1cc73dafe2a535bf52f9b09bc24fbe38.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
 Slide 1 San Diego Inter. CAD Project A Retrospective View ITS America Annual Meeting Long Beach, CA April 29 -May 2, 2002 Bruce Churchill, National Engineering Technology Corporation Pam Scanlon, Executive Director San Diego Automated Regional Justice Information System
Slide 1 San Diego Inter. CAD Project A Retrospective View ITS America Annual Meeting Long Beach, CA April 29 -May 2, 2002 Bruce Churchill, National Engineering Technology Corporation Pam Scanlon, Executive Director San Diego Automated Regional Justice Information System
 Slide 2 Topics Covered n n n n Incident Response Coordination Deficiencies Inter. CAD Results Interface Recommendations Standards Recommendations Institutional Recommendations Next Steps
Slide 2 Topics Covered n n n n Incident Response Coordination Deficiencies Inter. CAD Results Interface Recommendations Standards Recommendations Institutional Recommendations Next Steps
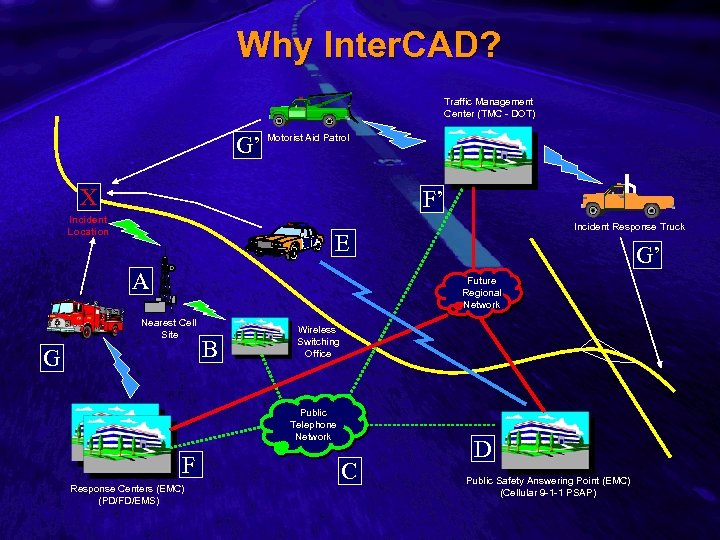 Slide 3 Why Inter. CAD? Traffic Management Center (TMC - DOT) G’ Motorist Aid Patrol X F’ Incident Location Incident Response Truck E A G’ Future Regional Network Nearest Cell Site G B Wireless Switching Office Public Telephone Network F Response Centers (EMC) (PD/FD/EMS) C D Public Safety Answering Point (EMC) (Cellular 9 -1 -1 PSAP)
Slide 3 Why Inter. CAD? Traffic Management Center (TMC - DOT) G’ Motorist Aid Patrol X F’ Incident Location Incident Response Truck E A G’ Future Regional Network Nearest Cell Site G B Wireless Switching Office Public Telephone Network F Response Centers (EMC) (PD/FD/EMS) C D Public Safety Answering Point (EMC) (Cellular 9 -1 -1 PSAP)
 Slide 4 Incident Response Analysis n From Previous Slide – Telephonic notifications slow down coordination process behind the scenes – on scene radio coordination is a separate set of issues – With regional network and evolving IEEE standards for TMC-EMC links, once call gets to PSAP, notification of other responders and regional TMC is nearly instantaneous and automatic, bypassing Telco delays and human error
Slide 4 Incident Response Analysis n From Previous Slide – Telephonic notifications slow down coordination process behind the scenes – on scene radio coordination is a separate set of issues – With regional network and evolving IEEE standards for TMC-EMC links, once call gets to PSAP, notification of other responders and regional TMC is nearly instantaneous and automatic, bypassing Telco delays and human error
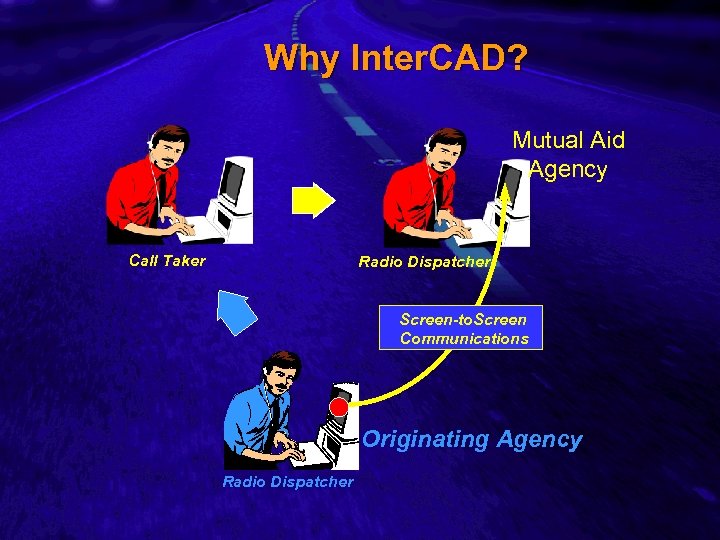 Slide 5 Why Inter. CAD? Mutual Aid Agency Call Taker Radio Dispatcher Screen-to. Screen Communications Originating Agency Radio Dispatcher
Slide 5 Why Inter. CAD? Mutual Aid Agency Call Taker Radio Dispatcher Screen-to. Screen Communications Originating Agency Radio Dispatcher
 Slide 6 Fundamental Barriers to Information Sharing n n n n n Institutional inertia – resistance to change Lack of appreciation for other agencies’ needs NIH syndrome Lack of a regional vision Lack of known and respected champions Legacy (closed) systems Lack of a regional architecture Security concerns CAD vendor involvement in ITS Public Safety Program
Slide 6 Fundamental Barriers to Information Sharing n n n n n Institutional inertia – resistance to change Lack of appreciation for other agencies’ needs NIH syndrome Lack of a regional vision Lack of known and respected champions Legacy (closed) systems Lack of a regional architecture Security concerns CAD vendor involvement in ITS Public Safety Program
 Slide 7 Operational Differences n TMC’s vs. Communications Centers n On-Scene Interoperability vs. “Center-to- Center” Interoperability n Law enforcement (patrol) vs. Fire/EMS (“inquarters”)
Slide 7 Operational Differences n TMC’s vs. Communications Centers n On-Scene Interoperability vs. “Center-to- Center” Interoperability n Law enforcement (patrol) vs. Fire/EMS (“inquarters”)
 Slide 8 Integrating Incident Information Fundamental System Differences TRANSPORTATION MANAGEMENT • Data Fusion/Dissemination • “Awareness” set by sensors • Multi-agency incident mgmt • Real-time facility mgmt • Traveler Information • New development systems PUBLIC SAFETY DISPATCH • Real-time mobile resource mgmt • “Awareness” set by radio comms • Multi-agency incident mgmt • Interface to motorists/public (call box + Mobile 9 -1 -1 + 9 -1 -1) • Legacy systems
Slide 8 Integrating Incident Information Fundamental System Differences TRANSPORTATION MANAGEMENT • Data Fusion/Dissemination • “Awareness” set by sensors • Multi-agency incident mgmt • Real-time facility mgmt • Traveler Information • New development systems PUBLIC SAFETY DISPATCH • Real-time mobile resource mgmt • “Awareness” set by radio comms • Multi-agency incident mgmt • Interface to motorists/public (call box + Mobile 9 -1 -1 + 9 -1 -1) • Legacy systems
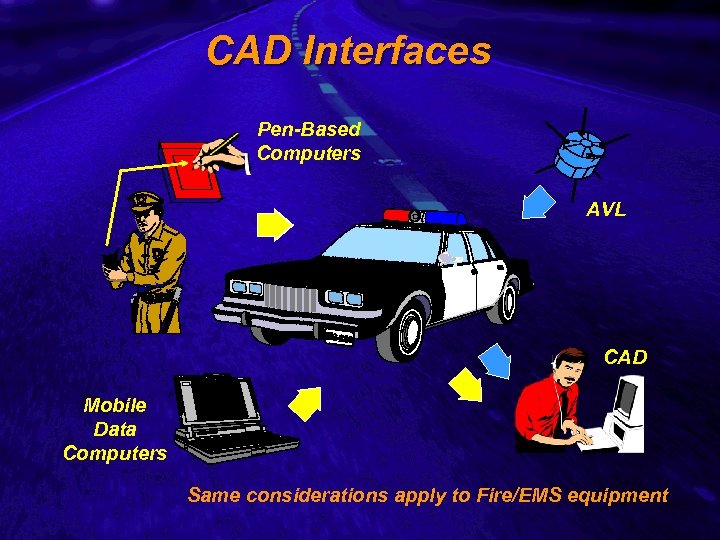 Slide 9 CAD Interfaces Pen-Based Computers AVL CAD Mobile Data Computers Same considerations apply to Fire/EMS equipment
Slide 9 CAD Interfaces Pen-Based Computers AVL CAD Mobile Data Computers Same considerations apply to Fire/EMS equipment
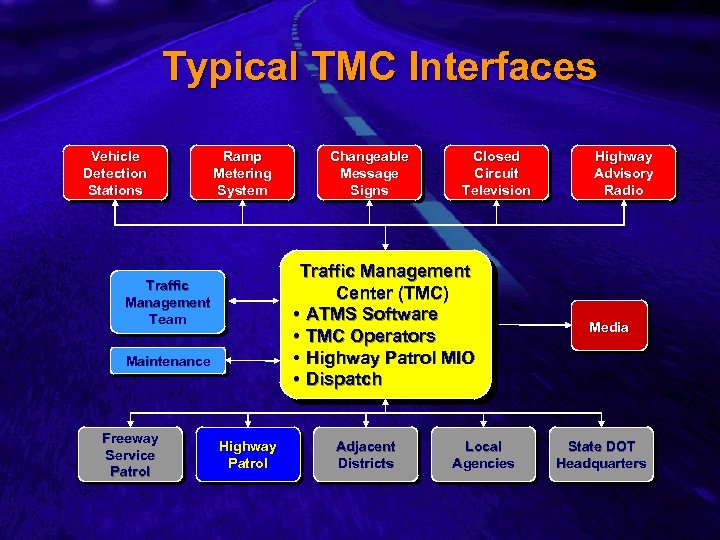 Slide 10 Typical TMC Interfaces Vehicle Detection Stations Ramp Metering System Closed Circuit Television Traffic Management Center (TMC) • ATMS Software • TMC Operators • Highway Patrol MIO • Dispatch Traffic Management Team Maintenance Freeway Service Patrol Changeable Message Signs Highway Patrol Adjacent Districts Local Agencies Highway Advisory Radio Media State DOT Headquarters
Slide 10 Typical TMC Interfaces Vehicle Detection Stations Ramp Metering System Closed Circuit Television Traffic Management Center (TMC) • ATMS Software • TMC Operators • Highway Patrol MIO • Dispatch Traffic Management Team Maintenance Freeway Service Patrol Changeable Message Signs Highway Patrol Adjacent Districts Local Agencies Highway Advisory Radio Media State DOT Headquarters
 Slide 11 Inter. CAD Results
Slide 11 Inter. CAD Results
 Slide 12 Inter. CAD PHASES 1 and 2 PARTICIPANTS • SAN DIEGO PD • SAN DIEGO SHERIFF • CHP BORDER DIV • OCEANSIDE PD/FD • CARLSBAD PD/FD • SAN DIEGO FD • CDF • HEARTLAND FIRE (JPA) • NO COUNTY FIRE (JPA) • FEDERAL FIRE • USFS • CALTRANS (TMC) • Phase 1 participants (limited success) • Planned Phase 2 participants • Eventual Phase 2 installations
Slide 12 Inter. CAD PHASES 1 and 2 PARTICIPANTS • SAN DIEGO PD • SAN DIEGO SHERIFF • CHP BORDER DIV • OCEANSIDE PD/FD • CARLSBAD PD/FD • SAN DIEGO FD • CDF • HEARTLAND FIRE (JPA) • NO COUNTY FIRE (JPA) • FEDERAL FIRE • USFS • CALTRANS (TMC) • Phase 1 participants (limited success) • Planned Phase 2 participants • Eventual Phase 2 installations
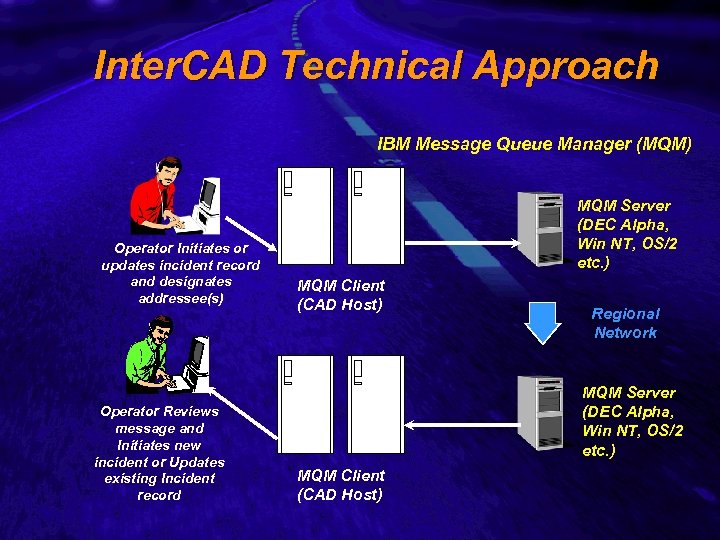 Slide 13 Inter. CAD Technical Approach IBM Message Queue Manager (MQM) Operator Initiates or updates incident record and designates addressee(s) Operator Reviews message and Initiates new incident or Updates existing Incident record MQM Server (DEC Alpha, Win NT, OS/2 etc. ) MQM Client (CAD Host) Regional Network MQM Server (DEC Alpha, Win NT, OS/2 etc. ) MQM Client (CAD Host)
Slide 13 Inter. CAD Technical Approach IBM Message Queue Manager (MQM) Operator Initiates or updates incident record and designates addressee(s) Operator Reviews message and Initiates new incident or Updates existing Incident record MQM Server (DEC Alpha, Win NT, OS/2 etc. ) MQM Client (CAD Host) Regional Network MQM Server (DEC Alpha, Win NT, OS/2 etc. ) MQM Client (CAD Host)
 Slide 14 Phase 2 Capabilities (Planned) n Addressable Consoles (& MDC’s) n Incident Type & Location n Units Assigned & Status n Addressed or Broadcast Messages n Message Priority Levels n “Update Incident” Entries
Slide 14 Phase 2 Capabilities (Planned) n Addressable Consoles (& MDC’s) n Incident Type & Location n Units Assigned & Status n Addressed or Broadcast Messages n Message Priority Levels n “Update Incident” Entries
 Slide 15 Inter. CAD Lessons Learned - I n n n Lost project “Champion” (CHP Communications Center Lt. ) No agency leadership to fill void Reliance on a single CAD vendor for technical solution to CAD modifications Lack of security vulnerability analysis Not enough reliance on existing LE assets (e. g. ARJIS communications and governance structure)
Slide 15 Inter. CAD Lessons Learned - I n n n Lost project “Champion” (CHP Communications Center Lt. ) No agency leadership to fill void Reliance on a single CAD vendor for technical solution to CAD modifications Lack of security vulnerability analysis Not enough reliance on existing LE assets (e. g. ARJIS communications and governance structure)
 Slide 16 Inter. CAD Lessons Learned - II n n n Need a clear Concept of Operations (i. e. start w/ recognized systems engineering principles) – follow up w/ Requirements-Based Engineering Find an agency/key person champion Design to standards (you can design to IEEE 1512 even if not mature…) Participate in standards effort to ensure its relevance to real world development Work within existing Public Safety technical environment to maximum degree possible
Slide 16 Inter. CAD Lessons Learned - II n n n Need a clear Concept of Operations (i. e. start w/ recognized systems engineering principles) – follow up w/ Requirements-Based Engineering Find an agency/key person champion Design to standards (you can design to IEEE 1512 even if not mature…) Participate in standards effort to ensure its relevance to real world development Work within existing Public Safety technical environment to maximum degree possible
 Slide 17 Interface Recommendations
Slide 17 Interface Recommendations
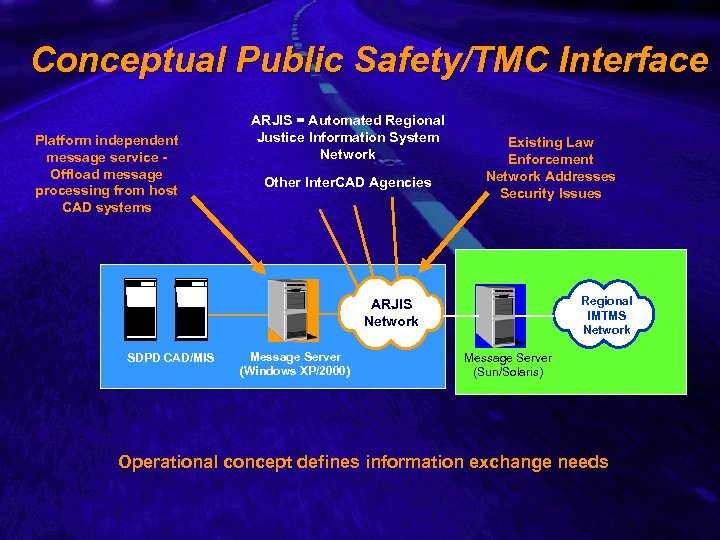 Slide 18 Conceptual Public Safety/TMC Interface Platform independent message service Offload message processing from host CAD systems ARJIS = Automated Regional Justice Information System Network Other Inter. CAD Agencies Existing Law Enforcement Network Addresses Security Issues Regional IMTMS Network ARJIS Network SDPD CAD/MIS Message Server (Windows XP/2000) Message Server (Sun/Solaris) Operational concept defines information exchange needs
Slide 18 Conceptual Public Safety/TMC Interface Platform independent message service Offload message processing from host CAD systems ARJIS = Automated Regional Justice Information System Network Other Inter. CAD Agencies Existing Law Enforcement Network Addresses Security Issues Regional IMTMS Network ARJIS Network SDPD CAD/MIS Message Server (Windows XP/2000) Message Server (Sun/Solaris) Operational concept defines information exchange needs
 Slide 19 Conceptual Information Sharing INCIDENT/TYPE/LOCATION HIGHWAY/ARTERIAL CONGESTION CONSTRUCTION/CLOSURES RECOMMENDED ROUTING CCTV VIDEO Transportation Public Safety INCIDENT TYPE/LOCATION UNIT ASSIGNMENT UNIT STATUS INCIDENT DETAILS (AS OCCURRING) Over 90% of initial incident notifications go to 9 -1 -1
Slide 19 Conceptual Information Sharing INCIDENT/TYPE/LOCATION HIGHWAY/ARTERIAL CONGESTION CONSTRUCTION/CLOSURES RECOMMENDED ROUTING CCTV VIDEO Transportation Public Safety INCIDENT TYPE/LOCATION UNIT ASSIGNMENT UNIT STATUS INCIDENT DETAILS (AS OCCURRING) Over 90% of initial incident notifications go to 9 -1 -1
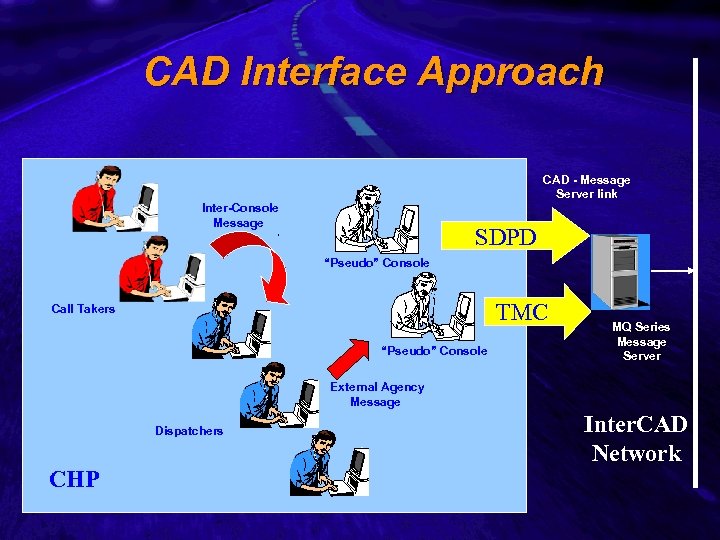 Slide 20 CAD Interface Approach CAD - Message Server link Inter-Console Message SDPD “Pseudo” Console TMC Call Takers “Pseudo” Console MQ Series Message Server External Agency Message Dispatchers CHP Inter. CAD Network
Slide 20 CAD Interface Approach CAD - Message Server link Inter-Console Message SDPD “Pseudo” Console TMC Call Takers “Pseudo” Console MQ Series Message Server External Agency Message Dispatchers CHP Inter. CAD Network
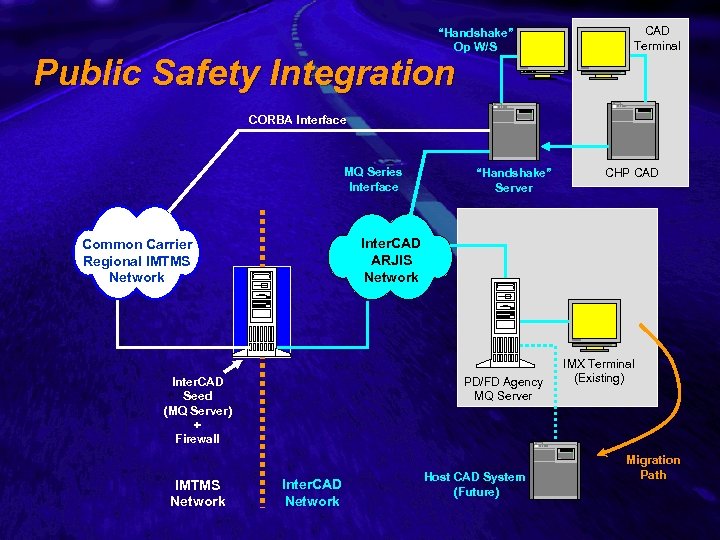 Slide 21 “Handshake” Op W/S Public Safety Integration CAD Terminal CORBA Interface MQ Series Interface CHP CAD Inter. CAD ARJIS Network Common Carrier Regional IMTMS Network Inter. CAD Seed (MQ Server) + Firewall IMTMS Network “Handshake” Server PD/FD Agency MQ Server Inter. CAD Network Host CAD System (Future) IMX Terminal (Existing) Migration Path
Slide 21 “Handshake” Op W/S Public Safety Integration CAD Terminal CORBA Interface MQ Series Interface CHP CAD Inter. CAD ARJIS Network Common Carrier Regional IMTMS Network Inter. CAD Seed (MQ Server) + Firewall IMTMS Network “Handshake” Server PD/FD Agency MQ Server Inter. CAD Network Host CAD System (Future) IMX Terminal (Existing) Migration Path
 Slide 22 Standards Recommendations
Slide 22 Standards Recommendations
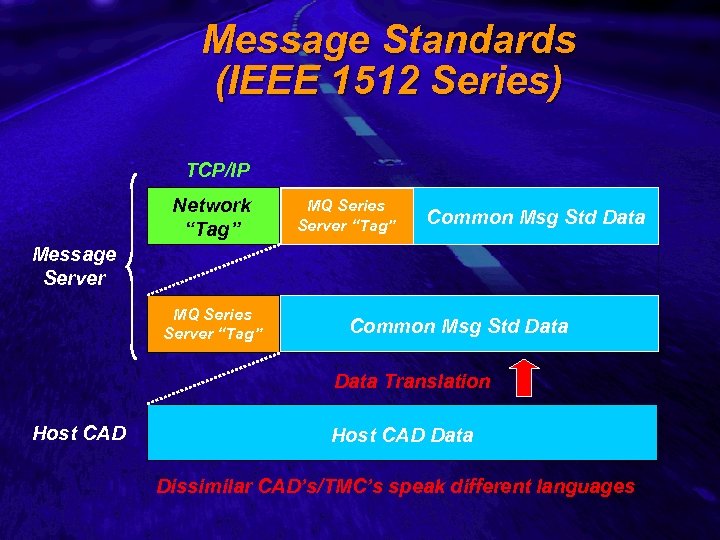 Slide 23 Message Standards (IEEE 1512 Series) TCP/IP Network “Tag” MQ Series Server “Tag” Common Msg Std Data Message Server MQ Series Server “Tag” Common Msg Std Data Translation Host CAD Data Dissimilar CAD’s/TMC’s speak different languages
Slide 23 Message Standards (IEEE 1512 Series) TCP/IP Network “Tag” MQ Series Server “Tag” Common Msg Std Data Message Server MQ Series Server “Tag” Common Msg Std Data Translation Host CAD Data Dissimilar CAD’s/TMC’s speak different languages
 Slide 24 P 1512 Future Requirements n Must support object-oriented and Web Services/XML development – Define standard “objects” for public safety – Standard “message” to “object” mappings – Transportation objects are being defined through NTCIP – may need extensions for broader IM concepts covered by P 1512 – Implementation Guide must address Web Services architectures
Slide 24 P 1512 Future Requirements n Must support object-oriented and Web Services/XML development – Define standard “objects” for public safety – Standard “message” to “object” mappings – Transportation objects are being defined through NTCIP – may need extensions for broader IM concepts covered by P 1512 – Implementation Guide must address Web Services architectures
 Slide 25 Institutional Recommendations
Slide 25 Institutional Recommendations
 Slide 26 Recommendations for Public Safety Integration Projects Involve Agency CEO’s and Keep Apprised n Governance Body – Agency Ownership n Public Safety Community Should Establish a Regional Architecture Approach to Information Sharing paralleling USDOT Effort n – Communications – Standards n n Adequate Outreach to Agencies at All Levels Develop a “Plug and Play” (Blueprint) Approach Mainstreaming Projects – RTP, O&M Involve multiple CAD vendors from the beginning
Slide 26 Recommendations for Public Safety Integration Projects Involve Agency CEO’s and Keep Apprised n Governance Body – Agency Ownership n Public Safety Community Should Establish a Regional Architecture Approach to Information Sharing paralleling USDOT Effort n – Communications – Standards n n Adequate Outreach to Agencies at All Levels Develop a “Plug and Play” (Blueprint) Approach Mainstreaming Projects – RTP, O&M Involve multiple CAD vendors from the beginning
 Slide 27 Inter. CAD Next Steps n Use lessons learned from original project n Use the regional architecture (currently being revised for Final Rule compliance) n Establish working level champions from both public safety and transportation n CEO buy-in from both communities n Establish vendor integration team n Start modestly and add capabilities using a phased approach
Slide 27 Inter. CAD Next Steps n Use lessons learned from original project n Use the regional architecture (currently being revised for Final Rule compliance) n Establish working level champions from both public safety and transportation n CEO buy-in from both communities n Establish vendor integration team n Start modestly and add capabilities using a phased approach
 Slide 28 Summary n Real Public Safety and Transportation integration is no longer a luxury or “nice to have” – it is essential for accommodating the increased complexity of regional incident management of all types: from traffic to terrorism n Like any other transportation initiative, integration investments and recurring costs must be made compelling to executive management and elected officials
Slide 28 Summary n Real Public Safety and Transportation integration is no longer a luxury or “nice to have” – it is essential for accommodating the increased complexity of regional incident management of all types: from traffic to terrorism n Like any other transportation initiative, integration investments and recurring costs must be made compelling to executive management and elected officials
 Slide 29 End
Slide 29 End


