125cf7b38e11b443c99ae55c7aedacd2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 Small animal PET as non-invasive tool for preclinical imaging Marta Oteo Vives marta. oteo@ciemat. es Biomedical Applications of Radioisotopes and Pharmacokinetic Unit
Small animal PET as non-invasive tool for preclinical imaging Marta Oteo Vives marta. oteo@ciemat. es Biomedical Applications of Radioisotopes and Pharmacokinetic Unit
 Small animal PET as non-invasive tool for preclinical imaging Ø Preclinical imaging - Animal models - Major challenge for small animal imaging Ø Available imaging modalities Ø Preclinical PET equipment design Ø Small animal PET as a tool for quick and cheaper translational research Ø PET tracer development Ø Micro. PET imaging examples Cracow PET Symposium 23/09/2014 (C) Marta Oteo, CIEMAT, Madrid 2
Small animal PET as non-invasive tool for preclinical imaging Ø Preclinical imaging - Animal models - Major challenge for small animal imaging Ø Available imaging modalities Ø Preclinical PET equipment design Ø Small animal PET as a tool for quick and cheaper translational research Ø PET tracer development Ø Micro. PET imaging examples Cracow PET Symposium 23/09/2014 (C) Marta Oteo, CIEMAT, Madrid 2
 Why do we need preclinical imaging on living animals? ØNon-invasive in vivo validation of the candidate drugs and probes (observing multi-scale changes, from organ, tissue, cell, down to molecular level induced by physiological, pathological or pharmacological effects) is critical prior to perform human trials. ØIn vitro and ex vivo systems lack the interacting physiological factors present in vivo, facilitating investigation of systemic aspects of physiological processes and disease What small animal models are commonly used? v. Mouse is the most used, followed by rat Mouse is the ideal model: ØProlific (fast breeding cycle) ØInexpensive to house ØReproductive and nervous system are like those of humans ØSame diseases as humans Ø 99% homology with human genome ØBig advances in mouse genomics ØWide range of animal models of human disease v. Rat is commonly used in Neuroscience (because of the bigger size of its brain) Cracow PET Symposium 23/09/2014 (C) Marta Oteo, CIEMAT, Madrid 3
Why do we need preclinical imaging on living animals? ØNon-invasive in vivo validation of the candidate drugs and probes (observing multi-scale changes, from organ, tissue, cell, down to molecular level induced by physiological, pathological or pharmacological effects) is critical prior to perform human trials. ØIn vitro and ex vivo systems lack the interacting physiological factors present in vivo, facilitating investigation of systemic aspects of physiological processes and disease What small animal models are commonly used? v. Mouse is the most used, followed by rat Mouse is the ideal model: ØProlific (fast breeding cycle) ØInexpensive to house ØReproductive and nervous system are like those of humans ØSame diseases as humans Ø 99% homology with human genome ØBig advances in mouse genomics ØWide range of animal models of human disease v. Rat is commonly used in Neuroscience (because of the bigger size of its brain) Cracow PET Symposium 23/09/2014 (C) Marta Oteo, CIEMAT, Madrid 3
 What is the major challenge for small animal imaging? To visualize anatomical structures and monitor physiological activities on such a small scale High resolution imaging modalities are required Spatial resolution Sensitivity Signal/Noise Cracow PET Symposium 23/09/2014 (C) Marta Oteo, CIEMAT, Madrid 4
What is the major challenge for small animal imaging? To visualize anatomical structures and monitor physiological activities on such a small scale High resolution imaging modalities are required Spatial resolution Sensitivity Signal/Noise Cracow PET Symposium 23/09/2014 (C) Marta Oteo, CIEMAT, Madrid 4
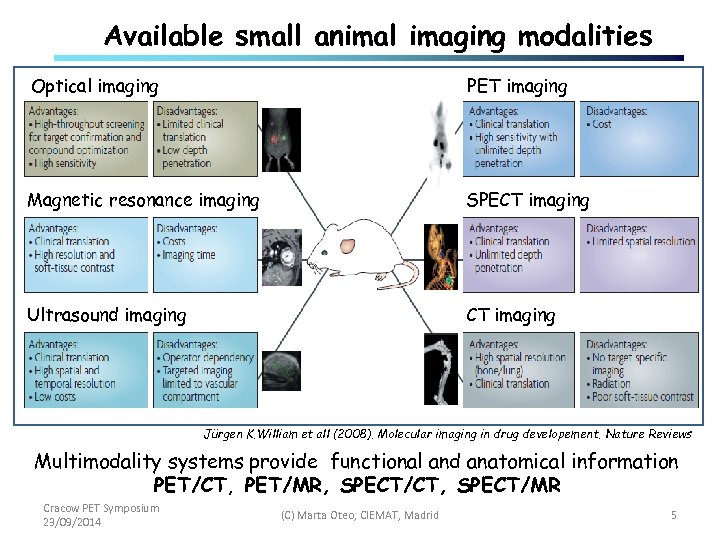 Available small animal imaging modalities Optical imaging PET imaging Magnetic resonance imaging SPECT imaging Ultrasound imaging CT imaging Jürgen K. William et all (2008). Molecular imaging in drug developement. Nature Reviews Multimodality systems provide functional and anatomical information PET/CT, PET/MR, SPECT/CT, SPECT/MR Cracow PET Symposium 23/09/2014 (C) Marta Oteo, CIEMAT, Madrid 5
Available small animal imaging modalities Optical imaging PET imaging Magnetic resonance imaging SPECT imaging Ultrasound imaging CT imaging Jürgen K. William et all (2008). Molecular imaging in drug developement. Nature Reviews Multimodality systems provide functional and anatomical information PET/CT, PET/MR, SPECT/CT, SPECT/MR Cracow PET Symposium 23/09/2014 (C) Marta Oteo, CIEMAT, Madrid 5
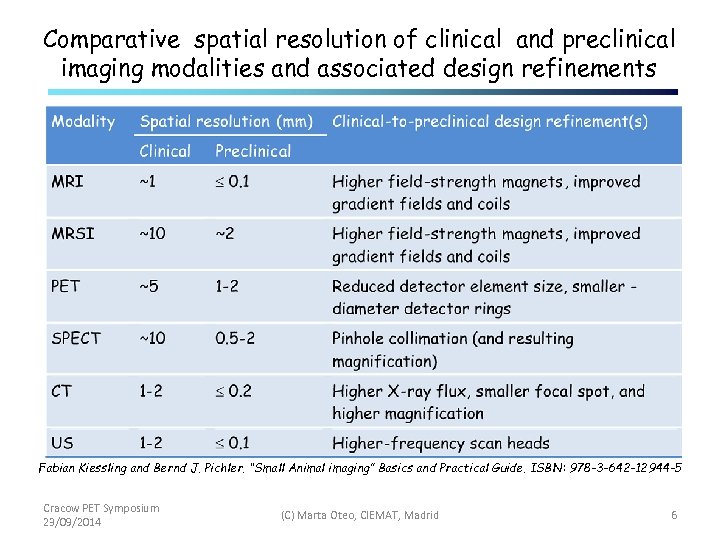 Comparative spatial resolution of clinical and preclinical imaging modalities and associated design refinements Fabian Kiessling and Bernd J. Pichler. “Small Animal imaging” Basics and Practical Guide. ISBN: 978 -3 -642 -12944 -5 Cracow PET Symposium 23/09/2014 (C) Marta Oteo, CIEMAT, Madrid 6
Comparative spatial resolution of clinical and preclinical imaging modalities and associated design refinements Fabian Kiessling and Bernd J. Pichler. “Small Animal imaging” Basics and Practical Guide. ISBN: 978 -3 -642 -12944 -5 Cracow PET Symposium 23/09/2014 (C) Marta Oteo, CIEMAT, Madrid 6
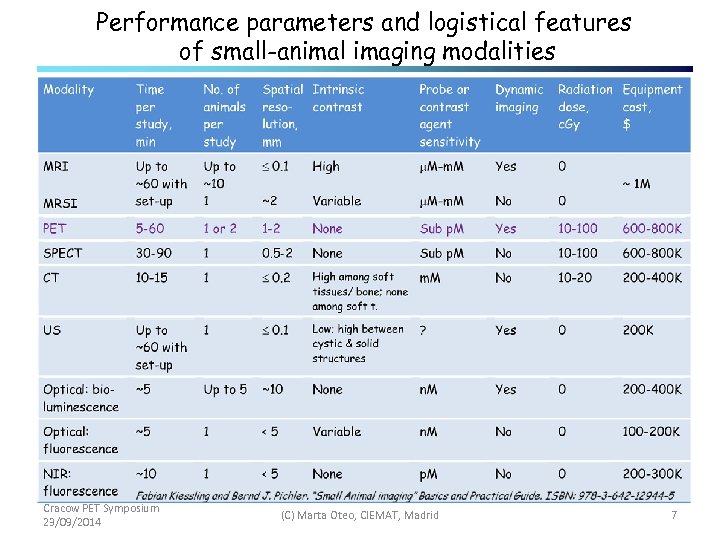 Performance parameters and logistical features of small-animal imaging modalities Cracow PET Symposium 23/09/2014 (C) Marta Oteo, CIEMAT, Madrid 7
Performance parameters and logistical features of small-animal imaging modalities Cracow PET Symposium 23/09/2014 (C) Marta Oteo, CIEMAT, Madrid 7
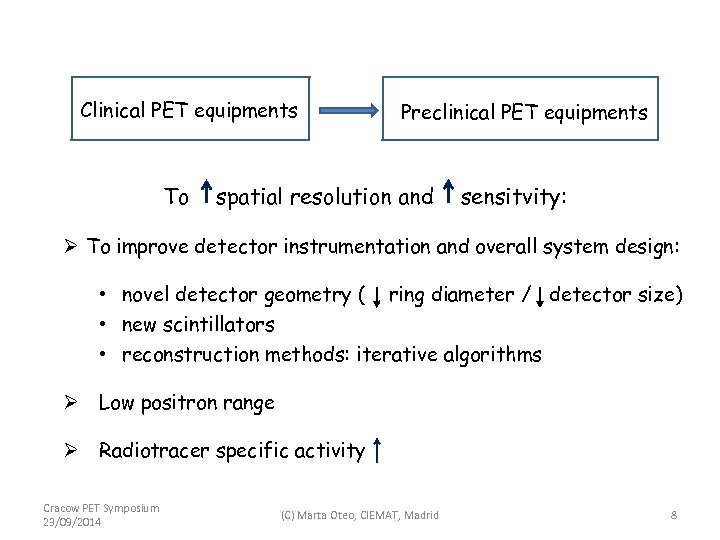 Clinical PET equipments To Preclinical PET equipments spatial resolution and sensitvity: Ø To improve detector instrumentation and overall system design: • novel detector geometry ( ring diameter / detector size) • new scintillators • reconstruction methods: iterative algorithms Ø Low positron range Ø Radiotracer specific activity Cracow PET Symposium 23/09/2014 (C) Marta Oteo, CIEMAT, Madrid 8
Clinical PET equipments To Preclinical PET equipments spatial resolution and sensitvity: Ø To improve detector instrumentation and overall system design: • novel detector geometry ( ring diameter / detector size) • new scintillators • reconstruction methods: iterative algorithms Ø Low positron range Ø Radiotracer specific activity Cracow PET Symposium 23/09/2014 (C) Marta Oteo, CIEMAT, Madrid 8
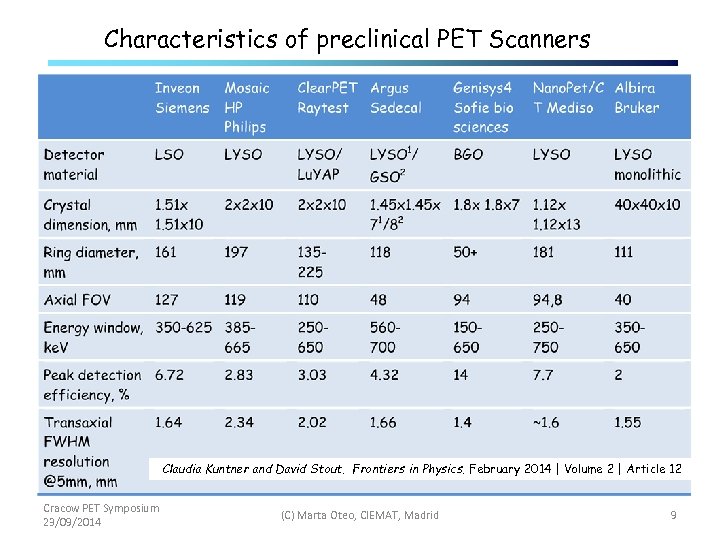 Characteristics of preclinical PET Scanners Claudia Kuntner and David Stout. Frontiers in Physics. February 2014 | Volume 2 | Article 12 Cracow PET Symposium 23/09/2014 (C) Marta Oteo, CIEMAT, Madrid 9
Characteristics of preclinical PET Scanners Claudia Kuntner and David Stout. Frontiers in Physics. February 2014 | Volume 2 | Article 12 Cracow PET Symposium 23/09/2014 (C) Marta Oteo, CIEMAT, Madrid 9
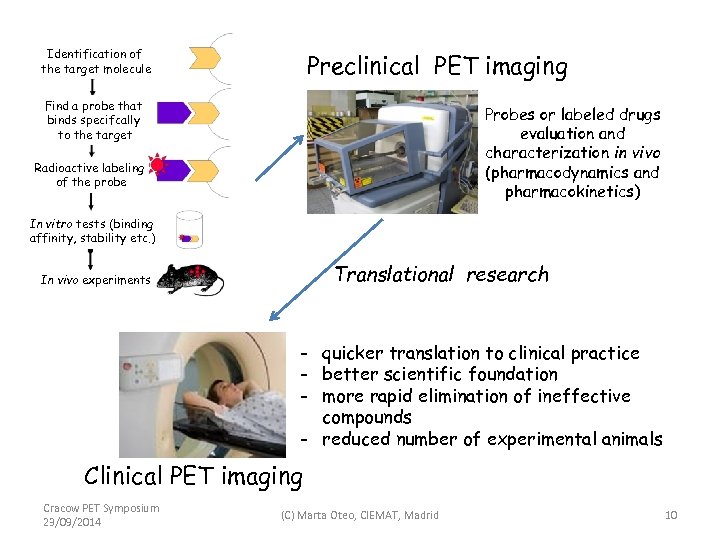 Identification of the target molecule Preclinical PET imaging Find a probe that binds specifcally to the target Probes or labeled drugs evaluation and characterization in vivo (pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics) Radioactive labeling of the probe In vitro tests (binding affinity, stability etc. ) Translational research In vivo experiments - quicker translation to clinical practice - better scientific foundation - more rapid elimination of ineffective compounds - reduced number of experimental animals Clinical PET imaging Cracow PET Symposium 23/09/2014 (C) Marta Oteo, CIEMAT, Madrid 10
Identification of the target molecule Preclinical PET imaging Find a probe that binds specifcally to the target Probes or labeled drugs evaluation and characterization in vivo (pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics) Radioactive labeling of the probe In vitro tests (binding affinity, stability etc. ) Translational research In vivo experiments - quicker translation to clinical practice - better scientific foundation - more rapid elimination of ineffective compounds - reduced number of experimental animals Clinical PET imaging Cracow PET Symposium 23/09/2014 (C) Marta Oteo, CIEMAT, Madrid 10
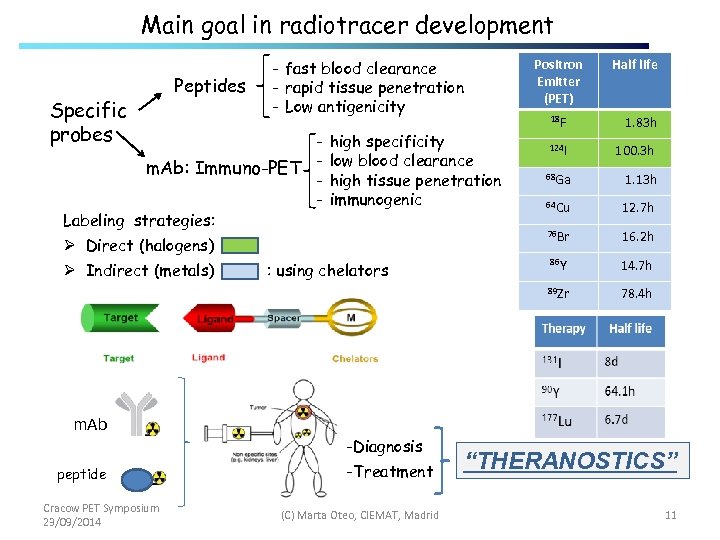 Main goal in radiotracer development Specific probes Peptides - fast blood clearance - rapid tissue penetration - Low antigenicity m. Ab: Immuno-PET Labeling strategies: high specificity low blood clearance high tissue penetration immunogenic Positron Emitter (PET) 18 F 124 I 68 Ga Half life 1. 83 h 100. 3 h 1. 13 h m. Ab peptide Cracow PET Symposium 23/09/2014 : using chelators -Diagnosis -Treatment (C) Marta Oteo, CIEMAT, Madrid 16. 2 h 86 Y 14. 7 h 89 Zr Ø Indirect (metals) 12. 7 h 76 Br Ø Direct (halogens) 64 Cu 78. 4 h “THERANOSTICS” 11
Main goal in radiotracer development Specific probes Peptides - fast blood clearance - rapid tissue penetration - Low antigenicity m. Ab: Immuno-PET Labeling strategies: high specificity low blood clearance high tissue penetration immunogenic Positron Emitter (PET) 18 F 124 I 68 Ga Half life 1. 83 h 100. 3 h 1. 13 h m. Ab peptide Cracow PET Symposium 23/09/2014 : using chelators -Diagnosis -Treatment (C) Marta Oteo, CIEMAT, Madrid 16. 2 h 86 Y 14. 7 h 89 Zr Ø Indirect (metals) 12. 7 h 76 Br Ø Direct (halogens) 64 Cu 78. 4 h “THERANOSTICS” 11
 68 Ga Applications 68 Ge/68 Ga generator GMP compliant Eckert & Ziegler Cracow PET Symposium 23/09/2014 (C) Marta Oteo, CIEMAT, Madrid 12
68 Ga Applications 68 Ge/68 Ga generator GMP compliant Eckert & Ziegler Cracow PET Symposium 23/09/2014 (C) Marta Oteo, CIEMAT, Madrid 12
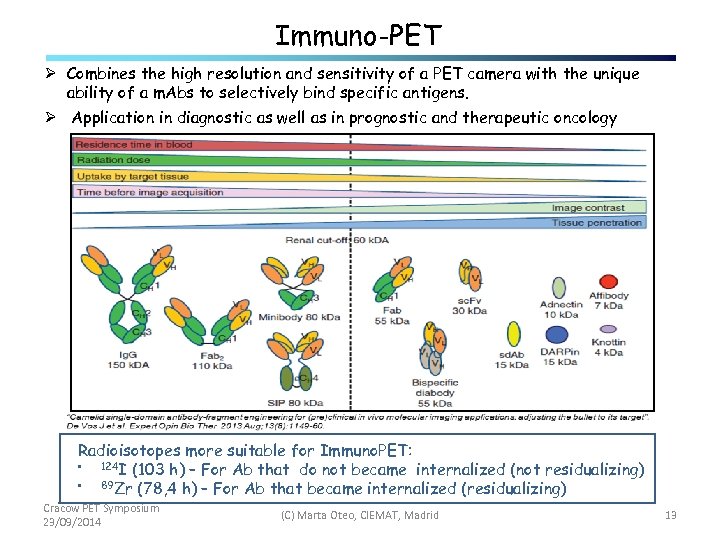 Immuno-PET Ø Combines the high resolution and sensitivity of a PET camera with the unique ability of a m. Abs to selectively bind specific antigens. Ø Application in diagnostic as well as in prognostic and therapeutic oncology Radioisotopes more suitable for Immuno. PET: • 124 I (103 h) – For Ab that do not became internalized (not residualizing) • 89 Zr (78, 4 h) – For Ab that became internalized (residualizing) Cracow PET Symposium 23/09/2014 (C) Marta Oteo, CIEMAT, Madrid 13
Immuno-PET Ø Combines the high resolution and sensitivity of a PET camera with the unique ability of a m. Abs to selectively bind specific antigens. Ø Application in diagnostic as well as in prognostic and therapeutic oncology Radioisotopes more suitable for Immuno. PET: • 124 I (103 h) – For Ab that do not became internalized (not residualizing) • 89 Zr (78, 4 h) – For Ab that became internalized (residualizing) Cracow PET Symposium 23/09/2014 (C) Marta Oteo, CIEMAT, Madrid 13
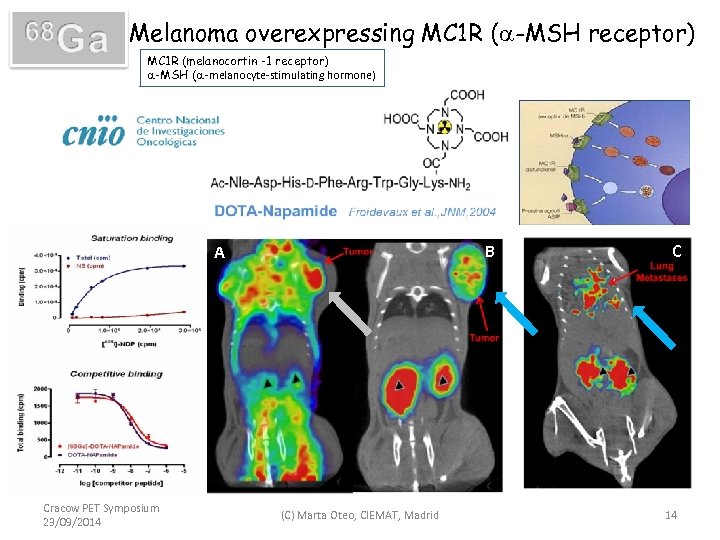 Melanoma overexpressing MC 1 R (a-MSH receptor) MC 1 R (melanocortin -1 receptor) a-MSH (a-melanocyte-stimulating hormone) B A Cracow PET Symposium 23/09/2014 (C) Marta Oteo, CIEMAT, Madrid C 14
Melanoma overexpressing MC 1 R (a-MSH receptor) MC 1 R (melanocortin -1 receptor) a-MSH (a-melanocyte-stimulating hormone) B A Cracow PET Symposium 23/09/2014 (C) Marta Oteo, CIEMAT, Madrid C 14
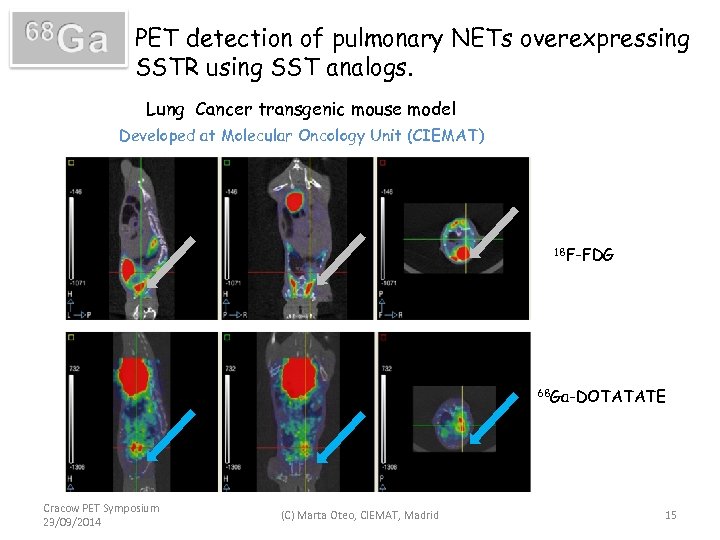 PET detection of pulmonary NETs overexpressing SSTR using SST analogs. Lung Cancer transgenic mouse model Developed at Molecular Oncology Unit (CIEMAT) 18 F-FDG 68 Ga-DOTATATE Cracow PET Symposium 23/09/2014 (C) Marta Oteo, CIEMAT, Madrid 15
PET detection of pulmonary NETs overexpressing SSTR using SST analogs. Lung Cancer transgenic mouse model Developed at Molecular Oncology Unit (CIEMAT) 18 F-FDG 68 Ga-DOTATATE Cracow PET Symposium 23/09/2014 (C) Marta Oteo, CIEMAT, Madrid 15
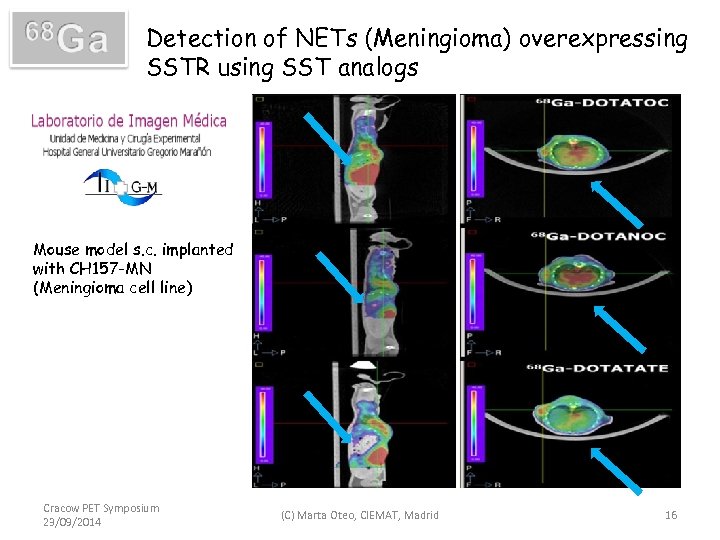 Detection of NETs (Meningioma) overexpressing SSTR using SST analogs Mouse model s. c. implanted with CH 157 -MN (Meningioma cell line) Cracow PET Symposium 23/09/2014 (C) Marta Oteo, CIEMAT, Madrid 16
Detection of NETs (Meningioma) overexpressing SSTR using SST analogs Mouse model s. c. implanted with CH 157 -MN (Meningioma cell line) Cracow PET Symposium 23/09/2014 (C) Marta Oteo, CIEMAT, Madrid 16
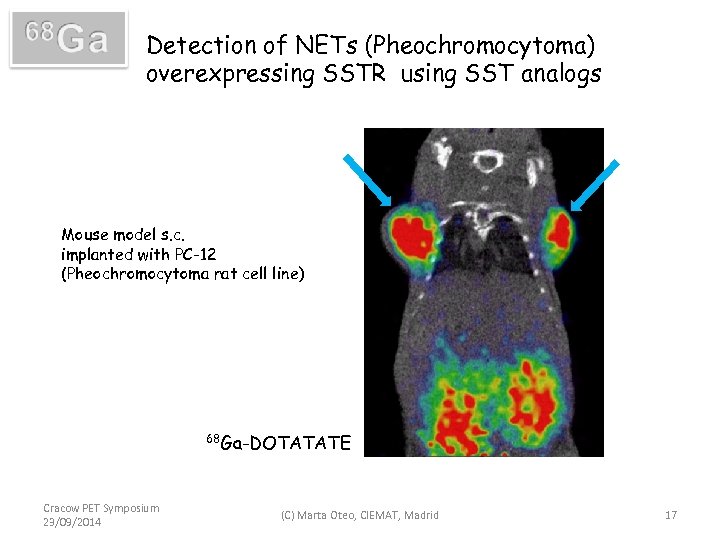 Detection of NETs (Pheochromocytoma) overexpressing SSTR using SST analogs Mouse model s. c. implanted with PC-12 (Pheochromocytoma rat cell line) 68 Ga-DOTATATE Cracow PET Symposium 23/09/2014 (C) Marta Oteo, CIEMAT, Madrid 17
Detection of NETs (Pheochromocytoma) overexpressing SSTR using SST analogs Mouse model s. c. implanted with PC-12 (Pheochromocytoma rat cell line) 68 Ga-DOTATATE Cracow PET Symposium 23/09/2014 (C) Marta Oteo, CIEMAT, Madrid 17
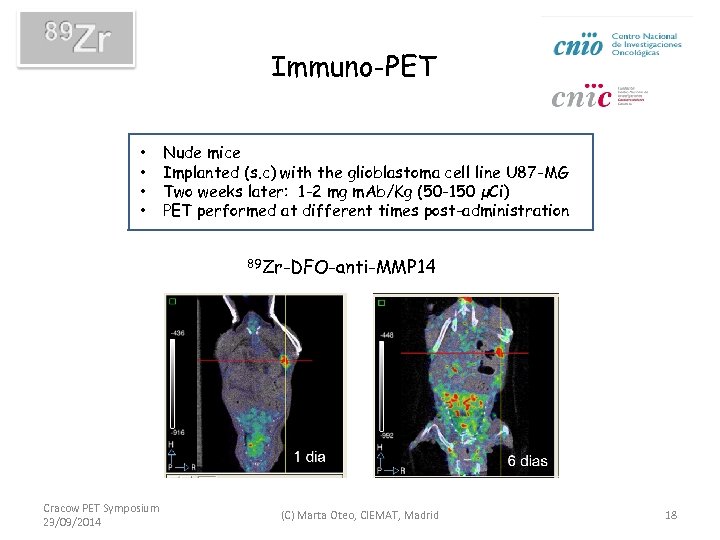 Immuno-PET • • Nude mice Implanted (s. c) with the glioblastoma cell line U 87 -MG Two weeks later: 1 -2 mg m. Ab/Kg (50 -150 µCi) PET performed at different times post-administration 89 Zr-DFO-anti-MMP 14 Cracow PET Symposium 23/09/2014 (C) Marta Oteo, CIEMAT, Madrid 18
Immuno-PET • • Nude mice Implanted (s. c) with the glioblastoma cell line U 87 -MG Two weeks later: 1 -2 mg m. Ab/Kg (50 -150 µCi) PET performed at different times post-administration 89 Zr-DFO-anti-MMP 14 Cracow PET Symposium 23/09/2014 (C) Marta Oteo, CIEMAT, Madrid 18
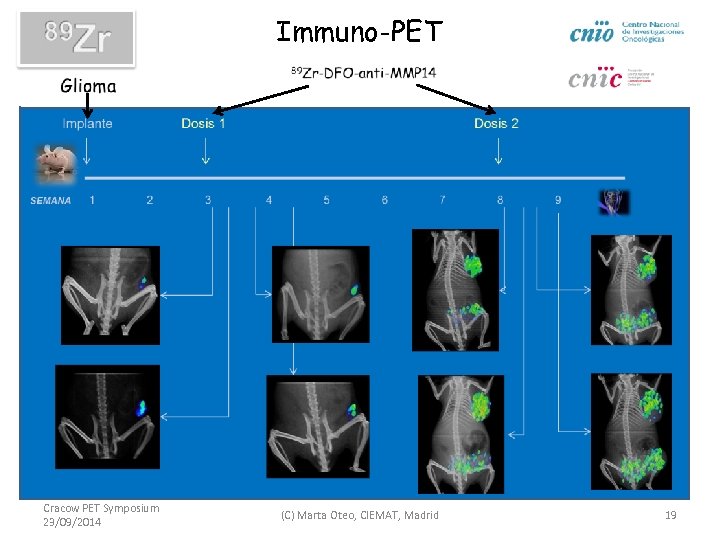 Immuno-PET Cracow PET Symposium 23/09/2014 (C) Marta Oteo, CIEMAT, Madrid 19
Immuno-PET Cracow PET Symposium 23/09/2014 (C) Marta Oteo, CIEMAT, Madrid 19
 Concluding remark PET molecular imaging allows for the non-invasive assessment of biological and biochemical processes in living subjects, contributing to improve our understanding of disease and drug activity during preclinical and clinical drug development. Cracow PET Symposium 23/09/2014 (C) Marta Oteo, CIEMAT, Madrid 20
Concluding remark PET molecular imaging allows for the non-invasive assessment of biological and biochemical processes in living subjects, contributing to improve our understanding of disease and drug activity during preclinical and clinical drug development. Cracow PET Symposium 23/09/2014 (C) Marta Oteo, CIEMAT, Madrid 20
 Biomedical Applications of Radioisotopes and Pharmacokinetic Unit (CIEMAT) Cracow PET Symposium 23/09/2014 marta. oteo@ciemat. es (C) Marta Oteo, CIEMAT, Madrid 21
Biomedical Applications of Radioisotopes and Pharmacokinetic Unit (CIEMAT) Cracow PET Symposium 23/09/2014 marta. oteo@ciemat. es (C) Marta Oteo, CIEMAT, Madrid 21


