Skeletal System Function of the Skeletal System Support-






9718-011_skeletal_system.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 49
 Skeletal System
Skeletal System
 Function of the Skeletal System Support- framework that supports body and cradles its soft organs Protection- for delicate organs, heart, lungs, brain Movement- bones act as levers for muscles Mineral storage- calcium & phosphate Blood cell formation- hematopoiesis
Function of the Skeletal System Support- framework that supports body and cradles its soft organs Protection- for delicate organs, heart, lungs, brain Movement- bones act as levers for muscles Mineral storage- calcium & phosphate Blood cell formation- hematopoiesis
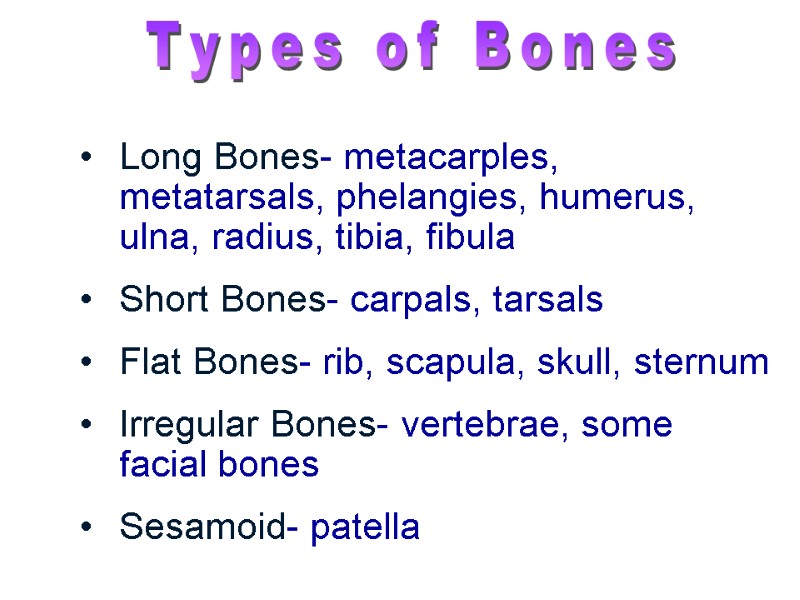
 Long Bones- metacarples, metatarsals, phelangies, humerus, ulna, radius, tibia, fibula Short Bones- carpals, tarsals Flat Bones- rib, scapula, skull, sternum Irregular Bones- vertebrae, some facial bones Sesamoid- patella Types of Bones
Long Bones- metacarples, metatarsals, phelangies, humerus, ulna, radius, tibia, fibula Short Bones- carpals, tarsals Flat Bones- rib, scapula, skull, sternum Irregular Bones- vertebrae, some facial bones Sesamoid- patella Types of Bones
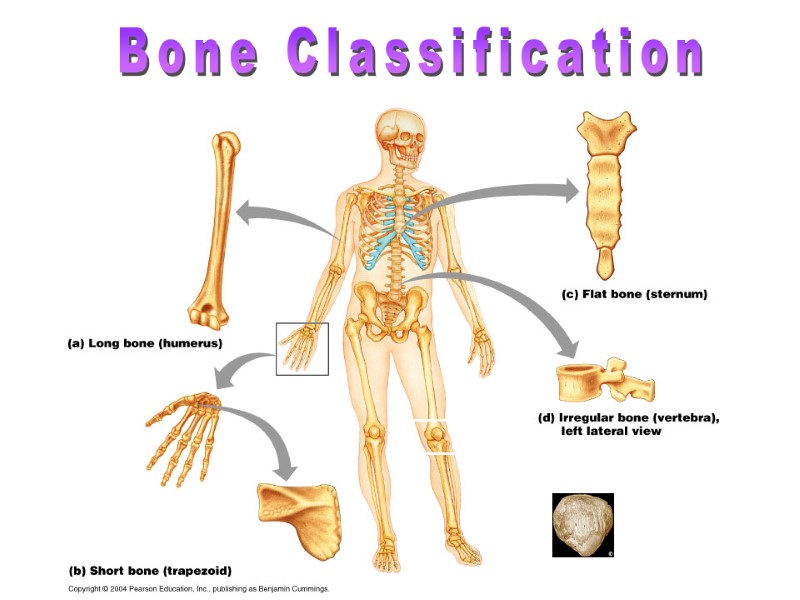
 Bone Classification
Bone Classification
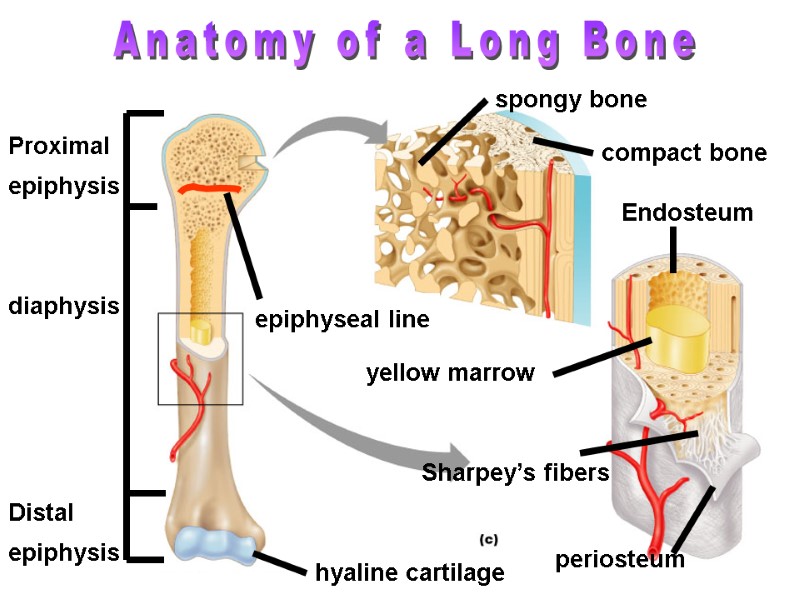
 Distal epiphysis Proximal epiphysis diaphysis yellow marrow epiphyseal line periosteum compact bone spongy bone Endosteum hyaline cartilage Anatomy of a Long Bone Sharpey’s fibers
Distal epiphysis Proximal epiphysis diaphysis yellow marrow epiphyseal line periosteum compact bone spongy bone Endosteum hyaline cartilage Anatomy of a Long Bone Sharpey’s fibers
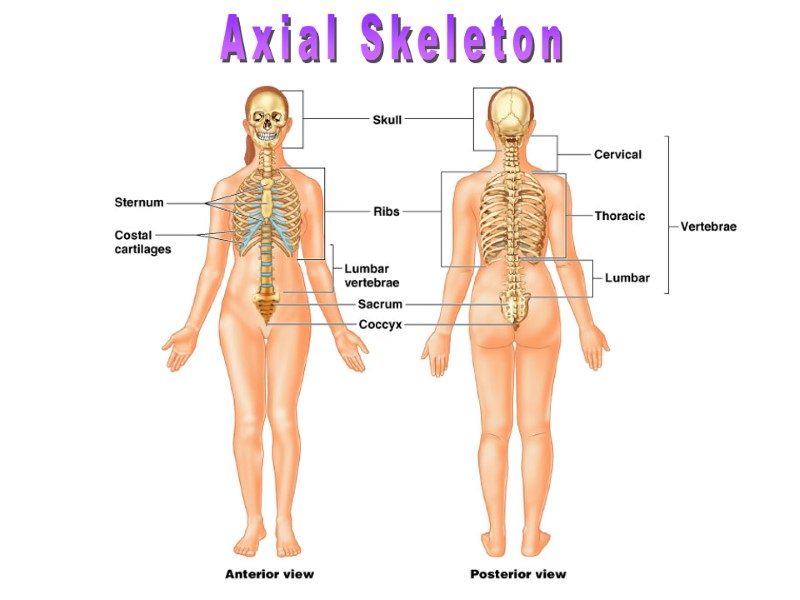
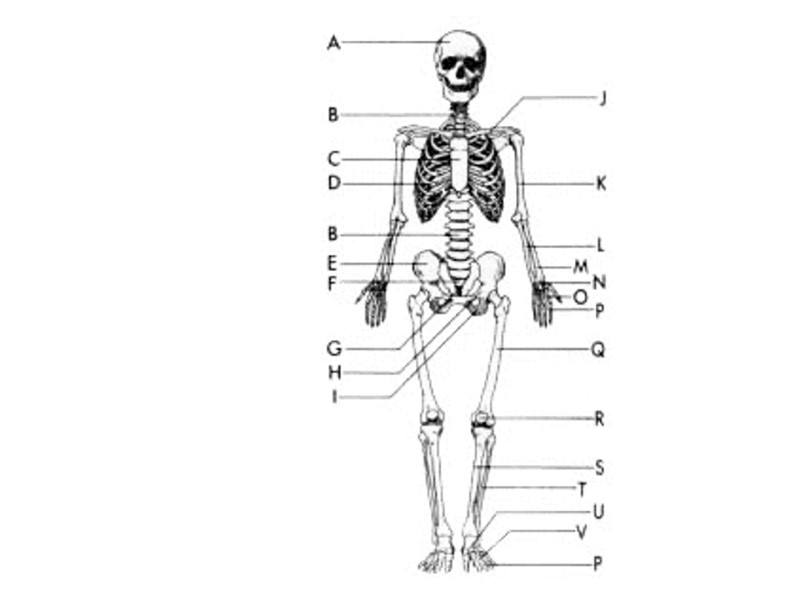
 Axial Skeleton
Axial Skeleton
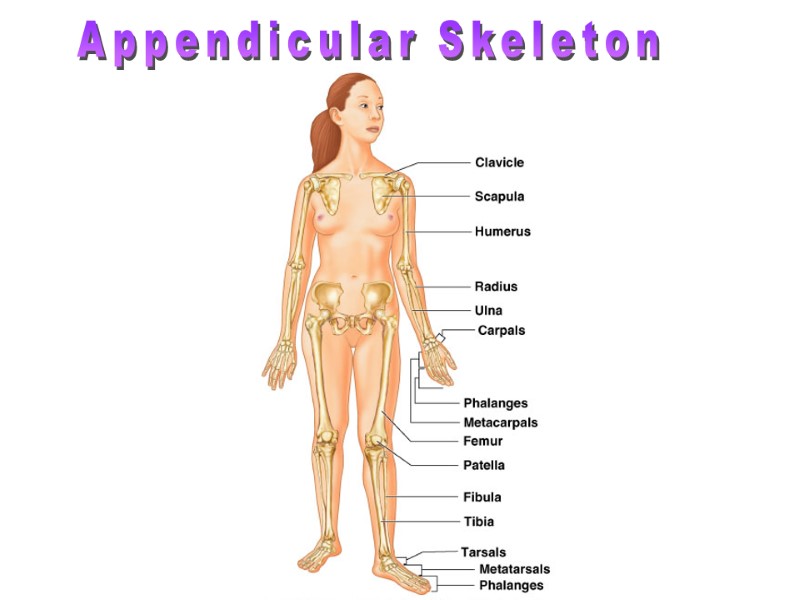
 Appendicular Skeleton
Appendicular Skeleton
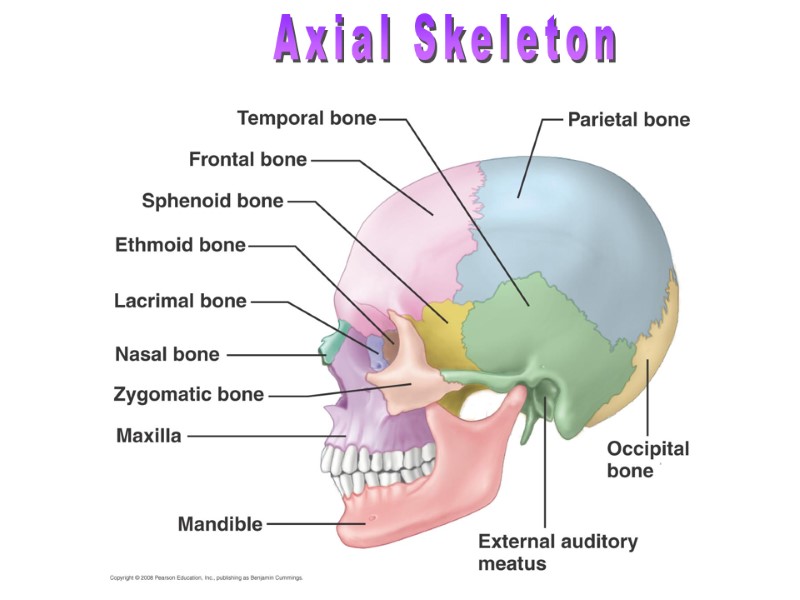
 Axial Skeleton
Axial Skeleton
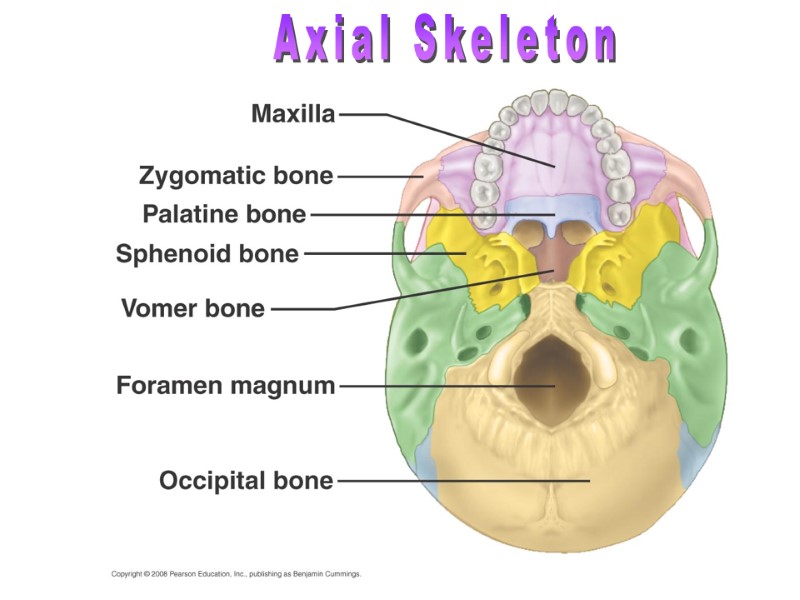
 Axial Skeleton
Axial Skeleton
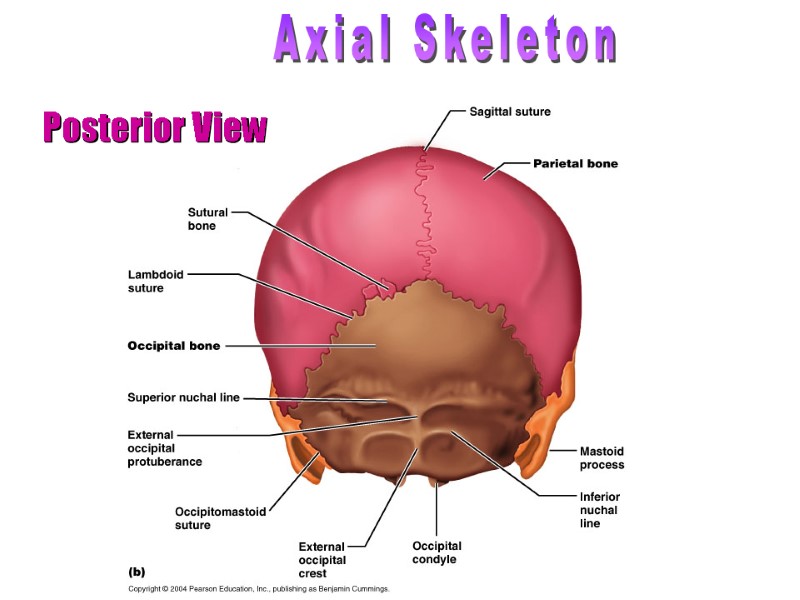
 Posterior View Axial Skeleton
Posterior View Axial Skeleton
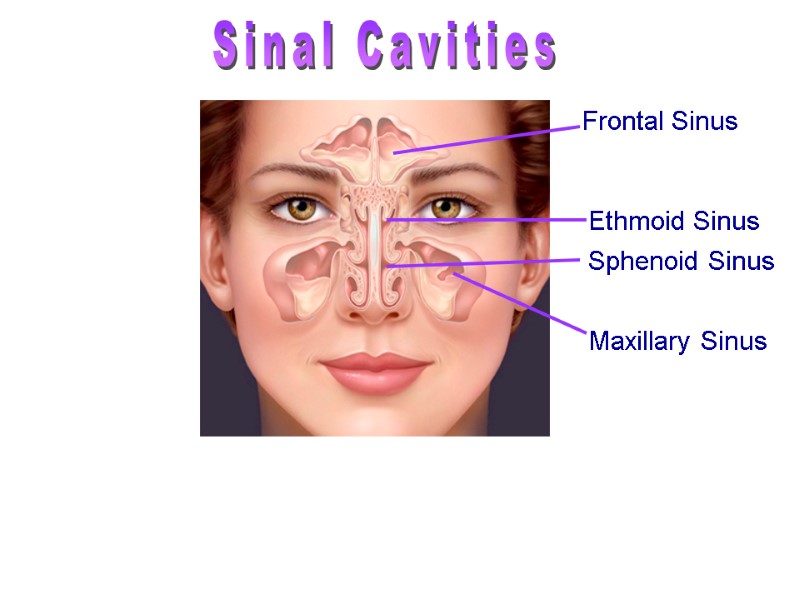
 Sinal Cavities Warm and moisten air Lighten the skull Enhance voice resonance Frontal Sinus Ethmoid Sinus Sphenoid Sinus Maxillary Sinus
Sinal Cavities Warm and moisten air Lighten the skull Enhance voice resonance Frontal Sinus Ethmoid Sinus Sphenoid Sinus Maxillary Sinus
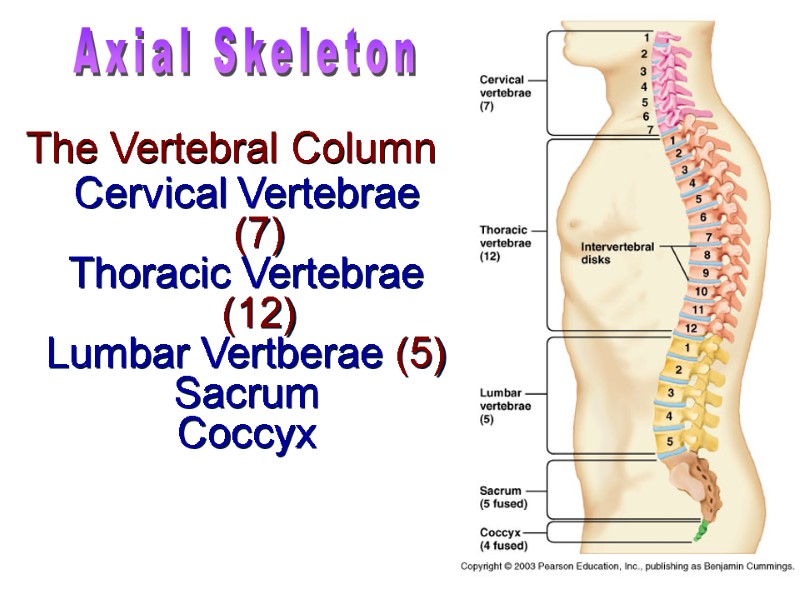
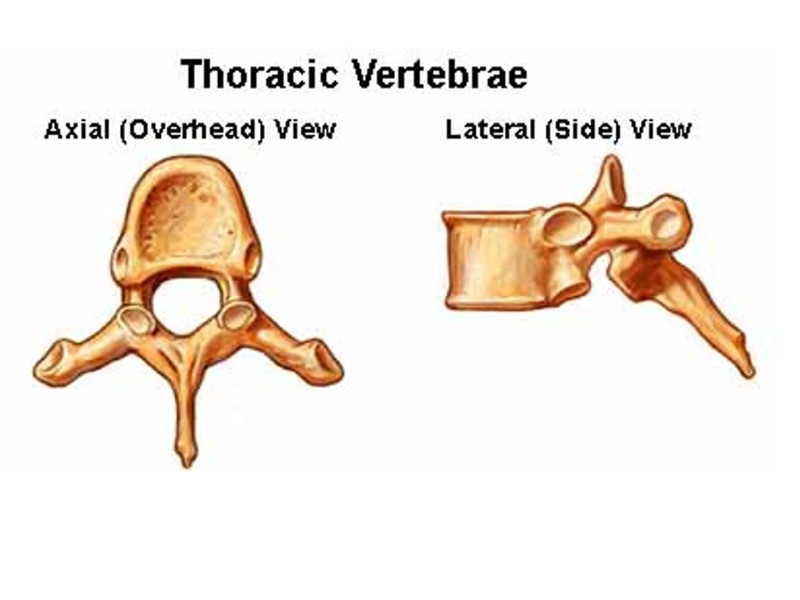
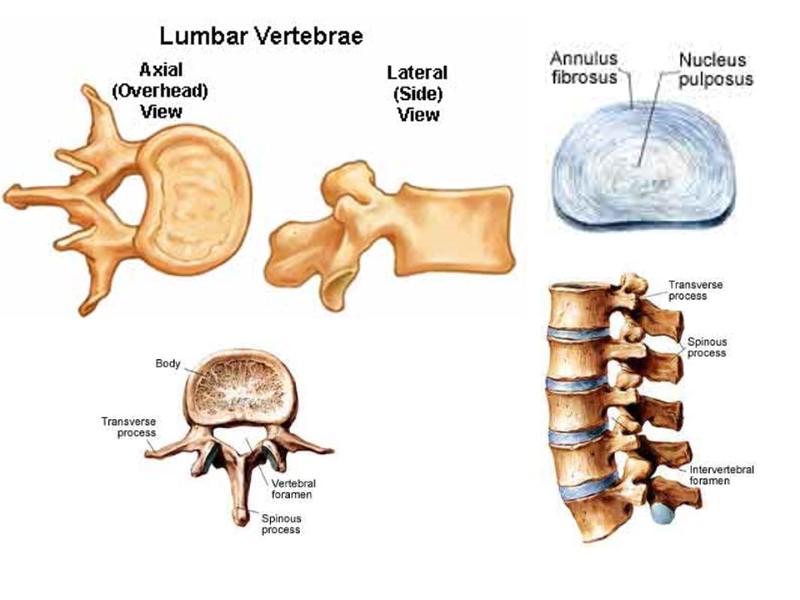
 Cervical Vertebrae (7) Thoracic Vertebrae (12) Lumbar Vertberae (5) Sacrum Coccyx The Vertebral Column Axial Skeleton
Cervical Vertebrae (7) Thoracic Vertebrae (12) Lumbar Vertberae (5) Sacrum Coccyx The Vertebral Column Axial Skeleton
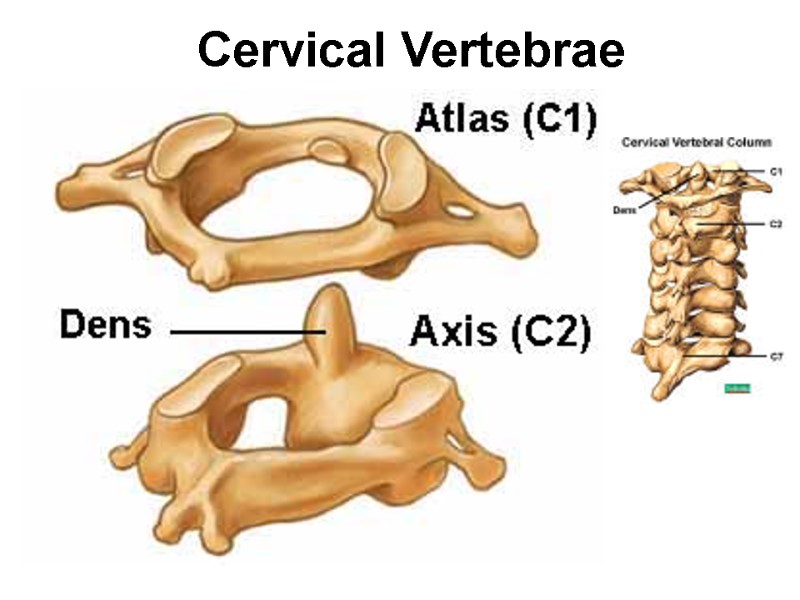
 Cervical Vertebrae
Cervical Vertebrae


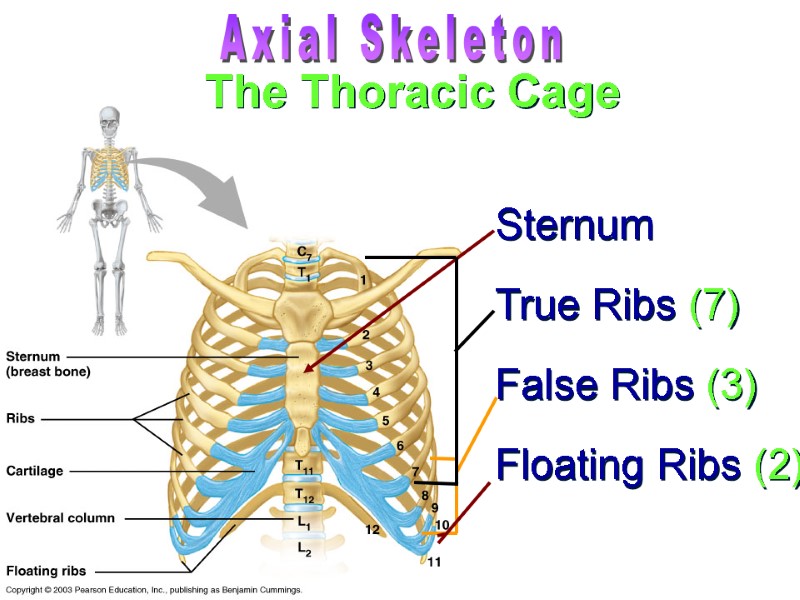
 Sternum True Ribs (7) False Ribs (3) Floating Ribs (2) The Thoracic Cage Axial Skeleton
Sternum True Ribs (7) False Ribs (3) Floating Ribs (2) The Thoracic Cage Axial Skeleton
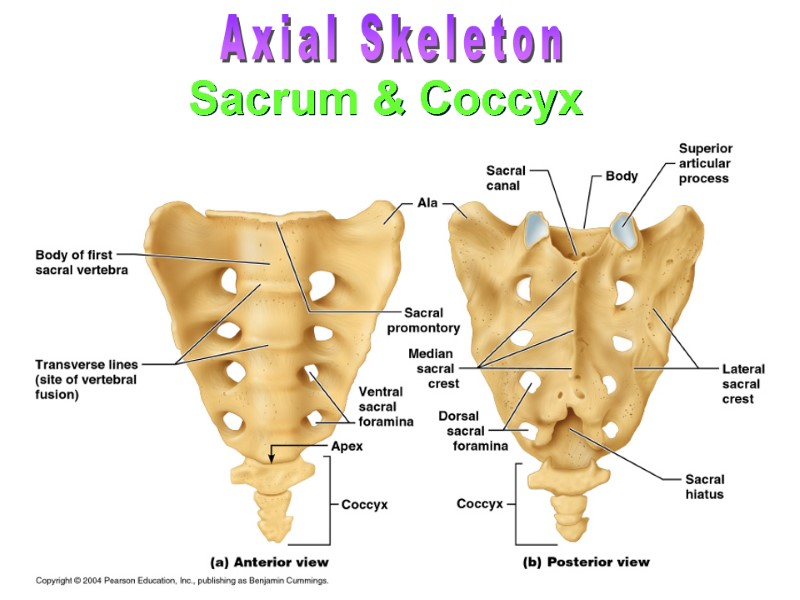
 Sacrum & Coccyx Axial Skeleton
Sacrum & Coccyx Axial Skeleton
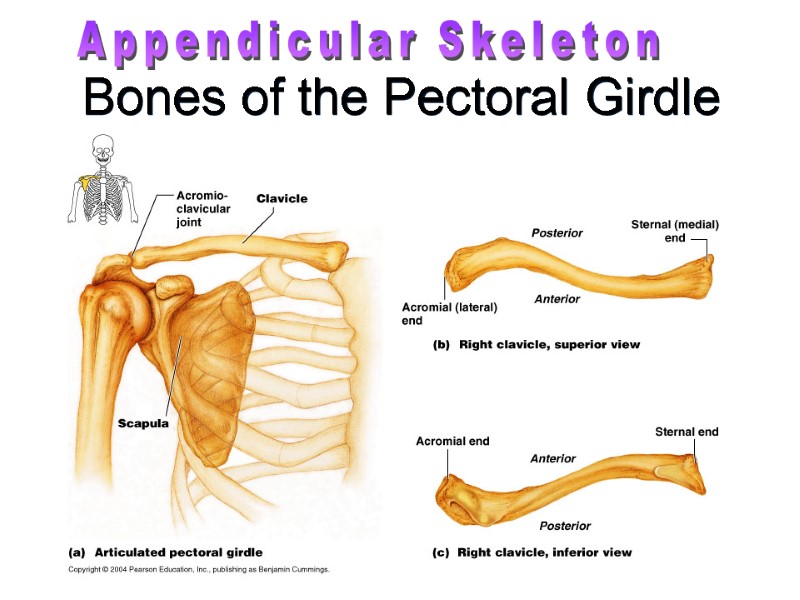
 Bones of the Pectoral Girdle Appendicular Skeleton
Bones of the Pectoral Girdle Appendicular Skeleton
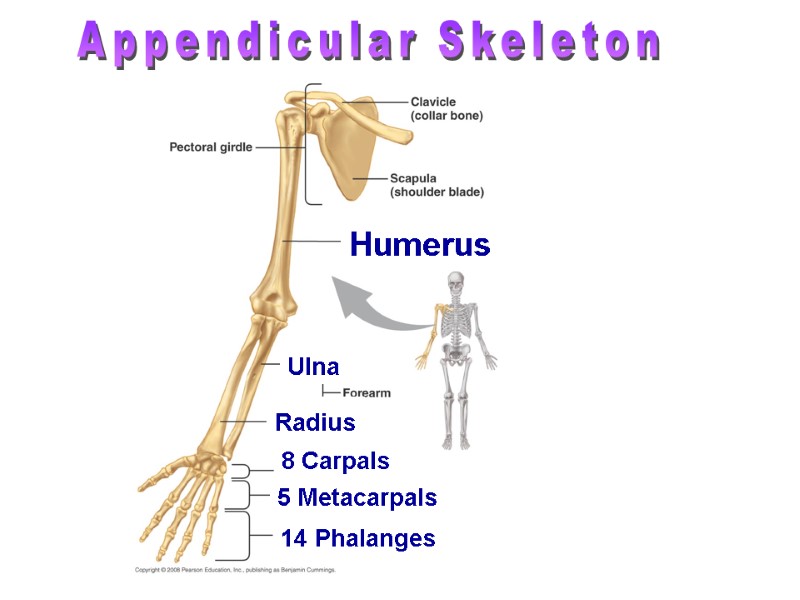
 Appendicular Skeleton Humerus Ulna Radius 8 Carpals 14 Phalanges 5 Metacarpals
Appendicular Skeleton Humerus Ulna Radius 8 Carpals 14 Phalanges 5 Metacarpals
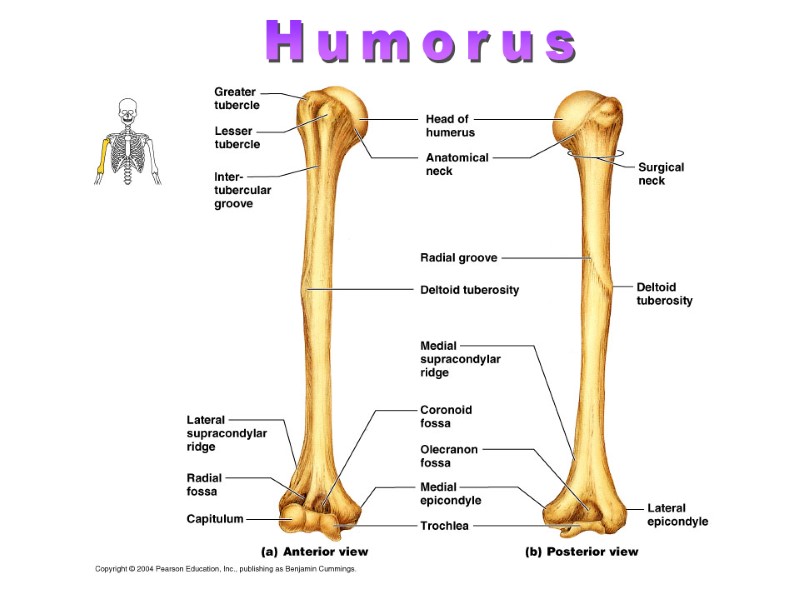
 Humorus
Humorus
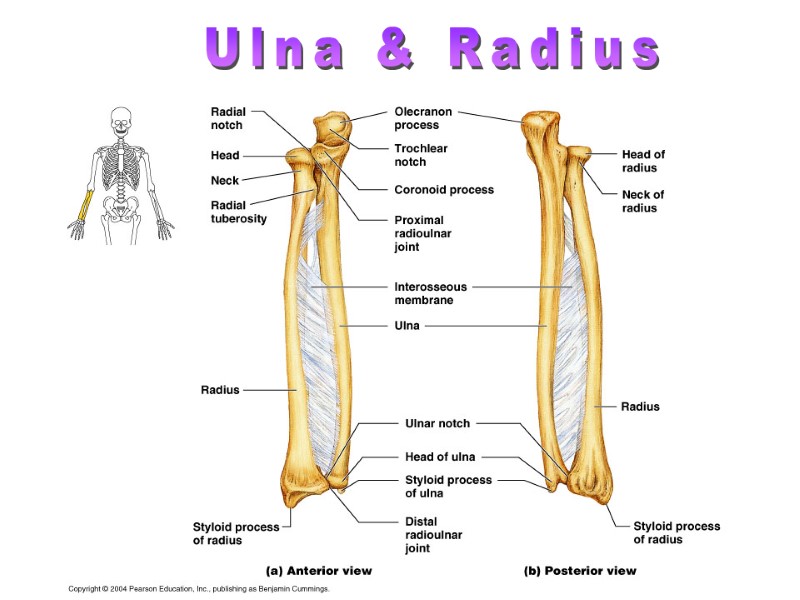
 Ulna & Radius
Ulna & Radius
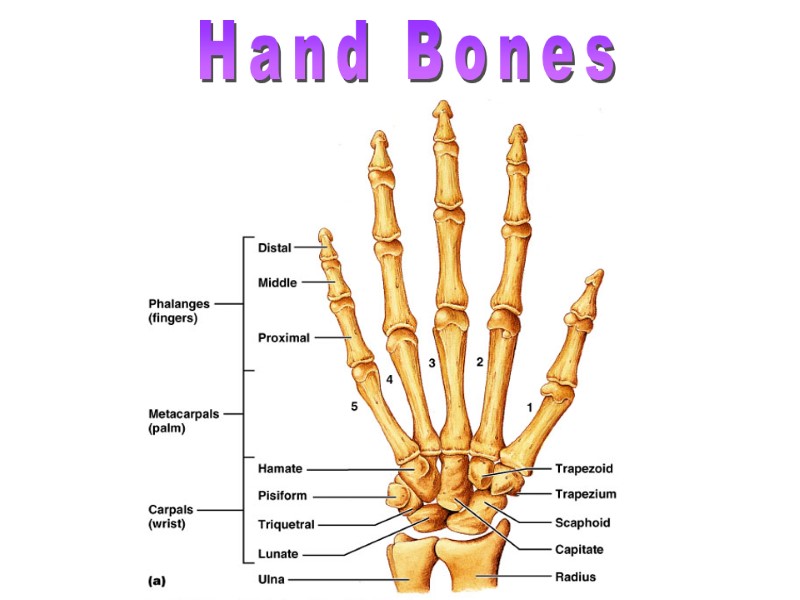
 Hand Bones
Hand Bones
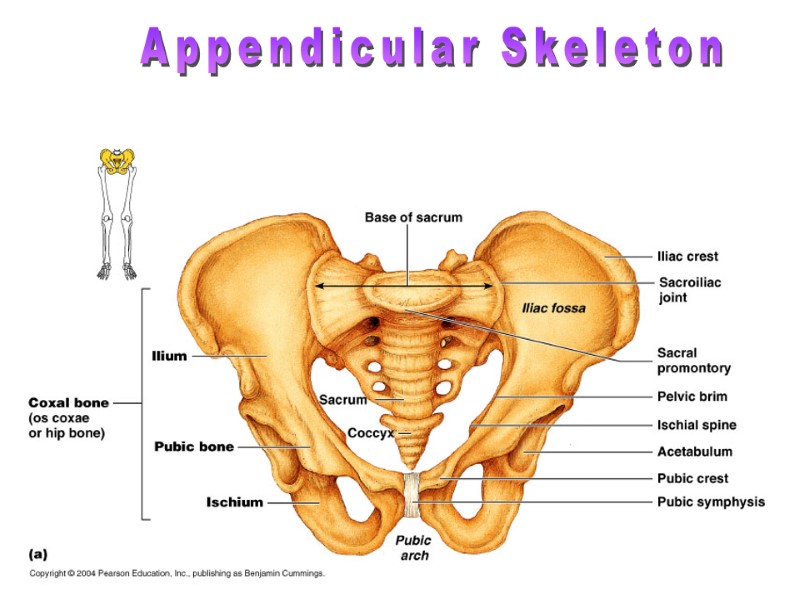
 Appendicular Skeleton Pelvis
Appendicular Skeleton Pelvis
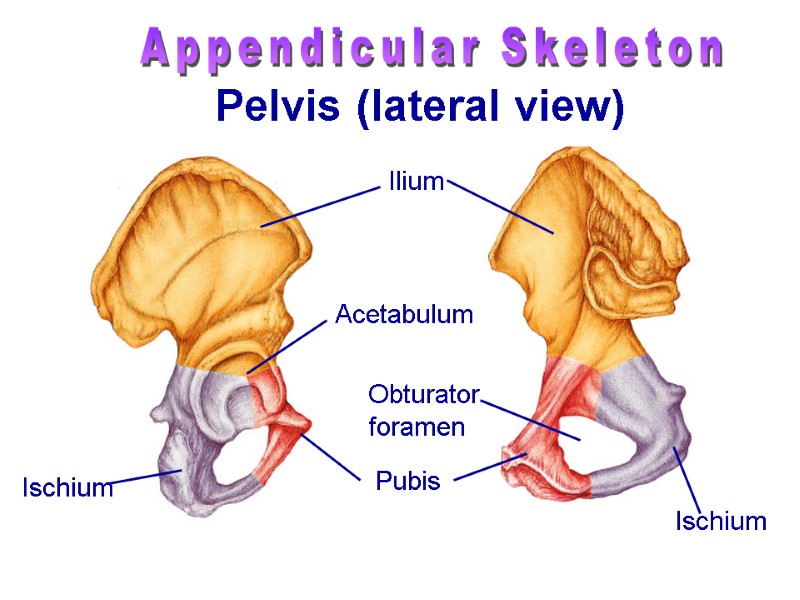
 Ischium Ilium Acetabulum Pubis Ischium Obturator foramen Appendicular Skeleton Pelvis (lateral view)
Ischium Ilium Acetabulum Pubis Ischium Obturator foramen Appendicular Skeleton Pelvis (lateral view)
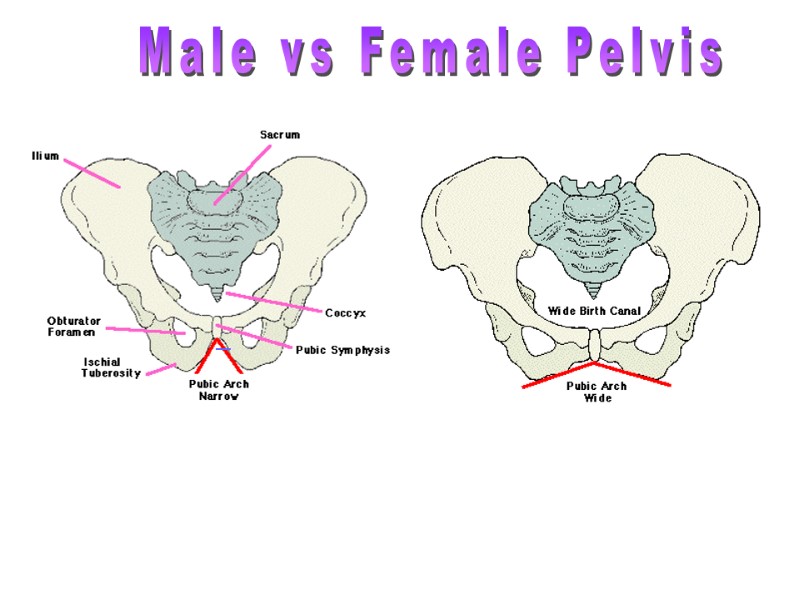
 Male Pelvic Girdle Female Pelvic Girdle Male vs Female Pelvis
Male Pelvic Girdle Female Pelvic Girdle Male vs Female Pelvis

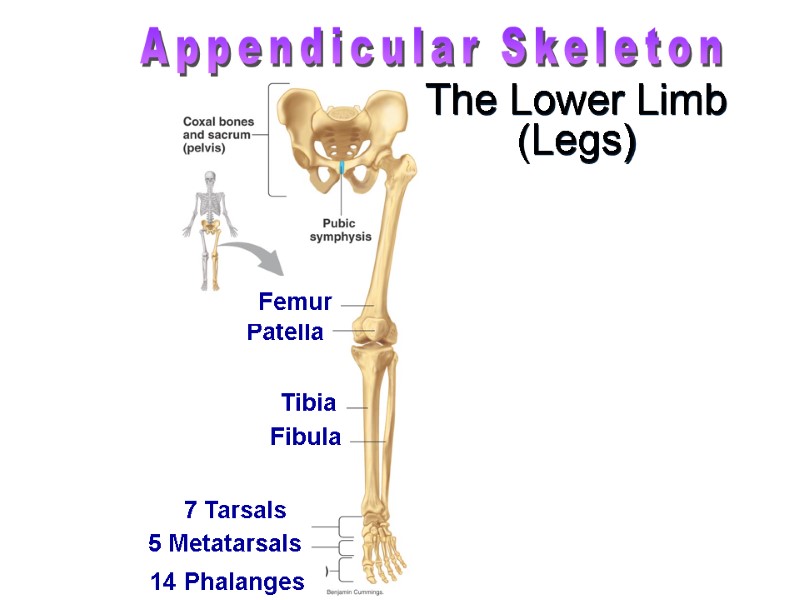
 Patella The Lower Limb (Legs) Appendicular Skeleton Femur Tibia Fibula 5 Metatarsals 14 Phalanges 7 Tarsals
Patella The Lower Limb (Legs) Appendicular Skeleton Femur Tibia Fibula 5 Metatarsals 14 Phalanges 7 Tarsals
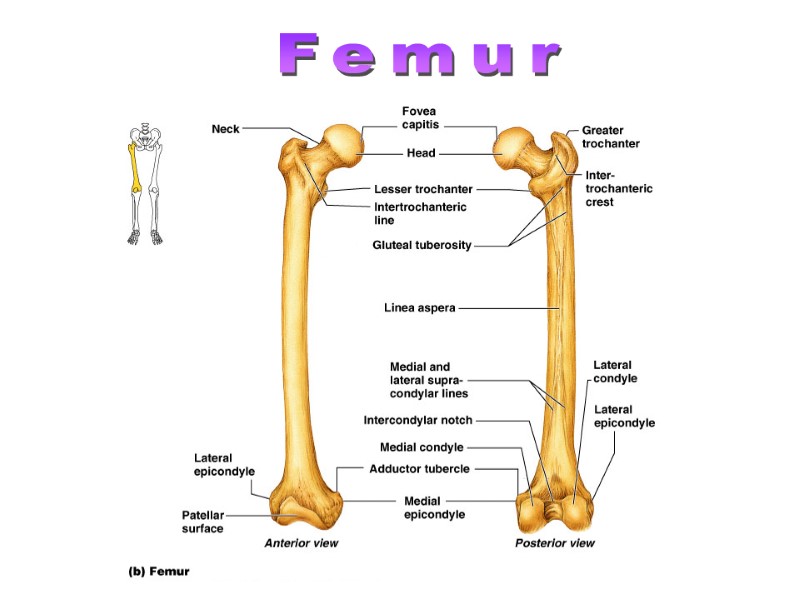
 Femur
Femur
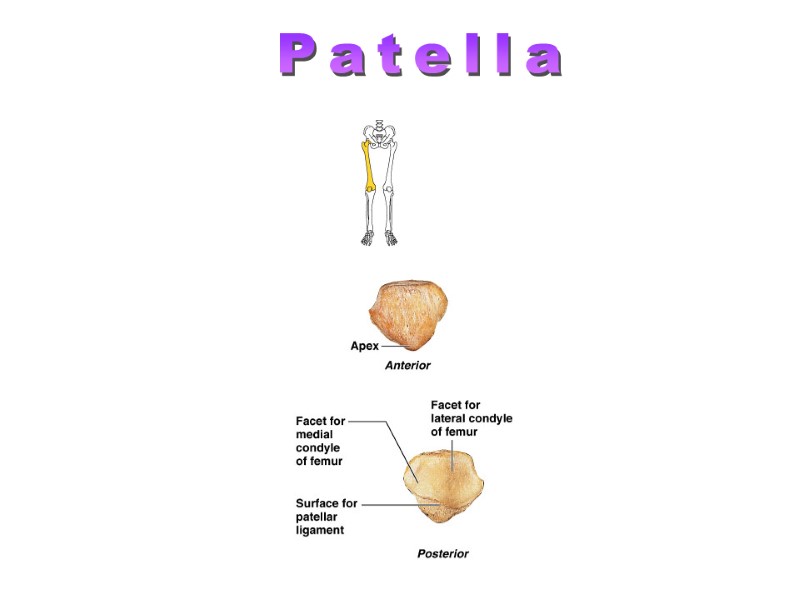
 Patella
Patella
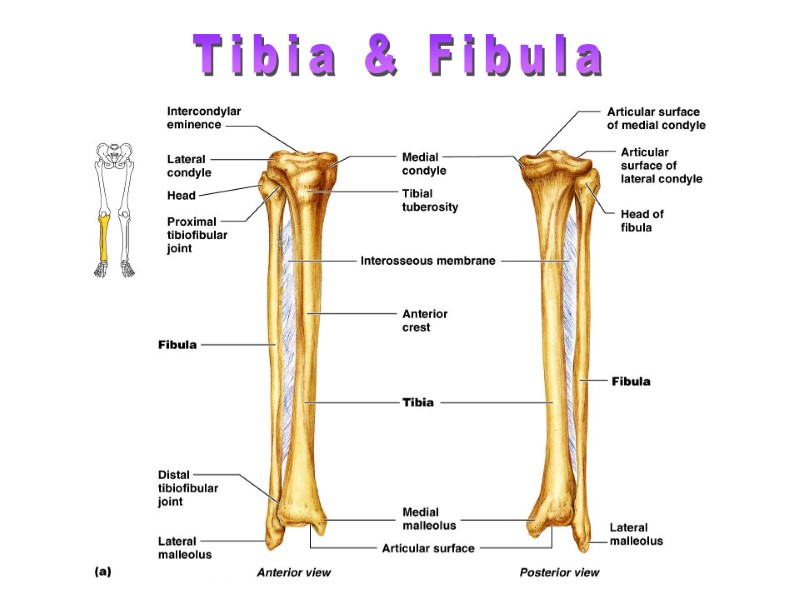
 Tibia & Fibula
Tibia & Fibula
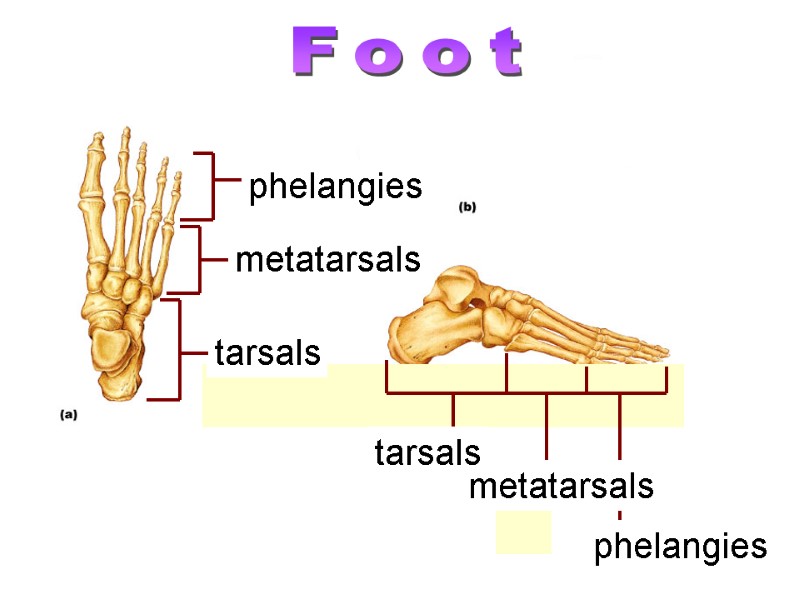
 metatarsals phelangies tarsals metatarsals phelangies tarsals Foot
metatarsals phelangies tarsals metatarsals phelangies tarsals Foot
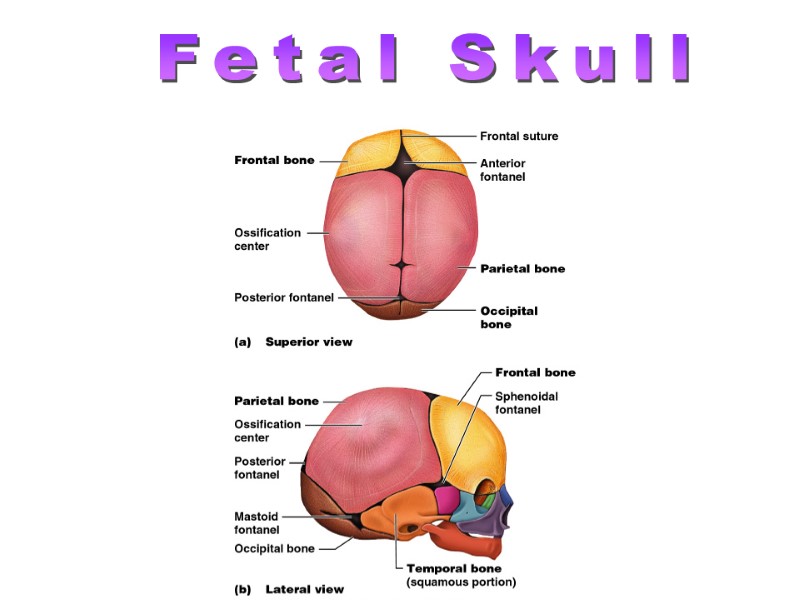
 Fetal Skull
Fetal Skull
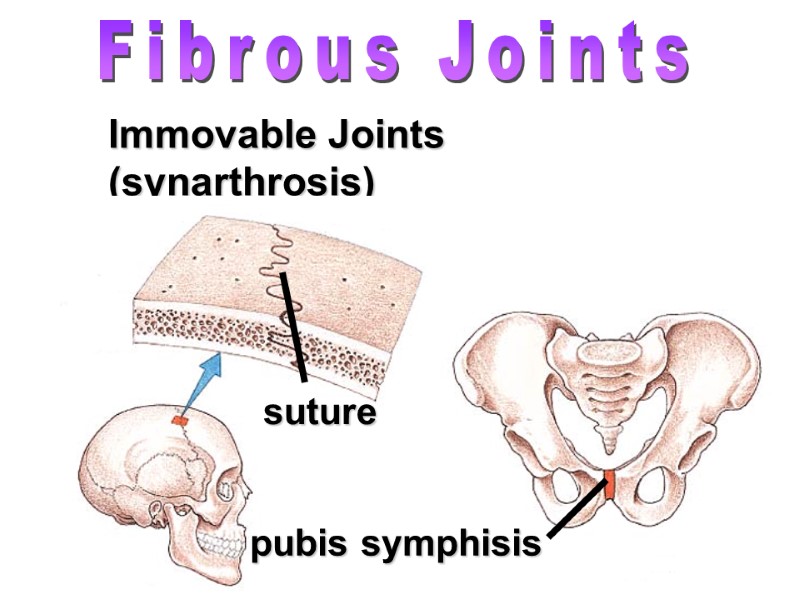
 Immovable Joints (synarthrosis) Fibrous Joints
Immovable Joints (synarthrosis) Fibrous Joints
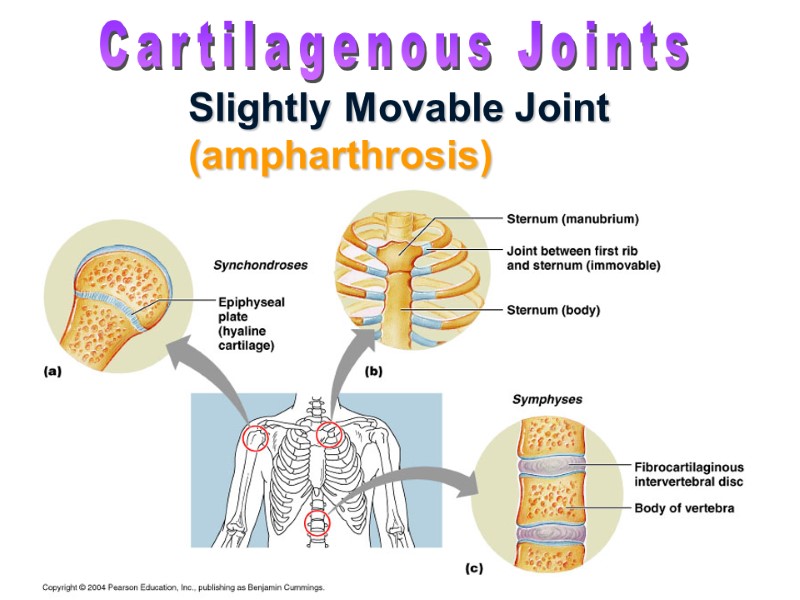
 Slightly Movable Joint (ampharthrosis) Cartilagenous Joints
Slightly Movable Joint (ampharthrosis) Cartilagenous Joints
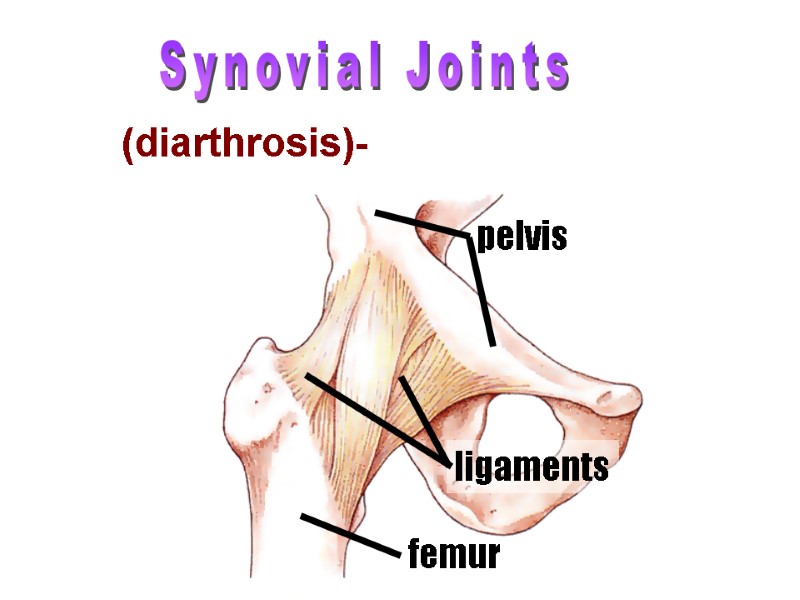
 Synovial Joints (diarthrosis)- freely moveable
Synovial Joints (diarthrosis)- freely moveable
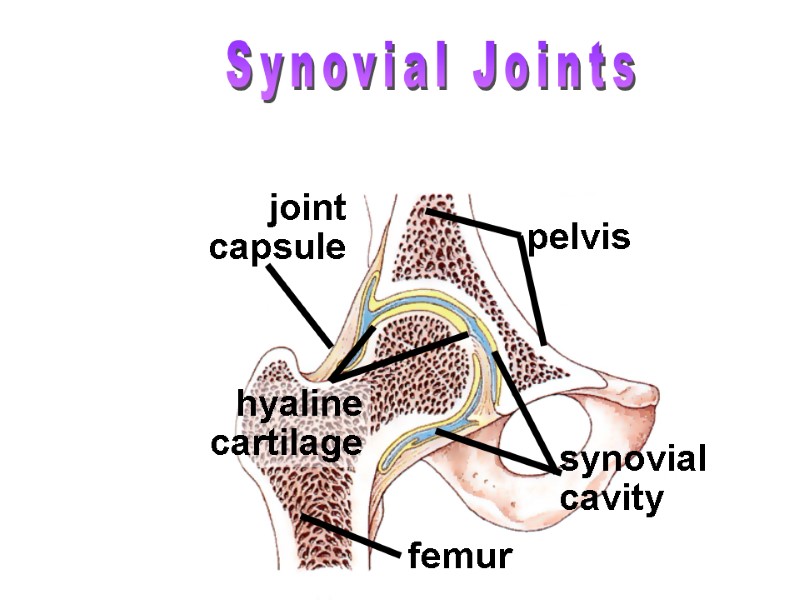
 Synovial Joints
Synovial Joints
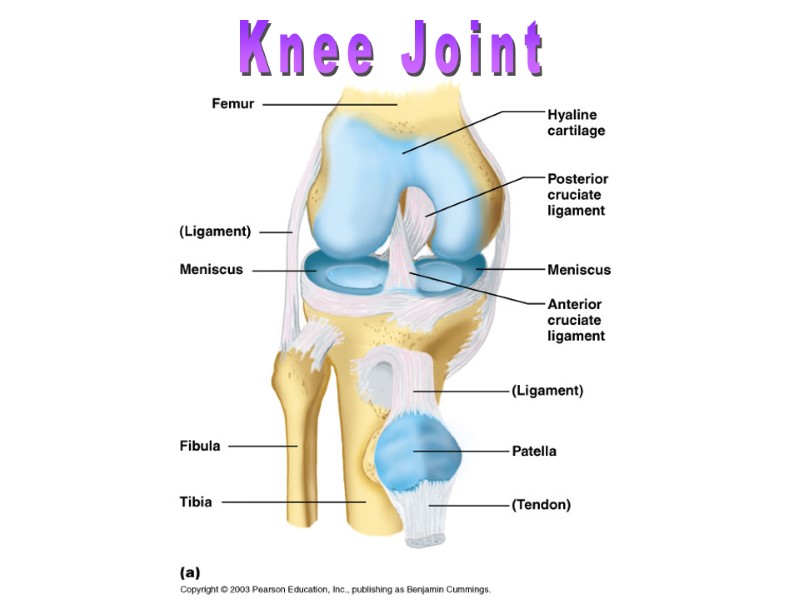
 Knee Joint
Knee Joint
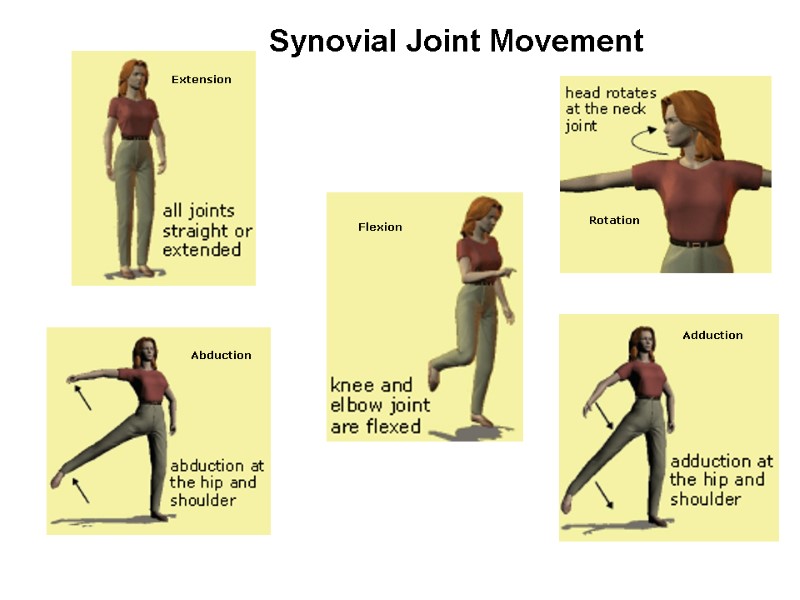
 Abduction Extension Rotation Flexion Adduction Synovial Joint Movement
Abduction Extension Rotation Flexion Adduction Synovial Joint Movement
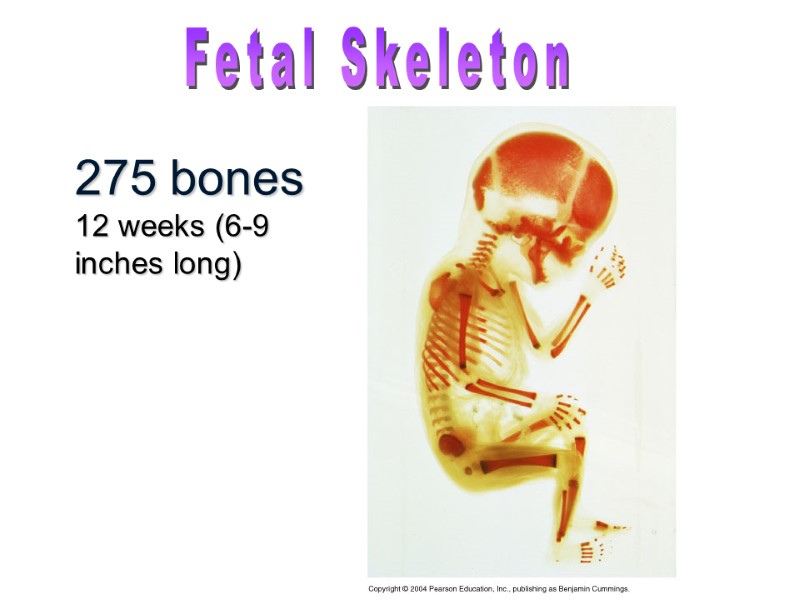
 275 bones 12 weeks (6-9 inches long) Fetal Skeleton
275 bones 12 weeks (6-9 inches long) Fetal Skeleton
 cartilage calcified cartilage bone epiphyseal plate epiphyseal line Endochondral Ossification 2o ossification center Fetus: 1st 2 months Adult Childhood Just before birth
cartilage calcified cartilage bone epiphyseal plate epiphyseal line Endochondral Ossification 2o ossification center Fetus: 1st 2 months Adult Childhood Just before birth
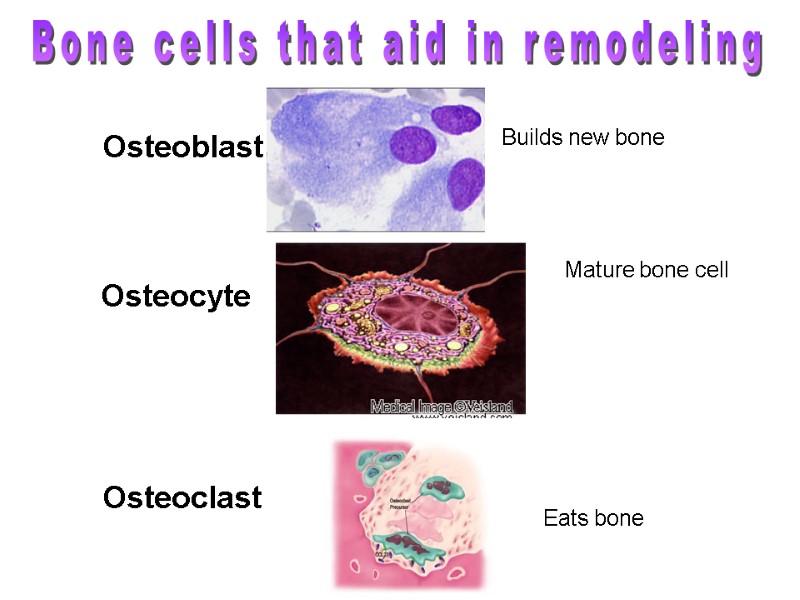
 Osteoblast Osteocyte Osteoclast Eats bone Builds new bone Mature bone cell Bone cells that aid in remodeling
Osteoblast Osteocyte Osteoclast Eats bone Builds new bone Mature bone cell Bone cells that aid in remodeling
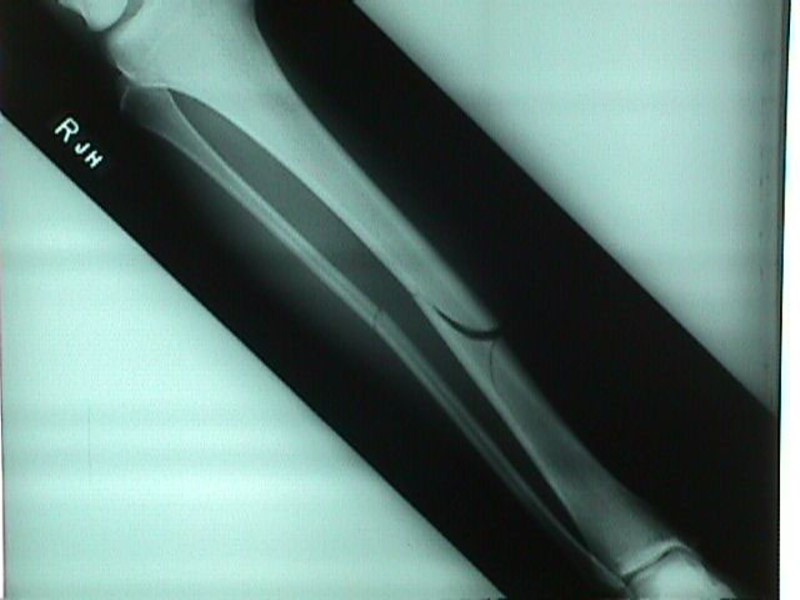
 Bone Repair: Electrical stimulation of the fracture site: Increases speed and completeness of healing The e- stimulation inhibits PTH and slow osteoclasts down from reabsorbing bone 2. Ultrasound treatment: Daily treatments reduce healing time of broken bones by 25-35% 3. Free vascular fibular graft technique: Transplant fibula in arm Gives good blood supply not available in other treatments 4. Bone substitutes: Crushed bone from cadaver- but risk of HIV and hepatitis Sea bone- coral Artificial bone- ceramic
Bone Repair: Electrical stimulation of the fracture site: Increases speed and completeness of healing The e- stimulation inhibits PTH and slow osteoclasts down from reabsorbing bone 2. Ultrasound treatment: Daily treatments reduce healing time of broken bones by 25-35% 3. Free vascular fibular graft technique: Transplant fibula in arm Gives good blood supply not available in other treatments 4. Bone substitutes: Crushed bone from cadaver- but risk of HIV and hepatitis Sea bone- coral Artificial bone- ceramic

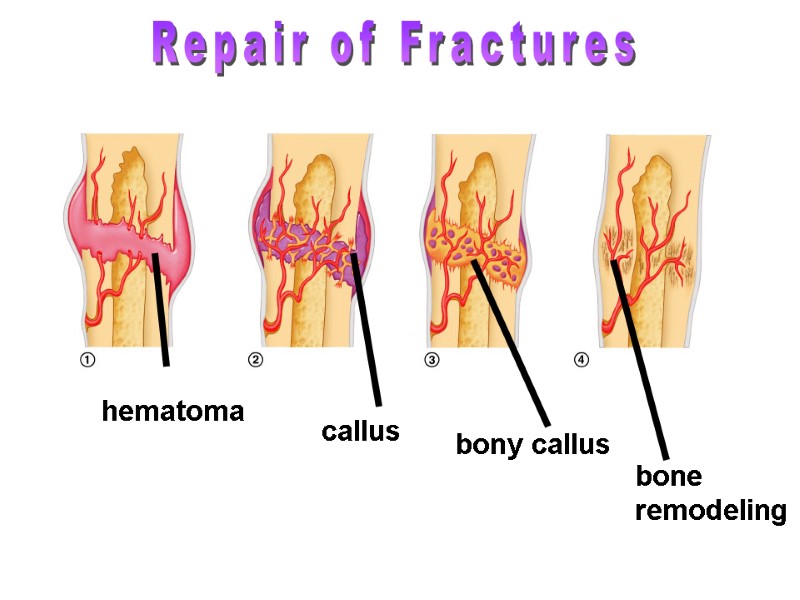
 hematoma callus bony callus Repair of Fractures bone remodeling
hematoma callus bony callus Repair of Fractures bone remodeling
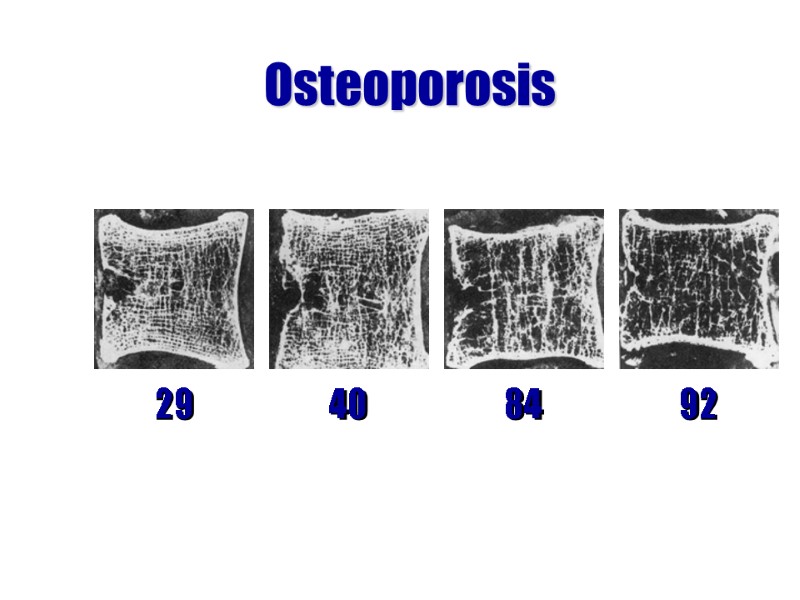
 Diseases of the Skeletal System: Osteoporosis- bone reabsorption outpaces bone deposit; bones become lighter and fracture easier Factors: age, gender (more in women) estrogen and testosterone decrease insufficient exercise (or too much) diet poor in Ca++ and protein abnormal vitamin D receptors smoking
Diseases of the Skeletal System: Osteoporosis- bone reabsorption outpaces bone deposit; bones become lighter and fracture easier Factors: age, gender (more in women) estrogen and testosterone decrease insufficient exercise (or too much) diet poor in Ca++ and protein abnormal vitamin D receptors smoking
 Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis
 Rickets- vitamin D deficiency Osteomalacia- soft bones, inadequate mineralization in bones, lack of vitamin D Pagets Disease- spotty weakening in the bones, excessive and abnormal bone remodeling Rheumatoid arthritis- autoimmune reaction Diseases of the Skeletal System:
Rickets- vitamin D deficiency Osteomalacia- soft bones, inadequate mineralization in bones, lack of vitamin D Pagets Disease- spotty weakening in the bones, excessive and abnormal bone remodeling Rheumatoid arthritis- autoimmune reaction Diseases of the Skeletal System:

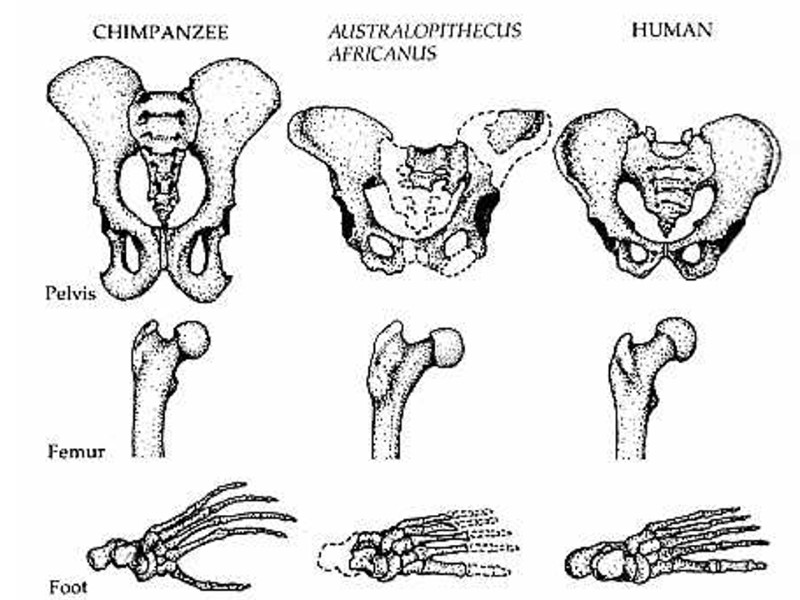
 INQUIRY http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DSHoonPWwXQ What is a fontanel? How many bones in the adult skeleton? What is the difference between the appendicular and axial skeleton? What is a meniscus? Demonstrate adduction. Weight bearing vertebrae are called? What does an osteoclast do? Extra Credit: 1-page reaction paper on bipedalism and problems associated with our human frame. Attach article. Turn in 1-week from today.
INQUIRY http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DSHoonPWwXQ What is a fontanel? How many bones in the adult skeleton? What is the difference between the appendicular and axial skeleton? What is a meniscus? Demonstrate adduction. Weight bearing vertebrae are called? What does an osteoclast do? Extra Credit: 1-page reaction paper on bipedalism and problems associated with our human frame. Attach article. Turn in 1-week from today.

