00b7e1ed1927db06061d460a52b5e92b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 Slavery and Western Expansion Chapter 8 Section 1
Slavery and Western Expansion Chapter 8 Section 1
 Impact of War w/Mexico • Heightened sectional tensions – Opened new lands to the issue of slavery • CURRENT LAW – MISSOURI COMPROMISE – Southerners wanted new laws to help return runaway slaves – Polk – believed the expansion of slavery a null and void issue – dry climate of southwest not suitable for growing cash crops – Ultimately – he believes slavery will destroy the Democrats & Union
Impact of War w/Mexico • Heightened sectional tensions – Opened new lands to the issue of slavery • CURRENT LAW – MISSOURI COMPROMISE – Southerners wanted new laws to help return runaway slaves – Polk – believed the expansion of slavery a null and void issue – dry climate of southwest not suitable for growing cash crops – Ultimately – he believes slavery will destroy the Democrats & Union
 Wilmot Proviso • Originally – Appropriations bill – started in the House --- amendment --- no slavery or involuntary servitude in land acquired through war • Passed in the House – Northern • Rejected --- Senate – balanced • Calhoun Resolution --– States own the United States – Fed Had no right to make laws in the states or territories
Wilmot Proviso • Originally – Appropriations bill – started in the House --- amendment --- no slavery or involuntary servitude in land acquired through war • Passed in the House – Northern • Rejected --- Senate – balanced • Calhoun Resolution --– States own the United States – Fed Had no right to make laws in the states or territories
 Popular Sovereignty • Allowing citizens to decide for themselves the issue of slavery --- idea of Michigan Senator Lewis Cass • Free Soilers – combination of two groups Northern “Conscience” Whigs & Northern Democrats – Whigs divided – “Cotton” vs “Conscience” – Democrats Divided – Northern vs Southern
Popular Sovereignty • Allowing citizens to decide for themselves the issue of slavery --- idea of Michigan Senator Lewis Cass • Free Soilers – combination of two groups Northern “Conscience” Whigs & Northern Democrats – Whigs divided – “Cotton” vs “Conscience” – Democrats Divided – Northern vs Southern
 What caused the development of the free soil party?
What caused the development of the free soil party?
 Election of 1848 • Cotton Whigs & Southern Dem – nominate Zahary Taylor • Free Soilers – Nominate – Martin Van Buren • Democrats – Lewis Cass • Zachary Taylor wins the Election
Election of 1848 • Cotton Whigs & Southern Dem – nominate Zahary Taylor • Free Soilers – Nominate – Martin Van Buren • Democrats – Lewis Cass • Zachary Taylor wins the Election
 California • Slavery brought to the forefront early on in Taylor’s Presidency • 1849 – California Gold Rush – 80, 000 people up an went to California – apply for statehood – (popular sovereignty) • 1849 – California applied as a Free State
California • Slavery brought to the forefront early on in Taylor’s Presidency • 1849 – California Gold Rush – 80, 000 people up an went to California – apply for statehood – (popular sovereignty) • 1849 – California applied as a Free State
 Great Debate (Southern Position) • 1. slaveholding states would be a minority in the senate • 2. northerners would dominate national politics • 3. threat of secession – • ** need for Compromise --- Henry Clay
Great Debate (Southern Position) • 1. slaveholding states would be a minority in the senate • 2. northerners would dominate national politics • 3. threat of secession – • ** need for Compromise --- Henry Clay
 Other Issues dealing w/ slavery in Congress • Texas / NM – border --- extend or stop slavery • District of Columbia – slavery in the nation’s capital • Slave trade within the US -regulate or not
Other Issues dealing w/ slavery in Congress • Texas / NM – border --- extend or stop slavery • District of Columbia – slavery in the nation’s capital • Slave trade within the US -regulate or not
 Clay’s Compromise • Offered as a package plan – A. Allow Calif – free state/ organize rest of Mexican cession w/out any restrictions (popular sovereignty) – B. settles border disputes bt/ Texas & NM – favored NM – gov’t acquired Texas’ debts. – Outlawed slave trade in D. C. – did not outlaw slavery itself – Congress would not interfere in domestic slave trade --- enforce a Stiffer Fugitive Slave Act
Clay’s Compromise • Offered as a package plan – A. Allow Calif – free state/ organize rest of Mexican cession w/out any restrictions (popular sovereignty) – B. settles border disputes bt/ Texas & NM – favored NM – gov’t acquired Texas’ debts. – Outlawed slave trade in D. C. – did not outlaw slavery itself – Congress would not interfere in domestic slave trade --- enforce a Stiffer Fugitive Slave Act
 Results of Compromise • 1. did not pass originally – because it was offered as a package deal – Makeup of Congress Changes • Calhoun Dies of TB • Taylor who opposed Clay’s Compromise – suddenly dies • VP – Millard Filmore now President supports Henry Clay • Webster – states right activist – Sect. of State • Clay – leaves the Senate
Results of Compromise • 1. did not pass originally – because it was offered as a package deal – Makeup of Congress Changes • Calhoun Dies of TB • Taylor who opposed Clay’s Compromise – suddenly dies • VP – Millard Filmore now President supports Henry Clay • Webster – states right activist – Sect. of State • Clay – leaves the Senate
 • Stephen Douglass – 33 yr old devises a plan – offer each idea individually – attain majority support – pass – -Known as Compromise of 1850
• Stephen Douglass – 33 yr old devises a plan – offer each idea individually – attain majority support – pass – -Known as Compromise of 1850
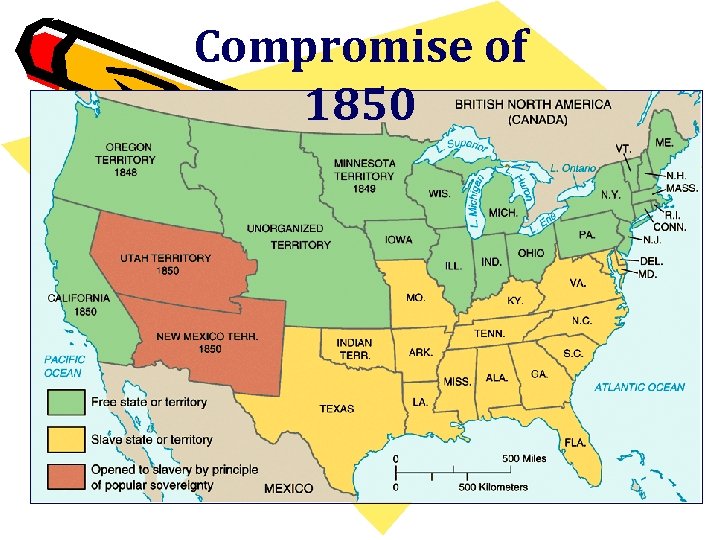 Compromise of 1850
Compromise of 1850
 How did the Gold Rush affect the issue of slavery?
How did the Gold Rush affect the issue of slavery?
 Uncle Tom’s Cabin • Written by Harrier Beecher Stowe came out (book form) 1852 – sold 300, 000 copies – Presented African American as – real people suffering form dreadful circumstances – – It depicted the harshness of the institution of slavery – She was motivated to write this book by the Fugitive Slave Act of 1850 – part of 1850 Compromise
Uncle Tom’s Cabin • Written by Harrier Beecher Stowe came out (book form) 1852 – sold 300, 000 copies – Presented African American as – real people suffering form dreadful circumstances – – It depicted the harshness of the institution of slavery – She was motivated to write this book by the Fugitive Slave Act of 1850 – part of 1850 Compromise
 Fugitive Slave Act • • • 1. all fugitives were not entitled to a trial by jury, despite the 6 th Amendment – 2. fugitives could not testify on their own behalf 3. A statement by the slaveowner describing the escapee was all that was needed to have a slave returned 4. Federal commissioners that enforced the law – granted $10 only $5 if they were let free 5. anyone convicted of helping a fugitive – $1, 000 fine 6. anyone could be compelled to help capture runaways – deputize on spot
Fugitive Slave Act • • • 1. all fugitives were not entitled to a trial by jury, despite the 6 th Amendment – 2. fugitives could not testify on their own behalf 3. A statement by the slaveowner describing the escapee was all that was needed to have a slave returned 4. Federal commissioners that enforced the law – granted $10 only $5 if they were let free 5. anyone convicted of helping a fugitive – $1, 000 fine 6. anyone could be compelled to help capture runaways – deputize on spot
 Harriet Beecher Stowe (1811 – 1896) -- So this is the lady who started the Civil War. Abraham Lincoln
Harriet Beecher Stowe (1811 – 1896) -- So this is the lady who started the Civil War. Abraham Lincoln
 Uncle Tom’s Cabin 1852 § Sold 300, 000 copies in the first year. § 2 million in a decade!
Uncle Tom’s Cabin 1852 § Sold 300, 000 copies in the first year. § 2 million in a decade!
 Uncle Tom’s Cabin, 1852
Uncle Tom’s Cabin, 1852
 Northern Resistance • Frederick Douglass – • Henry David Thoreau • C. The Underground Railroad – well organized system of freeing slaves – transporting them from the south – north. – Conductors • • Harriet Tubman Levi Coffin
Northern Resistance • Frederick Douglass – • Henry David Thoreau • C. The Underground Railroad – well organized system of freeing slaves – transporting them from the south – north. – Conductors • • Harriet Tubman Levi Coffin
 Continuing issue of Slavery • As people moved west with the opening of Calif, Oregon and the acquiring of new western territory – people didn’t lose their identity – pro/ anti slavery • One item everybody wanted – Transcontinental Railroad – reduced traveling time to 4 days – – Wagon (months) – Sailing around S. America - month
Continuing issue of Slavery • As people moved west with the opening of Calif, Oregon and the acquiring of new western territory – people didn’t lose their identity – pro/ anti slavery • One item everybody wanted – Transcontinental Railroad – reduced traveling time to 4 days – – Wagon (months) – Sailing around S. America - month
 What was an unintended consequence of the fugitive slave act?
What was an unintended consequence of the fugitive slave act?
 Problem w/ Transcontinental Railroad • People argued over its starting point – Many southerners favored a starting point in New Orleans --- required the railroad to travel through the northern part of Mexico – – Gadsen Purchase ---$10, 000 – Douglass – wanted the HUB to be in Chicago – his home state of Illinois – • • • land west had to be organized into territories/ states Prepared the Nebraska Bill Passes in House – repealed in Senate
Problem w/ Transcontinental Railroad • People argued over its starting point – Many southerners favored a starting point in New Orleans --- required the railroad to travel through the northern part of Mexico – – Gadsen Purchase ---$10, 000 – Douglass – wanted the HUB to be in Chicago – his home state of Illinois – • • • land west had to be organized into territories/ states Prepared the Nebraska Bill Passes in House – repealed in Senate
 Sectionalism over the Railroad • Southern Position – if US creates new territories – they should be open to slavery – like the territories acquired by war – if this happens they will agree to railroad beginning in the North • Stephen Douglass – knows that any attempt to repeal compromise – will divide the country
Sectionalism over the Railroad • Southern Position – if US creates new territories – they should be open to slavery – like the territories acquired by war – if this happens they will agree to railroad beginning in the North • Stephen Douglass – knows that any attempt to repeal compromise – will divide the country
 Douglas’ proposal • He proposed the – repeal Missouri Compromise , divide territories in 2 – Kansas -south/ Nebraska - north • Existing Laws – Missouri Compromise – for territories not acquired through war/ states – Compromise of 1850 – popular sovereignty for states acquired through war – ***Passed Congress 1854 – as Kansas/ Nebraska Act
Douglas’ proposal • He proposed the – repeal Missouri Compromise , divide territories in 2 – Kansas -south/ Nebraska - north • Existing Laws – Missouri Compromise – for territories not acquired through war/ states – Compromise of 1850 – popular sovereignty for states acquired through war – ***Passed Congress 1854 – as Kansas/ Nebraska Act
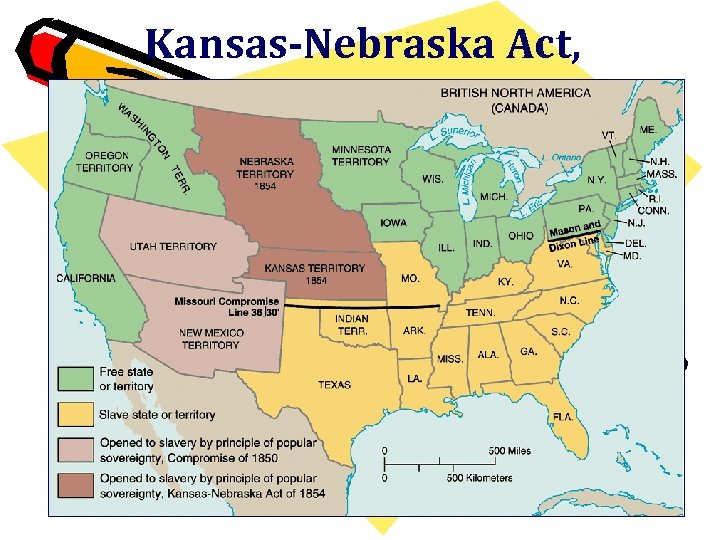 Kansas-Nebraska Act, 1854
Kansas-Nebraska Act, 1854
 Use the graphic organizer below to list the main elements of the compromise of 1850 Compromise of 1850
Use the graphic organizer below to list the main elements of the compromise of 1850 Compromise of 1850


