 SKARN DEPOSITS Ihor Dzhemesiuk
SKARN DEPOSITS Ihor Dzhemesiuk
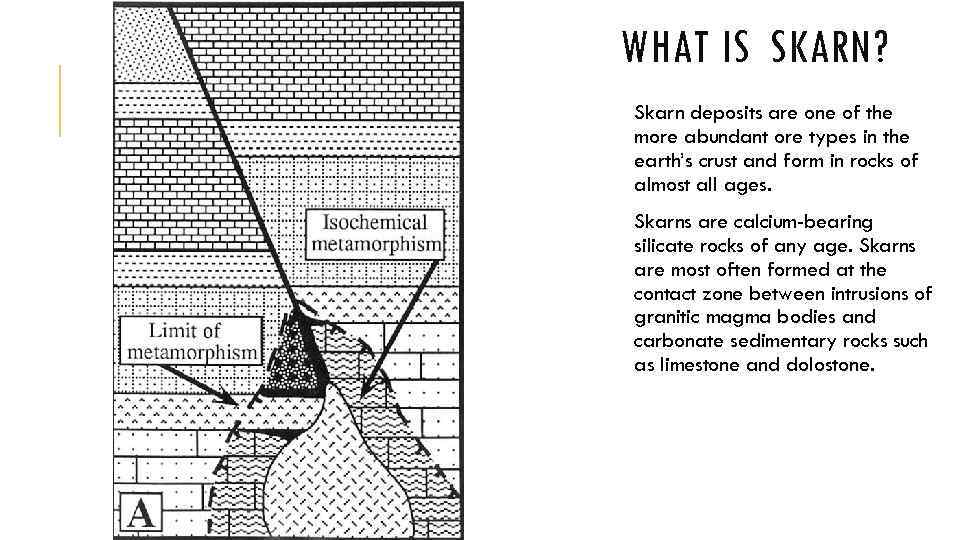 WHAT IS SKARN? Skarn deposits are one of the more abundant ore types in the earth’s crust and form in rocks of almost all ages. Skarns are calcium-bearing silicate rocks of any age. Skarns are most often formed at the contact zone between intrusions of granitic magma bodies and carbonate sedimentary rocks such as limestone and dolostone.
WHAT IS SKARN? Skarn deposits are one of the more abundant ore types in the earth’s crust and form in rocks of almost all ages. Skarns are calcium-bearing silicate rocks of any age. Skarns are most often formed at the contact zone between intrusions of granitic magma bodies and carbonate sedimentary rocks such as limestone and dolostone.
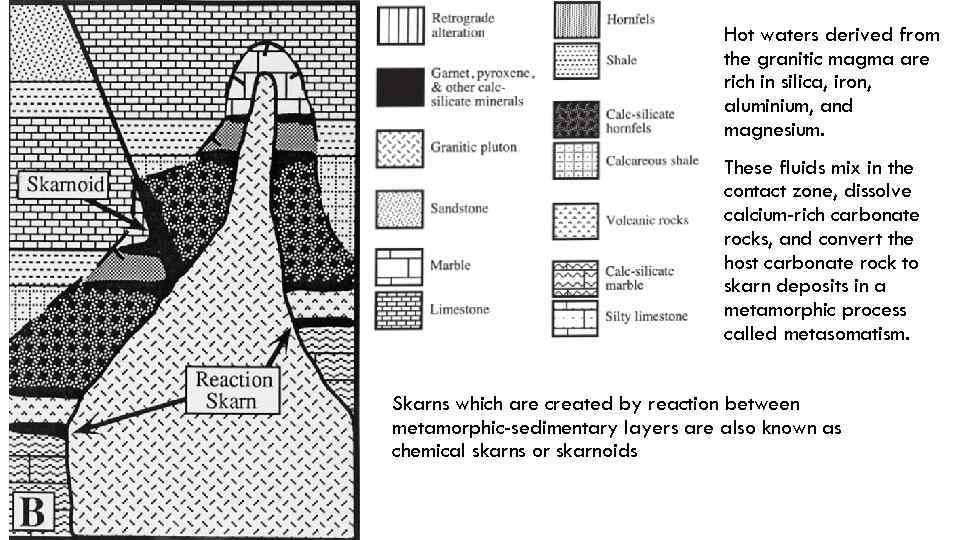 Hot waters derived from the granitic magma are rich in silica, iron, aluminium, and magnesium. These fluids mix in the contact zone, dissolve calcium-rich carbonate rocks, and convert the host carbonate rock to skarn deposits in a metamorphic process called metasomatism. Skarns which are created by reaction between metamorphic-sedimentary layers are also known as chemical skarns or skarnoids
Hot waters derived from the granitic magma are rich in silica, iron, aluminium, and magnesium. These fluids mix in the contact zone, dissolve calcium-rich carbonate rocks, and convert the host carbonate rock to skarn deposits in a metamorphic process called metasomatism. Skarns which are created by reaction between metamorphic-sedimentary layers are also known as chemical skarns or skarnoids
 MAJOR TYPES OF SKARN Fe Au Cu W Mo Sn Zn (Pb) Skarns are sometimes associated with mineable accumulations of metallic ores of iron, copper, zinc, lead, gold, and several others. In such cases these deposits are called "skarn deposits". The identification and classification of skarn deposits is based on their mineralogy
MAJOR TYPES OF SKARN Fe Au Cu W Mo Sn Zn (Pb) Skarns are sometimes associated with mineable accumulations of metallic ores of iron, copper, zinc, lead, gold, and several others. In such cases these deposits are called "skarn deposits". The identification and classification of skarn deposits is based on their mineralogy
 Sub-calcic garnet MAJOR MINERALS Such minerals as quartz and calcite, are present in almost all skarns. 1. Garnet 2. Pyroxene 3. Olivine 4. Pyroxenoid 5. Amphibole 6. Epidote 7. Plagioclase Calcic garnet & pyroxene 8. Scapolite
Sub-calcic garnet MAJOR MINERALS Such minerals as quartz and calcite, are present in almost all skarns. 1. Garnet 2. Pyroxene 3. Olivine 4. Pyroxenoid 5. Amphibole 6. Epidote 7. Plagioclase Calcic garnet & pyroxene 8. Scapolite
 W SKARNS Tungsten skarns are found on most continents in association with calc-alkaline plutons in major orogenic belts. W skarns are associated with coarse-grained, equigranular batholiths (with pegmatite and aplite dikes) surrounded by large, high-temperature, metamorphic aureoles. Total deposits in the world: 203
W SKARNS Tungsten skarns are found on most continents in association with calc-alkaline plutons in major orogenic belts. W skarns are associated with coarse-grained, equigranular batholiths (with pegmatite and aplite dikes) surrounded by large, high-temperature, metamorphic aureoles. Total deposits in the world: 203
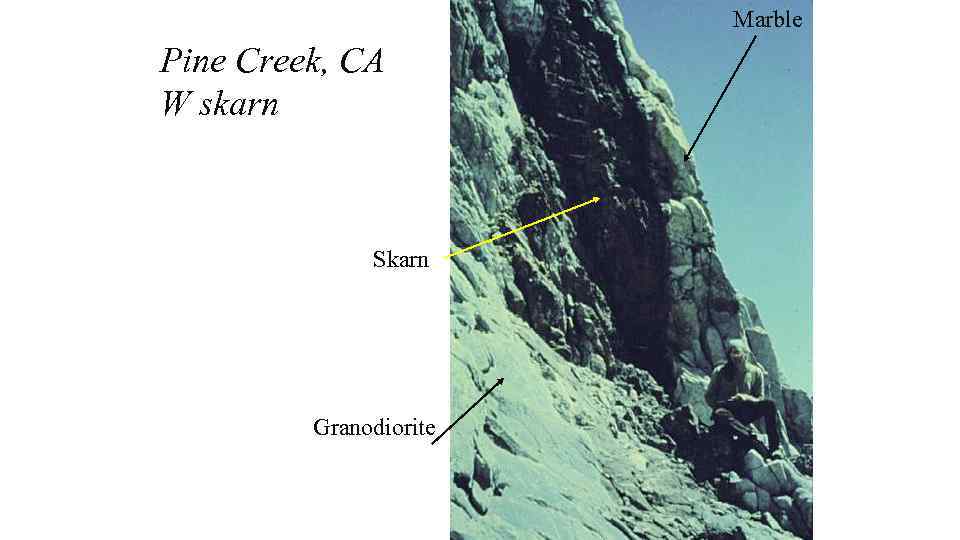 Marble Pine Creek, CA W skarn Skarn Granodiorite
Marble Pine Creek, CA W skarn Skarn Granodiorite
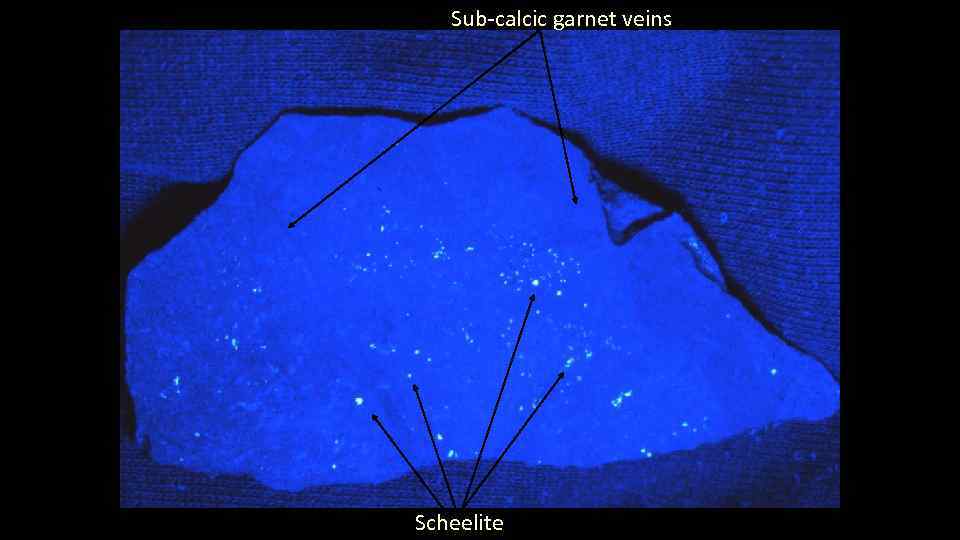 Sub-calcic garnet veins Scheelite
Sub-calcic garnet veins Scheelite
 FE SKARNS Many deposits are very large—>1, 000 million tons (Mt) ore, >500 Mt contained Fe (Musan in North Korea contains 5, 200 Mt Fe) —and consist dominantly of magnetite with only minor silicate gangue. Calcic Fe skarns in oceanic island arcs are associated with Fe-rich plutons intruded into limestone and volcanic wall rocks. Skarn minerals consist dominantly of garnet and pyroxene with lesser epidote, ilvaite, and actinolite; all are Fe-rich. Total deposits in the world: 398
FE SKARNS Many deposits are very large—>1, 000 million tons (Mt) ore, >500 Mt contained Fe (Musan in North Korea contains 5, 200 Mt Fe) —and consist dominantly of magnetite with only minor silicate gangue. Calcic Fe skarns in oceanic island arcs are associated with Fe-rich plutons intruded into limestone and volcanic wall rocks. Skarn minerals consist dominantly of garnet and pyroxene with lesser epidote, ilvaite, and actinolite; all are Fe-rich. Total deposits in the world: 398
 COPPER SKARNS • Igneous Composition - calc-alkaline diorite to quartz monzonite • Igneous geometry - m. g. to porphyritic stocks and dikes • Igneous alteration- K-silicate, sericitic, epidote endoskarn • Metamorphism- Variable metamorphic aureole (cm to km) lacks high T mineral assemblages Total deposits in the world: 573
COPPER SKARNS • Igneous Composition - calc-alkaline diorite to quartz monzonite • Igneous geometry - m. g. to porphyritic stocks and dikes • Igneous alteration- K-silicate, sericitic, epidote endoskarn • Metamorphism- Variable metamorphic aureole (cm to km) lacks high T mineral assemblages Total deposits in the world: 573
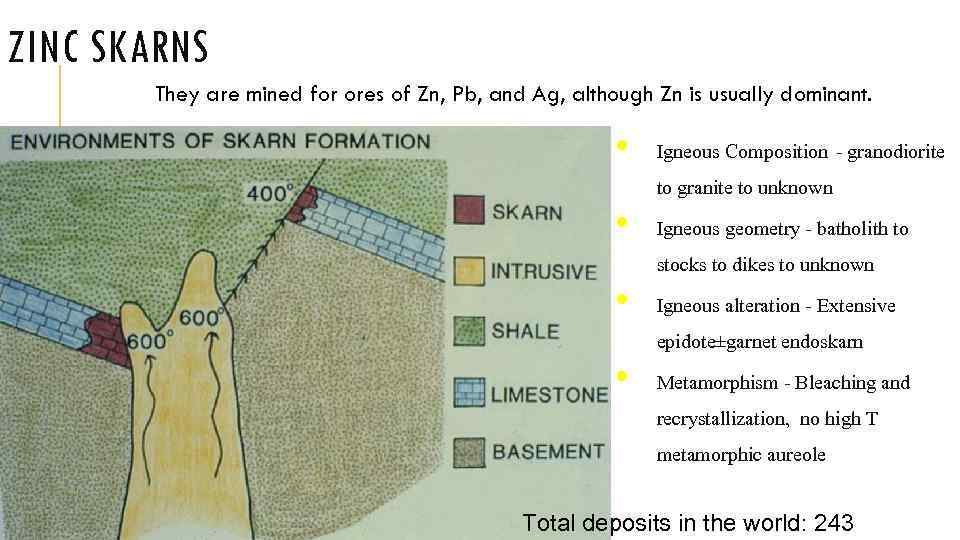 ZINC SKARNS They are mined for ores of Zn, Pb, and Ag, although Zn is usually dominant. • Igneous Composition - granodiorite to granite to unknown • Igneous geometry - batholith to stocks to dikes to unknown • Igneous alteration - Extensive epidote±garnet endoskarn • Metamorphism - Bleaching and recrystallization, no high T metamorphic aureole Total deposits in the world: 243
ZINC SKARNS They are mined for ores of Zn, Pb, and Ag, although Zn is usually dominant. • Igneous Composition - granodiorite to granite to unknown • Igneous geometry - batholith to stocks to dikes to unknown • Igneous alteration - Extensive epidote±garnet endoskarn • Metamorphism - Bleaching and recrystallization, no high T metamorphic aureole Total deposits in the world: 243
 Thank you for attention
Thank you for attention