Slide 13 -2 MANAGING MARKETING CHANNELS AND SUPPLY































questions_57,3_-_lecture10.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 58
 Slide 13-2 MANAGING MARKETING CHANNELS AND SUPPLY CHAINS Lecture 10_Place (Channels of distribution) Associate professor of Plekhanov REA marketing department Irina I.Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
Slide 13-2 MANAGING MARKETING CHANNELS AND SUPPLY CHAINS Lecture 10_Place (Channels of distribution) Associate professor of Plekhanov REA marketing department Irina I.Skorobogatykh (Ph.D)
 Slide 13-5 LECTURE QUESTIONS: What is marketing channel of distribution and why intermediaries are needed. Differences between marketing channels for consumer and business products and services, and between different types of vertical marketing systems.
Slide 13-5 LECTURE QUESTIONS: What is marketing channel of distribution and why intermediaries are needed. Differences between marketing channels for consumer and business products and services, and between different types of vertical marketing systems.
 Slide 13-6 LECTURE QUESTIONS Factors considered by marketing executives when selecting and managing a marketing channel. Explain what supply chain and logistics management are and how they relate to marketing strategy.
Slide 13-6 LECTURE QUESTIONS Factors considered by marketing executives when selecting and managing a marketing channel. Explain what supply chain and logistics management are and how they relate to marketing strategy.
 Slide 13-7 LECTURE QUESTIONS Explain how managers trade off different “logistics costs” relative to customer service in order to make a supply chain decision.
Slide 13-7 LECTURE QUESTIONS Explain how managers trade off different “logistics costs” relative to customer service in order to make a supply chain decision.
 NATURE AND IMPORTANCE OF MARKETING CHANNELS Slide 13-9 Marketing Channel What Is a Marketing Channel of Distribution?
NATURE AND IMPORTANCE OF MARKETING CHANNELS Slide 13-9 Marketing Channel What Is a Marketing Channel of Distribution?
 Slide 13-71 A marketing channel consists of individuals and firms involved in the process of making a product or service available. Marketing Channel
Slide 13-71 A marketing channel consists of individuals and firms involved in the process of making a product or service available. Marketing Channel
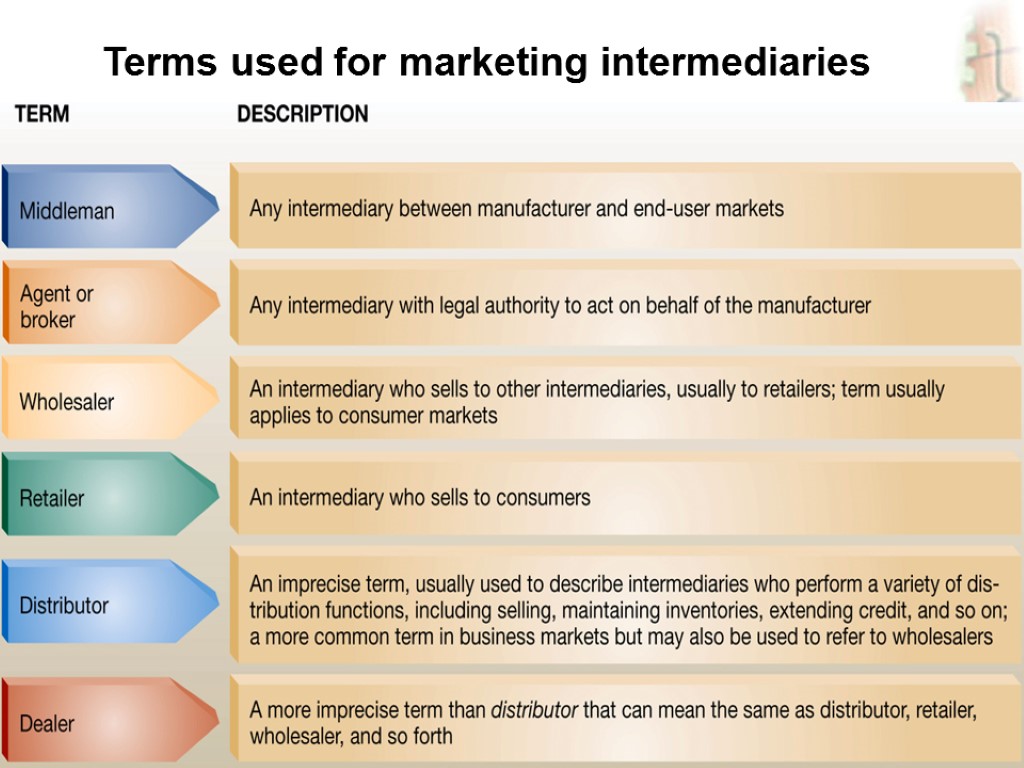
 Slide 13-10 Terms used for marketing intermediaries
Slide 13-10 Terms used for marketing intermediaries
 NATURE AND IMPORTANCE OF MARKETING CHANNELS Slide 13-11 Value Created by Intermediaries Functions Performed by Intermediaries Consumer Benefits from Intermediaries
NATURE AND IMPORTANCE OF MARKETING CHANNELS Slide 13-11 Value Created by Intermediaries Functions Performed by Intermediaries Consumer Benefits from Intermediaries
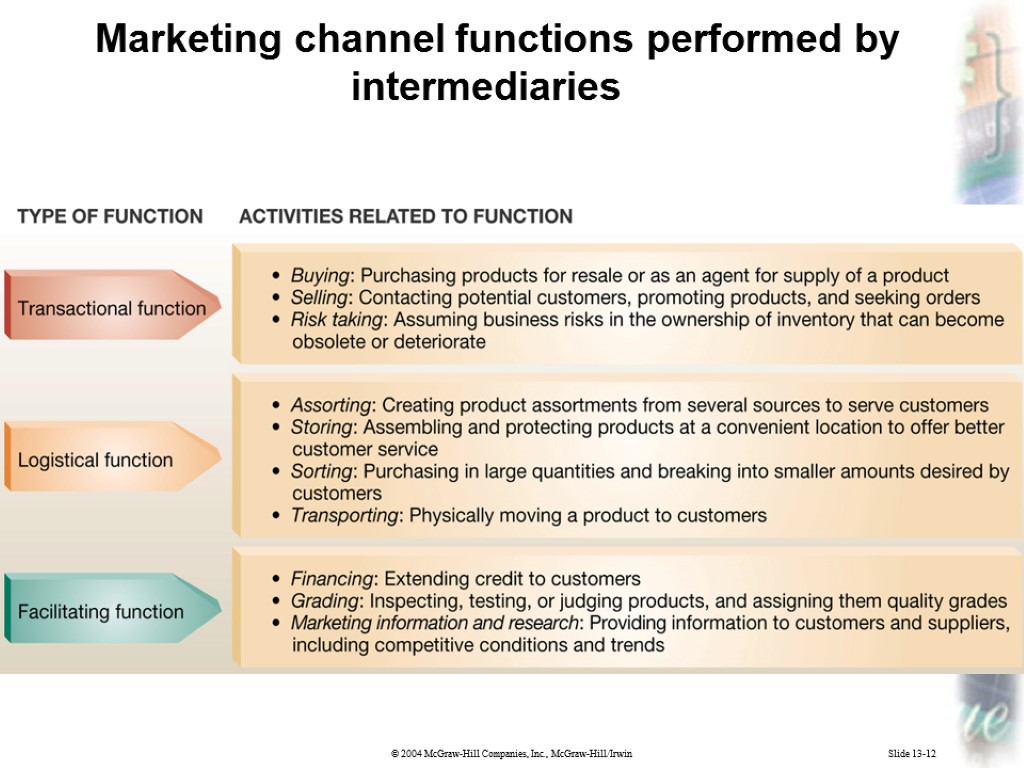
 Slide 13-12 Marketing channel functions performed by intermediaries
Slide 13-12 Marketing channel functions performed by intermediaries
 Slide 13-13 1. What is meant by a marketing channel? A: A marketing channel consists of individuals and firms involved in the process of making a product or service available. Concept Check
Slide 13-13 1. What is meant by a marketing channel? A: A marketing channel consists of individuals and firms involved in the process of making a product or service available. Concept Check
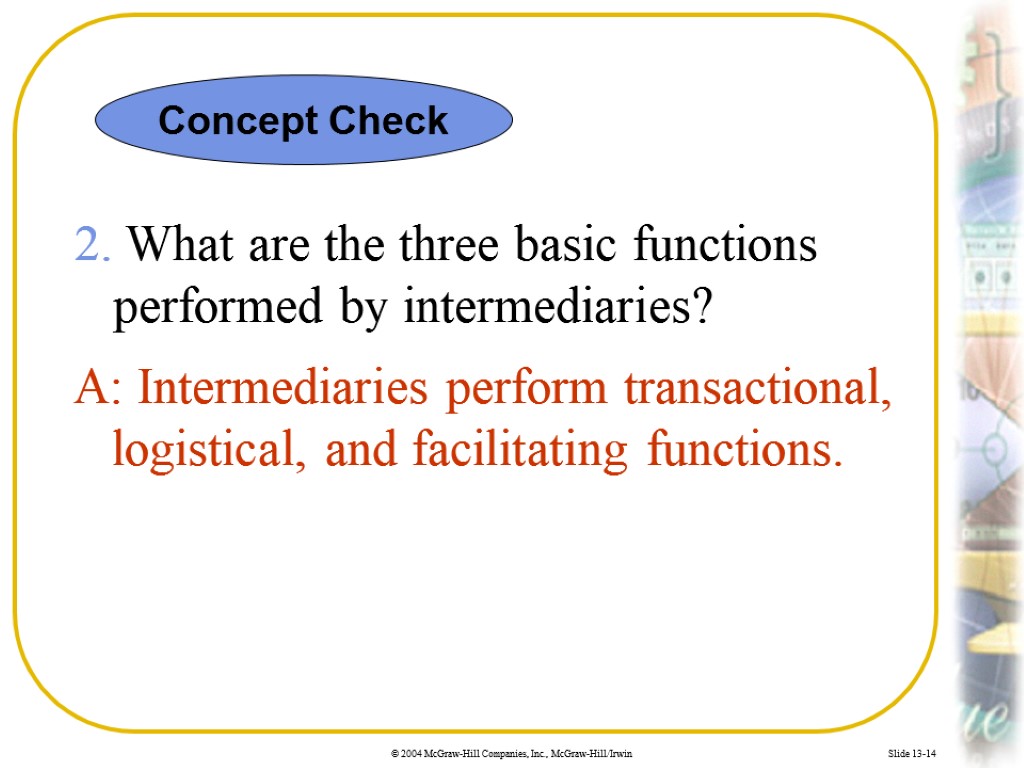
 Slide 13-14 2. What are the three basic functions performed by intermediaries? A: Intermediaries perform transactional, logistical, and facilitating functions. Concept Check
Slide 13-14 2. What are the three basic functions performed by intermediaries? A: Intermediaries perform transactional, logistical, and facilitating functions. Concept Check
 CHANNEL STRUCTURE AND ORGANIZATION Slide 13-15 Direct Channel Marketing Channels for Consumer Goods and Services Indirect Channel
CHANNEL STRUCTURE AND ORGANIZATION Slide 13-15 Direct Channel Marketing Channels for Consumer Goods and Services Indirect Channel
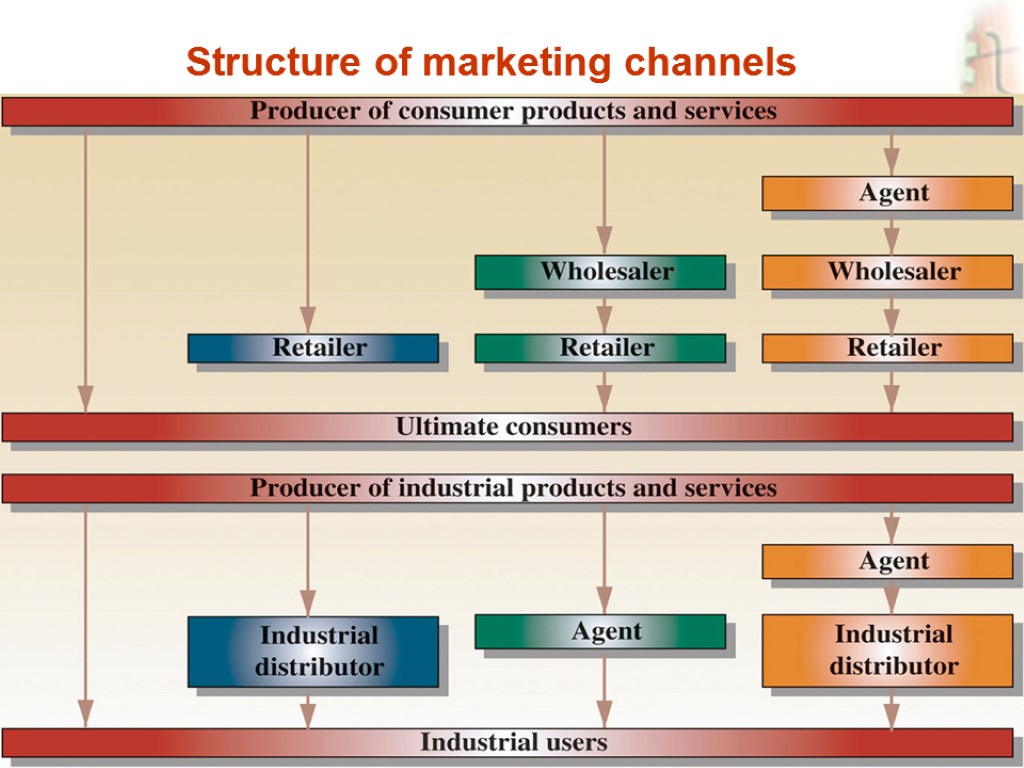
 Slide 13-16 Structure of marketing channels
Slide 13-16 Structure of marketing channels
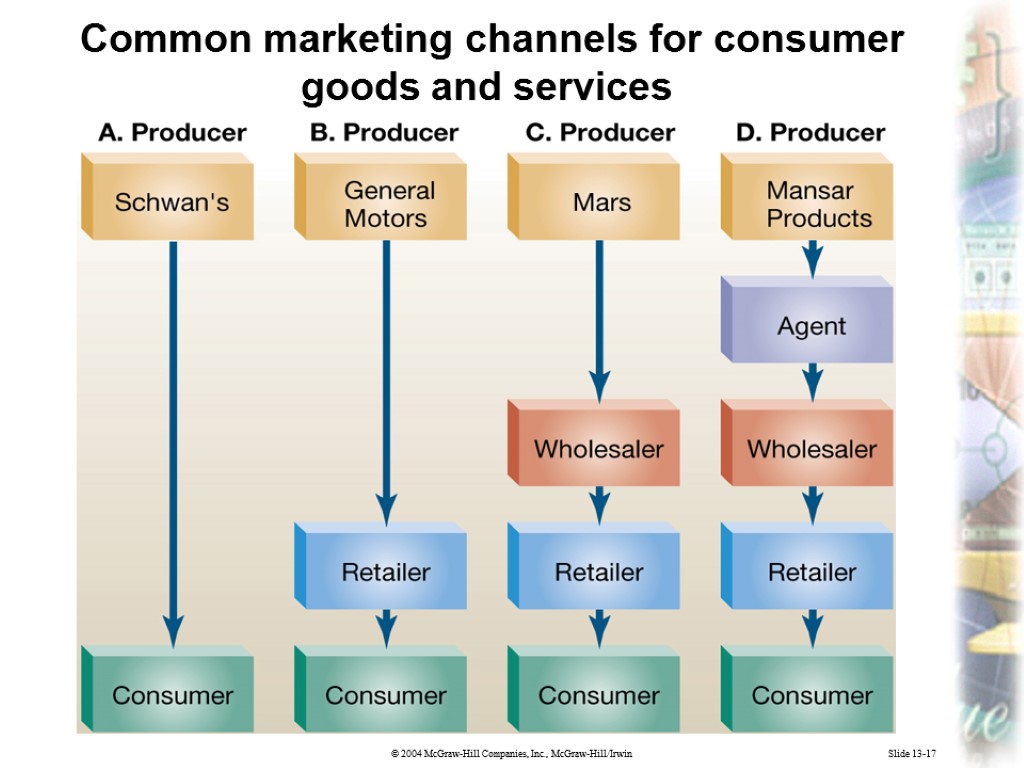
 Slide 13-17 Common marketing channels for consumer goods and services
Slide 13-17 Common marketing channels for consumer goods and services
 CHANNEL STRUCTURE AND ORGANIZATION Slide 13-18 Industrial Distributor Marketing Channels for Business Goods and Services Agent
CHANNEL STRUCTURE AND ORGANIZATION Slide 13-18 Industrial Distributor Marketing Channels for Business Goods and Services Agent
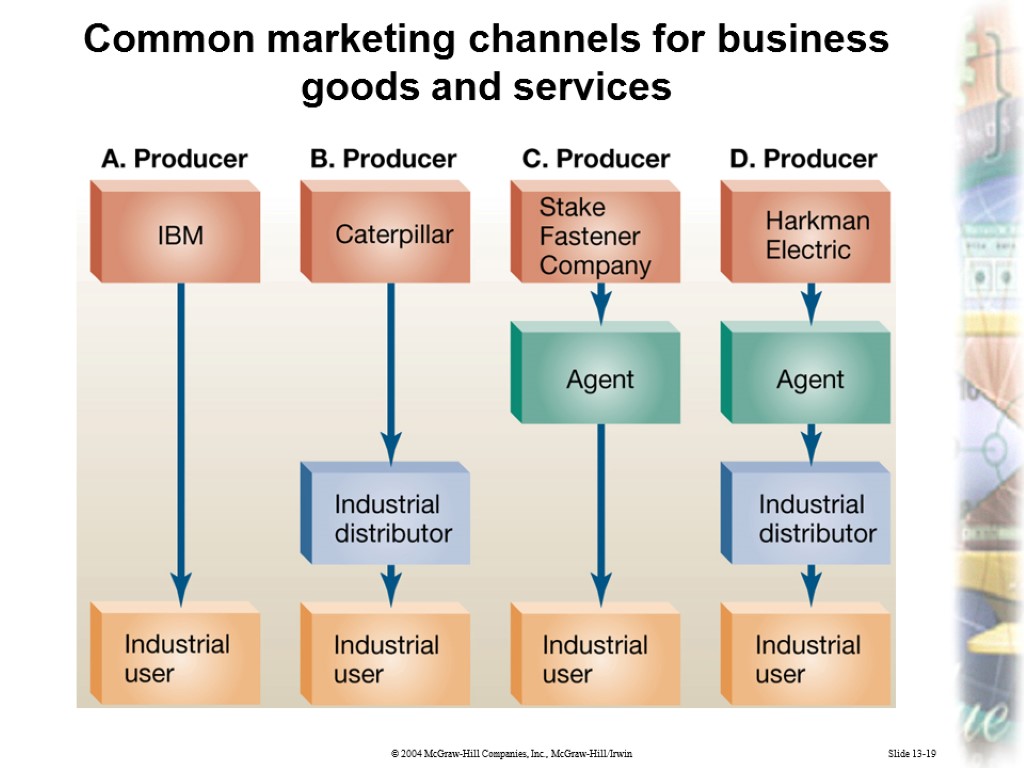
 Slide 13-19 Common marketing channels for business goods and services
Slide 13-19 Common marketing channels for business goods and services
 CHANNEL STRUCTURE AND ORGANIZATION Slide 13-20 Electronic Marketing Channels Dual Distribution Strategic Channel Alliances Multiple Channels and Strategic Alliances
CHANNEL STRUCTURE AND ORGANIZATION Slide 13-20 Electronic Marketing Channels Dual Distribution Strategic Channel Alliances Multiple Channels and Strategic Alliances
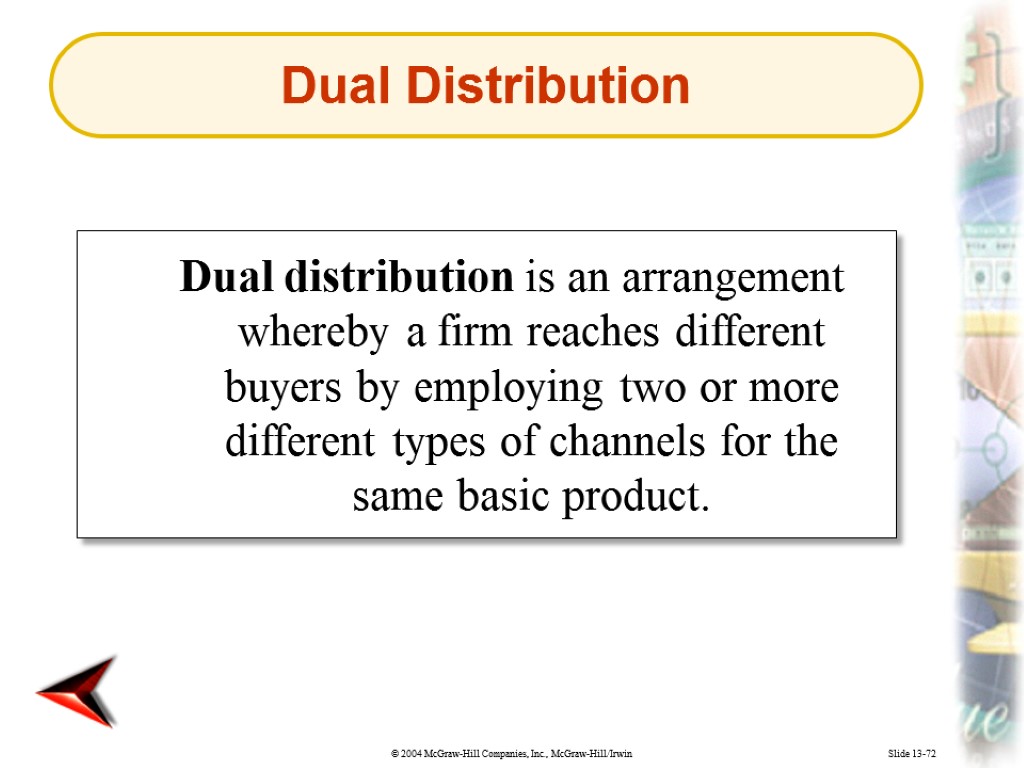
 Slide 13-72 Dual distribution is an arrangement whereby a firm reaches different buyers by employing two or more different types of channels for the same basic product. Dual Distribution
Slide 13-72 Dual distribution is an arrangement whereby a firm reaches different buyers by employing two or more different types of channels for the same basic product. Dual Distribution
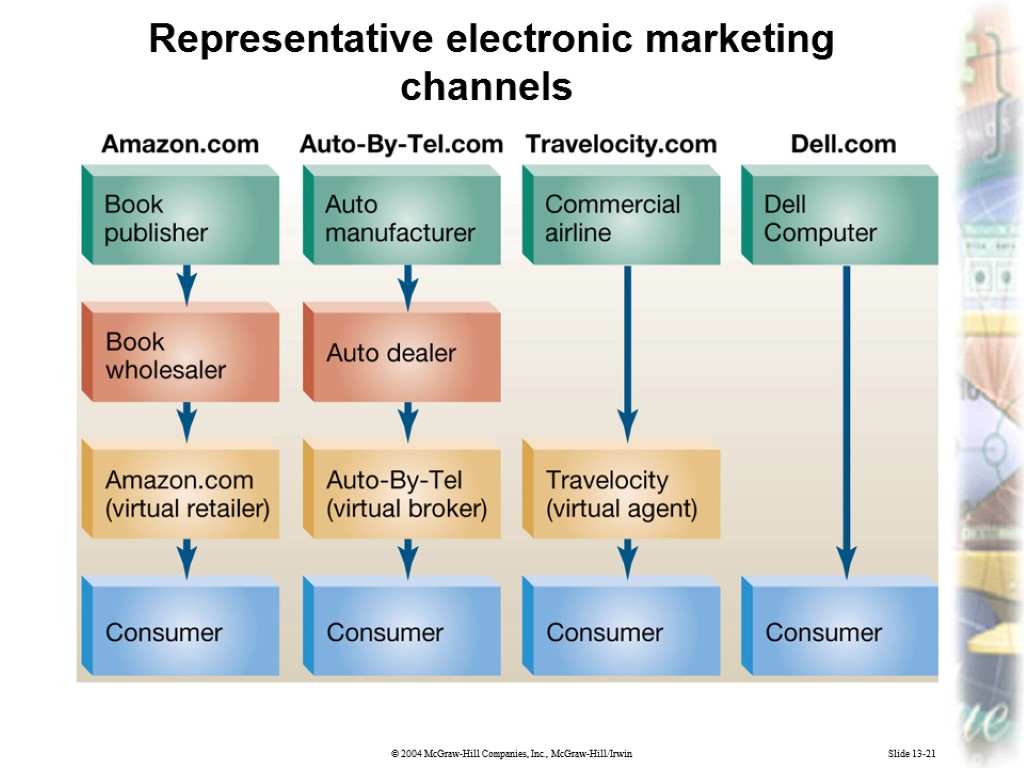
 Slide 13-21 Representative electronic marketing channels
Slide 13-21 Representative electronic marketing channels
 CHANNEL STRUCTURE AND ORGANIZATION Slide 13-23 Vertical Marketing Systems Corporate Systems Corporate Vertical Marketing System Forward Integration Backward Integration
CHANNEL STRUCTURE AND ORGANIZATION Slide 13-23 Vertical Marketing Systems Corporate Systems Corporate Vertical Marketing System Forward Integration Backward Integration
 Slide 13-73 Vertical marketing systems are professionally managed and centrally coordinated marketing channels designed to achieve channel economies and maximum marketing impact. Vertical Marketing Systems
Slide 13-73 Vertical marketing systems are professionally managed and centrally coordinated marketing channels designed to achieve channel economies and maximum marketing impact. Vertical Marketing Systems
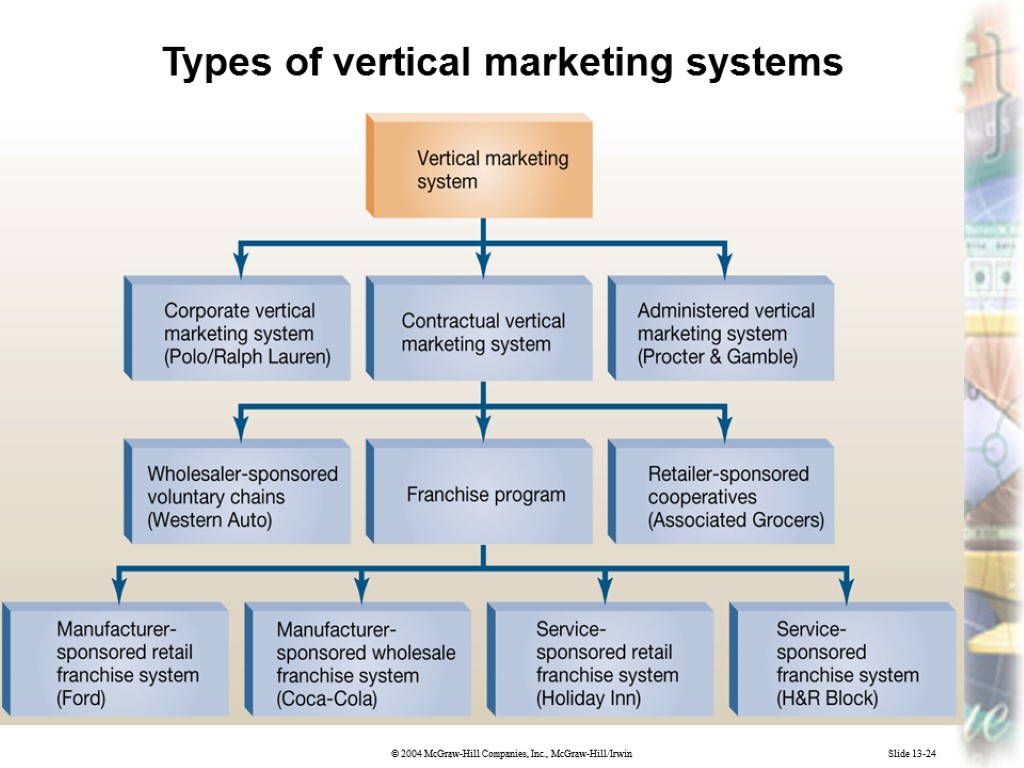
 Slide 13-24 Types of vertical marketing systems
Slide 13-24 Types of vertical marketing systems
 CHANNEL STRUCTURE AND ORGANIZATION Slide 13-26 Vertical Marketing Systems Contractual Systems Contractual Vertical Marketing System Wholesaler-Sponsored Voluntary Chains Retailer-Sponsored Cooperatives
CHANNEL STRUCTURE AND ORGANIZATION Slide 13-26 Vertical Marketing Systems Contractual Systems Contractual Vertical Marketing System Wholesaler-Sponsored Voluntary Chains Retailer-Sponsored Cooperatives
 CHANNEL STRUCTURE AND ORGANIZATION Slide 13-28 Vertical Marketing Systems Contractual Systems: Franchising Manufacturer-Sponsored Retail Franchise Systems Service-Sponsored Retail Franchise Systems Service-Sponsored Franchise Systems Manufacturer-Sponsored Wholesale Franchise Systems
CHANNEL STRUCTURE AND ORGANIZATION Slide 13-28 Vertical Marketing Systems Contractual Systems: Franchising Manufacturer-Sponsored Retail Franchise Systems Service-Sponsored Retail Franchise Systems Service-Sponsored Franchise Systems Manufacturer-Sponsored Wholesale Franchise Systems
 Slide 13-74 Franchising is a contractual arrangement between a parent company (a franchiser) and an individual or firm (a franchisee) that allows the franchise to operate a certain type of business under an established name and according to specific rules. Franchising
Slide 13-74 Franchising is a contractual arrangement between a parent company (a franchiser) and an individual or firm (a franchisee) that allows the franchise to operate a certain type of business under an established name and according to specific rules. Franchising
 CHANNEL STRUCTURE AND ORGANIZATION Slide 13-29 Vertical Marketing Systems Administered Systems Administered Vertical Marketing Systems
CHANNEL STRUCTURE AND ORGANIZATION Slide 13-29 Vertical Marketing Systems Administered Systems Administered Vertical Marketing Systems
 Slide 13-30 1. What is the difference between a direct and indirect channel? A: A direct channel is one in which a producer of consumer or business goods and services and ultimate consumers or industrial users deal directly with each other whereas an indirect channel has intermediaries that are inserted between the producer and consumers or industrial users and who perform numerous channel functions. Concept Check
Slide 13-30 1. What is the difference between a direct and indirect channel? A: A direct channel is one in which a producer of consumer or business goods and services and ultimate consumers or industrial users deal directly with each other whereas an indirect channel has intermediaries that are inserted between the producer and consumers or industrial users and who perform numerous channel functions. Concept Check
 Slide 13-31 2. What is the major distinction between a corporate vertical marketing system and an administered vertical marketing system? A: A corporate vertical marketing system combines the successive stages of production and distribution under a single ownership, whereas a administered vertical marketing system achieves the same thing by the size and influence of one channel member rather than through ownership. Concept Check
Slide 13-31 2. What is the major distinction between a corporate vertical marketing system and an administered vertical marketing system? A: A corporate vertical marketing system combines the successive stages of production and distribution under a single ownership, whereas a administered vertical marketing system achieves the same thing by the size and influence of one channel member rather than through ownership. Concept Check
 CHANNEL CHOICE AND MANAGEMENT Slide 13-32 Factors in Choosing a Marketing Channel Target Market Coverage Intensive Distribution Exclusive Distribution Selective Distribution
CHANNEL CHOICE AND MANAGEMENT Slide 13-32 Factors in Choosing a Marketing Channel Target Market Coverage Intensive Distribution Exclusive Distribution Selective Distribution
 Slide 13-75 Intensive distribution means that a firm tries to place its products and services in as many outlets as possible. Intensive Distribution
Slide 13-75 Intensive distribution means that a firm tries to place its products and services in as many outlets as possible. Intensive Distribution
 Slide 13-76 Exclusive distribution is the extreme opposite of intensive distribution because only one retail outlet in a specified geographical area carries the firm’s products. Exclusive Distribution
Slide 13-76 Exclusive distribution is the extreme opposite of intensive distribution because only one retail outlet in a specified geographical area carries the firm’s products. Exclusive Distribution
 Slide 13-77 Selective distribution lies between the two extremes of intensive and exclusive distribution and means that a firm selects a few retail outlets in a specified geographical area to carry its products. Selective Distribution
Slide 13-77 Selective distribution lies between the two extremes of intensive and exclusive distribution and means that a firm selects a few retail outlets in a specified geographical area to carry its products. Selective Distribution
 CHANNEL CHOICE AND MANAGEMENT Slide 13-33 Factors in Choosing a Marketing Channel Satisfying Buyer Requirements Profitability
CHANNEL CHOICE AND MANAGEMENT Slide 13-33 Factors in Choosing a Marketing Channel Satisfying Buyer Requirements Profitability
 CHANNEL CHOICE AND MANAGEMENT Slide 13-37 Channel Relationships: Conflict and Cooperation Conflict in Marketing Channels Channel Conflict Vertical Conflict Disintermediation Horizontal Conflict
CHANNEL CHOICE AND MANAGEMENT Slide 13-37 Channel Relationships: Conflict and Cooperation Conflict in Marketing Channels Channel Conflict Vertical Conflict Disintermediation Horizontal Conflict
 Slide 13-78 Channel conflict arises when one channel member believes another channel member is engaged in behavior that prevents it from achieving its goals. Channel Conflict
Slide 13-78 Channel conflict arises when one channel member believes another channel member is engaged in behavior that prevents it from achieving its goals. Channel Conflict
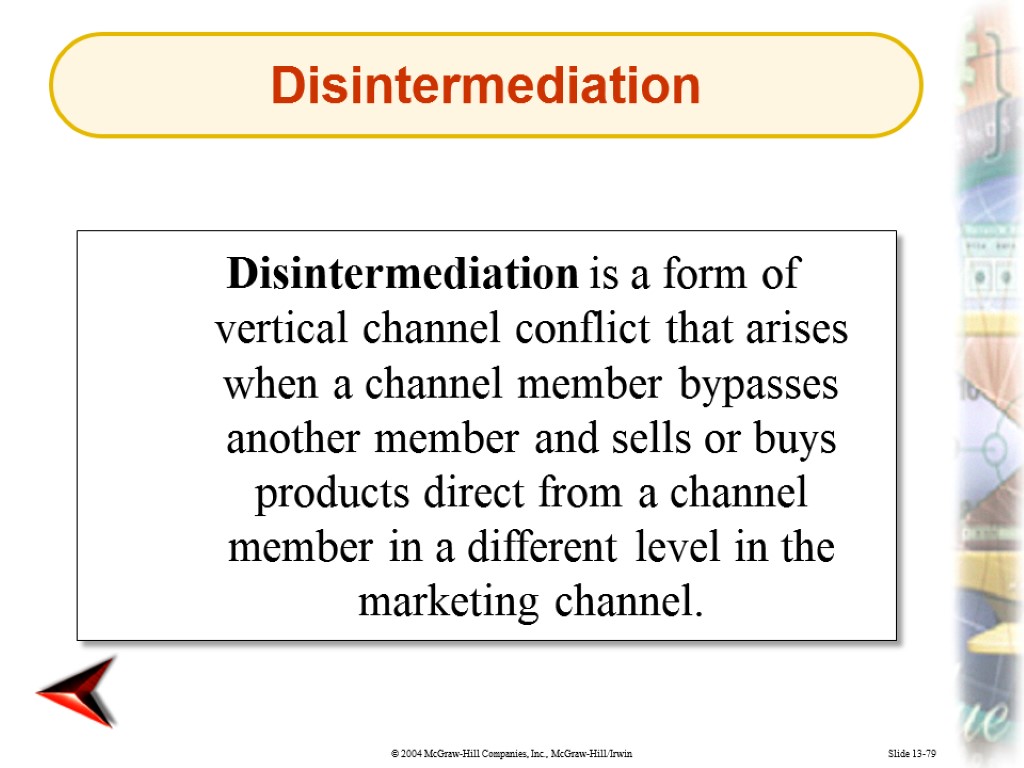
 Slide 13-79 Disintermediation is a form of vertical channel conflict that arises when a channel member bypasses another member and sells or buys products direct from a channel member in a different level in the marketing channel. Disintermediation
Slide 13-79 Disintermediation is a form of vertical channel conflict that arises when a channel member bypasses another member and sells or buys products direct from a channel member in a different level in the marketing channel. Disintermediation
 CHANNEL CHOICE AND MANAGEMENT Slide 13-38 Channel Relationships: Conflict and Cooperation Cooperation in Marketing Channels Channel Captain
CHANNEL CHOICE AND MANAGEMENT Slide 13-38 Channel Relationships: Conflict and Cooperation Cooperation in Marketing Channels Channel Captain
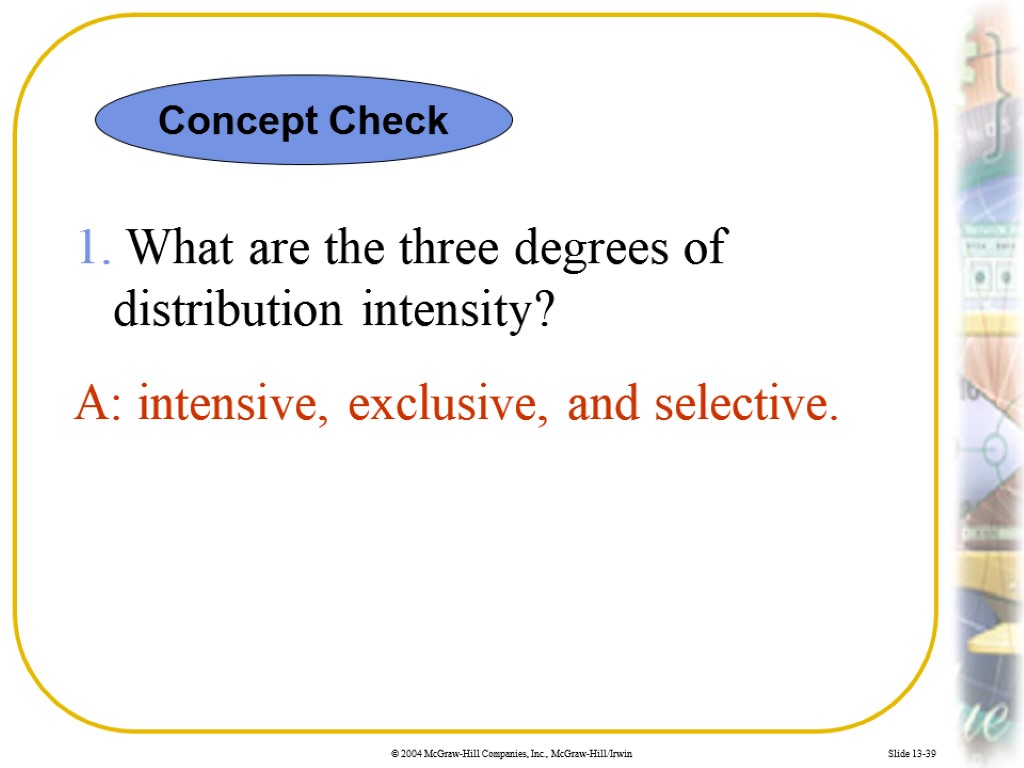
 Slide 13-39 1. What are the three degrees of distribution intensity? A: intensive, exclusive, and selective. Concept Check
Slide 13-39 1. What are the three degrees of distribution intensity? A: intensive, exclusive, and selective. Concept Check
 Slide 13-40 2. What are the three questions marketing executives consider when choosing a marketing channel and intermediaries? A: Which channel and intermediaries will: (1) provide the best coverage of the target market? (2) best satisfy the buying requirements of the target market? and (3) be the most profitable? Concept Check
Slide 13-40 2. What are the three questions marketing executives consider when choosing a marketing channel and intermediaries? A: Which channel and intermediaries will: (1) provide the best coverage of the target market? (2) best satisfy the buying requirements of the target market? and (3) be the most profitable? Concept Check
 LOGISTICS AND SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT Slide 13-41 Logistics Logistics Management Flow Cost Effective Customer Requirements
LOGISTICS AND SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT Slide 13-41 Logistics Logistics Management Flow Cost Effective Customer Requirements
 Slide 13-80 Logistics involves those activities that focus on getting the right amount of the right products to the right place at the right time at the lowest possible cost. Logistics
Slide 13-80 Logistics involves those activities that focus on getting the right amount of the right products to the right place at the right time at the lowest possible cost. Logistics
 Slide 13-42 Definition of logistics
Slide 13-42 Definition of logistics
 LOGISTICS AND SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT Slide 13-44 Supply Chain Supply Chains vs. Marketing Channels Supply Chain Management Sourcing, Assembling, and Delivering a New Car: The Automotive Supply Chain
LOGISTICS AND SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT Slide 13-44 Supply Chain Supply Chains vs. Marketing Channels Supply Chain Management Sourcing, Assembling, and Delivering a New Car: The Automotive Supply Chain
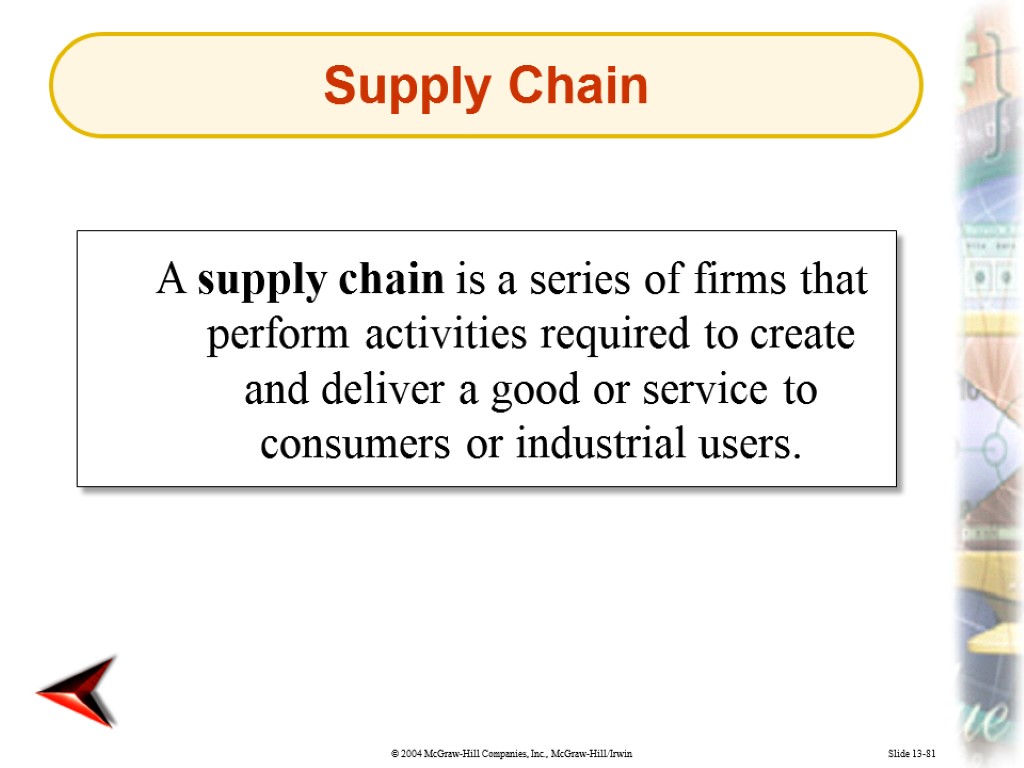
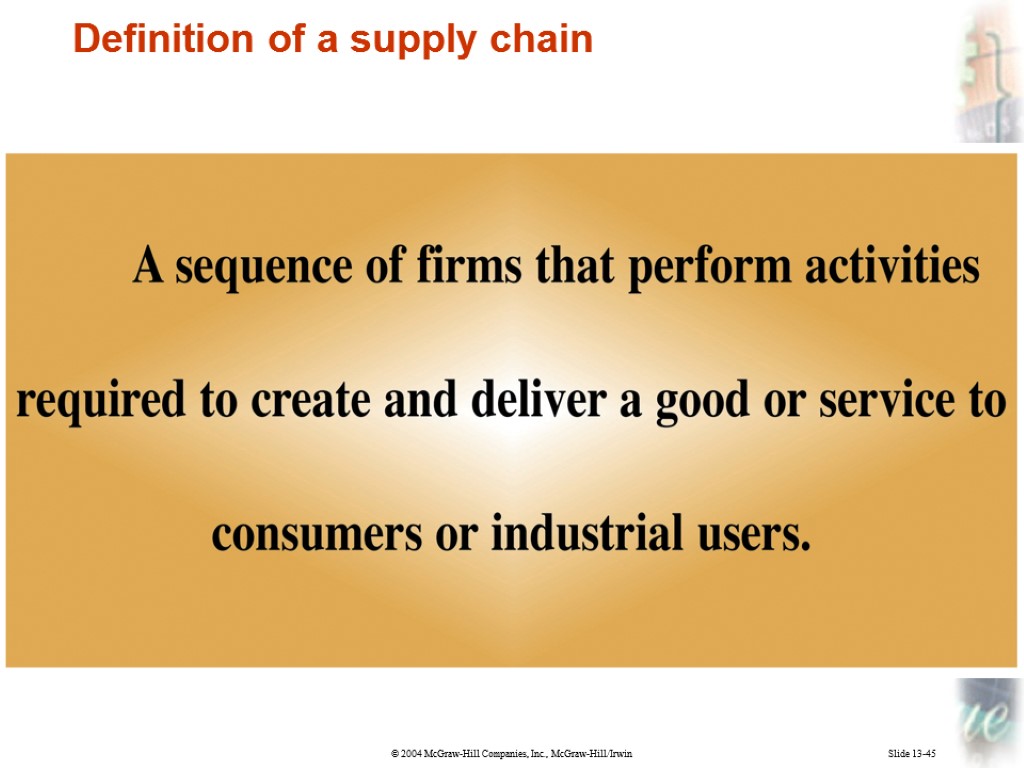
 Slide 13-81 A supply chain is a series of firms that perform activities required to create and deliver a good or service to consumers or industrial users. Supply Chain
Slide 13-81 A supply chain is a series of firms that perform activities required to create and deliver a good or service to consumers or industrial users. Supply Chain
 Slide 13-45 Definition of a supply chain
Slide 13-45 Definition of a supply chain
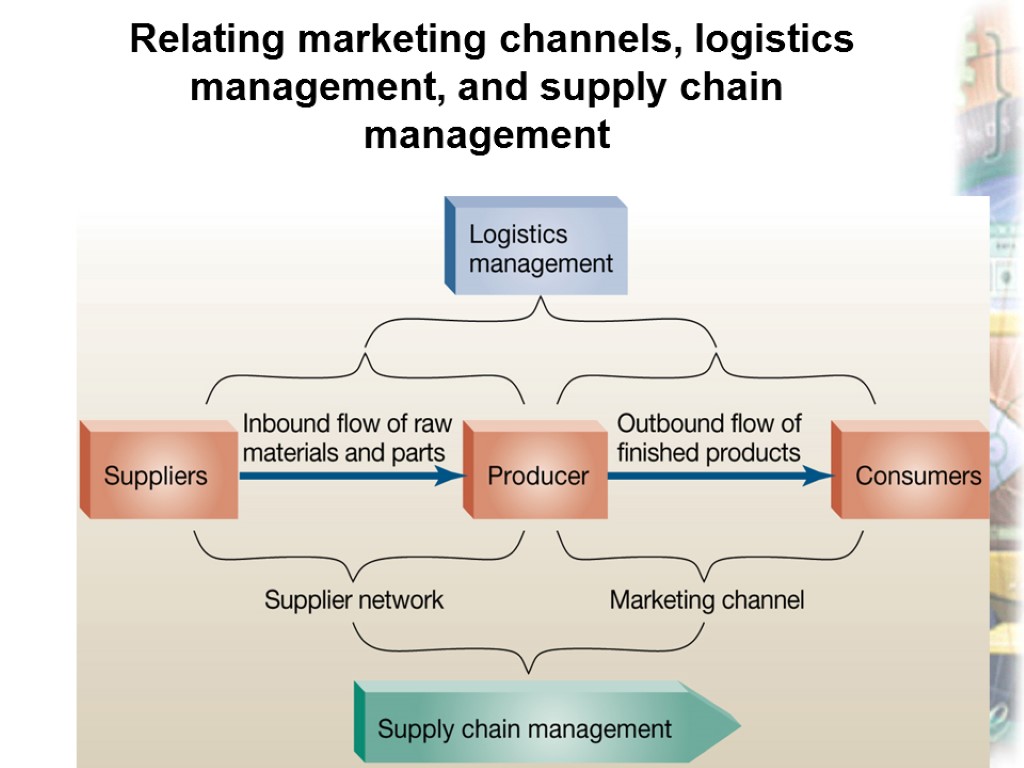
 Slide 13-46 Relating marketing channels, logistics management, and supply chain management
Slide 13-46 Relating marketing channels, logistics management, and supply chain management
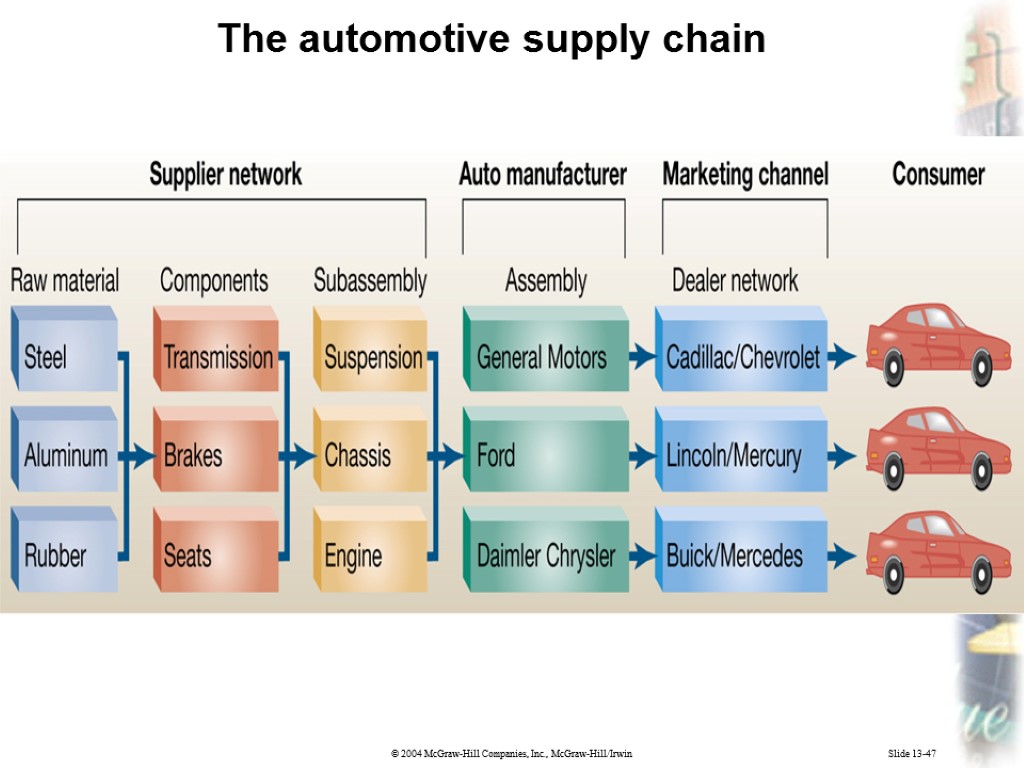
 Slide 13-47 The automotive supply chain
Slide 13-47 The automotive supply chain
 LOGISTICS AND SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT Slide 13-48 Aligning a Supply Chain with Marketing Strategy Supply Chain Management and Marketing Strategy Understand the Customer Understand the Supply Chain Harmonize the Supply Chain with the Marketing Strategy
LOGISTICS AND SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT Slide 13-48 Aligning a Supply Chain with Marketing Strategy Supply Chain Management and Marketing Strategy Understand the Customer Understand the Supply Chain Harmonize the Supply Chain with the Marketing Strategy
 LOGISTICS AND SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT Slide 13-49 Supply Chain Management and Marketing Strategy Dell Computer: A Responsive Supply Chain Cross-Docking Wal-Mart: An Efficient Supply Chain
LOGISTICS AND SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT Slide 13-49 Supply Chain Management and Marketing Strategy Dell Computer: A Responsive Supply Chain Cross-Docking Wal-Mart: An Efficient Supply Chain
 Slide 13-50 1. What is the principal difference between a marketing channel and a supply chain? A: A supply chain also includes suppliers who provide raw materials to a manufacturer as well as the wholesalers and retailers—the marketing channel—who deliver the finished goods to ultimate consumers. Concept Check
Slide 13-50 1. What is the principal difference between a marketing channel and a supply chain? A: A supply chain also includes suppliers who provide raw materials to a manufacturer as well as the wholesalers and retailers—the marketing channel—who deliver the finished goods to ultimate consumers. Concept Check
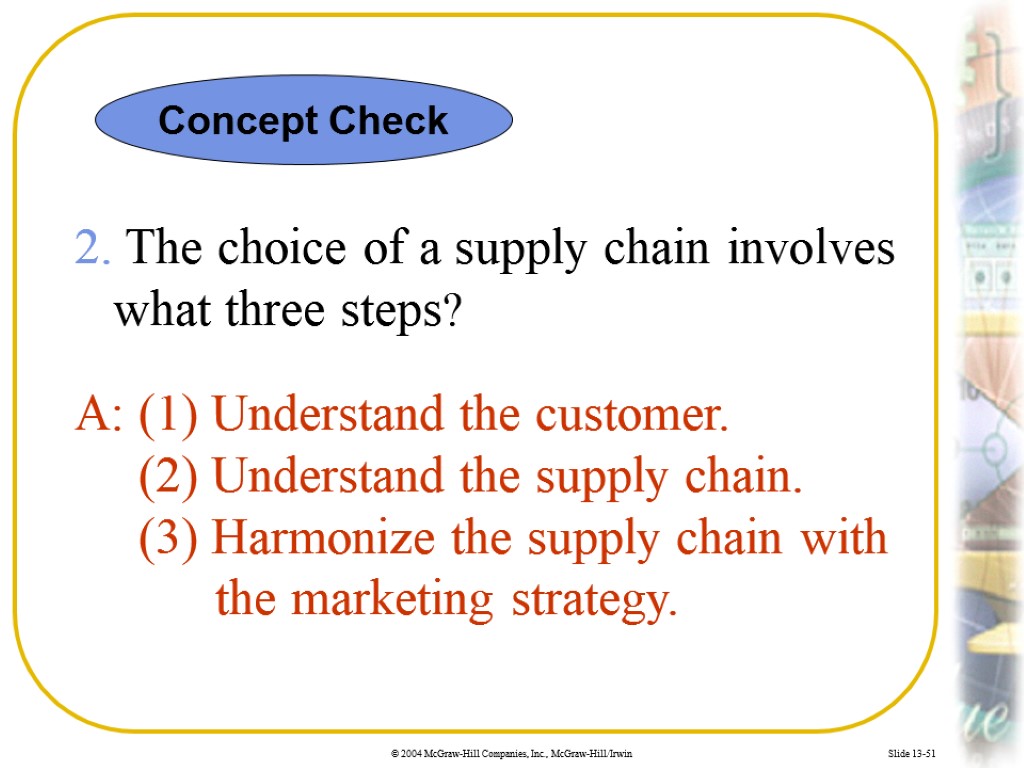
 Slide 13-51 2. The choice of a supply chain involves what three steps? A: (1) Understand the customer. (2) Understand the supply chain. (3) Harmonize the supply chain with the marketing strategy. Concept Check
Slide 13-51 2. The choice of a supply chain involves what three steps? A: (1) Understand the customer. (2) Understand the supply chain. (3) Harmonize the supply chain with the marketing strategy. Concept Check
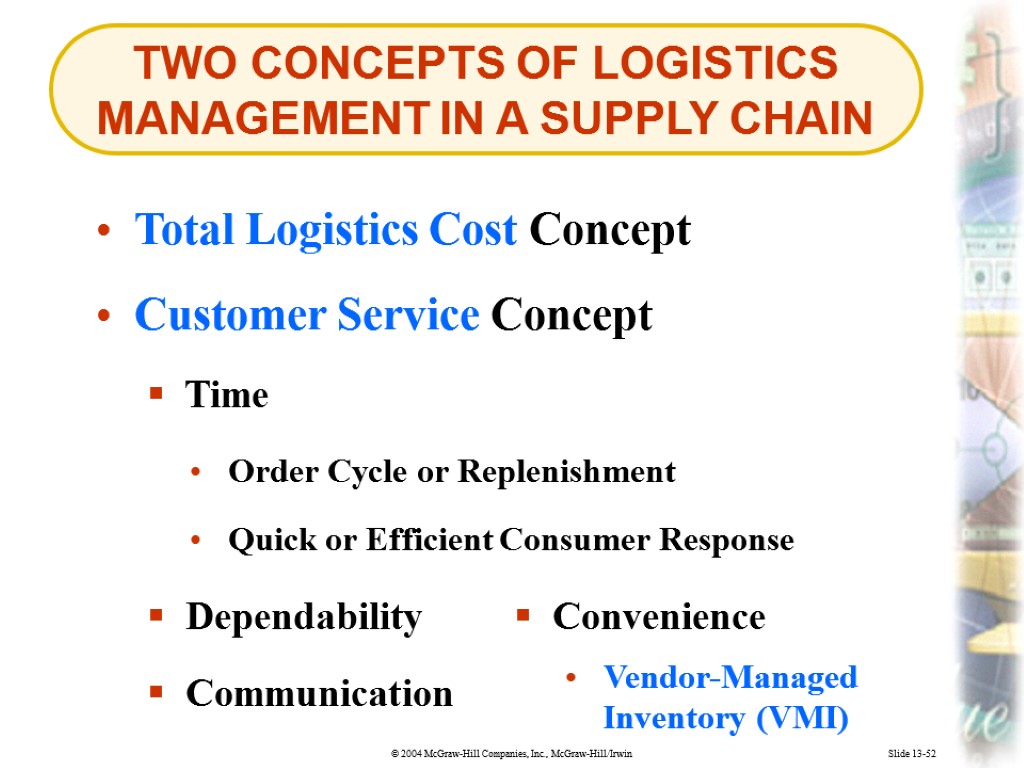
 TWO CONCEPTS OF LOGISTICS MANAGEMENT IN A SUPPLY CHAIN Slide 13-52 Total Logistics Cost Concept Time Customer Service Concept Dependability Order Cycle or Replenishment Quick or Efficient Consumer Response Communication Convenience Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI)
TWO CONCEPTS OF LOGISTICS MANAGEMENT IN A SUPPLY CHAIN Slide 13-52 Total Logistics Cost Concept Time Customer Service Concept Dependability Order Cycle or Replenishment Quick or Efficient Consumer Response Communication Convenience Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI)
 Slide 13-84 Vendor-managed inventory (VMI) is a customer service factor whereby the supplier determines the product amount and assortment a customer (such as a retailer) needs and automatically delivers the appropriate items. Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI)
Slide 13-84 Vendor-managed inventory (VMI) is a customer service factor whereby the supplier determines the product amount and assortment a customer (such as a retailer) needs and automatically delivers the appropriate items. Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI)
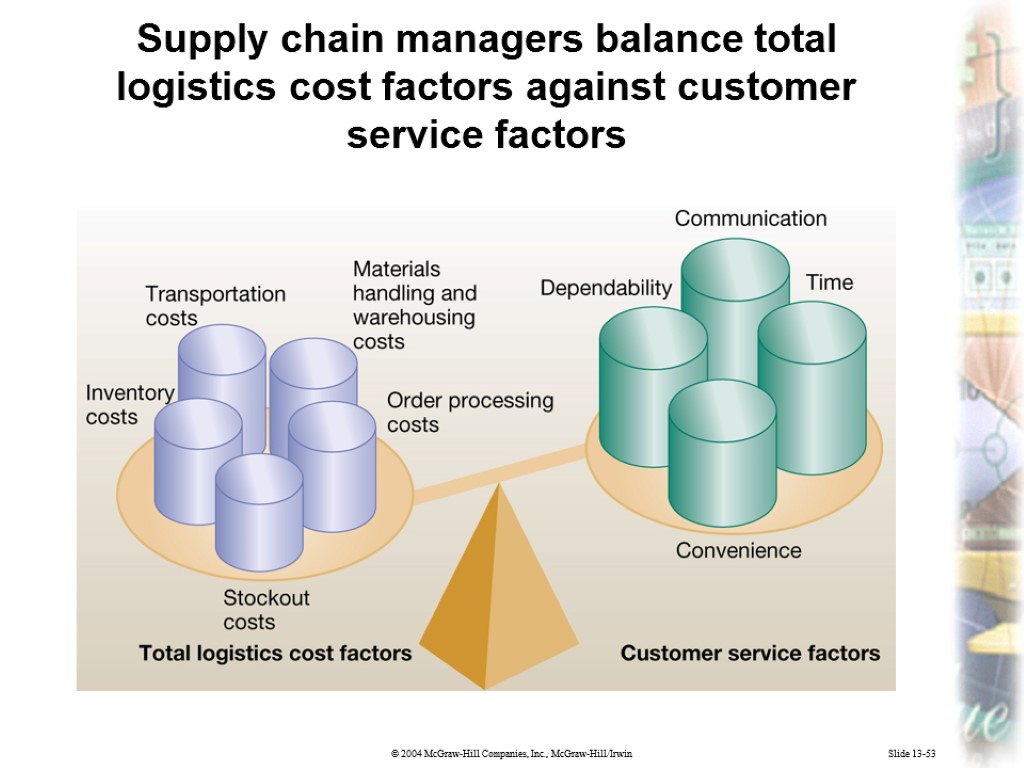
 Slide 13-53 Supply chain managers balance total logistics cost factors against customer service factors
Slide 13-53 Supply chain managers balance total logistics cost factors against customer service factors
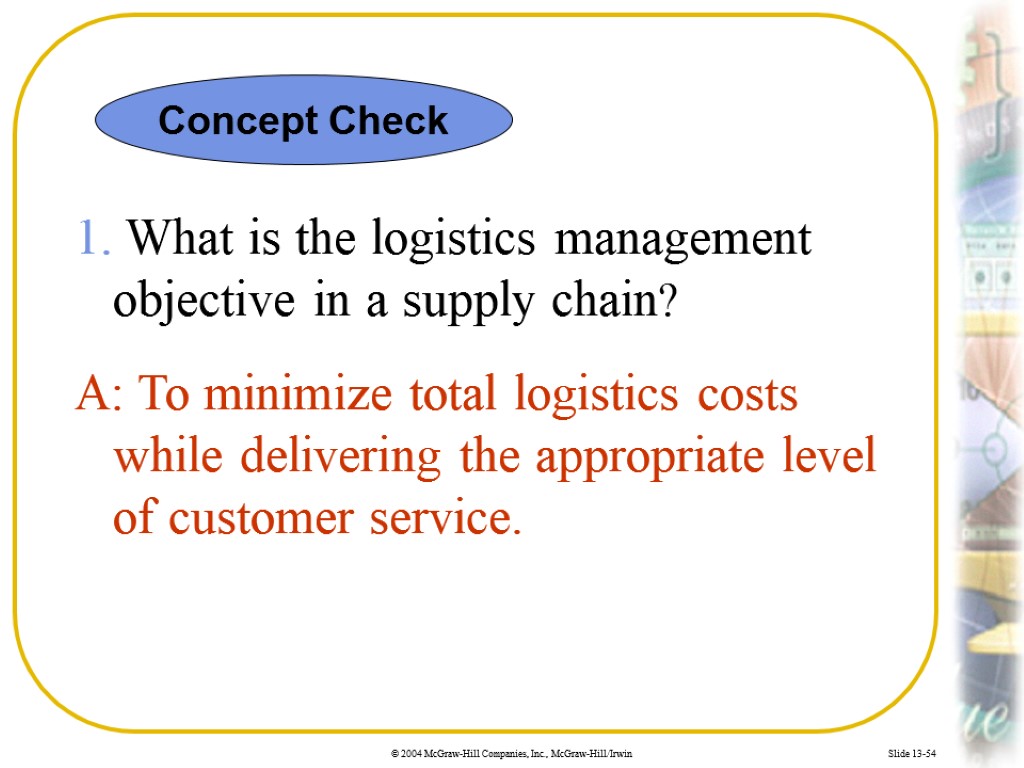
 Slide 13-54 1. What is the logistics management objective in a supply chain? A: To minimize total logistics costs while delivering the appropriate level of customer service. Concept Check
Slide 13-54 1. What is the logistics management objective in a supply chain? A: To minimize total logistics costs while delivering the appropriate level of customer service. Concept Check
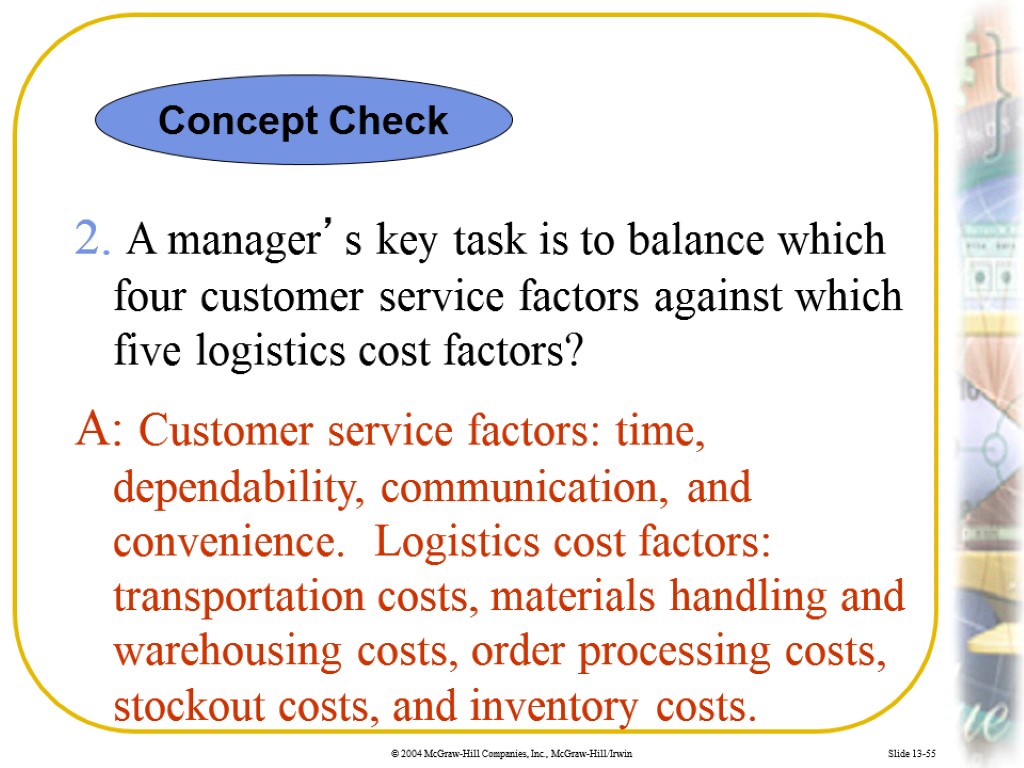
 Slide 13-55 2. A manager’s key task is to balance which four customer service factors against which five logistics cost factors? A: Customer service factors: time, dependability, communication, and convenience. Logistics cost factors: transportation costs, materials handling and warehousing costs, order processing costs, stockout costs, and inventory costs. Concept Check
Slide 13-55 2. A manager’s key task is to balance which four customer service factors against which five logistics cost factors? A: Customer service factors: time, dependability, communication, and convenience. Logistics cost factors: transportation costs, materials handling and warehousing costs, order processing costs, stockout costs, and inventory costs. Concept Check
 Slide 13-82 Total logistics cost includes expenses associated with transportation, materials handling and warehousing, inventory, stockouts (being out of inventory) order processing, and return goods handling. Total Logistics Cost
Slide 13-82 Total logistics cost includes expenses associated with transportation, materials handling and warehousing, inventory, stockouts (being out of inventory) order processing, and return goods handling. Total Logistics Cost
 Slide 13-83 Customer service is the ability of logistics management to satisfy users in terms of time, dependability, communication, and convenience. Customer Service
Slide 13-83 Customer service is the ability of logistics management to satisfy users in terms of time, dependability, communication, and convenience. Customer Service

