9af1a3081f7ebcfa3cf81fce470780de.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 Slide 1 Ch 5 - Morphology Ch 4 – Features Consider the following data from Mokilese Can you identify complementary distribution? If so, write a rule in feature to capture the overall process (not specific rules for specific sounds but for natural classes)
Slide 1 Ch 5 - Morphology Ch 4 – Features Consider the following data from Mokilese Can you identify complementary distribution? If so, write a rule in feature to capture the overall process (not specific rules for specific sounds but for natural classes)
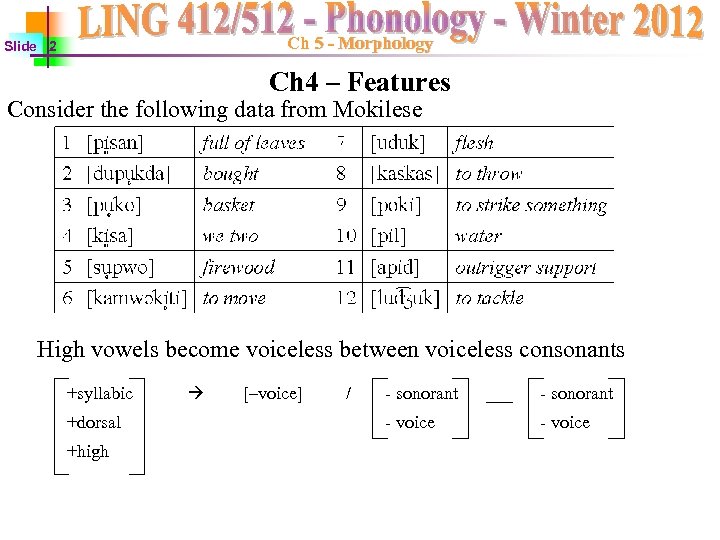 Ch 5 - Morphology Slide 2 Ch 4 – Features Consider the following data from Mokilese High vowels become voiceless between voiceless consonants +syllabic +dorsal +high [–voice] / - sonorant - voice ___ - sonorant - voice
Ch 5 - Morphology Slide 2 Ch 4 – Features Consider the following data from Mokilese High vowels become voiceless between voiceless consonants +syllabic +dorsal +high [–voice] / - sonorant - voice ___ - sonorant - voice
 Slide 3 Ch 5 - Morphology Ø The part of the grammar that is concerned with words and word formation Ø Lexicon - your mental dictionary - the filing cabinet drawer for how words are put together and what the meanings of this different parts are Ø Word - the smallest free form found in language (it does not have to occur in fixed position with respect to other forms)
Slide 3 Ch 5 - Morphology Ø The part of the grammar that is concerned with words and word formation Ø Lexicon - your mental dictionary - the filing cabinet drawer for how words are put together and what the meanings of this different parts are Ø Word - the smallest free form found in language (it does not have to occur in fixed position with respect to other forms)
 Slide 4 Ch 5 - Morphology Ø Morpheme - the smallest unit of language that carries information about meaning or function (builder has 2 morphemes: build and -er) Ø Simple words - contain only 1 morpheme Ø Complex words - contain more than 1 morpheme Ø Free morpheme - a morpheme that can be a word by itself Ø Bound morpheme - a morpheme that must be attached to another element
Slide 4 Ch 5 - Morphology Ø Morpheme - the smallest unit of language that carries information about meaning or function (builder has 2 morphemes: build and -er) Ø Simple words - contain only 1 morpheme Ø Complex words - contain more than 1 morpheme Ø Free morpheme - a morpheme that can be a word by itself Ø Bound morpheme - a morpheme that must be attached to another element
 Slide 5 Ch 5 - Morphology Ø Allomorphs - the variant forms of a morpheme Ø English indefinite article has 2 allomorphs: a and an ØEnglish plural has 3 allomorphs - what are they? cats, dogs, horses
Slide 5 Ch 5 - Morphology Ø Allomorphs - the variant forms of a morpheme Ø English indefinite article has 2 allomorphs: a and an ØEnglish plural has 3 allomorphs - what are they? cats, dogs, horses
 Slide 6 Ch 5 - Morphology Ø Word structure Ø Root - the core of the word and carries the major component of meaning Ø Lexical category - Noun (N), Adjective (A), Verb (V), Preposition (P) Ø Affixes - general term for a morpheme that does not have a lexical category, and is always bound ØBase is the form to which an affix is attached (most cases it is the root)
Slide 6 Ch 5 - Morphology Ø Word structure Ø Root - the core of the word and carries the major component of meaning Ø Lexical category - Noun (N), Adjective (A), Verb (V), Preposition (P) Ø Affixes - general term for a morpheme that does not have a lexical category, and is always bound ØBase is the form to which an affix is attached (most cases it is the root)
 Ch 5 - Morphology Slide 7 Ch 5 - Morphology Ø Word trees - (Af) means Affix Ø Base is the thing that an affixes to (sometimes the root, sometimes not) Ø kindness Ø 1) Identify the root A kindne ss
Ch 5 - Morphology Slide 7 Ch 5 - Morphology Ø Word trees - (Af) means Affix Ø Base is the thing that an affixes to (sometimes the root, sometimes not) Ø kindness Ø 1) Identify the root A kindne ss
 Ch 5 - Morphology Slide 8 Ch 5 - Morphology Ø Word trees - (Af) means Affix Ø Base is the thing that an affixes to (sometimes the root, sometimes not) Ø kindness Ø 2) Attach the suffix and determine lexical category of the word N A Af kindne ss
Ch 5 - Morphology Slide 8 Ch 5 - Morphology Ø Word trees - (Af) means Affix Ø Base is the thing that an affixes to (sometimes the root, sometimes not) Ø kindness Ø 2) Attach the suffix and determine lexical category of the word N A Af kindne ss
 Ch 5 - Morphology Slide 9 Ch 5 - Morphology Ø Word trees - (Af) means Affix Ø Base is the thing that an affixes to (sometimes the root, sometimes not) Ø kindnesses Ø 1) Identify the root A kindne sses
Ch 5 - Morphology Slide 9 Ch 5 - Morphology Ø Word trees - (Af) means Affix Ø Base is the thing that an affixes to (sometimes the root, sometimes not) Ø kindnesses Ø 1) Identify the root A kindne sses
 Ch 5 - Morphology Slide 10 Ch 5 - Morphology Ø Word trees - (Af) means Affix Ø Base is the thing that an affixes to (sometimes the root, sometimes not) Ø kindness Ø 2) Attach the 1 st affix and determine lexical category of the word N A Af kindne sses
Ch 5 - Morphology Slide 10 Ch 5 - Morphology Ø Word trees - (Af) means Affix Ø Base is the thing that an affixes to (sometimes the root, sometimes not) Ø kindness Ø 2) Attach the 1 st affix and determine lexical category of the word N A Af kindne sses
 Ch 5 - Morphology Slide 11 Ch 5 - Morphology Ø Word trees - (Af) means Affix Ø Base is the thing that an affixes to (sometimes the root, sometimes not) Ø kindness Ø 3) Attach the 2 nd affix to the new base and determine lexical category of the N resulting word Af N A Af kindne sses [[[[ kind ]A ness]N es]N
Ch 5 - Morphology Slide 11 Ch 5 - Morphology Ø Word trees - (Af) means Affix Ø Base is the thing that an affixes to (sometimes the root, sometimes not) Ø kindness Ø 3) Attach the 2 nd affix to the new base and determine lexical category of the N resulting word Af N A Af kindne sses [[[[ kind ]A ness]N es]N
 Slide 12 Ch 5 - Morphology Ø Affixes can be suffixes, prefixes or infixes ØInfixes must be morphemes inserted into the root of the word, and not just adding another prefix or suffix to an existing one Øfreakin’ as an infix: abso-freakin-lutely not *absolute-freakin-ly Øa true English infix? Ø Problems: some words that have an affix no longer allow the root to be a free form - unkempt, inept, overwhelmed - any others? Ø Some words appear to have affixes but are considered one morpheme receive, submit, permit (still formed with other affixes like they do have affixes though - permission, reception)
Slide 12 Ch 5 - Morphology Ø Affixes can be suffixes, prefixes or infixes ØInfixes must be morphemes inserted into the root of the word, and not just adding another prefix or suffix to an existing one Øfreakin’ as an infix: abso-freakin-lutely not *absolute-freakin-ly Øa true English infix? Ø Problems: some words that have an affix no longer allow the root to be a free form - unkempt, inept, overwhelmed - any others? Ø Some words appear to have affixes but are considered one morpheme receive, submit, permit (still formed with other affixes like they do have affixes though - permission, reception)
 Ch 5 - Morphology Slide 13 Ch 5 - Morphology Ø Derivation - an affixational process that forms a word with a meaning and/or category distinct from its base ØComplex derivations - when there are multiple affixes Ø Structurally ambiguous words - unlockable A V A Af Af V unlock able A Af unlock able
Ch 5 - Morphology Slide 13 Ch 5 - Morphology Ø Derivation - an affixational process that forms a word with a meaning and/or category distinct from its base ØComplex derivations - when there are multiple affixes Ø Structurally ambiguous words - unlockable A V A Af Af V unlock able A Af unlock able
 Slide 14 Ch 5 - Morphology Ø Constraints on derivation - suffix -ant cannot affix to native English words, only borrowed words from Latin ØSometimes constraint is phonological - -en can only attach as a suffix to a monosyllabic base ending in an obstruent.
Slide 14 Ch 5 - Morphology Ø Constraints on derivation - suffix -ant cannot affix to native English words, only borrowed words from Latin ØSometimes constraint is phonological - -en can only attach as a suffix to a monosyllabic base ending in an obstruent.
 Slide 15 Ch 5 - Morphology Ø 2 different classes of affixes: Ø Class 1 affix - triggers phonological changes in consonants or vowels of the base - stress shifts (not talking about spelling) Ø Class 2 affix - phonologically neutral, having no effect on base or stress of resulting word (not talking about spelling) Ø Usually, Class 2 affixes cannot come between Class 1 affixes and the root. Ø *fearlessity, but ok fearlessness, relational, divisiveness
Slide 15 Ch 5 - Morphology Ø 2 different classes of affixes: Ø Class 1 affix - triggers phonological changes in consonants or vowels of the base - stress shifts (not talking about spelling) Ø Class 2 affix - phonologically neutral, having no effect on base or stress of resulting word (not talking about spelling) Ø Usually, Class 2 affixes cannot come between Class 1 affixes and the root. Ø *fearlessity, but ok fearlessness, relational, divisiveness
 Slide 16 Ch 5 - Morphology On p. 110, un- is a prefix that attaches to an adjective and here it attaches to a noun
Slide 16 Ch 5 - Morphology On p. 110, un- is a prefix that attaches to an adjective and here it attaches to a noun
 Slide 17 Ch 5 - Morphology Ø Compounding - compound word is the combination of two already existing words Ø The right-most word determines the lexical category of the new compound word (greenhouse is a noun because house is a noun although green is an adjective) - the morpheme that determines the category is called the head Ø Spelling is not consistent with how compounds are represented - high school, high-school, highschool ØPronunciation differences between compound and A + N sequence blackbird versus black bird Ø Inflectional suffixes can only be added to second form in compound (tense or plural) so drop kicked but not *dropped kick
Slide 17 Ch 5 - Morphology Ø Compounding - compound word is the combination of two already existing words Ø The right-most word determines the lexical category of the new compound word (greenhouse is a noun because house is a noun although green is an adjective) - the morpheme that determines the category is called the head Ø Spelling is not consistent with how compounds are represented - high school, high-school, highschool ØPronunciation differences between compound and A + N sequence blackbird versus black bird Ø Inflectional suffixes can only be added to second form in compound (tense or plural) so drop kicked but not *dropped kick
 Slide 18 Ch 5 - Morphology Ø Inflection - the modification of a word’s form to indicate grammatical information of various sorts Ø The base that inflectional forms are added to is sometimes called a stem (like root for derivational affixation) Ø This is different from derivation ØIncludes Tense, Aspect, Number, person/number agreement, case
Slide 18 Ch 5 - Morphology Ø Inflection - the modification of a word’s form to indicate grammatical information of various sorts Ø The base that inflectional forms are added to is sometimes called a stem (like root for derivational affixation) Ø This is different from derivation ØIncludes Tense, Aspect, Number, person/number agreement, case
 Slide 19 Ch 5 - Morphology Ø There are many irregular forms in English that don’t use the affixation of inflection as discussed. (go + PAST = goed? no, went) Ø Inflection versus Derivation ØInflection does not change the grammatical category or the meaning of the word to which it is affixed Ø Derivation can change the category and does change the meaning (although still related) (All English prefixes are derivation even though they do not change the lexical category of the word) Ø Derivational affixes have to occur closest to base. neighborhoods but not *neighborshood Ø Inflectional affixes can combine with nearly every possible word (plural -s) but derivational affixes can combine with a more limited set (-ment)
Slide 19 Ch 5 - Morphology Ø There are many irregular forms in English that don’t use the affixation of inflection as discussed. (go + PAST = goed? no, went) Ø Inflection versus Derivation ØInflection does not change the grammatical category or the meaning of the word to which it is affixed Ø Derivation can change the category and does change the meaning (although still related) (All English prefixes are derivation even though they do not change the lexical category of the word) Ø Derivational affixes have to occur closest to base. neighborhoods but not *neighborshood Ø Inflectional affixes can combine with nearly every possible word (plural -s) but derivational affixes can combine with a more limited set (-ment)
 Slide 20 Ch 5 - Morphology Ø Inflection versus Derivation Ø Special case of -ing: There are 3 -ing affixes! Ø 1) Derivational: Verb + -ing = Noun - I watched the dancing in the room. Ø 2) Derivational: Verb + -ing = Adjective - The dancing frog Ø 3) Inflectional: Verb + -ing = Verb - The frog is dancing
Slide 20 Ch 5 - Morphology Ø Inflection versus Derivation Ø Special case of -ing: There are 3 -ing affixes! Ø 1) Derivational: Verb + -ing = Noun - I watched the dancing in the room. Ø 2) Derivational: Verb + -ing = Adjective - The dancing frog Ø 3) Inflectional: Verb + -ing = Verb - The frog is dancing
 Slide 21 Ch 5 - Morphology Ø Inflection - in English is usually marked with affixes (suffixes) Ø Can also be marked through Internal Change - a process that substitutes one nonmorphemic segment for another to mark a grammatical contrast Ø Ablaut (vowel alterations): sing, sink, drive - sang, sank, drove OR feet and geese from foot and goose - what about dive? Ø Suppletion - replaces a morpheme with an entirely different morpheme in order to indicate a grammatical contrast Ø to be in English is made up of a few different forms not related to each other through affixation or internal change: is, was, were, am, be
Slide 21 Ch 5 - Morphology Ø Inflection - in English is usually marked with affixes (suffixes) Ø Can also be marked through Internal Change - a process that substitutes one nonmorphemic segment for another to mark a grammatical contrast Ø Ablaut (vowel alterations): sing, sink, drive - sang, sank, drove OR feet and geese from foot and goose - what about dive? Ø Suppletion - replaces a morpheme with an entirely different morpheme in order to indicate a grammatical contrast Ø to be in English is made up of a few different forms not related to each other through affixation or internal change: is, was, were, am, be
 Ch 5 - Morphology Slide 22 Ch 5 - Morphology INFLECTION ØReduplication - total or partial - the repetition of all or part of a word to indicate a grammatical or semantic contrast Ø Tone placement - different pitch to indicate different tense (Spanish has an inflectional stress to indicate tense and person - hablo versus habló) Ø Agreement – when one word is inflected to match a certain grammatical properties of another word – number, person (Eng. 3 rd Sing Present –s: he speaks Ø Case - is a change in a word’s form to indicate its grammatical role (subject, direct object, indirect object, etc. ) Ø He/his/him, I/mine/me
Ch 5 - Morphology Slide 22 Ch 5 - Morphology INFLECTION ØReduplication - total or partial - the repetition of all or part of a word to indicate a grammatical or semantic contrast Ø Tone placement - different pitch to indicate different tense (Spanish has an inflectional stress to indicate tense and person - hablo versus habló) Ø Agreement – when one word is inflected to match a certain grammatical properties of another word – number, person (Eng. 3 rd Sing Present –s: he speaks Ø Case - is a change in a word’s form to indicate its grammatical role (subject, direct object, indirect object, etc. ) Ø He/his/him, I/mine/me
 Slide 23 Ch 5 - Morphology ØConversions - changing one word from one category to another without the use of affixes (zero derivation or zero affixation) ØAlso, productivity – still can write rules for non-productive morphology (like –en plural oxen)
Slide 23 Ch 5 - Morphology ØConversions - changing one word from one category to another without the use of affixes (zero derivation or zero affixation) ØAlso, productivity – still can write rules for non-productive morphology (like –en plural oxen)
 Slide 24 Ch 5 - Morphology
Slide 24 Ch 5 - Morphology
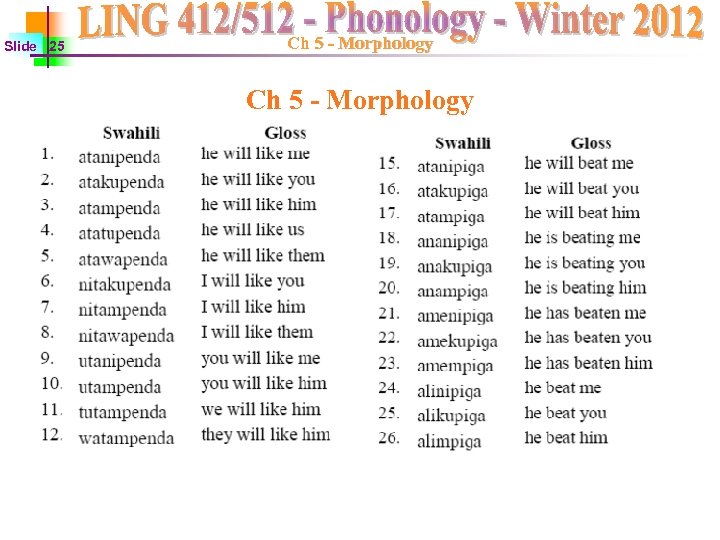 Slide 25 Ch 5 - Morphology
Slide 25 Ch 5 - Morphology
 Slide 26 Ch 5 - Morphology ØIn order to figure out the morphemes, must find morphological minimal pairs (2 words that differ with only 1 morpheme) then figure out what the diffs in meaning are and you can figure out the morphemes. Øatanipenda vs. atakupenda = he will like me vs. he will like you ØSo we know that –ni- must be me (Obj) and –ku- must be you (Obj) ØFigure out with the data that the order of the morphemes is: ØSUBJECT + TENSE + OBJECT + ROOT
Slide 26 Ch 5 - Morphology ØIn order to figure out the morphemes, must find morphological minimal pairs (2 words that differ with only 1 morpheme) then figure out what the diffs in meaning are and you can figure out the morphemes. Øatanipenda vs. atakupenda = he will like me vs. he will like you ØSo we know that –ni- must be me (Obj) and –ku- must be you (Obj) ØFigure out with the data that the order of the morphemes is: ØSUBJECT + TENSE + OBJECT + ROOT
 Ch 5 - Morphology Slide 27 Ch 5 - Morphology ØMorphological rules to derive the correct forms. Since there are 3 prefixes attaching to root, we start with the one closest to root. 1. )Object Marking ØX OP + X in [+Verb] ØWhere OP is selected from: Ø ni- [+me-object] Ø ku- [+you-object] Ø m- [+him-object] Ø tu- [+us-object] Ø wa- [+them-object]
Ch 5 - Morphology Slide 27 Ch 5 - Morphology ØMorphological rules to derive the correct forms. Since there are 3 prefixes attaching to root, we start with the one closest to root. 1. )Object Marking ØX OP + X in [+Verb] ØWhere OP is selected from: Ø ni- [+me-object] Ø ku- [+you-object] Ø m- [+him-object] Ø tu- [+us-object] Ø wa- [+them-object]
 Ch 5 - Morphology Slide 28 Ch 5 - Morphology ØMorphological rules to derive the correct forms. Since there are 3 prefixes attaching to root, we start with the one closest to root. 2. )Tense Marking ØX Tense + X in [+Verb] ØWhere TENSE is selected from: Ø ta- [+future] Ø na- [+present] Ø me- [+past]
Ch 5 - Morphology Slide 28 Ch 5 - Morphology ØMorphological rules to derive the correct forms. Since there are 3 prefixes attaching to root, we start with the one closest to root. 2. )Tense Marking ØX Tense + X in [+Verb] ØWhere TENSE is selected from: Ø ta- [+future] Ø na- [+present] Ø me- [+past]
 Ch 5 - Morphology Slide 29 Ø Ch 5 - Morphology Morphological rules to derive the correct forms. Since there are 3 prefixes attaching to root, we start with the one closest to root. 3. )Subject Marking Ø X SP + X in [+Verb] Ø Where SP is selected from: Ø Ø a- [+he-subject] ni- [+I-subject] u- [+you-subject] tu- [+we-subject] 1. 2. 3. penda nipenda tanipenda atanipenda root Object Marking Tense Marking Subject Marking Output of morphology
Ch 5 - Morphology Slide 29 Ø Ch 5 - Morphology Morphological rules to derive the correct forms. Since there are 3 prefixes attaching to root, we start with the one closest to root. 3. )Subject Marking Ø X SP + X in [+Verb] Ø Where SP is selected from: Ø Ø a- [+he-subject] ni- [+I-subject] u- [+you-subject] tu- [+we-subject] 1. 2. 3. penda nipenda tanipenda atanipenda root Object Marking Tense Marking Subject Marking Output of morphology
 Slide 30 Ch 5 - Morphology ØQuestions about morphological rules?
Slide 30 Ch 5 - Morphology ØQuestions about morphological rules?


