f03e4841e2342174460762755519ad3e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32

Small local CSDs in a world of globalization and consolidation Peter Falk, Product Director, EXIGO CSD AMEDA meeting, Marrakech, 20 – 21 April 2006

OMX owns exchanges in the Nordic Baltic region and develops and provides technology and system services to financial companies around the globe. 2
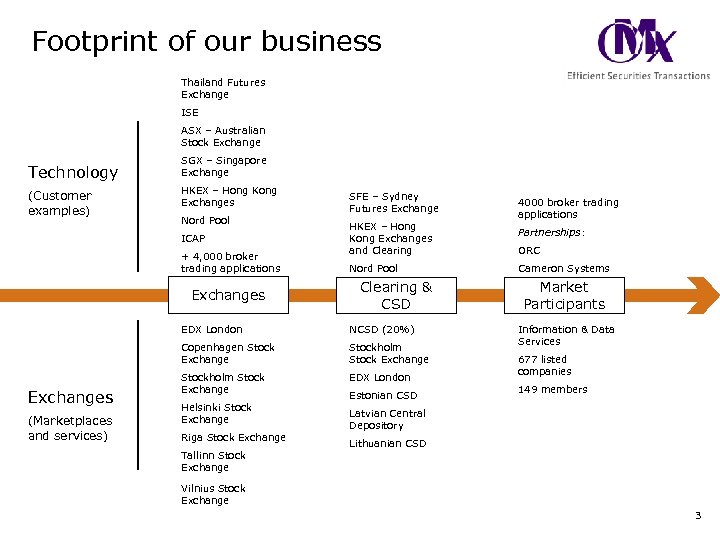
Footprint of our business Thailand Futures Exchange ISE ASX – Australian Stock Exchange Technology (Customer examples) SGX – Singapore Exchange HKEX – Hong Kong Exchanges Nord Pool ICAP + 4, 000 broker trading applications Exchanges SFE – Sydney Futures Exchange HKEX – Hong Kong Exchanges and Clearing Nord Pool Clearing & CSD EDX London Copenhagen Stock Exchanges (Marketplaces and services) NCSD (20%) Stockholm Stock Exchange EDX London Helsinki Stock Exchange Riga Stock Exchange Tallinn Stock Exchange Estonian CSD 4000 broker trading applications Partnerships: ORC Cameron Systems Market Participants Information & Data Services 677 listed companies 149 members Latvian Central Depository Lithuanian CSD Vilnius Stock Exchange 3
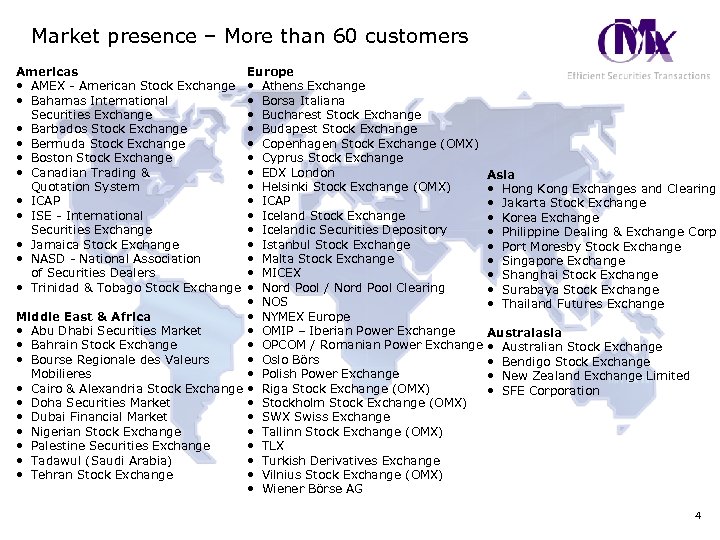
Market presence – More than 60 customers Americas • AMEX - American Stock Exchange • Bahamas International Securities Exchange • Barbados Stock Exchange • Bermuda Stock Exchange • Boston Stock Exchange • Canadian Trading & Quotation System • ICAP • ISE - International Securities Exchange • Jamaica Stock Exchange • NASD - National Association of Securities Dealers • Trinidad & Tobago Stock Exchange Europe • Athens Exchange • Borsa Italiana • Bucharest Stock Exchange • Budapest Stock Exchange • Copenhagen Stock Exchange (OMX) • Cyprus Stock Exchange • EDX London Asia • Helsinki Stock Exchange (OMX) • Hong Kong Exchanges and Clearing • ICAP • Jakarta Stock Exchange • Iceland Stock Exchange • Korea Exchange • Icelandic Securities Depository • Philippine Dealing & Exchange Corp • Istanbul Stock Exchange • Port Moresby Stock Exchange • Malta Stock Exchange • Singapore Exchange • MICEX • Shanghai Stock Exchange • Nord Pool / Nord Pool Clearing • Surabaya Stock Exchange • NOS • Thailand Futures Exchange Middle East & Africa • NYMEX Europe • Abu Dhabi Securities Market • OMIP – Iberian Power Exchange Australasia • Bahrain Stock Exchange • OPCOM / Romanian Power Exchange • Australian Stock Exchange • Bourse Regionale des Valeurs • Oslo Börs • Bendigo Stock Exchange Mobilieres • Polish Power Exchange • New Zealand Exchange Limited • Cairo & Alexandria Stock Exchange • Riga Stock Exchange (OMX) • SFE Corporation • Doha Securities Market • Stockholm Stock Exchange (OMX) • Dubai Financial Market • SWX Swiss Exchange • Nigerian Stock Exchange • Tallinn Stock Exchange (OMX) • Palestine Securities Exchange • TLX • Tadawul (Saudi Arabia) • Turkish Derivatives Exchange • Tehran Stock Exchange • Vilnius Stock Exchange (OMX) • Wiener Börse AG 4
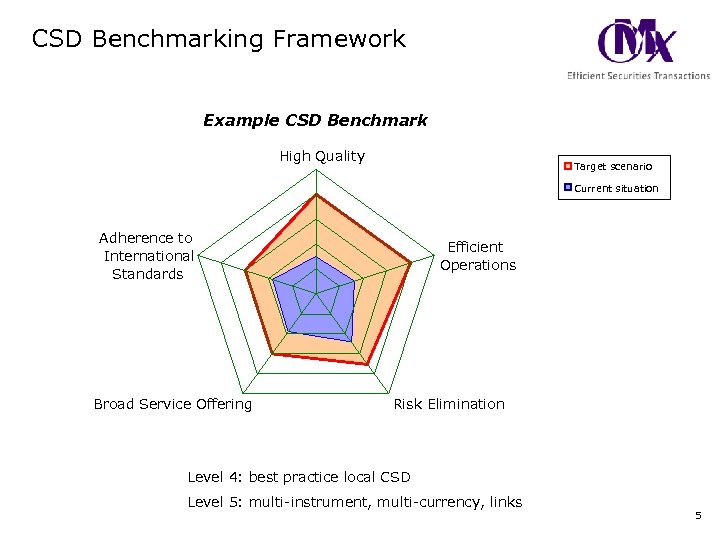
CSD Benchmarking Framework Example CSD Benchmark High Quality Target scenario Current situation Adherence to International Standards Broad Service Offering Efficient Operations Risk Elimination Level 4: best practice local CSD Level 5: multi-instrument, multi-currency, links 5
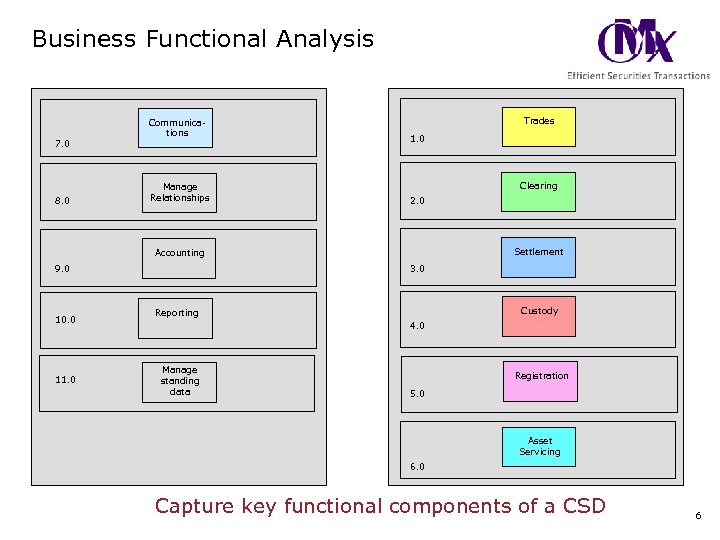
Business Functional Analysis 7. 0 8. 0 Communications Manage Relationships Trades 1. 0 Clearing 2. 0 Settlement Accounting 9. 0 10. 0 11. 0 3. 0 Custody Reporting 4. 0 Manage standing data Registration 5. 0 Asset Servicing 6. 0 Capture key functional components of a CSD 6

Agenda • The current situation • Problems and challenges • Driving forces • Elements to a strategy 7

Some characteristics • Local participants • Local securities • Small part of regional and global market • Small volume but also a broad offering of securities • Local market consolidation not yet feasible • Dematerialized? 8
Baltic region 8 markets 8 currencies A small corner of Europe (only a few percent) A small corner of The Nordic Region (only a few percent) 9

20. 000 million € in custody 10
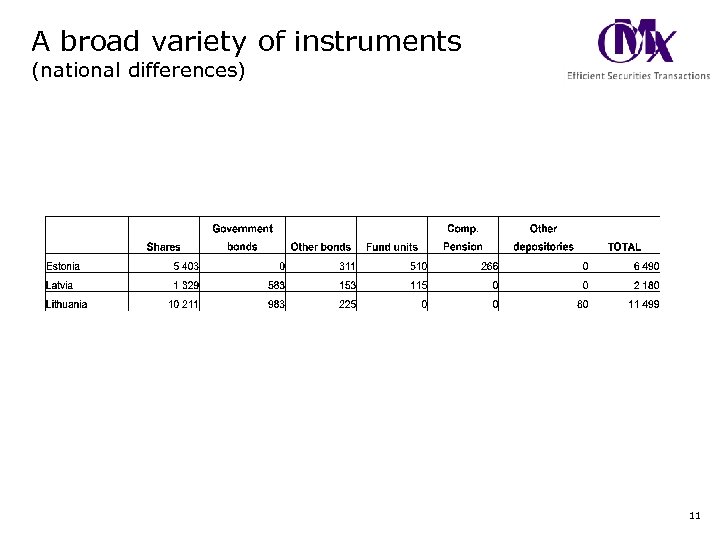
A broad variety of instruments (national differences) 11
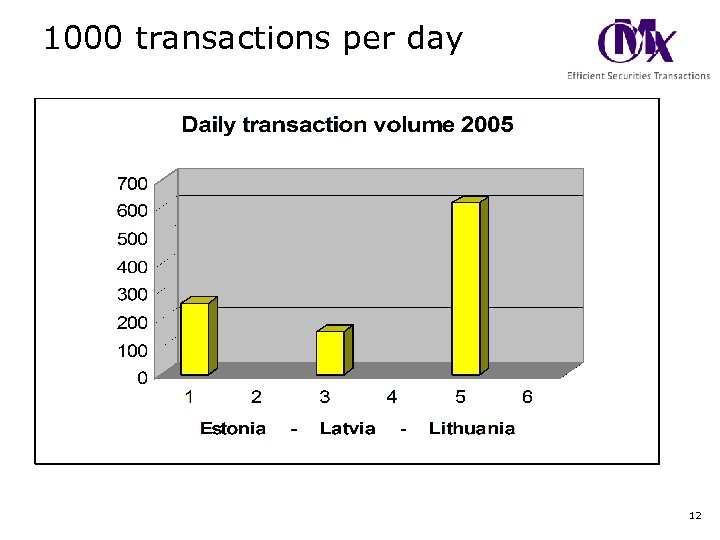
1000 transactions per day 12

Agenda • The current situation • Problems and challenges • Driving forces • Elements to a strategy 13

Problems and challenges – local level • Size – Small size = small revenues – Small size = lack of development resources • Lack of standard interfaces • Lack of functionality – Real time Dv. P – More than one batch settlement 14

Problems and challenges – regional level • Different market practices – Account structure – Corporate actions processing – Settlement procedures – Reporting requirements • Different rules and regulations – Account structure – Unlisted companies – Reporting requirements • Different custody service solutions Not all differences are important! 15

Agenda • The current situation • Problems and challenges • Driving forces • Elements to a strategy 16

Driving forces • Globalization, regionalization, single market • Localization • Regional and international players • Moving towards standards • Efficiency, costs, competitive pressure 17

CSDs – a historical view Improvement market by market • Local models, local systems Role models • Frankfurter Kassenverein and DTC • Euroclear • VP and Sicovam Decades of convergence • ISSA, FIBV, G-30, BIS, IOSCO … CSDs are mature businesses undergoing great change 18
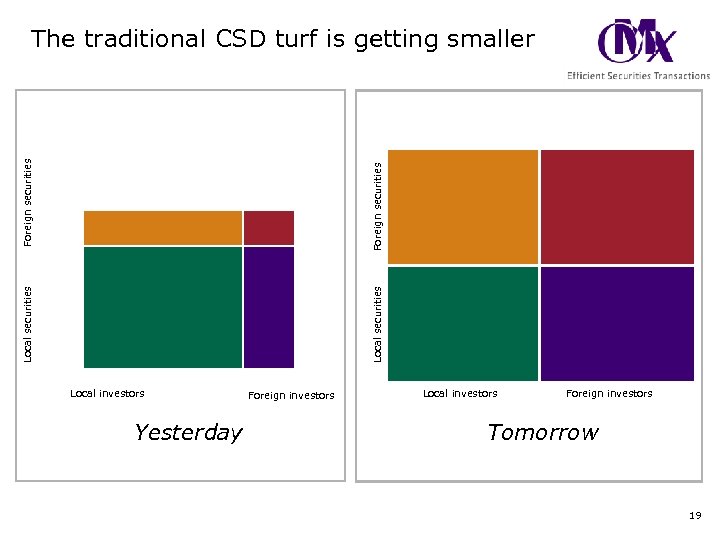
Local securities Foreign securities The traditional CSD turf is getting smaller Local investors Yesterday Foreign investors Local investors Foreign investors Tomorrow 19

Global initiatives with implications for CSDs • G-30 • The Giovannini Group – 1989: 9 recommendations (*) – 2003: 20 recommendations • CPSS (BIS/IOSCO) – 2001: Core principles – payment systems – 2001: Recommendations for securities settlement systems (*) – 2002: Assessment methodology – 2004: Risk management for CCPs • IMF and World Bank: FSAP assessments • Hague Convention: removal of conflict-of-law (*) = local scope – Action plan for removing the 15 barriers • ECB – 9 minimum operational standards for SSS • ECB / CESR – Moving 19 CPSS recommendations binding standards • The European Commission – Directives on collateral, finality, investment services – Principles for functional regulation. 20

Conflict: International vs. local Regional and international market participants request easy, secure and low cost access to several markets. Large issuers require large liquidity pool Small and medium-sized issuers, local investors, local participants and domestic considerations request extremely efficient STP transaction flows for domestic trades 21
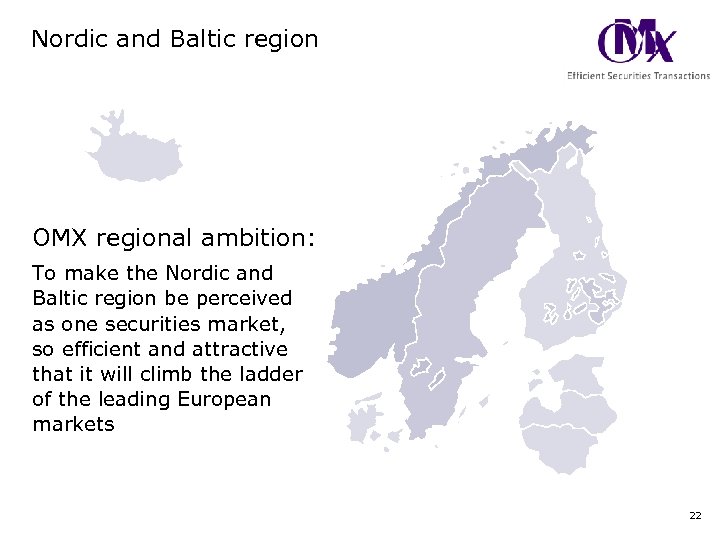
Nordic and Baltic region OMX regional ambition: To make the Nordic and Baltic region be perceived as one securities market, so efficient and attractive that it will climb the ladder of the leading European markets 22
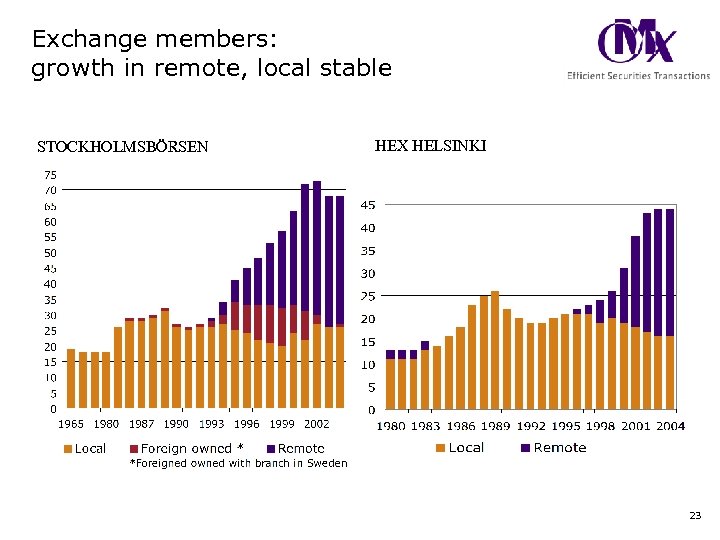
Exchange members: growth in remote, local stable STOCKHOLMSBÖRSEN HEX HELSINKI 23
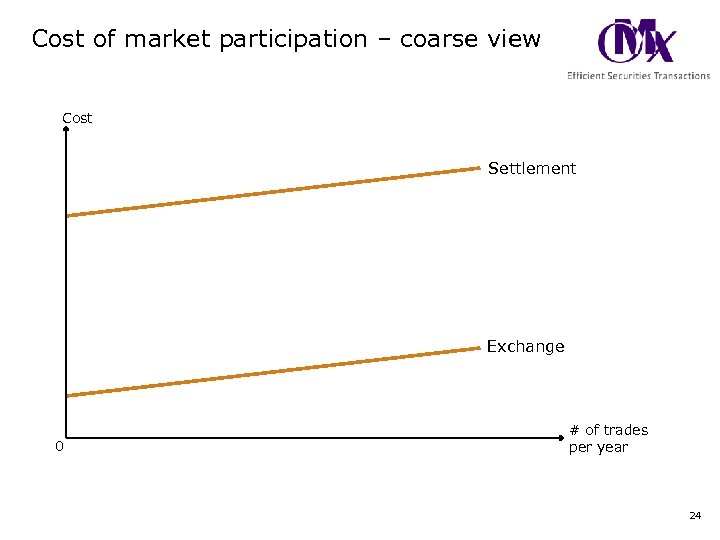
Cost of market participation – coarse view Cost Settlement Exchange 0 # of trades per year 24
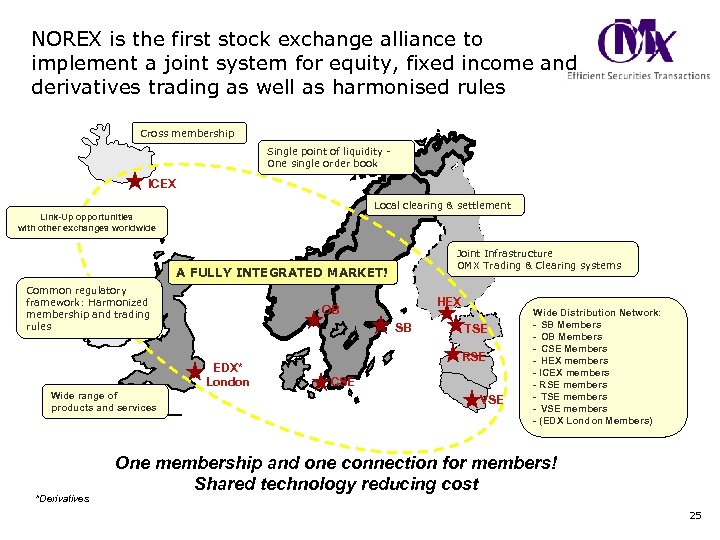
NOREX is the first stock exchange alliance to implement a joint system for equity, fixed income and derivatives trading as well as harmonised rules Cross membership Single point of liquidity One single order book ICEX Local clearing & settlement Link-Up opportunities with other exchanges worldwide Joint Infrastructure OMX Trading & Clearing systems A FULLY INTEGRATED MARKET! Common regulatory framework: Harmonized membership and trading rules SB EDX* London Wide range of products and services *Derivatives HEX OB TSE RSE CSE VSE Wide Distribution Network: - SB Members - OB Members - CSE Members - HEX members - ICEX members - RSE members - TSE members - VSE members - (EDX London Members) One membership and one connection for members! Shared technology reducing cost 25
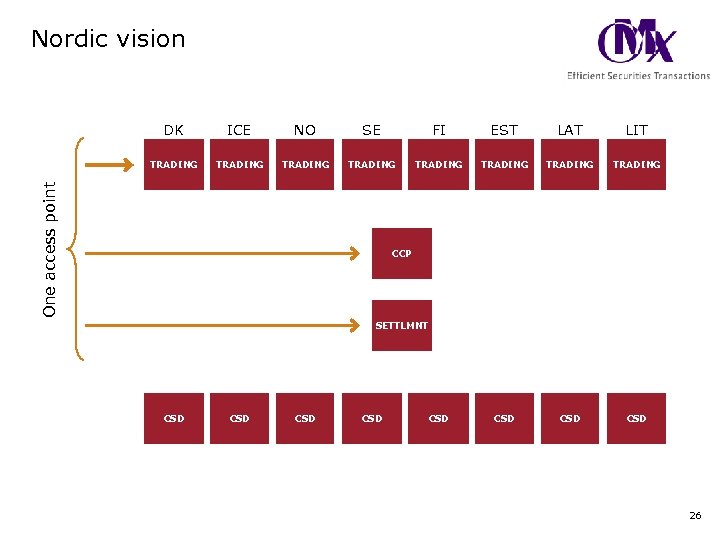
Nordic vision ICE NO SE FI EST LAT LIT TRADING TRADING CSD CSD One access point DK DK CCP SETTLMNT CSD CSD CSD 26

Agenda • The current situation • Problems and challenges • Driving forces • Elements to a strategy 27

Elements to a strategy • Local CSDs with local registers, local service and support • SWIFT standard messages • Realignment of rules and market practices (not all!) • Shared settlement • A single standard systems platform • Possibility to handle a broad list of instruments • Step by step implementation 28
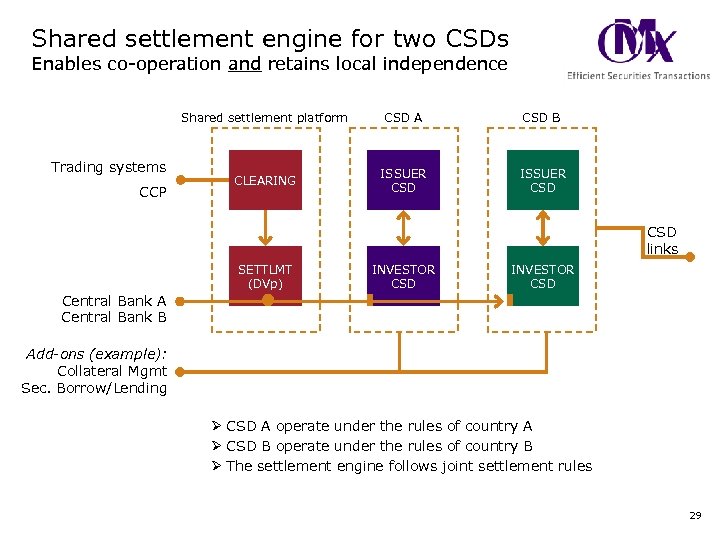
Shared settlement engine for two CSDs Enables co-operation and retains local independence Shared settlement platform Trading systems CCP CSD A CSD B CLEARING ISSUER CSD CSD links SETTLMT (DVp) INVESTOR CSD Central Bank A Central Bank B Add-ons (example): Collateral Mgmt Sec. Borrow/Lending Ø CSD A operate under the rules of country A Ø CSD B operate under the rules of country B Ø The settlement engine follows joint settlement rules 29
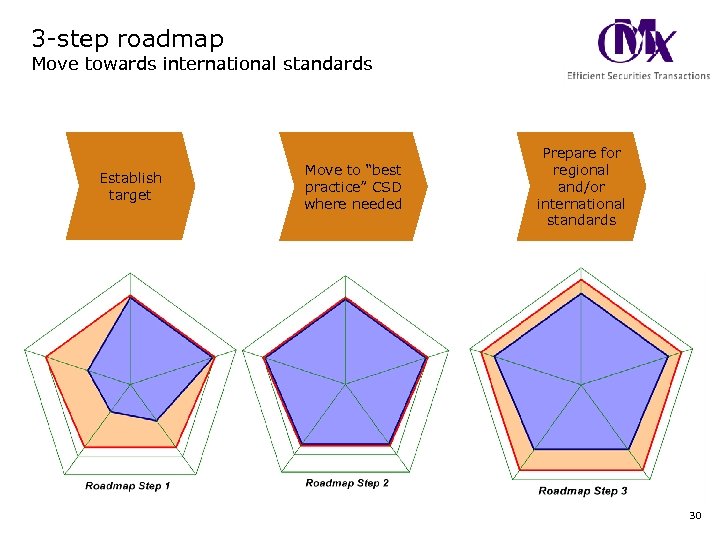
3 -step roadmap Move towards international standards Establish target Move to “best practice” CSD where needed Prepare for regional and/or international standards 30
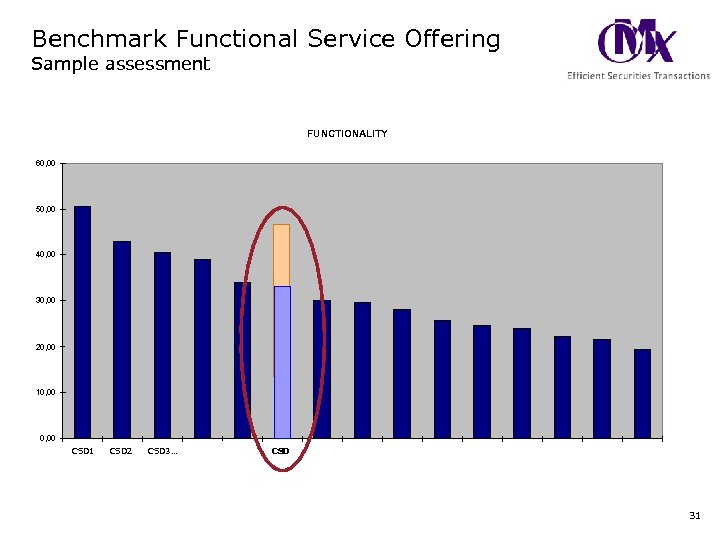
Benchmark Functional Service Offering Sample assessment FUNCTIONALITY 60, 00 50, 00 40, 00 30, 00 20, 00 10, 00 CSD 1 CSD 2 CSD 3… CSD 31

End of presentation Peter Falk, Product Director, EXIGO CSD AMEDA meeting, Marrakech, 20 – 21 April 2006
f03e4841e2342174460762755519ad3e.ppt