Small Cell Molecules.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 37

Small molecules in Cells Arnat Balabiyev Ph. D student Arizona State University
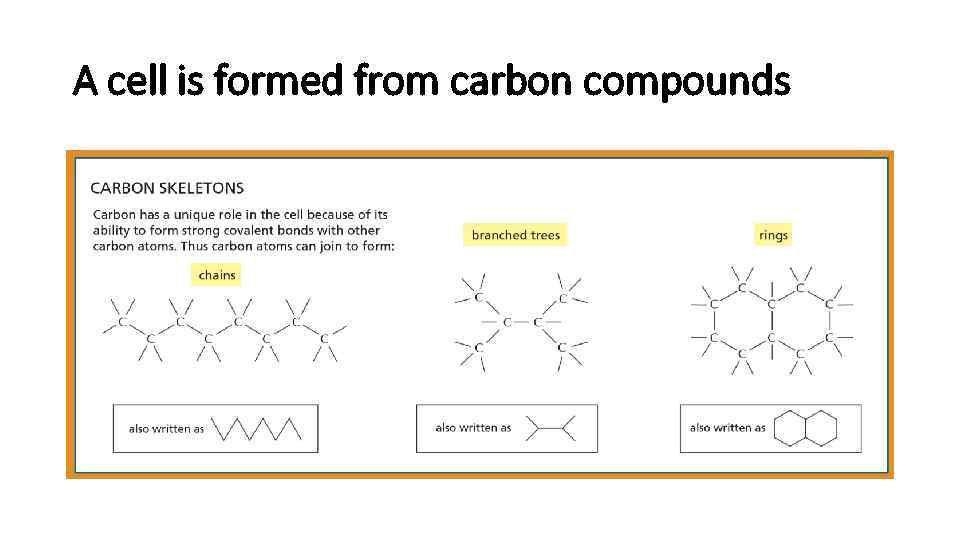
A cell is formed from carbon compounds
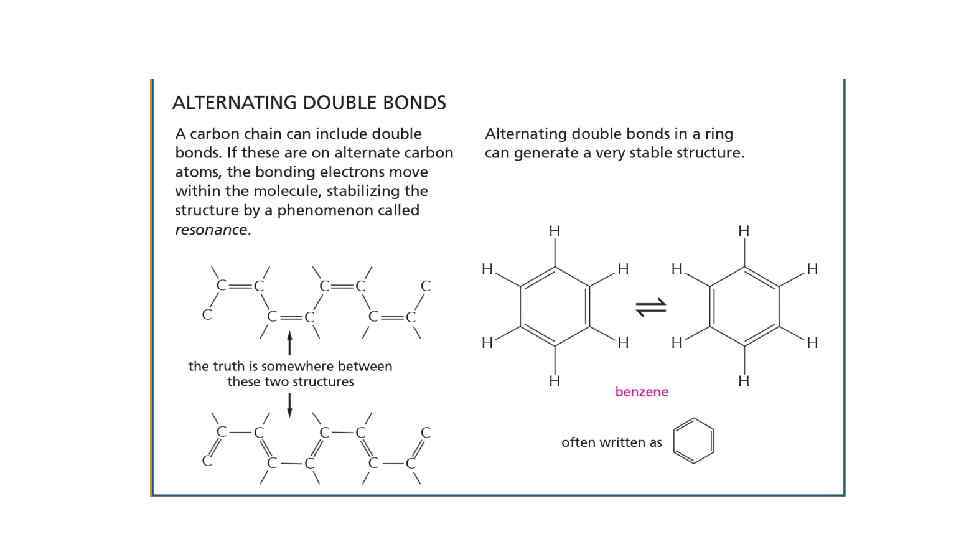
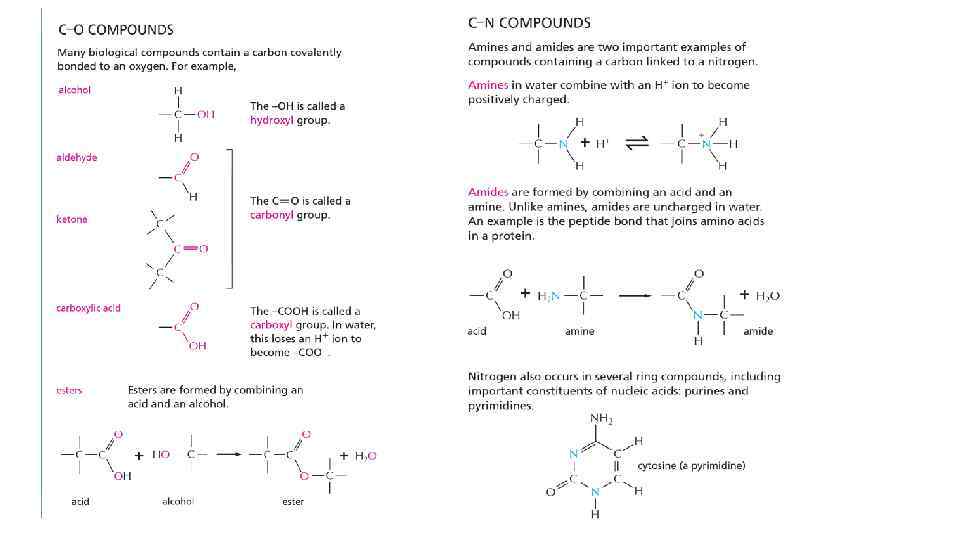
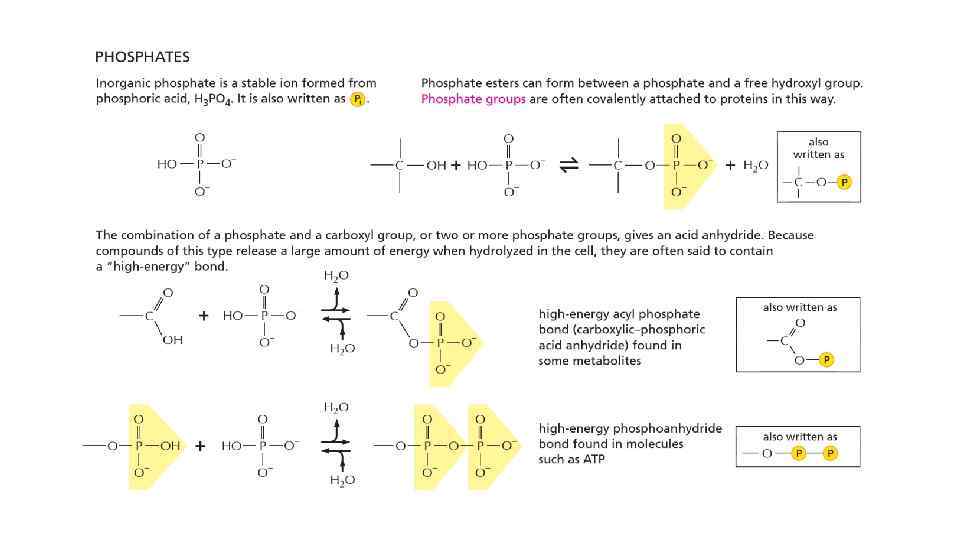
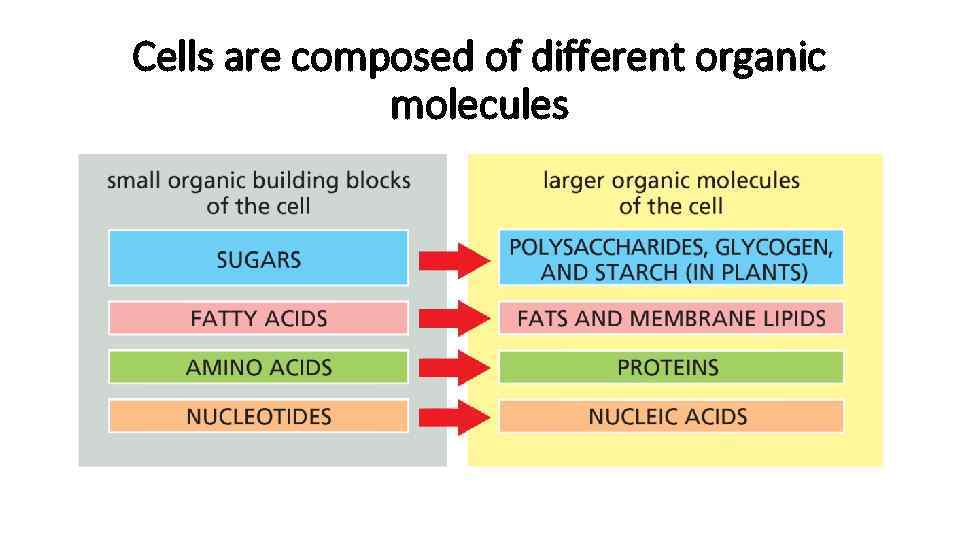
Cells are composed of different organic molecules
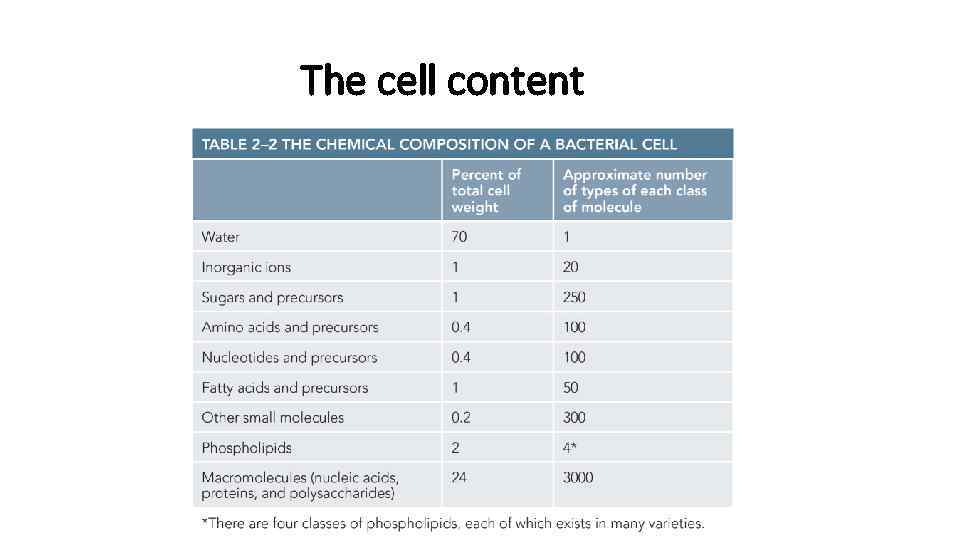
The cell content

Carbohydrates • The simplest sugars are monomers with general formula Cn. H 2 n. On • The "n" can be 3, 4, 5 or 6 • Glucose monomer can differ in its structure by moving OH group, thus creating new isomers • Therefore, glucose can also be in D(right) and L(left) forms thar are mirror images of each other. Therefore we call them optical isomers
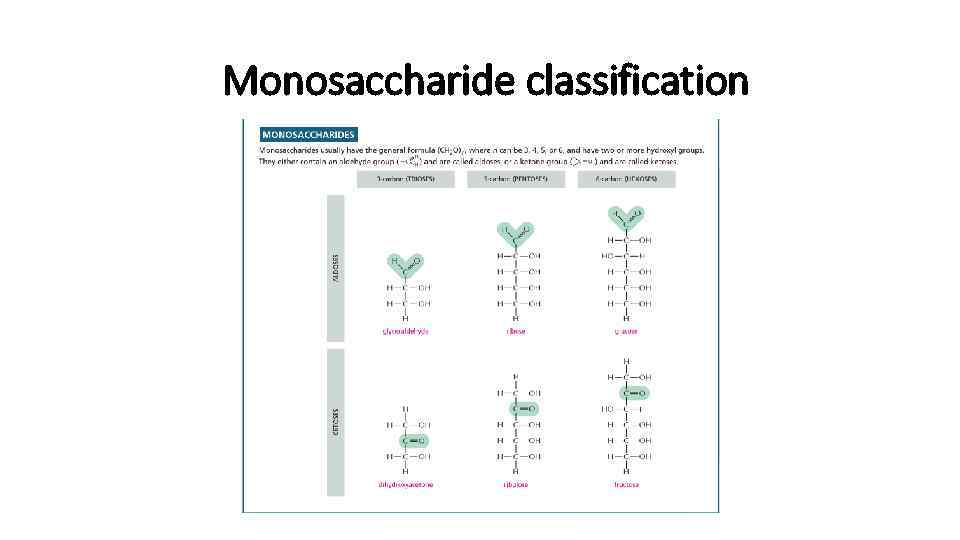
Monosaccharide classification
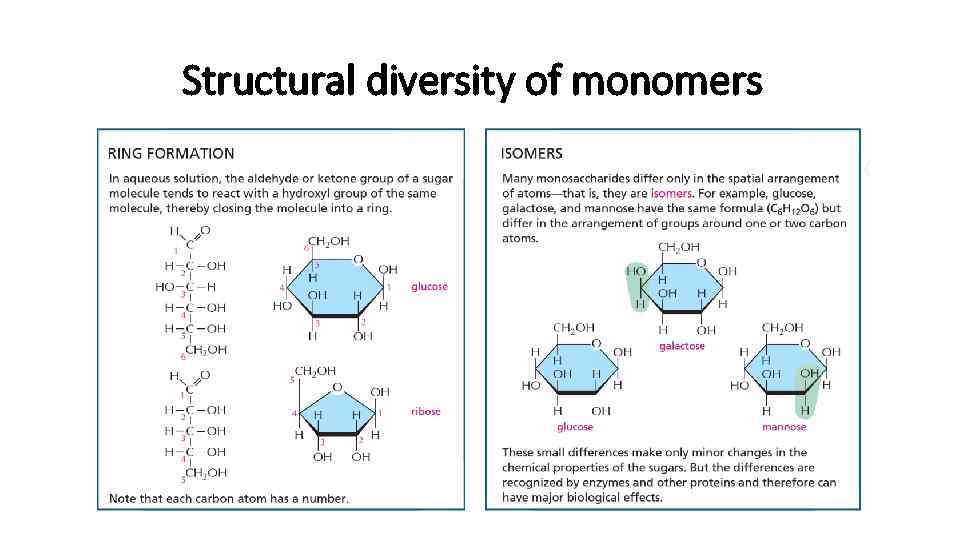
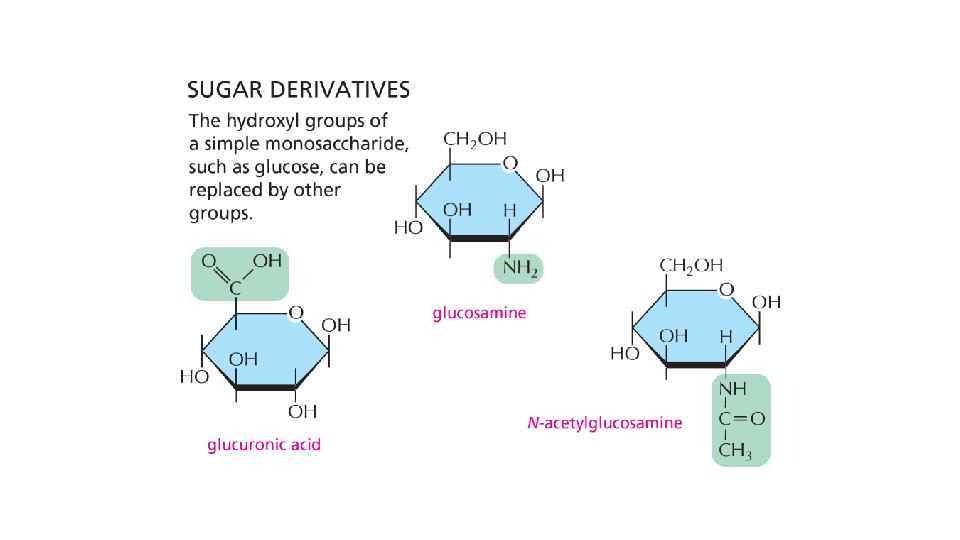
Structural diversity of monomers
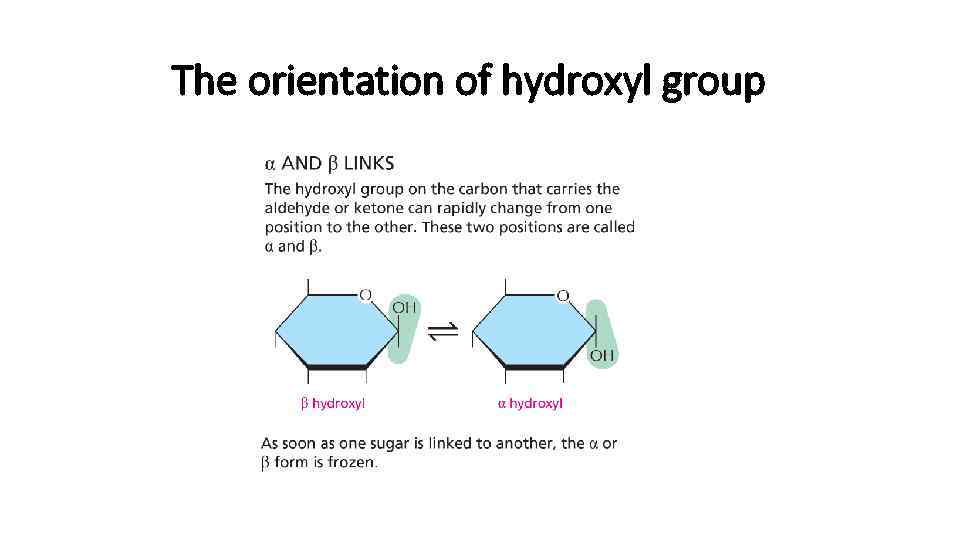
The orientation of hydroxyl group
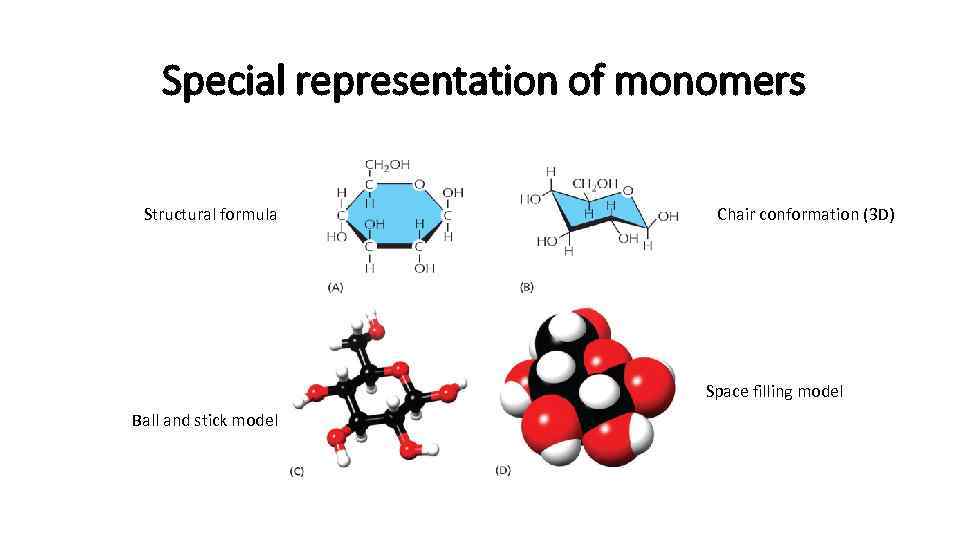
Special representation of monomers Structural formula Chair conformation (3 D) Space filling model Ball and stick model
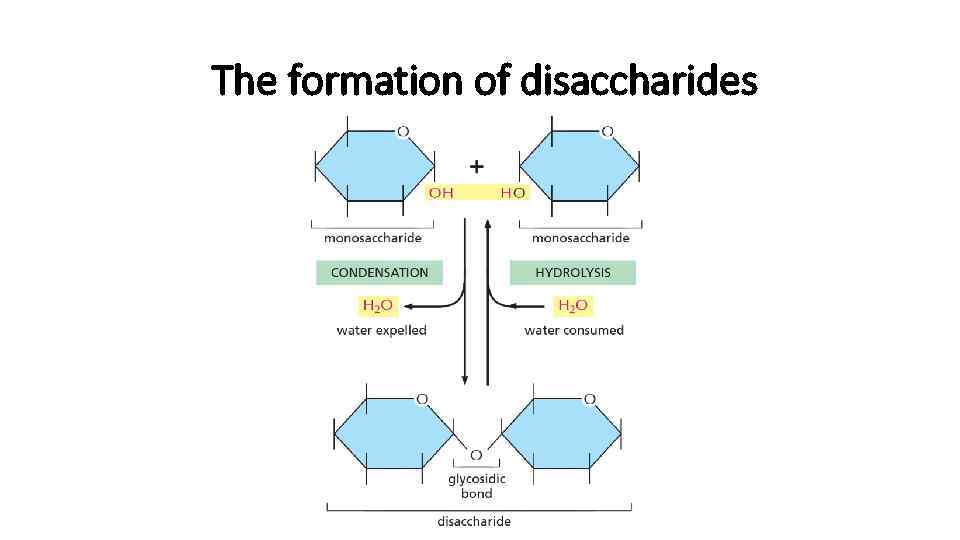
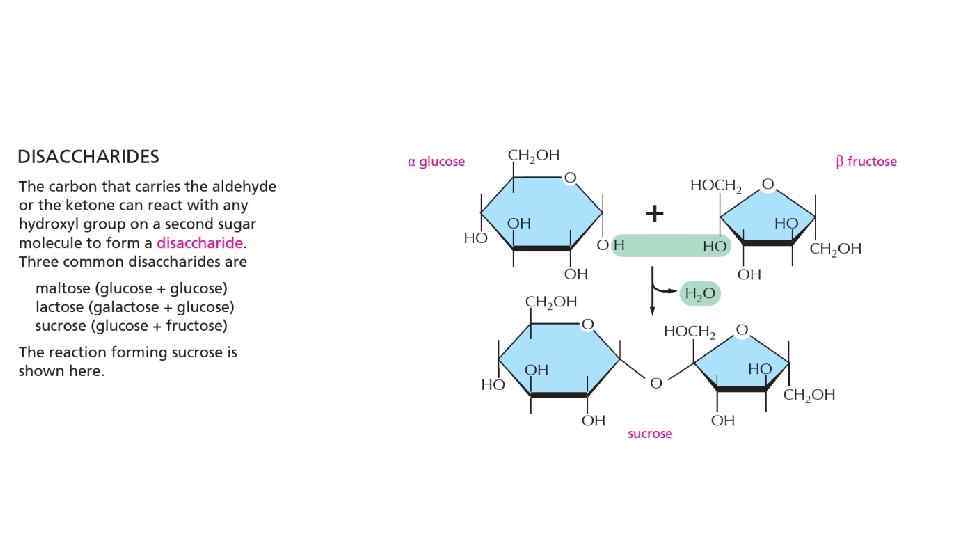
The formation of disaccharides
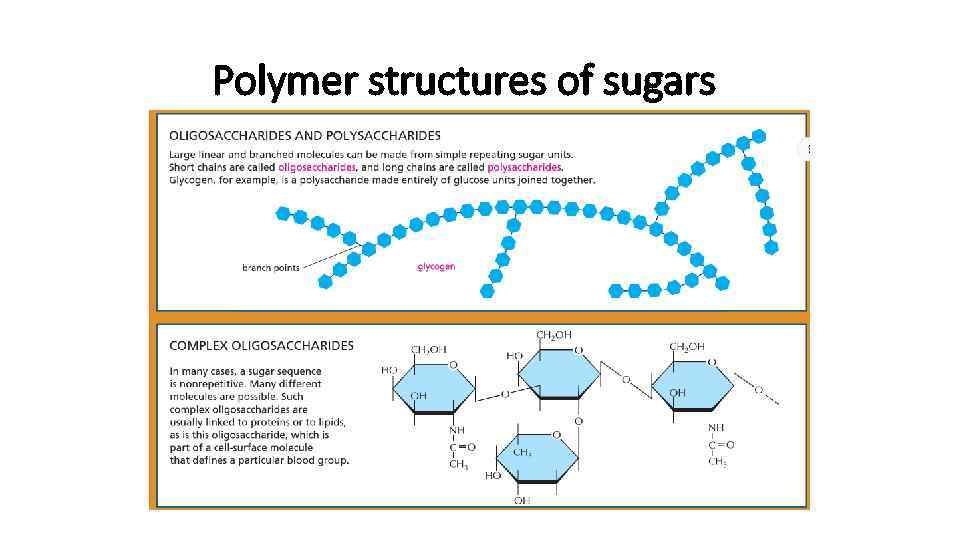
Polymer structures of sugars
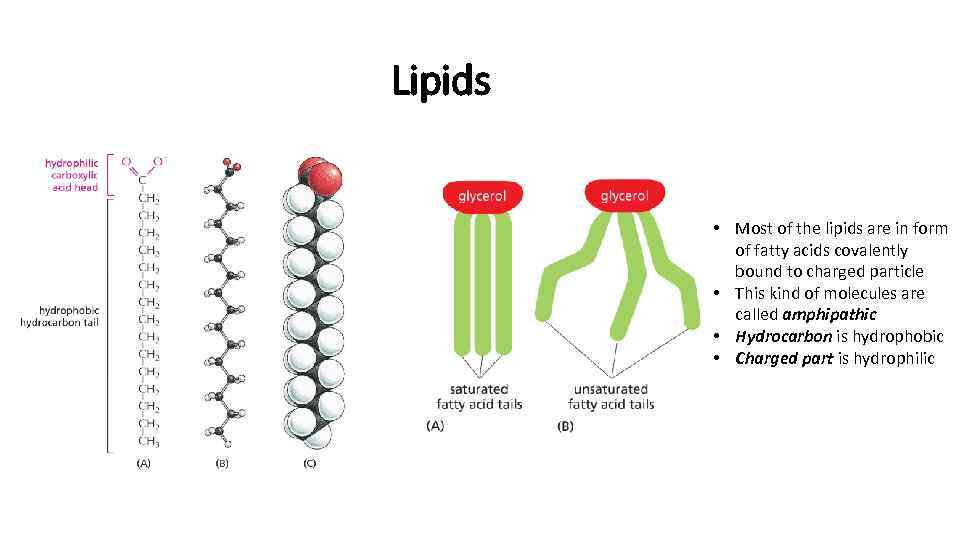
Lipids • Most of the lipids are in form of fatty acids covalently bound to charged particle • This kind of molecules are called amphipathic • Hydrocarbon is hydrophobic • Charged part is hydrophilic
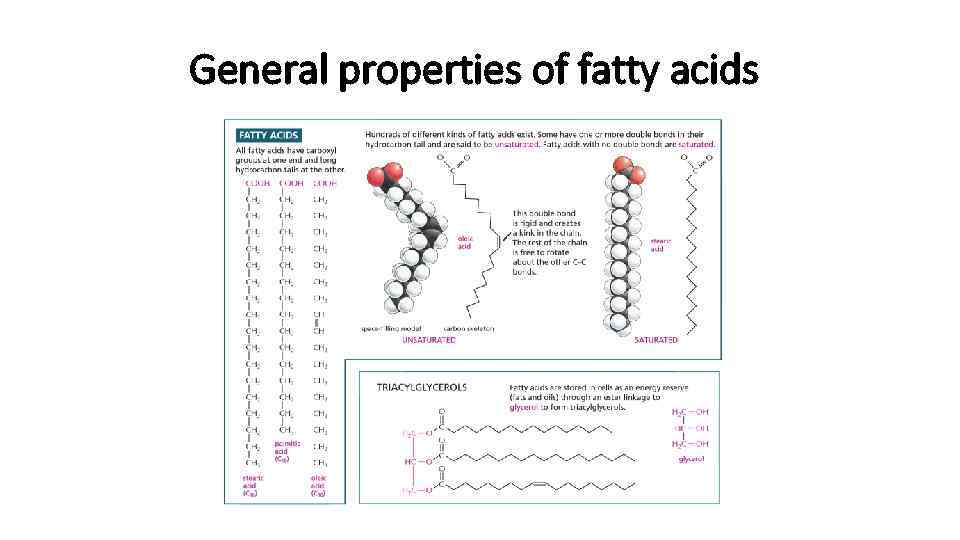
General properties of fatty acids
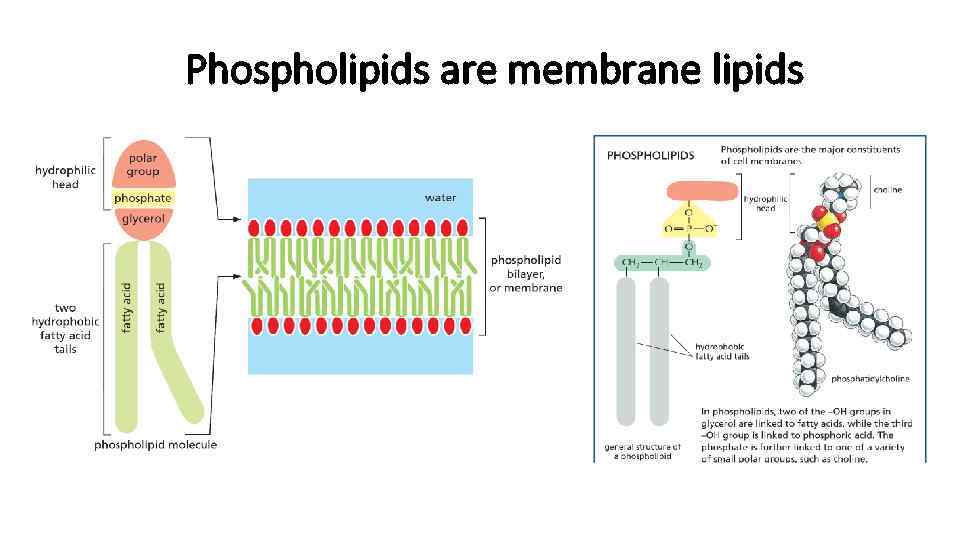
Phospholipids are membrane lipids
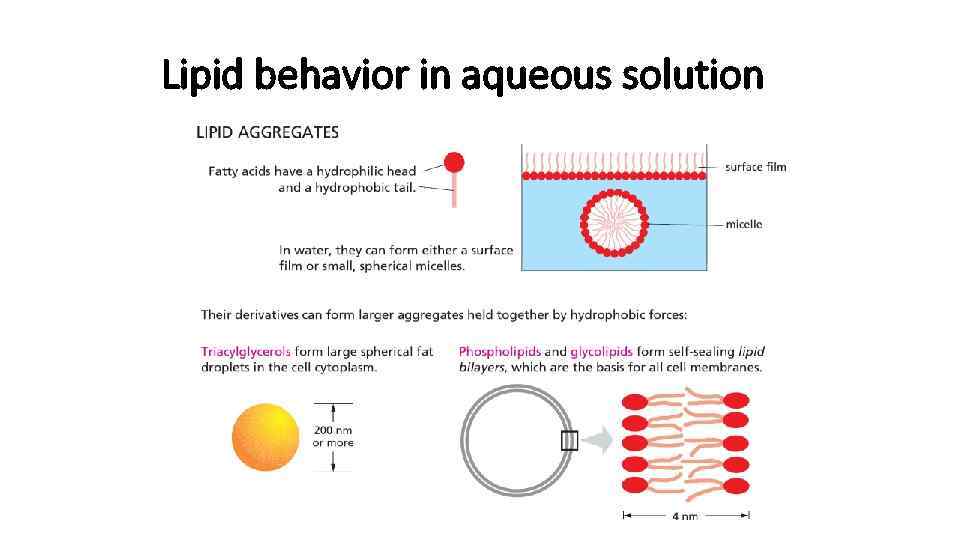
Lipid behavior in aqueous solution
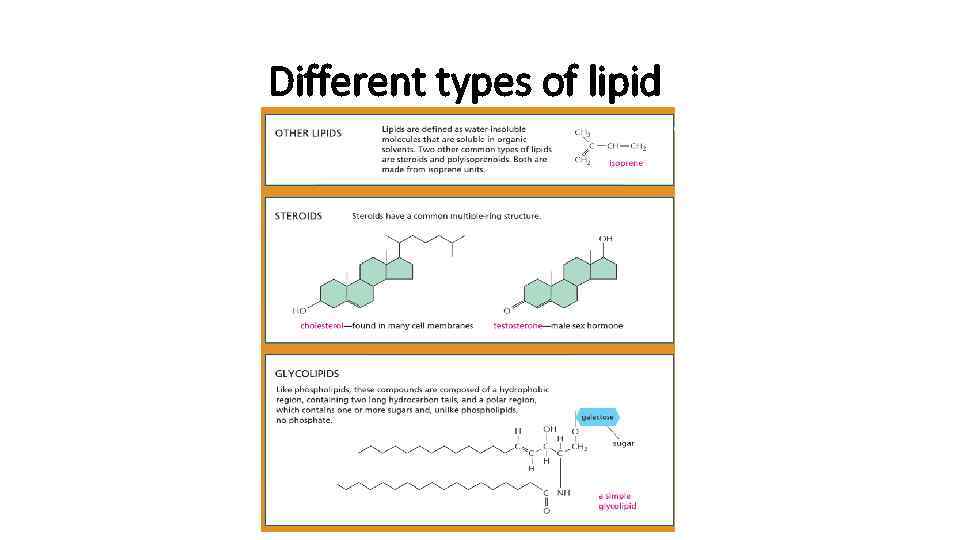
Different types of lipid
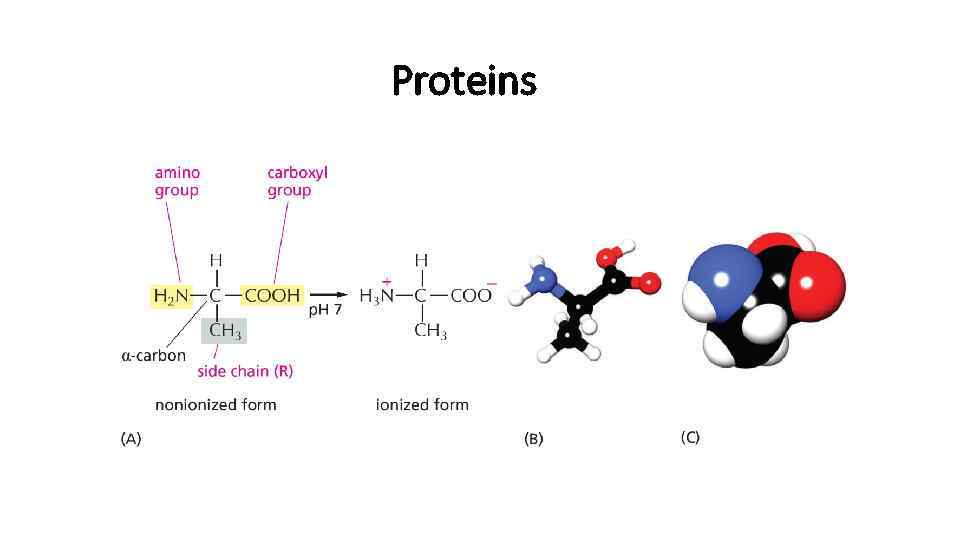
Proteins
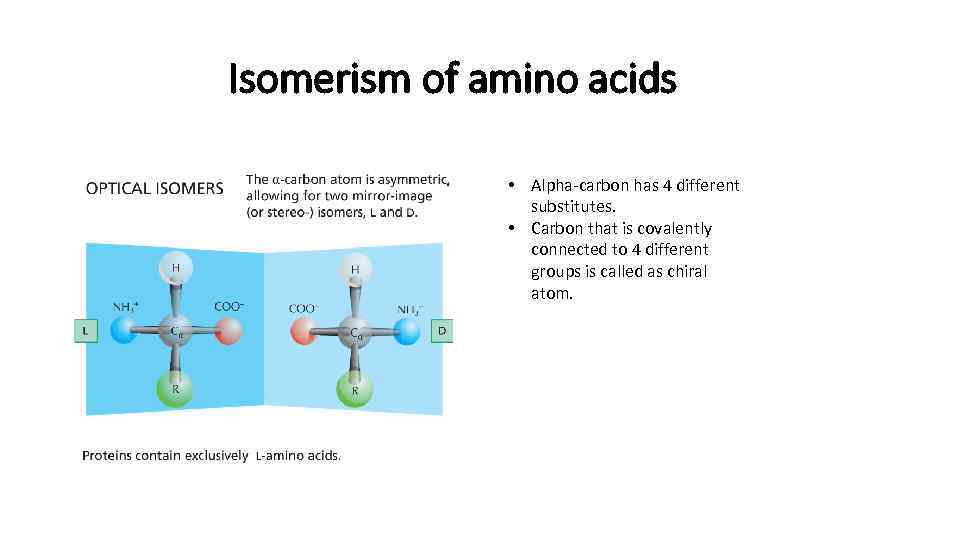
Isomerism of amino acids • Alpha-carbon has 4 different substitutes. • Carbon that is covalently connected to 4 different groups is called as chiral atom.
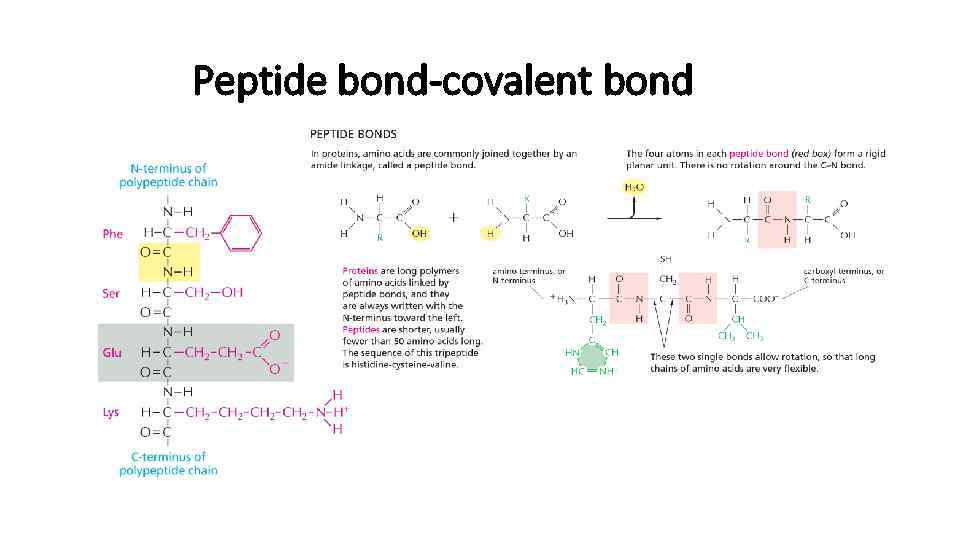
Peptide bond-covalent bond
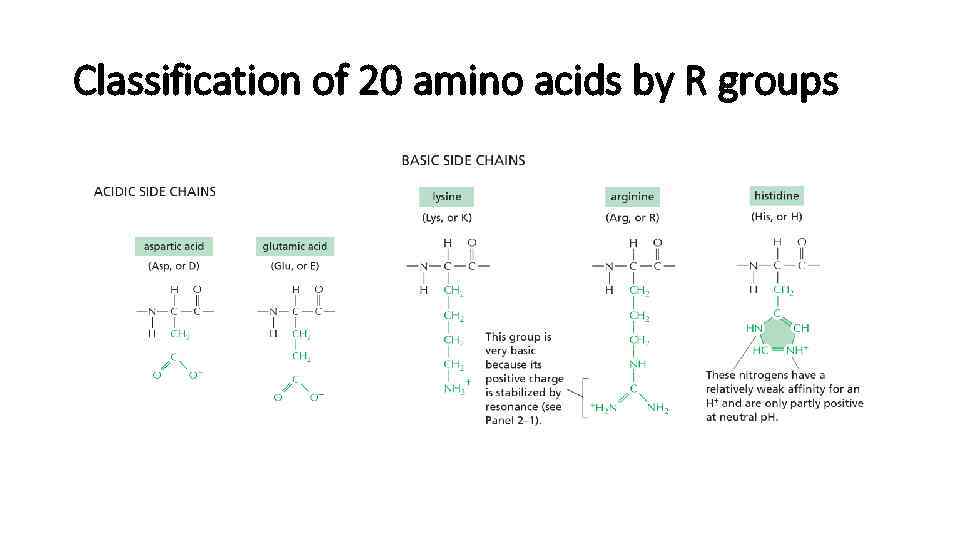
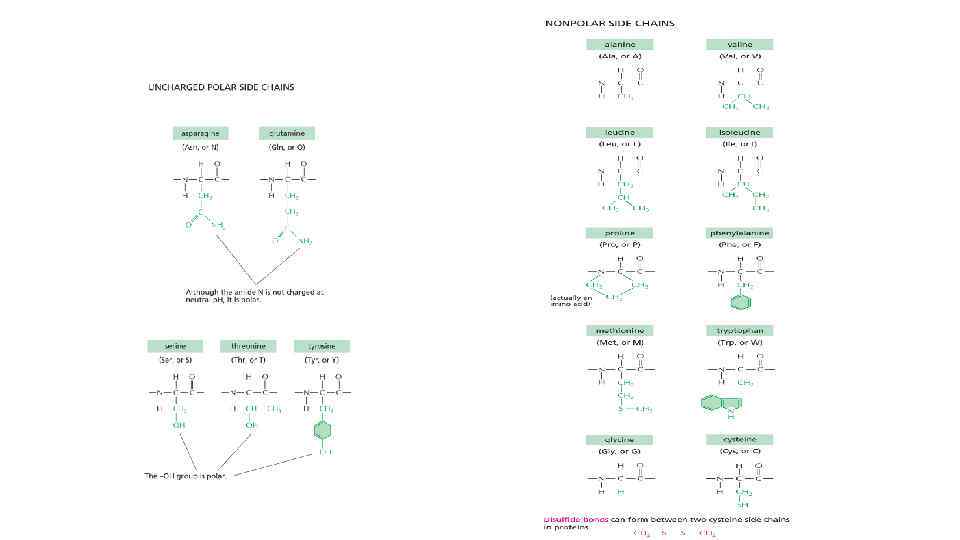
Classification of 20 amino acids by R groups
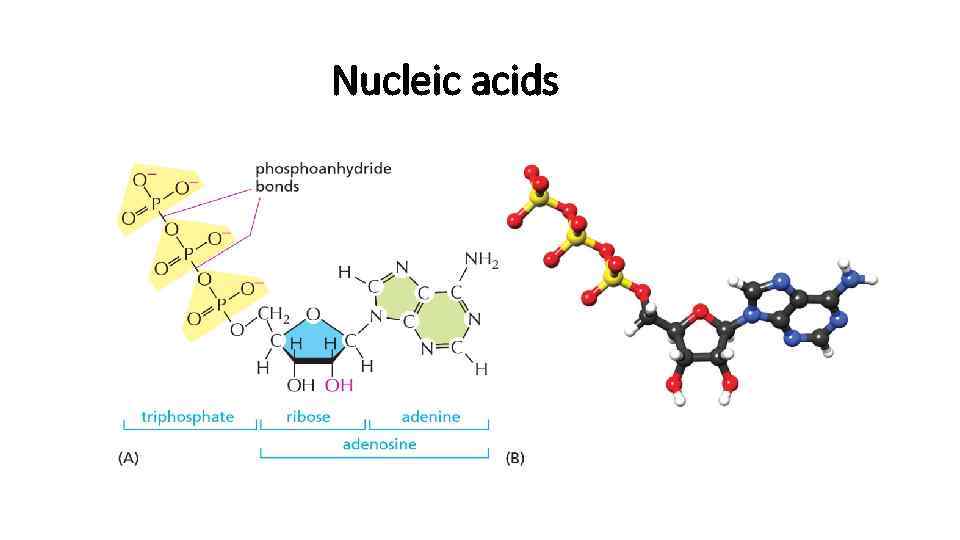
Nucleic acids
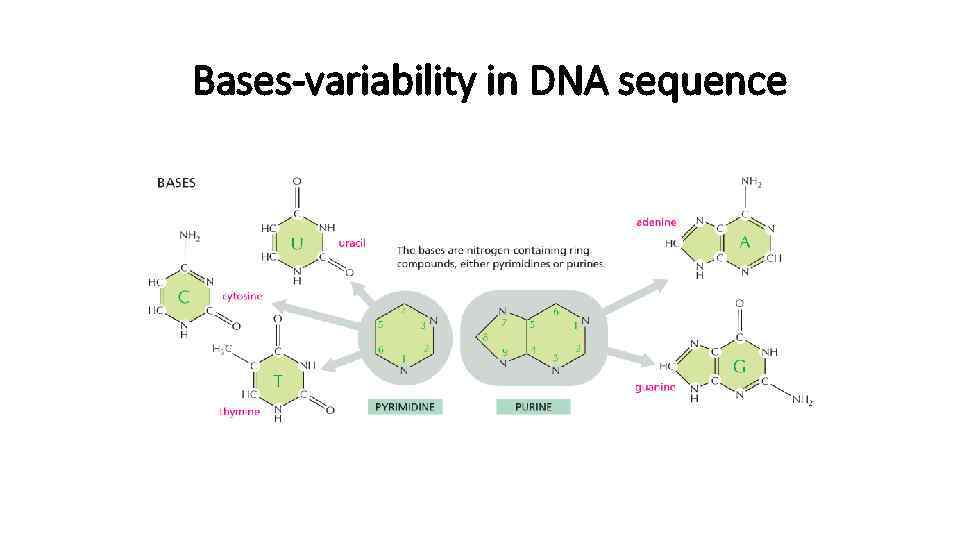
Bases-variability in DNA sequence
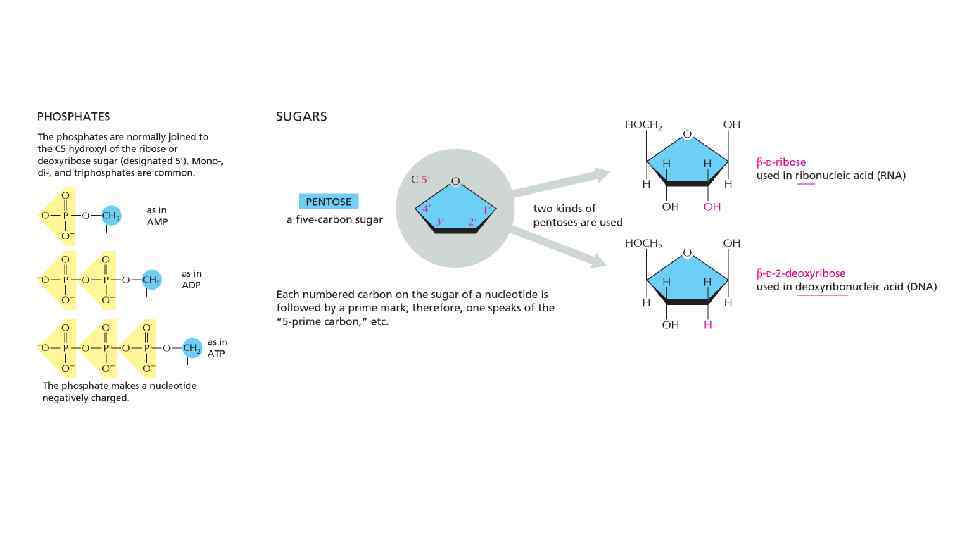
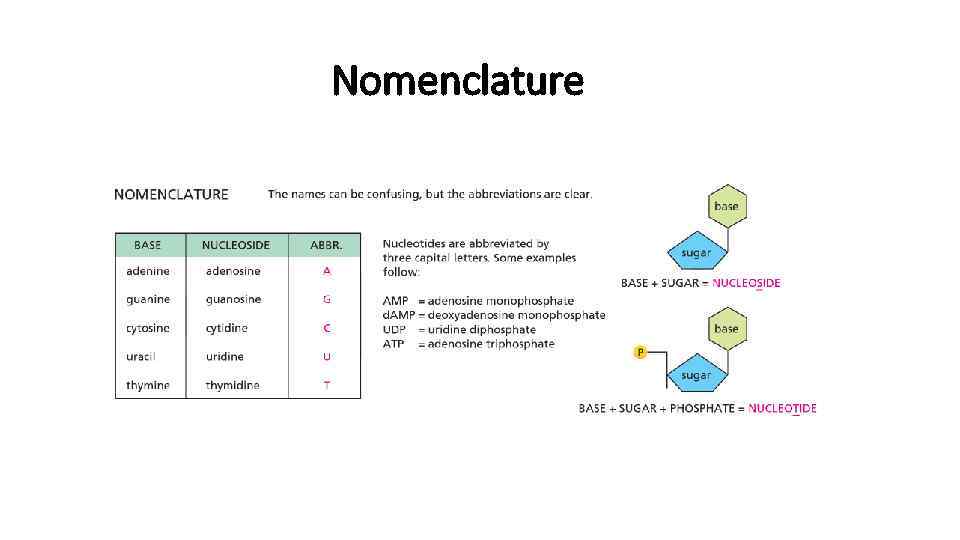
Nomenclature
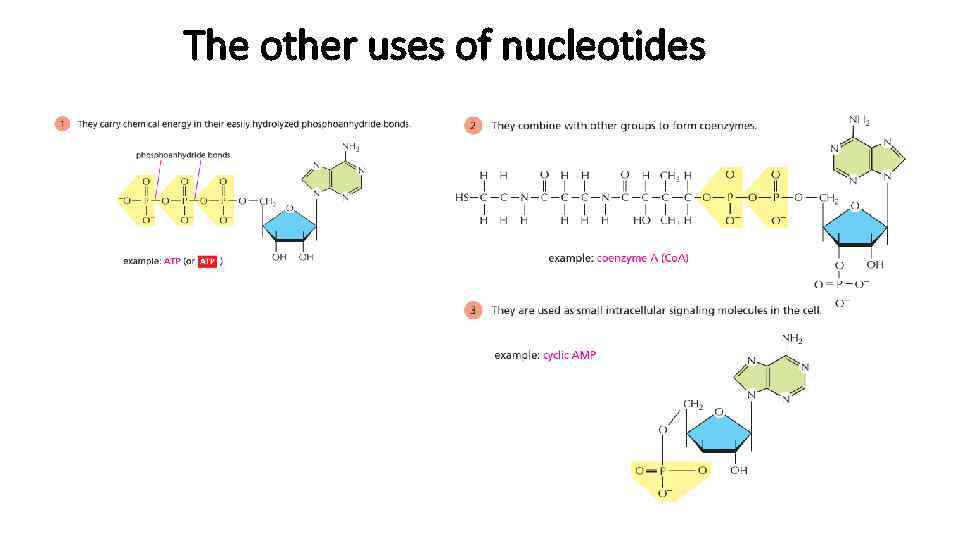
The other uses of nucleotides
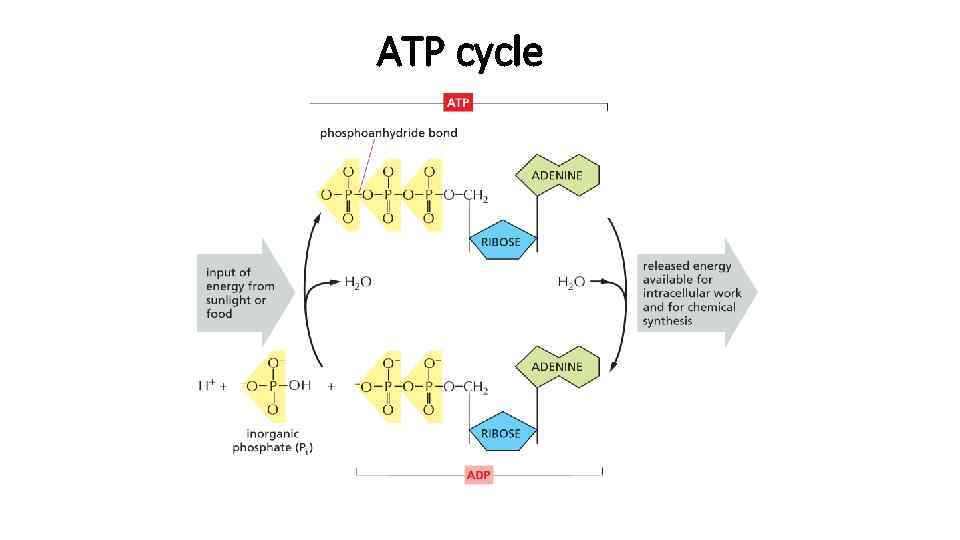
ATP cycle
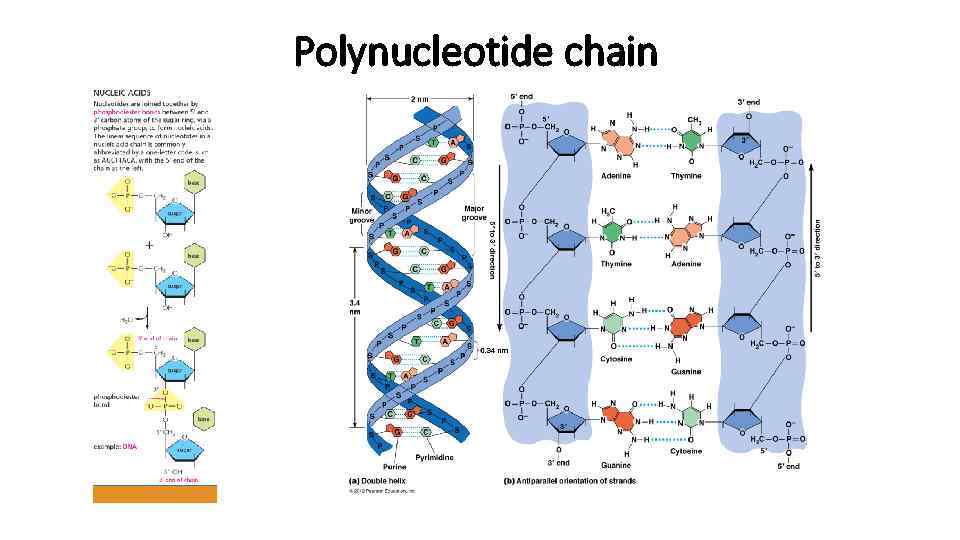
Polynucleotide chain
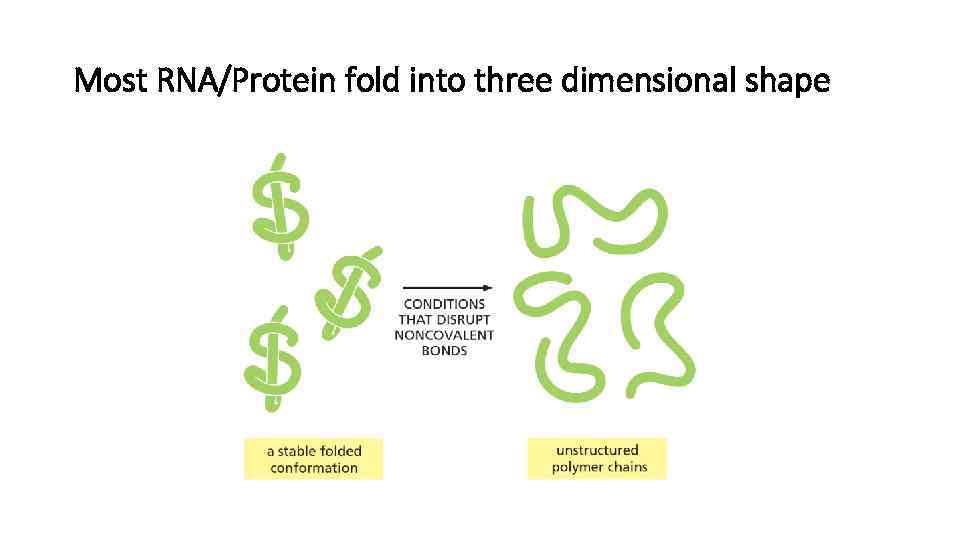
Most RNA/Protein fold into three dimensional shape
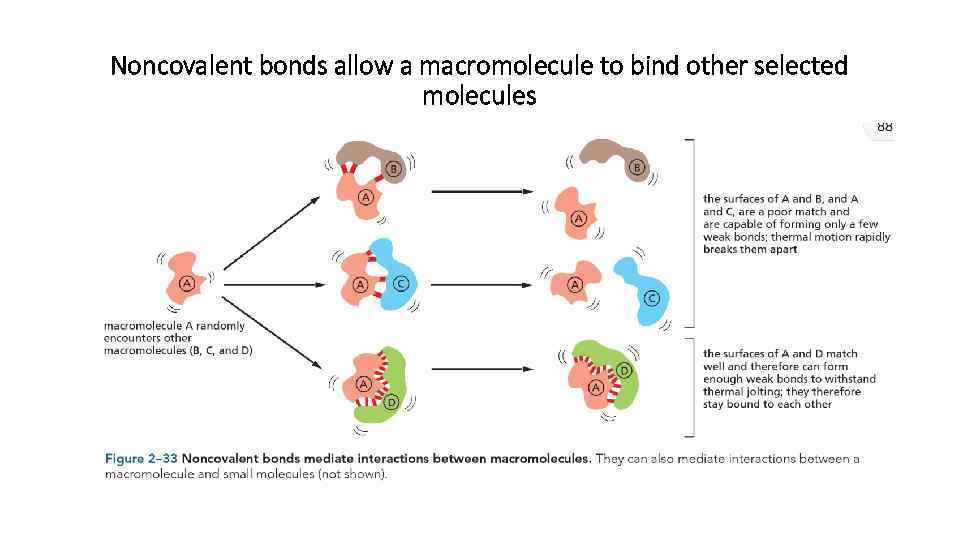
Noncovalent bonds allow a macromolecule to bind other selected molecules
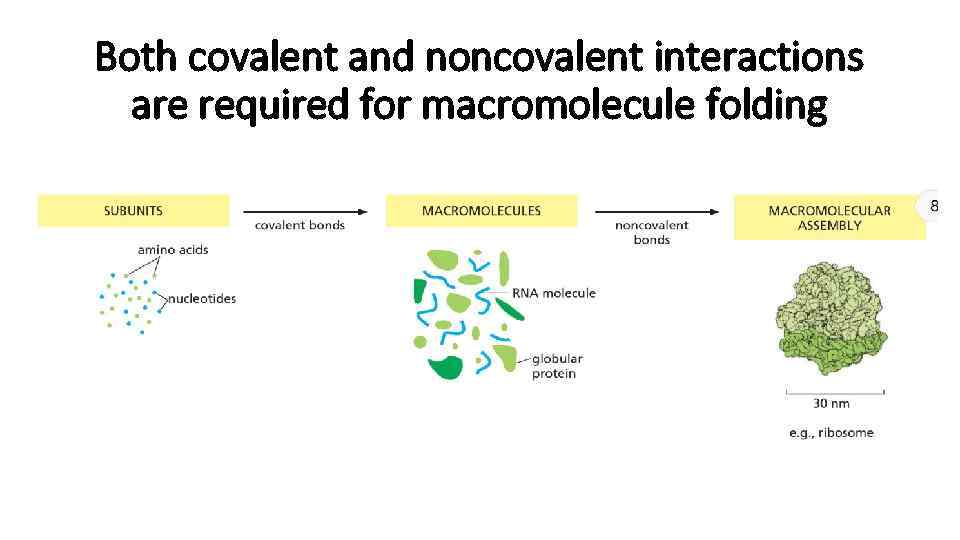
Both covalent and noncovalent interactions are required for macromolecule folding

Reference • Essential Cell Biology 4 th edition. Chapter 2
Small Cell Molecules.pptx