758febe46b87280a8b33082fe881b7e7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
 Slide 8. 1 Chapter 8 Management of research and development Paul Trott, Innovation Management and New Product Development , 4 th Edition, © Pearson Education Limited 2008
Slide 8. 1 Chapter 8 Management of research and development Paul Trott, Innovation Management and New Product Development , 4 th Edition, © Pearson Education Limited 2008
 Slide 8. 2 Structure of lecture n n n n Introduction Background: The management of R&D within organisations R&D and the link with corporate strategy R&D strategic planning R&D operational activities Allocating funds to R&D Summary and recap Paul Trott, Innovation Management and New Product Development , 4 th Edition, © Pearson Education Limited 2008
Slide 8. 2 Structure of lecture n n n n Introduction Background: The management of R&D within organisations R&D and the link with corporate strategy R&D strategic planning R&D operational activities Allocating funds to R&D Summary and recap Paul Trott, Innovation Management and New Product Development , 4 th Edition, © Pearson Education Limited 2008
 Slide 8. 3 Nov 2007 US leads way as global R&D spending rises 10% China and India both recorded growth of more than 30 per cent, albeit from low bases – £ 766 m for China and £ 268 m for India. Paul Trott, Innovation Management and New Product Development , 4 th Edition, © Pearson Education Limited 2008
Slide 8. 3 Nov 2007 US leads way as global R&D spending rises 10% China and India both recorded growth of more than 30 per cent, albeit from low bases – £ 766 m for China and £ 268 m for India. Paul Trott, Innovation Management and New Product Development , 4 th Edition, © Pearson Education Limited 2008
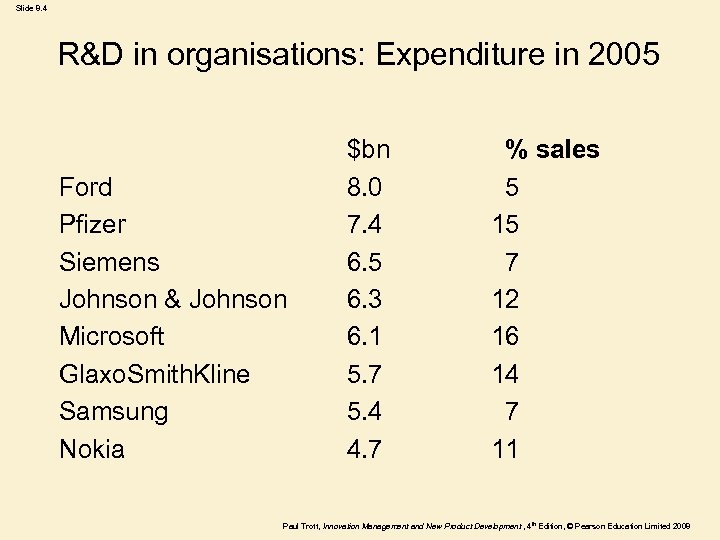 Slide 8. 4 R&D in organisations: Expenditure in 2005 Ford Pfizer Siemens Johnson & Johnson Microsoft Glaxo. Smith. Kline Samsung Nokia $bn 8. 0 7. 4 6. 5 6. 3 6. 1 5. 7 5. 4 4. 7 % sales 5 15 7 12 16 14 7 11 Paul Trott, Innovation Management and New Product Development , 4 th Edition, © Pearson Education Limited 2008
Slide 8. 4 R&D in organisations: Expenditure in 2005 Ford Pfizer Siemens Johnson & Johnson Microsoft Glaxo. Smith. Kline Samsung Nokia $bn 8. 0 7. 4 6. 5 6. 3 6. 1 5. 7 5. 4 4. 7 % sales 5 15 7 12 16 14 7 11 Paul Trott, Innovation Management and New Product Development , 4 th Edition, © Pearson Education Limited 2008
 Slide 8. 5 What is R&D? “R&D is the purposeful and systematic use of scientific knowledge to improve man’s lot even though some of its manifestations do not meet with universal approval. ” (Twiss, 1992) “To develop new knowledge and apply scientific or engineering knowledge to connect the knowledge in one field to that in others. ” (Roussel et al. , 1991) Paul Trott, Innovation Management and New Product Development , 4 th Edition, © Pearson Education Limited 2008
Slide 8. 5 What is R&D? “R&D is the purposeful and systematic use of scientific knowledge to improve man’s lot even though some of its manifestations do not meet with universal approval. ” (Twiss, 1992) “To develop new knowledge and apply scientific or engineering knowledge to connect the knowledge in one field to that in others. ” (Roussel et al. , 1991) Paul Trott, Innovation Management and New Product Development , 4 th Edition, © Pearson Education Limited 2008
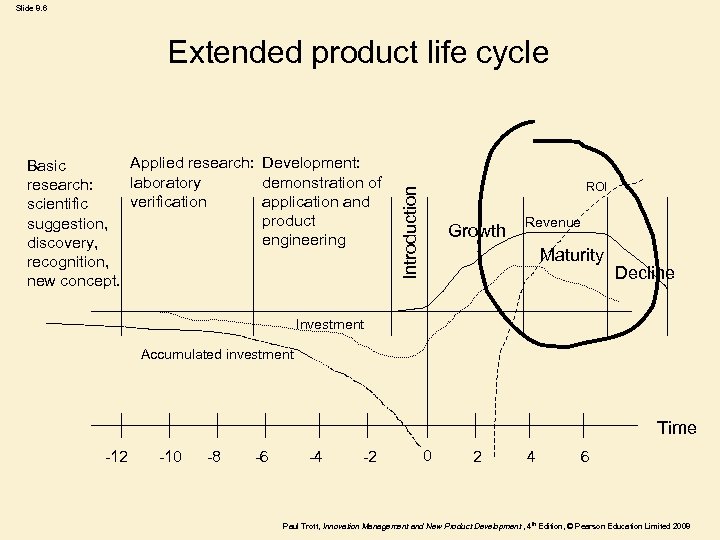 Slide 8. 6 Extended product life cycle ROI Introduction Applied research: Development: Basic laboratory demonstration of research: verification application and scientific product suggestion, engineering discovery, recognition, new concept. Growth Revenue Maturity Decline Investment Accumulated investment Time -12 -10 -8 -6 -4 -2 0 2 4 6 Paul Trott, Innovation Management and New Product Development , 4 th Edition, © Pearson Education Limited 2008
Slide 8. 6 Extended product life cycle ROI Introduction Applied research: Development: Basic laboratory demonstration of research: verification application and scientific product suggestion, engineering discovery, recognition, new concept. Growth Revenue Maturity Decline Investment Accumulated investment Time -12 -10 -8 -6 -4 -2 0 2 4 6 Paul Trott, Innovation Management and New Product Development , 4 th Edition, © Pearson Education Limited 2008
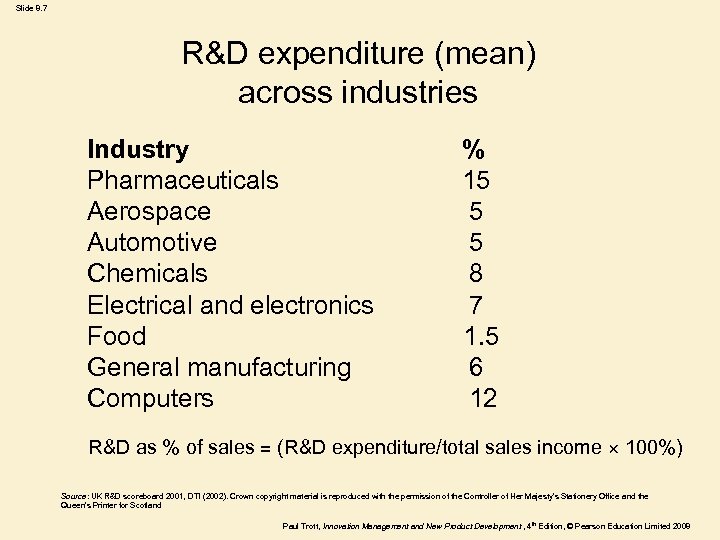 Slide 8. 7 R&D expenditure (mean) across industries Industry % Pharmaceuticals 15 Aerospace 5 Automotive 5 Chemicals 8 Electrical and electronics 7 Food 1. 5 General manufacturing 6 Computers 12 R&D as % of sales = (R&D expenditure/total sales income × 100%) Source: UK R&D scoreboard 2001, DTI (2002). Crown copyright material is reproduced with the permission of the Controller of Her Majesty’s Stationery Office and the Queen’s Printer for Scotland Paul Trott, Innovation Management and New Product Development , 4 th Edition, © Pearson Education Limited 2008
Slide 8. 7 R&D expenditure (mean) across industries Industry % Pharmaceuticals 15 Aerospace 5 Automotive 5 Chemicals 8 Electrical and electronics 7 Food 1. 5 General manufacturing 6 Computers 12 R&D as % of sales = (R&D expenditure/total sales income × 100%) Source: UK R&D scoreboard 2001, DTI (2002). Crown copyright material is reproduced with the permission of the Controller of Her Majesty’s Stationery Office and the Queen’s Printer for Scotland Paul Trott, Innovation Management and New Product Development , 4 th Edition, © Pearson Education Limited 2008
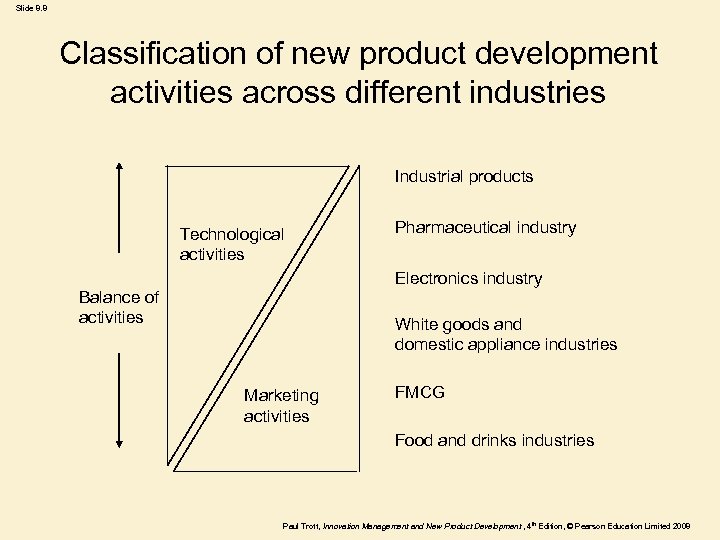 Slide 8. 8 Classification of new product development activities across different industries Industrial products Technological activities Pharmaceutical industry Electronics industry Balance of activities White goods and domestic appliance industries Marketing activities FMCG Food and drinks industries Paul Trott, Innovation Management and New Product Development , 4 th Edition, © Pearson Education Limited 2008
Slide 8. 8 Classification of new product development activities across different industries Industrial products Technological activities Pharmaceutical industry Electronics industry Balance of activities White goods and domestic appliance industries Marketing activities FMCG Food and drinks industries Paul Trott, Innovation Management and New Product Development , 4 th Edition, © Pearson Education Limited 2008
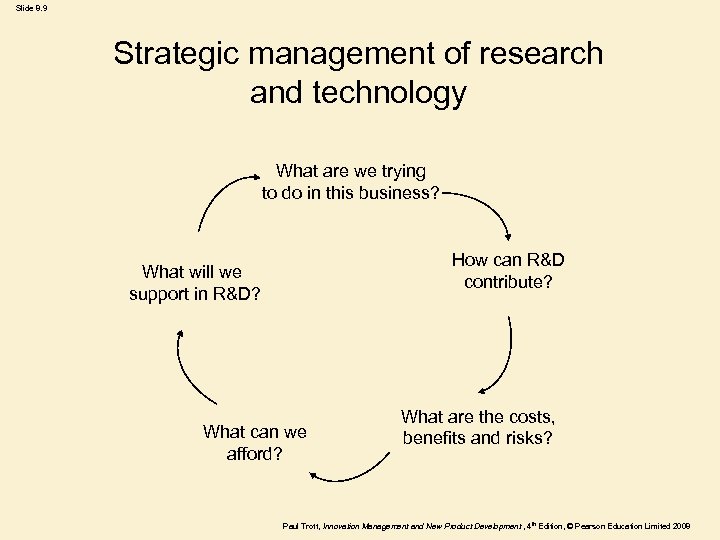 Slide 8. 9 Strategic management of research and technology What are we trying to do in this business? How can R&D contribute? What will we support in R&D? What can we afford? What are the costs, benefits and risks? Paul Trott, Innovation Management and New Product Development , 4 th Edition, © Pearson Education Limited 2008
Slide 8. 9 Strategic management of research and technology What are we trying to do in this business? How can R&D contribute? What will we support in R&D? What can we afford? What are the costs, benefits and risks? Paul Trott, Innovation Management and New Product Development , 4 th Edition, © Pearson Education Limited 2008
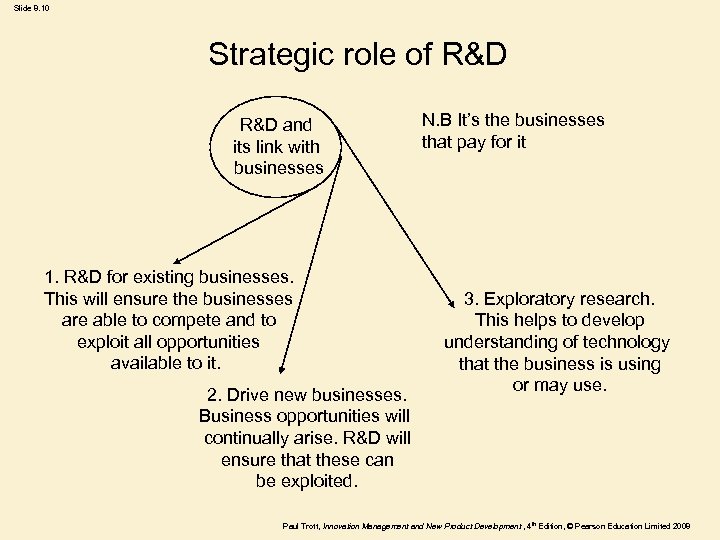 Slide 8. 10 Strategic role of R&D and its link with businesses 1. R&D for existing businesses. This will ensure the businesses are able to compete and to exploit all opportunities available to it. 2. Drive new businesses. Business opportunities will continually arise. R&D will ensure that these can be exploited. N. B It’s the businesses that pay for it 3. Exploratory research. This helps to develop understanding of technology that the business is using or may use. Paul Trott, Innovation Management and New Product Development , 4 th Edition, © Pearson Education Limited 2008
Slide 8. 10 Strategic role of R&D and its link with businesses 1. R&D for existing businesses. This will ensure the businesses are able to compete and to exploit all opportunities available to it. 2. Drive new businesses. Business opportunities will continually arise. R&D will ensure that these can be exploited. N. B It’s the businesses that pay for it 3. Exploratory research. This helps to develop understanding of technology that the business is using or may use. Paul Trott, Innovation Management and New Product Development , 4 th Edition, © Pearson Education Limited 2008
 Slide 8. 11 R&D strategic planning means developing a technology portfolio • Core technologies Central to all or most of the company’s products • Complementary technologies Additional technologies • Peripheral technologies Whose application contributes to the business • Emerging technologies Long-term significance Paul Trott, Innovation Management and New Product Development , 4 th Edition, © Pearson Education Limited 2008
Slide 8. 11 R&D strategic planning means developing a technology portfolio • Core technologies Central to all or most of the company’s products • Complementary technologies Additional technologies • Peripheral technologies Whose application contributes to the business • Emerging technologies Long-term significance Paul Trott, Innovation Management and New Product Development , 4 th Edition, © Pearson Education Limited 2008
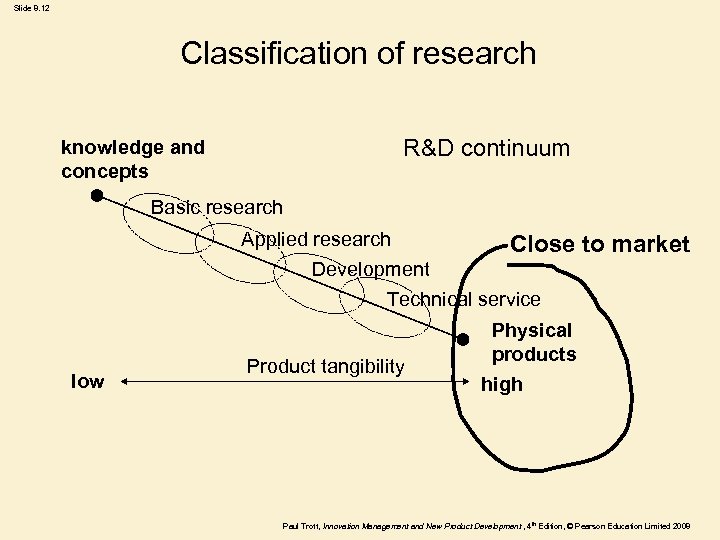 Slide 8. 12 Classification of research R&D continuum knowledge and concepts Basic research Applied research Close Development Technical service low Product tangibility to market Physical products high Paul Trott, Innovation Management and New Product Development , 4 th Edition, © Pearson Education Limited 2008
Slide 8. 12 Classification of research R&D continuum knowledge and concepts Basic research Applied research Close Development Technical service low Product tangibility to market Physical products high Paul Trott, Innovation Management and New Product Development , 4 th Edition, © Pearson Education Limited 2008
 Slide 8. 13 R&D operational activities Basic research Work of a general nature intended to apply to a broad range of uses or to new knowledge about an area. Applied research Work involving basic knowledge for the solution of a problem. Development The application of known facts and theory to solve a particular problem through exploratory study. Technical service Cost and performance improvements to existing products, processes or systems. Paul Trott, Innovation Management and New Product Development , 4 th Edition, © Pearson Education Limited 2008
Slide 8. 13 R&D operational activities Basic research Work of a general nature intended to apply to a broad range of uses or to new knowledge about an area. Applied research Work involving basic knowledge for the solution of a problem. Development The application of known facts and theory to solve a particular problem through exploratory study. Technical service Cost and performance improvements to existing products, processes or systems. Paul Trott, Innovation Management and New Product Development , 4 th Edition, © Pearson Education Limited 2008
 Slide 8. 14 Resource allocation to R&D • • • Inter-firm comparisons A fixed relationship to turnover A fixed relationship to profits Reference to previous levels of expenditure Costing of an agreed programme Internal customer–contractor relationship Paul Trott, Innovation Management and New Product Development , 4 th Edition, © Pearson Education Limited 2008
Slide 8. 14 Resource allocation to R&D • • • Inter-firm comparisons A fixed relationship to turnover A fixed relationship to profits Reference to previous levels of expenditure Costing of an agreed programme Internal customer–contractor relationship Paul Trott, Innovation Management and New Product Development , 4 th Edition, © Pearson Education Limited 2008
 Slide 8. 15 Key points from the lecture n n R&D can be managed and is managed Technology for today, tomorrow and the future R&D operational activities R&D Project evaluation Paul Trott, Innovation Management and New Product Development , 4 th Edition, © Pearson Education Limited 2008
Slide 8. 15 Key points from the lecture n n R&D can be managed and is managed Technology for today, tomorrow and the future R&D operational activities R&D Project evaluation Paul Trott, Innovation Management and New Product Development , 4 th Edition, © Pearson Education Limited 2008
 Slide 8. 16 References Roussel, P. A. , et al. (1991) Third Generation R&D, Harvard Business School Press, Boston, MA. Trott P (2005) Innovation Management & NPD 3 rd ed. , Prentice Hall. Twiss, B. (1992) Managing Technological Innovation, Lithedin FT: Pitman publishing, London. UK R&D scoreboard 2001, DTI (2002). Paul Trott, Innovation Management and New Product Development , 4 th Edition, © Pearson Education Limited 2008
Slide 8. 16 References Roussel, P. A. , et al. (1991) Third Generation R&D, Harvard Business School Press, Boston, MA. Trott P (2005) Innovation Management & NPD 3 rd ed. , Prentice Hall. Twiss, B. (1992) Managing Technological Innovation, Lithedin FT: Pitman publishing, London. UK R&D scoreboard 2001, DTI (2002). Paul Trott, Innovation Management and New Product Development , 4 th Edition, © Pearson Education Limited 2008


