Lecture_8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13
 Slide 7. 1 Lecture 8: Selecting samples Research Methods Mukhametzhan Seitzhapparuly seitzhapparuly 1@gmail. com Saunders, Lewis and Thornhill, Research Methods for Business Students , 5 th Edition, © Mark Saunders, Philip Lewis and Adrian Thornhill 2009
Slide 7. 1 Lecture 8: Selecting samples Research Methods Mukhametzhan Seitzhapparuly seitzhapparuly 1@gmail. com Saunders, Lewis and Thornhill, Research Methods for Business Students , 5 th Edition, © Mark Saunders, Philip Lewis and Adrian Thornhill 2009
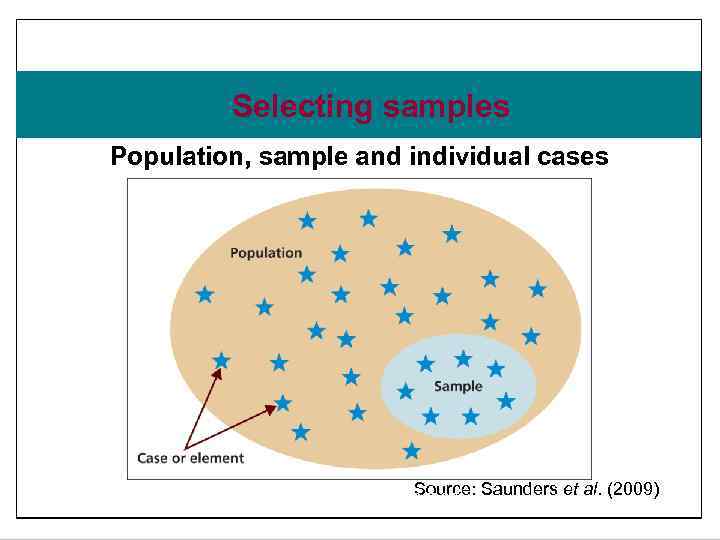 Slide 7. 2 Selecting samples Population, sample and individual cases Source: Figure 7. 1 Population, sample and individual cases Saunders et al. (2009) Saunders, Lewis and Thornhill, Research Methods for Business Students , 5 th Edition, © Mark Saunders, Philip Lewis and Adrian Thornhill 2009
Slide 7. 2 Selecting samples Population, sample and individual cases Source: Figure 7. 1 Population, sample and individual cases Saunders et al. (2009) Saunders, Lewis and Thornhill, Research Methods for Business Students , 5 th Edition, © Mark Saunders, Philip Lewis and Adrian Thornhill 2009
 Slide 7. 3 The need to sample Sampling- a valid alternative to a census when • A survey of the entire population is impracticable • Budget constraints restrict data collection • Time constraints restrict data collection • Results from data collection are needed quickly (tight deadlines) Saunders, Lewis and Thornhill, Research Methods for Business Students , 5 th Edition, © Mark Saunders, Philip Lewis and Adrian Thornhill 2009
Slide 7. 3 The need to sample Sampling- a valid alternative to a census when • A survey of the entire population is impracticable • Budget constraints restrict data collection • Time constraints restrict data collection • Results from data collection are needed quickly (tight deadlines) Saunders, Lewis and Thornhill, Research Methods for Business Students , 5 th Edition, © Mark Saunders, Philip Lewis and Adrian Thornhill 2009
 Slide 7. 4 The four stage process 1. Identify sampling frame from research objectives 2. Decide on a suitable sample size 3. Select the appropriate technique and the sample 4. Check that the sample is representative Saunders, Lewis and Thornhill, Research Methods for Business Students , 5 th Edition, © Mark Saunders, Philip Lewis and Adrian Thornhill 2009
Slide 7. 4 The four stage process 1. Identify sampling frame from research objectives 2. Decide on a suitable sample size 3. Select the appropriate technique and the sample 4. Check that the sample is representative Saunders, Lewis and Thornhill, Research Methods for Business Students , 5 th Edition, © Mark Saunders, Philip Lewis and Adrian Thornhill 2009
 Slide 7. 5 Identifying a suitable sampling frame Key points to consider • Problems of using existing databases • Extent of possible generalisation from the sample • Validity and reliability • Avoidance of bias Saunders, Lewis and Thornhill, Research Methods for Business Students , 5 th Edition, © Mark Saunders, Philip Lewis and Adrian Thornhill 2009
Slide 7. 5 Identifying a suitable sampling frame Key points to consider • Problems of using existing databases • Extent of possible generalisation from the sample • Validity and reliability • Avoidance of bias Saunders, Lewis and Thornhill, Research Methods for Business Students , 5 th Edition, © Mark Saunders, Philip Lewis and Adrian Thornhill 2009
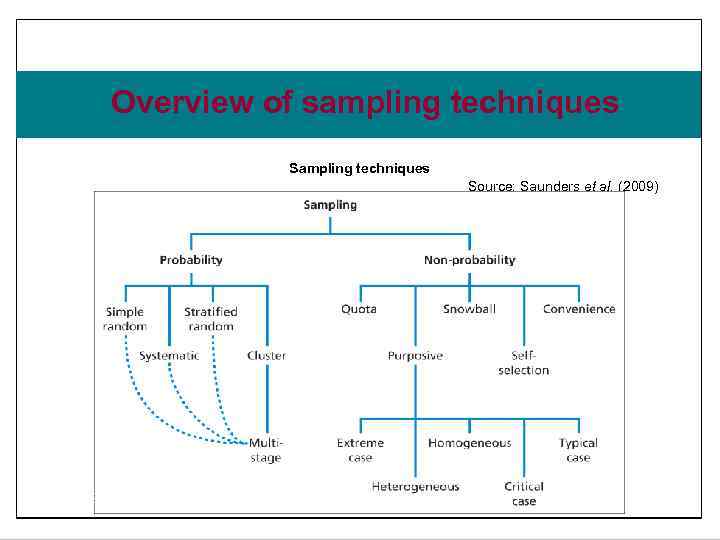 Slide 7. 6 Overview of sampling techniques Source: Saunders et al. (2009) Figure 7. 2 Sampling techniques Saunders, Lewis and Thornhill, Research Methods for Business Students , 5 th Edition, © Mark Saunders, Philip Lewis and Adrian Thornhill 2009
Slide 7. 6 Overview of sampling techniques Source: Saunders et al. (2009) Figure 7. 2 Sampling techniques Saunders, Lewis and Thornhill, Research Methods for Business Students , 5 th Edition, © Mark Saunders, Philip Lewis and Adrian Thornhill 2009
 Slide 7. 7 Probability – – Random sampling from population More expensive and time consuming More generalization of the results Techniques: Simple; Systematic; Stratified; Cluster Saunders, Lewis and Thornhill, Research Methods for Business Students , 5 th Edition, © Mark Saunders, Philip Lewis and Adrian Thornhill 2009
Slide 7. 7 Probability – – Random sampling from population More expensive and time consuming More generalization of the results Techniques: Simple; Systematic; Stratified; Cluster Saunders, Lewis and Thornhill, Research Methods for Business Students , 5 th Edition, © Mark Saunders, Philip Lewis and Adrian Thornhill 2009
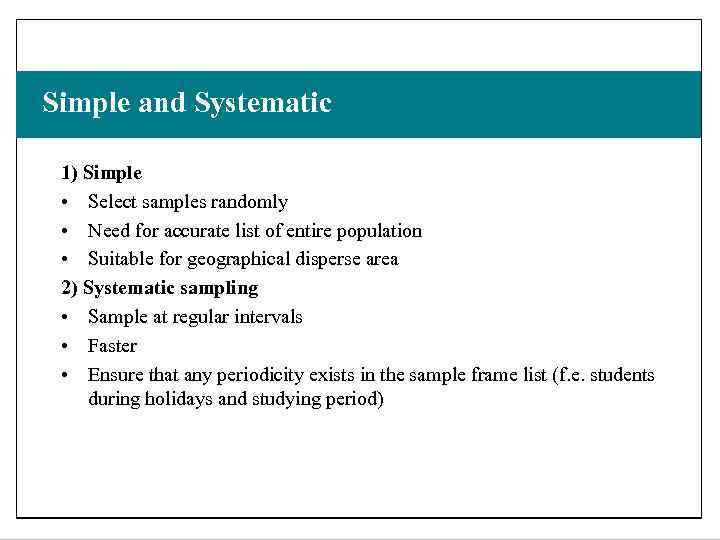 Slide 7. 8 Simple and Systematic 1) Simple • Select samples randomly • Need for accurate list of entire population • Suitable for geographical disperse area 2) Systematic sampling • Sample at regular intervals • Faster • Ensure that any periodicity exists in the sample frame list (f. e. students during holidays and studying period) Saunders, Lewis and Thornhill, Research Methods for Business Students , 5 th Edition, © Mark Saunders, Philip Lewis and Adrian Thornhill 2009
Slide 7. 8 Simple and Systematic 1) Simple • Select samples randomly • Need for accurate list of entire population • Suitable for geographical disperse area 2) Systematic sampling • Sample at regular intervals • Faster • Ensure that any periodicity exists in the sample frame list (f. e. students during holidays and studying period) Saunders, Lewis and Thornhill, Research Methods for Business Students , 5 th Edition, © Mark Saunders, Philip Lewis and Adrian Thornhill 2009
 Slide 7. 9 Stratified and Cluster 3) Stratified random sampling • Division of the population in groups according to significant attributes (f. e. social status, wage amount) • Random sampling for each group • Each group must represent proportionally the population • Longer, expensive, and difficult to explain 4) Cluster Sampling • The population is naturally clustered (f. e. Age, Gender) • Sample frame is a complete list of clusters Saunders, Lewis and Thornhill, Research Methods for Business Students , 5 th Edition, © Mark Saunders, Philip Lewis and Adrian Thornhill 2009
Slide 7. 9 Stratified and Cluster 3) Stratified random sampling • Division of the population in groups according to significant attributes (f. e. social status, wage amount) • Random sampling for each group • Each group must represent proportionally the population • Longer, expensive, and difficult to explain 4) Cluster Sampling • The population is naturally clustered (f. e. Age, Gender) • Sample frame is a complete list of clusters Saunders, Lewis and Thornhill, Research Methods for Business Students , 5 th Edition, © Mark Saunders, Philip Lewis and Adrian Thornhill 2009
 Slide 7. 10 Non-probability – Not random – Can be effective when trying to generate ideas and getting feedback – Lower capacity to generalize the results – More convenient and less costly – Techniques: Quota; Purposive; Snowball; Selfselective; convenience Saunders, Lewis and Thornhill, Research Methods for Business Students , 5 th Edition, © Mark Saunders, Philip Lewis and Adrian Thornhill 2009
Slide 7. 10 Non-probability – Not random – Can be effective when trying to generate ideas and getting feedback – Lower capacity to generalize the results – More convenient and less costly – Techniques: Quota; Purposive; Snowball; Selfselective; convenience Saunders, Lewis and Thornhill, Research Methods for Business Students , 5 th Edition, © Mark Saunders, Philip Lewis and Adrian Thornhill 2009
 Slide 7. 11 Quota and Purposive 1) Quota sampling • Premise that the sample will represent the population • Type of stratified sample in which the selection of samples is entirely nonrandom • Less costly and quickly than probability sampling • Sample size between 2000 -5000 2) Purposive sampling • The selection of the cases by personal judgement • Small samples • It is not considered representative of the population Saunders, Lewis and Thornhill, Research Methods for Business Students , 5 th Edition, © Mark Saunders, Philip Lewis and Adrian Thornhill 2009
Slide 7. 11 Quota and Purposive 1) Quota sampling • Premise that the sample will represent the population • Type of stratified sample in which the selection of samples is entirely nonrandom • Less costly and quickly than probability sampling • Sample size between 2000 -5000 2) Purposive sampling • The selection of the cases by personal judgement • Small samples • It is not considered representative of the population Saunders, Lewis and Thornhill, Research Methods for Business Students , 5 th Edition, © Mark Saunders, Philip Lewis and Adrian Thornhill 2009
 Slide 7. 12 Snowball, Self selecting and Convenience 3) Snowball sampling • Used when it is difficult to identify members of the desired population • Make an initial contact to identify further contacts • Difficult to make an initial contact • Induces to bias 4) Self selecting sampling • Allow each case to identify their desire to take part in the research (Publication of the need for the cases) • Collect data from those who respond 5) Convenience sampling • Selecting haphazardly cases that are easily to obtain for sample • Sample selection process continues until sample size is reached • Widely used- subject to bias Saunders, Lewis and Thornhill, Research Methods for Business Students , 5 th Edition, © Mark Saunders, Philip Lewis and Adrian Thornhill 2009
Slide 7. 12 Snowball, Self selecting and Convenience 3) Snowball sampling • Used when it is difficult to identify members of the desired population • Make an initial contact to identify further contacts • Difficult to make an initial contact • Induces to bias 4) Self selecting sampling • Allow each case to identify their desire to take part in the research (Publication of the need for the cases) • Collect data from those who respond 5) Convenience sampling • Selecting haphazardly cases that are easily to obtain for sample • Sample selection process continues until sample size is reached • Widely used- subject to bias Saunders, Lewis and Thornhill, Research Methods for Business Students , 5 th Edition, © Mark Saunders, Philip Lewis and Adrian Thornhill 2009
 Slide 7. 13 Reading Materials • Read Chapter 7. Selecting Samples, 210 -255 pages. • Book: M. Saunders, P. Lewis, and A. Thornhill, 2009, Research methods for business students, 5 th ed. , Harlow: Pearson Education Limited Saunders, Lewis and Thornhill, Research Methods for Business Students , 5 th Edition, © Mark Saunders, Philip Lewis and Adrian Thornhill 2009
Slide 7. 13 Reading Materials • Read Chapter 7. Selecting Samples, 210 -255 pages. • Book: M. Saunders, P. Lewis, and A. Thornhill, 2009, Research methods for business students, 5 th ed. , Harlow: Pearson Education Limited Saunders, Lewis and Thornhill, Research Methods for Business Students , 5 th Edition, © Mark Saunders, Philip Lewis and Adrian Thornhill 2009


