course_328.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 Слайд по дисциплине «История языка» на тему: Old English Period
Слайд по дисциплине «История языка» на тему: Old English Period
 ПЛАН ЛЕКЦИИ 1. Old English Phonetics. 2. Old English Dialects. 3. Old English Written Records. 4. Old English Grammar. 5. Old English Vocabulary.
ПЛАН ЛЕКЦИИ 1. Old English Phonetics. 2. Old English Dialects. 3. Old English Written Records. 4. Old English Grammar. 5. Old English Vocabulary.
 Old English Phonetics q In OE a syllable was made prominent by an increase in the force of articulation. q In disyllabic and polysyllabic words the accent fell on the root-morpheme or on the first syllable. q Word stress was fixed. q Polysyllabic words, especially compounds, may have had two stresses, chief and secondary, e. g. norюryhte [‘norθ, ryx’te].
Old English Phonetics q In OE a syllable was made prominent by an increase in the force of articulation. q In disyllabic and polysyllabic words the accent fell on the root-morpheme or on the first syllable. q Word stress was fixed. q Polysyllabic words, especially compounds, may have had two stresses, chief and secondary, e. g. norюryhte [‘norθ, ryx’te].
 Old English Phonetics Sound changes, particularly vowel changes, took place in English at every period of history. The development of vowels in Early OE consisted of the modification of separate vowels, and also of the modification of entire sets of vowels.
Old English Phonetics Sound changes, particularly vowel changes, took place in English at every period of history. The development of vowels in Early OE consisted of the modification of separate vowels, and also of the modification of entire sets of vowels.
 Old English Dialects The Germanic tribes who settled in Britain in the 5 th and 6 th c. spoke closely related tribal dialects belonging to the West Ger manic subgroup.
Old English Dialects The Germanic tribes who settled in Britain in the 5 th and 6 th c. spoke closely related tribal dialects belonging to the West Ger manic subgroup.
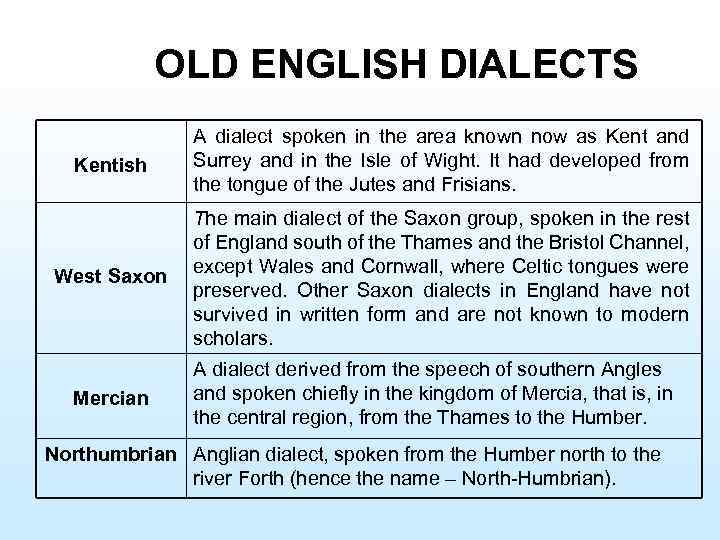 OLD ENGLISH DIALECTS Kentish A dialect spoken in the area known now as Kent and Surrey and in the Isle of Wight. It had developed from the tongue of the Jutes and Frisians. West Saxon The main dialect of the Saxon group, spoken in the rest of England south of the Thames and the Bristol Channel, except Wales and Cornwall, where Celtic tongues were preserved. Other Saxon dialects in England have not survived in written form and are not known to modern scholars. Mercian A dialect derived from the speech of southern Angles and spoken chiefly in the kingdom of Mercia, that is, in the central region, from the Thames to the Humber. Northumbrian Anglian dialect, spoken from the Humber north to the river Forth (hence the name – North Humbrian).
OLD ENGLISH DIALECTS Kentish A dialect spoken in the area known now as Kent and Surrey and in the Isle of Wight. It had developed from the tongue of the Jutes and Frisians. West Saxon The main dialect of the Saxon group, spoken in the rest of England south of the Thames and the Bristol Channel, except Wales and Cornwall, where Celtic tongues were preserved. Other Saxon dialects in England have not survived in written form and are not known to modern scholars. Mercian A dialect derived from the speech of southern Angles and spoken chiefly in the kingdom of Mercia, that is, in the central region, from the Thames to the Humber. Northumbrian Anglian dialect, spoken from the Humber north to the river Forth (hence the name – North Humbrian).
 Old English Written Records Runic Inscriptions q The earliest written records of English are inscriptions on hard material made in a special alphabet known as the runes. q The two best known runic inscriptions in England are the earliest extant OE written records: "Franks Casket” and "Ruth well Cross".
Old English Written Records Runic Inscriptions q The earliest written records of English are inscriptions on hard material made in a special alphabet known as the runes. q The two best known runic inscriptions in England are the earliest extant OE written records: "Franks Casket” and "Ruth well Cross".
 Old English Written Records Old English Manuscripts Our knowledge of the OE language comes mainly from manu scripts written in Latin characters. q The greatest poem of the time was BEOWULF, an epic of the 7 th or 8 th c. q The earliest samples of continuous prose are the first pages CHRONICLES of the ANGLO SAXON
Old English Written Records Old English Manuscripts Our knowledge of the OE language comes mainly from manu scripts written in Latin characters. q The greatest poem of the time was BEOWULF, an epic of the 7 th or 8 th c. q The earliest samples of continuous prose are the first pages CHRONICLES of the ANGLO SAXON
 Old English Grammar OE was a synthetic, or inflected type of language; it showed the relations between words mainly with the help of simple (synthetic) grammatical forms.
Old English Grammar OE was a synthetic, or inflected type of language; it showed the relations between words mainly with the help of simple (synthetic) grammatical forms.
 Old English Grammar Inflected parts of speech possessed certain grammatical categories, which are usually subdivided into nominal categories, found in nominal parts of speech (the noun, the adjective, the pronoun, the numeral) and verbal categories found mainly in the finite verb.
Old English Grammar Inflected parts of speech possessed certain grammatical categories, which are usually subdivided into nominal categories, found in nominal parts of speech (the noun, the adjective, the pronoun, the numeral) and verbal categories found mainly in the finite verb.
 Old English Grammar There were 5 nominal grammatical categories in OE: number, case, gender, degrees of comparison, and the category of definiteness/indefiniteness.
Old English Grammar There were 5 nominal grammatical categories in OE: number, case, gender, degrees of comparison, and the category of definiteness/indefiniteness.
 Old English Grammar Verbal grammatical categories were not numerous: tense and mood – verbal categories – and number and person, showing agreement between the verb predicate and the subject of the sentence.
Old English Grammar Verbal grammatical categories were not numerous: tense and mood – verbal categories – and number and person, showing agreement between the verb predicate and the subject of the sentence.
 Old English Vocabulary
Old English Vocabulary
 Old English Vocabulary Native OE words can be subdivided into a number of etymological layers coming from different historical periods. The three main layers in the native OE words: • • • common IE words; common Germanic words; specifically OE words.
Old English Vocabulary Native OE words can be subdivided into a number of etymological layers coming from different historical periods. The three main layers in the native OE words: • • • common IE words; common Germanic words; specifically OE words.
 There were two sources of borrowings in Old English: • Celtic • Latin
There were two sources of borrowings in Old English: • Celtic • Latin
 Old English Vocabulary Borrowings from Celtic q There are very few Celtic loan-words in the OE vocabulary, since there must have been little intermixture between the Germanic settlers and the Celtic in Britain. q Most borrowings from Celtic are to be found only in proper names. Such names as Thames, Avon, Dover, Kent, York and perhaps London are of Celtic origin (Celtic dūn meant ‘hill’).
Old English Vocabulary Borrowings from Celtic q There are very few Celtic loan-words in the OE vocabulary, since there must have been little intermixture between the Germanic settlers and the Celtic in Britain. q Most borrowings from Celtic are to be found only in proper names. Such names as Thames, Avon, Dover, Kent, York and perhaps London are of Celtic origin (Celtic dūn meant ‘hill’).
 Old English Vocabulary Latin Influence on the English Vocabulary The role of the Latin language in Medieval Britain was determined by such historical events as: • the Roman occupation of Britain; • the influence of the Roman civilization; • the introduction of Christianity.
Old English Vocabulary Latin Influence on the English Vocabulary The role of the Latin language in Medieval Britain was determined by such historical events as: • the Roman occupation of Britain; • the influence of the Roman civilization; • the introduction of Christianity.


