061a3b5d56780294c07674d4cfc79473.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 58
 SKOS-2 -HIVE UNT workshop
SKOS-2 -HIVE UNT workshop
 Introductions Craig Willis (craig. willis@unc. edu)
Introductions Craig Willis (craig. willis@unc. edu)
 Afternoon Session Schedule n Overview n Using HIVE as a service n Installing and configuring HIVE n Using HIVE Core API n Understanding HIVE Internals n HIVE supporting technologies n Developing and customizing HIVE
Afternoon Session Schedule n Overview n Using HIVE as a service n Installing and configuring HIVE n Using HIVE Core API n Understanding HIVE Internals n HIVE supporting technologies n Developing and customizing HIVE
 Block 1: Introduction
Block 1: Introduction
 Workshop Overview n Schedule n Interactive, less structure n Hands-on (work together) n Activities: n Installing and configuring HIVE n Programming examples (HIVE Core API, HIVE REST API)
Workshop Overview n Schedule n Interactive, less structure n Hands-on (work together) n Activities: n Installing and configuring HIVE n Programming examples (HIVE Core API, HIVE REST API)
 Background and Interests n What are you most interested in getting out of this part of the workshop? n What is your background? n n Programming and databases n n Cataloging, indexing, and classification Systems administration What is your level of familiarity with the following technologies? n Java, Tomcat, Lucene n REST n RDF, SPARQL, SKOS, Sesame
Background and Interests n What are you most interested in getting out of this part of the workshop? n What is your background? n n Programming and databases n n Cataloging, indexing, and classification Systems administration What is your level of familiarity with the following technologies? n Java, Tomcat, Lucene n REST n RDF, SPARQL, SKOS, Sesame
 HIVE Technical Overview n HIVE consists of many technologies combined to provide a framework for vocabulary services n System for management of multiple controlled vocabularies in SKOS/RDF format n Java-based web services can run in any Java application server n Demonstration website (http: //hive. nescent. org/) n Google Code project (http: //code. google. com/p/hive-mrc/)
HIVE Technical Overview n HIVE consists of many technologies combined to provide a framework for vocabulary services n System for management of multiple controlled vocabularies in SKOS/RDF format n Java-based web services can run in any Java application server n Demonstration website (http: //hive. nescent. org/) n Google Code project (http: //code. google. com/p/hive-mrc/)
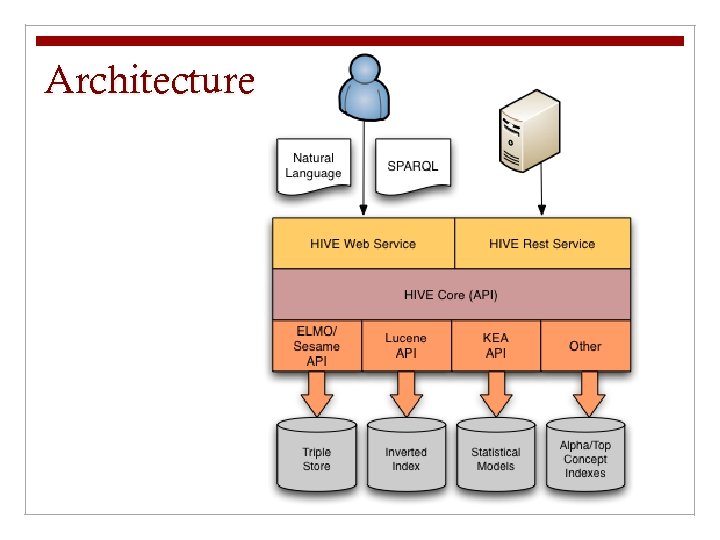 Architecture
Architecture
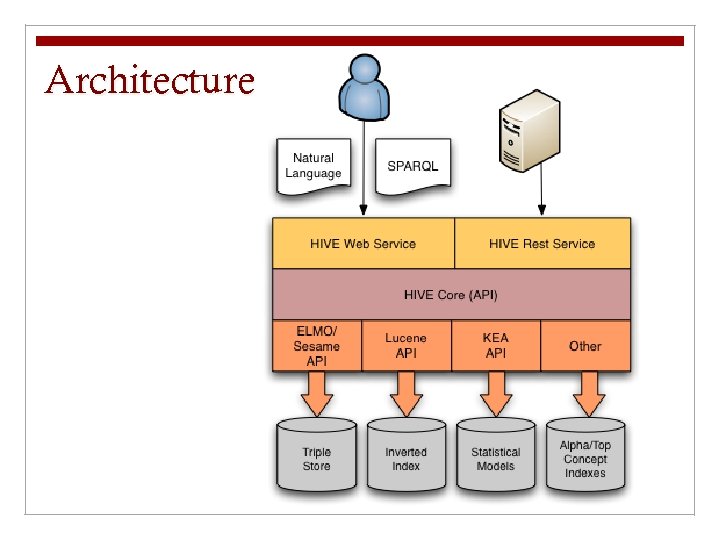
 HIVE Architecture n SPARQL: RDF query language (W 3 C recommendation) n REST: Web-based API and software architecture n Triple store: Database for the storage and retrieval of RDF data. Supports queries using SPARQL. n Sesame: Open source triple store n Elmo: Sesame API for common ontologies (OWL, Dublin Core, SKOS) n Lucene: Java-based search engine n KEA++: Algorithm and Java API for automatic subject suggestions from controlled vocabularies.
HIVE Architecture n SPARQL: RDF query language (W 3 C recommendation) n REST: Web-based API and software architecture n Triple store: Database for the storage and retrieval of RDF data. Supports queries using SPARQL. n Sesame: Open source triple store n Elmo: Sesame API for common ontologies (OWL, Dublin Core, SKOS) n Lucene: Java-based search engine n KEA++: Algorithm and Java API for automatic subject suggestions from controlled vocabularies.
 HIVE Functions n Conversion of vocabularies to SKOS n Rich internet application (RIA) for browsing and searching multiple SKOS vocabularies n Java API and REST application interfaces for programmatic access to multiple SKOS vocabularies n Support for natural language and SPARQL queries n Automatic keyphrase indexing using multiple SKOS vocabularies. HIVE supports two indexers: n KEA++ indexer n Basic Lucene indexer
HIVE Functions n Conversion of vocabularies to SKOS n Rich internet application (RIA) for browsing and searching multiple SKOS vocabularies n Java API and REST application interfaces for programmatic access to multiple SKOS vocabularies n Support for natural language and SPARQL queries n Automatic keyphrase indexing using multiple SKOS vocabularies. HIVE supports two indexers: n KEA++ indexer n Basic Lucene indexer
 Block 2: Using HIVE as a service
Block 2: Using HIVE as a service
 Using HIVE as a Service n HIVE web application n http: //hive. nescent. org/ n Developed by Jose Perez-Aguera, Lina Huang n Java servlet, Google Web Toolkit (GWT) n n http: //code. google. com/p/hive-mrc/wiki/About. Hive. Web HIVE REST service n http: //hive. nescent. org/rs n Developed by Duane Costa, Long-Term Ecological Research Network n http: //code. google. com/p/hive-mrc/wiki/About. Hive. Rest. Service
Using HIVE as a Service n HIVE web application n http: //hive. nescent. org/ n Developed by Jose Perez-Aguera, Lina Huang n Java servlet, Google Web Toolkit (GWT) n n http: //code. google. com/p/hive-mrc/wiki/About. Hive. Web HIVE REST service n http: //hive. nescent. org/rs n Developed by Duane Costa, Long-Term Ecological Research Network n http: //code. google. com/p/hive-mrc/wiki/About. Hive. Rest. Service
 Activity: Calling HIVE-RS n Demonstrate calling the HIVE-RS web service (Java)
Activity: Calling HIVE-RS n Demonstrate calling the HIVE-RS web service (Java)
 Block 3: Install and Configure HIVE
Block 3: Install and Configure HIVE
 Installing and Configuring HIVE n Requirements n n n Java 1. 6 Tomcat (HIVE is currently using 6. x) Detailed installation instructions: n http: //code. google. com/p/hive-mrc/wiki/Installing. Hive. Web n http: //code. google. com/p/hive-mrc/wiki/Installing. Hive. Rest. Service
Installing and Configuring HIVE n Requirements n n n Java 1. 6 Tomcat (HIVE is currently using 6. x) Detailed installation instructions: n http: //code. google. com/p/hive-mrc/wiki/Installing. Hive. Web n http: //code. google. com/p/hive-mrc/wiki/Installing. Hive. Rest. Service
 Installing and Configuring HIVE-web n Detailed installation instructions (hive-web) n n http: //code. google. com/p/hive-mrc/wiki/Installing. Hive. Web Quick start (hive-web) n Download and extract Tomcat 6. x n Download and extract latest hive-web war n Download and extract sample vocabulary n Configure hive. properties and agrovoc. properties n Start Tomcat n http: //localhost: 8080/
Installing and Configuring HIVE-web n Detailed installation instructions (hive-web) n n http: //code. google. com/p/hive-mrc/wiki/Installing. Hive. Web Quick start (hive-web) n Download and extract Tomcat 6. x n Download and extract latest hive-web war n Download and extract sample vocabulary n Configure hive. properties and agrovoc. properties n Start Tomcat n http: //localhost: 8080/
 Properties files u hive. properties u u u Specifies enabled vocabularies and selected indexing algorithm http: //code. google. com/p/hive-mrc/source/browse/trunk/hiveweb/war/WEB-INF/conf/hive. properties
Properties files u hive. properties u u u Specifies enabled vocabularies and selected indexing algorithm http: //code. google. com/p/hive-mrc/source/browse/trunk/hiveweb/war/WEB-INF/conf/hive. properties
 Installing and Configuring HIVE-web from source n Detailed installation instructions (hive-web) n n n http: //code. google. com/p/hive-mrc/wiki/Developing. HIVE http: //code. google. com/p/hive-mrc/wiki/Installing. Hive. Web Requirements n Eclipse IDE for J 2 EE Developers n Subclipse plugin n Google Eclipse Plugin n Apache Ant n Google Web Toolkit 1. 7. 1 n Tomcat 6. x
Installing and Configuring HIVE-web from source n Detailed installation instructions (hive-web) n n n http: //code. google. com/p/hive-mrc/wiki/Developing. HIVE http: //code. google. com/p/hive-mrc/wiki/Installing. Hive. Web Requirements n Eclipse IDE for J 2 EE Developers n Subclipse plugin n Google Eclipse Plugin n Apache Ant n Google Web Toolkit 1. 7. 1 n Tomcat 6. x
 Installing and Configuring HIVE REST Service n Detailed installation instructions (hive-rs) n n http: //code. google. com/p/hive-mrc/wiki/Installing. Hive. Rest. Service Quick start (hive-rs) n Download and extract latest webapp n Download and extract sample vocabulary n Configure hive. properties n Start Tomcat
Installing and Configuring HIVE REST Service n Detailed installation instructions (hive-rs) n n http: //code. google. com/p/hive-mrc/wiki/Installing. Hive. Rest. Service Quick start (hive-rs) n Download and extract latest webapp n Download and extract sample vocabulary n Configure hive. properties n Start Tomcat
 Importing SKOS Vocabularies n http: //code. google. com/p/hive-mrc/wiki/Importing. Vocabularies n Note memory requirements for each vocabulary n n http: //code. google. com/p/hive-mrc/wiki/HIVEMemory. Usage java –Xmx 1024 m -Djava. ext. dirs=path/to/hive/lib edu. unc. ils. mrc. hive. admin. Admin. Vocabularies [/path/to/hive/conf/] [vocabulary] [train]
Importing SKOS Vocabularies n http: //code. google. com/p/hive-mrc/wiki/Importing. Vocabularies n Note memory requirements for each vocabulary n n http: //code. google. com/p/hive-mrc/wiki/HIVEMemory. Usage java –Xmx 1024 m -Djava. ext. dirs=path/to/hive/lib edu. unc. ils. mrc. hive. admin. Admin. Vocabularies [/path/to/hive/conf/] [vocabulary] [train]
 Block 4: Using the HIVE Core Library
Block 4: Using the HIVE Core Library
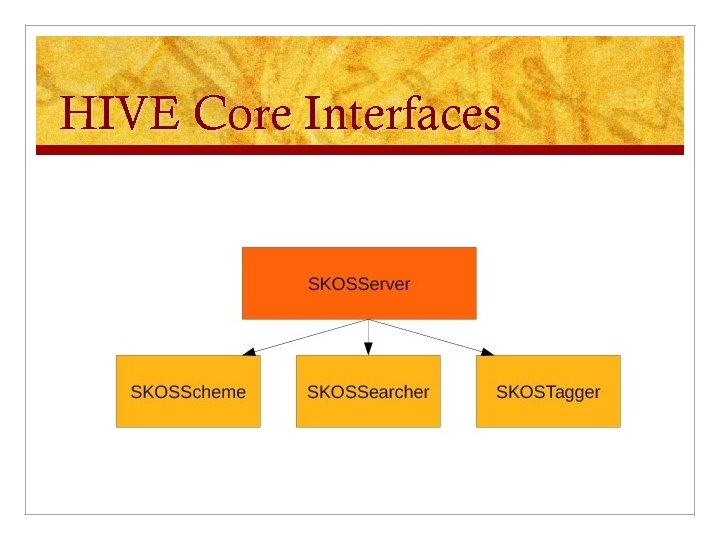 HIVE Core Interfaces
HIVE Core Interfaces
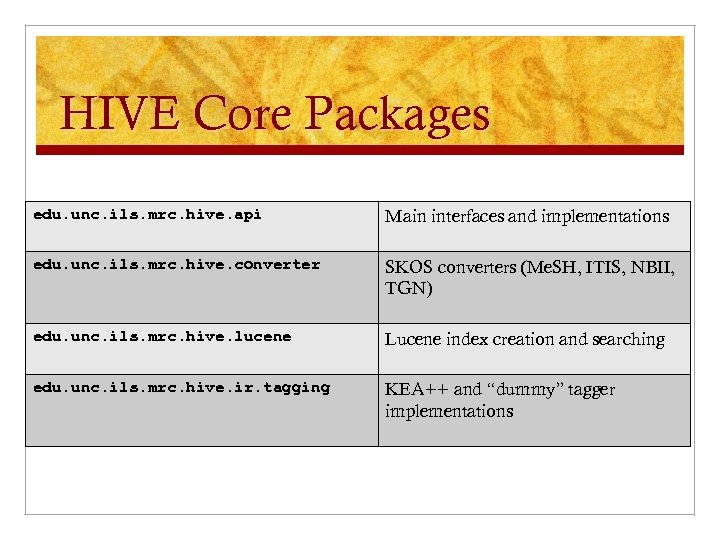 HIVE Core Packages edu. unc. ils. mrc. hive. api Main interfaces and implementations edu. unc. ils. mrc. hive. converter SKOS converters (Me. SH, ITIS, NBII, TGN) edu. unc. ils. mrc. hive. lucene Lucene index creation and searching edu. unc. ils. mrc. hive. ir. tagging KEA++ and “dummy” tagger implementations
HIVE Core Packages edu. unc. ils. mrc. hive. api Main interfaces and implementations edu. unc. ils. mrc. hive. converter SKOS converters (Me. SH, ITIS, NBII, TGN) edu. unc. ils. mrc. hive. lucene Lucene index creation and searching edu. unc. ils. mrc. hive. ir. tagging KEA++ and “dummy” tagger implementations
 edu. unc. ils. hive. api n SKOSServer: n n SKOSSearcher: n n Supports searching across multiple vocabularies SKOSTagger: n n Provides access to one or more vocabularies Supports tagging/keyphrase extraction across multiple vocabularies SKOSScheme: n Represents an individual vocabulary (location of vocabulary on file system)
edu. unc. ils. hive. api n SKOSServer: n n SKOSSearcher: n n Supports searching across multiple vocabularies SKOSTagger: n n Provides access to one or more vocabularies Supports tagging/keyphrase extraction across multiple vocabularies SKOSScheme: n Represents an individual vocabulary (location of vocabulary on file system)
 SKOSServer n SKOSServer is the top-level class used to initialize the vocabulary server. n Reads the hive. properties file and initializes the SKOSScheme (vocabulary management), SKOSSearcher (concept searching), SKOSTagger (indexing) instances based on the vocabulary configurations. n edu. unc. ils. mrc. hive. api. SKOSServer n Tree. Map
SKOSServer n SKOSServer is the top-level class used to initialize the vocabulary server. n Reads the hive. properties file and initializes the SKOSScheme (vocabulary management), SKOSSearcher (concept searching), SKOSTagger (indexing) instances based on the vocabulary configurations. n edu. unc. ils. mrc. hive. api. SKOSServer n Tree. Map
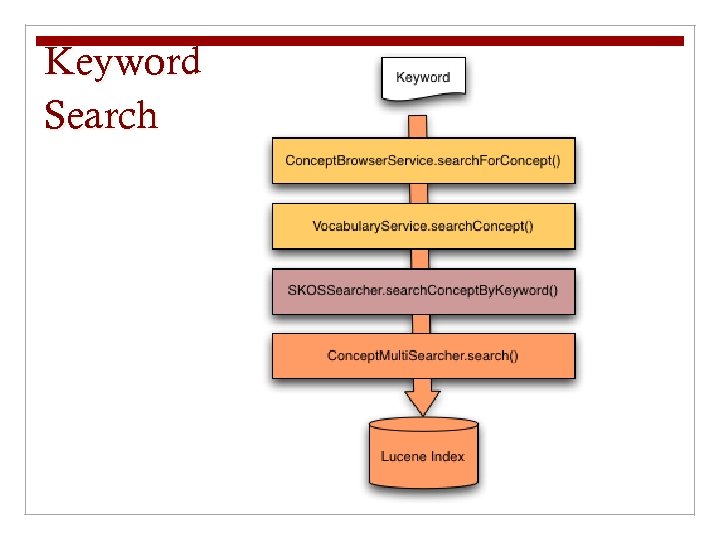
 SKOSSearcher n Supports searching across one or more configured vocabularies. n Keyword queries using Lucene, SPARQL queries using Open. RDF/Sesame n edu. unc. ils. mrc. hive. api. SKOSSearcher n search. Concept. By. Keyword(uri, lp) n search. Concept. By. URI(uri, lp) n search. Children. By. URI(uri, lp) n SPARQLSelect()
SKOSSearcher n Supports searching across one or more configured vocabularies. n Keyword queries using Lucene, SPARQL queries using Open. RDF/Sesame n edu. unc. ils. mrc. hive. api. SKOSSearcher n search. Concept. By. Keyword(uri, lp) n search. Concept. By. URI(uri, lp) n search. Children. By. URI(uri, lp) n SPARQLSelect()
 SKOSTagger n Keyphrase extraction using multiple vocabularies n Depends on setting in hive. properties n edu. unc. ils. mrc. hive. api. SKOSTagger n “dummy” or “KEA” n List
SKOSTagger n Keyphrase extraction using multiple vocabularies n Depends on setting in hive. properties n edu. unc. ils. mrc. hive. api. SKOSTagger n “dummy” or “KEA” n List
 SKOSScheme n Represents an individual vocabulary, based on settings in
SKOSScheme n Represents an individual vocabulary, based on settings in
 Activity n Demonstrate a simple Java class that allows the user to query for a given term. n Demonstrate a simple Java class that can read a text file and call the tagger.
Activity n Demonstrate a simple Java class that allows the user to query for a given term. n Demonstrate a simple Java class that can read a text file and call the tagger.
 Block 5: Understanding HIVE Internals
Block 5: Understanding HIVE Internals
 Architecture
Architecture
 Data Directory Layout n /usr/local/hive-data n vocabulary/ n vocabulary. rdf SKOS RDF/XML n vocabulary. Alpha. Index Serialized map n vocabulary. H 2 database (used by KEA) n vocabulary. Index Lucene Index n vocabulary. KEA model and training data n vocabulary. Store Sesame/Open. RDF store n top. Concept. Index Serialized map of top concepts
Data Directory Layout n /usr/local/hive-data n vocabulary/ n vocabulary. rdf SKOS RDF/XML n vocabulary. Alpha. Index Serialized map n vocabulary. H 2 database (used by KEA) n vocabulary. Index Lucene Index n vocabulary. KEA model and training data n vocabulary. Store Sesame/Open. RDF store n top. Concept. Index Serialized map of top concepts
 Keyword Search
Keyword Search
 Indexing
Indexing
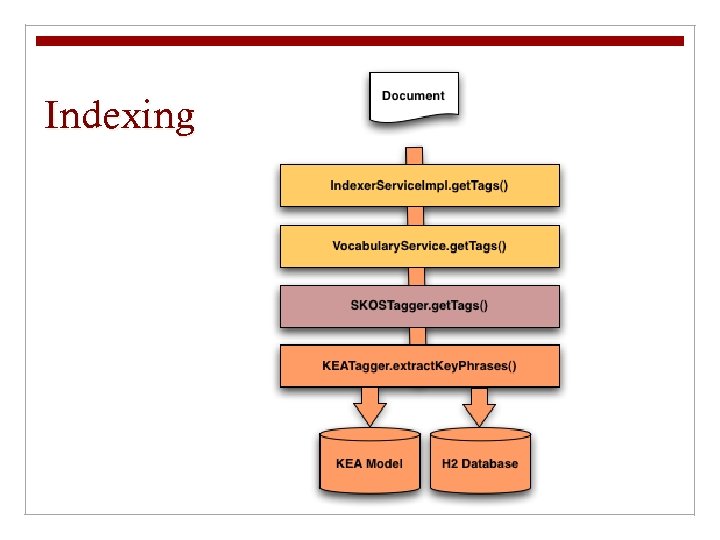
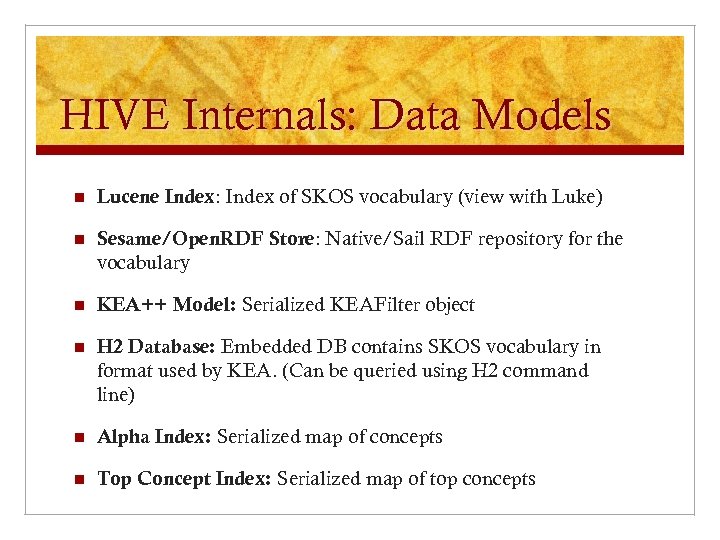 HIVE Internals: Data Models n Lucene Index: Index of SKOS vocabulary (view with Luke) n Sesame/Open. RDF Store: Native/Sail RDF repository for the vocabulary n KEA++ Model: Serialized KEAFilter object n H 2 Database: Embedded DB contains SKOS vocabulary in format used by KEA. (Can be queried using H 2 command line) n Alpha Index: Serialized map of concepts n Top Concept Index: Serialized map of top concepts
HIVE Internals: Data Models n Lucene Index: Index of SKOS vocabulary (view with Luke) n Sesame/Open. RDF Store: Native/Sail RDF repository for the vocabulary n KEA++ Model: Serialized KEAFilter object n H 2 Database: Embedded DB contains SKOS vocabulary in format used by KEA. (Can be queried using H 2 command line) n Alpha Index: Serialized map of concepts n Top Concept Index: Serialized map of top concepts
 HIVE Internals: HIVE Web n GWT Entry Points: n n Concept. Browser n n Home. Page Indexer Servlets n Vocabulary. Service: Singleton vocabulary server n File. Upload: Handles the file upload for indexing n Concept. Browser. Service. Impl n Indexer. Service. Impl
HIVE Internals: HIVE Web n GWT Entry Points: n n Concept. Browser n n Home. Page Indexer Servlets n Vocabulary. Service: Singleton vocabulary server n File. Upload: Handles the file upload for indexing n Concept. Browser. Service. Impl n Indexer. Service. Impl
 HIVE Internals: HIVE-RS n Java API for RESTful Web Services (JAX-RS) n Classes n Concepts. Resource: n Schemes. Resource
HIVE Internals: HIVE-RS n Java API for RESTful Web Services (JAX-RS) n Classes n Concepts. Resource: n Schemes. Resource
 Block 6: HIVE Supporting Technologies
Block 6: HIVE Supporting Technologies
 HIVE supporting technologies n Lucene http: //lucene. apache. org n Sesame http: //www. openrdf. org/ n KEA http: //www. nzdl. org/Kea/ n H 2 http: //www. h 2 database. com/ n GWT http: //code. google. com/webtoolkit/
HIVE supporting technologies n Lucene http: //lucene. apache. org n Sesame http: //www. openrdf. org/ n KEA http: //www. nzdl. org/Kea/ n H 2 http: //www. h 2 database. com/ n GWT http: //code. google. com/webtoolkit/
 Activity n Explore Lucene index with Luke n n http: //luke. googlecode. com/ Explore Sesame store with SPARQL n http: //www. xml. com/pub/a/2005/11/16/introducing-sparqlquerying-semantic-web-tutorial. html n http: //www. cambridgesemantics. com/2008/09/sparql-byexample/
Activity n Explore Lucene index with Luke n n http: //luke. googlecode. com/ Explore Sesame store with SPARQL n http: //www. xml. com/pub/a/2005/11/16/introducing-sparqlquerying-semantic-web-tutorial. html n http: //www. cambridgesemantics. com/2008/09/sparql-byexample/
 Block 7: Customizing HIVE
Block 7: Customizing HIVE
 Obtaining Vocabularies n Several vocabularies can be freely downloaded n Some vocabularies require licensing n HIVE Core includes converters for each of the supported vocabularies. n List of HIVE vocabularieshttp: //code. google. com/p/hivemrc/wiki/Vocabulary. Conversion
Obtaining Vocabularies n Several vocabularies can be freely downloaded n Some vocabularies require licensing n HIVE Core includes converters for each of the supported vocabularies. n List of HIVE vocabularieshttp: //code. google. com/p/hivemrc/wiki/Vocabulary. Conversion
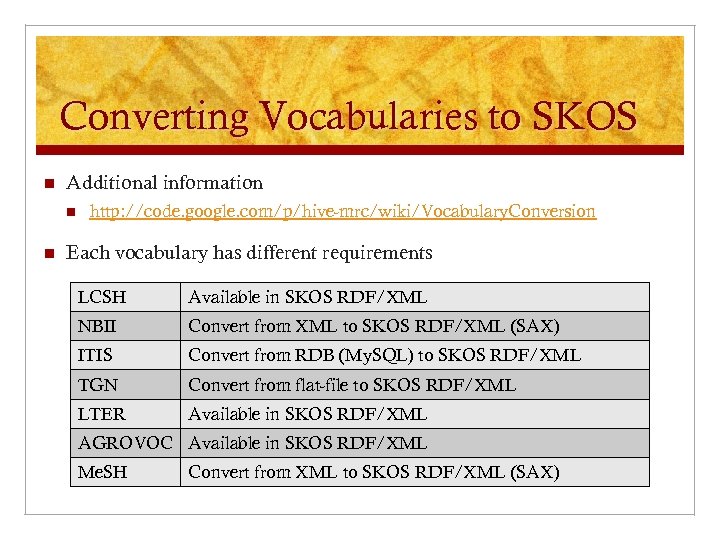 Converting Vocabularies to SKOS n Additional information n n http: //code. google. com/p/hive-mrc/wiki/Vocabulary. Conversion Each vocabulary has different requirements LCSH Available in SKOS RDF/XML NBII Convert from XML to SKOS RDF/XML (SAX) ITIS Convert from RDB (My. SQL) to SKOS RDF/XML TGN Convert from flat-file to SKOS RDF/XML LTER Available in SKOS RDF/XML AGROVOC Available in SKOS RDF/XML Me. SH Convert from XML to SKOS RDF/XML (SAX)
Converting Vocabularies to SKOS n Additional information n n http: //code. google. com/p/hive-mrc/wiki/Vocabulary. Conversion Each vocabulary has different requirements LCSH Available in SKOS RDF/XML NBII Convert from XML to SKOS RDF/XML (SAX) ITIS Convert from RDB (My. SQL) to SKOS RDF/XML TGN Convert from flat-file to SKOS RDF/XML LTER Available in SKOS RDF/XML AGROVOC Available in SKOS RDF/XML Me. SH Convert from XML to SKOS RDF/XML (SAX)
 Converting Vocabularies to SKOS n A Method to Convert Thesauri to SKOS (van Assem et al) n n IPSV, GTAA, Me. SH n n Prolog implementation http: //thesauri. cs. vu. nl/eswc 06/ Converting Me. SH to SKOS for HIVE n Java SAX-based parser n http: //code. google. com/p/hive-mrc/wiki/Mesh. To. SKOS
Converting Vocabularies to SKOS n A Method to Convert Thesauri to SKOS (van Assem et al) n n IPSV, GTAA, Me. SH n n Prolog implementation http: //thesauri. cs. vu. nl/eswc 06/ Converting Me. SH to SKOS for HIVE n Java SAX-based parser n http: //code. google. com/p/hive-mrc/wiki/Mesh. To. SKOS
 LTER Sample Service http: //scoria. lternet. edu: 8080/lter-hive-prototypes
LTER Sample Service http: //scoria. lternet. edu: 8080/lter-hive-prototypes
 Block 8: KEA++
Block 8: KEA++
 About KEA++ n http: //www. nzdl. org/Kea/ n Algorithm and open-source Java library for extracting keyphrases from documents using SKOS vocabularies. n Developed by Alyona Medelyan (KEA++), based on earlier work by Ian Whitten (KEA) from the Digital Libraries and Machine Learning Lab at the University of Waikato, New Zealand. n Problem: How can we automatically identify the topic of documents?
About KEA++ n http: //www. nzdl. org/Kea/ n Algorithm and open-source Java library for extracting keyphrases from documents using SKOS vocabularies. n Developed by Alyona Medelyan (KEA++), based on earlier work by Ian Whitten (KEA) from the Digital Libraries and Machine Learning Lab at the University of Waikato, New Zealand. n Problem: How can we automatically identify the topic of documents?
 Automatic Indexing n Free keyphrase indexing (KEA) n n Keyphrase indexing (KEA++) n n Significant terms in a document are determined based on intrinsic properties (e. g. , frequency and length). Terms from a controlled vocabulary are assigned based on intrinsic properties. Controlled indexing/term assignment: n Documents are classified based on content that corresponds to a controlled vocabulary. n e. g. , Pouliquen, Steinberger, and Camelia (2003) Medelyan, O. and Whitten I. A. (2008). “Domain independent automatic keyphrase indexing with small training sets. ” Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, (59) 7: 1026 -1040).
Automatic Indexing n Free keyphrase indexing (KEA) n n Keyphrase indexing (KEA++) n n Significant terms in a document are determined based on intrinsic properties (e. g. , frequency and length). Terms from a controlled vocabulary are assigned based on intrinsic properties. Controlled indexing/term assignment: n Documents are classified based on content that corresponds to a controlled vocabulary. n e. g. , Pouliquen, Steinberger, and Camelia (2003) Medelyan, O. and Whitten I. A. (2008). “Domain independent automatic keyphrase indexing with small training sets. ” Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, (59) 7: 1026 -1040).
 KEA++ at a Glance n KEA++ uses a machine learning approach to keyphrase extraction n Two stages: n Candidate identification: Find terms that relate to the document’s content n Keyphrase selection: Uses a model to identify the most significant terms.
KEA++ at a Glance n KEA++ uses a machine learning approach to keyphrase extraction n Two stages: n Candidate identification: Find terms that relate to the document’s content n Keyphrase selection: Uses a model to identify the most significant terms.
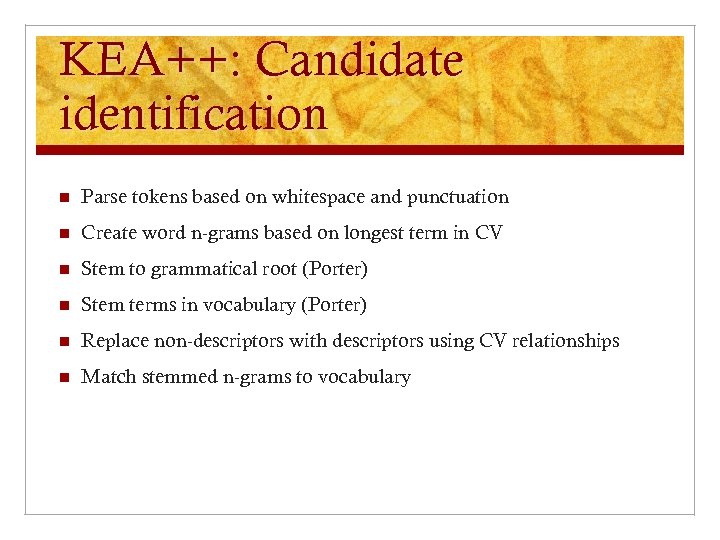 KEA++: Candidate identification n Parse tokens based on whitespace and punctuation n Create word n-grams based on longest term in CV n Stem to grammatical root (Porter) n Stem terms in vocabulary (Porter) n Replace non-descriptors with descriptors using CV relationships n Match stemmed n-grams to vocabulary
KEA++: Candidate identification n Parse tokens based on whitespace and punctuation n Create word n-grams based on longest term in CV n Stem to grammatical root (Porter) n Stem terms in vocabulary (Porter) n Replace non-descriptors with descriptors using CV relationships n Match stemmed n-grams to vocabulary
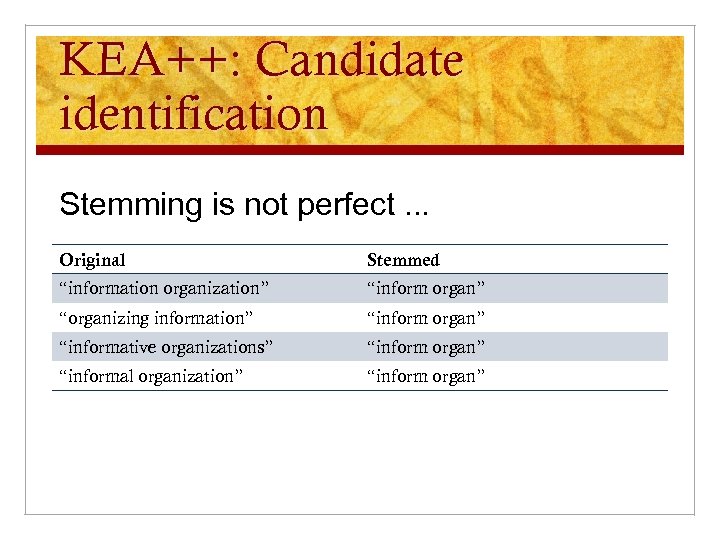 KEA++: Candidate identification Stemming is not perfect. . . Original Stemmed “information organization” “inform organ” “organizing information” “inform organ” “informative organizations” “inform organ” “informal organization” “inform organ”
KEA++: Candidate identification Stemming is not perfect. . . Original Stemmed “information organization” “inform organ” “organizing information” “inform organ” “informative organizations” “inform organ” “informal organization” “inform organ”
 KEA++: Feature definition n Term Frequency/Inverse Document Frequency n n Position of first occurrence: n n Distance from the beginning of the document. Candidates with high/low values are more likely to be valid (introduction/conclusion) Phrase length: n n Frequency of a phrase’s occurrence in a document with frequency in general use. Analysis suggests that indexers prefer to assign two-word descriptors Node degree: n Number of relationships between the term in the CV.
KEA++: Feature definition n Term Frequency/Inverse Document Frequency n n Position of first occurrence: n n Distance from the beginning of the document. Candidates with high/low values are more likely to be valid (introduction/conclusion) Phrase length: n n Frequency of a phrase’s occurrence in a document with frequency in general use. Analysis suggests that indexers prefer to assign two-word descriptors Node degree: n Number of relationships between the term in the CV.
 Dummy. Tagger n Primarily intended as baseline for analysis of KEA++ n Uses Ling. Pipe for part-of-speech identification (limits indexing to certain parts of speech) n Uses Lucene vocabulary index n Simple TF*IDF implementation n Configurable in hive. properties
Dummy. Tagger n Primarily intended as baseline for analysis of KEA++ n Uses Ling. Pipe for part-of-speech identification (limits indexing to certain parts of speech) n Uses Lucene vocabulary index n Simple TF*IDF implementation n Configurable in hive. properties
 Who’s Using HIVE n NESCENT/Dryad n n Evaluating HIVE for automatic term suggestion from multiple vocabularies for scientific article metadata. Long-Term Ecological Research Network (LTERNet) n n n http: //scoria. lternet. edu: 8080/lter-hive-prototypes/ Prototype application for automatic term suggestion for EML metadata files. Library of Congress Web Archives n Evaluating HIVE for automatic term suggestion for web archive (WARC) files
Who’s Using HIVE n NESCENT/Dryad n n Evaluating HIVE for automatic term suggestion from multiple vocabularies for scientific article metadata. Long-Term Ecological Research Network (LTERNet) n n n http: //scoria. lternet. edu: 8080/lter-hive-prototypes/ Prototype application for automatic term suggestion for EML metadata files. Library of Congress Web Archives n Evaluating HIVE for automatic term suggestion for web archive (WARC) files
 Plans n n Automatic updates to vocabularies Integration of other concept extraction algorithms n Maui n Dryad integration n Other n Maven integration n Spring integration n Data directory and property file restructuring n Concept browser updates
Plans n n Automatic updates to vocabularies Integration of other concept extraction algorithms n Maui n Dryad integration n Other n Maven integration n Spring integration n Data directory and property file restructuring n Concept browser updates
 Discussion n Pros and Con n n HIVE Core vs. HIVE Web vs. HIVE-RS Brainstorm applications that could benefit from HIVE, discuss implementations
Discussion n Pros and Con n n HIVE Core vs. HIVE Web vs. HIVE-RS Brainstorm applications that could benefit from HIVE, discuss implementations
 Credits n Ryan Scherle n José Ramón Pérez Agüera n Lina Huang n Alyona Medelyan n Ian Whitten
Credits n Ryan Scherle n José Ramón Pérez Agüera n Lina Huang n Alyona Medelyan n Ian Whitten
 Questions /Comments Craig Willis craig. willis@unc. edu
Questions /Comments Craig Willis craig. willis@unc. edu


