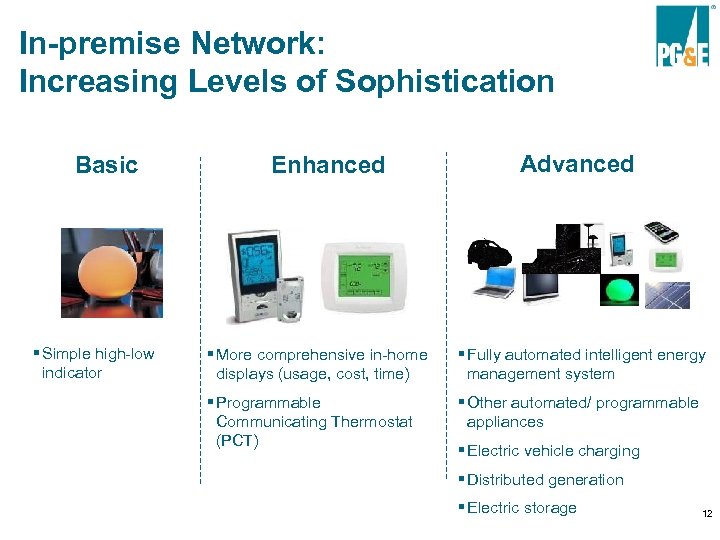 In-premise Network: Increasing Levels of Sophistication Basic § Simple high-low indicator Enhanced Advanced § More comprehensive in-home displays (usage, cost, time) § Fully automated intelligent energy management system § Programmable Communicating Thermostat (PCT) § Other automated/ programmable appliances § Electric vehicle charging § Distributed generation § Electric storage 12
In-premise Network: Increasing Levels of Sophistication Basic § Simple high-low indicator Enhanced Advanced § More comprehensive in-home displays (usage, cost, time) § Fully automated intelligent energy management system § Programmable Communicating Thermostat (PCT) § Other automated/ programmable appliances § Electric vehicle charging § Distributed generation § Electric storage 12
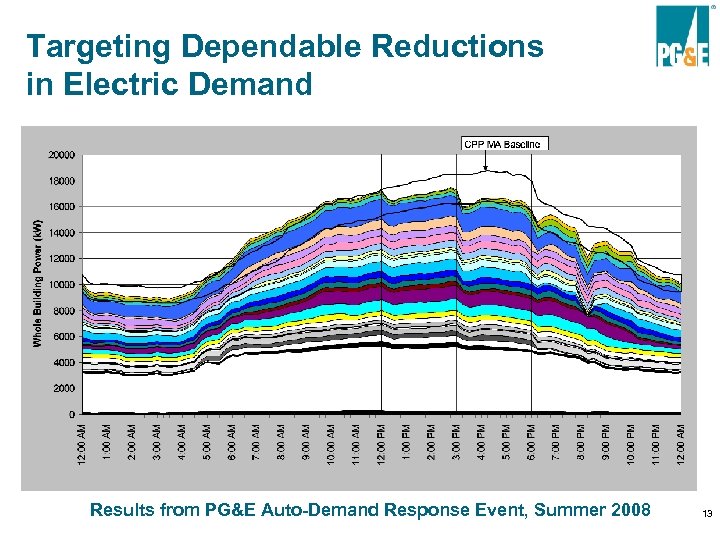 Targeting Dependable Reductions in Electric Demand Results from PG&E Auto-Demand Response Event, Summer 2008 13
Targeting Dependable Reductions in Electric Demand Results from PG&E Auto-Demand Response Event, Summer 2008 13
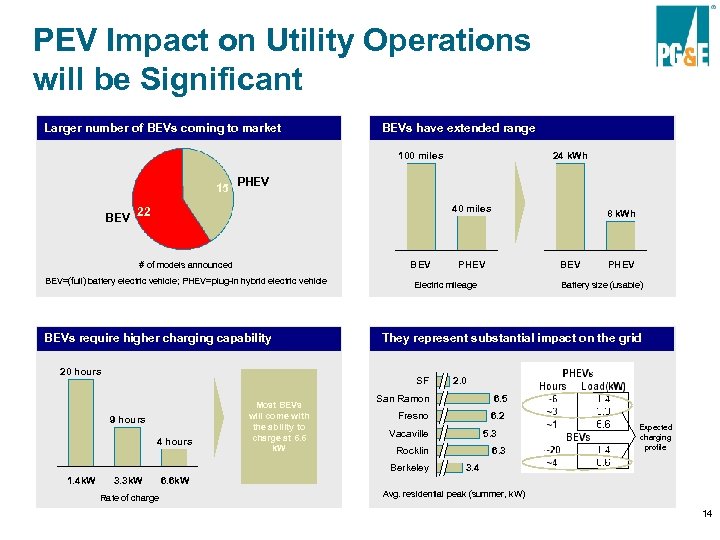 PEV Impact on Utility Operations will be Significant Larger number of BEVs coming to market BEVs have extended range 100 miles 24 k. Wh 15 PHEV 40 miles BEV 22 BEV # of models announced BEV=(full) battery electric vehicle; PHEV=plug-in hybrid electric vehicle BEVs require higher charging capability 20 hours 9 hours 4 hours 3. 3 k. W Rate of charge BEV PHEV Battery size (usable) They represent substantial impact on the grid 2. 0 San Ramon 6. 5 Fresno 6. 2 Vacaville 5. 3 Rocklin Berkeley 1. 4 k. W PHEV Electric mileage SF Most BEVs will come with the ability to charge at 6. 6 k. W 8 k. Wh 6. 3 Expected charging profile 3. 4 6. 6 k. W Avg. residential peak (summer, k. W) 14
PEV Impact on Utility Operations will be Significant Larger number of BEVs coming to market BEVs have extended range 100 miles 24 k. Wh 15 PHEV 40 miles BEV 22 BEV # of models announced BEV=(full) battery electric vehicle; PHEV=plug-in hybrid electric vehicle BEVs require higher charging capability 20 hours 9 hours 4 hours 3. 3 k. W Rate of charge BEV PHEV Battery size (usable) They represent substantial impact on the grid 2. 0 San Ramon 6. 5 Fresno 6. 2 Vacaville 5. 3 Rocklin Berkeley 1. 4 k. W PHEV Electric mileage SF Most BEVs will come with the ability to charge at 6. 6 k. W 8 k. Wh 6. 3 Expected charging profile 3. 4 6. 6 k. W Avg. residential peak (summer, k. W) 14
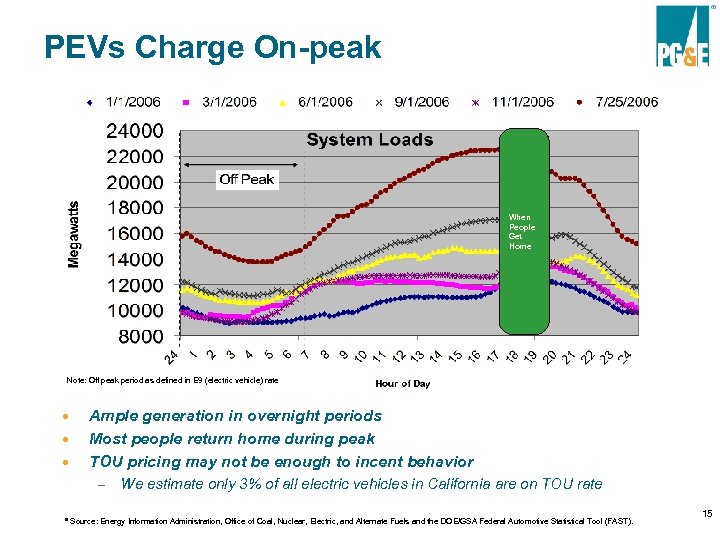 PEVs Charge On-peak When People Get Home Note: Off peak period as defined in E 9 (electric vehicle) rate · · · Ample generation in overnight periods Most people return home during peak TOU pricing may not be enough to incent behavior – We estimate only 3% of all electric vehicles in California are on TOU rate ª Source: Energy Information Administration, Office of Coal, Nuclear, Electric, and Alternate Fuels and the DOE/GSA Federal Automotive Statistical Tool (FAST). 15
PEVs Charge On-peak When People Get Home Note: Off peak period as defined in E 9 (electric vehicle) rate · · · Ample generation in overnight periods Most people return home during peak TOU pricing may not be enough to incent behavior – We estimate only 3% of all electric vehicles in California are on TOU rate ª Source: Energy Information Administration, Office of Coal, Nuclear, Electric, and Alternate Fuels and the DOE/GSA Federal Automotive Statistical Tool (FAST). 15
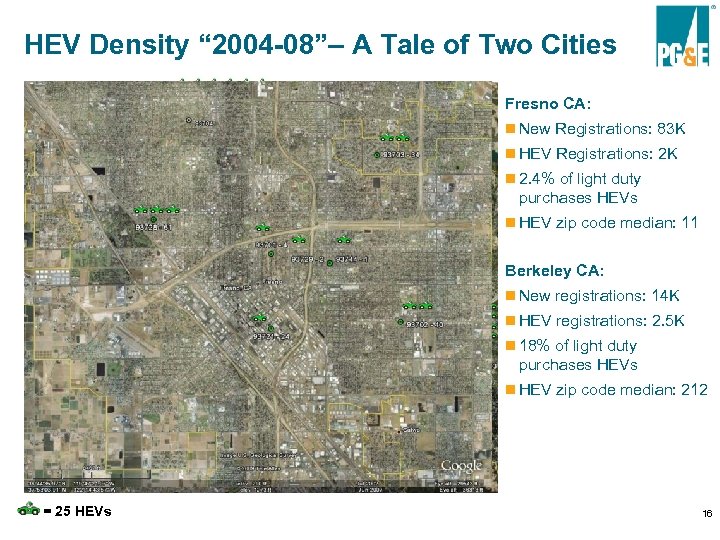 HEV Density “ 2004 -08”– A Tale of Two Cities Fresno CA: n New Registrations: 83 K n HEV Registrations: 2 K n 2. 4% of light duty purchases HEVs n HEV zip code median: 11 Berkeley CA: n New registrations: 14 K n HEV registrations: 2. 5 K n 18% of light duty purchases HEVs n HEV zip code median: 212 = 25 HEVs 16
HEV Density “ 2004 -08”– A Tale of Two Cities Fresno CA: n New Registrations: 83 K n HEV Registrations: 2 K n 2. 4% of light duty purchases HEVs n HEV zip code median: 11 Berkeley CA: n New registrations: 14 K n HEV registrations: 2. 5 K n 18% of light duty purchases HEVs n HEV zip code median: 212 = 25 HEVs 16
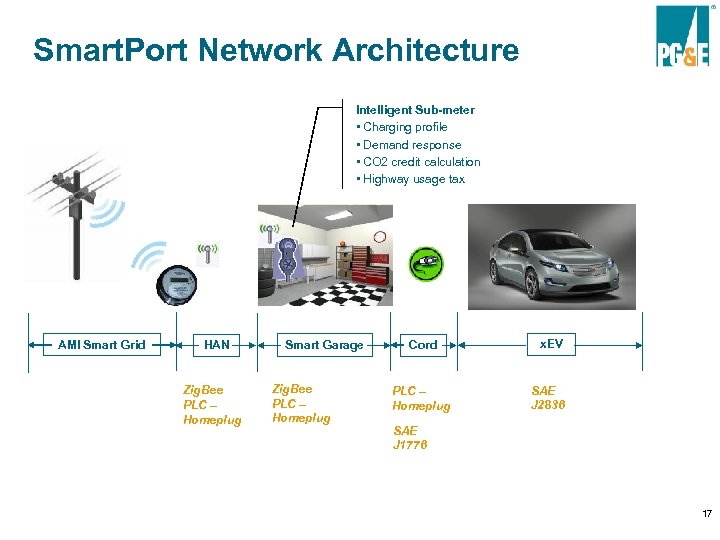 Smart. Port Network Architecture Intelligent Sub-meter • Charging profile • Demand response • CO 2 credit calculation • Highway usage tax AMI Smart Grid HAN Zig. Bee PLC – Homeplug Smart Garage Zig. Bee PLC – Homeplug Cord PLC – Homeplug x. EV SAE J 2836 SAE J 1776 17
Smart. Port Network Architecture Intelligent Sub-meter • Charging profile • Demand response • CO 2 credit calculation • Highway usage tax AMI Smart Grid HAN Zig. Bee PLC – Homeplug Smart Garage Zig. Bee PLC – Homeplug Cord PLC – Homeplug x. EV SAE J 2836 SAE J 1776 17
 At PG&E, We Are Committed To Sustainability 18
At PG&E, We Are Committed To Sustainability 18


