578ad638180d2e5a472578f85799907b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 110

SLIDES SET NUMBER 1.

Class 478/578: General 1 1. My name is Marek Perkowski 2. You can call my Marek, or Dr. Perkowski or whatever you like. 3. This class is fun, at least for me. 4. I hope that you will have fun also. 5. We build practical robots – embedded systems 6. Class is graded based on practical achievements, a little bit similar to Capstone Project. 7. You can find all information on my webpage, find me through Google.

Class 478/578: General 2 1. If you are a graduate student your project is more difficult, otherwise the same. 2. Two homeworks and Project 3. No exam. 4. Student presentations (related to homeworks or projects) 5. I expect high quality of reports (many graduate students had publications based on these reports) 6. Robots connected to Internet (demo and explanation next Thursday).

Class 478/578: grading 1. Homework 1 – 10 % (evolutionary algorithms and foraging) 2. Homework 2 – 10 % (any subset of your project) 3. Presentation – 10 % 4. Project – 70 % 5. Groups – 1 to 5 students, group leader. 6. In final report, each student has a separate part to demonstrate his/her work. 7. Each student presents a separate presentation of his work.

Class 478/578: book 1. Braunl. – – • • You can find slides to this book on internet Book was ordered early but it must be reprinted “on demand”. If you have no book, do not worry. All is in my slides. Somebody told me that PDF of all text is also on internet Slides of my class on my webpage – look for “Embedded Robotics” on my main webpage. To find my webpage do search on Google “Marek Perkowski”

Class 478/578: your background 1. Programming – – Matlab C C++ Java 2. Some basic digital design and interfacing experience (only in some projects) 3. Some basic math, Boolean Algebra, probability. 4. Digital Signal Processing, Image Processing (for some projects, will be covered in debth in ECE 479 next quarter)

Class 478/578: your background review 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Boolean functions, gates and circuits Finite State Machines Probabilistic State Machines Grammars Linked Lists Arduino

Class 478/578: your background information Please give me today the following information: 1. Your first name, last name and contact (email, phone) 2. Do you want to be on my Facebook – send me message on Facebook. 3. Programming classes you have taken. 4. Programming projects you have done. 5. Robot projects you have done. Please write more. 6. Any hardware projects you have done, like fixing a radio or a computer, building a FPGA controller etc. 7. Your background (hardware, software, art, physics, math, biology, etc) 8. Are you a graduate or undergraduate student. 9. For each of three areas: theory, programming and practical robot building, write percentages of your project’s grade (I am not sure I will be able to take this into account in every case) 10. Do you prefer to work alone or in a team for this class?

Class 478/578: your background information Please give me today the following information: 1. Your first name, last name and contact (email, phone) 2. Do you want to be on my Facebook – send me message on Facebook. 3. Programming classes you have taken. 4. Programming projects you have done. 5. Robot projects you have done. Please write more. 6. Any hardware projects you have done, like fixing a radio or a computer, building a FPGA controller etc. 7. Your background (hardware, software, art, physics, math, biology, etc) 8. Are you a graduate or undergraduate student. 9. For each of three areas: theory, programming and practical robot building, write percentages of your project’s grade (I am not sure I will be able to take this into account in every case) 10. Do you prefer to work alone or in a team for this class?

Class 478/578: Projects and Lab 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Meeting with Chris Clark Meeting with class TA Webpages with previous projects Interfacing to internet Lab keys (cards)

Class 478/578: Projects for this year 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Dancing hexapods Foraging hexapods Robot Theatre Sustainable Robot for advertising Robot Guide for PSU Robots controlled by i. Phones, Ipads, etc. Advanced theories for robotics (only for individual graduate students)
EMBEDDED SYSTEMS

• Textbook: • T. Bräunl Embedded Robotics, Springer 2003

Plan of class • Week 1: – Servo programming – Evolutionary algorithms • Week 2: – Humanoid Robots – Models of robotics • Mapping, grammars, automata, probabilistic, Braitenberg Vehicles, natural language, logic based learning.
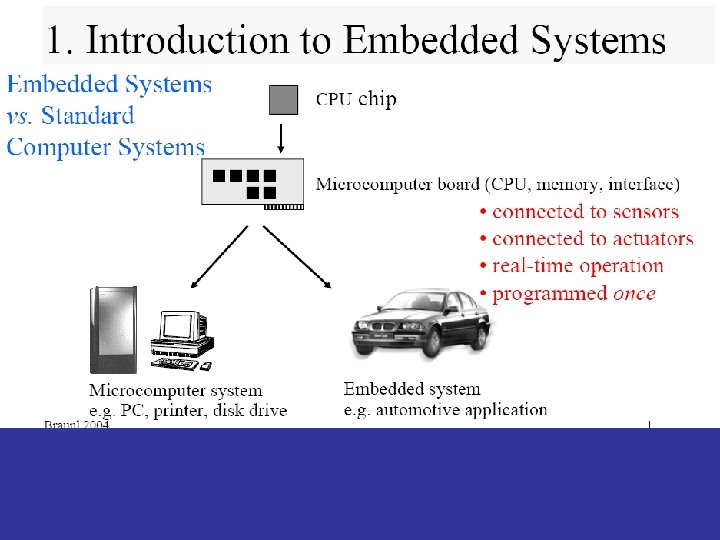
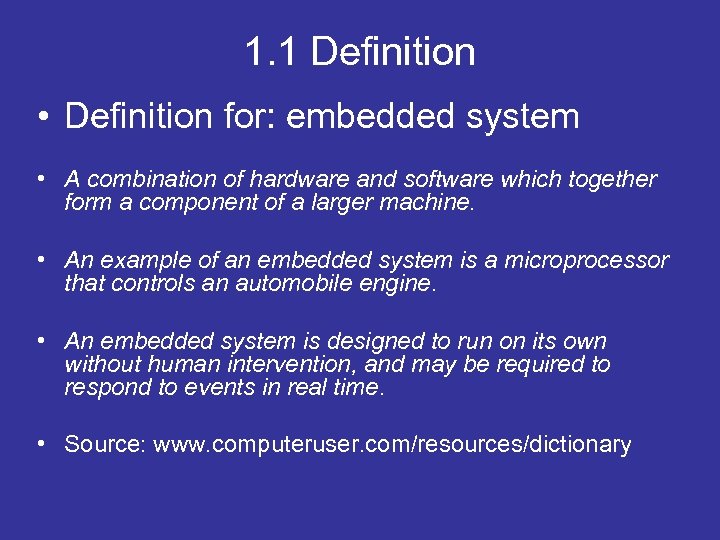
1. 1 Definition • Definition for: embedded system • A combination of hardware and software which together form a component of a larger machine. • An example of an embedded system is a microprocessor that controls an automobile engine. • An embedded system is designed to run on its own without human intervention, and may be required to respond to events in real time. • Source: www. computeruser. com/resources/dictionary

Applications Areas

Application Areas • TV • stereo • remote control • phone / mobile phone • refrigerator • microwave • washing machine • electric tooth brush • oven / rice or bread cooker • watch • alarm clock • electronic musical instruments • electronic toys (stuffed animals, handheld toys, pinballs, etc. ) • medical home equipment (e. g. blood pressure, thermometer) • … • [PDAs? ? More like standard computer system] Consumer Products

Application Areas • Medical Systems – pace maker, patient monitoring systems, injection systems, intensive care units, … • Office Equipment – printer, copier, fax, … • Tools – multimeter, oscilloscope, line tester, GPS, … • Banking – ATMs, statement printers, … • Transportation – (Planes/Trains/[Automobiles] and Boats) • radar, traffic lights, signalling systems, …

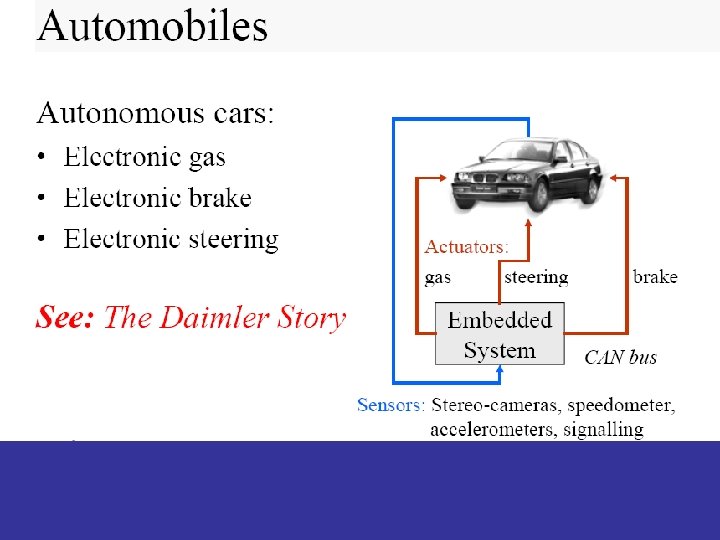
Application Areas • Automobiles – engine management, trip computer, cruise control, immobilizer, car alarm, – airbag, ABS, ESP, … • Building Systems – elevator, heater, air conditioning, lighting, key card entries, locks, alarm systems, … • Agriculture – feeding systems, milking systems, … • Space – satellite systems, …

Application Areas • Facts: – 1997: The average U. S. household has over 10 embedded computers (source: www. it. dtu. dk/~jan) • 1998: 90% Embedded Systems vs. 10% Computers – (source: Frautschi, www. caliberlearning. com) • 2001: The Volvo S 80 has 18 embedded controllers and 2 busses (source: Volvo)
Automobiles


Robot Metaphors and Models
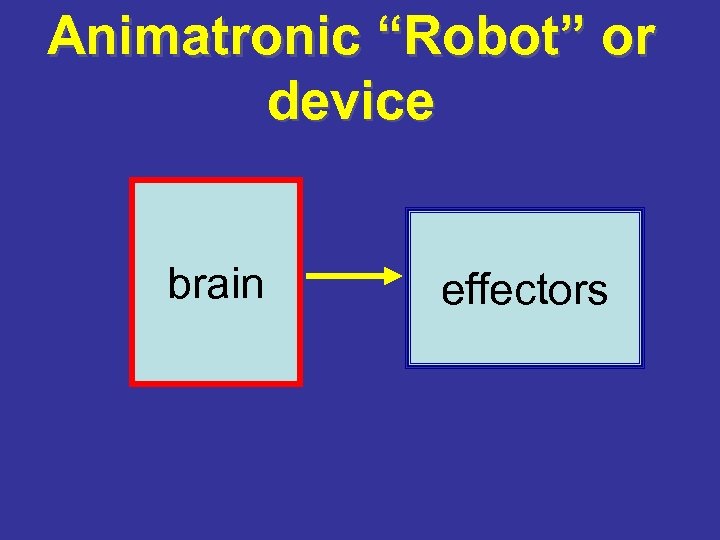
Animatronic “Robot” or device brain effectors
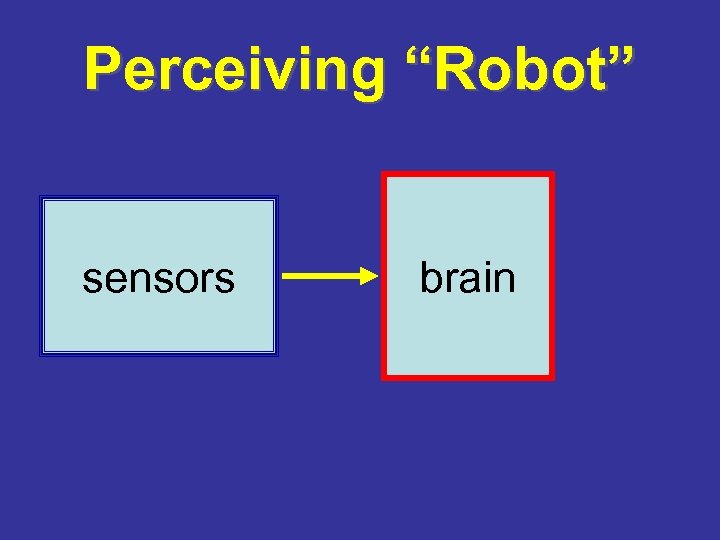
Perceiving “Robot” sensors brain
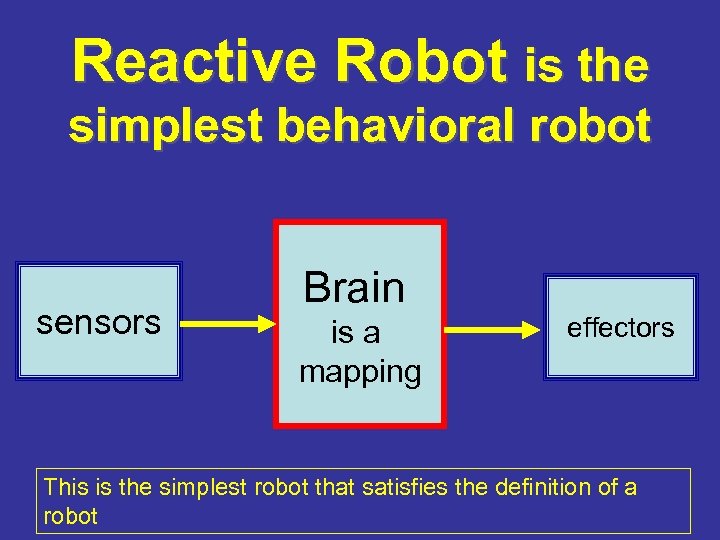
Reactive Robot is the simplest behavioral robot sensors Brain is a mapping effectors This is the simplest robot that satisfies the definition of a robot
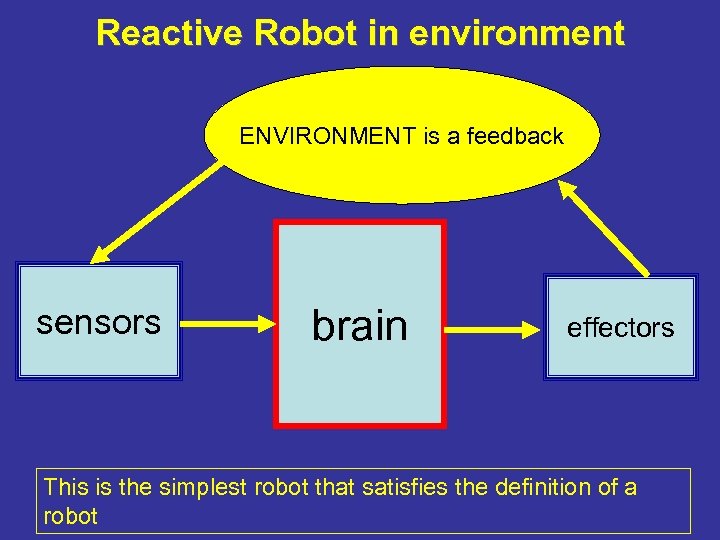
Reactive Robot in environment ENVIRONMENT is a feedback sensors brain effectors This is the simplest robot that satisfies the definition of a robot

Braitenberg Vehicles and Quantum Automata Robots
Another Example: Braitenberg Vehicles and Quantum BV
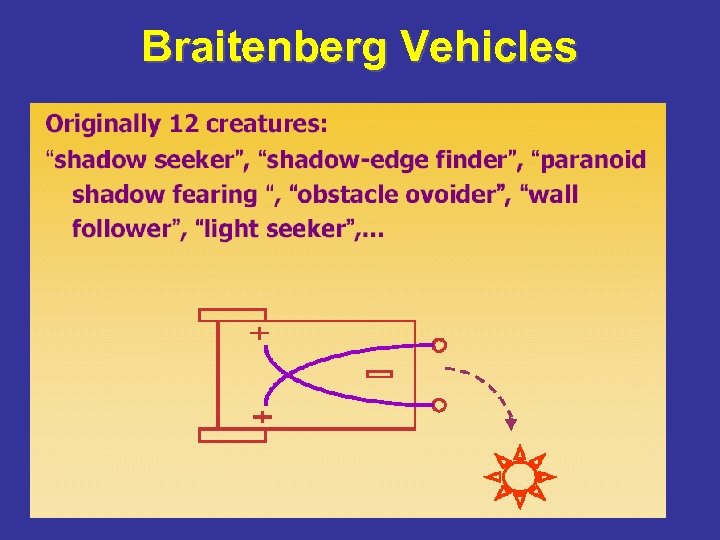
Braitenberg Vehicles

Braitenberg Vehicles: Homework 1 idea 1. Can you think about other robot behaviors? 2. Can you develop software for robots with other mechanics/kinematics but the same emergent principles? 3. Design circuits for switchable behaviors: like sound that switches from shy to aggressive robot.
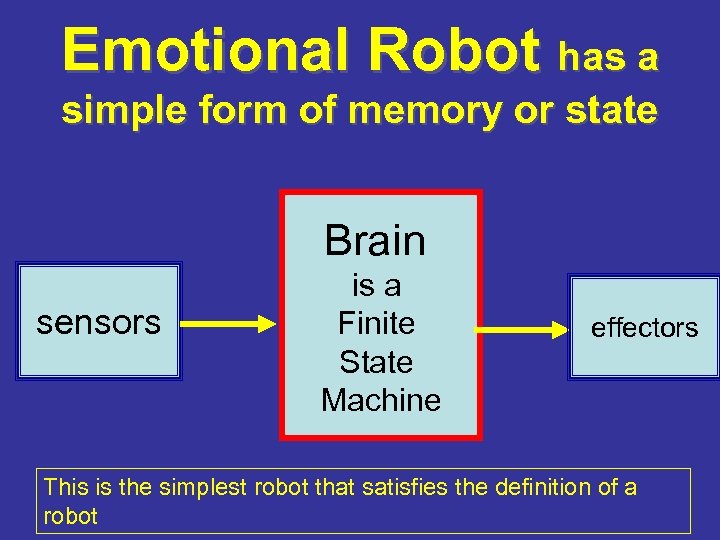
Emotional Robot has a simple form of memory or state Brain sensors is a Finite State Machine effectors This is the simplest robot that satisfies the definition of a robot
Behavior as an interpretation of a string • • Newton, Einstein and Bohr. Hello Professor Hello Sir Turn Left. Turn right. behavior
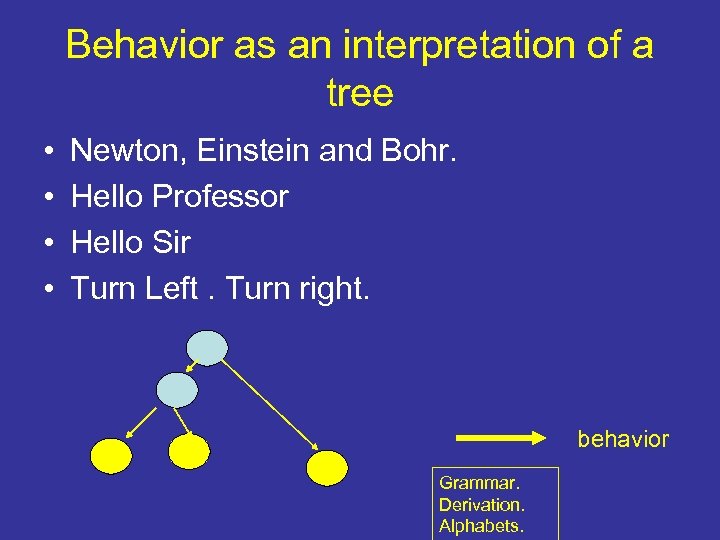
Behavior as an interpretation of a tree • • Newton, Einstein and Bohr. Hello Professor Hello Sir Turn Left. Turn right. behavior Grammar. Derivation. Alphabets.
Our First Base Robot Architecture and Designs
Neck and upper body movement generation
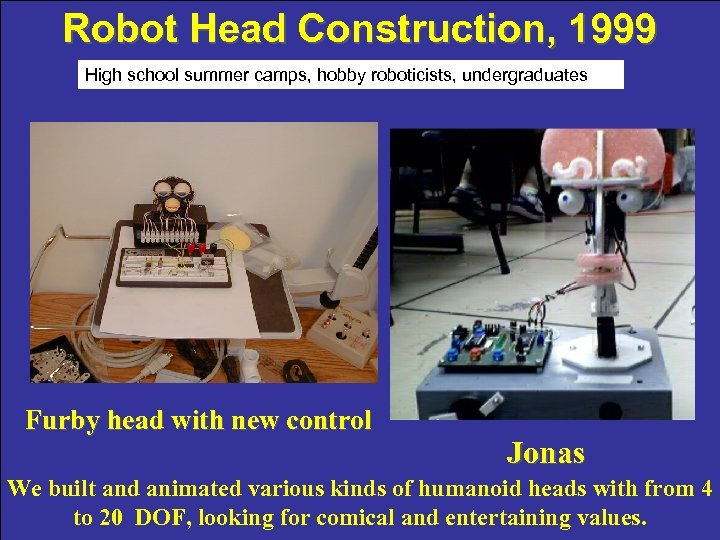
Robot Head Construction, 1999 High school summer camps, hobby roboticists, undergraduates Furby head with new control Jonas We built and animated various kinds of humanoid heads with from 4 to 20 DOF, looking for comical and entertaining values.

Mister Butcher Latex skin from Hollywood 4 degree of freedom neck
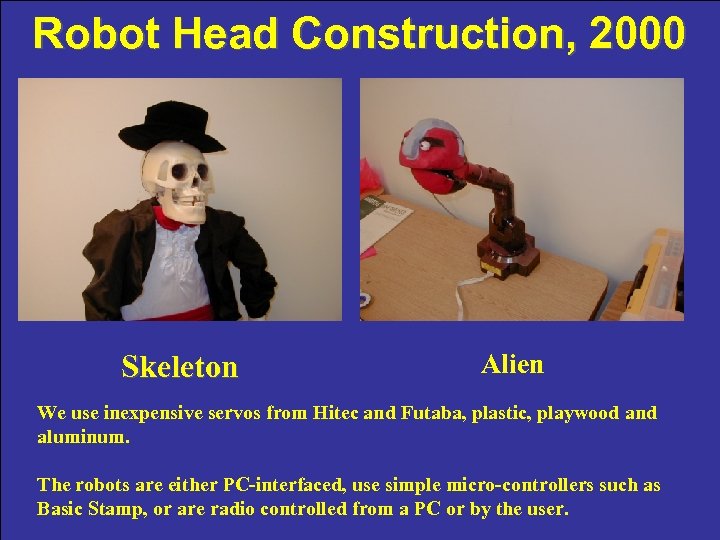
Robot Head Construction, 2000 Skeleton Alien We use inexpensive servos from Hitec and Futaba, plastic, playwood and aluminum. The robots are either PC-interfaced, use simple micro-controllers such as Basic Stamp, or are radio controlled from a PC or by the user.

Technical Construction, 2001 Details Adam Marvin the Crazy Robot

Virginia Woolf 2001 heads equipped with microphones, USB cameras, sonars and CDS light sensors

2002 Max BUG (Big Ugly Robot) Image processing and pattern recognition uses software developed at PSU, CMU and Intel (public domain software available on WWW). Software is in Visual C++, Visual Basic, Lisp and Prolog.

Visual Feedback and Learning based on Constructive Induction Uland Wong, 17 years old 2002

2002, Japan Professor Perky with automated speech recognition (ASR) and text -to-speech (TTS) capabilities • We compared several commercial speech systems from Microsoft, Sensory and Fonix. • Based on experiences in highly noisy environments and with a variety of speakers, we selected Fonix for both ASR and TTS for Professor Perky and Maria robots. 1 dollar latex skin from China • We use microphone array from Andrea Electronics.

Maria, 2002/2003 20 DOF
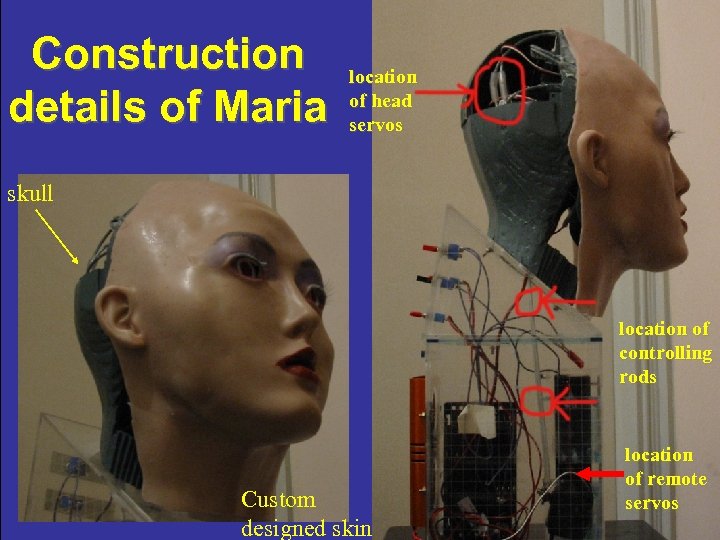
Construction details of Maria location of head servos skull location of controlling rods Custom designed skin location of remote servos

Animation of eyes and eyelids

Cynthia, 2004, June

Currently the hands are not moveable. We have a separate hand design project.
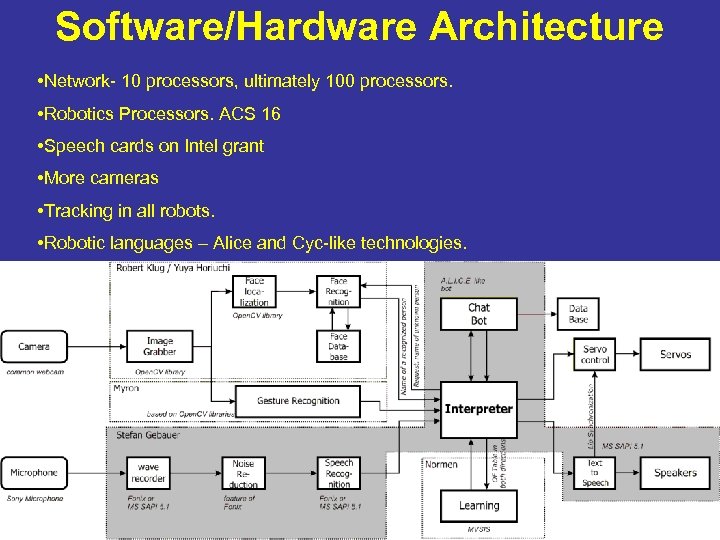
Software/Hardware Architecture • Network- 10 processors, ultimately 100 processors. • Robotics Processors. ACS 16 • Speech cards on Intel grant • More cameras • Tracking in all robots. • Robotic languages – Alice and Cyc-like technologies.
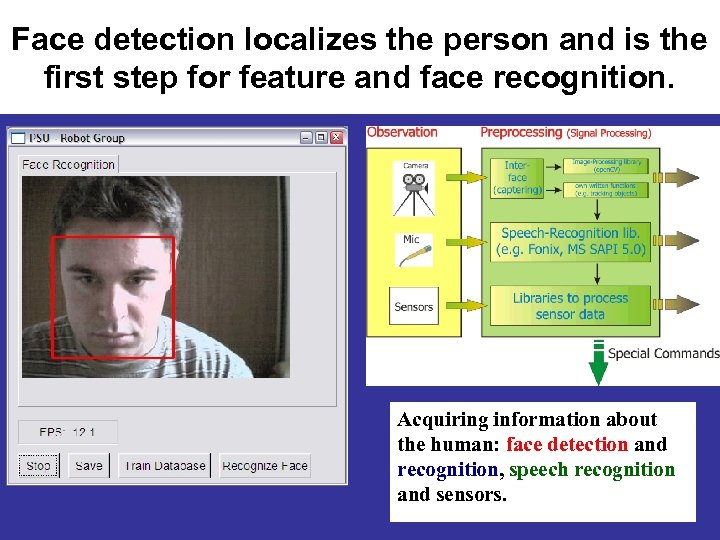
Face detection localizes the person and is the first step for feature and face recognition. Acquiring information about the human: face detection and recognition, speech recognition and sensors.
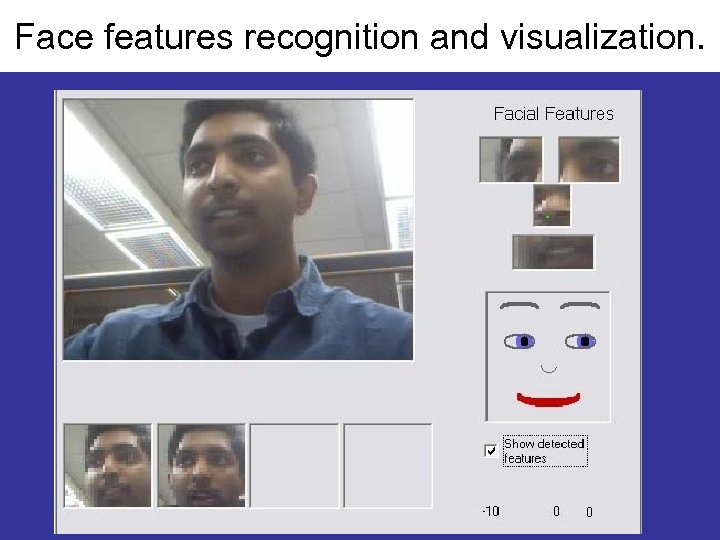
Face features recognition and visualization.

Use of Multiple. Valued (fivevalued) variables Smile, Mouth_Open and Eye_Brow_Raise for facial feature and face recognition.

HAHOE KAIST ROBOT THEATRE, KOREA, SUMMER 2004 Czy znacie dobra sztuke dla teatru robotow? Sonbi, the Confucian Scholar Paekchong, the bad butcher

Editing movements

Yangban the Aristocrat and Pune his concubine The Narrator

The Narrator
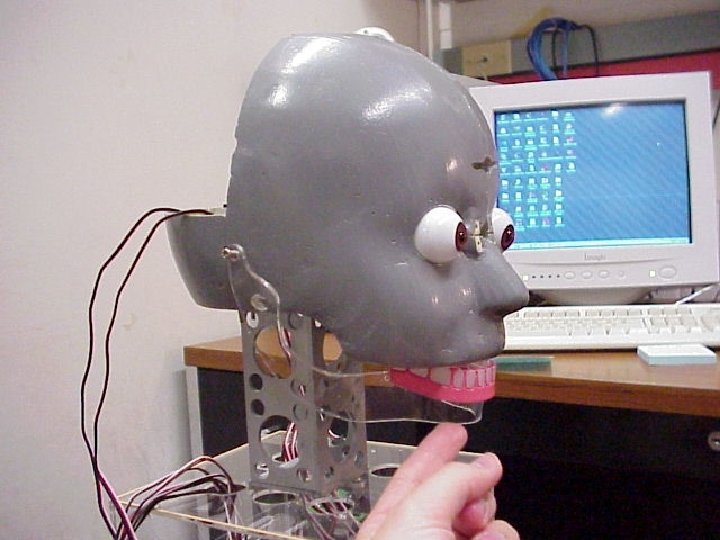


We base all our robots on inexpensive radiocontrolled servo technology.

We are familiar with latex and polyester technologies for faces Martin Lukac and Jeff Allen wait for your help, whether you want to program, design behaviors, add muscles, improve vision, etc.

New Silicone Skins
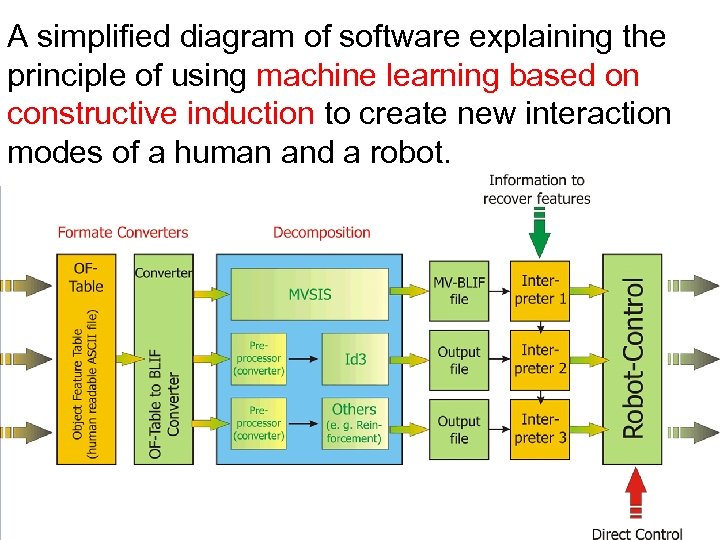
A simplified diagram of software explaining the principle of using machine learning based on constructive induction to create new interaction modes of a human and a robot.

Probabilistic and Finite State Machines
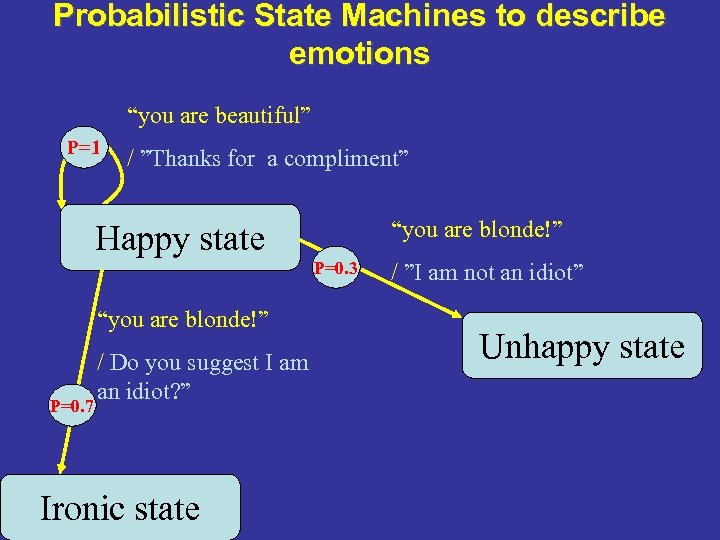
Probabilistic State Machines to describe emotions “you are beautiful” P=1 / ”Thanks for a compliment” Happy state “you are blonde!” P=0. 7 / Do you suggest I am an idiot? ” Ironic state “you are blonde!” P=0. 3 / ”I am not an idiot” Unhappy state

Facial Behaviors of Maria asks: Response: Do I look like younger than twenty three? §“no” §“yes” 0. 3 Maria smiles §“no” 0. 7 Maria frowns
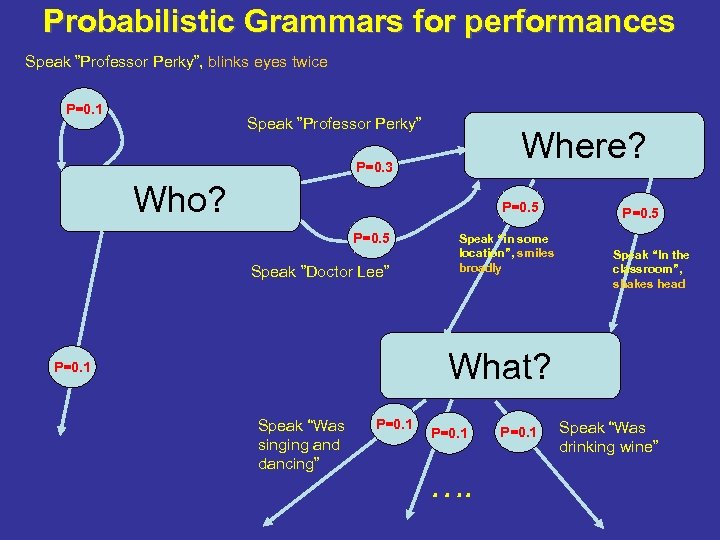
Probabilistic Grammars for performances Speak ”Professor Perky”, blinks eyes twice P=0. 1 Speak ”Professor Perky” Where? P=0. 3 Who? P=0. 5 Speak ”Doctor Lee” Speak “in some location”, smiles broadly P=0. 5 Speak “In the classroom”, shakes head What? P=0. 1 Speak “Was singing and dancing” P=0. 1 …. P=0. 1 Speak “Was drinking wine”
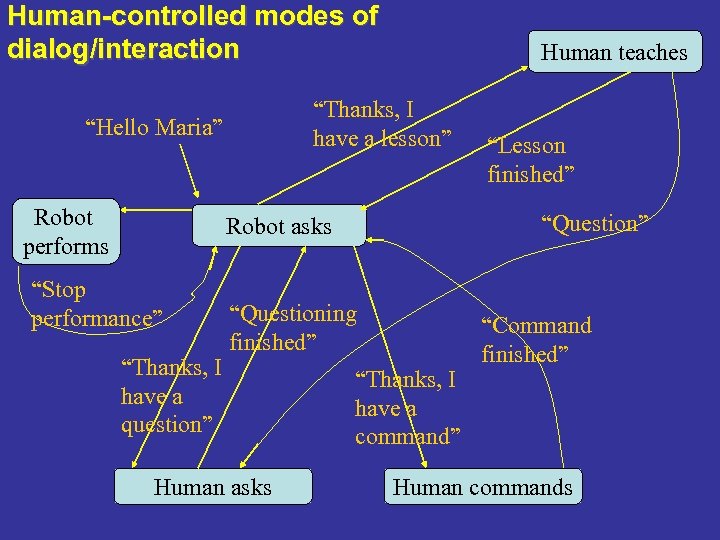
Human-controlled modes of dialog/interaction “Thanks, I have a lesson” “Hello Maria” Robot performs Human teaches “Question” Robot asks “Stop performance” “Thanks, I have a question” “Questioning finished” Human asks “Lesson finished” “Thanks, I have a command” “Command finished” Human commands

Dialog and Robot’s Knowledge
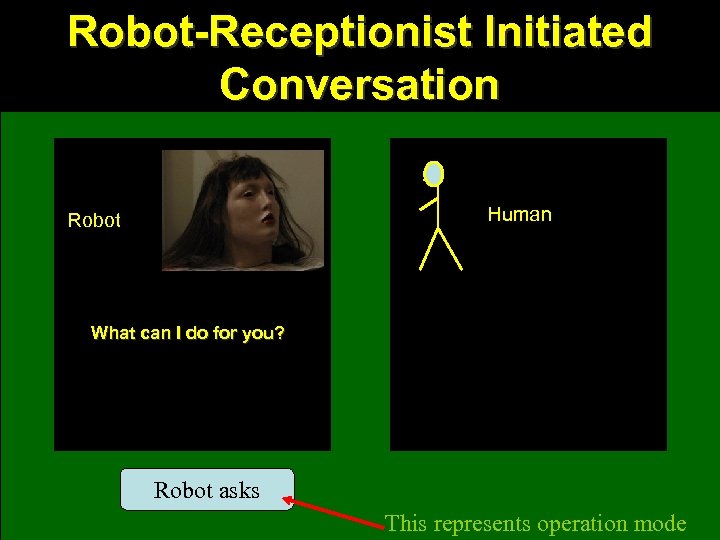
Robot-Receptionist Initiated Conversation Human Robot What can I do for you? Robot asks This represents operation mode

Robot-Receptionist Initiated Conversation Human Robot What can I do for you? Robot asks I would like to order a table for two
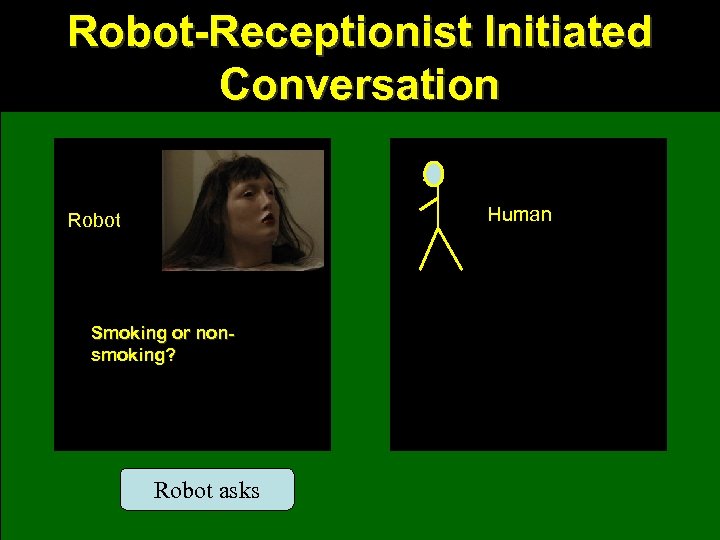
Robot-Receptionist Initiated Conversation Human Robot Smoking or nonsmoking? Robot asks

Robot-Receptionist Initiated Conversation Human Robot Smoking or nonsmoking? Robot asks I do not understand

Robot-Receptionist Initiated Conversation Human Robot Do you want a table in a smoking or non-smoking section of the restaurant? Non-smoking section is near the terrace. Robot asks
Robot-Receptionist Initiated Conversation Human Robot Do you want a table in a smoking or non-smoking section of the restaurant? Non-smoking section is near the terrace. Robot asks A table near the terrace, please

Human-Initiated Conversation Human Robot Hello Maria initialization Robot asks

Human-Initiated Conversation Robot What can I do for you? Robot asks Human Hello Maria

Human-Asking Human Robot Question Robot asks Question Human asks

Human-Asking Robot Yes, you ask a question. Human Question Human asks

Human-Asking Robot Yes, you ask a question. Human What book wrote Lee? Human asks

Human-Asking Robot I have no sure information. Human What book wrote Lee? Human asks

Human-Asking Robot I have no sure information. Human Try to guess. Human asks

Human-Asking Robot Lee wrote book “Flowers”. Human Try to guess. Human asks

Human-Asking Robot Lee wrote book “Flowers”. Human This is not true. Human asks

Human ends questioning Human-Teaching Human Robot Questioning finished Human asks “Questioning finished” Human teaches Robot asks Thanks, I have a lesson
Robot enters asking mode Human-Teaching Human Robot What can I do for you? Questioning finished Human asks “Questioning finished” Human teaches Robot asks Thanks, I have a lesson

Human starts teaching Human-Teaching Human Robot What can I do for you? Thanks, I have a lesson Human asks “Questioning finished” Human teaches Robot asks Thanks, I have a lesson

Human-Teaching Robot Yes Human Thanks, I have a lesson Human teaches

Human-Teaching Robot Yes Human I give you questionanswer pattern Human teaches

Human-Teaching Robot Human Question pattern: Yes What book Smith wrote? Human teaches

Human-Teaching Robot Human Answer pattern: Yes Smith wrote book “Automata Theory” Human teaches

Human-Teaching Robot Human Checking question: Yes What book wrote Smith? Human teaches

Human-Teaching Robot Human Checking question: Smith wrote book “Automata Theory” What book wrote Smith? Human teaches

Human-Teaching Robot Yes Human I give you questionanswer pattern Human teaches

Human-Teaching Robot Human Question pattern: Yes Where is room of Lee? Human teaches

Human-Teaching Robot Human Answer pattern: Yes Lee is in room 332 Human teaches

Human-Checking what robot learned Human Robot Lesson finished Robot asks “Lesson finished” Question Human teaches Human asks

Human-Checking what robot learned Human Robot Lesson finished What can I do for you? Robot asks “Lesson finished” Question Human teaches Human asks
Human-Checking what robot learned Human Robot Question What can I do for you? Robot asks “Lesson finished” Question Human teaches Human asks

Human-Asking Human Robot Yes, you ask a question. Robot asks “Lesson finished” Question Human teaches Human asks

Human-Asking Robot Yes, you ask a question. Human What book wrote Lee? Human asks

Human-Asking Robot I have no sure information. Human What book wrote Lee? Human asks

Human-Asking Robot I have no sure information. Human Try to guess. Human asks

Human-Asking Robot Lee wrote book “Automata Theory” Observe that robot found similarity between Smith and Lee and generalized (incorrectly) Human Try to guess. Human asks

Behavior, Dialog and Learning • The dialog/behavior has the following components: – (1) Eliza-like natural language dialogs based on pattern matching and limited parsing. • Commercial products like Memoni, Dog. Com, Heart, Alice, and Doctor all use this technology, very successfully – for instance Alice program won the 2001 Turing competition. – This is a “conversational” part of the robot brain, based on pattern-matching, parsing and black-board principles. – It is also a kind of “operating system” of the robot, which supervises other subroutines.

Behavior, Dialog and Learning • (2) Subroutines with logical data base and natural language parsing (CHAT). – This is the logical part of the brain used to find connections between places, timings and all kind of logical and relational reasonings, such as answering questions about Japanese geography.

Behavior, Dialog and Learning • (3) Use of generalization and analogy in dialog on many levels. – Random and intentional linking of spoken language, sound effects and facial gestures. – Use of Constructive Induction approach to help generalization, analogy reasoning and probabilistic generations in verbal and non-verbal dialog, like learning when to smile or turn the head off the partner.

Behavior, Dialog and Learning • (4) Model of the robot, model of the user, scenario of the situation, history of the dialog, all used in the conversation. • (5) Use of word spotting in speech recognition rather than single word or continuous speech recognition. • • (6) Continuous speech recognition (Microsoft) • (7) Avoidance of “I do not know”, “I do not understand” answers from the robot. – Our robot will have always something to say, in the worst case, over-generalized, with not valid analogies or even nonsensical and random.

Questions to students 1. Present a concept of a robot with architecture based on combinational logic mapping. Design a function from gates. 2. Present a concept of a robot with architecture based on deterministic Finite State Machine. Show a graph or table of the machine. You can also draw a flowchart. 3. Present a concept of a robot with architecture based on probabilistic Finite State Machine. Show a graph or table of the machine. 4. Present a software internet robot for natural language conversation, similar to receptionist robot from this set of slides. The robot should discuss Intelligent Robotics Laboratory, its research, faculty and students. What are the “states of robot”? What are the key-words to transit from state to state, draw a diagram. 5. Analyze four different Braitenberg Vehicles based on a robot with kinematics of a standard car. Two of them can be similar to Shy and Aggressive robots from class. 6. Analyze four different “Braitenberg-like robots” that have a head and one hand. Two of them can be similar to Shy and Aggressive robots from class This is not a homework, just to test your knowledge. You do not have to give it to me but you may if you want.
578ad638180d2e5a472578f85799907b.ppt