061c8de2c37e97940c5cb1efde019a4a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 45
 Slow Intelligence Systems Session and Panel 1
Slow Intelligence Systems Session and Panel 1
 Panelists • • Erland Jungert Francesco Colace Tiansi Dong Shi-Kuo Chang (Moderator) 2
Panelists • • Erland Jungert Francesco Colace Tiansi Dong Shi-Kuo Chang (Moderator) 2
 Outline • • • Motivation Introduction to SIS Application: Ontological Filters Application: Topic/Trend Detection Discussion 3
Outline • • • Motivation Introduction to SIS Application: Ontological Filters Application: Topic/Trend Detection Discussion 3
 Motivation: Common Characteristics of New Generation Information Systems • • • Connected Multiple sourced Knowledge-based Personalized Hybrid 4
Motivation: Common Characteristics of New Generation Information Systems • • • Connected Multiple sourced Knowledge-based Personalized Hybrid 4
 Smarter Planet • We are all now connected - economically, technically and socially. Our planet is becoming smarter via integration of information scattered in many different data sources: from the sensors, on the web, in our personal devices, in documents and in databases, or hidden within application programs. Often we need to get information from several of these sources to complete a task. Examples include healthcare, science, the business world and our personal lives. (Quoted from Josephine M. Cheng, IBM Fellow and Vice President of IBM Research) 5
Smarter Planet • We are all now connected - economically, technically and socially. Our planet is becoming smarter via integration of information scattered in many different data sources: from the sensors, on the web, in our personal devices, in documents and in databases, or hidden within application programs. Often we need to get information from several of these sources to complete a task. Examples include healthcare, science, the business world and our personal lives. (Quoted from Josephine M. Cheng, IBM Fellow and Vice President of IBM Research) 5
 (courtesy of IBM) 6
(courtesy of IBM) 6
 Hybrid Intelligence • While processor speed and storage capacity have grown remarkably, the geometric growth in user communities, online computer usage, and the availability of data is in some ways is even more remarkable. Hybrid Intelligence offers great opportunities we have to harness this data availability to build systems of immense potential. While today s large scale systems are evolutionarily based on the distributed computing technologies envisioned in the 70 s and 80 s, sheer scaling has led to many unanticipated challenges. (quoted from Alfred Z. Spector, Vice President, Research and Special Initiatives, Google, USA) 7
Hybrid Intelligence • While processor speed and storage capacity have grown remarkably, the geometric growth in user communities, online computer usage, and the availability of data is in some ways is even more remarkable. Hybrid Intelligence offers great opportunities we have to harness this data availability to build systems of immense potential. While today s large scale systems are evolutionarily based on the distributed computing technologies envisioned in the 70 s and 80 s, sheer scaling has led to many unanticipated challenges. (quoted from Alfred Z. Spector, Vice President, Research and Special Initiatives, Google, USA) 7
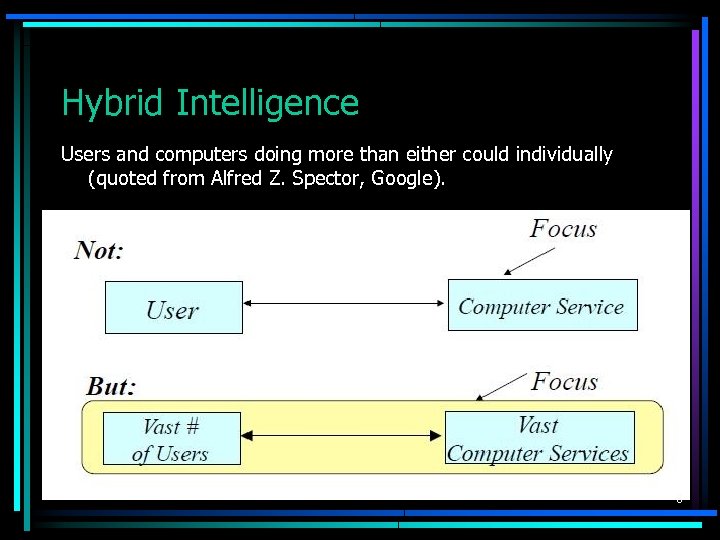 Hybrid Intelligence Users and computers doing more than either could individually (quoted from Alfred Z. Spector, Google). 8
Hybrid Intelligence Users and computers doing more than either could individually (quoted from Alfred Z. Spector, Google). 8
 Slow Intelligence Systems • • Slow Intelligence Systems are generalpurpose systems characterized by being able to improve performance over time. A slow intelligence system is a system that (i) solves problems by trying different solutions, (ii) is contextaware to adapt to different situations and to propagate knowledge, and (iii) may not perform well in the short run but continuously learns to improve its performance over time. 9
Slow Intelligence Systems • • Slow Intelligence Systems are generalpurpose systems characterized by being able to improve performance over time. A slow intelligence system is a system that (i) solves problems by trying different solutions, (ii) is contextaware to adapt to different situations and to propagate knowledge, and (iii) may not perform well in the short run but continuously learns to improve its performance over time. 9
 Slow Intelligence Systems • Slow Intelligence Systems are generalpurpose systems characterized by being able to improve performance over time through a process involving • Enumeration 10
Slow Intelligence Systems • Slow Intelligence Systems are generalpurpose systems characterized by being able to improve performance over time through a process involving • Enumeration 10
 Slow Intelligence Systems • Slow Intelligence Systems are generalpurpose systems characterized by being able to improve performance over time through a process involving • Enumeration • Propagation 11
Slow Intelligence Systems • Slow Intelligence Systems are generalpurpose systems characterized by being able to improve performance over time through a process involving • Enumeration • Propagation 11
 Slow Intelligence Systems • Slow Intelligence Systems are generalpurpose systems characterized by being able to improve performance over time through a process involving • Enumeration • Propagation • Adaptation 12
Slow Intelligence Systems • Slow Intelligence Systems are generalpurpose systems characterized by being able to improve performance over time through a process involving • Enumeration • Propagation • Adaptation 12
 Slow Intelligence Systems • Slow Intelligence Systems are generalpurpose systems characterized by being able to improve performance over time through a process involving • Enumeration • Propagation • Adaptation • Elimination 13
Slow Intelligence Systems • Slow Intelligence Systems are generalpurpose systems characterized by being able to improve performance over time through a process involving • Enumeration • Propagation • Adaptation • Elimination 13
 Slow Intelligence Systems • Slow Intelligence Systems are generalpurpose systems characterized by being able to improve performance over time through a process involving • Enumeration • Propagation • Adaptation • Elimination • Concentration 14
Slow Intelligence Systems • Slow Intelligence Systems are generalpurpose systems characterized by being able to improve performance over time through a process involving • Enumeration • Propagation • Adaptation • Elimination • Concentration 14
 Slow Intelligence Systems • Slow Intelligence Systems are generalpurpose systems characterized by being able to improve performance over time through a process involving • Enumeration • Propagation • Adaptation • Elimination • Concentration • Slow Decision Cycle to complement Fast Decision Cycle 15
Slow Intelligence Systems • Slow Intelligence Systems are generalpurpose systems characterized by being able to improve performance over time through a process involving • Enumeration • Propagation • Adaptation • Elimination • Concentration • Slow Decision Cycle to complement Fast Decision Cycle 15
 Slow Intelligence Systems • A SIS continuously learns, searches for new solutions and propagates and shares its experience with other peers. • From the structural point of view, a SIS is a system with multiple decision cycles such that actions of slow decision cycle(s) may override actions of quick decision cycle(s), resulting in poorer performance in the short run but better performance in the long-run. 16
Slow Intelligence Systems • A SIS continuously learns, searches for new solutions and propagates and shares its experience with other peers. • From the structural point of view, a SIS is a system with multiple decision cycles such that actions of slow decision cycle(s) may override actions of quick decision cycle(s), resulting in poorer performance in the short run but better performance in the long-run. 16
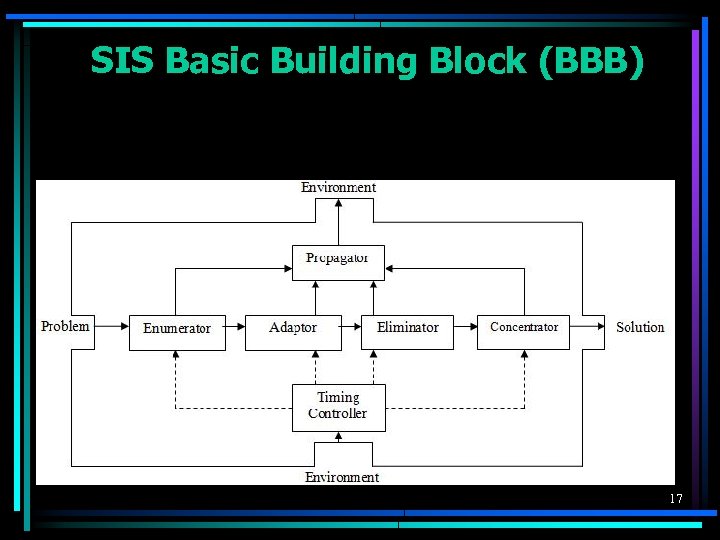 SIS Basic Building Block (BBB) 17
SIS Basic Building Block (BBB) 17
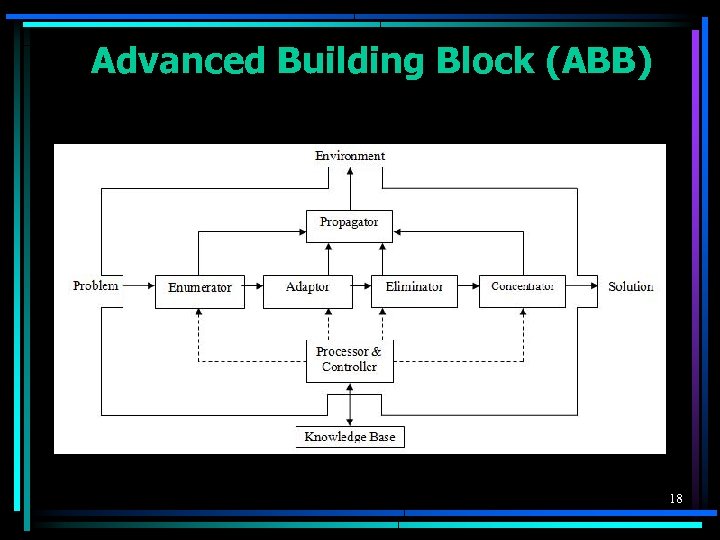 Advanced Building Block (ABB) 18
Advanced Building Block (ABB) 18
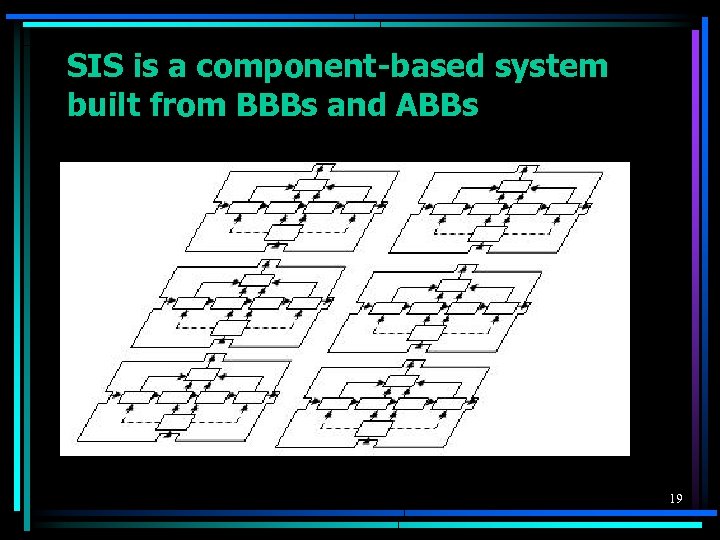 SIS is a component-based system built from BBBs and ABBs 19
SIS is a component-based system built from BBBs and ABBs 19
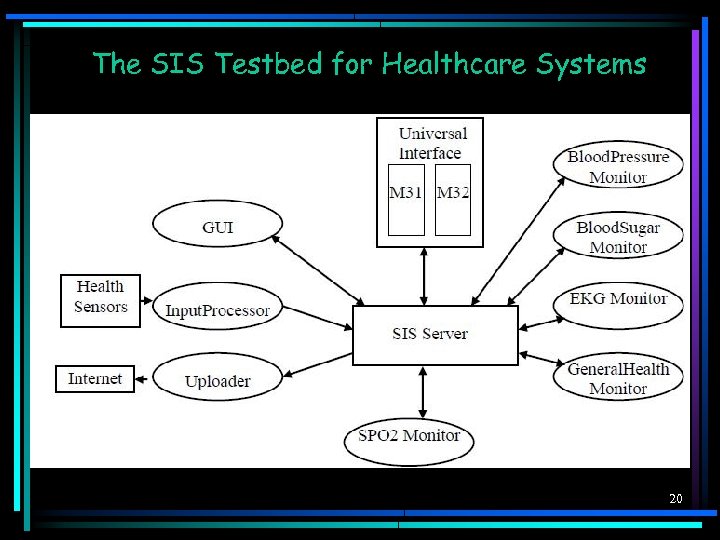 The SIS Testbed for Healthcare Systems 20
The SIS Testbed for Healthcare Systems 20
 Ontological Filters for Slow Intelligence Systems Shi-Kuo Chang, Emilio Zegarra, Francesco Colace and Massimo De Santo 21
Ontological Filters for Slow Intelligence Systems Shi-Kuo Chang, Emilio Zegarra, Francesco Colace and Massimo De Santo 21
 SIS Application to Product Configuration Production of personalized or custom-tailored goods or services to meet consumers' diverse and changing needs 22
SIS Application to Product Configuration Production of personalized or custom-tailored goods or services to meet consumers' diverse and changing needs 22
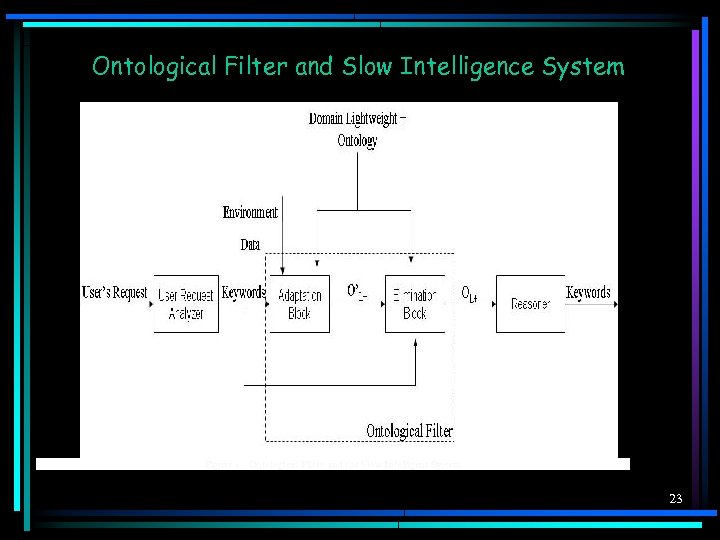 Ontological Filter and Slow Intelligence System Figure 6 - Ontological Filter and the Slow Intelligent System 23
Ontological Filter and Slow Intelligence System Figure 6 - Ontological Filter and the Slow Intelligent System 23
 A Scenario • • • A customer would like to buy a Personal Computer in order to play videogames and surf on the internet. He knows that he needs an operating system, a web browser and an antivirus package. In particular, the user prefers a Microsoft Windows operating system. He lives in the United States and prefers to have a desktop. He also prefers low cost components. 24
A Scenario • • • A customer would like to buy a Personal Computer in order to play videogames and surf on the internet. He knows that he needs an operating system, a web browser and an antivirus package. In particular, the user prefers a Microsoft Windows operating system. He lives in the United States and prefers to have a desktop. He also prefers low cost components. 24
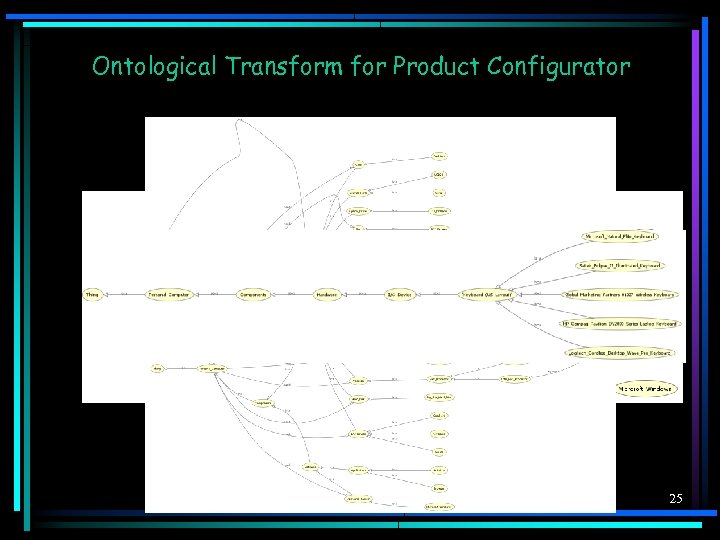 Ontological Transform for Product Configurator 25
Ontological Transform for Product Configurator 25
 Building Topic/Trend Detection System based on Slow Intelligence Chia-Chun Shih & Ting-Chun Peng Institute for Information Industry Taipei, Taiwan 26
Building Topic/Trend Detection System based on Slow Intelligence Chia-Chun Shih & Ting-Chun Peng Institute for Information Industry Taipei, Taiwan 26
 • An online trend detection system requires careful resource allocation and automatic algorithm adaptation to process huge size of heterogeneous data. • This research adopts Slow Intelligence, which provides a framework for systems with insufficient computing resources to gradually adapt to environments, to response the challenges. • Four Slow Intelligence subsystems are proposed, and each subsystem targets a challenge in designing online topic/trend detection systems. 27
• An online trend detection system requires careful resource allocation and automatic algorithm adaptation to process huge size of heterogeneous data. • This research adopts Slow Intelligence, which provides a framework for systems with insufficient computing resources to gradually adapt to environments, to response the challenges. • Four Slow Intelligence subsystems are proposed, and each subsystem targets a challenge in designing online topic/trend detection systems. 27
 Introduction • Topic Detection and Tracking (TDT) – Initiated by DARPA at 1996 – discover the topical structure in unsegmented streams of news reporting as it appears across multiple media – Tasks: • • • Topic Detection Topic Tracking First Story Detection Story Segmentation Link Detection 28
Introduction • Topic Detection and Tracking (TDT) – Initiated by DARPA at 1996 – discover the topical structure in unsegmented streams of news reporting as it appears across multiple media – Tasks: • • • Topic Detection Topic Tracking First Story Detection Story Segmentation Link Detection 28
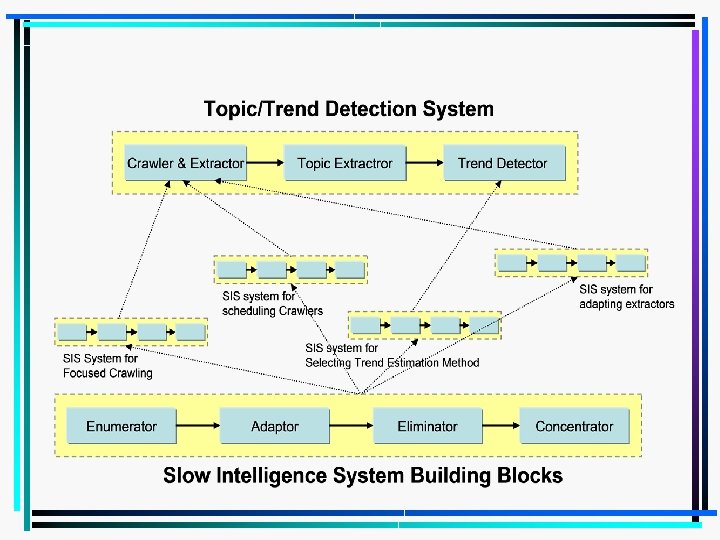
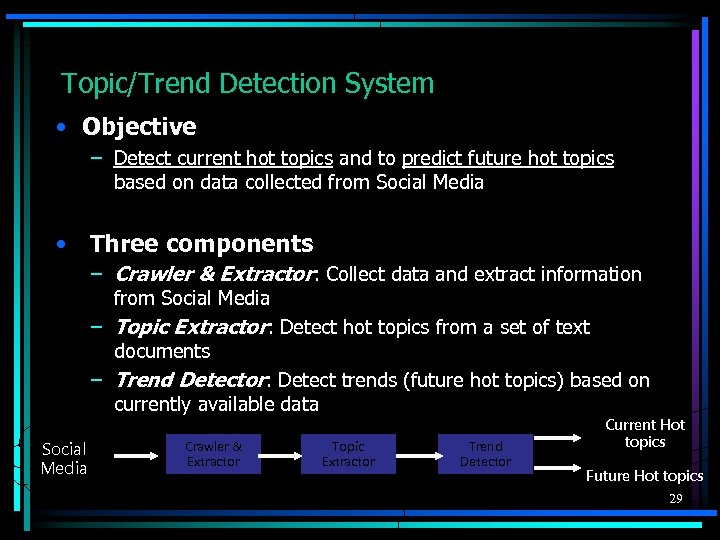 Topic/Trend Detection System • Objective – Detect current hot topics and to predict future hot topics based on data collected from Social Media • Three components – Crawler & Extractor: Collect data and extract information from Social Media – Topic Extractor: Detect hot topics from a set of text documents – Trend Detector: Detect trends (future hot topics) based on currently available data Social Media Crawler & Extractor Topic Extractor Trend Detector Current Hot topics Future Hot topics 29
Topic/Trend Detection System • Objective – Detect current hot topics and to predict future hot topics based on data collected from Social Media • Three components – Crawler & Extractor: Collect data and extract information from Social Media – Topic Extractor: Detect hot topics from a set of text documents – Trend Detector: Detect trends (future hot topics) based on currently available data Social Media Crawler & Extractor Topic Extractor Trend Detector Current Hot topics Future Hot topics 29
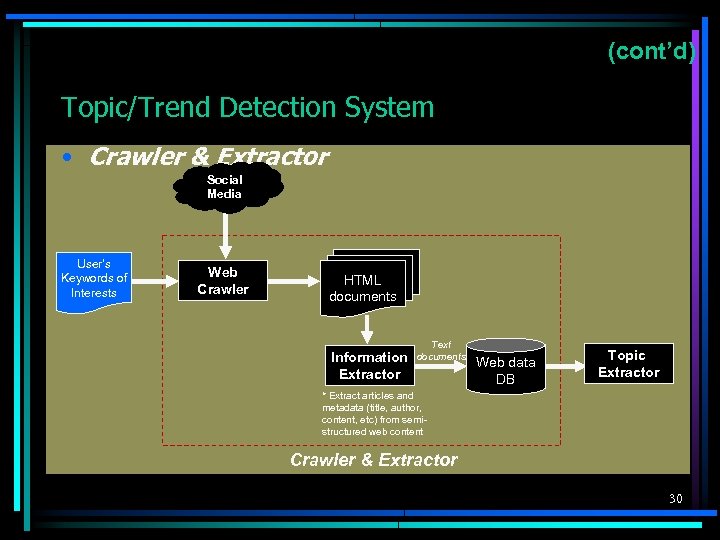 (cont’d) Topic/Trend Detection System • Crawler & Extractor Social Media User’s Keywords of Interests Web Crawler HTML documents Information Extractor Text documents Web data DB Topic Extractor * Extract articles and metadata (title, author, content, etc) from semistructured web content Crawler & Extractor 30
(cont’d) Topic/Trend Detection System • Crawler & Extractor Social Media User’s Keywords of Interests Web Crawler HTML documents Information Extractor Text documents Web data DB Topic Extractor * Extract articles and metadata (title, author, content, etc) from semistructured web content Crawler & Extractor 30
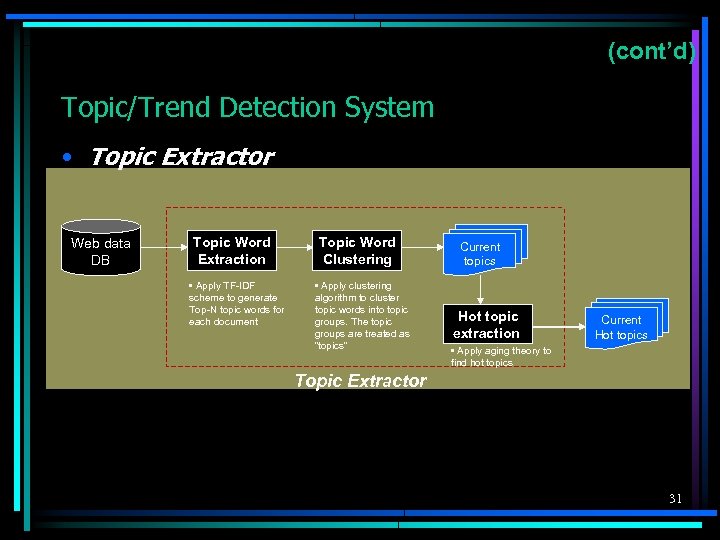 (cont’d) Topic/Trend Detection System • Topic Extractor Web data DB Topic Word Extraction • Apply TF-IDF scheme to generate Top-N topic words for each document Topic Word Clustering • Apply clustering algorithm to cluster topic words into topic groups. The topic groups are treated as “topics” Current topics Hot topic extraction Current Hot topics • Apply aging theory to find hot topics Topic Extractor 31
(cont’d) Topic/Trend Detection System • Topic Extractor Web data DB Topic Word Extraction • Apply TF-IDF scheme to generate Top-N topic words for each document Topic Word Clustering • Apply clustering algorithm to cluster topic words into topic groups. The topic groups are treated as “topics” Current topics Hot topic extraction Current Hot topics • Apply aging theory to find hot topics Topic Extractor 31
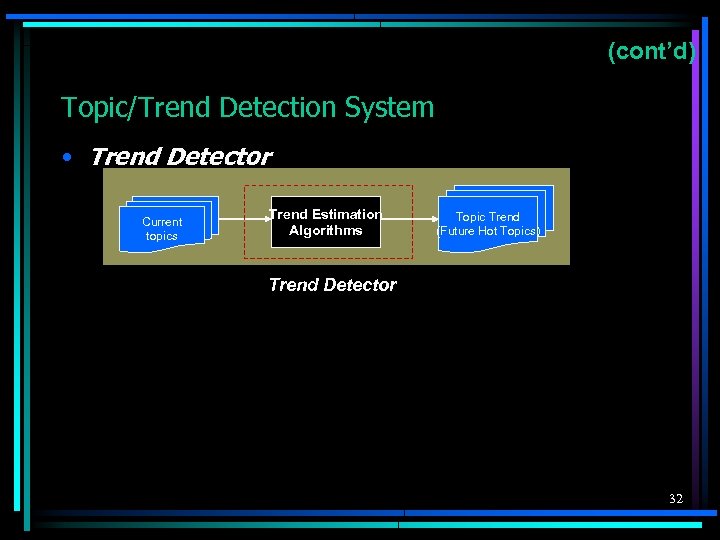 (cont’d) Topic/Trend Detection System • Trend Detector Current topics Trend Estimation Algorithms Topic Trend (Future Hot Topics) Trend Detector 32
(cont’d) Topic/Trend Detection System • Trend Detector Current topics Trend Estimation Algorithms Topic Trend (Future Hot Topics) Trend Detector 32
 T/TD System with Slow Intelligence • Four complexities of designing online topic/trend detection systems • 1. It is unlikely to collect all web data based on limited amount of computing resources. The system needs to develop data collection strategies which can concentrate limited resources on collecting important web data. 33
T/TD System with Slow Intelligence • Four complexities of designing online topic/trend detection systems • 1. It is unlikely to collect all web data based on limited amount of computing resources. The system needs to develop data collection strategies which can concentrate limited resources on collecting important web data. 33
 (cont’d) T/TD System with Slow Intelligence • 2. Many computation methods are available for estimating trends. If parameter settings are also taken into account, there are too many combinations to choose. Furthermore, Internet is a changing environment, which means current best solution may not perform well in the future. The system needs to automatically (or at least quasi-automatically) find best solution from many alternatives in a changing environment. 34
(cont’d) T/TD System with Slow Intelligence • 2. Many computation methods are available for estimating trends. If parameter settings are also taken into account, there are too many combinations to choose. Furthermore, Internet is a changing environment, which means current best solution may not perform well in the future. The system needs to automatically (or at least quasi-automatically) find best solution from many alternatives in a changing environment. 34
 (cont’d) T/TD System with Slow Intelligence • 3. The crawler needs to revisit websites to collect up-to-date data in hourly or daily intervals. Each site has different amount of to -be-update data and different policy to restrict frequent access, which are unknown beforehand. The system needs to find feasible data collection schedule based on past experience. 35
(cont’d) T/TD System with Slow Intelligence • 3. The crawler needs to revisit websites to collect up-to-date data in hourly or daily intervals. Each site has different amount of to -be-update data and different policy to restrict frequent access, which are unknown beforehand. The system needs to find feasible data collection schedule based on past experience. 35
 (cont’d) T/TD System with Slow Intelligence • 4. Any changes in web pages may disrupt Extractors. It needs automatic repair mechanism for Extractors if many websites are being monitored. The repair mechanism needs to detect errors of Extractors, find Crawler & alternatives, and choose the best solution Extractor from alternatives to fix the disrupted Extractors. 36
(cont’d) T/TD System with Slow Intelligence • 4. Any changes in web pages may disrupt Extractors. It needs automatic repair mechanism for Extractors if many websites are being monitored. The repair mechanism needs to detect errors of Extractors, find Crawler & alternatives, and choose the best solution Extractor from alternatives to fix the disrupted Extractors. 36
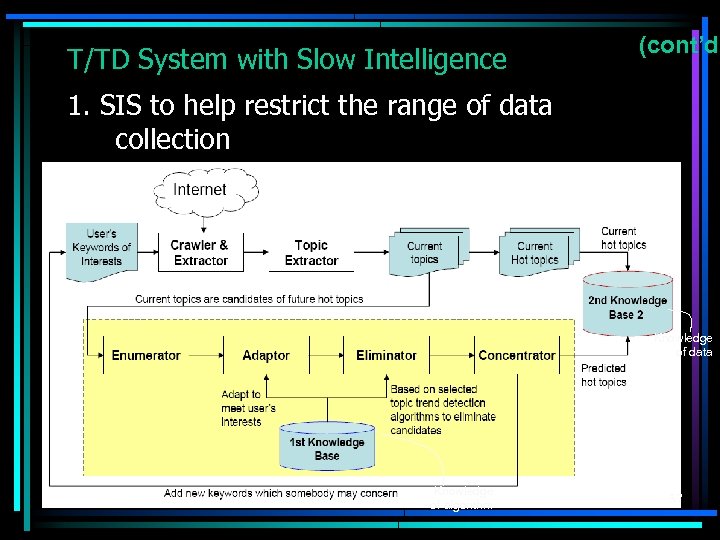 T/TD System with Slow Intelligence (cont’d) 1. SIS to help restrict the range of data collection Knowledge of data Knowledge of algorithm 37
T/TD System with Slow Intelligence (cont’d) 1. SIS to help restrict the range of data collection Knowledge of data Knowledge of algorithm 37
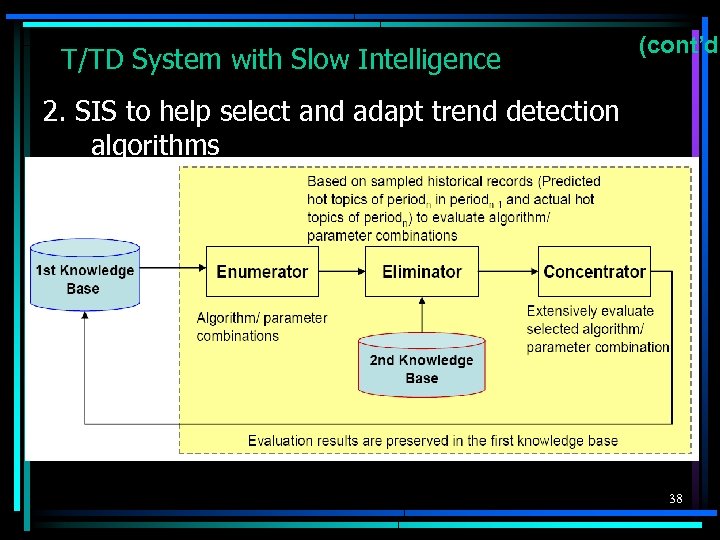 T/TD System with Slow Intelligence (cont’d) 2. SIS to help select and adapt trend detection algorithms 38
T/TD System with Slow Intelligence (cont’d) 2. SIS to help select and adapt trend detection algorithms 38
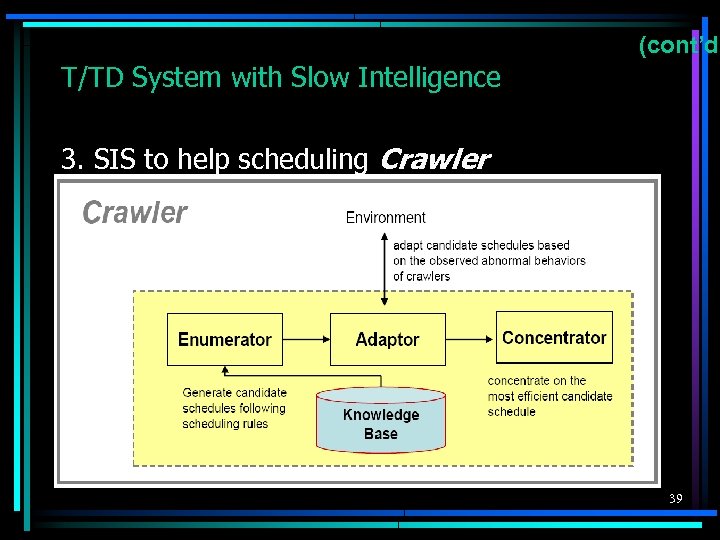 (cont’d) T/TD System with Slow Intelligence 3. SIS to help scheduling Crawler 39
(cont’d) T/TD System with Slow Intelligence 3. SIS to help scheduling Crawler 39
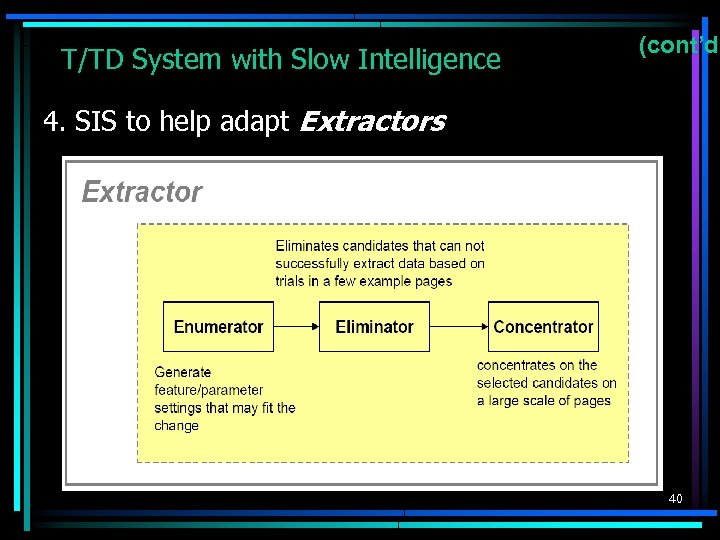 T/TD System with Slow Intelligence (cont’d) 4. SIS to help adapt Extractors 40
T/TD System with Slow Intelligence (cont’d) 4. SIS to help adapt Extractors 40
 41
41
 Discussion • There a large number of intelligent systems, quasi-intelligent systems and semi-intelligent systems that are "slow". Distributed intelligence systems, multiple agents systems and emergency management systems are mostly slow intelligence systems that exhibit the characteristics of multiple decision cycles. 42
Discussion • There a large number of intelligent systems, quasi-intelligent systems and semi-intelligent systems that are "slow". Distributed intelligence systems, multiple agents systems and emergency management systems are mostly slow intelligence systems that exhibit the characteristics of multiple decision cycles. 42
 Discussion (continued) • Since time is relative, "slow" intelligence systems for some can also be "fast" for others. • A slow intelligence system can evolve into a fast intelligence system. • A framework for knowledge-based software engineering. 43
Discussion (continued) • Since time is relative, "slow" intelligence systems for some can also be "fast" for others. • A slow intelligence system can evolve into a fast intelligence system. • A framework for knowledge-based software engineering. 43
 Q&A 44
Q&A 44
 The End 45
The End 45


