55b98a8d0076c684de08ea6394d6f78c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28

Slide 1 Summary Briefing Provided to the State of Connecticut May 7, 2008 Steven Anderson Vice-President NSGIC Spring Conference held March 9 -12, 2008 © 2008 Applied Geographics

Slide 2 Presentation Agenda § § § § § Fifty States Initiative Workshop Keynote: Maryland CIO, Elliot Schlanger NSGIC Goals for the NSDI Imagery for the Nation Airborne Imagery Technologies Nation Land Parcel Data USGS National Map Technical Plan Addressing Work Group Transportation Work Group (Transportation for the Nation) © 2008 Applied Geographics

Slide 3 NSGIC Spring 2008: Fifty States Initiative Workshop § CAT 1: Metadata Training and Outreach ($25 k) ú University Metadata Training and Regional Outreach (CA) § CAT 2: Best Practices with Geospatial SOA ($100 k) ú Cubewerx – Role based access control for Geospatial SOA § CAT 3: Strategic and business planning ($50 k) ú CO, GA, HI, ID, NE, PA, SC, Virgin Islands received grants ú CO 2006 Recipient of USGS Partnership Funds, additional funds for BP Development (integration of Geo. IT and IT) ú SC Improving relationships with Local Government § CAT 4: Joint Canadian and US Spatial Data Infrastructure ($75 k) ú Pending § CAT 5: Building Data Stewardship (structures & transportation data) $50 k ú 4, $50 k grants, IA, WV, MN, Towson University ú Build process to provide structures and transportation data to NSDI and maintenance process § CAT 6: Standards Implementation and Outreach; 4, $50 k grants ú Delta State University (MS): Develop on-line educational materials for FGDC standards adoption ú Oklahoma Biological Survey and Private Company: Implementation of National Vegetation Classification System ú State of North Carolina: Implementing National Grid © 2008 Applied Geographics

Slide 4 Business Plans that have been completed or are under development through the CAP program § Data Centric Business Plans ú CA: Imagery Business Plan ú IN: Indiana. Map Framework Planning and GIS Council Business Plan ú CT: Funding CT’s Statewide GIS Program (Imagery, Parcels, Street Cl’s, & Addressing) ú IA: Creating an Iowa Geospatial Infrastructure (7 framework layers) ú SD: Cadastral Strategic and Business plans for the State of South Dakota ú KS: Statewide High Resolution Elevation Data ú UT: Statewide Inventory of Geospatial Resources § GIS Coordination Business Plans ú FL: GIS Coordination Business Plan (under development) ú IN: Indiana. Map Framework Planning and GIS Council Business Plan ú WV: New Coordinating Body Business Plan ú CT: Funding Connecticut’s Statewide GIS Program (Creation of GIS Office) ú WY: Establishing a GIO and supporting GIS Technical Services Program ú NH: Business Plan for Creation of a Geospatial Information Officer © 2008 Applied Geographics
Slide 5 Business Plans that have been completed or are under development through the CAP program § Infrastructure Business Plans ú OK: Business Environment Assessment ú RI: RI Enterprise GIS ú ME: Framework specification for an Integrated Land Records Information System Business Plan – Rhode Island Enterprise GIS ú NC: Business Case to Support Sustainable Funding for NC One. Map (clearinghouse) § Funding Related Business Plans ú IA: Creating an Iowa Geospatial Infrastructure (GITA) ú IN: Indiana. Map Business Plan Return on Investment Study ú CT: Funding Connecticut’s Statewide GIS Program © 2008 Applied Geographics

Slide 6 Keynote: Elliot Schlanger, Maryland CIO § CIO of Baltimore when Gov. Martin O’Malley was Mayor § Issue not technology, it’s people and process § GIS is one of government’s greatest business enablers and decision making tools § Early adopter of Com. Stat/City. Stat – developed in NYC as real-time performance measurement tool for police activities § Spread to other areas of government § Now being implemented as “State. Stat” in Maryland § Biggest issues to be concerned with in regards to GIS ú Development of silos of information (departmental) ú Disconnect with end-users ú Lack of cohesiveness between state and local government © 2008 Applied Geographics

Slide 7 Keynote: Elliot Schlanger, Maryland CIO § Common challenges and issues ú Managing state and local data and delivery systems ú Finding ways to resource enterprise GIS ú Statewide licensing of GIS software applications ú The need for standards and policies and guidelines that work for all ú How to sufficiently build the IT infrastructure to work with all of this ú Deciding what sort of governance will work best ú And how to pay for all this capability in tough fiscal times © 2008 Applied Geographics

Slide 8 NSGIC Goals for the NSDI; Cy Smith, NSGIC President § § NSGIC Planning to release a discussion draft for a strategic framework for the NSDI Key Initiatives that have been identified: ú 50 States Initiative ú Strategic and Business Planning Templates ú RAMONA GIS Inventory ú Imagery for the Nation ú Other “for the Nation” initiatives to follow (transportation, addressing) § NSDI should be built on SSDI ú Sustainable funding is key, most funding is “pay as you go” ú Will require a strong shared vision to be effective § Data Stewardship is required: ú Includes lifespan planning, metadata, and sustainable funding Larry English, a well-known consultant in knowledge management, defines data stewardship as: The willingness to be accountable for a set of business information for the well-being of the larger organization, by operating in service, rather than in control, of those around us. * *English, Larry. Information Stewardship—Giving IQ and Happiness (Business Intelligence Network, 2006). © 2008 Applied Geographics

Slide 9 NSGIC Goals for the NSDI; Cy Smith, NSGIC President § What is needed to accelerate the implementation of NSDI? ú Information and outreach, especially with mainstream IT § Jill Saligoe Simmel (IN)suggested 3 “L’s” to keep in mind: ú Local data is best and needs to be the ultimate source ú Licensing (copyright and data agreements) can interfere with overall goals ú Leverage is needed to maintain a balance of equity and fairness among all levels of government. § National Geospatial Advisory Committee (NGAC) has been formed ú ú ú Federal Advisory Committee sponsored by DOI Reports to FGDC (or Secretary of Interior) Advice and recommendations on national geospatial programs Development of the National Spatial Data Infrastructure Review and comment upon geospatial policy and management issues Provide a forum to convey views representative of non-federal stakeholders in the geospatial community © 2008 Applied Geographics
Slide 10 NSGIC Goals for the NSDI; Cy Smith, NSGIC President § RAMONA © 2008 Applied Geographics
Slide 11 Imagery for the Nation: Ted Koch, State of Wisconsin § Cost Benefit Analysis Completed – Four Options: 1. Original IFTN concept ú ú 2. 3. 4. § Nationwide, Leaf-on 1 meter, Annual program Eastern US, 1 foot, color, leaf off, 3 year program Buy-up program options State required to develop Business Plan Nationwide 1 -foot program 50% cost-share mandatory 50% cost-share optional (3 -6 year program cycle) Results: ú ú ú #1 and #4 scored very closely #1 had highest risk #4 fewer barriers to implement • • ú ú ú Lowest risk Adoption rates higher October 2007 meeting recommended going forward with option #4 Developing draft report which is due by October 2008 • Technical Specifications • Acquisition Management • Program Management • Developing State Business Plan Template for implementing 33 states have provided letters of support © 2008 Applied Geographics
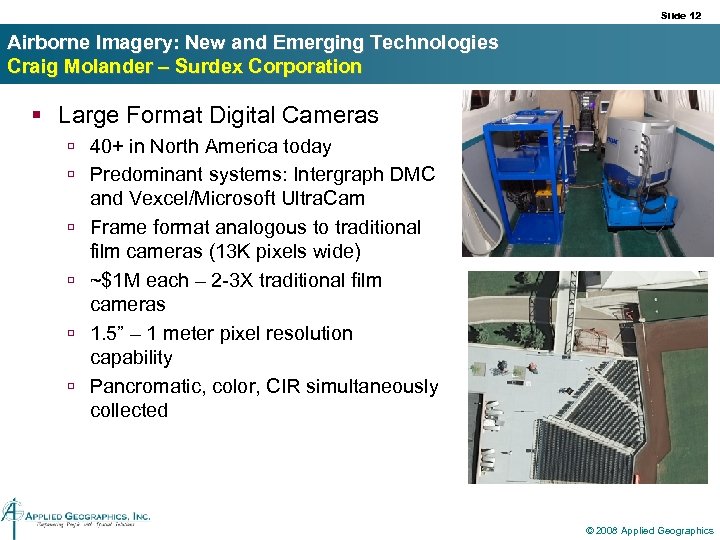
Slide 12 Airborne Imagery: New and Emerging Technologies Craig Molander – Surdex Corporation § Large Format Digital Cameras ú 40+ in North America today ú Predominant systems: Intergraph DMC and Vexcel/Microsoft Ultra. Cam ú Frame format analogous to traditional film cameras (13 K pixels wide) ú ~$1 M each – 2 -3 X traditional film cameras ú 1. 5” – 1 meter pixel resolution capability ú Pancromatic, color, CIR simultaneously collected © 2008 Applied Geographics

Slide 13 Airborne Imagery: New and Emerging Technologies Bob Williams – Sanborn Map Company § Small Format Cameras & Oblique Imagery ú Most Cameras are not certified by USGS ú 8 X to 10 x more frames for processing ú Different flight objectives ú Leaf free season is often ignored ú DEM extraction is more difficult ú Super-wide focal lengths ú Poor base to height ratio & excessive building lean © 2008 Applied Geographics
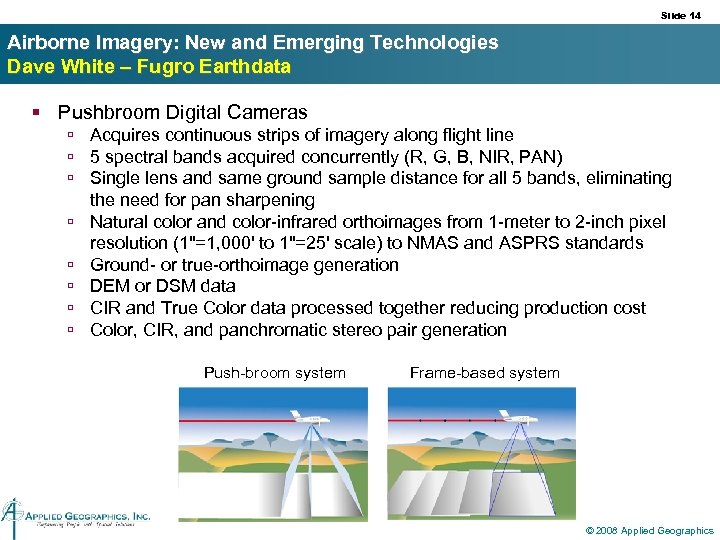
Slide 14 Airborne Imagery: New and Emerging Technologies Dave White – Fugro Earthdata § Pushbroom Digital Cameras ú Acquires continuous strips of imagery along flight line ú 5 spectral bands acquired concurrently (R, G, B, NIR, PAN) ú Single lens and same ground sample distance for all 5 bands, eliminating the need for pan sharpening ú Natural color and color-infrared orthoimages from 1 -meter to 2 -inch pixel resolution (1"=1, 000' to 1"=25' scale) to NMAS and ASPRS standards ú Ground- or true-orthoimage generation ú DEM or DSM data ú CIR and True Color data processed together reducing production cost ú Color, CIR, and panchromatic stereo pair generation Push-broom system Frame-based system © 2008 Applied Geographics

Slide 15 Airborne Imagery: New and Emerging Technologies Dave White – Fugro Earthdata § Pushbroom Digital Cameras ú Ground- or true-orthoimage generation Ground 1 -foot orthophoto 1 -foot True. Ortho © 2008 Applied Geographics
Slide 16 Airborne Imagery: New and Emerging Technologies Jay Arnold – 3001 § LIDAR and other imagery sensors ú Airborne Li. DAR includes topographic, bathymetric (and atmospheric) ú Approximately 50 topo systems and 4 hydro systems in service in North America ú Systems have matured over the past decade ú Typical system costs > $1 M ú 1 m topo Li. DAR product provides 25 x more surface detail than a 5 m Li. DAR product but also requires much more storage ú 5’ posting typical statewide collection © 2008 Applied Geographics
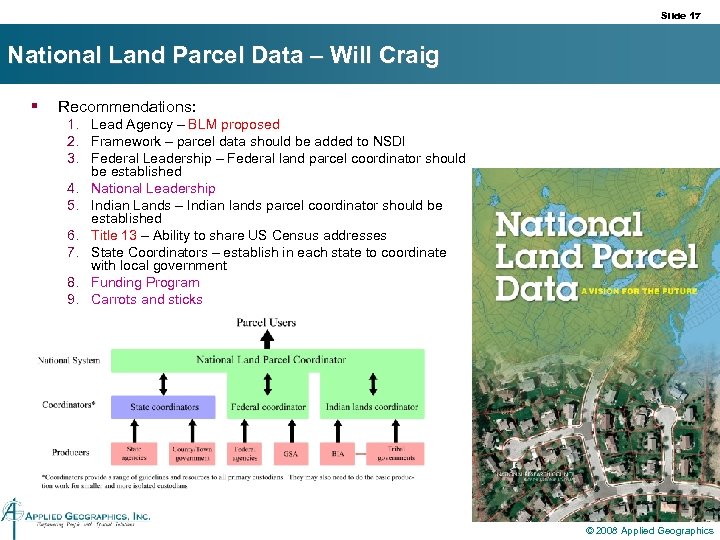
Slide 17 National Land Parcel Data – Will Craig § Recommendations: 1. Lead Agency – BLM proposed 2. Framework – parcel data should be added to NSDI 3. Federal Leadership – Federal land parcel coordinator should be established 4. National Leadership 5. Indian Lands – Indian lands parcel coordinator should be established 6. Title 13 – Ability to share US Census addresses 7. State Coordinators – establish in each state to coordinate with local government 8. Funding Program 9. Carrots and sticks © 2008 Applied Geographics

Slide 18 USGS National Map Technical Plan - NGPO § USGS National Map Version 1. 0 Accomplishments ú Completed 1: 100, 000 and 1: 24, 000 -scale National Hydrography Dataset ú Completed 30 -meter seamless National Elevation Dataset; substantial progress toward 10 -meter or better national elevation coverage ú Developed and implemented a program to leverage Federal, state, and local funds to acquire high-resolution ortho-imagery over the nation’s urban areas ú Developed and implemented “best practices” national geodatabases for transportation, structures, and governmental units ú Improved Geographic Names Information for the nation ú Developed and implemented an Open GIS Consortium Compliant Catalog Database and Web Catalog Service and registered more than 12, 000 USGS and Partner GIS data layers in the initial The National Map Catalog implementation © 2008 Applied Geographics
Slide 19 USGS National Map Technical Plan - NGPO § FY’ 07 Imagery Partnership Program ú Partnership with the NGA to acquire highresolution imagery and elevation data for the nation’s largest 133 urban areas ú NGA provided $4. 6 million and the USGS funded an additional $2. 1 million ú Collaborated with 55 partners, primarily local agencies, to leverage the acquisition of data ú The data acquired through this process totaled an overall value of $25 million ú Resulting data are publicly accessible in The National Map and serve a myriad of Federal, state and local government uses and fuel private sector applications such as Google Map and Google Earth © 2008 Applied Geographics

Slide 20 USGS National Map Technical Plan - NGPO § Plan for the Future The National Map 2. 0 ú ú Integration into consistent, quality-assured, seamless databases Revitalization of the topographic map Online services from consistent national data Centralized data delivery to users § Planned Components ú Elevation: 10 meter gridded data over 100% of area ú Geographic Names: Collect names along east coast, agreement for Google Earth to use, credit USGS ú Hydrography: National 1: 24, 000 coverage through partnership agreements ú Land Cover: NLCD 2001 land cover, impervious product, and canopy product completed ú Orthoimagery: 10% of quads acquired each year § Liaisons charged with working with States to develop business plans for data discovery and acquisition © 2008 Applied Geographics

Slide 21 Addressing Workgroup § Vision: ú Create a nation-wide, publicly available address dataset, complete with geographic coordinates, that is supported by all stakeholders ú Use standards for assigning addresses, best practices for disseminating them ú Every department uses same address database ú Provide updates to regional custodian § Approach (Regional Custodian; County or 911 authority) ú ú Receives and verifies addresses from local authorities Maintains regional database using feedback from users Distributes address and coordinate data to the public, free of charge Provide updates to regional/statewide integrator © 2008 Applied Geographics

Slide 22 Addressing Workgroup § State’ s Role: ú ú ú Roll-up of regional databases Provide technical assistance Serve as backup Fill blank spots Provide matching grants § Federal Role: ú Major data user: Census, DHS, USPS ú Notify state or regional custodians of discrepancies ú Long-term goal: Share their data with state and locals. § Private Sector: ú Assist with implementation ú Provide technical assistance ú Use nation-wide data as the basis for new products and services © 2008 Applied Geographics
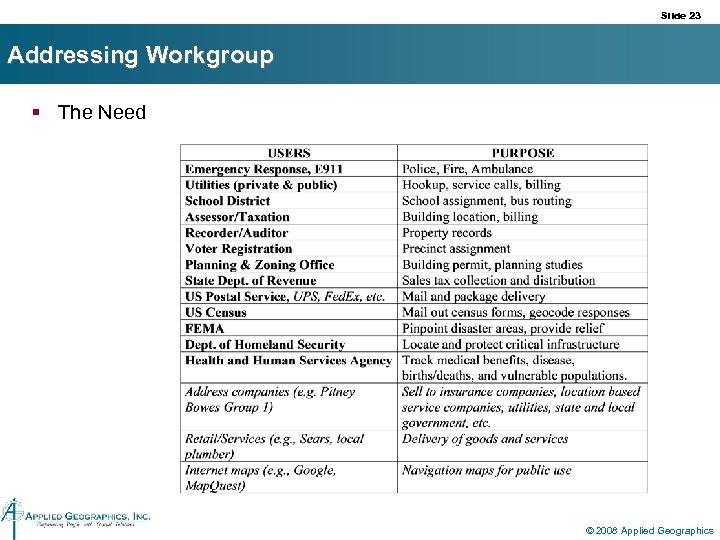
Slide 23 Addressing Workgroup § The Need © 2008 Applied Geographics

Slide 24 Transportation Workgroup – US Census – TIGER Update § § § Vision: A Seamless Digital Map of the United States Where Street Centerlines, Based on State/County/Local/Tribal GIS Files, and Publicly Available Via Standard OGC Protocols “Thank You For Making The Vision Come to Fruition” 1, 870 whole county files 67 partial counties 289 failed files that were spatially enhanced 2, 226 EXISTING files used for realignment plus NHD Imagery - NAIP, DOQQs, Project Completed and delivered by April 1 Looking for State leadership to ensure those areas for which the Harris Corp had to provide a source will now be maintained at State/County/Local/Tribal level “Will not be completed again” 2008 Data in shapefile format, downloadable by feature or geographic region © 2008 Applied Geographics
Slide 25 Transportation Workgroup – US DOT – Steve Lewis § Status: Four Different Network Datasets in use by US DOT Offices ú National Highway Planning Network (FHWA Office of Environment and Planning) • • Public Domain ~455, 000 miles (11. 4% of total road miles) Routable Used to inventory and map the National Highway System and the Strategic Highway Network ú Freight Analysis Framework Network (FHWA Office of Freight Management and Operations) • • Public Domain ~450, 000 miles (11. 25% of total road miles) Routable Used to model and flow truck traffic across the nation ú Highway Performance Monitoring System (FHWA Office of Policy) • • Collected from the State DOTs Mileage Varies by State Not routable, maybe not even connected Used to map and analyze highway conditions and performance © 2008 Applied Geographics
Slide 26 Transportation Workgroup – US DOT – Steve Lewis § Status: Four Different Network Datasets in use by US DOT Offices ú TIGER/Line (Various USDOT Offices) • • • Public Domain ~4, 000 miles (complete coverage) Not routable Used for some address matching and mapping To be replaced by new version ú Tele. Atlas (RITA/BTS) • • Proprietary ~4, 000 miles (complete coverage) Routable Used for routing, address matching and mapping § Why not just one? ú No “quick fix” to get there ú Get rid of the stovepipes! ú Work with the State DOTs and NSGIC to develop from the ground up © 2008 Applied Geographics
Slide 27 Transportation Workgroup – USPS § Status: ú ú ú 147 million possible deliveries 270, 000 delivery routes 42, 000 ZIP Codes 37, 000 facilities nationwide 8 terabytes of address data § Opportunity ú ú 2 million new delivery points per year USPS accepts new addresses from various levels of addressing authorities Enters theses addresses through various methods of data capture Significant opportunity to reduce the cost and improve the time frame for new addressing ú A standardized process can improve address quality and assist controlling the cost of new delivery through Growth Management. © 2008 Applied Geographics
Slide 28 Transportation Workgroup – USPS – Ruth Jones § Partnership: ú USPS - Assist Addressing Authorities with addressing standards and a standardized process flow of data from local planning authorities to the USPS. ú In return – USPS provides relevant data to the Addressing Authority: ú ZIP + 4 ú Geographical reference ú Municipality data ú Carrier route information © 2008 Applied Geographics
55b98a8d0076c684de08ea6394d6f78c.ppt