6adef32d4bb080b7b29900adefd9fec8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 SLC 500 Communications SLC 500 COMMUNICATIONS 1
SLC 500 Communications SLC 500 COMMUNICATIONS 1
 SLC 500 Communications Requirements for Industrial Networks n n n An industrial communication link Capable of supporting real-time control High data integrity High noise immunity High reliability in harsh environments Suitable for large installations 2
SLC 500 Communications Requirements for Industrial Networks n n n An industrial communication link Capable of supporting real-time control High data integrity High noise immunity High reliability in harsh environments Suitable for large installations 2
 SLC 500 Communications Local Area Network - Applications Centralized Data Monitering and Acquisition n Manufacturing n SCADA n MMI Distributed Control n Communication between programmable controllers n Upload to a programmer or host computer from any PLC n Download from a programmer or host computer to any PLC n Read/write I/O values, registers of any PLC n Monitoring of PLC status and control of PLC operation 3
SLC 500 Communications Local Area Network - Applications Centralized Data Monitering and Acquisition n Manufacturing n SCADA n MMI Distributed Control n Communication between programmable controllers n Upload to a programmer or host computer from any PLC n Download from a programmer or host computer to any PLC n Read/write I/O values, registers of any PLC n Monitoring of PLC status and control of PLC operation 3
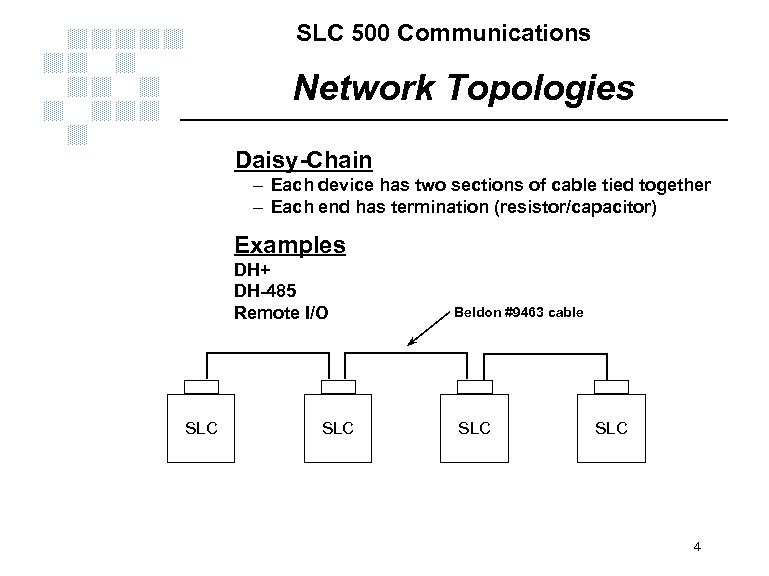 SLC 500 Communications Network Topologies Daisy-Chain – Each device has two sections of cable tied together – Each end has termination (resistor/capacitor) Examples DH+ DH-485 Remote I/O SLC Beldon #9463 cable SLC 4
SLC 500 Communications Network Topologies Daisy-Chain – Each device has two sections of cable tied together – Each end has termination (resistor/capacitor) Examples DH+ DH-485 Remote I/O SLC Beldon #9463 cable SLC 4
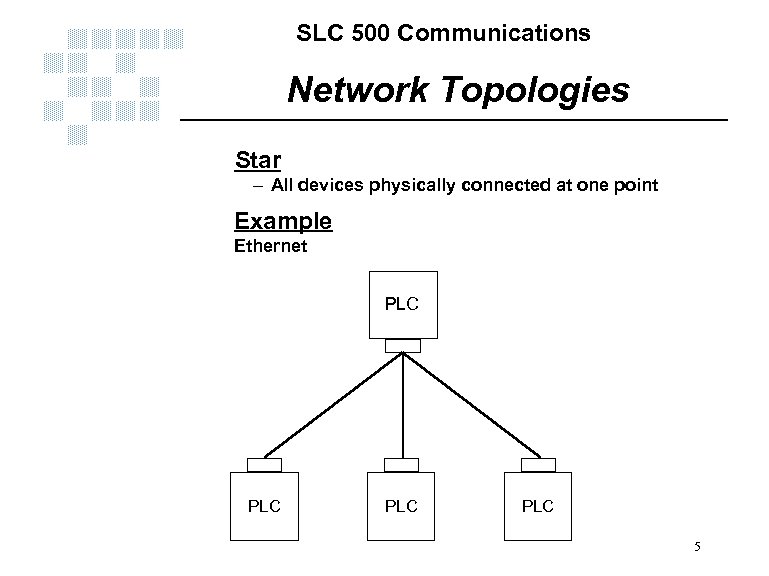 SLC 500 Communications Network Topologies Star – All devices physically connected at one point Example Ethernet PLC PLC 5
SLC 500 Communications Network Topologies Star – All devices physically connected at one point Example Ethernet PLC PLC 5
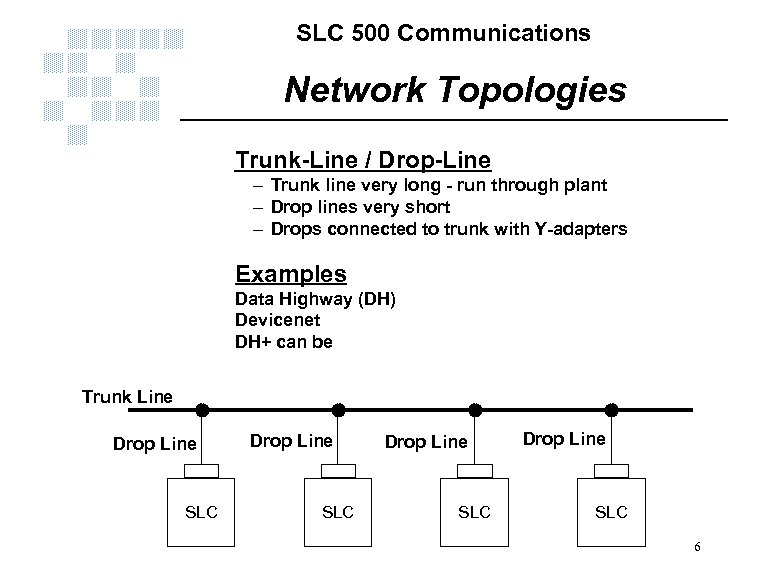 SLC 500 Communications Network Topologies Trunk-Line / Drop-Line – Trunk line very long - run through plant – Drop lines very short – Drops connected to trunk with Y-adapters Examples Data Highway (DH) Devicenet DH+ can be Trunk Line Drop Line SLC 6
SLC 500 Communications Network Topologies Trunk-Line / Drop-Line – Trunk line very long - run through plant – Drop lines very short – Drops connected to trunk with Y-adapters Examples Data Highway (DH) Devicenet DH+ can be Trunk Line Drop Line SLC 6
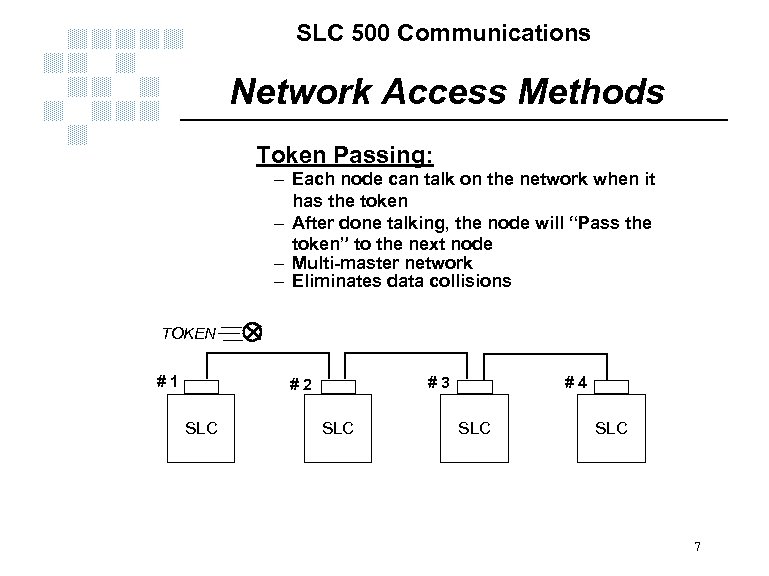 SLC 500 Communications Network Access Methods Token Passing: – Each node can talk on the network when it has the token – After done talking, the node will “Pass the token” to the next node – Multi-master network – Eliminates data collisions TOKEN #1 #3 #2 SLC #4 SLC 7
SLC 500 Communications Network Access Methods Token Passing: – Each node can talk on the network when it has the token – After done talking, the node will “Pass the token” to the next node – Multi-master network – Eliminates data collisions TOKEN #1 #3 #2 SLC #4 SLC 7
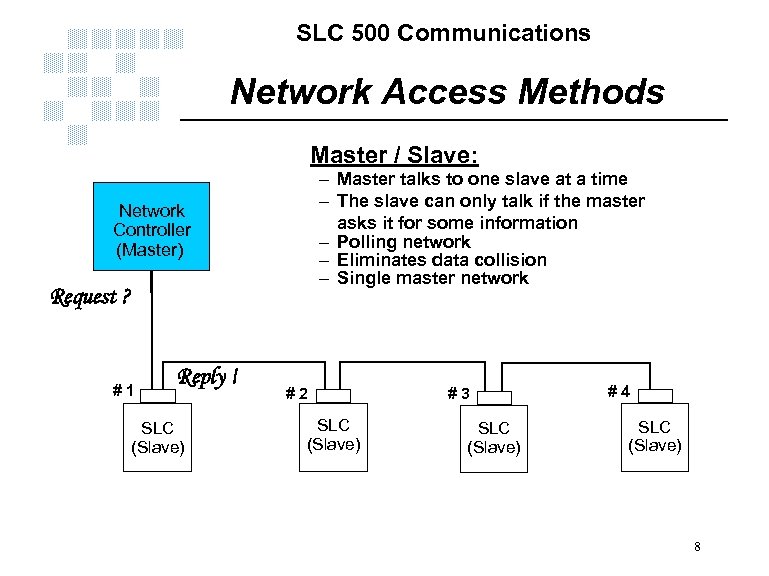 SLC 500 Communications Network Access Methods Master / Slave: – Master talks to one slave at a time – The slave can only talk if the master asks it for some information – Polling network – Eliminates data collision – Single master network Network Controller (Master) Request ? #1 Reply ! SLC (Slave) #2 SLC (Slave) #3 SLC (Slave) #4 SLC (Slave) 8
SLC 500 Communications Network Access Methods Master / Slave: – Master talks to one slave at a time – The slave can only talk if the master asks it for some information – Polling network – Eliminates data collision – Single master network Network Controller (Master) Request ? #1 Reply ! SLC (Slave) #2 SLC (Slave) #3 SLC (Slave) #4 SLC (Slave) 8
 SLC 500 Communications Networks - How to Decide on One? n Maximum number of devices – How many nodes are required for the application? – How many nodes should be reserved for future expansion? n Maximum network length – Usually specified as the physical cable distance from the first node to the last node on the network – Drop length is the length of cable from the main cable to the node n Device supported – – n n Programmable controllers Programming devices Operator Interfaces Other Computers - PCs, Workstations, Minis, Mainframes. . . Response time Application interface 9
SLC 500 Communications Networks - How to Decide on One? n Maximum number of devices – How many nodes are required for the application? – How many nodes should be reserved for future expansion? n Maximum network length – Usually specified as the physical cable distance from the first node to the last node on the network – Drop length is the length of cable from the main cable to the node n Device supported – – n n Programmable controllers Programming devices Operator Interfaces Other Computers - PCs, Workstations, Minis, Mainframes. . . Response time Application interface 9
 SLC 500 Communications A-B Communication Network Terms RS-232 RS-422 RS-485 What the hell do all these mean? DH-485 REMOTE I/O DF 1 DH+ 10
SLC 500 Communications A-B Communication Network Terms RS-232 RS-422 RS-485 What the hell do all these mean? DH-485 REMOTE I/O DF 1 DH+ 10
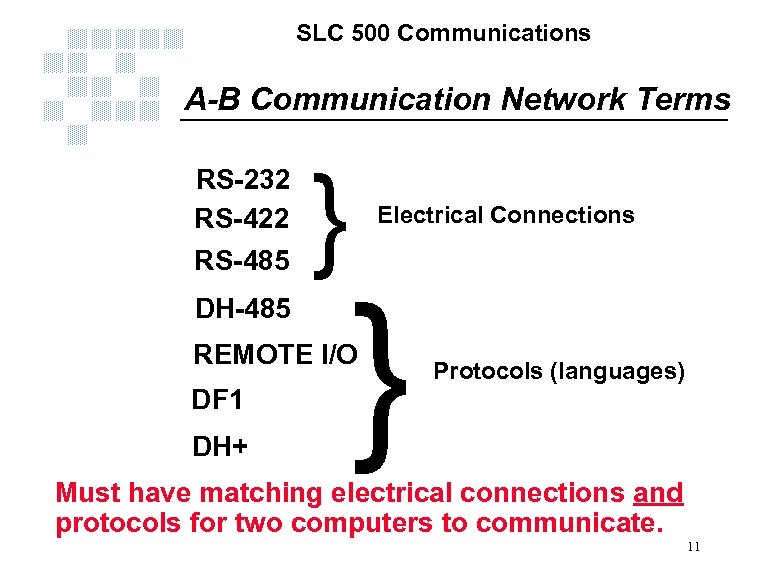 SLC 500 Communications A-B Communication Network Terms RS-232 RS-422 RS-485 DH-485 } Electrical Connections } REMOTE I/O DF 1 DH+ Protocols (languages) Must have matching electrical connections and protocols for two computers to communicate. 11
SLC 500 Communications A-B Communication Network Terms RS-232 RS-422 RS-485 DH-485 } Electrical Connections } REMOTE I/O DF 1 DH+ Protocols (languages) Must have matching electrical connections and protocols for two computers to communicate. 11
 SLC 500 Communications - Like a Phone Call. . . 12
SLC 500 Communications - Like a Phone Call. . . 12
 SLC 500 Communications - Like a Phone Call. . . Electrical Connection is made when person answers phone 13
SLC 500 Communications - Like a Phone Call. . . Electrical Connection is made when person answers phone 13
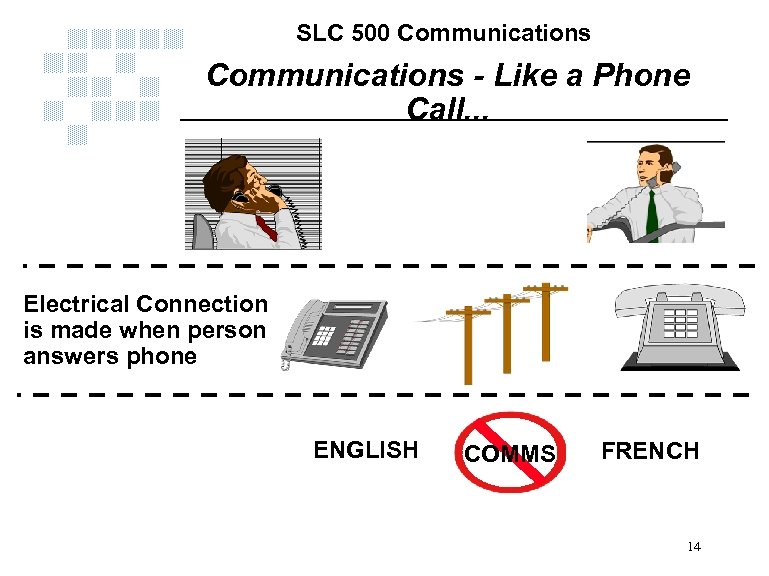 SLC 500 Communications - Like a Phone Call. . . Electrical Connection is made when person answers phone ENGLISH COMMS FRENCH 14
SLC 500 Communications - Like a Phone Call. . . Electrical Connection is made when person answers phone ENGLISH COMMS FRENCH 14
 SLC 500 Communications - Like a Phone Call. . . Electrical Connection is made when person answers phone Communication when connection make AND both people speak the same language ENGLISH COMMS FRENCH ENGLISH COMMS ENGLISH 15
SLC 500 Communications - Like a Phone Call. . . Electrical Connection is made when person answers phone Communication when connection make AND both people speak the same language ENGLISH COMMS FRENCH ENGLISH COMMS ENGLISH 15
 SLC 500 Communications Networks: DH-485 and DH+ n Network Communications – Program support and monitering – Supervisory control for distributed hierarchy – Operator interface for monitoring and control 16
SLC 500 Communications Networks: DH-485 and DH+ n Network Communications – Program support and monitering – Supervisory control for distributed hierarchy – Operator interface for monitoring and control 16
 SLC 500 Communications DH-485 Characteristics n DH-485 Multi-drop link n Daisy chain configuration n Token passing system n 9. 6 or 19. 2 Kbaud data rate n Connect up to 32 devices on network n Up to 4000 cable feet (1200 meters) of network lenght 17
SLC 500 Communications DH-485 Characteristics n DH-485 Multi-drop link n Daisy chain configuration n Token passing system n 9. 6 or 19. 2 Kbaud data rate n Connect up to 32 devices on network n Up to 4000 cable feet (1200 meters) of network lenght 17
 SLC 500 Communications DH 485 Peer-to-peer Comms. n Send/Recv messages from other SLC 500 s n Multi-master token-passing ring; 32 nodes n 5/02, 5/03 + 5/04 can initiate communications to other processors n 5/03 can using Channel 0, Channel 1, or both n 5/04 can using Channel 0 only n Fixed and 5/01 respond only n Initiate comms. with MESSAGE instruction in ladder logic n NO ladder programming necessary to respond 18 to a message from another processor
SLC 500 Communications DH 485 Peer-to-peer Comms. n Send/Recv messages from other SLC 500 s n Multi-master token-passing ring; 32 nodes n 5/02, 5/03 + 5/04 can initiate communications to other processors n 5/03 can using Channel 0, Channel 1, or both n 5/04 can using Channel 0 only n Fixed and 5/01 respond only n Initiate comms. with MESSAGE instruction in ladder logic n NO ladder programming necessary to respond 18 to a message from another processor
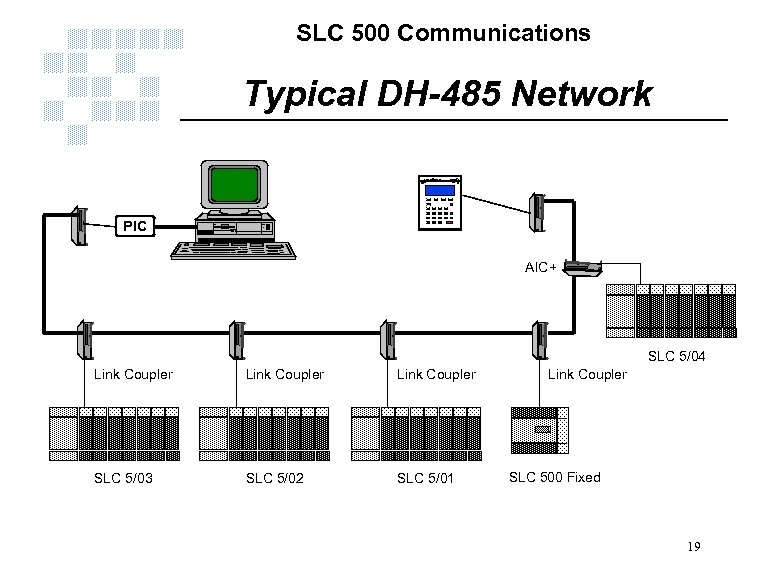 SLC 500 Communications Typical DH-485 Network ALLEN-BRADLEY RUN DTAM Plus ALARM PIC AIC+ SLC 5/04 Link Coupler SLC 5/03 SLC 5/02 SLC 5/01 Link Coupler SLC 500 Fixed 19
SLC 500 Communications Typical DH-485 Network ALLEN-BRADLEY RUN DTAM Plus ALARM PIC AIC+ SLC 5/04 Link Coupler SLC 5/03 SLC 5/02 SLC 5/01 Link Coupler SLC 500 Fixed 19
 SLC 500 Communications DH+ Characteristics • Peer-to-Peer Communication – Utilizes Tolken Passing • • • 64 nodes maximum Remote Programming of SLC 500’S, PLC-2, PLC-3, and PLC-5 Direct Connections to 5/04, PLC-5, Panelview, and Industrial Terminals 57. 6, 115. 2, OR 230 Kbaud data rate Pub # 1770 -6. 5. 16 DH/DH-485/DH+ Ref Manual Robust Industrial Network 20
SLC 500 Communications DH+ Characteristics • Peer-to-Peer Communication – Utilizes Tolken Passing • • • 64 nodes maximum Remote Programming of SLC 500’S, PLC-2, PLC-3, and PLC-5 Direct Connections to 5/04, PLC-5, Panelview, and Industrial Terminals 57. 6, 115. 2, OR 230 Kbaud data rate Pub # 1770 -6. 5. 16 DH/DH-485/DH+ Ref Manual Robust Industrial Network 20
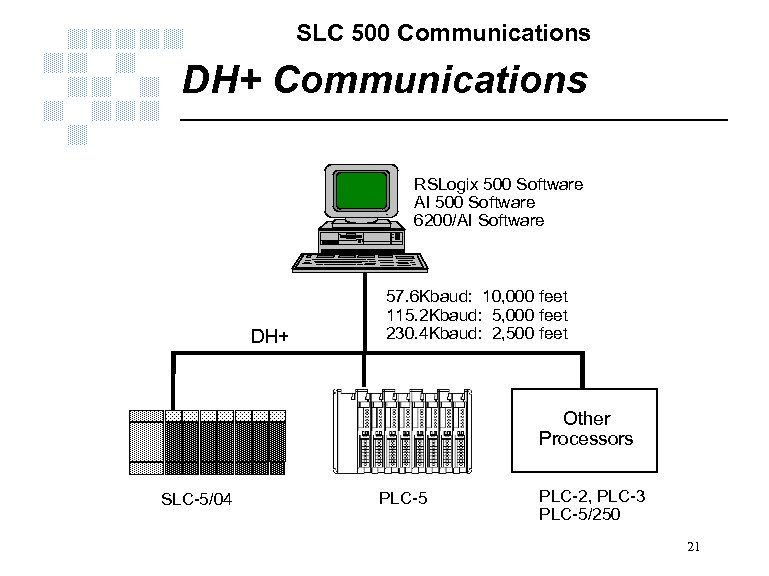 SLC 500 Communications DH+ Communications RSLogix 500 Software AI 500 Software 6200/AI Software DH+ 57. 6 Kbaud: 10, 000 feet 115. 2 Kbaud: 5, 000 feet 230. 4 Kbaud: 2, 500 feet Other Processors SLC-5/04 PLC-5 PLC-2, PLC-3 PLC-5/250 21
SLC 500 Communications DH+ Communications RSLogix 500 Software AI 500 Software 6200/AI Software DH+ 57. 6 Kbaud: 10, 000 feet 115. 2 Kbaud: 5, 000 feet 230. 4 Kbaud: 2, 500 feet Other Processors SLC-5/04 PLC-5 PLC-2, PLC-3 PLC-5/250 21
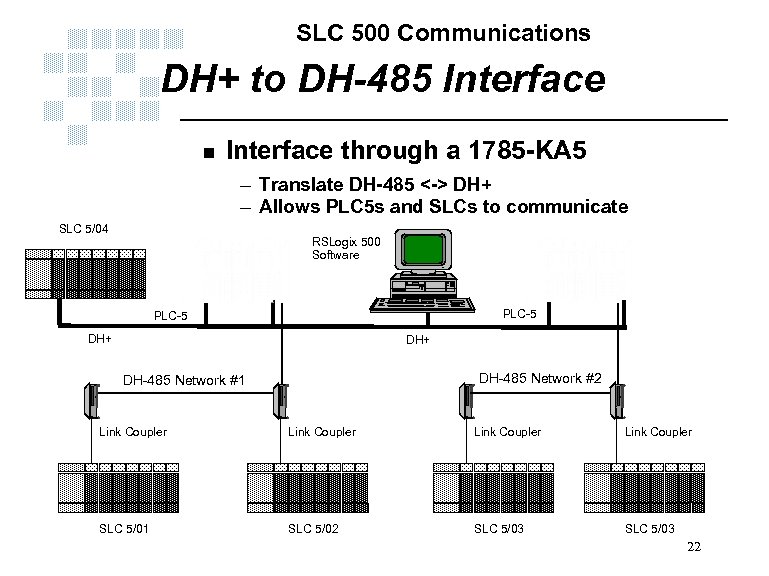 SLC 500 Communications DH+ to DH-485 Interface n Interface through a 1785 -KA 5 – Translate DH-485 <-> DH+ – Allows PLC 5 s and SLCs to communicate SLC 5/04 RSLogix 500 Software PLC-5 DH+ DH-485 Network #2 DH-485 Network #1 Link Coupler SLC 5/01 SLC 5/02 SLC 5/03 22
SLC 500 Communications DH+ to DH-485 Interface n Interface through a 1785 -KA 5 – Translate DH-485 <-> DH+ – Allows PLC 5 s and SLCs to communicate SLC 5/04 RSLogix 500 Software PLC-5 DH+ DH-485 Network #2 DH-485 Network #1 Link Coupler SLC 5/01 SLC 5/02 SLC 5/03 22
 SLC 500 Communications RS-232 Communications SLC-5/03 and 5/04 Support: n Full-Duplex (Point-to-Point) n Half- Duplex n ASCII n Modem Communication
SLC 500 Communications RS-232 Communications SLC-5/03 and 5/04 Support: n Full-Duplex (Point-to-Point) n Half- Duplex n ASCII n Modem Communication
 SLC 500 Communications RS-232: DF 1 Full-Duplex AKA: DF 1 Point-to-Point Simultaneous transmission between two devices in both directions n - Programming Port - Peer Messaging
SLC 500 Communications RS-232: DF 1 Full-Duplex AKA: DF 1 Point-to-Point Simultaneous transmission between two devices in both directions n - Programming Port - Peer Messaging
 SLC 500 Communications RS-232: DF 1 Half-Duplex n Mulit-Drop, Single Master, Multiple Slave n Slaves are Polled for Response from the Master n Supports up to 255 Slave Devices n Slaves: Any SLC Processor n Master: PLC-5, SLC-5/03, 5/04, CV
SLC 500 Communications RS-232: DF 1 Half-Duplex n Mulit-Drop, Single Master, Multiple Slave n Slaves are Polled for Response from the Master n Supports up to 255 Slave Devices n Slaves: Any SLC Processor n Master: PLC-5, SLC-5/03, 5/04, CV
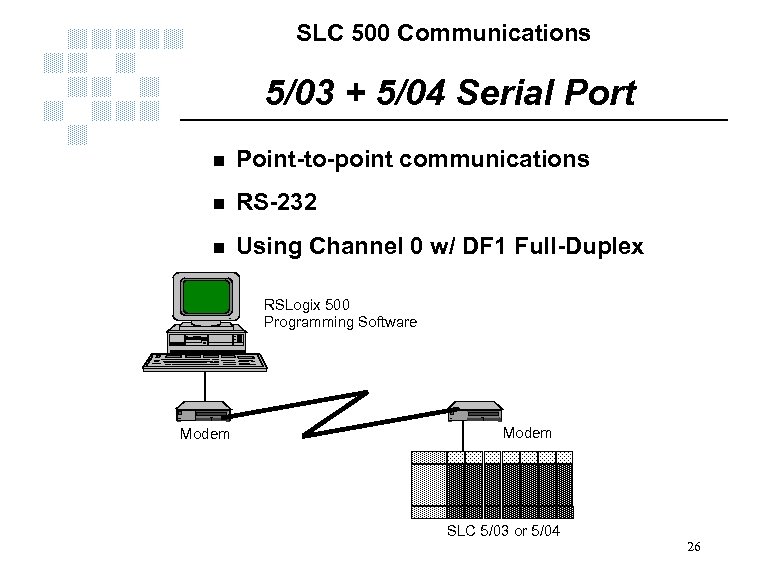 SLC 500 Communications 5/03 + 5/04 Serial Port n Point-to-point communications n RS-232 n Using Channel 0 w/ DF 1 Full-Duplex RSLogix 500 Programming Software Modem SLC 5/03 or 5/04 26
SLC 500 Communications 5/03 + 5/04 Serial Port n Point-to-point communications n RS-232 n Using Channel 0 w/ DF 1 Full-Duplex RSLogix 500 Programming Software Modem SLC 5/03 or 5/04 26
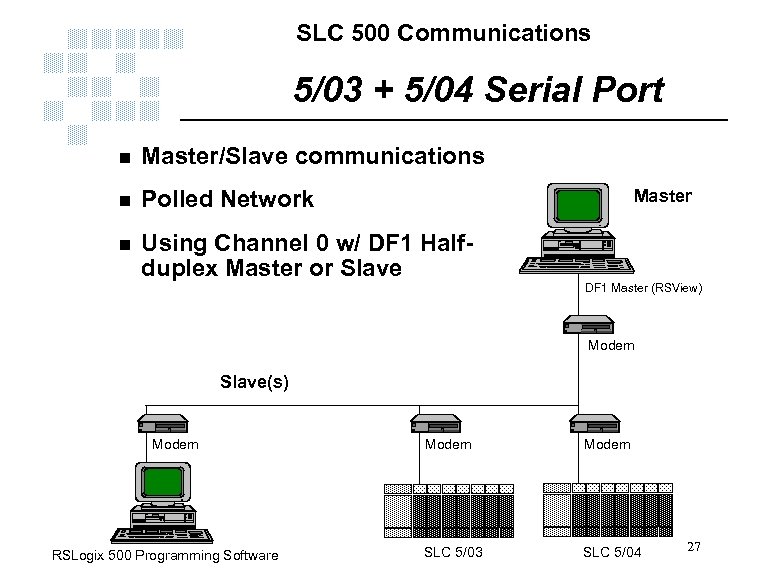 SLC 500 Communications 5/03 + 5/04 Serial Port n Master/Slave communications n Polled Network n Using Channel 0 w/ DF 1 Halfduplex Master or Slave Master DF 1 Master (RSView) Modem Slave(s) Modem RSLogix 500 Programming Software Modem SLC 5/03 SLC 5/04 27
SLC 500 Communications 5/03 + 5/04 Serial Port n Master/Slave communications n Polled Network n Using Channel 0 w/ DF 1 Halfduplex Master or Slave Master DF 1 Master (RSView) Modem Slave(s) Modem RSLogix 500 Programming Software Modem SLC 5/03 SLC 5/04 27
 SLC 500 Communications ASCII Communications n 5/03 and 5/04 n Direct connection to devices such as barcode decoders and printers n Eliminates requirement of BASIC module for this task SLC 5/03 CPU RUN FORCE FLT DH 485 BATT RS 232 RUN REM PROG 28
SLC 500 Communications ASCII Communications n 5/03 and 5/04 n Direct connection to devices such as barcode decoders and printers n Eliminates requirement of BASIC module for this task SLC 5/03 CPU RUN FORCE FLT DH 485 BATT RS 232 RUN REM PROG 28
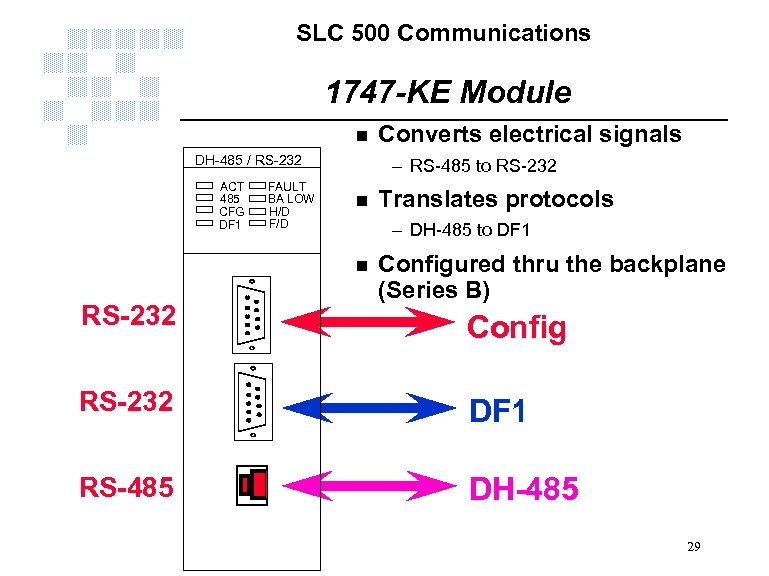 SLC 500 Communications 1747 -KE Module n DH-485 / RS-232 ACT 485 CFG DF 1 FAULT BA LOW H/D F/D – RS-485 to RS-232 n Translates protocols – DH-485 to DF 1 n RS-232 Converts electrical signals Configured thru the backplane (Series B) Config RS-232 DF 1 RS-485 DH-485 29
SLC 500 Communications 1747 -KE Module n DH-485 / RS-232 ACT 485 CFG DF 1 FAULT BA LOW H/D F/D – RS-485 to RS-232 n Translates protocols – DH-485 to DF 1 n RS-232 Converts electrical signals Configured thru the backplane (Series B) Config RS-232 DF 1 RS-485 DH-485 29
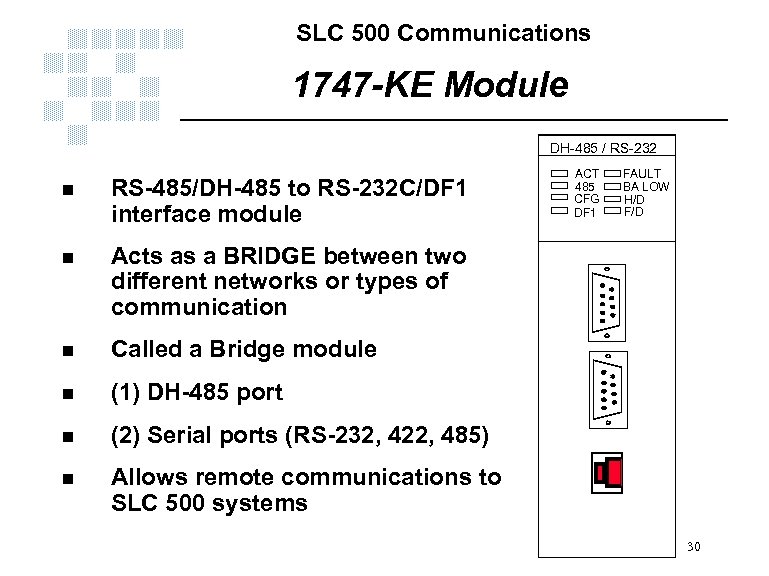 SLC 500 Communications 1747 -KE Module DH-485 / RS-232 n RS-485/DH-485 to RS-232 C/DF 1 interface module n Called a Bridge module n (1) DH-485 port n (2) Serial ports (RS-232, 422, 485) n FAULT BA LOW H/D F/D Acts as a BRIDGE between two different networks or types of communication n ACT 485 CFG DF 1 Allows remote communications to SLC 500 systems 30
SLC 500 Communications 1747 -KE Module DH-485 / RS-232 n RS-485/DH-485 to RS-232 C/DF 1 interface module n Called a Bridge module n (1) DH-485 port n (2) Serial ports (RS-232, 422, 485) n FAULT BA LOW H/D F/D Acts as a BRIDGE between two different networks or types of communication n ACT 485 CFG DF 1 Allows remote communications to SLC 500 systems 30
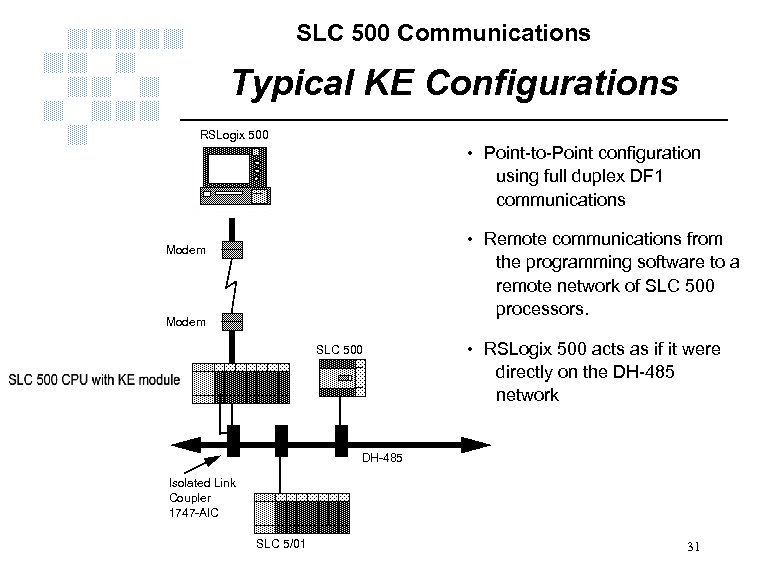 SLC 500 Communications Typical KE Configurations RSLogix 500 • Point-to-Point configuration using full duplex DF 1 communications • Remote communications from the programming software to a remote network of SLC 500 processors. Modem SLC 500 • RSLogix 500 acts as if it were directly on the DH-485 network DH-485 Isolated Link Coupler 1747 -AIC SLC 5/01 31
SLC 500 Communications Typical KE Configurations RSLogix 500 • Point-to-Point configuration using full duplex DF 1 communications • Remote communications from the programming software to a remote network of SLC 500 processors. Modem SLC 500 • RSLogix 500 acts as if it were directly on the DH-485 network DH-485 Isolated Link Coupler 1747 -AIC SLC 5/01 31
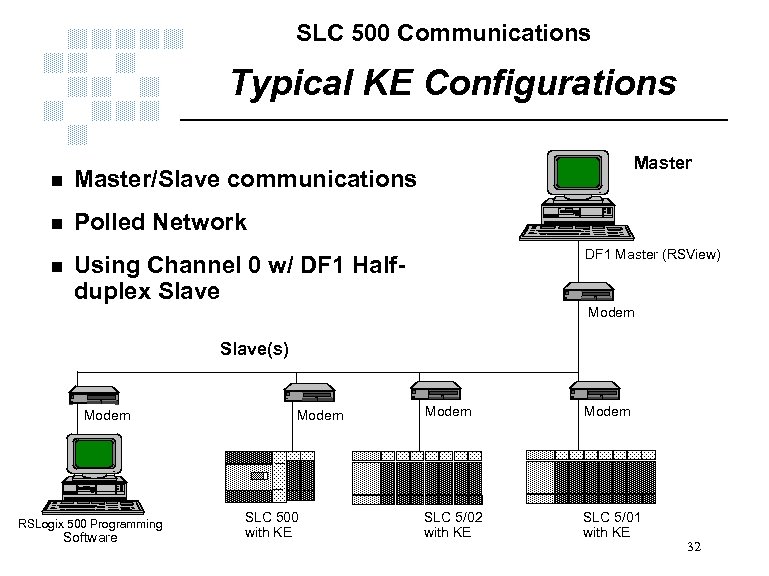 SLC 500 Communications Typical KE Configurations n Master/Slave communications n Master Polled Network n DF 1 Master (RSView) Using Channel 0 w/ DF 1 Halfduplex Slave Modem Slave(s) Modem RSLogix 500 Programming Software Modem SLC 500 with KE Modem SLC 5/02 with KE SLC 5/01 with KE 32
SLC 500 Communications Typical KE Configurations n Master/Slave communications n Master Polled Network n DF 1 Master (RSView) Using Channel 0 w/ DF 1 Halfduplex Slave Modem Slave(s) Modem RSLogix 500 Programming Software Modem SLC 500 with KE Modem SLC 5/02 with KE SLC 5/01 with KE 32
 SLC 500 Communications Peer-to-Peer Communications Read/Write: Read - local processor is receiving data Write - local processor is sending data Target Device: 500 CPU if target is another SLC Processor 485 CIF if target is a non-SLC device on the network PLC 5 if target device accepts PLC-5 commands Local/Remote: Local - the message is to be communicated via a local network Remote - the message is to be communicated to a remote device on another network through a bridge Control Block: Contains - target node address, local file address, target file address, status bits MSG Control Block Length: Fixed at 14 elements Setup Screen: Advanced setup parameters EN: enable bit - set when rung is true DN: done bit - message successfully transmitted ER: error bit - transmission failed Read/Write Message Type Peer-To-Peer Read/Write Read Target Device 500 CPU Local/Remote Local Control Block ? Control Block Length 14 Setup Screen ( EN ) ( DN ) ( ER ) 33
SLC 500 Communications Peer-to-Peer Communications Read/Write: Read - local processor is receiving data Write - local processor is sending data Target Device: 500 CPU if target is another SLC Processor 485 CIF if target is a non-SLC device on the network PLC 5 if target device accepts PLC-5 commands Local/Remote: Local - the message is to be communicated via a local network Remote - the message is to be communicated to a remote device on another network through a bridge Control Block: Contains - target node address, local file address, target file address, status bits MSG Control Block Length: Fixed at 14 elements Setup Screen: Advanced setup parameters EN: enable bit - set when rung is true DN: done bit - message successfully transmitted ER: error bit - transmission failed Read/Write Message Type Peer-To-Peer Read/Write Read Target Device 500 CPU Local/Remote Local Control Block ? Control Block Length 14 Setup Screen ( EN ) ( DN ) ( ER ) 33


